The Hydrophilic Loop of Arabidopsis PIN1 Auxin Efflux Carrier Harbors Hallmarks of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
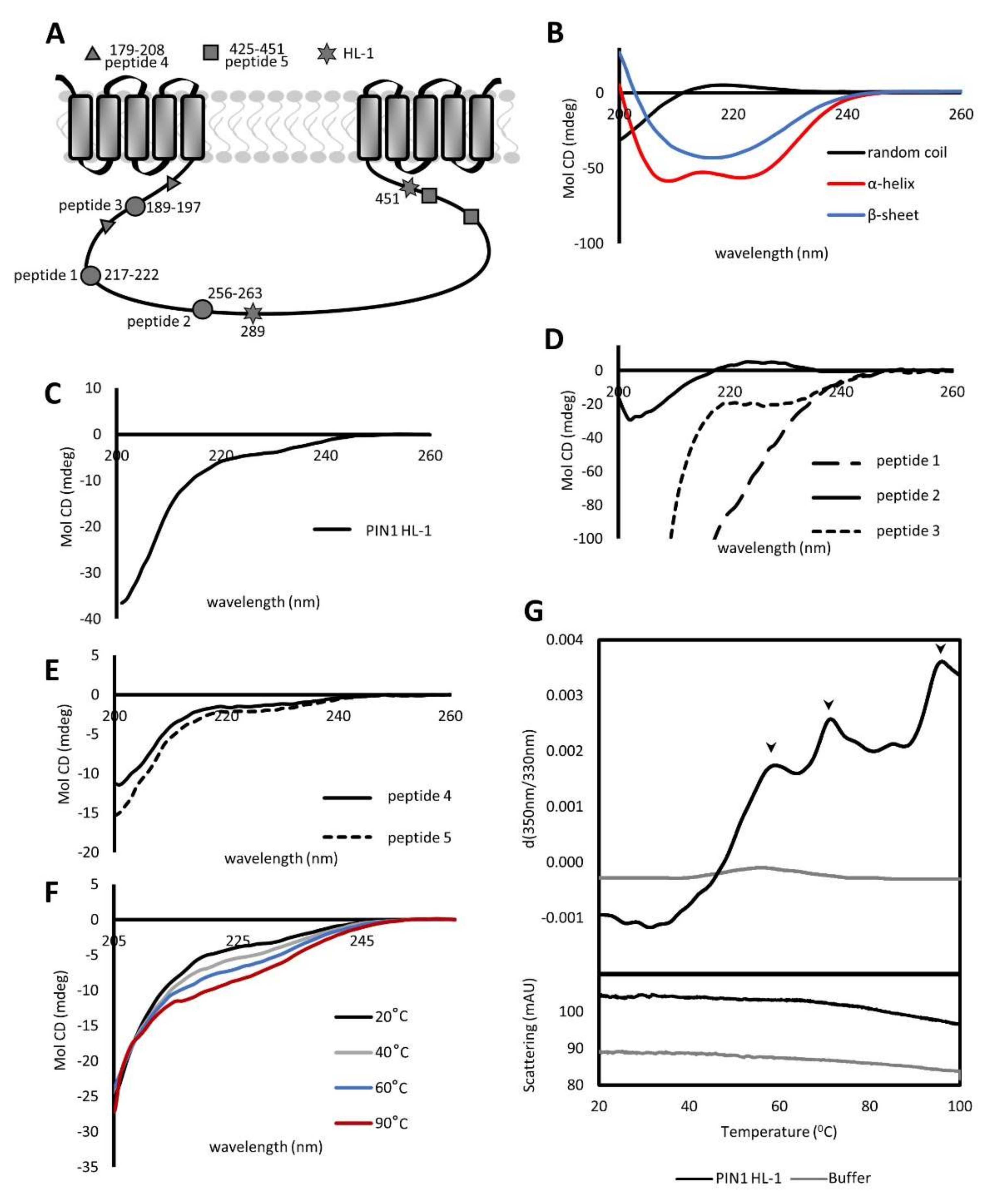
2.1. PIN1 HL Contains Unstructured and Structured Regions Resistant to Thermal Melting
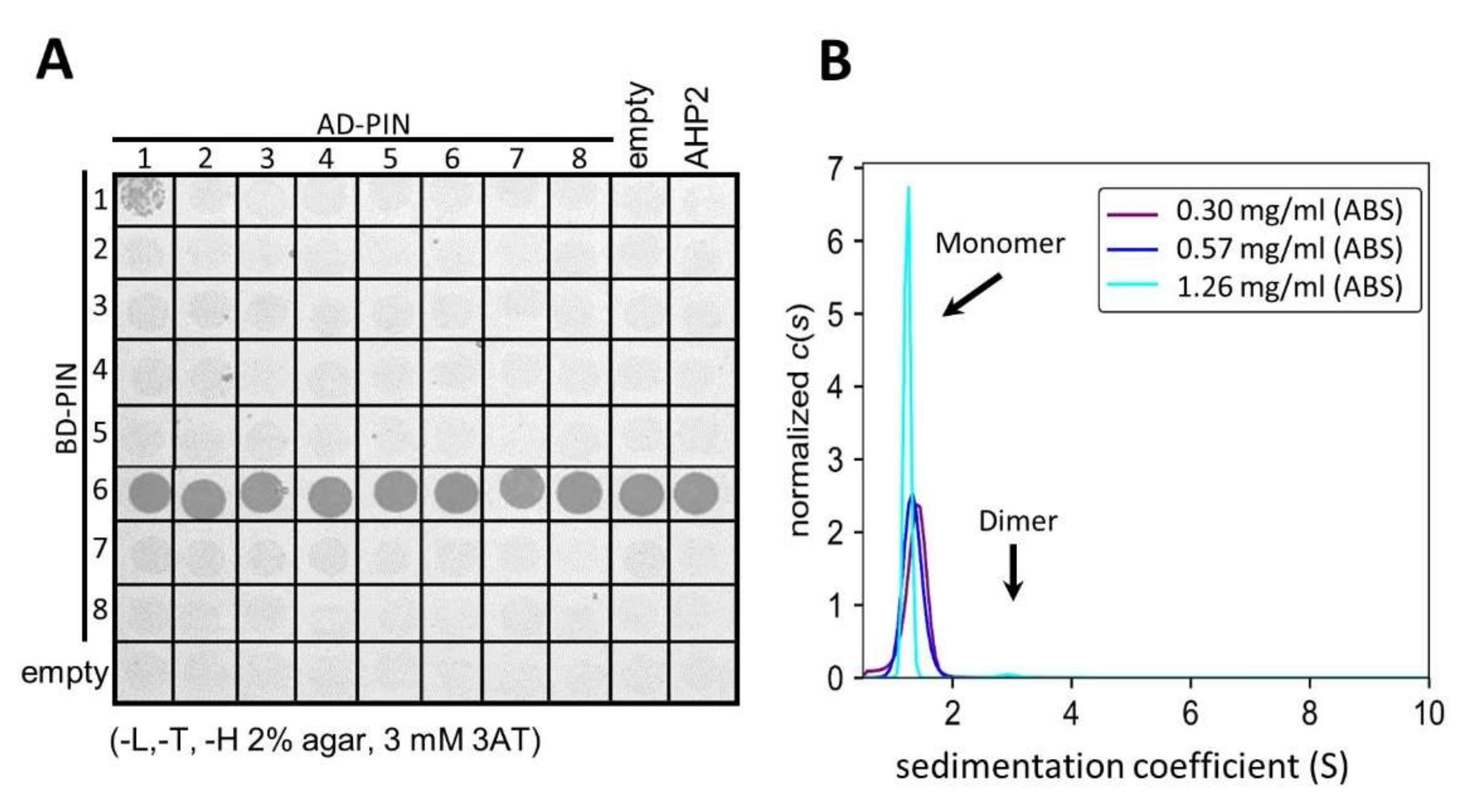
2.2. PIN1 HL Exists in a Monomeric and Dimeric State
2.3. PIN1 HL–GFP Overexpression Alters the Trafficking of Long PINs and Causes PIN1–Related Developmental Defects
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Material and Growth Conditions
4.2. In Silico Bioinformatical Analysis
4.3. Protein Expression, Purification, and Peptide Synthesis
4.4. Protein Stability Assay
4.5. Circular Dichroism
4.6. Nano Differential Scanning Fluorimetry
4.7. Analytical Ultracentrifugation
4.8. Yeast Two-Hybrid
4.9. Whole-Mount In Situ Immunolocalization and Quantification of BFA Body Formation, PIN Clustering, and Polarity
4.10. FM4−64 Staining and Colocalization
4.11. Leaf Vasculature Pattern
4.12. Primary Root Length
4.13. Lateral Root Density
4.14. Primary Root Gravitropism
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Paque, S.; Weijers, D. Q&A: Auxin: The Plant Molecule That Influences Almost Anything. BMC Biol. 2016, 14, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Robert, H.S.; Park, C.; Gutièrrez, C.L.; Wójcikowska, B.; Pěnčík, A.; Novák, O.; Chen, J.; Grunewald, W.; Dresselhaus, T.; Friml, J.; et al. Maternal Auxin Supply Contributes to Early Embryo Patterning in Arabidopsis. Nat. Plants 2018, 4, 548–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanneste, S.; Friml, J. Auxin: A Trigger for Change in Plant Development. Cell 2009, 136, 1005–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrášek, J.; Mravec, J.; Bouchard, R.; Blakeslee, J.J.; Abas, M.; Seifertová, D.; Wiśniewska, J.; Tadele, Z.; Kubeš, M.; Čovanová, M.; et al. PIN Proteins Perform a Rate-Limiting Function in Cellular Auxin Efflux. Science 2006, 312, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gälweiler, L.; Guan, C.; Müller, A.; Wisman, E.; Mendgen, K.; Yephremov, A.; Palme, K. Regulation of Polar Auxin Transport by AtPIN1 in Arabidopsis Vascular Tissue. Science 1998, 282, 2226–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wisniewska, J.; Xu, J.; Seifartová, D.; Brewer, P.B.; Růžička, K.; Blilou, L.; Rouquié, D.; Benková, E.; Scheres, B.; Friml, J. Polar PIN Localization Directs Auxin Flow in Plants. Science 2006, 312, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Michniewicz, M.; Zago, M.K.; Abas, L.; Weijers, D.; Schweighofer, A.; Meskiene, I.; Heisler, M.G.; Ohno, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, F.; et al. Antagonistic Regulation of PIN Phosphorylation by PP2A and PINOID Directs Auxin Flux. Cell 2007, 130, 1044–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Benková, E.; Michniewicz, M.; Sauer, M.; Teichmann, T.; Seifertová, D.; Jürgens, G.; Friml, J. Local, Efflux-Dependent Auxin Gradients as a Common Module for Plant Organ Formation. Cell 2003, 115, 591–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friml, J.; Vieten, A.; Sauer, M.; Weijers, D.; Schwarz, H.; Hamann, T.; Offringa, R.; Jürgens, G. Efflux-Dependent Auxin Gradients Establish the Apical-Basal Axis of Arabidopsis. Nature 2003, 426, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, M.; Balla, J.; Luschnig, C.; Wiśniewska, J.; Reinöhl, V.; Friml, J.; Benková, E. Canalization of Auxin Flow by Aux/IAA-ARF-Dependent Feedback Regulation of PIN Polarity. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 2902–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nodzyński, T.; Vanneste, S.; Zwiewka, M.; Pernisová, M.; Hejátko, J.; Friml, J. Enquiry into the Topology of Plasma Membrane-Localized PIN Auxin Transport Components. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 1504–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Křeček, P.; Skůpa, P.; Libus, J.; Naramoto, S.; Tejos, R.; Friml, J.; Zažímalová, E. The PIN-FORMED (PIN) Protein Family of Auxin Transporters. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zwiewka, M.; Bilanovičová, V.; Seifu, Y.W.; Nodzyński, T. The Nuts and Bolts of PIN Auxin Efflux Carriers. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Narasimhan, M.; Johnson, A.; Prizak, R.; Kaufmann, W.A.; Tan, S.; Casillas-Pérez, B.; Friml, J. Evolutionarily Unique Mechanistic Framework of Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis in Plants. eLife 2020, 9, e52067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nodzyński, T.; Vanneste, S.; Friml, J. Endocytic Trafficking of PIN Proteins and Auxin Transport. In Endocytosis in Plants; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Sancho-Andrés, G.; Soriano-Ortega, E.; Gao, C.; Bernabé-Orts, J.M.; Narasimhan, M.; Müller, A.O.; Tejos, R.; Jiang, L.; Friml, J.; Aniento, F.; et al. Sorting Motifs Involved in the Trafficking and Localization of the PIN1 Auxin Efflux Carrier. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1965–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Nodzyński, T.; Pěnčík, A.; Rolčík, J.; Friml, J. PIN Phosphorylation Is Sufficient to Mediate PIN Polarity and Direct Auxin Transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 918–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, F.; Zago, M.K.; Abas, L.; van Marion, A.; Galván-Ampudia, C.S.; Offringa, R. Phosphorylation of Conserved PIN Motifs Directs Arabidopsis PIN1 Polarity and Auxin Transport. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 1129–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abas, L.; Benjamins, R.; Malenica, N.; Paciorek, T.T.; Wiřniewska, J.; Moulinier-Anzola, J.C.; Sieberer, T.; Friml, J.; Luschnig, C. Intracellular Trafficking and Proteolysis of the Arabidopsis Auxin-Efflux Facilitator PIN2 Are Involved in Root Gravitropism. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, J.; Petrášek, J.; Tomanov, K.; Retzer, K.; Pařezová, M.; Korbei, B.; Bachmair, A.; Zažímalová, E.; Luschnig, C. Lysine63-Linked Ubiquitylation of PIN2 Auxin Carrier Protein Governs Hormonally Controlled Adaptation of Arabidopsis Root Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 8322–8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Friml, J.; Yang, X.; Michniewicz, M.; Weijers, D.; Quint, A.; Tietz, O.; Benjamins, R.; Ouwerkerk, P.B.F.; Ljung, K.; Sandberg, G.; et al. A PINOID-Dependent Binary Switch in Apical-Basal PIN Polar Targeting Directs Auxin Efflux. Science 2004, 306, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zourelidou, M.; Müller, I.; Willige, B.C.; Nill, C.; Jikumaru, Y.; Li, H.; Schwechheimer, C. The Polarly Localized D6 PROTEIN KINASE Is Required for Efficient Auxin Transport in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Development 2009, 136, 627–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zourelidou, M.; Absmanner, B.; Weller, B.; Barbosa, I.C.R.; Willige, B.C.; Fastner, A.; Streit, V.; Port, S.A.; Colcombet, J.; de la Fuente van Bentem, S.; et al. Auxin Efflux by PIN-FORMED Proteins Is Activated by Two Different Protein Kinases, D6 PROTEIN KINASE and PINOID. eLife 2014, 3, e02860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbosa, I.C.R.; Hammes, U.Z.; Schwechheimer, C. Activation and Polarity Control of PIN-FORMED Auxin Transporters by Phosphorylation. Trends Plant Sci. 2018, 23, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleine-Vehn, J.; Huang, F.; Naramoto, S.; Zhang, J.; Michniewicz, M.; Offringa, R.; Friml, J. PIN Auxin Efflux Carrier Polarity Is Regulated by PINOID Kinase-Mediated Recruitment into GNOM-Independent Trafficking in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 3839–3849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weller, B.; Zourelidou, M.; Frank, L.; Barbosa, I.C.R.; Fastner, A.; Richter, S.; Jürgens, G.; Hammes, U.Z.; Schwechheimer, C. Dynamic PIN-FORMED Auxin Efflux Carrier Phosphorylation at the Plasma Membrane Controls Auxin Efflux-Dependent Growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E887–E896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xi, W.; Gong, X.; Yang, Q.; Yu, H.; Liou, Y.C. Pin1At Regulates PIN1 Polar Localization and Root Gravitropism. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnson, L.N.; Lewis, R.J. Structural Basis for Control by Phosphorylation. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 2209–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlicky, S.; Tang, X.; Willems, A.; Tyers, M.; Sicheri, F. Structural Basis for Phosphodependent Substrate Selection and Orientation by the SCFCdc4 Ubiquitin Ligase. Cell 2003, 112, 243–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kleine-Vehn, J.; Wabnik, K.; Martinière, A.; Łangowski, Ł.; Willig, K.; Naramoto, S.; Leitner, J.; Tanaka, H.; Jakobs, S.; Robert, S.; et al. Recycling, Clustering, and Endocytosis Jointly Maintain PIN Auxin Carrier Polarity at the Plasma Membrane. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2011, 7, 540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; von Wangenheim, D.; Zhang, X.; Tan, S.; Darwish-Miranda, N.; Naramoto, S.; Wabnik, K.; de Rycke, R.; Kaufmann, W.A.; Gütl, D.; et al. Cellular Requirements for PIN Polar Cargo Clustering in Arabidopsis Thaliana. New Phytol. 2021, 229, 351–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retzer, K.; Lacek, J.; Skokan, R.; del Genio, C.I.; Vosolsobě, S.; Laňková, M.; Malínská, K.; Konstantinova, N.; Zažímalová, E.; Napier, R.M.; et al. Evolutionary Conserved Cysteines Function as Cis-Acting Regulators of Arabidopsis PIN-FORMED 2 Distribution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abas, L.; Kolb, M.; Stadlmann, J.; Janacek, D.P.; Lukic, K.; Schwechheimer, C.; Sazanov, L.A.; Mach, L.; Friml, J.; Hammes, U.Z. Naphthylphthalamic Acid Associates with and Inhibits PIN Auxin Transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 118, e2020857118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feraru, E.; Feraru, M.I.; Kleine-Vehn, J.; Martinière, A.; Mouille, G.; Vanneste, S.; Vernhettes, S.; Runions, J.; Friml, J. PIN Polarity Maintenance by the Cell Wall in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adamowski, M.; Friml, J. PIN-Dependent Auxin Transport: Action, Regulation, and Evolution. Plant Cell 2015, 27, 20–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using Circular Dichroism Spectra to Estimate Protein Secondary Structure. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 Web Portal for Protein Modeling, Prediction and Analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pauling, L.; Corey, R.B.; Branson, H.R. The Structure of Proteins; Two Hydrogen-Bonded Helical Configurations of the Polypeptide Chain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1951, 37, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chou, P.Y.; Fasman, G.D. Prediction of Protein Conformation. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 222–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically Disordered Proteins and Their Environment: Effects of Strong Denaturants, Temperature, PH, Counter Ions, Membranes, Binding Partners, Osmolytes, and Macromolecular Crowding. Protein J. 2009, 28, 305–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tompa, P.; Schad, E.; Tantos, A.; Kalmar, L. Intrinsically Disordered Proteins: Emerging Interaction Specialists. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2015, 35, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrasek, J.; Hoyerova, K.; Motyka, V.; Hejatko, J.; Dobrev, P.; Kaminek, M.; Vankova, R. Auxins and Cytokinins in Plant Development 2018. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blakeslee, J.J.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Ok, R.L.; Mravec, J.; Titapiwatanakun, B.; Sauer, M.; Makam, S.N.; Cheng, Y.; Bouchard, R.; Adamec, J.; et al. Interactions among PIN-FORMED and P-Glycoprotein Auxin Transporters in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rojas-Pierce, M.; Titapiwatanakun, B.; Sohn, E.J.; Fang, F.; Larive, C.K.; Blakeslee, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cuttler, S.; Peer, W.A.; Murphy, A.S.; et al. Arabidopsis P-Glycoprotein19 Participates in the Inhibition of Gravitropism by Gravacin. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Uversky, V.N. Functional Roles of Transiently and Intrinsically Disordered Regions within Proteins. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelínková, A.; Malínská, K.; Simon, S.; Kleine-Vehn, J.; Pařezová, M.; Pejchar, P.; Kubeš, M.; Martinec, J.; Friml, J.; Zažímalová, E.; et al. Probing Plant Membranes with FM Dyes: Tracking, Dragging or Blocking? Plant J. 2010, 61, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geldner, N.; Anders, N.; Wolters, H.; Keicher, J.; Kornberger, W.; Muller, P.; Delbarre, A.; Ueda, T.; Nakano, A.; Jürgens, G. The Arabidopsis GNOM ARF-GEF Mediates Endosomal Recycling, Auxin Transport, and Auxin-Dependent Plant Growth. Cell 2003, 112, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleine-Vehn, J.; Leitner, J.; Zwiewka, M.; Sauer, M.; Abas, L.; Luschnig, C.; Friml, J. Differential Degradation of PIN2 Auxin Efflux Carrier by Retromer-Dependent Vacuolar Targeting. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 17812–17817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kuhn, B.M.; Nodzyński, T.; Errafi, S.; Bucher, R.; Gupta, S.; Aryal, B.; Dobrev, P.; Bigler, L.; Geisler, M.; Zažímalová, E.; et al. Flavonol-Induced Changes in PIN2 Polarity and Auxin Transport in the Arabidopsis Thaliana Rol1-2 Mutant Require Phosphatase Activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scarpella, E.; Marcos, D.; Friml, J.; Berleth, T. Control of Leaf Vascular Patterning by Polar Auxin Transport. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1015–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luschnig, C.; Gaxiola, R.A.; Grisafi, P.; Fink, G.R. EIR1, a Root-Specific Protein Involved in Auxin Transport, Is Required for Gravitropism in Arabidopsis Thaliana. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 2175–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hegyi, H.; Gerstein, M. The Relationship between Protein Structure and Function: A Comprehensive Survey with Application to the Yeast Genome. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 288, 147–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dunker, A.K.; Brown, C.J.; Lawson, J.D.; Iakoucheva, L.M.; Obradović, Z. Intrinsic Disorder and Protein Function. Biochemistry 2002, 41, 6573–6582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, R.; Mulder, F.A.A.; Nielsen, J.T. ODiNPred: Comprehensive Prediction of Protein Order and Disorder. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paciorek, T.; Zažímalová, E.; Ruthardt, N.; Petrášek, J.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Kleine-Vehn, J.; Morris, D.A.; Emans, N.; Jürgens, G.; Geldner, N.; et al. Auxin Inhibits Endocytosis and Promotes Its Own Efflux from Cells. Nature 2005, 435, 1251–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Permyakov, S.E.; Permyakov, E.A.; Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically Disordered Caldesmon Binds Calmodulin via the “Buttons on a String” Mechanism. PeerJ 2015, 2015, 1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blondelle, S.E.; Forood, B.; Houghten, R.A.; Pérez-Payé, E. Secondary Structure Induction in Aqueous vs Membrane-like Environments. Biopolymers 1997, 42, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joerger, A.C.; Fersht, A.R. The Tumor Suppressor P53: From Structures to Drug Discovery. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alberti, S.; Gladfelter, A.; Mittag, T. Considerations and Challenges in Studying Liquid-Liquid Phase Separation and Biomolecular Condensates. Cell 2019, 176, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Franzmann, T.M.; Alberti, S. Prion-like Low-Complexity Sequences: Key Regulators of Protein Solubility and Phase Behavior. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 7128–7136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Case, L.B.; Ditlev, J.A.; Rosen, M.K. Regulation of Transmembrane Signaling by Phase Separation. Annu. Rev. Biophys. 2019, 48, 465–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, B.J.; Yu, J. Protein Clusters in Phosphotyrosine Signal Transduction. J. Mol. Biol. 2018, 430, 4547–4556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, A.; Sovero, V.; Vincenzetti, V.; Santelia, D.; Bartnik, D.; Koenig, B.W.; Mancuso, S.; Martinoia, E.; Geisler, M. Modulation of P-Glycoproteins by Auxin Transport Inhibitors Is Mediated by Interaction with Immunophilins. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21817–21826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mravec, J.; Skůpa, P.; Bailly, A.; Hoyerová, K.; Křeček, P.; Bielach, A.; Petrášek, J.; Zhang, J.; Gaykova, V.; Stierhof, Y.D.; et al. Subcellular Homeostasis of Phytohormone Auxin Is Mediated by the ER-Localized PIN5 Transporter. Nature 2009, 459, 1136–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.S. Forty Years of Clathrin-Coated Vesicles. Traffic 2015, 16, 1210–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hajný, J.; Prát, T.; Rydza, N.; Rodriguez, L.; Tan, S.; Verstraeten, I.; Domjan, D.; Mazur, E.; Smakowska-Luzan, E.; Smet, W.; et al. Receptor Kinase Module Targets PIN-Dependent Auxin Transport during Canalization. Science 2020, 370, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naramoto, S.; Nodzyński, T.; Dainobu, T.; Takatsuka, H.; Okada, T.; Friml, J.; Fukuda, H. VAN4 Encodes a Putative TRS120 That Is Required for Normal Cell Growth and Vein Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 2014, 55, 750–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Titapiwatanakun, B.; Blakeslee, J.J.; Bandyopadhyay, A.; Yang, H.; Mravec, J.; Sauer, M.; Cheng, Y.; Adamec, J.; Nagashima, A.; Geisler, M.; et al. ABCB19/PGP19 Stabilises PIN1 in Membrane Microdomains in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2009, 57, 27–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Scheres, B. Dissection of Arabidopsis ADP-Ribosylation Factor 1 Function in Epidermal Cell Polarity. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 525–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cutler, S.R.; Ehrhardt, D.W.; Griffitts, J.S.; Somerville, C.R. Random GFP::CDNA Fusions Enable Visualization of Subcellular Structures in Cells of Arabidopsis at a High Frequency. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 3718–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dhonukshe, P.; Aniento, F.; Hwang, I.; Robinson, D.G.; Mravec, J.; Stierhof, Y.D.; Friml, J. Clathrin-Mediated Constitutive Endocytosis of PIN Auxin Efflux Carriers in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, H.; Kitakura, S.; de Rycke, R.; De Groodt, R.; Friml, J. Fluorescence Imaging-Based Screen Identifies ARF GEF Component of Early Endosomal Trafficking. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshed, Y.; Baum, S.F.; Perea, J.V.; Bowman, J.L. Establishment of Polarity in Lateral Organs of Plants. Curr. Biol. 2001, 11, 1251–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lancaster, A.K.; Nutter-Upham, A.; Lindquist, S.; King, O.D. PLAAC: A Web and Command-Line Application to Identify Proteins with Prion-like Amino Acid Composition. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2501–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golovanov, A.P.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Wilson, S.A.; Lian, L.Y. A Simple Method for Improving Protein Solubility and Long-Term Stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 8933–8939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Brautigam, C.A.; Ghirlando, R.; Schuck, P. Overview of Current Methods in Sedimentation Velocity and Sedimentation Equilibrium Analytical Ultracentrifugation. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2013, 71, 20.12.1–20.12.49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schuck, P. Size-Distribution Analysis of Macromolecules by Sedimentation Velocity Ultracentrifugation and Lamm Equation Modeling. Biophys. J. 2000, 78, 1606–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mravec, J.; Petrášek, J.; Li, N.; Boeren, S.; Karlova, R.; Kitakura, S.; Pařezová, M.; Naramoto, S.; Nodzyński, T.; Dhonukshe, P.; et al. Cell Plate Restricted Association of DRP1A and PIN Proteins Is Required for Cell Polarity Establishment in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1055–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degtjarik, O.; Dopitova, R.; Puehringer, S.; Nejedla, E.; Kuty, M.; Weiss, M.S.; Hejatko, J.; Janda, L.; Kuta Smatanova, I. Cloning, Expression, Purification, Crystallization and Preliminary X-Ray Diffraction Analysis of AHP2, a Signal Transmitter Protein from Arabidopsis Thaliana. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. F Struct. Biol. Cryst. Commun. 2013, 69, 158–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skokan, R.; Medvecká, E.; Viaene, T.; Vosolsobě, S.; Zwiewka, M.; Müller, K.; Skůpa, P.; Karady, M.; Zhang, Y.; Janacek, D.P.; et al. PIN-Driven Auxin Transport Emerged Early in Streptophyte Evolution. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 1114–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abràmoff, M.D.; Magalhães, P.J.; Ram, S.J. Image Processing with ImageJ. Biophotonics Int. 2004, 11, 36–42. [Google Scholar]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bilanovičová, V.; Rýdza, N.; Koczka, L.; Hess, M.; Feraru, E.; Friml, J.; Nodzyński, T. The Hydrophilic Loop of Arabidopsis PIN1 Auxin Efflux Carrier Harbors Hallmarks of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116352
Bilanovičová V, Rýdza N, Koczka L, Hess M, Feraru E, Friml J, Nodzyński T. The Hydrophilic Loop of Arabidopsis PIN1 Auxin Efflux Carrier Harbors Hallmarks of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2022; 23(11):6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116352
Chicago/Turabian StyleBilanovičová, Veronika, Nikola Rýdza, Lilla Koczka, Martin Hess, Elena Feraru, Jiří Friml, and Tomasz Nodzyński. 2022. "The Hydrophilic Loop of Arabidopsis PIN1 Auxin Efflux Carrier Harbors Hallmarks of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23, no. 11: 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116352
APA StyleBilanovičová, V., Rýdza, N., Koczka, L., Hess, M., Feraru, E., Friml, J., & Nodzyński, T. (2022). The Hydrophilic Loop of Arabidopsis PIN1 Auxin Efflux Carrier Harbors Hallmarks of an Intrinsically Disordered Protein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(11), 6352. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23116352





