Screening for Interacting Proteins with Peptide Biomarker of Blood–Brain Barrier Alteration under Inflammatory Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
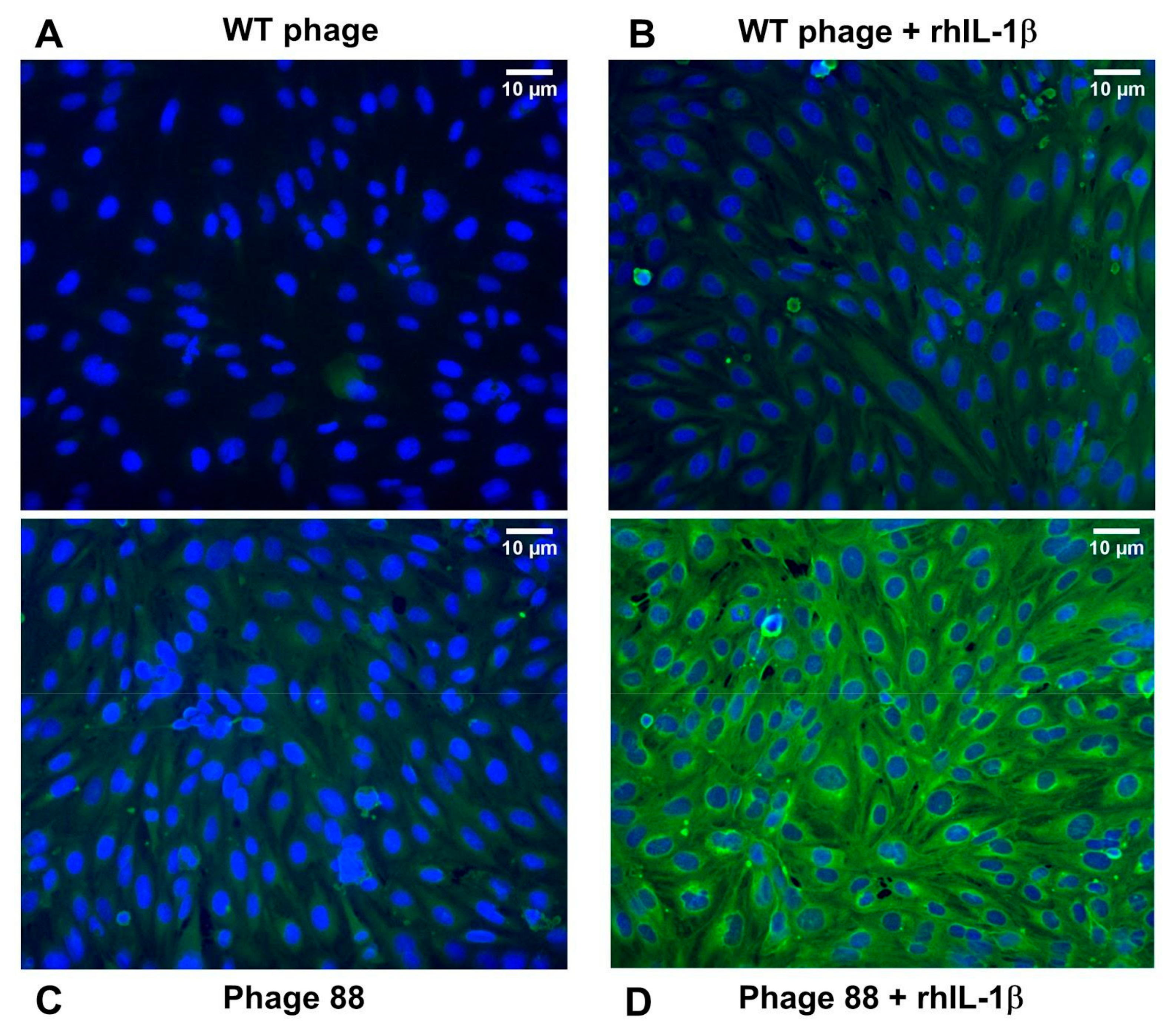
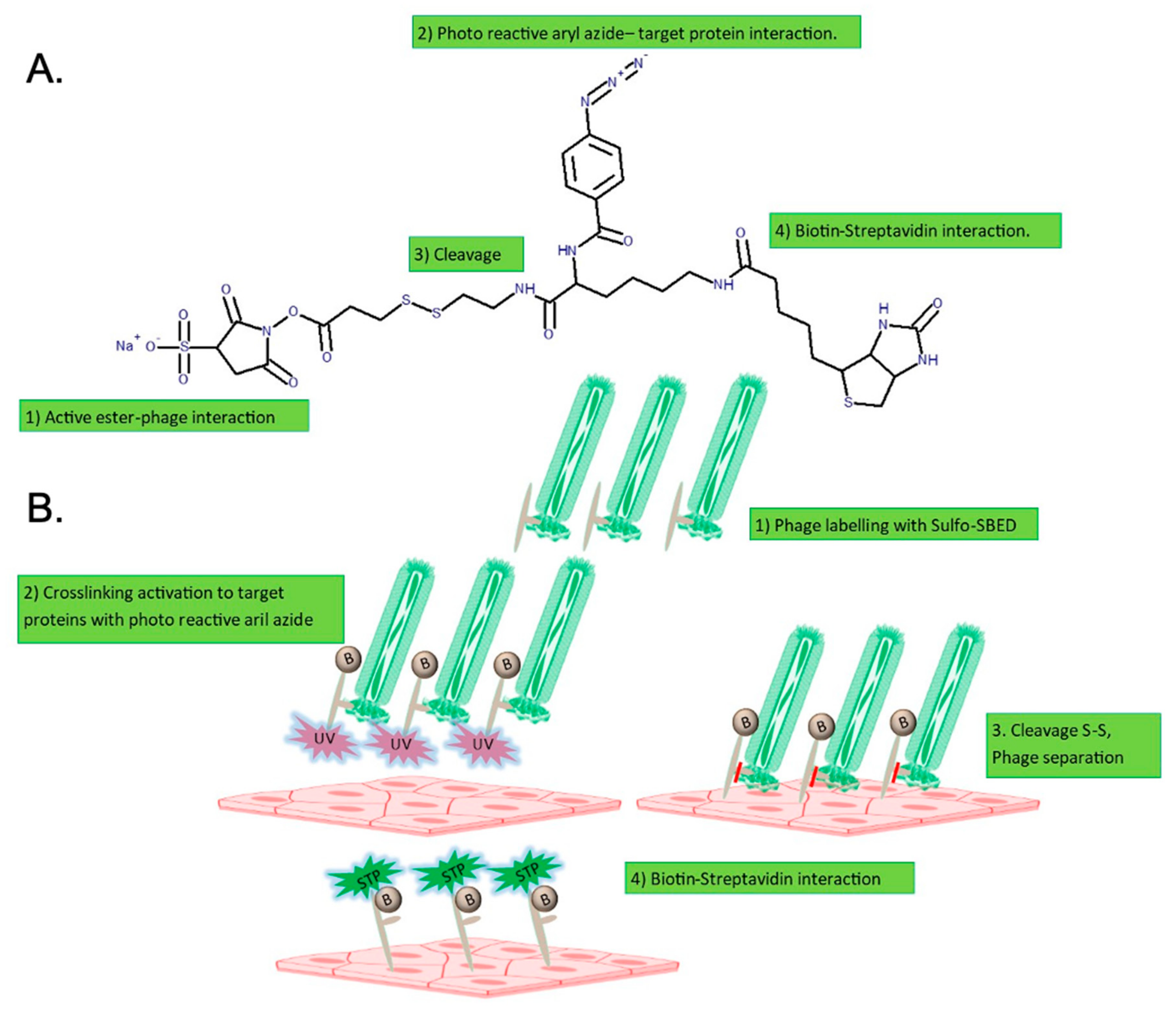
2.1. Phage 88 Crosslinks with Target Proteins of a Human BBB In Vitro Model
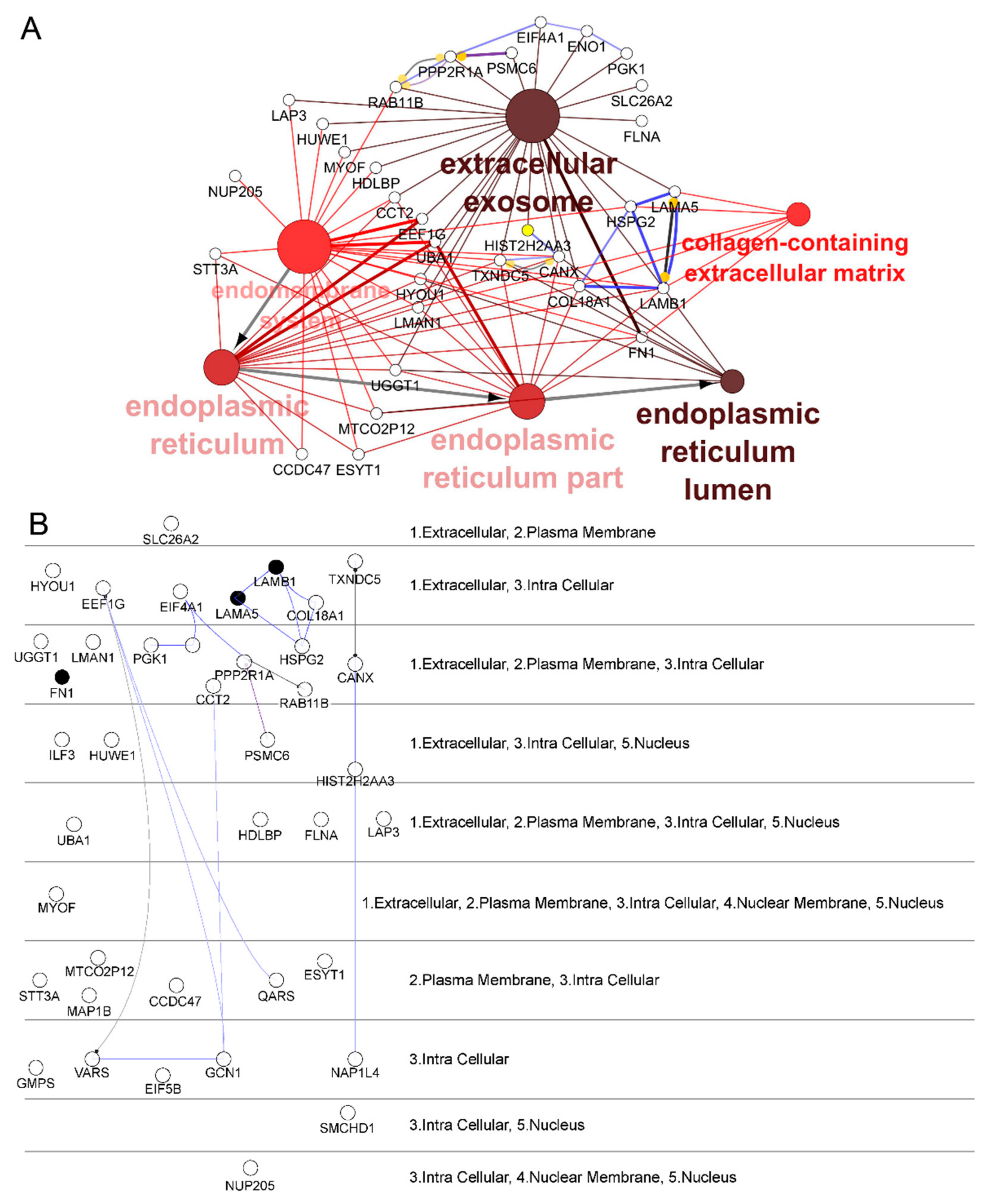
2.2. Identification and Selection of Target Proteins Crosslinked with Phage 88
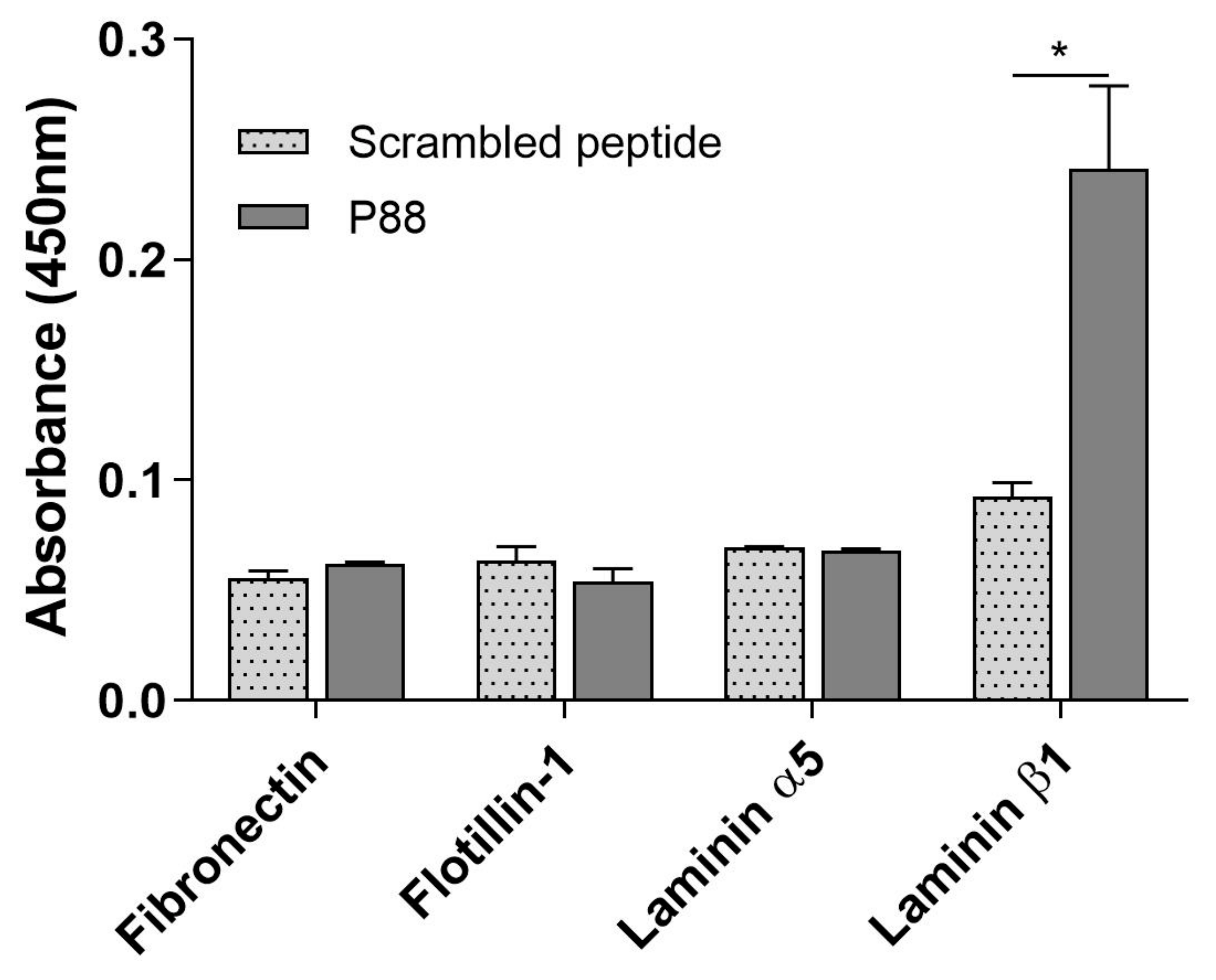
2.3. Peptide-88 Binds to the Laminin Subunit Beta-1
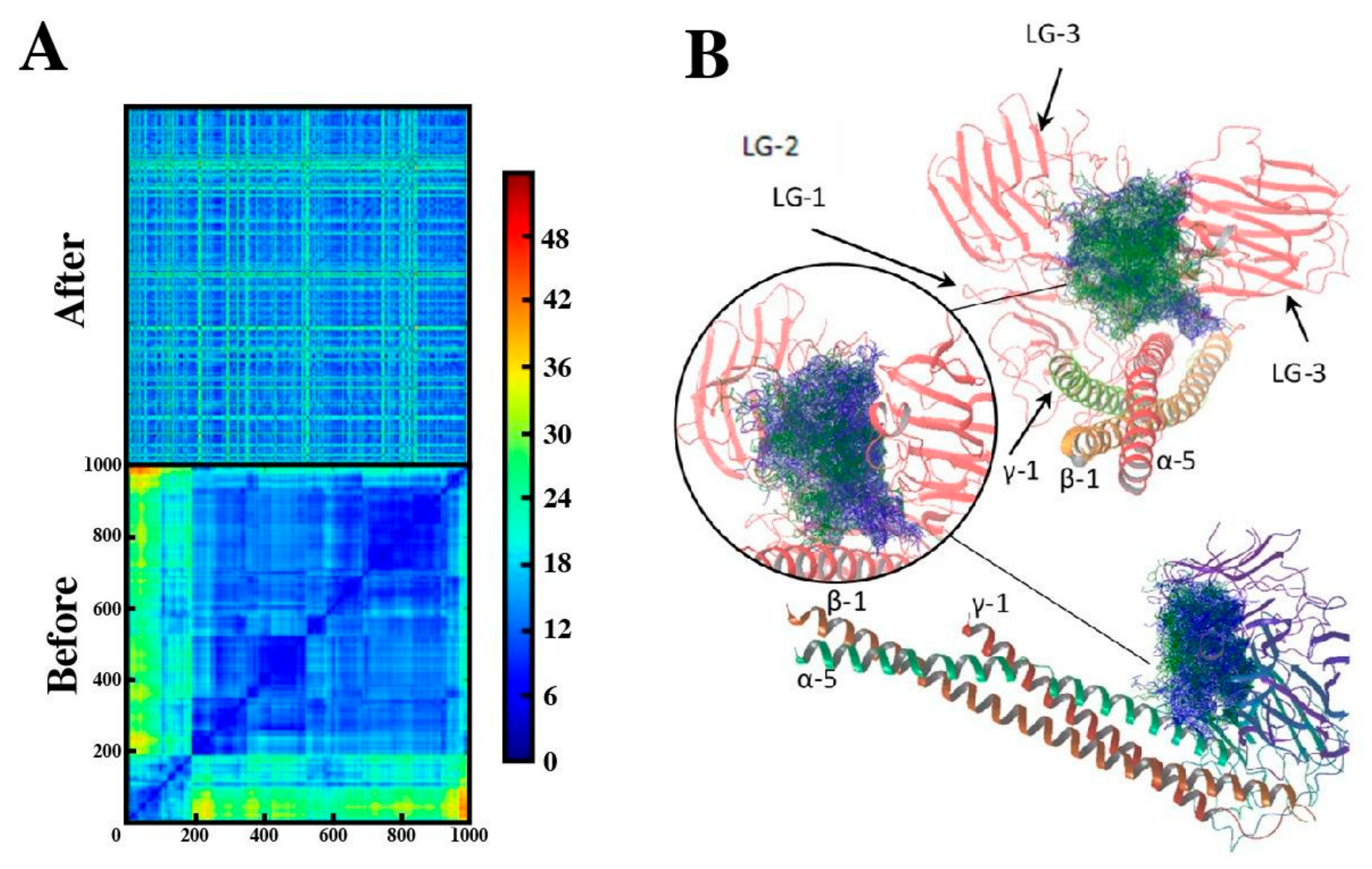
2.4. Binding Mode of Peptide-88 to Laminin 511
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Amplification and Purification of Phages
4.2. hCMEC/D3 Cell Culture
4.3. Crosslinking of Phage 88 and Target Proteins on hCMEC/D3 Cells
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Isolation of Target Proteins of Phage 88 Crosslinked on hCMEC/D3 Cells
4.6. Sample Preparation
4.7. LC-MS/MS
4.8. Protein Identification and Quantification
4.9. Bioinformatic Analysis of Proteomic Data
4.10. Evaluation of Peptide-88 Binding to Target Proteins
4.11. Computational Studies
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACN | acetonitrile |
| AMBIC | ammonium bicarbonate buffer |
| CID | collision-induced dissociation |
| DTT | dithiothreitol |
| IAA | iodoacetamide |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TFA | Trifluoroacetic acid |
| Sulfo-SBED | Sulfo-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl-2-(6-[biotinamido]-2-(p-azido benzamido)-hexanoamido) ethyl-1,3′-dithioproprionate |
References
- Sweeney, M.D.; Sagare, A.P.; Zlokovic, B.V. Blood–Brain Barrier Breakdown in Alzheimer’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derada Troletti, C.; de Goede, P.; Kamermans, A.; de Vries, H.E. Molecular Alterations of the Blood–Brain Barrier under Inflammatory Conditions: The Role of Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiuolo, J.; Gliozzi, M.; Musolino, V.; Scicchitano, M.; Carresi, C.; Scarano, F.; Bosco, F.; Nucera, S.; Ruga, S.; Zito, M.C.; et al. The “Frail” Brain Blood Barrier in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Role of Early Disruption of Endothelial Cell-to-Cell Connections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bordone, M.P.; Salman, M.M.; Titus, H.E.; Amini, E.; Andersen, J.V.; Chakraborti, B.; Diuba, A.V.; Dubouskaya, T.G.; Ehrke, E.; de Freitas, A.E.; et al. The Energetic Brain—A Review from Students to Students. J. Neurochem. 2019, 151, 139–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araque, A.; Parpura, V.; Sanzgiri, R.P.; Haydon, P.G. Tripartite Synapses: Glia, the Unacknowledged Partner. Trends Neurosci. 1999, 22, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencurova, E.; Mlynarcik, P.; Bhide, M. An Insight into the Ligand-Receptor Interactions Involved in the Translocation of Pathogens across Blood-Brain Barrier. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 63, 297–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engelhardt, B.; Liebner, S. Novel Insights into the Development and Maintenance of the Blood–Brain Barrier. Cell Tissue Res. 2014, 355, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dendrou, C.A.; Fugger, L.; Friese, M.A. Immunopathology of Multiple Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 15, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo-González, T.; Chavarría, A.; Pérez-H, J. Central Nervous System: A Modified Immune Surveillance Circuit? Brain Behav. Immun. 2012, 26, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.; Heasman, S.J.; Alvarez, J.I.; Prat, A.; Lyck, R.; Engelhardt, B. Review: Leucocyte-Endothelial Cell Crosstalk at the Blood-Brain Barrier: A Prerequisite for Successful Immune Cell Entry to the Brain. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2011, 37, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milner, R.; Hung, S.; Wang, X.; Berg, G.I.; Spatz, M.; del Zoppo, G.J. Responses of Endothelial Cell and Astrocyte Matrix-Integrin Receptors to Ischemia Mimic Those Observed in the Neurovascular Unit. Stroke 2008, 39, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strecker, J.-K.; Minnerup, J.; Schütte-Nütgen, K.; Gess, B.; Schäbitz, W.-R.; Schilling, M. Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1-Deficiency Results in Altered Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown after Experimental Stroke. Stroke 2013, 44, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejana, E.; Hirschi, K.K.; Simons, M. The Molecular Basis of Endothelial Cell Plasticity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troletti, C.D.; Fontijn, R.D.; Gowing, E.; Charabati, M.; van Het Hof, B.; Didouh, I.; van der Pol, S.M.A.; Geerts, D.; Prat, A.; van Horssen, J.; et al. Inflammation-Induced Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition Promotes Brain Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and Occurs during Multiple Sclerosis Pathophysiology. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deutscher, S.L. Phage Display in Molecular Imaging and Diagnosis of Cancer. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 3196–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rooy, I.; Cakir-Tascioglu, S.; Couraud, P.-O.; Romero, I.A.; Weksler, B.; Storm, G.; Hennink, W.E.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Mastrobattista, E. Identification of Peptide Ligands for Targeting to the Blood-Brain Barrier. Pharm. Res. 2010, 27, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Sanchez, K.; Vekris, A.; Petry, K.G. DNA Subtraction of In Vivo Selected Phage Repertoires for Efficient Peptide Pathology Biomarker Identification in Neuroinflammation Multiple Sclerosis Model. Biomark. Insights 2016, 11, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boiziau, C.; Nikolski, M.; Mordelet, E.; Aussudre, J.; Vargas-Sanchez, K.; Petry, K.G. A Peptide Targeting Inflammatory CNS Lesions in the EAE Rat Model of Multiple Sclerosis. Inflammation 2018, 41, 932–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Del Palacio, J.; Díaz, C.; de la Cruz, M.; Annang, F.; Martín, J.; Pérez-Victoria, I.; González-Menéndez, V.; de Pedro, N.; Tormo, J.R.; Algieri, F.; et al. High-Throughput Screening Platform for the Discovery of New Immunomodulator Molecules from Natural Product Extract Libraries. J. Biomol. Screen. 2016, 21, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldewachi, H.; Al-Zidan, R.N.; Conner, M.T.; Salman, M.M. High-Throughput Screening Platforms in the Discovery of Novel Drugs for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Bioengineering 2021, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlik, S.J.; Roscoe, W.A.; Patinote, C.; Contino-Pepin, C. Targeting Vascular Changes in Lesions in Multiple Sclerosis and Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. Cent. Nerv. Syst. Agents Med. Chem. 2012, 12, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, C.; Hiestand, P.; Kindler-Baumann, D.; Rudin, M.; Rausch, M. Analysis of Lesion Development during Acute Inflammation and Remission in a Rat Model of Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis by Visualization of Macrophage Infiltration, Demyelination and Blood-Brain Barrier Damage. NMR Biomed. 2006, 19, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floris, S.; Blezer, E.L.A.; Schreibelt, G.; Döpp, E.; van der Pol, S.M.A.; Schadee-Eestermans, I.L.; Nicolay, K.; Dijkstra, C.D.; de Vries, H.E. Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability and Monocyte Infiltration in Experimental Allergic Encephalomyelitis: A Quantitative MRI Study. Brain 2004, 127, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weksler, B.B.; Subileau, E.A.; Perrière, N.; Charneau, P.; Holloway, K.; Leveque, M.; Tricoire-Leignel, H.; Nicotra, A.; Bourdoulous, S.; Turowski, P.; et al. Blood-Brain Barrier-Specific Properties of a Human Adult Brain Endothelial Cell Line. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1872–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomsen, M.S.; Routhe, L.J.; Moos, T. The Vascular Basement Membrane in the Healthy and Pathological Brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 3300–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilling, T.; Korte, D.; Hoheisel, D.; Galla, H.J. Basement Membrane Proteins Influence Brain Capillary Endothelial Barrier Function in Vitro. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 1151–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salman, M.M.; Marsh, G.; Kusters, I.; Delincé, M.; Di Caprio, G.; Upadhyayula, S.; de Nola, G.; Hunt, R.; Ohashi, K.G.; Gray, T.; et al. Design and Validation of a Human Brain Endothelial Microvessel-on-a-Chip Open Microfluidic Model Enabling Advanced Optical Imaging. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2020, 8, 573775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wevers, N.R.; Kasi, D.G.; Gray, T.; Wilschut, K.J.; Smith, B.; van Vught, R.; Shimizu, F.; Sano, Y.; Kanda, T.; Marsh, G.; et al. A Perfused Human Blood-Brain Barrier on-a-Chip for High-Throughput Assessment of Barrier Function and Antibody Transport. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takizawa, M.; Arimori, T.; Taniguchi, Y.; Kitago, Y.; Yamashita, E.; Takagi, J.; Sekiguchi, K. Mechanistic Basis for the Recognition of Laminin-511 by A6β1 Integrin. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1701497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharif, K.A.; Baker, H.; Gudas, L.J. Differential Regulation of Laminin B1 Transgene Expression in the Neonatal and Adult Mouse Brain. Neuroscience 2004, 126, 967–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indyk, J.A.; Chen, Z.L.; Tsirka, S.E.; Strickland, S. Laminin Chain Expression Suggests That Laminin-10 Is a Major Isoform in the Mouse Hippocampus and Is Degraded by the Tissue Plasminogen Activator/Plasmin Protease Cascade during Excitotoxic Injury. Neuroscience 2003, 116, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, R.N.; Metheny-Barlow, L.J.; Peiffer, A.M.; Hanbury, D.B.; Tooze, J.A.; Bourland, J.D.; Hampson, R.E.; Deadwyler, S.A.; Cline, J.M. Cerebrovascular Remodeling and Neuroinflammation Is a Late Effect of Radiation-Induced Brain Injury in Non-Human Primates. Radiat. Res. 2017, 187, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boroujerdi, A.; Welser-Alves, J.V.; Milner, R. Extensive Vascular Remodeling in the Spinal Cord of Pre-Symptomatic Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis Mice; Increased Vessel Expression of Fibronectin and the A5β1 Integrin. Exp. Neurol. 2013, 250, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espitia, N.P.; Brevé, J.J.P.; Bol, J.; Drukarch, B.; Baron, W.; van Dam, A.M. Tissue Transglutaminase in Astrocytes Is Enhanced by Inflammatory Mediators and Is Involved in the Formation of Fibronectin Fibril-like Structures. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, J.; Miner, J.H.; Yao, Y. Loss of Endothelial Laminin A5 Exacerbates Hemorrhagic Brain Injury. Transl. Stroke Res. 2019, 10, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangwantas, K.; Pinteaux, E.; Penny, J. The Extracellular Matrix Protein Laminin-10 Promotes Blood–Brain Barrier Repair after Hypoxia and Inflammation In Vitro. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labus, J.; Wöltje, K.; Stolte, K.N.; Stolte, K.N.; Häckel, S.; Kim, K.S.; Hildmann, A.; Danker, K. IL-1β Promotes Transendothelial Migration of PBMCs by Upregulation of the FN/A5 Β1 Signalling Pathway in Immortalised Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells. Available online: https://www.meta.org/papers/il-1-promotes-transendothelial-migration-of-pbmcs/30342992 (accessed on 29 July 2019).
- Sikkema, A.H.; Stoffels, J.M.J.; Wang, P.; Basedow, F.J.; Bulsink, R.; Bajramovic, J.J.; Baron, W. Fibronectin Aggregates Promote Features of a Classically and Alternatively Activated Phenotype in Macrophages. J. Neuroinflamm. 2018, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, M.S.; Birkelund, S.; Burkhart, A.; Stensballe, A.; Moos, T. Synthesis and Deposition of Basement Membrane Proteins by Primary Brain Capillary Endothelial Cells in a Murine Model of the Blood-Brain Barrier. J. Neurochem. 2017, 140, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toti, P.; Villanova, M.; De Felice, C.; Megha, T.; Bartolommei, S.; Tosi, P. Expression of Laminin 1 and 2 in Brain Tumor Vessels. An Immunohistochemical Study. J. Submicrosc. Cytol. Pathol. 1998, 30, 227–230. [Google Scholar]
- Hahn, S.; Trendelenburg, G.; Scharf, M.; Denno, Y.; Brakopp, S.; Teegen, B.; Probst, C.; Wandinger, K.P.; Buttmann, M.; Haarmann, A.; et al. Identification of the Flotillin-1/2 Heterocomplex as a Target of Autoantibodies in Bona Fide Multiple Sclerosis. J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z. Shenmai Injection Maintains Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity Following Focal Cerebral Ischemia via Modulating the Expression and Trafficking of Occludin in Lipid Rafts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 237, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, D.; Bedoya, M.; Kiper, A.K.; Rinné, S.; Morales-Navarro, S.; Hernández-Rodríguez, E.W.; Sepúlveda, F.V.; Decher, N.; González, W. Structure/Activity Analysis of TASK-3 Channel Antagonists Based on a 5,6,7,8 Tetrahydropyrido[4,3-d]Pyrimidine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, D.; Arévalo, B.; Martínez, G.; Rinné, S.; Sepúlveda, F.V.; Decher, N.; González, W. Side Fenestrations Provide an “Anchor” for a Stable Binding of A1899 to the Pore of TASK-1 Potassium Channels. Mol. Pharm. 2017, 14, 2197–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Russo, J.; Luik, A.; Yousif, L.; Budny, S.; Oberleithner, H.; Hofschröer, V.; Klingauf, J.; van Bavel, E.; Bakker, E.N.; Hellstrand, P.; et al. Endothelial Basement Membrane Laminin 511 Is Essential for Shear Stress Response. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Zhang, X.; Buscher, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Di, J.R.; Li, L.; Lütke-Enking, S.; Zarbock, A.; Stadtmann, A.; et al. Endothelial Basement Membrane Laminin 511 Contributes to Endothelial Junctional Tightness and Thereby Inhibits Leukocyte Transmigration. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 1256–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Ivars, F.; Anderson, P.; Hallmann, R.; Vestweber, D.; Nilsson, P.; Robenek, H.; Tryggvason, K.; Song, J.; Korpos, E. Endothelial Basement Membrane Laminin Alpha5 Selectively Inhibits T Lymphocyte Extravasation into the Brain. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, M.J.; McClenahan, F.K.; Leiton, C.V.; Aranmolate, A.; Shan, X.; Colognato, H. The Extracellular Matrix Protein Laminin A2 Regulates the Maturation and Function of the Blood-Brain Barrier. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 15260–15280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgačevski, J.; Zorec, R.; Potokar, M. Insights into Cell Surface Expression, Supramolecular Organization, and Functions of Aquaporin 4 Isoforms in Astrocytes. Cells 2020, 9, 2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.; Yu, X.; Xu, W.; Lenahan, C.; Tu, S.; Shao, A. The Role of Glymphatic System in the Cerebral Edema Formation after Ischemic Stroke. Exp. Neurol. 2021, 340, 113685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.; Choi, S.-H.; Kong, M.-J.; Kang, T.-C. Dysfunction of 67-KDa Laminin Receptor Disrupts BBB Integrity via Impaired Dystrophin/AQP4 Complex and P38 MAPK/VEGF Activation Following Status Epilepticus. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitchen, P.; Salman, M.M.; Halsey, A.M.; Clarke-Bland, C.; MacDonald, J.A.; Ishida, H.; Vogel, H.J.; Almutiri, S.; Logan, A.; Kreida, S.; et al. Targeting Aquaporin-4 Subcellular Localization to Treat Central Nervous System Edema. Cell 2020, 181, 784–799.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvain, N.J.; Salman, M.M.; Pushie, M.J.; Hou, H.; Meher, V.; Herlo, R.; Peeling, L.; Kelly, M.E. The Effects of Trifluoperazine on Brain Edema, Aquaporin-4 Expression and Metabolic Markers during the Acute Phase of Stroke Using Photothrombotic Mouse Model. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2021, 1863, 183573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahab, S.N.; Khooei, A.; Samini, F.; Gorji, A. Laminin-Derived Ile-Lys-Val-Ala-Val: A Promising Bioactive Peptide in Neural Tissue Engineering in Traumatic Brain Injury. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 371, 223–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Mateo, S.; Castillo, J.; Estanyol, J.M.; Ballescà, J.L.; Oliva, R. Proteomic Characterization of the Human Sperm Nucleus. Proteomics 2011, 11, 2714–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aalto, K.; Autio, A.; Kiss, E.A.; Elima, K.; Nymalm, Y.; Veres, T.Z.; Marttila-Ichihara, F.; Elovaara, H.; Saanijoki, T.; Crocker, P.R.; et al. Siglec-9 Is a Novel Leukocyte Ligand for Vascular Adhesion Protein-1 and Can Be Used in PET Imaging of Inflammation and Cancer. Blood 2011, 118, 3725–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutknecht, M.F.; Seaman, M.E.; Ning, B.; Cornejo, D.A.; Mugler, E.; Antkowiak, P.F.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Hu, S.; Epstein, F.H.; Kelly, K.A. Identification of the S100 Fused-Type Protein Hornerin as a Regulator of Tumor Vascularity. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Zhang, X.F.; Fu, B.M.; Tarbell, J.M. The Role of Endothelial Surface Glycocalyx in Mechanosensing and Transduction. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2018, 1097, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santa-Maria, A.R.; Walter, F.R.; Figueiredo, R.; Kincses, A.; Vigh, J.P.; Heymans, M.; Culot, M.; Winter, P.; Gosselet, F.; Dér, A.; et al. Flow Induces Barrier and Glycocalyx-Related Genes and Negative Surface Charge in a Lab-on-a-Chip Human Blood-Brain Barrier Model. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béguin, E.P.; Janssen, E.F.J.; Hoogenboezem, M.; Meijer, A.B.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; van den Biggelaar, M. Flow-Induced Reorganization of Laminin-Integrin Networks Within the Endothelial Basement Membrane Uncovered by Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2020, 19, 1179–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ader, M.; Tanaka, E.M. Modeling Human Development in 3D Culture. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 31, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, F.; Panneer, N.; Tutino, C.M.; Wu, M.; Skrabal, W.R.; Moskaluk, C.; Kelly, K.A. A Functional Proteomic Method for Biomarker Discovery. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Purushotham, S.; Lee, J.-Y.; Na, M.-H.; Park, H.; Oh, S.-J.; Park, R.-W.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, E.; Cho, B.C.; et al. In Vivo Imaging of Tumor Apoptosis Using Histone H1-Targeting Peptide. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Hackl, H.; Charoentong, P.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Fridman, W.-H.; Pagès, F.; Trajanoski, Z.; Galon, J. ClueGO: A Cytoscape Plug-in to Decipher Functionally Grouped Gene Ontology and Pathway Annotation Networks. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1091–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Galon, J.; Mlecnik, B. CluePedia Cytoscape Plugin: Pathway Insights Using Integrated Experimental and in Silico Data. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesiadecki, B.J.; Jin, J.-P. A High-Throughput Solid-Phase Microplate Protein-Binding Assay to Investigate Interactions between Myofilament Proteins. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 421701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumailley, M.; Bruckner-Tuderman, L.; Carter, W.G.; Deutzmann, R.; Edgar, D.; Ekblom, P.; Engel, J.; Engvall, E.; Hohenester, E.; Jones, J.C.R.; et al. A Simplified Laminin Nomenclature. Matrix Biol. 2005, 24, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trott, O.; Olson, J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem. 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez Bernal, J.; Buendía-Atencio, C.; Ramírez, D. Massive Docking with Vina (Versión 1.0); Zenodo: Geneva, Switzerland, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vargas-Sanchez, K.; Losada-Barragán, M.; Mogilevskaya, M.; Novoa-Herrán, S.; Medina, Y.; Buendía-Atencio, C.; Lorett-Velásquez, V.; Martínez-Bernal, J.; Gonzalez-Reyes, R.E.; Ramírez, D.; et al. Screening for Interacting Proteins with Peptide Biomarker of Blood–Brain Barrier Alteration under Inflammatory Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094725
Vargas-Sanchez K, Losada-Barragán M, Mogilevskaya M, Novoa-Herrán S, Medina Y, Buendía-Atencio C, Lorett-Velásquez V, Martínez-Bernal J, Gonzalez-Reyes RE, Ramírez D, et al. Screening for Interacting Proteins with Peptide Biomarker of Blood–Brain Barrier Alteration under Inflammatory Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(9):4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094725
Chicago/Turabian StyleVargas-Sanchez, Karina, Monica Losada-Barragán, Maria Mogilevskaya, Susana Novoa-Herrán, Yehidi Medina, Cristian Buendía-Atencio, Vaneza Lorett-Velásquez, Jessica Martínez-Bernal, Rodrigo E. Gonzalez-Reyes, David Ramírez, and et al. 2021. "Screening for Interacting Proteins with Peptide Biomarker of Blood–Brain Barrier Alteration under Inflammatory Conditions" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 9: 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094725
APA StyleVargas-Sanchez, K., Losada-Barragán, M., Mogilevskaya, M., Novoa-Herrán, S., Medina, Y., Buendía-Atencio, C., Lorett-Velásquez, V., Martínez-Bernal, J., Gonzalez-Reyes, R. E., Ramírez, D., & Petry, K. G. (2021). Screening for Interacting Proteins with Peptide Biomarker of Blood–Brain Barrier Alteration under Inflammatory Conditions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(9), 4725. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22094725







