Identification of QTLs and a Candidate Gene for Reducing Pre-Harvest Sprouting in Aegilops tauschii–Triticum aestivum Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
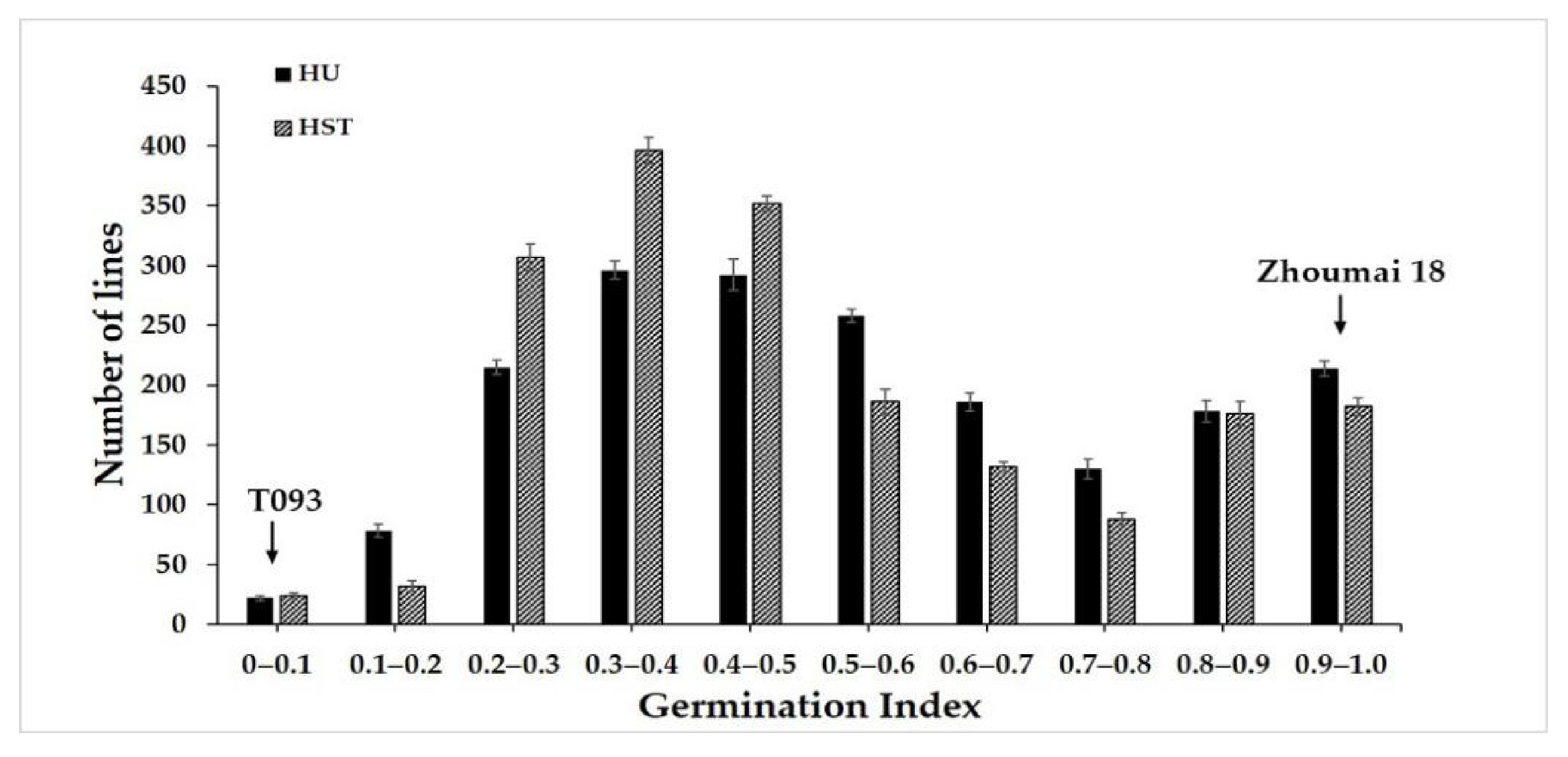
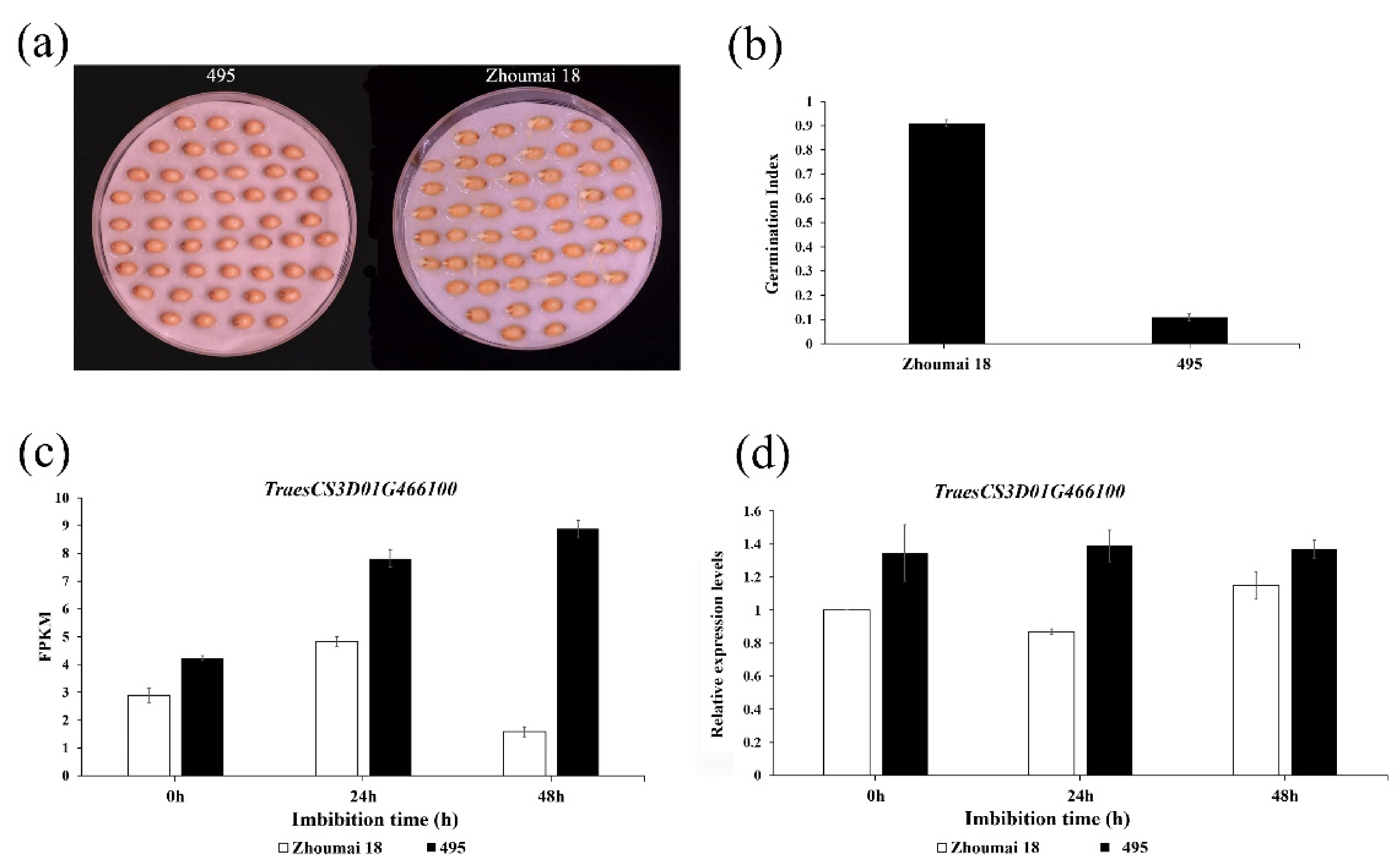
2.1. Phenotypic Characterization of PHS
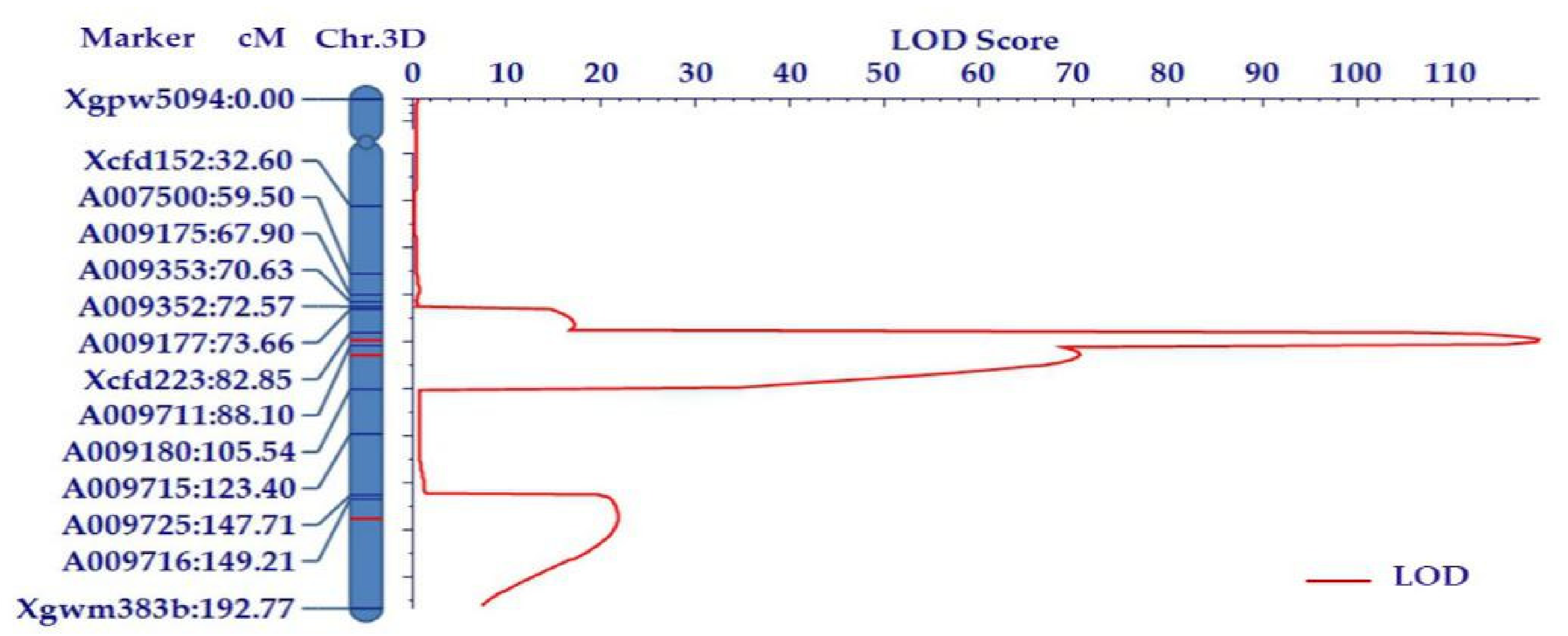
2.2. Precise Mapping of Qphs-3D Using the SSR and KASP Markers
2.3. RNA-Seq and qRT-PCR Assay
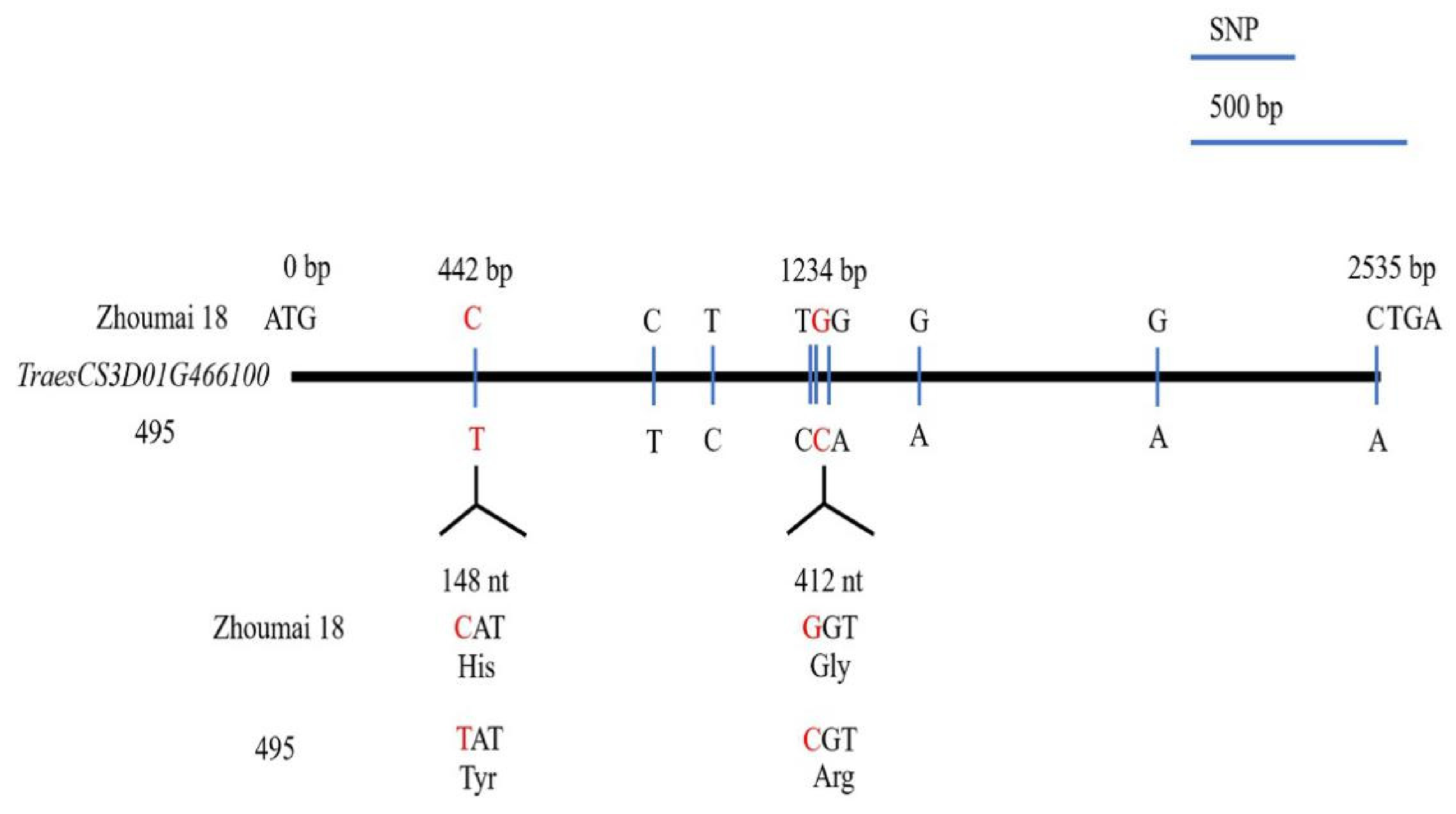
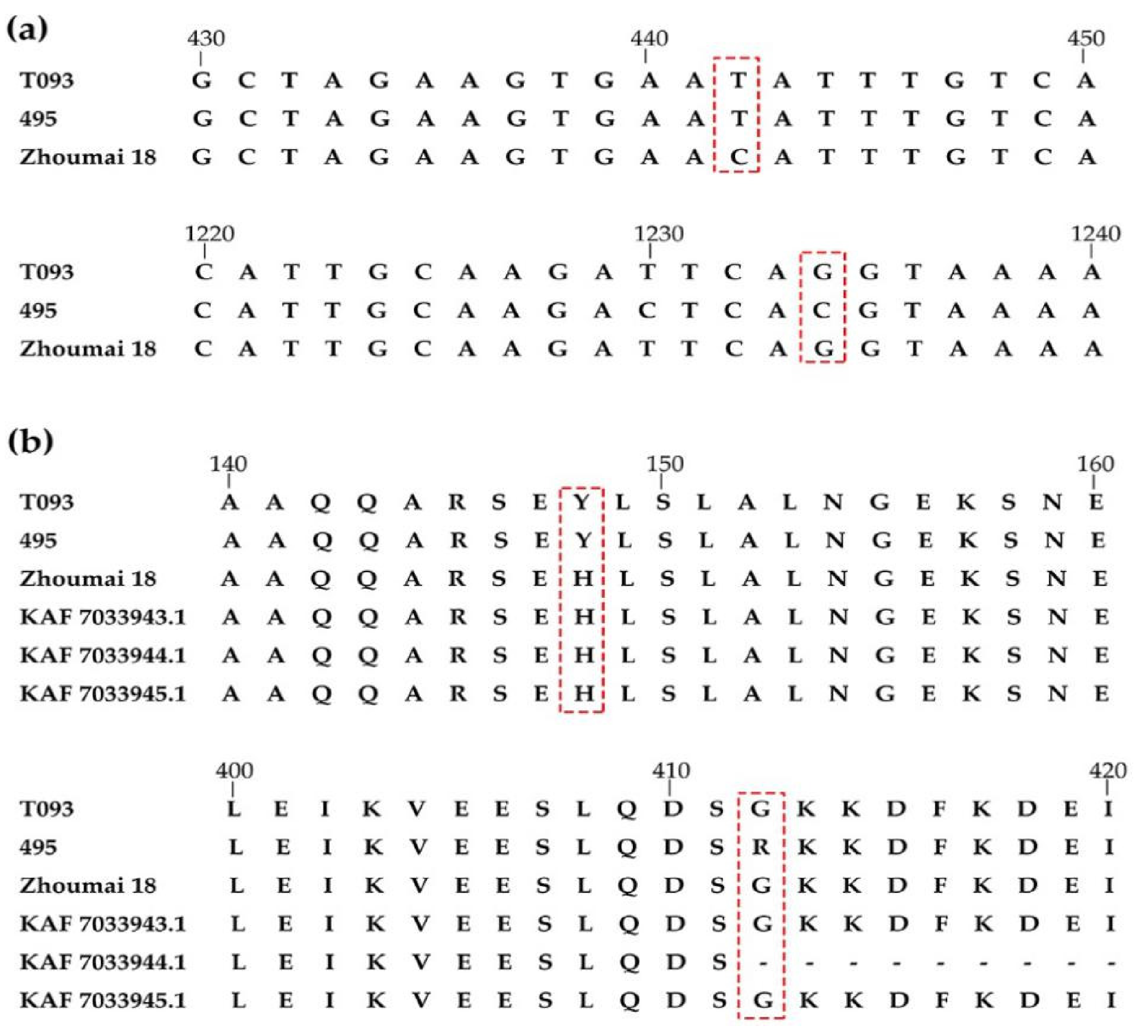
2.4. TraesCS3D01G466100 cDNA Sequencing and Protein BLAST
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
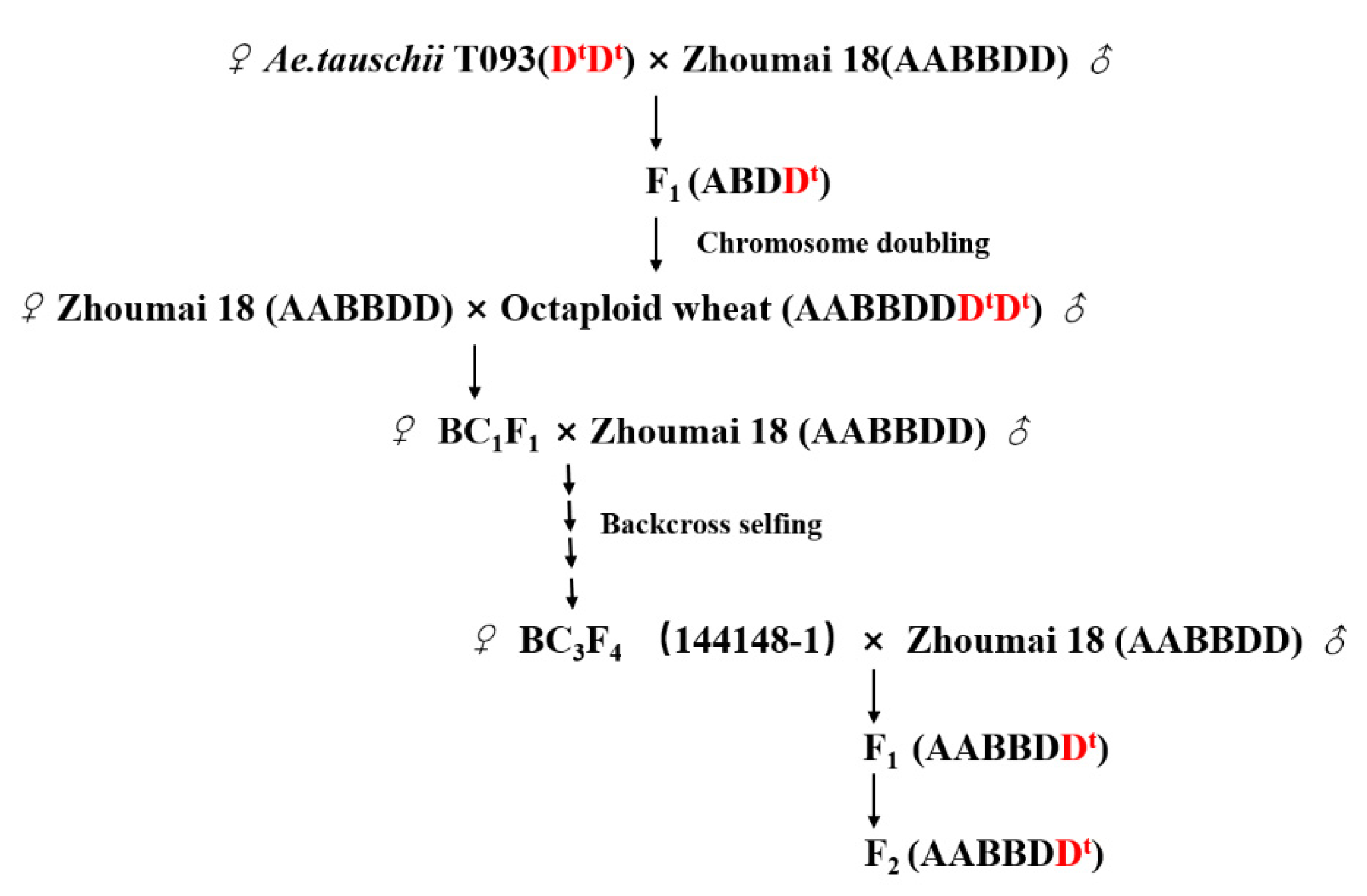
4.1. Plant Materials and Mapping Populations
4.2. Assessment of PHS in the Wheat F2 Population
4.3. DNA Extraction and Marker Analysis
4.4. Bulk Segregation Analysis (BSA) with the 660K Chip Array and KASP Marker Development
4.5. QTL Analysis
4.6. RNA Isolation and Sequencing
4.7. Gene Expression Using Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. TraesCS3D01G466100 cDNA Sequencing and Protein BLAST
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oluwaseyi, S.; Nicholas, B.; James, S.; Simon, B.; Tina, H.; Peter, J.; Peter, W.; Tanja, G.; Duncan, S.; Barbara, B.; et al. The wheat Phs-A1 pre-harvest sprouting resistance locus delays the rate of seed dormancy loss and maps 0.3 cM distal to the PM19 genes in UK germplasm. J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 4169–4178. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Tan, C.; Lang, J.; Tang, H.; Hao, M.; Tan, Z.; Yu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, M.; et al. Identification of qPHS.sicau-1B and qPHS.sicau-3D from synthetic wheat for pre-harvest sprouting resistance wheat improvement. Mol. Breed. 2019, 39, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depauw, R.M.; Hucl, P.; Knox, R.E.; Singh, A.K.; Fox, S.L.; Humphreys, D.G. Developing standardized methods for breeding preharvest sprouting resistant wheat, challenges and successes in Canadian wheat. Euphytica 2012, 188, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Ni, P.; Francki, M.; Hunter, A.; Zhang, Y.; Schibeci, D.; Li, H.; Tarr, A.; Wang, J.; Cakir, M.; et al. Genes controlling seed dormancy and pre-harvest sprouting in a rice-wheat-barley comparison. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2004, 4, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.; Richards, R. Water uptake in relation to pre-harvest sprouting damage in wheat: Ear characteristics. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 1984, 35, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, D.J.; Mrva, K. Wheat grain preharvest sprouting and late maturity alpha-amylase. Planta 2014, 240, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, A.H.; Sorrells, M.E.; Obendorf, R.L. Methods of evaluation for preharvest sprouting resistance in wheat breeding programs. Can. J. Plant Sci. 1989, 69, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flintham, J.; Adlam, R.; Bassoi, M.; Holdsworth, M.; Gale, M. Mapping genes for resistance to sprouting damage in wheat. Euphytica 2002, 126, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulwal, P.; Ishikawa, G.; Benscher, D.; Feng, Z.; Zongyun, F.; Jadhav, A.; Mehetre, S.; Sorrells, M.E. Association mapping for pre-harvest sprouting resistance in white winter wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 125, 793–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graybosch, R.A.; Amand, P.S.; Bai, G.H. Evaluation of genetic markers for prediction of preharvest sprouting tolerance in hard white winter wheats. Plant Breed. 2013, 132, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vetch, J.M.; Stougaard, R.N.; Martin, J.M.; Giroux, M.J. Review: Revealing the genetic mechanisms of pre-harvest sprouting in hexaploid wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Plant Sci. 2019, 281, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hareland, G.A. Effects of pearling on falling number and α-amylase activity of preharvest sprouted spring Wheat. Cereal Chem. J. 2003, 80, 232–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bamard, A.; Bona, L. Sprout damage and falling number in South Mrican and Hungarian wheats. Cereal Res. Commun. 2004, 32, 259–264. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, F.R.; Knox, R.E.; Depauw, R.M. Expression of dormancy in a spring wheat cross grown in field and controlled environment conditions. Euphytica 2005, 143, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, C.M.; Wayne, M. Quantitative Trait Locus (QTL) Analysis. Nat. Educ. 2008, 1, 208. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Hu, C.H.; Li, H.Z.; Yao, Y.J.; Meng, M.; Dong, J.; Zhao, W.C.; Chen, Q.J.; Li, X.Y. Factors affecting pre-harvest sprouting resistance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): A review. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2013, 23, 556–565. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, J.A.; Sorrells, M.E.S.; Tanksley, S.D. RFLP analysis of genomic regions associated with resistance to pre-harvest sprouting in wheat. Crop Sci. 1993, 33, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Nakamura, W.; Tabiki, T.; Miura, H.; Sawada, S. Detection of loci controlling seed dormancy on group 4 chromosomes of wheat and comparative mapping with rice and barley genomes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 102, 980–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, D.; Mrva, K.; Cheong, J.; Williams, K.; Watson, B.; Storlie, E.; Sutherland, M.; Zou, Y. A QTL located on chromosome 4A associated with dormancy in white- and red-grained wheats of diverse origin. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M.; Uchino, N.; Chono, M.; Kato, K.; Miura, H. Mapping QTLs for grain dormancy on wheat chromosome 3A and the group 4 chromosomes, and their combined effect. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 110, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ogbonnaya, F.C.; Imtiaz, M.; Ye, G.; Hearnden, P.R.; Hernandez, E.; Eastwood, R.F.; Van Ginkel, M.; Shorter, S.C.; Winchester, J.M. Genetic and QTL analyses of seed dormancy and preharvest sprouting resistance in the wheat germplasm CN10955. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 116, 891–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munkvold, J.D.; Tanaka, J.; Benscher, D.; Sorrells, M.E. Mapping quantitative trait loci for preharvest sprouting resistance in white wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 119, 1223–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasul, G.; Humphreys, D.G.; Brûlé-Babel, A.; McCartney, C.A.; Knox, R.E.; Depauw, R.M.; Somers, D.J. Mapping QTLs for pre-harvest sprouting traits in the spring wheat cross ‘RL4452/AC Domain’. Euphytica 2009, 168, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Sehgal, S.K.; Li, J.; Lin, M.; Trick, H.N.; Yu, J.; Gill, B.S.; Bai, G. Cloning and characterization of a critical regulator for preharvest sprouting in wheat. Genetics 2013, 195, 263–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Somyong, S.; Ishikawa, G.; Munkvold, J.D.; Tanaka, J.; Benscher, D.; Cho, Y.G.; Sorrells, M.E. Fine mapping of a preharvest sprouting QTL interval on chromosome 2B in white wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2014, 127, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Hayashi, K.; Tokui, M.; Mori, M.; Miura, H.; Onishi, K. Detection of QTLs for traits associated with pre-harvest sprouting resistance in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Breed. Sci. 2016, 66, 260–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Y.L.; Wang, S.X.; Zhang, H.P.; Zhao, L.X.; Wu, Z.Y.; Jiang, H.; Cao, J.J.; Liu, K.; Qin, M.; Lu, J.; et al. Identification of major loci for seed dormancy at different post-ripening stages after harvest and validation of a novel locus on chromosome 2AL in common wheat. Mol. Breed. 2016, 36, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groos, C.; Gay, G.; Perretant, M.R.; Gervais, L.; Bernard, M.; Dedryver, F.; Charmet, G. Study of the relationship between preharvest sprouting and grain color by quantitative trait loci analysis in a white× red grain bread wheat cross. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 104, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Tang, H.; Cheng, M.P.; Dankwa, K.O.; Chen, Z.X.; Li, Z.Y.; Gao, S.; Liu, Y.X.; Jiang, Q.T.; Lan, X.J.; et al. Genome-Wide association study for pre-harvest sprouting resistance in a large germplasm collection of Chinese wheat Landraces. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martinez, S.A.; Godoy, J.; Huang, M.; Zhang, Z.W.; Carter, A.H.; Garland Campbell, K.A.; Steber, C.M. Genome-wide association mapping for tolerance to preharvest sprouting and low falling numbers in wheat. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.; Cai, S.; Graybosch, R.; Chen, C.; Bai, G. Quantitative trait loci for resistance to pre-harvest sprouting in US hard white winter wheat Rio Blanco. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2008, 117, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.X.; Cai, S.B.; Bai, G.H. A major QTL controlling seed dormancy and pre-harvest sprouting resistance on chromosome 4A in a Chinese wheat landrace. Mol. Breed. 2007, 21, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, S.; Gupta, P.K. Meta-analysis of QTLs involved in pre-harvest sprouting tolerance and dormancy in bread wheat. Triticeae Genom. Genet. 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Zhang, D.; Liu, S.; Zhang, G.; Yu, J.; Fritz, A.K.; Bai, G. Genome-wide association analysis on pre-harvest sprouting resistance and grain color in U.S. winter wheat. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McCarty, D.R.; Hattori, T.; Carson, C.B.; Vasil, V.; Lazar, M.; Vasil, I.K. The Viviparous-1 developmental gene of maize encodes a novel transcriptional activator. Cell 1991, 66, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himi, E.; Mares, D.J.; Yanagisawa, A.; Noda, K. Effect of grain colour gene (R) on grain dormancy and sensitivity of the embryo to abscisic acid (ABA) in wheat. J. Exp. Bot. 2002, 53, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bentsink, L.; Jowett, J.; Hanhart, C.J.; Koornneef, M. Cloning of DOG1, a quantitative trait locus controlling seed dormancy in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 17042–17047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugimoto, K.; Takeuchi, Y.; Ebana, K.; Miyao, A.; Hirochika, H.; Hara, N.; Ishiyama, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Ban, Y.; Hattori, T.; et al. Molecular cloning of Sdr4, a regulator involved in seed dormancy and domestication of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 5792–5797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, S.B.; Sehgal, S.K.; Lin, M.; Li, J.R.; Trick, H.N.; Gill, B.S.; Bai, G.H. Independent mis-splicing mutations in TaPHS1 causing loss of preharvest sprouting (PHS) resistance during wheat domestication. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torada, A.; Koike, M.; Ogawa, T.; Takenouchi, Y.; Tadamura, K.; Wu, J.; Matsumoto, T.; Kawaura, K.; Ogihara, Y. A causal gene for seed dormancy on wheat chromosome 4A encodes a MAP kinase kinase. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 782–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Qu, R.D.; Liu, S.M.; Yang, Y. Rich haplotypes of Viviparous-1 in Triticum aestivum subsp. spelta with different abscisic acid sensitivities. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 97, 497–504. [Google Scholar]
- Onishi, K.; Yamane, M.; Yamaji, N.; Tokui, M.; Kanamori, H.; Wu, J.; Komatsuda, T.; Sato, K. Sequence differences in the seed dormancy gene Qsd1 among various wheat genomes. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Xia, X.C.; He, Z.H. The seed dormancy allele TaSdr-A1a associated with pre-harvest sprouting tolerance is mainly present in Chinese wheat landraces. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.H.; Fu, L.; Wu, Q.H.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Xie, J.Z.; Wang, Z.Z.; Wang, G.X.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liang, Y.; et al. QTL mapping revealed TaVp-1A conferred pre-harvest sprouting resistance in wheat population Yanda 1817× Beinong 6. J. Integr. Agric. 2017, 16, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Zhao, L.X.; Chen, X.J.; Cao, J.J.; Wu, Z.Y.; Liu, K.; Zhang, C.; Wei, W.X.; Xie, H.Y.; Li, L.; et al. A novel 33-bp insertion in the promoter of TaMFT-3A is associated with pre-harvest sprouting resistance in common wheat. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, N.; Tsuchiya, W.; Moresco, J.J.; Hayashi, Y.; Satoh, K.; Kaiwa, N.; Irisa, T.; Kinoshita, T.; Schroeder, J.I.; Yates, J.R.; et al. Control of seed dormancy and germination by DOG1-AHG1 PP2C phosphatase complex via binding to heme. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, S. Grain dormancy genes responsible for preventing pre-harvest sprouting in barley and wheat. Breed. Sci. 2018, 68, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Danquah, A.; De Zélicourt, A.; Boudsocq, M.; Neubauer, J.; Frey, N.F.D.; Leonhardt, N.; Pateyron, S.; Gwinner, F.; Tamby, J.P.; Ortiz-Masia, D.; et al. Identification and characterization of an ABA-activated MAP kinase cascade in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2015, 82, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, P.C.; McKibbin, R.S.; Lenton, J.R.; Holdsworth, M.J.; Flintham, J.E.; Gale, M.D. Genetic map locations for orthologous Vp1 genes in wheat and rice. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1999, 98, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, C. Wild Crop Relatives Genomic and Breeding Resources Cereals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.R.; Luo, M.C.; Chen, Z.X.; You, F.M.; Wei, Y.M.; Zheng, Y.L.; Dvorak, J. Aegilops tauschii single nucleotide polymorphisms shed light on the origins of wheat D-genome genetic diversity and pinpoint the geographic origin of hexaploid wheat. New Phytol. 2013, 198, 925–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; He, J.; Huang, L.Y.; Zhang, C.C.; Zhou, Y.; Su, Y.R.; Li, S.P. An advanced backcross population through synthetic octaploid wheat as a “bridge”: Development and QTL detection for seed dormancy. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 2123. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Koornneef, M.; Soppe, W.J. The absence of histone H2B monoubiquitination in the Arabidopsis hub1 (rdo4) mutant reveals a role for chromatin remodeling in seed dormancy. Plant Cell 2007, 19, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, D.C.; Lan, X.J.; Rong Wang, Z.R.; Zheng, Y.L.; Zhou, Y.H.; Yang, J.L.; Chi, Y. Evaluation of Aegilops tauschii Cosson for preharvest sprouting tolerance. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 1998, 45, 495–498. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, M.; Chen, G.Y.; Zhang, L.Q.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, D.C.; Wang, J.R.; Pu, Z.E.; Zhang, L.; Lan, X.J.; Wei, Y.M.; et al. QTL Mapping for important agronomic traits in synthetic hexaploid wheat derived from Aegiliops tauschii ssp. tauschii. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 1835–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, S.K.; Kaur, S.; Gupta, S.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, R.; Bains, N.S. A direct hybridization approach to gene transfer from Aegilops tauschii Coss. to Triticum aestivum L. Plant Breed. 2010, 130, 98–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, E.L.; Rouse, M.N.; Pumphrey, M.O.; Bowden, R.L.; Gill, B.S.; Poland, J.A. Simultaneous transfer, introgression, and genomic localization of genes for resistance to stem rust race TTKSK (Ug99) from Aegilops tauschii to wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, B.S.; Raupp, W.J. Direct genetic transfers from Aegilops squarrosa L. to hexaploid wheat. Crop. Sci. 1987, 27, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Han, B.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Cui, D.; Geng, L.; Zhou, H.; Li, M.; Han, L. Construction of chromosome segment substitution lines of Dongxiang common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.) in the background of the japonica rice cultivar Nipponbare (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 144, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Wang, W.; He, Q.; Xiang, S.; Tian, D.; Zhao, T.; Gai, J. Identifying a wild allele conferring small seed size, high protein content and low oil content using chromosome segment substitution lines in soybean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2019, 132, 2793–2807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fofana, B.; Humphreys, D.G.; Rasul, G.; Cloutier, S.; Brûlé-Babel, A.; Woods, S.; Lukow, O.M.; Somers, D.J. Mapping quantitative trait loci controlling pre-harvest sprouting resistance in a red × white seeded spring wheat cross. Euphytica 2009, 165, 509–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Knox, R.E.; Clarke, F.R.; Pozniak, C.J.; DePauw, R.M.; Cuthbert, R.D.; Fox, S. Maximizing the identification of QTL for pre-harvest sprouting resistance using seed dormancy measures in a white-grained hexaploid wheat population. Euphytica 2015, 205, 287–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huh, S.M.; Hwang, Y.S.; Shin, Y.S.; Nam, M.H.; Kim, O.Y.; Yoon, I.S. Comparative transcriptome profiling of developing caryopses from two rice cultivars with differential dormancy. J. Plant Physiol. 2013, 170, 1090–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ma, L.; Liao, C. The ubiquitin E3 ligase RHA2b promotes degradation of MYB30 in abscisic acid signaling. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, J.; He, F.; Wang, Z.; Ning, Y.; Wang, G.L. OsHUB1 and OsHUB2 interact with SPIN6 and form homo- and hetero-dimers in rice. Plant Signal. Behav. 2015, 10, e1039212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hwang, W.W.; Venkatasubrahmanyam, S.; Ianculescu, A.G.; Tong, A.; Boone, C.; Madhani, H.D. A conserved RING finger protein required for histone H2B monoubiquitination and cell size control. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.; Krogan, N.J.; Dover, J.; Schneider, J.; Heidt, J.; Boateng, M.A.; Dean, K.; Golshani, A.; Zhang, Y.; Greenblatt, J.F.; et al. Bre1, an E3 ubiquitin ligase required for recruitment and substrate selection of Rad6 at a promoter. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hake, S.B.; Roeder, R.G. The human homolog of yeast BRE1 functions as a transcriptional coactivator through direct activator interactions. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Zheng, Y.; Pham, A.D.; Mandal, S.S.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; Tempst, P.; Reinberg, D. Monoubiquitination of human histone H2B: The factors involved and their roles in HOX gene regulation. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 601–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.R.; Liao, P.A.; Song, D.Y.; Huang, S.Q.; He, J.; Gao, X.F.; Li, S.P. Application of Aegilops tauschii—Triticum aestivum recombinant inbred lines for grain protein content QTL detection and wheat improvement. Can. J. Plant Sci. 2020, 100, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, X.P.; Lv, L.L.; Zhang, C.C.; Li, J.H.; Sun, G.L.; Li, S.P.; Song, C.P. Development and utilization of introgression lines using synthetic octaploid wheat (Aegilops tauschii x hexaploid wheat) as donor. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, S.O.; Bendich, A.J. Extraction of DNA from Plant Tissues. In Plant Molecular Biology Manual; Gelvin, S.B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, J.Z.; Zhao, S.C.; Kong, X.Y.; Li, Y.R.; Zhao, G.Y.; He, W.M.; Appels, R.; Pfeifer, M.; Tao, Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; et al. Aegilops tauschii draft genome sequence reveals a gene repertoire for wheat adaptation. Nature 2013, 496, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.C.; Gu, Y.Q.; Puiu, D.; Wang, H.; Twardziok, S.O.; Deal, K.R.; Huo, N.; Zhu, T.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; et al. Genome sequence of the progenitor of the wheat D genome Aegilops tauschii. Nature 2017, 551, 498–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röder, M.S.; Korzun, V.; Wendehake, K.; Plaschke, J.; Tixier, M.H.; Leroy, P.; Ganal, M.W. A microsatellite map of wheat. Genetics 1998, 149, 2007–2023. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanguinetti, C.; Dias-Neto, E. RAPD silver staining and recovery of PCR products separated on polyacrylamide gels. BioTechniques 1994, 17, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Semagn, F.K.; Babu, R.; Hearne, S.; Olsen, M. Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping using Kompetitive Allele Specific PCR (KASP): Overview of the technology and its application in crop improvement. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, L.D.C.E.; Wang, S.; Zeng, Z.B. Composite Interval Mapping and Multiple Interval Mapping: Procedures and Guidelines for using Windows QTL Cartographer. In Quantitative Trait Loci; Rifkin, S.A., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| QTL | Chromosome Arm | QTL Peak Location (cM a) | Left Marker | Right Marker | LOD b | PVE c (%) | Additive Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| QDor-3D.1 | 3DL | 86.00 | Xcfd223 | A009711 | 119.44 | 24.16 | −16.61 |
| QDor-3D.2 | 3DL | 92.00 | A009711 | A009180 | 70.28 | 15.49 | −12.03 |
| QDor-3D.3 | 3DL | 157.00 | A009716 | Xgwm383b | 22.17 | 4.74 | −6.02 |
| Marker’s Name | Chromosomes | Genetic Position (cM) | Physical Position (Mb) | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xgpw5094 | 3D | 0 | none | GACGATCAACAGCGAGTCAA |
| TTACAATCTCACCCTGGCAA | ||||
| Xcfd152 | 3D | 32.60 | 538177121 | TGGAAGTCTGGAACCACTCC |
| GCAACCAGACCACACTCTCA | ||||
| Xcfd223 | 3D | 82.85 | 564608827 | AAGAGCTACAATGACCAGCAGA |
| GCAGTGTATGTCAGGAGAAGCA | ||||
| Xgwm383b | 3D | 192.77 | none | ACGCCAGTTGATCCGTAAAC |
| GACATCAATAACCGTGGATGG |
| Marker’s Name | Genetic Position (cM) | SNP Probe | Physical Position (Mb) | T093 Allele | Zhoumai 18 Allele | Allele-Specific Primer (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A007500 | 59.5 | AX108732216 | 541371314 | C/C | G/G | FAM: TTGATAGGTTCGCATAAATATATCACAC VIC: TTGATAGGTTCGCATAAATATATCACAG Com: ATGACTCAAGGCAGAAGGGTGCAAA |
| A009175 | 67.9 | AX110029380 | 553359206 | A/A | G/G | FAM: AGCAGCGTCGGCAAATTTTCTCT VIC: GCAGCGTCGGCAAATTTTCTCC Com: CCATGTCGCCCACGATCACGTAT |
| A009353 | 70.63 | AX108860278 | 553418567 | A/A | G/G | FAM: GCTCATGTCTCTTTCCCTGCAT VIC: CTCATGTCTCTTTCCCTGCAC Com: GCACCAAAGTGTCGCAGGCT |
| A009352 | 72.57 | AX110476153 | 554404315 | G/G | C/C | FAM: ATCGGCACGTAAGAGACCTCAC VIC: ATCGGCACGTAAGAGACCTCAG Com: CTCGTGCTGACATGGTTCAGTACA |
| A009177 | 73.66 | AX111845176 | 554025909 | C/C | T/T | FAM: ATACCCTCACCAACACCCCG VIC: CATACCCTCACCAACACCCCA Com: GCTGGCTCACTACATTCTTCCACTT |
| A009711 | 88.1 | AX111543252 | 566738033 | G/G | T/T | FAM: TGGTGATTAGCATCATCGGAATGG VIC: TTGGTGATTAGCATCATCGGAATGT Com: ATCAAATCTATCGAGTTAAAGCTGCCCAA |
| A009180 | 105.54 | AX111453429 | 573611727 | T/T | G/G | FAM: TAAGTGAATTTTTAAAGTTCGCATACCCT VIC: AGTGAATTTTTAAAGTTCGCATACCCC Com: CAACGGCGTACCCCGGATTTTAAAT |
| A009715 | 123.4 | AX109868172 | 584987956 | G/G | A/A | FAM: ACTGACTCTAGCTTGATGACACG VIC: CACTGACTCTAGCTTGATGACACT Com: ATGGCCCCCACGAGTCAAAAACATT |
| A009725 | 147.71 | AX94407298 | 597069714 | G/G | T/T | FAM: ACAAGTATTCAGCCTCTTTGCCAC VIC: CACAAGTATTCAGCCTCTTTGCCAA Com: GCAATATGGAAGCCTACACTCCCTT |
| A009716 | 149.21 | AX111561378 | 596719275 | T/T | G/G | FAM: GTTGCTATGTAACGGAATAAGAACG VIC: CGTTGCTATGTAACGGAATAAGAACT Com: CCAAATAGAAGTATCACTTGAACAATGCTT |
| Locus | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Predicted Product Size to Reference (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| β-actin | Forward: AGTGGACGCACAACAGGTA Reverse: GTCAAGACGAAGGATGGCA | 105 |
| TraesCS3D01G466100 | Forward: CACCAAATGCTTCCACCTA Reverse: GGCACCAACGACCTACTAC | 173 |
| TraesCS3D01G466100 | Forward: ACACGGGAAAGTAGCT Reverse: GAGACAAGCACGGAGA | 2535 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
He, J.; Zhang, D.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Hu, M.; Sun, S.; Su, Q.; Su, Y.; Li, S. Identification of QTLs and a Candidate Gene for Reducing Pre-Harvest Sprouting in Aegilops tauschii–Triticum aestivum Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073729
He J, Zhang D, Chen X, Li Y, Hu M, Sun S, Su Q, Su Y, Li S. Identification of QTLs and a Candidate Gene for Reducing Pre-Harvest Sprouting in Aegilops tauschii–Triticum aestivum Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(7):3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073729
Chicago/Turabian StyleHe, Jie, Dale Zhang, Xian Chen, Yuge Li, Minjie Hu, Shaoguang Sun, Qing Su, Yarui Su, and Suoping Li. 2021. "Identification of QTLs and a Candidate Gene for Reducing Pre-Harvest Sprouting in Aegilops tauschii–Triticum aestivum Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 7: 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073729
APA StyleHe, J., Zhang, D., Chen, X., Li, Y., Hu, M., Sun, S., Su, Q., Su, Y., & Li, S. (2021). Identification of QTLs and a Candidate Gene for Reducing Pre-Harvest Sprouting in Aegilops tauschii–Triticum aestivum Chromosome Segment Substitution Lines. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(7), 3729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22073729






