Screening of 5- and 6-Substituted Amiloride Libraries Identifies Dual-uPA/NHE1 Active and Single Target-Selective Inhibitors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. uPA Activity Screening
2.2. NHE1 Activity Screening
2.3. Mammalian Cell Cytotoxicity Screening
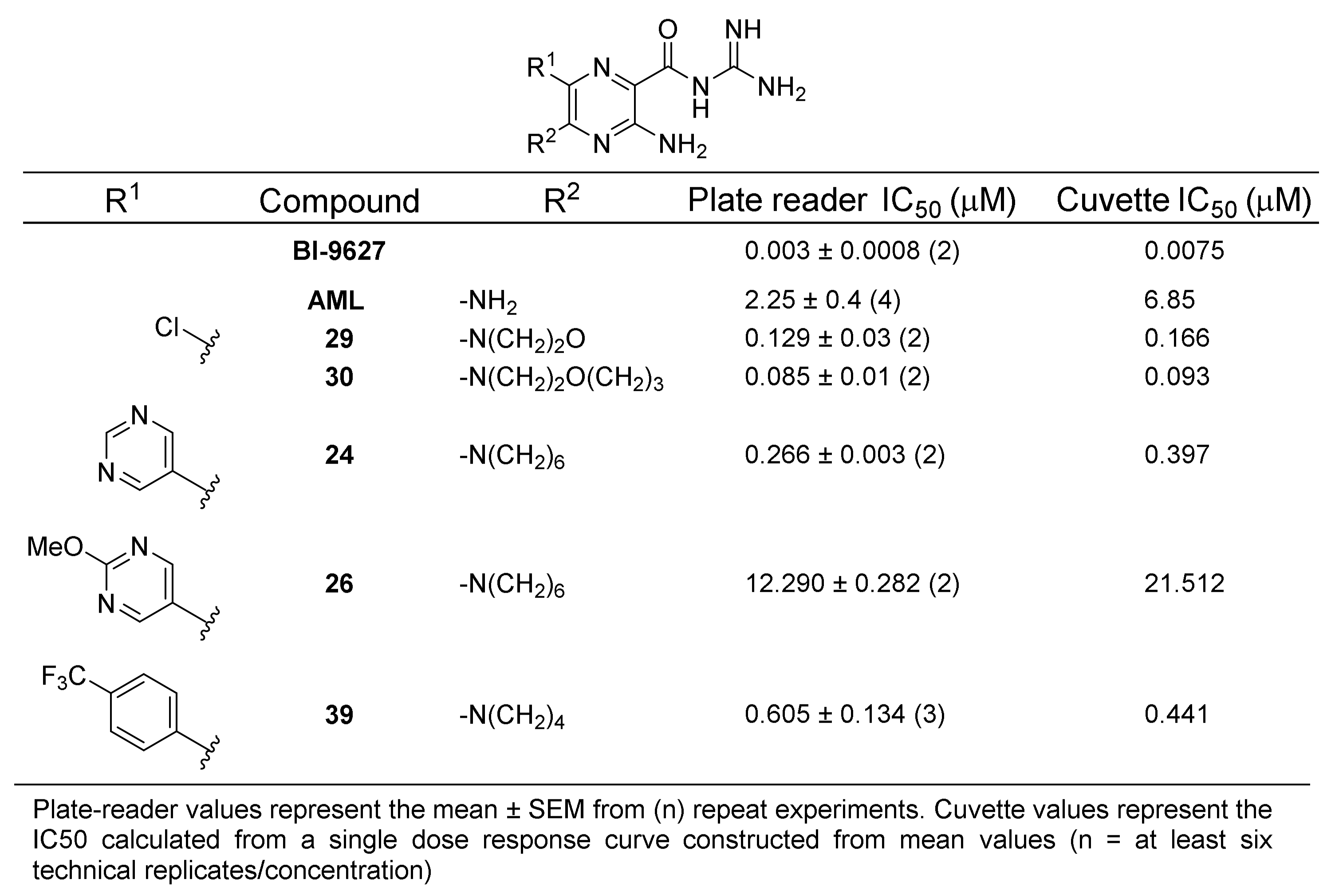
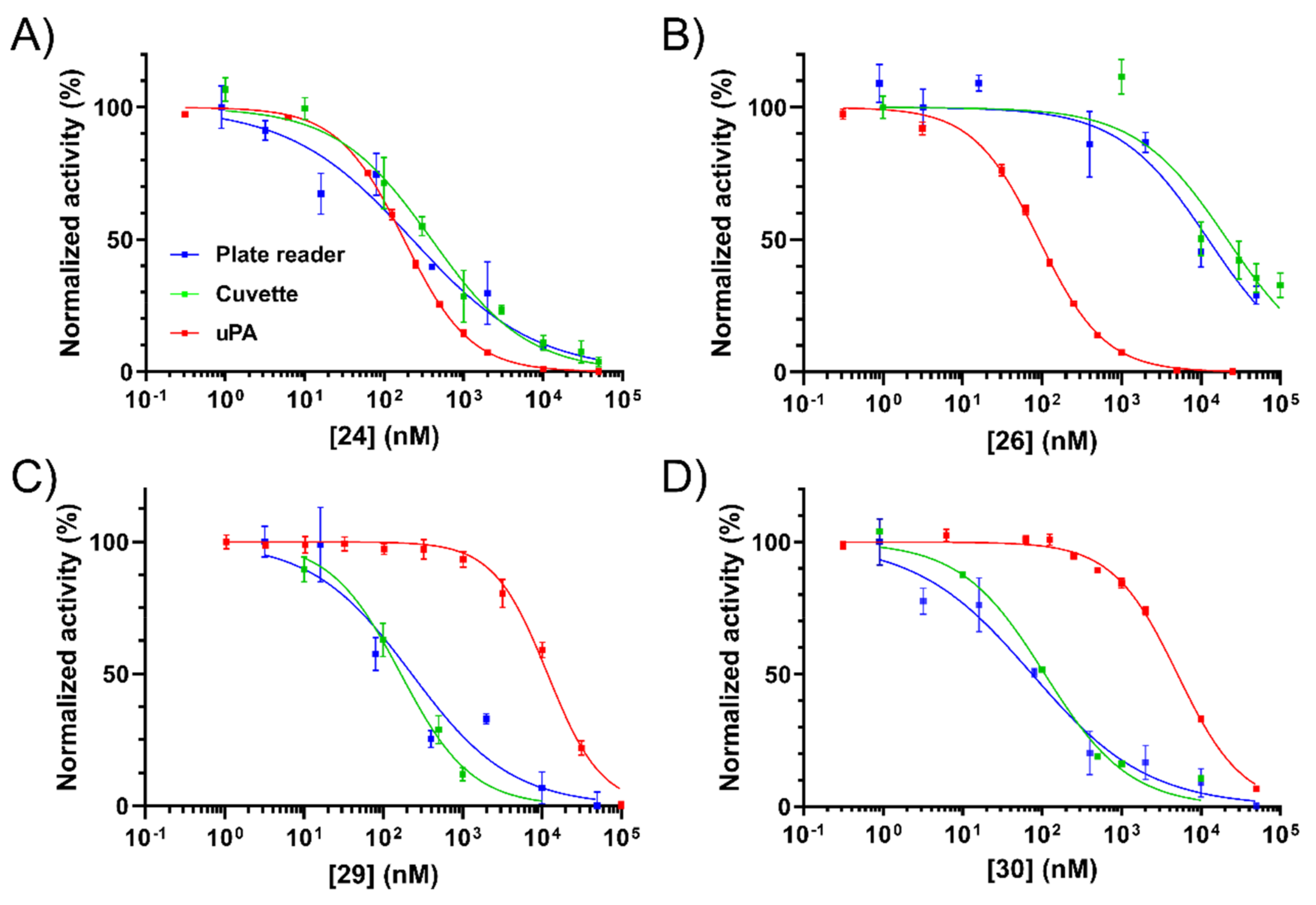
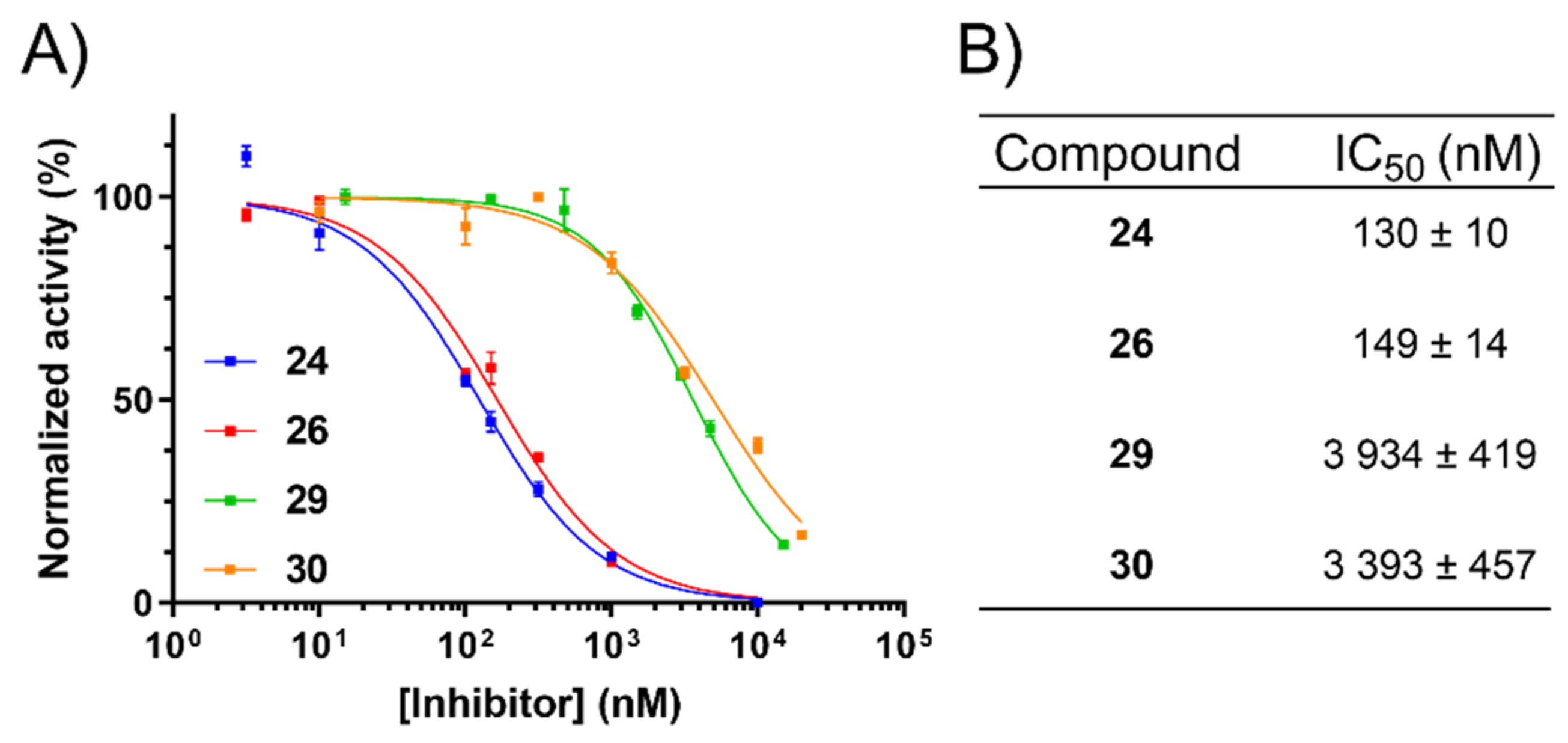
2.4. NHE1 IC50 Measurements
2.5. Inhibition of uPA Activity at the Cell Surface
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. uPA Inhibition Assays
4.2. Cell Culture Conditions
4.3. Cell Viability (Cytotoxicity) Assays
4.4. Plate-Based NHE1 Inhibition Assays
4.5. Cuvette-Based NHE1 Inhibition Assays
4.6. Cell-Surface uPA Activity Assays
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Amiloride |
| ASIC | Acid-sensing ion channel |
| BCECF-AM | 2′,7′-bis(carboxyethyl)-5(6)-carboxyfluorescein-acetoxymethyl ester |
| EIPA | 5-(N-ethyl-N-isopropyl)amiloride |
| ENaC | Epithelial sodium channel |
| HMA | 5-(N,N-hexamethylene)amiloride |
| NHE1 | Na+/H+ exchanger isoform-1 |
| SAR | Structure–activity relationship |
| TLSP | Trypsin-like serine protease |
| uPA | urokinase plasminogen activator |
| uPAR | urokinase plasminogen activator receptor |
References
- Gerweck, L.E.; Seetharaman, K. Cellular pH gradient in tumor versus normal tissue: Potential exploitation for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 1194–1198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slepkov, E.R.; Rainey, J.K.; Sykes, B.D.; Fliegel, L. Structural and functional analysis of the Na+/H+ exchanger. Biochem. J. 2007, 401, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avkiran, M.; Haworth, R.S. Regulatory effects of G protein-coupled receptors on cardiac sarcolemmal Na+/H+ exchanger activity: Signalling and significance. Cardiovasc. Res. 2003, 57, 942–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cardone, R.A.; Alfarouk, K.O.; Elliott, R.L.; Alqahtani, S.S.; Ahmed, S.B.M.; Aljarbou, A.N.; Greco, M.R.; Cannone, S.; Reshkin, S.J. The Role of Sodium Hydrogen Exchanger 1 in Dysregulation of Proton Dynamics and Reprogramming of Cancer Metabolism as a Sequela. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amith, S.R.; Fliegel, L. Regulation of the Na+/H+ Exchanger (NHE1) in Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1259–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, B.A.; Chimenti, M.; Jacobson, M.P.; Barber, D.L. Dysregulated pH: A perfect storm for cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Tannock, I.F. Inhibition of the regulation of intracellular pH: Potential of 5-(N,N-hexamethylene) amiloride in tumour-selective therapy. Br. J. Cancer 1994, 70, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cardone, R.A.; Casavola, V.; Reshkin, S.J. The role of disturbed pH dynamics and the Na+/H+ exchanger in metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 786–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshkin, S.J.; Cardone, R.A.; Harguindey, S. Na+-H+ exchanger, pH regulation and cancer. Recent Pat. Anti-Cancer Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amith, S.R.; Fliegel, L. Na(+)/H(+) exchanger-mediated hydrogen ion extrusion as a carcinogenic signal in triple-negative breast cancer etiopathogenesis and prospects for its inhibition in therapeutics. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2017, 43, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranson, M.; Andronicos, N.M. Plasminogen binding and cancer: Promises and pitfalls. Front. Biosci. A J. Virtual Libr. 2003, 8, s294–s304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croucher, D.R.; Saunders, D.N.; Lobov, S.; Ranson, M. Revisiting the biological roles of PAI2 (SERPINB2) in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 535–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulisse, S.; Baldini, E.; Sorrenti, S.; D’Armiento, M. The urokinase plasminogen activator system: A target for anti-cancer therapy. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2009, 9, 32–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, J.C.; Jiang, L.; Lin, Z.; Yuan, C.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.; Huang, M. Structural basis for therapeutic intervention of uPA/uPAR system. Curr. Drug Targets 2011, 12, 1729–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lant, A.F.; Smith, A.J.; Wilson, G.M. Clinical evaluation of amiloride, a potassium-sparing diuretic. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 1969, 10, 50–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragoe, E.J.J.; Woltersdorf, O.W.J.; Bicking, J.B.; Kwong, S.F.; Jones, J.H. Pyrazine diuretics. II. N-amidino-3-amino-5-substituted 6-halopyrazinecarboxamides. J. Med. Chem. 1967, 10, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleyman, T.R.; Cragoe, E.J.J. The mechanism of action of amiloride. Sem. Nephrol. 1988, 8, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Palmer, B.F. Regulation of Potassium Homeostasis. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 10, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidt, D.G. Mechanism of action, pharmacokinetics, adverse effects, and therapeutic uses of amiloride hydrochloride, a new potassium-sparing diuretic. Pharmacotherapy 1981, 1, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whiting, G.F.; McLaran, C.J.; Bochner, F. Severe hyperkalaemia with Moduretic. Med. J. Aust. 1979, 1, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankun, J.; Keck, R.W.; Skrzypczak-Jankun, E.; Swiercz, R. Inhibitors of urokinase reduce size of prostate cancer xenografts in severe combined immunodeficient mice. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stepanova, V.; Dergilev, K.V.; Holman, K.R.; Parfyonova, Y.V.; Tsokolaeva, Z.I.; Teter, M.; Atochina-Vasserman, E.N.; Volgina, A.; Zaitsev, S.V.; Lewis, S.P.; et al. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) is critical for progression of tuberous sclerosis complex 2 (TSC2)-deficient tumors. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 20528–20543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, H.; Ranson, M.; Kelso, M.J. Anti-tumour/metastasis effects of the potassium-sparing diuretic amiloride: An orally active anti-cancer drug waiting for its call-of-duty? Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2051–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, H.; Ranson, M.; Tyndall, J.D.; Kelso, M.J. Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of amiloride analogs as inhibitors of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 6760–6766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, B.J.; Aboelela, A.; Minaei, E.; Jiang, L.X.; Xu, Z.; Ali, U.; Fildes, K.; Cheung, C.Y.; Cook, S.M.; Johnson, D.C.; et al. 6-Substituted Hexamethylene Amiloride (HMA) Derivatives as Potent and Selective Inhibitors of the Human Urokinase Plasminogen Activator for Use in Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8299–8320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, B.J.; Majed, H.; Aboelela, A.; Minaei, E.; Jiang, L.; Fildes, K.; Cheung, C.Y.; Johnson, D.; Bachovchin, D.; Cook, G.M.; et al. 6-Substituted amiloride derivatives as inhibitors of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator for use in metastatic disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2019, 29, 126753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleyman, T.R.; Cragoe, E.J., Jr. Amiloride and its analogs as tools in the study of ion transport. J. Membr. Biol. 1988, 105, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigne, P.; Frelin, C.; Cragoe, E.J., Jr.; Lazdunski, M. Structure-activity relationships of amiloride and certain of its analogues in relation to the blockade of the Na+/H+ exchange system. Mol. Pharmacol. 1984, 25, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simchowitz, L.; Cragoe, E.J., Jr. Inhibition of chemotactic factor-activated Na+/H+ exchange in human neutrophils by analogues of amiloride: Structure-activity relationships in the amiloride series. Mol. Pharmacol. 1986, 30, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cuthbert, A.W.; Fanelli, G.M. Effects of some pyrazinecarboxamides on sodium transport in frog skin. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1978, 63, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verrey, F.; Schaerer, E.; Zoerkler, P.; Paccolat, M.P.; Geering, K.; Kraehenbuhl, J.P.; Rossier, B.C. Regulation by aldosterone of Na+,K+-ATPase mRNAs, protein synthesis, and sodium transport in cultured kidney cells. J. Cell Biol. 1987, 104, 1231–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsh, A.J.; Molino, B.F.; Zhang, J.; Astakhova, N.; Geiss, W.B.; Sargent, B.J.; Swenson, B.D.; Usyatinsky, A.; Wyle, M.J.; Boucher, R.C.; et al. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationships of novel 2-substituted pyrazinoylguanidine epithelial sodium channel blockers: Drugs for cystic fibrosis and chronic bronchitis. J. Med. Chem. 2006, 49, 4098–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuduk, S.D.; Di Marco, C.N.; Chang, R.K.; Dipardo, R.M.; Cook, S.P.; Cato, M.J.; Jovanovska, A.; Urban, M.O.; Leitl, M.; Spencer, R.H.; et al. Amiloride derived inhibitors of acid-sensing ion channel-3 (ASIC3). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2514–2518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amith, S.R.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Fliegel, L. Assessing Na(+)/H(+) exchange and cell effector functionality in metastatic breast cancer. Biochim. Open 2016, 2, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, J.D.; Bentzien, J.; Boyer, S.J.; Burke, J.; De Lombaert, S.; Eickmeier, C.; Guo, X.; Haist, J.V.; Hickey, E.R.; Kaplita, P.; et al. Identification of a potent sodium hydrogen exchanger isoform 1 (NHE1) inhibitor with a suitable profile for chronic dosing and demonstrated cardioprotective effects in a preclinical model of myocardial infarction in the rat. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 7114–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Counillon, L.; Scholz, W.; Lang, H.J.; Pouysségur, J. Pharmacological characterization of stably transfected Na+/H+ antiporter isoforms using amiloride analogs and a new inhibitor exhibiting anti-ischemic properties. Mol. Pharmacol. 1993, 44, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ranson, M.; Andronicos, N.M.; O’Mullane, M.J.; Baker, M.S. Increased plasminogen binding is associated with metastatic breast cancer cells: Differential expression of plasminogen binding proteins. Br. J. Cancer 1998, 77, 1586–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andronicos, N.M.; Ranson, M. The topology of plasminogen binding and activation on the surface of human breast cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 909–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, N.L.E.; Vennin, C.; Conway, J.R.W.; Vine, K.L.; Pinese, M.; Cowley, M.J.; Shearer, R.F.; Lucas, M.C.; Herrmann, D.; Allam, A.H.; et al. SerpinB2 regulates stromal remodelling and local invasion in pancreatic cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 4288–4298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commisso, C.; Davidson, S.M.; Soydaner-Azeloglu, R.G.; Parker, S.J.; Kamphorst, J.J.; Hackett, S.; Grabocka, E.; Nofal, M.; Drebin, J.A.; Thompson, C.B.; et al. Macropinocytosis of protein is an amino acid supply route in Ras-transformed cells. Nature 2013, 497, 633–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Akhoundi, M.S.; Rokn, A.; Bagheri, R.; Momeni, N.; Hodjat, M. Urokinase-plasminogen activator protects periodontal ligament fibroblast from oxidative induced-apoptosis and DNA damage. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zhao, D.; Li, Y.L.; Sun, Y.; Lei, X.H.; Zhang, J.N.; Wu, M.M.; Li, R.Y.; Zhao, Z.F.; Zhang, Z.R.; et al. Regulation of ASIC1 by Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in human glioblastoma multiforme. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 2852–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, M.A.; Deryugina, E.I.; Niessen, S.; Cravatt, B.F.; Quigley, J.P. Activity-based protein profiling implicates urokinase activation as a key step in human fibrosarcoma intravasation. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 15997–16005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Peng, C.; Huang, H.; Lai, Y.; Hu, C.; Li, F.; Wang, D. Effects of amiloride on physiological activity of stem cells of human lung cancer and possible mechanism. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 504, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oka, N.; Okumura, Y.; Kanayama, H.O.; Izaki, H.; Okamoto, M.; Kido, H.; Kagawa, S. Amiloride and urinary trypsin inhibitor inhibit urothelial cancer invasion. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 737–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Cragoe, E.J., Jr.; Edwards, A.M. Control of hepatocyte DNA synthesis by intracellular pH and its role in the action of tumor promoters. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 195, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, R.; Wang, H.; Jin, H.; Wen, G.; Tuo, B.; Xu, J. NHE1 is upregulated in gastric cancer and regulates gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1451–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Cho, Y.L.; Lee, K.S.; Lee, S.J.; Namkoong, S.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, H.; Ha, K.S.; Han, J.A.; Kwon, Y.G.; Kim, Y.M. Amiloride potentiates TRAIL-induced tumor cell apoptosis by intracellular acidification-dependent Akt inactivation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 752–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanukoglu, I.; Hanukoglu, A. Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) family: Phylogeny, structure-function, tissue distribution, and associated inherited diseases. Gene 2016, 579, 95–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.X.; O’Brien, E.R. Ethyl isopropyl amiloride inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration by inducing apoptosis and antagonizing urokinase plasminogen activator activity. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 81, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reshkin, S.J.; Bellizzi, A.; Albarani, V.; Guerra, L.; Tommasino, M.; Paradiso, A.; Casavola, V. Phosphoinositide 3-kinase is involved in the tumor-specific activation of human breast cancer cell Na(+)/H(+) exchange, motility, and invasion induced by serum deprivation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 5361–5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amith, S.R.; Wilkinson, J.M.; Fliegel, L. KR-33028, a potent inhibitor of the Na(+)/H(+) exchanger NHE1, suppresses metastatic potential of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 118, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guffey, S.C.; Fliegel, L.; Goss, G.G. Cloning and characterization of Na(+)/H(+) Exchanger isoforms NHE2 and NHE3 from the gill of Pacific dogfish Squalus suckleyi. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2015, 188, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Rainey, J.K.; Xu, C.; Sykes, B.D.; Fliegel, L. Structural and functional characterization of transmembrane segment VII of the Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 29817–29829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buckley, B.J.; Kumar, A.; Aboelela, A.; Bujaroski, R.S.; Li, X.; Majed, H.; Fliegel, L.; Ranson, M.; Kelso, M.J. Screening of 5- and 6-Substituted Amiloride Libraries Identifies Dual-uPA/NHE1 Active and Single Target-Selective Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062999
Buckley BJ, Kumar A, Aboelela A, Bujaroski RS, Li X, Majed H, Fliegel L, Ranson M, Kelso MJ. Screening of 5- and 6-Substituted Amiloride Libraries Identifies Dual-uPA/NHE1 Active and Single Target-Selective Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(6):2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062999
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuckley, Benjamin J., Ashna Kumar, Ashraf Aboelela, Richard S. Bujaroski, Xiuju Li, Hiwa Majed, Larry Fliegel, Marie Ranson, and Michael J. Kelso. 2021. "Screening of 5- and 6-Substituted Amiloride Libraries Identifies Dual-uPA/NHE1 Active and Single Target-Selective Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 6: 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062999
APA StyleBuckley, B. J., Kumar, A., Aboelela, A., Bujaroski, R. S., Li, X., Majed, H., Fliegel, L., Ranson, M., & Kelso, M. J. (2021). Screening of 5- and 6-Substituted Amiloride Libraries Identifies Dual-uPA/NHE1 Active and Single Target-Selective Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(6), 2999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22062999






