Application of 5-Methylcytosine DNA Glycosylase to the Quantitative Analysis of DNA Methylation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
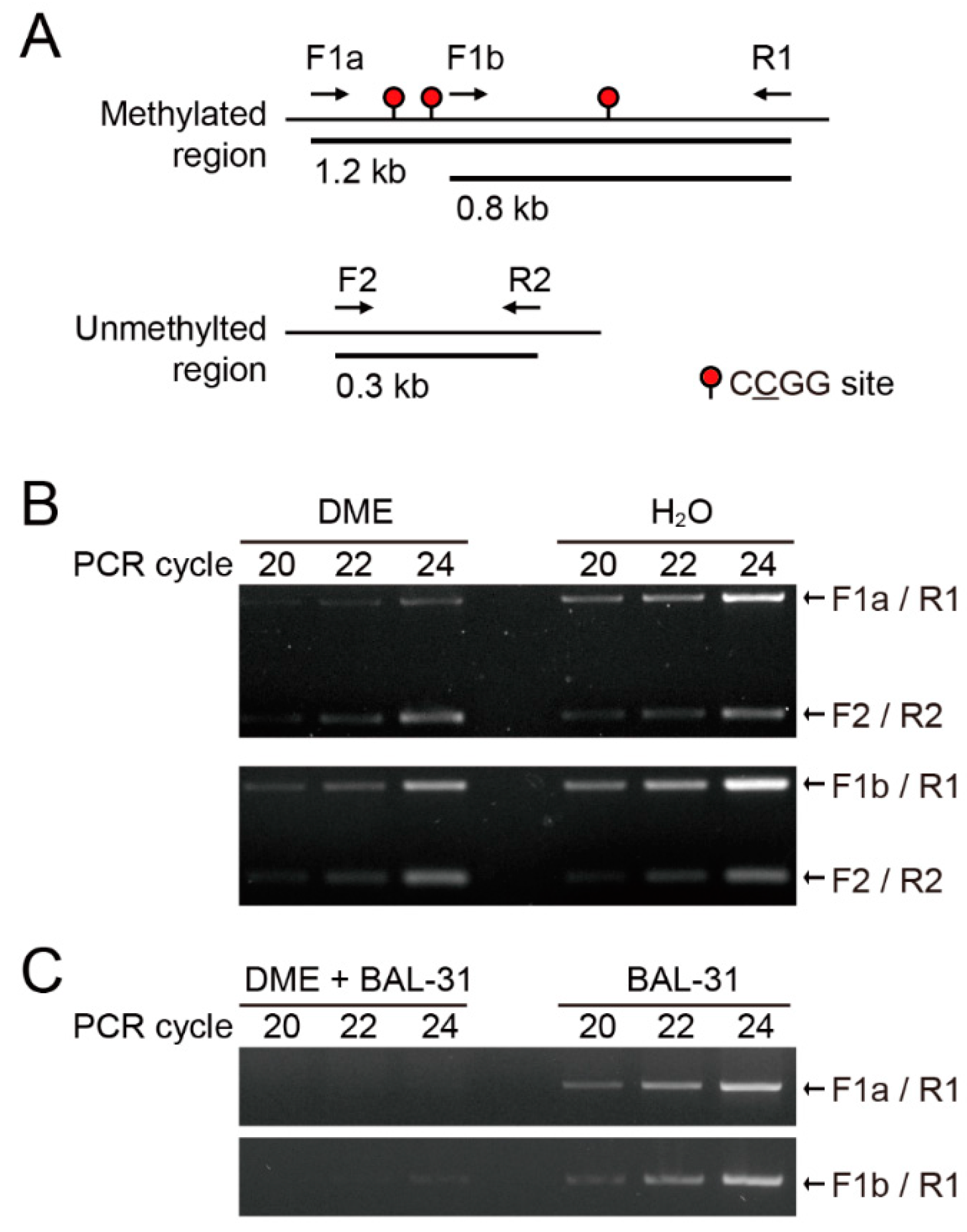
2.1. DME Induces Single-Strand DNA Breaks Proportional to DNA Methylation Density
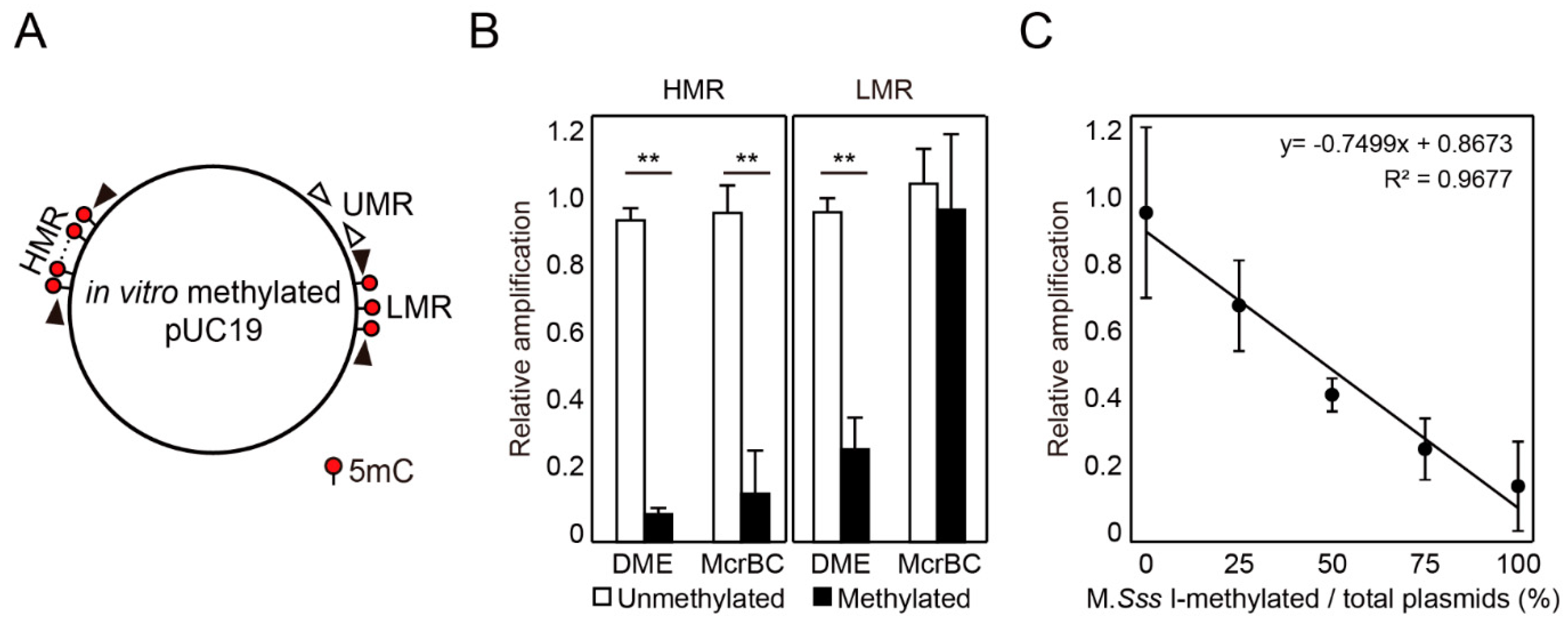
2.2. DME-qPCR Allows a Quantitative DNA Methylation Analysis
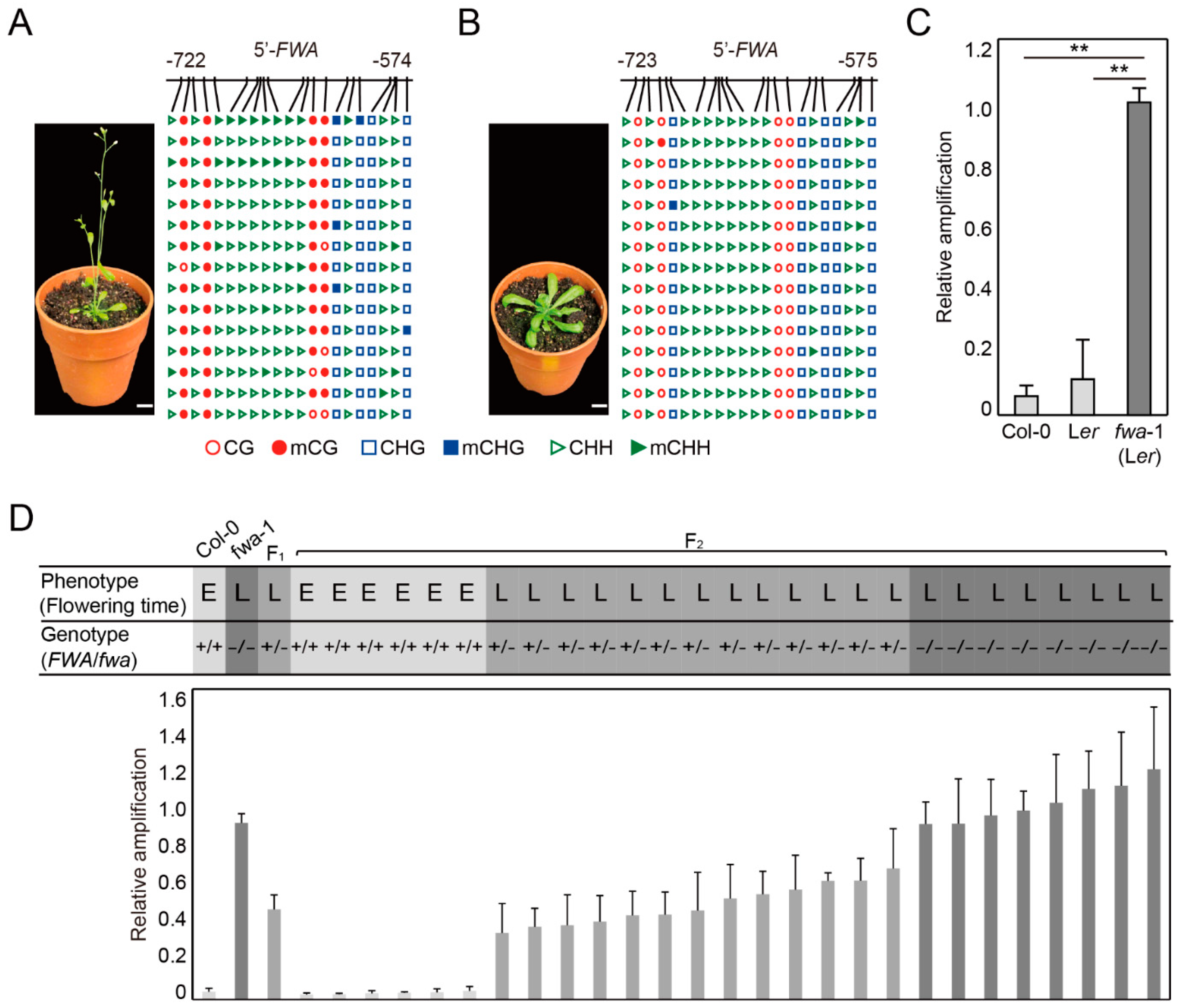
2.3. DME-qPCR Distinguishes DNA Methylation Levels at the FWA Gene in Wild Type and Late Flowering Mutants in Arabidopsis
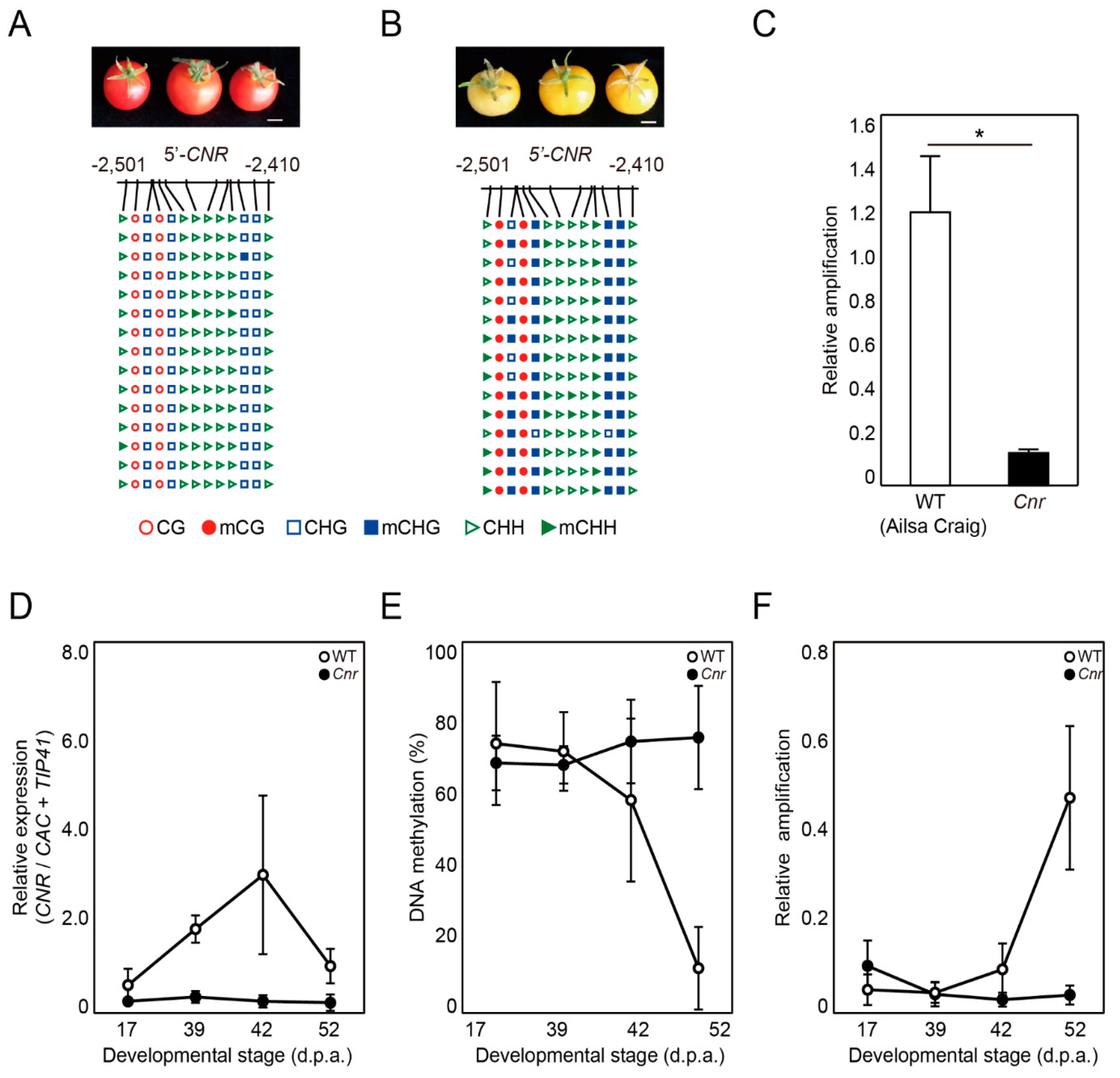
2.4. DME-qPCR Detects Changes in DNA Methylation Levels at the CNR Gene during Fruit Ripening in Tomato
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Protein Expression and Purification
4.2. DME Treatment and Bal-31 Digestion Followed by PCR on Methylated DNA Fragments
4.3. Comparison of DME Treatment and McrBC Digestion
4.4. Plant Materials
4.5. CAPS Analysis
4.6. Reverse Transcriptase-qPCR
4.7. Locus-Specific Bisulfite Sequencing
4.8. DME-qPCR
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huh, J.H.; Bauer, M.J.; Hsieh, T.F.; Fischer, R.L. Cellular Programming of Plant Gene Imprinting. Cell 2008, 132, 735–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.A.; Jacobsen, S.E. Establishing, maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 204–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Y. Reversing DNA methylation: Mechanisms, genomics, and biological functions. Cell 2014, 156, 45–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.; Joosten, S.C.; Feng, Z.; de Ruijter, T.C.; Draht, M.X.; Melotte, V.; Smits, K.M.; Veeck, J.; Herman, J.G.; Van Neste, L.; et al. Analysis of DNA methylation in cancer: Location revisited. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodson, K.; O’Reilly, K.J.; Hanson, J.C.; Nelson, D.; Walk, E.L.; Tangrea, J.A. The Usefulness of the Detection of GSTP1 Methylation in Urine as a Biomarker in the Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. J. Urol. 2008, 179, 508–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, R.J. The Secret Garden-Epigenetic Alleles Underlie Complex Traits. Science 2014, 343, 1082–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubas, P.; Vincent, C.; Coen, E. An epigenetic mutation responsible for natural variation in floral symmetry. Nature 1999, 401, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soppe, W.J.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Alonso-Blanco, C.; Jackson, J.P.; Kakutani, T.; Koornneef, M.; Peeters, A.J. The Late Flowering Phenotype of fwa Mutants Is Caused by Gain-of-Function Epigenetic Alleles of a Homeodomain Gene. Mol. Cell 2000, 6, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, K.; Tor, M.; Poole, M.; Hong, Y.; Thompson, A.J.; King, G.J.; Giovannoni, J.J.; Seymour, G.B. A naturally occurring epigenetic mutation in a gene encoding an SBP-box transcription factor inhibits tomato fruit ripening. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.; Troadec, C.; Boualem, A.; Rajab, M.; Fernandez, R.; Morin, H.; Pitrat, M.; Dogimont, C.; Bendahmane, A. A transposon-induced epigenetic change leads to sex determination in melon. Nature 2009, 461, 1135–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrana, L.; Almeida, J.; Asis, R.; Duffy, T.; Dominguez, P.G.; Bermudez, L.; Conti, G.; Correa da Silva, J.V.; Peralta, I.E.; Colot, V.; et al. Natural occurring epialleles determine vitamin E accumulation in tomato fruits. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong-Abdullah, M.; Ordway, J.M.; Jiang, N.; Ooi, S.E.; Kok, S.Y.; Sarpan, N.; Azimi, N.; Hashim, A.T.; Ishak, Z.; Rosli, S.K.; et al. Loss of Karma transposon methylation underlies the mantled somaclonal variant of oil palm. Nature 2015, 525, 533–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cross, S.H.; Charlton, J.A.; Nan, X.S.; Bird, A.P. Purification of CpG islands using a methylated DNA binding column. Nat. Genet. 1994, 6, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebhard, C.; Schwarzfischer, L.; Pham, T.H.; Andreesen, R.; Mackensen, A.; Rehli, M. Rapid and sensitive detection of CpG-methylation using methyl-binding (MB)-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhopadhyay, R.; Yu, W.; Whitehead, J.; Xu, J.; Lezcano, M.; Pack, S.; Kanduri, C.; Kanduri, M.; Ginjala, V.; Vostrov, A.; et al. The Binding Sites for the Chromatin Insulator Protein CTCF Map to DNA Methylation-Free Domains Genome-Wide. Genome Res. 2004, 14, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frommer, M.; Mcdonald, L.E.; Millar, D.S.; Collis, C.M.; Watt, F.; Grigg, G.W.; Molloy, P.L.; Paul, C.L. A genomic sequencing protocol that yields a positive display of 5-methylcytosine residues in individual DNA Strands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laird, P.W. Principles and challenges of genome-wide DNA methylation analysis. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 191–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pidsley, R.; Zotenko, E.; Peters, T.J.; Lawrence, M.G.; Risbridger, G.P.; Molloy, P.; Van Djik, S.; Muhlhausler, B.; Stirzaker, C.; Clark, S.J. Critical evaluation of the Illumina MethylationEPIC BeadChip microarray for whole-genome DNA methylation profiling. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiba, T.; Saito, T.; Hayashi, A.; Sato, S.; Yunokawa, H.; Maruyama, T.; Fujibuchi, W.; Kurita, H.; Tohyama, C.; Ohsako, S. Methylated site display (MSD)-AFLP, a sensitive and affordable method for analysis of CpG methylation profiles. BMC Mol. Biol. 2017, 18, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bird, A.P.; Southern, E.M. Use of Restriction Enzymes to Study Eukaryotic DNA Methylation: I. The Methylation Pattern in Ribosomal DNA from Xenopus laevis. J. Mol. Biol. 1978, 118, 27–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, F.J.; Panne, D.; Bickle, T.A.; Raleigh, E.A. Methyl-specific DNA Binding by McrBC, a Modification-dependent Restriction Enzyme. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 298, 611–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehring, M.; Huh, J.H.; Hsieh, T.F.; Penterman, J.; Choi, Y.; Harada, J.J.; Goldberg, R.B.; Fischer, R.L. DEMETER DNA Glycosylase Establishes MEDEA Polycomb Gene Self-Imprinting by Allele-Specific Demethylation. Cell 2006, 124, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, S.; Fei, Z.; Chen, Y.R.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, M.; Vrebalov, J.; McQuinn, R.; Gapper, N.; Liu, B.; Xiang, J.; et al. Single-base resolution methylomes of tomato fruit development reveal epigenome modifications associated with ripening. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proffitt, J.H.; Davie, J.R.; Swinton, D.; Hattman, S. 5-Methylcytosine Is Not Detectable in Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA. Mol. Cell Biol. 1984, 4, 985–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Saze, H.; Kinoshita, T.; Miura, A.; Soppe, W.J.; Koornneef, M.; Kakutani, T. Control of FWA gene silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana by SINE-related direct repeats. Plant J. 2006, 49, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Exposito-Rodriguez, M.; Borges, A.A.; Borges-Perez, A.; Perez, J.A. Selection of internal control genes for quantitative real-time RT-PCR studies during tomato development process. BMC Plant Biol. 2008, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Gehring, M.; Johnson, L.; Hannon, M.; Harada, J.J.; Goldberg, R.B.; Jacobsen, S.E.; Fischer, R.L. DEMETER, a DNA Glycosylase Domain Protein, Is Required for Endosperm Gene Imprinting and Seed Viability in Arabidopsis. Cell 2002, 110, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jang, H.; Shin, H.; Choi, W.L.; Mok, Y.G.; Huh, J.H. AP endonucleases process 5-methylcytosine excision intermediates during active DNA demethylation in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, 11408–11418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, Y.G.; Uzawa, R.; Lee, J.; Weiner, G.M.; Eichman, B.F.; Fischer, R.L.; Huh, J.H. Domain structure of the DEMETER 5-methylcytosine DNA glycosylase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19225–19230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, B.; Wu, X.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Q.; DeMott, M.S.; Gu, C.; Wang, L.; You, D.; et al. Nick-seq for single-nucleotide resolution genomic maps of DNA modifications and damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, 6715–6725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdasco, M.; Esteller, M. Clinical epigenetics: Seizing opportunities for translation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 109–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, H.; Shin, H.; Eichman, B.F.; Huh, J.H. Excision of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine by DEMETER family DNA glycosylases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 446, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Sambrook, J.; Sambrook, J. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 4th ed.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Schmittgen, T.D.; Livak, K.J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1101–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koornneef, M.; Hanhart, C.J.; van der Veen, J.H. A genetic and physiological analysis of late flowering mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1991, 229, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoft, V.K.; Chumak, N.; Choi, Y.; Hannon, M.; Garcia-Aguilar, M.; Machlicova, A.; Slusarz, L.; Mosiolek, M.; Park, J.S.; Park, G.T.; et al. Function of the DEMETER DNA glycosylase in the Arabidopsis thaliana male gametophyte. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 8042–8047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, W.L.; Mok, Y.G.; Huh, J.H. Application of 5-Methylcytosine DNA Glycosylase to the Quantitative Analysis of DNA Methylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031072
Choi WL, Mok YG, Huh JH. Application of 5-Methylcytosine DNA Glycosylase to the Quantitative Analysis of DNA Methylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(3):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031072
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Woo Lee, Young Geun Mok, and Jin Hoe Huh. 2021. "Application of 5-Methylcytosine DNA Glycosylase to the Quantitative Analysis of DNA Methylation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 3: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031072
APA StyleChoi, W. L., Mok, Y. G., & Huh, J. H. (2021). Application of 5-Methylcytosine DNA Glycosylase to the Quantitative Analysis of DNA Methylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(3), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22031072




