Tumor-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression and PD-L1 Regulation in M0 Macrophages via IL-6/STAT3 and TLR4 Signaling Pathways
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Tumor-Derived SEVs Are Internalized by M0-M
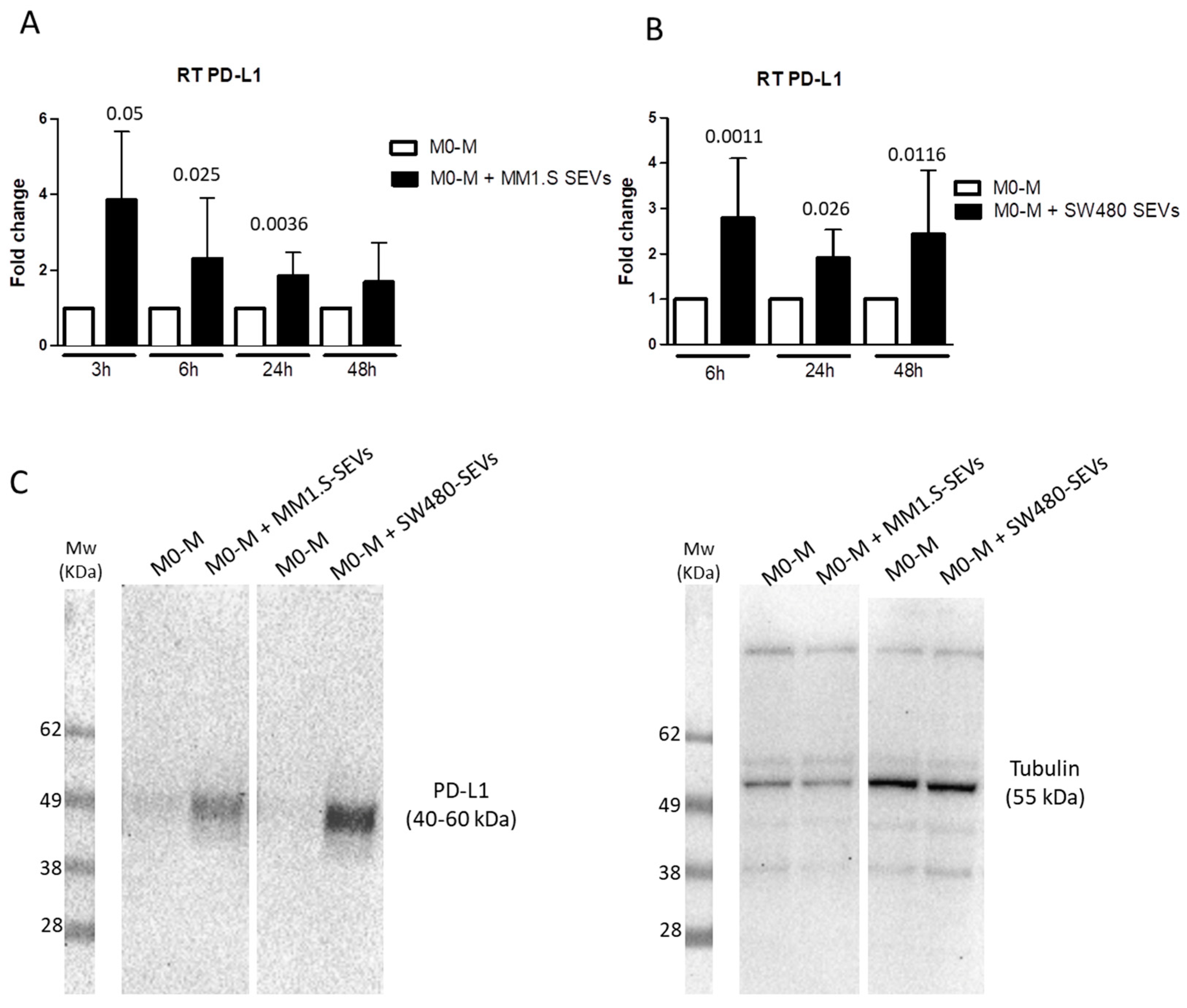
2.2. Tumor-Derived SEVs Upregulate PD-L1 Expression in M0-M
2.3. MM- and CRC-SEVs Increase IL-6 Expression and STAT3 Phosphorylation in M0-M
2.4. MM and CRC-Derived SEVs Increase NF-kB Expression in M0 Macrophages
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. THP1-Derived Macrophage Culture
4.3. Small Extracellular Vesicles Isolation
4.4. Trasmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
4.5. Internalization of SEVs by M0 Macrophages
4.6. MTT (3-[4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 Diphenyl Tetrazolium Bromide) Assay
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Real-Time PCR
4.9. Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vinay, D.S.; Ryan, E.P.; Pawelec, G.; Talib, W.H.; Stagg, J.; Elkord, E.; Lichtor, T.; Decker, W.K.; Whelan, R.L.; Kumara, H.; et al. Immune evasion in cancer: Mechanistic basis and therapeutic strategies. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S185–S198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmaninejad, A.; Valilou, S.F.; Shabgah, A.G.; Aslani, S.; Alimardani, M.; Pasdar, A.; Sahebkar, A. Pd-1/pd-l1 pathway: Basic biology and role in cancer immunotherapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 16824–16837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dermani, F.K.; Samadi, P.; Rahmani, G.; Kohlan, A.K.; Najafi, R. Pd-1/pd-l1 immune checkpoint: Potential target for cancer therapy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 1313–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. Pd-1/pd-l1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar]
- Butte, M.J.; Keir, M.E.; Phamduy, T.B.; Sharpe, A.H.; Freeman, G.J. Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically with the b7-1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit t cell responses. Immunity 2007, 27, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Francisco, L.M.; Salinas, V.H.; Brown, K.E.; Vanguri, V.K.; Freeman, G.J.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Sharpe, A.H. Pd-l1 regulates the development, maintenance, and function of induced regulatory t cells. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 3015–3029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mittendorf, E.A.; Philips, A.V.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Qiao, N.; Wu, Y.; Harrington, S.; Su, X.; Wang, Y.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Akcakanat, A.; et al. Pd-l1 expression in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thiem, A.; Hesbacher, S.; Kneitz, H.; di Primio, T.; Heppt, M.V.; Hermanns, H.M.; Goebeler, M.; Meierjohann, S.; Houben, R.; Schrama, D. Ifn-gamma-induced pd-l1 expression in melanoma depends on p53 expression. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schoenfeld, A.J.; Rizvi, H.; Bandlamudi, C.; Sauter, J.L.; Travis, W.D.; Rekhtman, N.; Plodkowski, A.J.; Perez-Johnston, R.; Sawan, P.; Beras, A.; et al. Clinical and molecular correlates of pd-l1 expression in patients with lung adenocarcinomas. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, R.W.; Millis, S.Z.; Carballido, E.M.; Bryant, D.; Gatalica, Z.; Reddy, S.; Bryce, A.H.; Vogelzang, N.J.; Stanton, M.L.; Castle, E.P.; et al. Pd-1 and pd-l1 expression in renal cell carcinoma with sarcomatoid differentiation. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, X.; Choi, M.G.; Kim, K.; Kim, K.M.; Kim, S.T.; Park, S.H.; Cristescu, R.; Peter, S.; Lee, J. High pd-l1 expression in gastric cancer (gc) patients and correlation with molecular features. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2020, 216, 152881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litak, J.; Mazurek, M.; Grochowski, C.; Kamieniak, P.; Rolinski, J. Pd-l1/pd-1 axis in glioblastoma multiforme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, P.; Huang, T.; Zou, Q.; Liu, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, X.; Wei, Y.; Qiu, H. Fgfr2 promotes expression of pd-l1 in colorectal cancer via the jak/stat3 signaling pathway. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 3065–3075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Xu, S. Tumor-associated cd204-positive macrophage is a prognostic marker in clinical stage i lung adenocarcinoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8459193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kubota, K.; Moriyama, M.; Furukawa, S.; Rafiul, H.; Maruse, Y.; Jinno, T.; Tanaka, A.; Ohta, M.; Ishiguro, N.; Yamauchi, M.; et al. Cd163(+)cd204(+) tumor-associated macrophages contribute to t cell regulation via interleukin-10 and pd-l1 production in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, S.; Pucci, M.; Alessandro, R.; Fontana, S. Extracellular vesicles and tumor-immune escape: Biological functions and clinical perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mills, C.D. M1 and m2 macrophages: Oracles of health and disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mills, C.D.; Kincaid, K.; Alt, J.M.; Heilman, M.J.; Hill, A.M. M-1/m-2 macrophages and the th1/th2 paradigm. J. Immunol. 2000, 164, 6166–6173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, A.; Wei, J.; Kong, L.Y.; Wang, Y.; Priebe, W.; Qiao, W.; Sawaya, R.; Heimberger, A.B. Glioma cancer stem cells induce immunosuppressive macrophages/microglia. Neuro Oncol. 2010, 12, 1113–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petty, A.J.; Dai, R.; Lapalombella, R.; Baiocchi, R.A.; Benson, D.M.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Yang, Y. Hedgehog-induced pd-l1 on tumor-associated macrophages is critical for suppression of tumor-infiltrating cd8+ t cell function. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e146707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, D.M.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, C.; Xu, J.; Zhang, J.P.; Wu, C.; Zheng, L. Activated monocytes in peritumoral stroma of hepatocellular carcinoma foster immune privilege and disease progression through pd-l1. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 1327–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.; Wei, S.; Hurt, E.M.; Green, M.D.; Zhao, L.; Vatan, L.; Szeliga, W.; Herbst, R.; Harms, P.W.; Fecher, L.A.; et al. Host expression of pd-l1 determines efficacy of pd-l1 pathway blockade-mediated tumor regression. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tang, H.; Liang, Y.; Anders, R.A.; Taube, J.M.; Qiu, X.; Mulgaonkar, A.; Liu, X.; Harrington, S.M.; Guo, J.; Xin, Y.; et al. Pd-l1 on host cells is essential for pd-l1 blockade-mediated tumor regression. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, L.C.; Lee, Y.H.; Chang, C.J.; Shun, C.T.; Fang, C.Y.; Shao, Y.Y.; Liu, T.H.; Cheng, A.L.; Hsu, C.H. Increased expression of programmed death-ligand 1 in infiltrating immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues after sorafenib treatment. Liver Cancer 2019, 8, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellmunt, J.; Mullane, S.A.; Werner, L.; Fay, A.P.; Callea, M.; Leow, J.J.; Taplin, M.E.; Choueiri, T.K.; Hodi, F.S.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. Association of pd-l1 expression on tumor-infiltrating mononuclear cells and overall survival in patients with urothelial carcinoma. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 812–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatogai, K.; Kitano, S.; Fujii, S.; Kojima, T.; Daiko, H.; Nomura, S.; Yoshino, T.; Ohtsu, A.; Takiguchi, Y.; Doi, T.; et al. Comprehensive immunohistochemical analysis of tumor microenvironment immune status in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 47252–47264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cordonnier, M.; Nardin, C.; Chanteloup, G.; Derangere, V.; Algros, M.P.; Arnould, L.; Garrido, C.; Aubin, F.; Gobbo, J. Tracking the evolution of circulating exosomal-pd-l1 to monitor melanoma patients. J. Extracell Vesicles 2020, 9, 1710899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haderk, F.; Schulz, R.; Iskar, M.; Cid, L.L.; Worst, T.; Willmund, K.V.; Schulz, A.; Warnken, U.; Seiler, J.; Benner, A.; et al. Tumor-derived exosomes modulate pd-l1 expression in monocytes. Sci. Immunol. 2017, 2, eaah5509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, J.E.; Sung, K.J.; Sung, Y.H.; Pack, C.G.; Jung, M.K.; Han, B.; et al. Exosomal pd-l1 promotes tumor growth through immune escape in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2019, 51, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gabrusiewicz, K.; Li, X.; Wei, J.; Hashimoto, Y.; Marisetty, A.L.; Ott, M.; Wang, F.; Hawke, D.; Yu, J.; Healy, L.M.; et al. Glioblastoma stem cell-derived exosomes induce m2 macrophages and pd-l1 expression on human monocytes. Oncoimmunology 2018, 7, e1412909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Chen, M.; Nie, H.; Yuan, Y. Pd-1 and pd-l1 in cancer immunotherapy: Clinical implications and future considerations. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2019, 15, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMillan, D.C. Cancer and systemic inflammation: Stage the tumour and stage the host. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, X.; Huang, J.; Zhong, H.; Shen, N.; Faggioni, R.; Fung, M.; Yao, Y. Targeting interleukin-6 in inflammatory autoimmune diseases and cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 141, 125–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamano, J.B.; Li, Y.D.; DiDomenico, J.D.; Choy, W.; Veliceasa, D.; Oyon, D.E.; Fakurnejad, S.; Ampie, L.; Kesavabhotla, K.; Kaur, R.; et al. Glioblastoma-derived il6 induces immunosuppressive peripheral myeloid cell pd-l1 and promotes tumor growth. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3643–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Xu, J.; Yan, X.; Jin, K.; Li, W.; Zhang, R. Targeting interleukin-6 (il-6) sensitizes anti-pd-l1 treatment in a colorectal cancer preclinical model. Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 5501–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hamrouni, A.; Wolowiec, D.; Coiteux, V.; Kuliczkowski, K.; Hetuin, D.; Saudemont, A.; Quesnel, B. Plasma cells from multiple myeloma patients express b7-h1 (pd-l1) and increase expression after stimulation with ifn-{gamma} and tlr ligands via a myd88-, traf6-, and mek-dependent pathway. Blood 2007, 110, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Antonangeli, F.; Natalini, A.; Garassino, M.C.; Sica, A.; Santoni, A.; Di Rosa, F. Regulation of pd-l1 expression by nf-kappab in cancer. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 584626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betzler, A.C.; Theodoraki, M.N.; Schuler, P.J.; Doscher, J.; Laban, S.; Hoffmann, T.K.; Brunner, C. Nf-kappab and its role in checkpoint control. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, V.; Hu, X.; Weller, C.; Weber, R.; Groth, C.; Riester, Z.; Huser, L.; Sun, Q.; Nagibin, V.; Kirschning, C.; et al. Melanoma extracellular vesicles generate immunosuppressive myeloid cells by upregulating pd-l1 via tlr4 signaling. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 4715–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, S.K.; Lewis, C.E. Nf-kappab as a central regulator of macrophage function in tumors. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2010, 88, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ubanako, P.; Xelwa, N.; Ntwasa, M. Lps induces inflammatory chemokines via tlr-4 signalling and enhances the warburg effect in thp-1 cells. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0222614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Thery, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, M.; Wang, Q. Tumor-associated macrophages induce pd-l1 expression in gastric cancer cells through il-6 and tnf-a signaling. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 396, 112315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Jiao, Q.; Shen, C.T.; Song, H.J.; Zhang, H.Z.; Qiu, Z.L.; Luo, Q.Y. Interleukin 6 regulates the expression of programmed cell death ligand 1 in thyroid cancer. Cancer Sci. 2021, 112, 997–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, X.; Shen, M.; Yang, D.R.; Fang, L.; Weng, G.; Tsai, Y.; Keng, P.C.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.O. Inhibition of il-6-jak/stat3 signaling in castration-resistant prostate cancer cells enhances the nk cell-mediated cytotoxicity via alteration of pd-l1/nkg2d ligand levels. Mol. Oncol. 2018, 12, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Z.; Yang, H.; Sun, W.; Yao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, R. Il-6 promotes pd-l1 expression in monocytes and macrophages by decreasing protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type o expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e000285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.F.; Peng, Z.X.; Ding, L.; Peng, Y.R. Baishouwu extract suppresses the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via tlr4/myd88/nf-kappab pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beswick, E.J.; Johnson, J.R.; Saada, J.I.; Humen, M.; House, J.; Dann, S.; Qiu, S.; Brasier, A.R.; Powell, D.W.; Reyes, V.E.; et al. Tlr4 activation enhances the pd-l1-mediated tolerogenic capacity of colonic cd90+ stromal cells. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2218–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Guo, D.; Weng, L.; Wang, S.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Cai, Z. Tumor-derived exosomes educate dendritic cells to promote tumor metastasis via hsp72/hsp105-tlr2/tlr4 pathway. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1362527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chase, M.A.; Wheeler, D.S.; Lierl, K.M.; Hughes, V.S.; Wong, H.R.; Page, K. Hsp72 induces inflammation and regulates cytokine production in airway epithelium through a tlr4- and nf-kappab-dependent mechanism. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 6318–6324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Li, H.; Deng, Y.; Tai, Y.; Zeng, K.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, Y. Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce pdl1+ neutrophils through the il6-stat3 pathway that foster immune suppression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorina, R.; Font-Nieves, M.; Marquez-Kisinousky, L.; Santalucia, T.; Planas, A.M. Astrocyte tlr4 activation induces a proinflammatory environment through the interplay between myd88-dependent nfkappab signaling, mapk, and jak1/stat1 pathways. Glia 2011, 59, 242–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, W.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.; Zhang, N.; Ma, J.; Ding, F.; Li, F.; Miao, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Q.; et al. Hsp60 is involved in the neuroprotective effects of naloxone. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 2172–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shiratori, H.; Feinweber, C.; Luckhardt, S.; Linke, B.; Resch, E.; Geisslinger, G.; Weigert, A.; Parnham, M.J. Thp-1 and human peripheral blood mononuclear cell-derived macrophages differ in their capacity to polarize in vitro. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 88, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pucci, M.; Raimondo, S.; Zichittella, C.; Tinnirello, V.; Corleone, V.; Aiello, G.; Moschetti, M.; Conigliaro, A.; Fontana, S.; Alessandro, R. Biological properties of a citral-enriched fraction of Citrus limon essential oil. Foods 2020, 9, 1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, S.; Urzi, O.; Conigliaro, A.; Bosco, G.L.; Parisi, S.; Carlisi, M.; Siragusa, S.; Raimondi, L.; Luca, A.; Giavaresi, G.; et al. Extracellular vesicle micrornas contribute to the osteogenic inhibition of mesenchymal stem cells in multiple myeloma. Cancers 2020, 12, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schillaci, O.; Fontana, S.; Monteleone, F.; Taverna, S.; Di Bella, M.A.; Di Vizio, D.; Alessandro, R. Exosomes from metastatic cancer cells transfer amoeboid phenotype to non-metastatic cells and increase endothelial permeability: Their emerging role in tumor heterogeneity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raimondo, S.; Naselli, F.; Fontana, S.; Monteleone, F.; Lo Dico, A.; Saieva, L.; Zito, G.; Flugy, A.; Manno, M.; Di Bella, M.A.; et al. Citrus limon-derived nanovesicles inhibit cancer cell proliferation and suppress cml xenograft growth by inducing trail-mediated cell death. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 19514–19527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]




| Primers | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | ATGGGGAAGGTGAAGGTCG | GGGTCATTGATGGCAACAATAT |
| PD-L1 | TCACGGTTCCCAAGGACCTA | AGGTCTTCCTCTCCATGCAC |
| IL-6 | GGTACATCCTCGACGGCATCT | GTGCCTCTTTGCTGCTTTCAC |
| IL-1β | ACAGATGAAGTGCTCCTTCCA | GTCGGAGATTCGTAGCTGGAT |
| TNF-α | CCAGGCAGTCAGATCATCTTCTC | AGCTGGTTATCTCTCAGCTCCAC |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pucci, M.; Raimondo, S.; Urzì, O.; Moschetti, M.; Di Bella, M.A.; Conigliaro, A.; Caccamo, N.; La Manna, M.P.; Fontana, S.; Alessandro, R. Tumor-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression and PD-L1 Regulation in M0 Macrophages via IL-6/STAT3 and TLR4 Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212118
Pucci M, Raimondo S, Urzì O, Moschetti M, Di Bella MA, Conigliaro A, Caccamo N, La Manna MP, Fontana S, Alessandro R. Tumor-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression and PD-L1 Regulation in M0 Macrophages via IL-6/STAT3 and TLR4 Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(22):12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212118
Chicago/Turabian StylePucci, Marzia, Stefania Raimondo, Ornella Urzì, Marta Moschetti, Maria Antonietta Di Bella, Alice Conigliaro, Nadia Caccamo, Marco Pio La Manna, Simona Fontana, and Riccardo Alessandro. 2021. "Tumor-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression and PD-L1 Regulation in M0 Macrophages via IL-6/STAT3 and TLR4 Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 22: 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212118
APA StylePucci, M., Raimondo, S., Urzì, O., Moschetti, M., Di Bella, M. A., Conigliaro, A., Caccamo, N., La Manna, M. P., Fontana, S., & Alessandro, R. (2021). Tumor-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Induce Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Expression and PD-L1 Regulation in M0 Macrophages via IL-6/STAT3 and TLR4 Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(22), 12118. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222212118










