Stem Cell and Macrophage Roles in Skeletal Muscle Regenerative Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
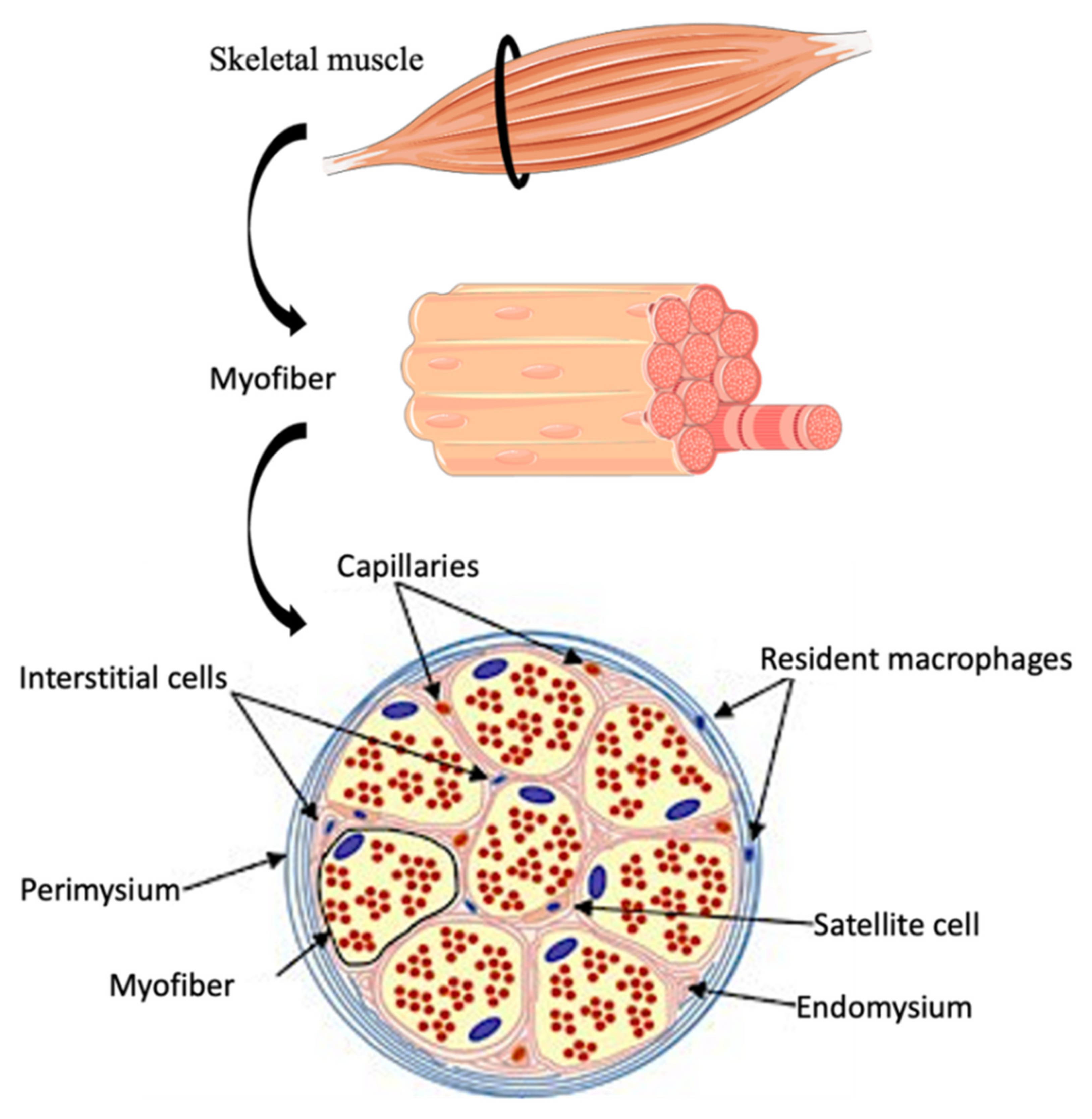
2. SkMR Biology
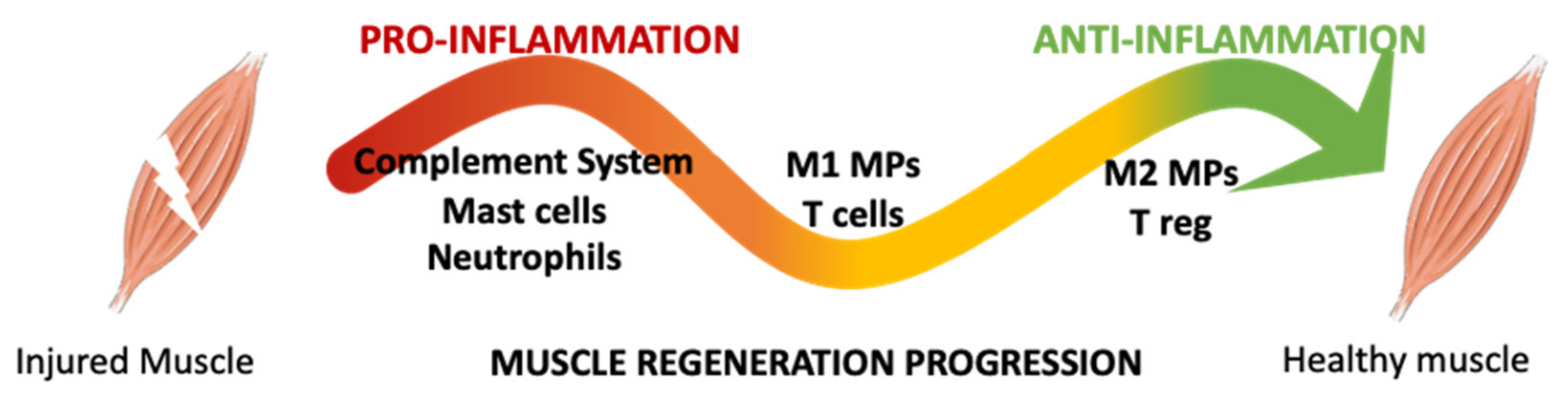
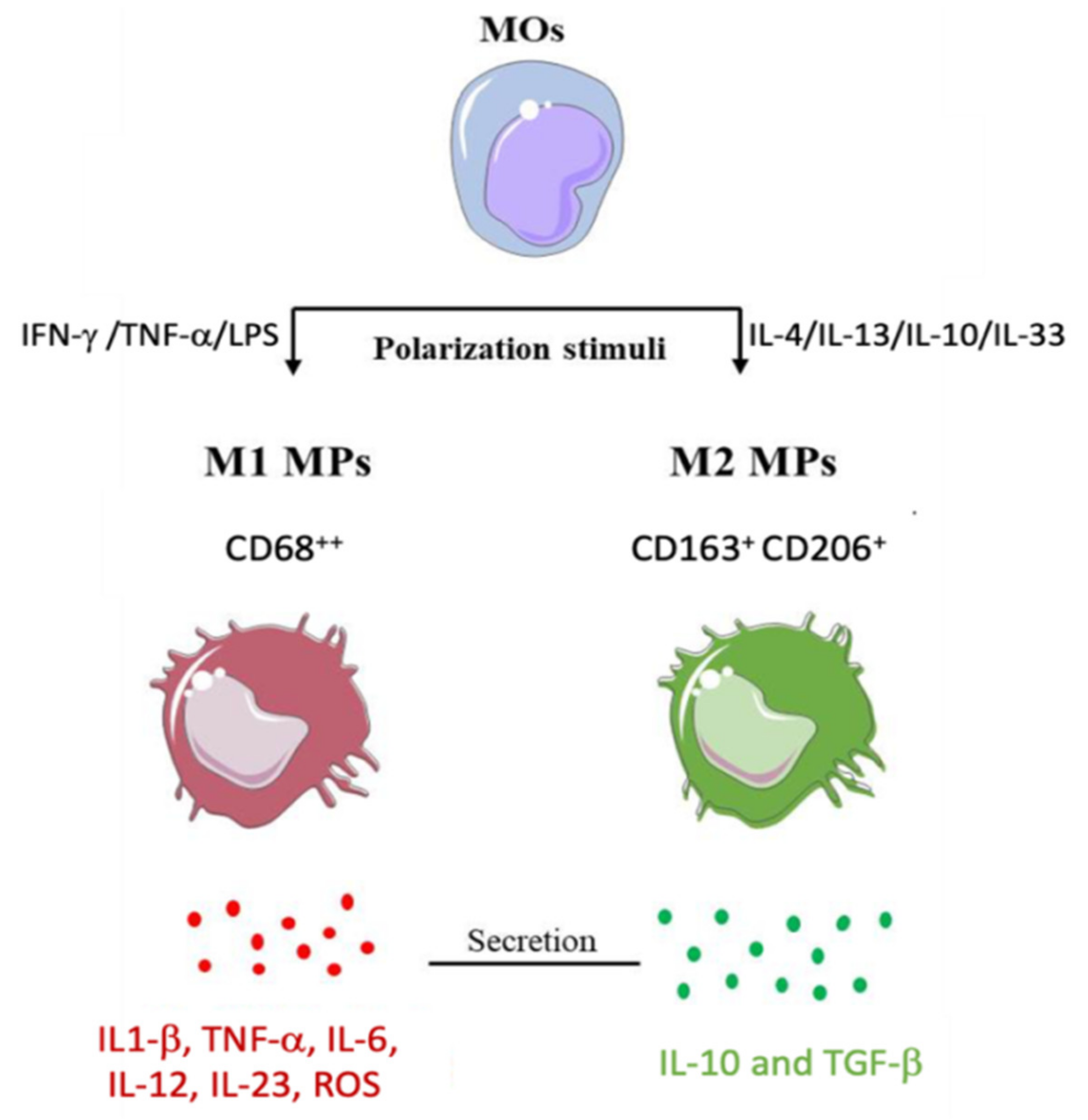
3. Macrophages and Muscle Healing
4. Macrophages and Muscle Healing: In Vivo Evidence
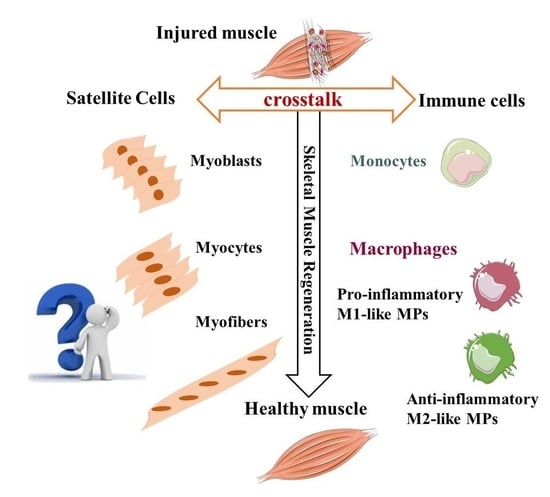
5. Macrophages and Myogenic Precursors: A Functional Crosstalk
6. Cytokines and Muscle Healing
6.1. TNF-α
6.2. IFN-γ
6.3. IL-6
6.4. IL-1
6.5. IL-10
| Cell Culture | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|
| C2C12 | After differentiation induction, TNF-α expression increases | [80] |
| Murine myoblasts | Myoblast migration stimulation | [82] |
| Murine myoblasts | Myoblast migration induction | [83] |
| C2C12 | Inhibition of myoblast differentiation into myotubes | [81] |
| C2C12, Primary myoblasts | Inhibition of myoblast differentiation | [86] |
| C2C12 | Reduction of myoblast proliferation | [87] |
| Muscle-derived fibroblasts C2C12 | Decrease TGFβ-1 expression | [88] |
| Mice MPs, C2C12 | Induction of myoblast proliferation | [90] |
| C2C12, Primary human myoblasts | Proliferation and differentiation due to different IL-6 concentrations | [91] |
| C2C12 | Increase of myoblast fusion index | [92] |
| C2C12 | IL-1 induces muscle catabolic pathway | [93] |
| Mice satellite cells | IL-1 induces cell proliferation | [94] |
| Mice MPs, C2C12 | IL-10 activated macrophages promote myoblasts proliferation | [54] |
| Animals | Injury | Injection | Muscle | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mice | Cooled probe | - | Tibialis anterior | TNF-α involved in muscle strength recovery | [84] |
| Mice | - | TNF-α | Soleus Diaphragm | TNF-α stimulates satellite cell proliferation | [82] |
| Mice | HS/RL | TNF-α | Soleus Gastrocnemius | Decrease of Myog expression | [85] |
| Mice | Cardiotoxin | - | Soleus | SkMR impairment | [80] |
| Mice | Cardiotoxin | IFN-γR blocking antibody | Extensor digitorum longus Tibialis anterior | Reduction of regenerating myofiber formation | [87] |
| Mice | Laceration | IFN-γ | Gastrocnemius | Minor fibrosis rate | [88] |
| Mice | Cardiotoxin | IL-6 | Tibialis anterior Gastrocnemius | Inhibition of proliferating cells | [90] |
| Mice | Overloading | - | Soleus Plantaris muscles | Stimulation of migration and proliferation | [89] |
| Mice | BaCl2 injection | - | Tibialis anterior | Early increase of IL-1β expression | [95] |
| Mice | Cardiotoxin | - | Tibialis anterior | Reduction of inflammatory cells infiltration | [94] |
| Mice | Contusion | - | Gastrocnemius | IL-10 peak at 7 days | [96] |
| Mice | HU/RL | - | Soleus | SkMR impairment | [54] |
| Mice | FAE | - | Hindlimb muscles | Necrotic myofibers persistence; fat accumulation | [73] |
| Mice | TK-I/R | - | Gastrocnemius | Recovery of muscle functionality by M1-MPs delivery | [74] |
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal Muscle: A Brief Review of Structure and Function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, T.L.; Pedrinelli, A.; Hernandez, A.J. Muscle injury—Physiopathology, diagnosis, treatment and clinical presentation. Rev. Bras. Ortop. Engl. Ed. 2011, 46, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, E.H.; Caterson, E.J.; Jackson, W.M.; Nesti, L.J. Quality of Healing: Defining, Quantifying, and Enhancing Skeletal Muscle Healing: Muscle Injury Repair and Regeneration. Wound Repair Regen. 2014, 22, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karalaki, M.; Fili, S.; Philippou, A.; Koutsilieris, M. Muscle Regeneration: Cellular and Molecular Events. Vivo Athens Greece 2009, 23, 779–796. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, H.; Price, F.; Rudnicki, M.A. Satellite Cells and the Muscle Stem Cell Niche. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 23–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oustanina, S.; Hause, G.; Braun, T. Pax7 Directs Postnatal Renewal and Propagation of Myogenic Satellite Cells but Not Their Specification. EMBO J. 2004, 23, 3430–3439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, S.; Chargé, S.B.; Seale, P.; Huh, M.; Rudnicki, M.A. Distinct Roles for Pax7 and Pax3 in Adult Regenerative Myogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Maltzahn, J.; Jones, A.E.; Parks, R.J.; Rudnicki, M.A. Pax7 Is Critical for the Normal Function of Satellite Cells in Adult Skeletal Muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 16474–16479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.; Schüler, S.C.; Hüttner, S.S.; von Eyss, B.; von Maltzahn, J. Adult Stem Cells at Work: Regenerating Skeletal Muscle. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2019, 76, 2559–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, N.C.; Rudnicki, M.A. Satellite Cells. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 107, pp. 161–181. ISBN 978-0-12-416022-4. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X.; Yang, M.; Shi, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhu, M.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Ge, Z.; Bian, X.; Lv, J.; et al. Interleukin-15 Facilitates Muscle Regeneration through Modulation of Fibro/Adipogenic Progenitors. Cell Commun. Signal. 2018, 16, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joe, A.W.B.; Yi, L.; Natarajan, A.; Le Grand, F.; So, L.; Wang, J.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Rossi, F.M.V. Muscle Injury Activates Resident Fibro/Adipogenic Progenitors That Facilitate Myogenesis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moratal, C.; Raffort, J.; Arrighi, N.; Rekima, S.; Schaub, S.; Dechesne, C.A.; Chinetti, G.; Dani, C. IL-1β- and IL-4-Polarized Macrophages Have Opposite Effects on Adipogenesis of Intramuscular Fibro-Adipogenic Progenitors in Humans. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 17005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heredia, J.E.; Mukundan, L.; Chen, F.M.; Mueller, A.A.; Deo, R.C.; Locksley, R.M.; Rando, T.A.; Chawla, A. Type 2 Innate Signals Stimulate Fibro/Adipogenic Progenitors to Facilitate Muscle Regeneration. Cell 2013, 153, 376–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, M.P.; Malide, D.; Hoffman, G.; Pandey, G.; D’Escamard, V.; Nomura-Kitabayashi, A.; Rovira, I.; Kataoka, H.; Ochando, J.; Harvey, R.P.; et al. Tissue-Resident PDGFRα+ Progenitor Cells Contribute to Fibrosis versus Healing in a Context- and Spatiotemporally Dependent Manner. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 555–570.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uezumi, A.; Fukada, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Takeda, S.; Tsuchida, K. Mesenchymal Progenitors Distinct from Satellite Cells Contribute to Ectopic Fat Cell Formation in Skeletal Muscle. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shefer, G.; Wleklinski-Lee, M.; Yablonka-Reuveni, Z. Skeletal Muscle Satellite Cells Can Spontaneously Enter an Alternative Mesenchymal Pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 5393–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huard, J. Differentiation of Muscle-Derived Cells into Myofibroblasts in Injured Skeletal Muscle. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 161, 895–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Järvinen, T.A.H.; Järvinen, T.L.N.; Kääriäinen, M.; Kalimo, H.; Järvinen, M. Muscle Injuries: Biology and Treatment. Am. J. Sports Med. 2005, 33, 745–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancaccio, P.; Lippi, G.; Maffulli, N. Biochemical Markers of Muscular Damage. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2010, 48, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudenzio, N.; Sibilano, R.; Marichal, T.; Starkl, P.; Reber, L.L.; Cenac, N.; McNeil, B.D.; Dong, X.; Hernandez, J.D.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R.; et al. Different Activation Signals Induce Distinct Mast Cell Degranulation Strategies. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 3981–3998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Miwa, T.; Liu, C.; Cui, W.; Song, W.-C.; Du, J. Complement C3a Signaling Facilitates Skeletal Muscle Regeneration by Regulating Monocyte Function and Trafficking. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaffidi, P.; Misteli, T.; Bianchi, M.E. Release of Chromatin Protein HMGB1 by Necrotic Cells Triggers Inflammation. Nature 2002, 418, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenette, J.; Cai, B.; Tidball, J.G. Complement Activation Promotes Muscle Inflammation during Modified Muscle Use. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 156, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, E.; Bouchard, P.; Roussel, M.-P.; Côté, C.H. Mast Cells Can Regulate Skeletal Muscle Cell Proliferation by Multiple Mechanisms: Mast Cells and Muscle Healing. Muscle Nerve 2013, 48, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Hu, P. Skeletal Muscle Regeneration Is Modulated by Inflammation. J. Orthop. Transl. 2018, 13, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duchesne, E.; Dufresne, S.S.; Dumont, N.A. Impact of Inflammation and Anti-Inflammatory Modalities on Skeletal Muscle Healing: From Fundamental Research to the Clinic. Phys. Ther. 2017, 97, 807–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, N.; Bouchard, P.; Frenette, J. Neutrophil-Induced Skeletal Muscle Damage: A Calculated and Controlled Response Following Hindlimb Unloading and Reloading. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2008, 295, R1831–R1838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qazi, T.H.; Duda, G.N.; Ort, M.J.; Perka, C.; Geissler, S.; Winkler, T. Cell Therapy to Improve Regeneration of Skeletal Muscle Injuries. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2019, 10, 501–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montarras, D. Direct Isolation of Satellite Cells for Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Science 2005, 309, 2064–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, C.A.; Olsen, I.; Zammit, P.S.; Heslop, L.; Petrie, A.; Partridge, T.A.; Morgan, J.E. Stem Cell Function, Self-Renewal, and Behavioral Heterogeneity of Cells from the Adult Muscle Satellite Cell Niche. Cell 2005, 122, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacco, A.; Doyonnas, R.; Kraft, P.; Vitorovic, S.; Blau, H.M. Self-Renewal and Expansion of Single Transplanted Muscle Stem Cells. Nature 2008, 456, 502–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, M.T.; Manor, U.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J.; Fan, C.-M. Intravital Imaging Reveals Ghost Fibers as Architectural Units Guiding Myogenic Progenitors during Regeneration. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerletti, M.; Jurga, S.; Witczak, C.A.; Hirshman, M.F.; Shadrach, J.L.; Goodyear, L.J.; Wagers, A.J. Highly Efficient, Functional Engraftment of Skeletal Muscle Stem Cells in Dystrophic Muscles. Cell 2008, 134, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usas, A.; Huard, J. Muscle-Derived Stem Cells for Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Therapy. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 5401–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorant, J.; Saury, C.; Schleder, C.; Robriquet, F.; Lieubeau, B.; Négroni, E.; Leroux, I.; Chabrand, L.; Viau, S.; Babarit, C.; et al. Skeletal Muscle Regenerative Potential of Human MuStem Cells Following Transplantation into Injured Mice Muscle. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 618–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trucillo, E.; Bisceglia, B.; Valdrè, G.; Giordano, E.; Reverchon, E.; Maffulli, N.; Della Porta, G. Growth Factor Sustained Delivery from Poly-lactic-co-glycolic Acid Microcarriers and Its Mass Transfer Modeling by Finite Element in a Dynamic and Static Three-dimensional Environment Bioengineered with Stem Cells. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2019, 116, 1777–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamparelli, E.P.; Lovecchio, J.; Ciardulli, M.C.; Giudice, V.; Dale, T.P.; Selleri, C.; Forsyth, N.; Giordano, E.; Maffulli, N.; Della Porta, G. Chondrogenic Commitment of Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Perfused Collagen Hydrogel Functionalized with HTGF-Β1-Releasing PLGA Microcarrier. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardulli, M.C.; Marino, L.; Lovecchio, J.; Giordano, E.; Forsyth, N.R.; Selleri, C.; Maffulli, N.; Della Porta, G. Tendon and Cytokine Marker Expression by Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Hyaluronate/Poly-Lactic-Co-Glycolic Acid (PLGA)/Fibrin Three-Dimensional (3D) Scaffold. Cells 2020, 9, 1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardulli, M.C.; Marino, L.; Lamparelli, E.P.; Guida, M.; Forsyth, N.R.; Selleri, C.; Della Porta, G.; Maffulli, N. Dose-Response Tendon-Specific Markers Induction by Growth Differentiation Factor-5 in Human Bone Marrow and Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciardulli, M.C.; Lovecchio, J.; Scala, P.; Lamparelli, E.P.; Dale, T.P.; Giudice, V.; Giordano, E.; Selleri, C.; Forsyth, N.R.; Maffulli, N.; et al. 3D Biomimetic Scaffold for Growth Factor Controlled Delivery: An In-Vitro Study of Tenogenic Events on Wharton’s Jelly Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scala, P.; Lovecchio, J.; Lamparelli, E.P.; Vitolo, R.; Giudice, V.; Giordano, E.; Selleri, C.; Rehak, L.; Maffulli, N.; Della Porta, G. Myogenic Commitment of Human Stem Cells by Myoblasts Co-Culture: A Static Vs. Dynamic Approach. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2021. In press. [Google Scholar]
- Elahi, K.C.; Klein, G.; Avci-Adali, M.; Sievert, K.D.; MacNeil, S.; Aicher, W.K. Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Different Sources Diverge in Their Expression of Cell Surface Proteins and Display Distinct Differentiation Patterns. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 5646384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, T.; von Roth, P.; Matziolis, G.; Mehta, M.; Perka, C.; Duda, G.N. Dose–Response Relationship of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation and Functional Regeneration after Severe Skeletal Muscle Injury in Rats. Tissue Eng. Part A 2009, 15, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matziolis, G.; Winkler, T.; Schaser, K.; Wiemann, M.; Krocker, D.; Tuischer, J.; Perka, C.; Duda, G.N. Autologous Bone Marrow-Derived Cells Enhance Muscle Strength Following Skeletal Muscle Crush Injury in Rats. Tissue Eng. 2006, 12, 361–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Roth, P.; Duda, G.N.; Radojewski, P.; Preininger, B.; Strohschein, K.; Röhner, E.; Perka, C.; Winkler, T. Intra-Arterial MSC Transplantation Restores Functional Capacity After Skeletal Muscle Trauma. Open Orthop. J. 2012, 6, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Peçanha, R.; de Bagno, L.L.E.S.; Ribeiro, M.B.; Robottom Ferreira, A.B.; Moraes, M.O.; Zapata-Sudo, G.; Kasai-Brunswick, T.H.; Campos-de-Carvalho, A.C.; dos Goldenberg, R.C.S.; Saar Werneck-de-Castro, J.P. Adipose-Derived Stem-Cell Treatment of Skeletal Muscle Injury. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2012, 94, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helal, M.A.M.; Shaheen, N.E.M.; Abu Zahra, F.A. Immunomodulatory Capacity of the Local Mesenchymal Stem Cells Transplantation after Severe Skeletal Muscle Injury in Female Rats. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2016, 38, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zheng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P.; Xiao, W. BMSC Transplantation Aggravates Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Fibrosis and Impairs Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shapouri-Moghaddam, A.; Mohammadian, S.; Vazini, H.; Taghadosi, M.; Esmaeili, S.; Mardani, F.; Seifi, B.; Mohammadi, A.; Afshari, J.T.; Sahebkar, A. Macrophage Plasticity, Polarization, and Function in Health and Disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 6425–6440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidball, J.G.; Villalta, S.A. Regulatory Interactions between Muscle and the Immune System during Muscle Regeneration. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R1173–R1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Taylor, P.R. Monocyte and Macrophage Heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stout, R.D.; Jiang, C.; Matta, B.; Tietzel, I.; Watkins, S.K.; Suttles, J. Macrophages Sequentially Change Their Functional Phenotype in Response to Changes in Microenvironmental Influences. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, B.; Wehling-Henricks, M.; Villalta, S.A.; Wang, Y.; Tidball, J.G. IL-10 Triggers Changes in Macrophage Phenotype That Promote Muscle Growth and Regeneration. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 3669–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigitte, M.; Schilte, C.; Plonquet, A.; Baba-Amer, Y.; Henri, A.; Charlier, C.; Tajbakhsh, S.; Albert, M.; Gherardi, R.K.; Chrétien, F. Muscle Resident Macrophages Control the Immune Cell Reaction in a Mouse Model of Notexin-Induced Myoinjury. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 268–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chazaud, B.; Sonnet, C.; Lafuste, P.; Bassez, G.; Rimaniol, A.-C.; Poron, F.; Authier, F.-J.; Dreyfus, P.A.; Gherardi, R.K. Satellite Cells Attract Monocytes and Use Macrophages as a Support to Escape Apoptosis and Enhance Muscle Growth. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouaoui Boudjeltia, K.; Moguilevsky, N.; Legssyer, I.; Babar, S.; Guillaume, M.; Delree, P.; Vanhaeverbeek, M.; Brohee, D.; Ducobu, J.; Remacle, C. Oxidation of Low Density Lipoproteins by Myeloperoxidase at the Surface of Endothelial Cells: An Additional Mechanism to Subendothelium Oxidation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 325, 434–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, L.; Henry, A.; Poron, F.; Baba-Amer, Y.; van Rooijen, N.; Plonquet, A.; Gherardi, R.K.; Chazaud, B. Inflammatory Monocytes Recruited after Skeletal Muscle Injury Switch into Antiinflammatory Macrophages to Support Myogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1057–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suelves, M.; López-Alemany, R.; Lluís, F.; Aniorte, G.; Serrano, E.; Parra, M.; Carmeliet, P.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Plasmin Activity Is Required for Myogenesis in Vitro and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration in Vivo. Blood 2002, 99, 2835–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, M.L.; Bryer, S.C.; Cheng, M.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Conley, K.L.; Cunningham, A.K.; Xue, B.; Sisson, T.H.; You, J.-S.; Hornberger, T.A.; et al. Macrophage-Specific Expression of Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Promotes Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koh, T.J.; Bryer, S.C.; Pucci, A.M.; Sisson, T.H. Mice Deficient in Plasminogen Activator Inhibitor-1 Have Improved Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2005, 289, C217–C223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, T.; Mounier, R.; Horvath, A.; Cuvellier, S.; Dumont, F.; Poliska, S.; Ardjoune, H.; Juban, G.; Nagy, L.; Chazaud, B. Highly Dynamic Transcriptional Signature of Distinct Macrophage Subsets during Sterile Inflammation, Resolution, and Tissue Repair. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 4771–4782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, M.L.; Weinheimer-Haus, E.M.; Koh, T.J. Macrophage Activation and Skeletal Muscle Healing Following Traumatic Injury: Macrophage Activation in Muscle Trauma. J. Pathol. 2014, 232, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdiguero, E.; Sousa-Victor, P.; Ruiz-Bonilla, V.; Jardí, M.; Caelles, C.; Serrano, A.L.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. P38/MKP-1–Regulated AKT Coordinates Macrophage Transitions and Resolution of Inflammation during Tissue Repair. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 195, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mounier, R.; Théret, M.; Arnold, L.; Cuvellier, S.; Bultot, L.; Göransson, O.; Sanz, N.; Ferry, A.; Sakamoto, K.; Foretz, M.; et al. AMPKα1 Regulates Macrophage Skewing at the Time of Resolution of Inflammation during Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 251–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Melton, D.W.; Porter, L.; Sarwar, Z.U.; McManus, L.M.; Shireman, P.K. Altered Macrophage Phenotype Transition Impairs Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1167–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Côté, C.H.; Bouchard, P.; van Rooijen, N.; Marsolais, D.; Duchesne, E. Monocyte Depletion Increases Local Proliferation of Macrophage Subsets after Skeletal Muscle Injury. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summan, M.; Warren, G.L.; Mercer, R.R.; Chapman, R.; Hulderman, T.; Van Rooijen, N.; Simeonova, P.P. Macrophages and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration: A Clodronate-Containing Liposome Depletion Study. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R1488–R1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warren, G.L.; Hulderman, T.; Mishra, D.; Gao, X.; Millecchia, L.; O’Farrell, L.; Kuziel, W.A.; Simeonova, P.P. Chemokine Receptor CCR2 Involvement in Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras-Shannon, V.; Ochoa, O.; Reyes-Reyna, S.M.; Sun, D.; Michalek, J.E.; Kuziel, W.A.; McManus, L.M.; Shireman, P.K. Fat Accumulation with Altered Inflammation and Regeneration in Skeletal Muscle of CCR2−/− Mice Following Ischemic Injury. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C953–C967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Huang, D.; Saederup, N.; Charo, I.F.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Zhou, L. Macrophages Recruited via CCR2 Produce Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 to Repair Acute Skeletal Muscle Injury. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 358–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Huang, D.; Ransohoff, R.M.; Zhou, L. Acute Skeletal Muscle Injury: CCL2 Expression by Both Monocytes and Injured Muscle Is Required for Repair. FASEB J. 2011, 25, 3344–3355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shireman, P.K.; Contreras-Shannon, V.; Ochoa, O.; Karia, B.P.; Michalek, J.E.; McManus, L.M. MCP-1 Deficiency Causes Altered Inflammation with Impaired Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2007, 81, 775–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rybalko, V.; Hsieh, P.-L.; Merscham-Banda, M.; Suggs, L.J.; Farrar, R.P. The Development of Macrophage-Mediated Cell Therapy to Improve Skeletal Muscle Function after Injury. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratnayake, D.; Nguyen, P.D.; Rossello, F.J.; Wimmer, V.C.; Tan, J.L.; Galvis, L.A.; Julier, Z.; Wood, A.J.; Boudier, T.; Isiaku, A.I.; et al. Macrophages Provide a Transient Muscle Stem Cell Niche via NAMPT Secretion. Nature 2021, 591, 281–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnet, C. Human Macrophages Rescue Myoblasts and Myotubes from Apoptosis through a Set of Adhesion Molecular Systems. J. Cell Sci. 2006, 119, 2497–2507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choo, H.-J.; Canner, J.P.; Vest, K.E.; Thompson, Z.; Pavlath, G.K. A Tale of Two Niches: Differential Functions for VCAM-1 in Satellite Cells under Basal and Injured Conditions. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 313, C392–C404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saclier, M.; Yacoub-Youssef, H.; Mackey, A.L.; Arnold, L.; Ardjoune, H.; Magnan, M.; Sailhan, F.; Chelly, J.; Pavlath, G.K.; Mounier, R.; et al. Differentially Activated Macrophages Orchestrate Myogenic Precursor Cell Fate During Human Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantini, M.; Giurisato, E.; Radu, C.; Tiozzo, S.; Pampinella, F.; Senigaglia, D.; Zaniolo, G.; Mazzoleni, F.; Vitiello, L. Macrophage-Secreted Myogenic Factors: A Promising Tool for Greatly Enhancing the Proliferative Capacity of Myoblasts in Vitro and in Vivo. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 23, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-E.; Jin, B.; Li, Y.-P. TNF-α Regulates Myogenesis and Muscle Regeneration by Activating P38 MAPK. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C1660–C1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Yang, S.T.; Wang, J.J.; Zhou, J.; Xing, S.S.; Shen, C.C.; Wang, X.X.; Yue, Y.X.; Song, J.; Chen, M.; et al. TNF Alpha Inhibits Myogenic Differentiation of C2C12 Cells through NF-ΚB Activation and Impairment of IGF-1 Signaling Pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 458, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-P. TNF-α Is a Mitogen in Skeletal Muscle. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2003, 285, C370–C376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torrente, Y.; Fahime, E.E.; Caron, N.J.; Del Bo, R.; Belicchi, M.; Pisati, F.; Tremblay, J.P.; Bresolin, N. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNF-α) Stimulates Chemotactic Response in Mouse Myogenic Cells. Cell Transplant. 2003, 12, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, G.L.; Hulderman, T.; Jensen, N.; McKinstry, M.; Mishra, M.; Luster, M.I.; Simeonova, P.P. Physiological Role of Tumor Necrosis Factor α in Traumatic Muscle Injury. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1630–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langen, R.C.J.; Velden, J.L.J.; Schols, A.M.W.J.; Kelders, M.C.J.M.; Wouters, E.F.M.; Janssen-Heininger, Y.M.W. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Inhibits Myogenic Differentiation through MyoD Protein Destabilization. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Londhe, P.; Davie, J.K. Gamma Interferon Modulates Myogenesis through the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II Transactivator, CIITA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 2854–2866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Fantuzzi, G.; Koh, T.J. Endogenous Interferon-γ Is Required for Efficient Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2008, 294, C1183–C1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, W.; Li, Y.; Usas, A.; Somogyi, G.; Huard, J. Gamma Interferon as an Antifibrosis Agent in Skeletal Muscle. J. Orthop. Res. 2003, 21, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, A.L.; Baeza-Raja, B.; Perdiguero, E.; Jardí, M.; Muñoz-Cánoves, P. Interleukin-6 Is an Essential Regulator of Satellite Cell-Mediated Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy. Cell Metab. 2008, 7, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Wu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.; Du, J. Interleukin-6/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) Pathway Is Essential for Macrophage Infiltration and Myoblast Proliferation during Muscle Regeneration. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyn, P.J.; Dzobo, K.; Smith, R.I.; Myburgh, K.H. Interleukin-6 Induces Myogenic Differentiation via JAK2-STAT3 Signaling in Mouse C2C12 Myoblast Cell Line and Primary Human Myoblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabiec, K.; Tokarska, J.; Milewska, M.; Błaszczyk, M.; Gajewska, M.; Grzelkowska-Kowalczyk, K. Interleukin-1β Stimulates Early Myogenesis of Mouse C2C12 Myoblasts: The Impact on Myogenic Regulatory Factors, Extracellular Matrix Components, IGF Binding Proteins and Protein Kinases. Pol. J. Vet. Sci. 2013, 16, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Moylan, J.S.; Chambers, M.A.; Smith, J.; Reid, M.B. Interleukin-1 Stimulates Catabolism in C2C12 Myotubes. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2009, 297, C706–C714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaweewannakorn, C.; Tsuchiya, M.; Koide, M.; Hatakeyama, H.; Tanaka, Y.; Yoshida, S.; Sugawara, S.; Hagiwara, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Kanzaki, M. Roles of IL-1α/β in Regeneration of Cardiotoxin-Injured Muscle and Satellite Cell Function. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2018, 315, R90–R103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otis, J.S.; Niccoli, S.; Hawdon, N.; Sarvas, J.L.; Frye, M.A.; Chicco, A.J.; Lees, S.J. Pro-Inflammatory Mediation of Myoblast Proliferation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, Z.; Zhao, L.; Xiao, W.; Chen, P. Changes in Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Factors and the Protein Synthesis Pathway in Injured Skeletal Muscle after Contusion. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 15, 2196–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.-G.; Ahn, E.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Leem, S.-H.; Heo, J.; Kim, H. Effects of Harvesting Sites and Ages on Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells in Rat. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2014, 11, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cianfarani, F.; Toietta, G.; Di Rocco, G.; Cesareo, E.; Zambruno, G.; Odorisio, T. Diabetes Impairs Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cell Function and Efficiency in Promoting Wound Healing: Impaired Prohealing Function of Diabetic ASCs. Wound Repair Regen. 2013, 21, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, S.M.; Glowacki, J. Age-Related Decline in the Osteogenic Potential of Human Bone Marrow Cells Cultured in Three-Dimensional Collagen Sponges. J. Cell. Biochem. 2001, 82, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Huang, B. The Multi-Differentiation Potential of Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2012, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spaltro, G.; Straino, S.; Gambini, E.; Bassetti, B.; Persico, L.; Zoli, S.; Zanobini, M.; Capogrossi, M.C.; Spirito, R.; Quarti, C.; et al. Characterization of the Pall Celeris System as a Point-of-Care Device for Therapeutic Angiogenesis. Cytotherapy 2015, 17, 1302–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigato, M.; Monami, M.; Fadini, G.P. Autologous Cell Therapy for Peripheral Arterial Disease: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Nonrandomized, and Noncontrolled Studies. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1326–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Animals | Transplanted SCs | Injury | Muscle | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mdx mice | MuSCs | Notexin injection | Tibialis anterior | Self-renewal of host SC niche | [29] |
| Mice | MuSCs | Notexin injection | Tibialis anterior | High engraftment percentage | [30] |
| Mdx mice | MuSCs | Cardiotoxin injection | Tibialis anterior | Muscle contractility improvement | [32] |
| Mice | Human MDSCs | Cryolesion | Tibialis anterior | Fusion with host myofibers | [34] |
| SD rats | Autologous MSCs | Open crush trauma | Soleus muscle | Muscle force improvement | [44] |
| SD rats | Autologous BM-MSCs | Open crush trauma | Soleus muscle | Contraction force increase | [45] |
| SD rats | Autologous BM-MSCs | Open crush trauma | Soleus muscle | Muscle force improvement | [46] |
| Wistar rats | Autologous ADSCs | Surgical laceration | Soleus muscle | Regenerating myofibers increase | [47] |
| Wistar rats | Autologous BM-MSCs | Scalpel laceration | Adductor brevis | Regenerating myofibers increase | [48] |
| Mice | BM-MSCs | Contusion | Gastrocnemius muscle | Muscle fibrosis and inflammation | [49] |
| Animals | Injury | Muscle | Depletion Strategy | Results | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mice | Notexin | Tibialis anterior | Diphtheria toxin | M1-MPs, switching in M2-MPs | [58] |
| Mice | Cardiotoxin | Tibialis anterior | - | M1- MPs, switching in M2-MPs | [62] |
| Mice | Laceration | Gastrocnemius | - | M1/M2 phenotype-like classification | [63] |
| Mice | Cardiotoxin | Gastrocnemius | - | Phenotype transition | [64] |
| Mouse | Cardiotoxin | Tibialis anterior | - | AMPK⍺1 involved in M2 polarization | [65] |
| Mice | Cardiotoxin | Tibialis anterior | Diphtheria toxin | SkMR impairment | [66] |
| Wistar rats | Bupivacaine | Tibialis anterior | Cl2MDP liposome & γ-rays | MP number decrease | [67] |
| Mice | Cooled probe | Tibialis anterior | Clodronate liposomes | Regeneration impairment | [68] |
| Mice | Cooled probe | Tibialis anterior | - | Muscle strength recovery impairment | [69] |
| Mice | FAE | Hindlimb muscles | - | Necrotic myofiber persistence | [70] |
| Mice | Barium Chloride | Quadriceps | - | Necrotic myofiber persistence | [71] |
| Mice | Barium Chloride | Quadriceps | - | CCL2 for immune cell recruitment | [72] |
| Mice | FAE | Hindlimb muscles | - | Necrotic myofiber persistence fat accumulation occurrence | [73] |
| Mice | TK-I/R | Gastrocnemius | - | Muscle functionalities recover by M1-MPs | [74] |
| Cell Culture | Results | Ref | |||
| In vitro | MPCs/MPs co-culture | MPs rescue MPCs from spontaneous apoptosis | [76] | ||
| MPCs/MPs co-culture | Direct contacts between MPs on MPCs are not required | [78] | |||
| Graft | Muscle | Injury | Results | Ref | |
| In vivo | Mice | Tibialis anterior | Notexin injection | MPs and MPCs anti-apoptotic contacts establishment | [76] |
| Human | Vastus lateralis | Electrically stimulation | Different spatial position of MPs in regenerating areas | [78] | |
| Wistar rats | Tibialis anterior | Surgery ablation | MPs conditioned medium enhances SkMR | [79] | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Scala, P.; Rehak, L.; Giudice, V.; Ciaglia, E.; Puca, A.A.; Selleri, C.; Della Porta, G.; Maffulli, N. Stem Cell and Macrophage Roles in Skeletal Muscle Regenerative Medicine. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910867
Scala P, Rehak L, Giudice V, Ciaglia E, Puca AA, Selleri C, Della Porta G, Maffulli N. Stem Cell and Macrophage Roles in Skeletal Muscle Regenerative Medicine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910867
Chicago/Turabian StyleScala, Pasqualina, Laura Rehak, Valentina Giudice, Elena Ciaglia, Annibale Alessandro Puca, Carmine Selleri, Giovanna Della Porta, and Nicola Maffulli. 2021. "Stem Cell and Macrophage Roles in Skeletal Muscle Regenerative Medicine" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910867
APA StyleScala, P., Rehak, L., Giudice, V., Ciaglia, E., Puca, A. A., Selleri, C., Della Porta, G., & Maffulli, N. (2021). Stem Cell and Macrophage Roles in Skeletal Muscle Regenerative Medicine. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10867. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910867