The Ephb2 Receptor Uses Homotypic, Head-to-Tail Interactions within Its Ectodomain as an Autoinhibitory Control Mechanism
Abstract
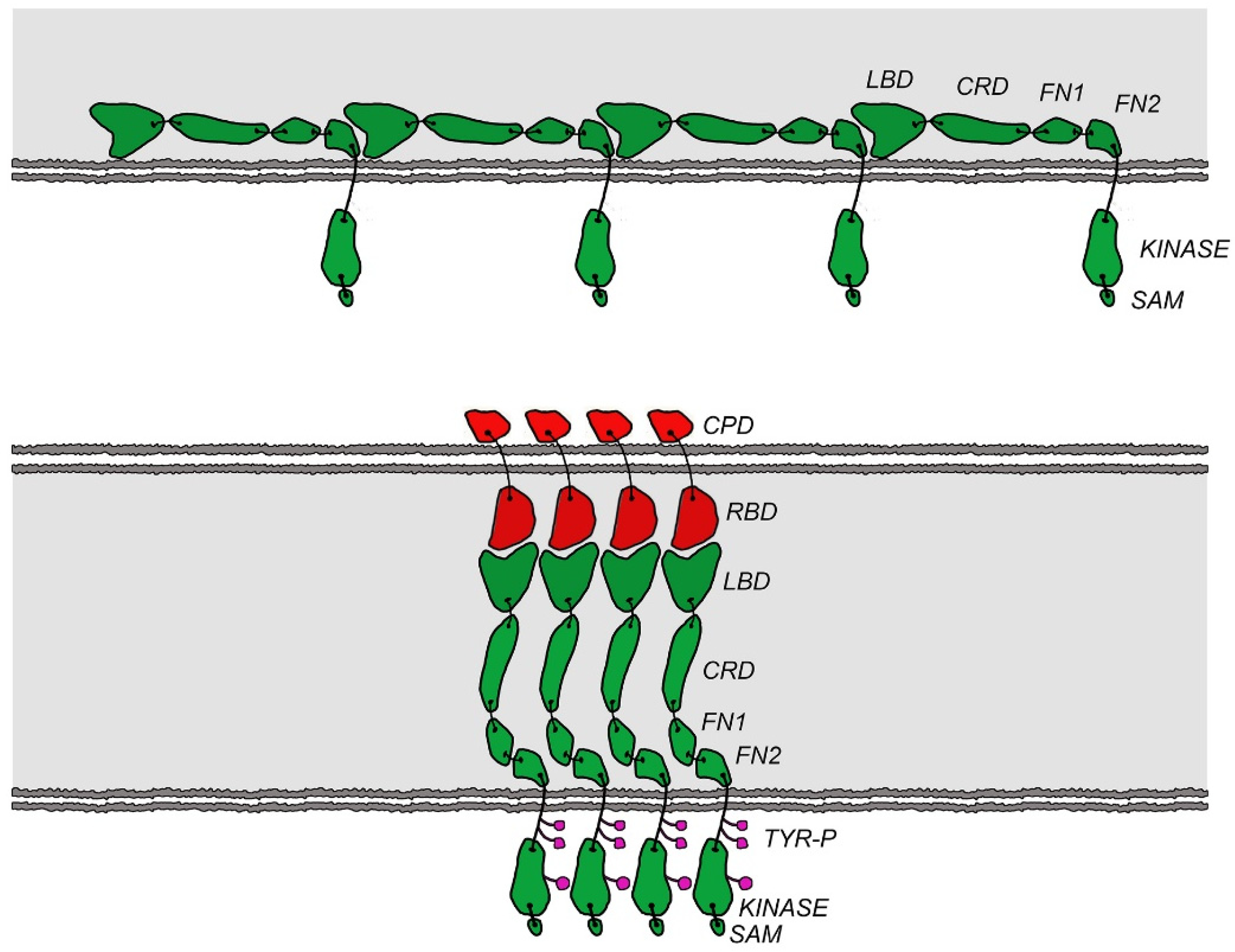
1. Introduction
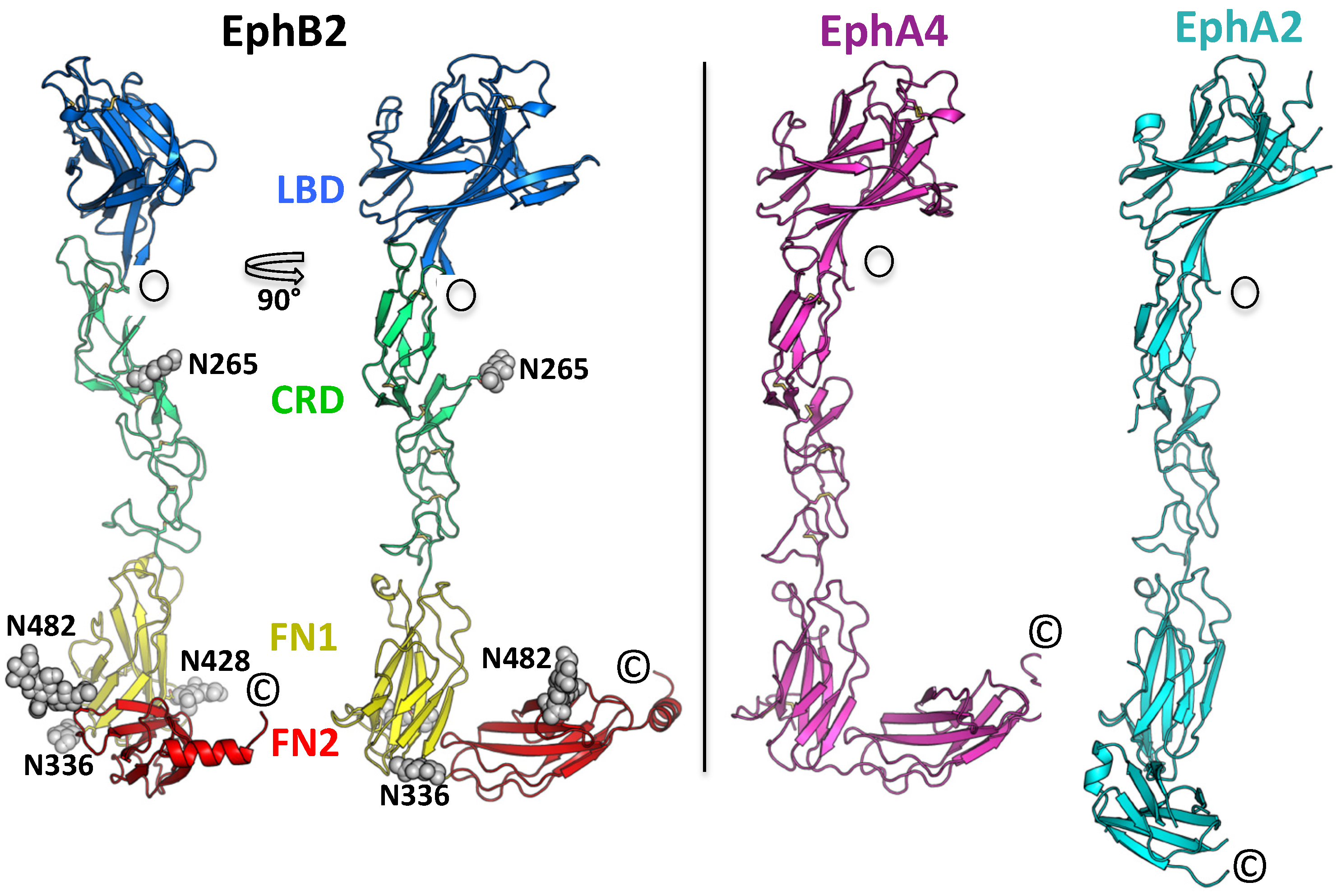
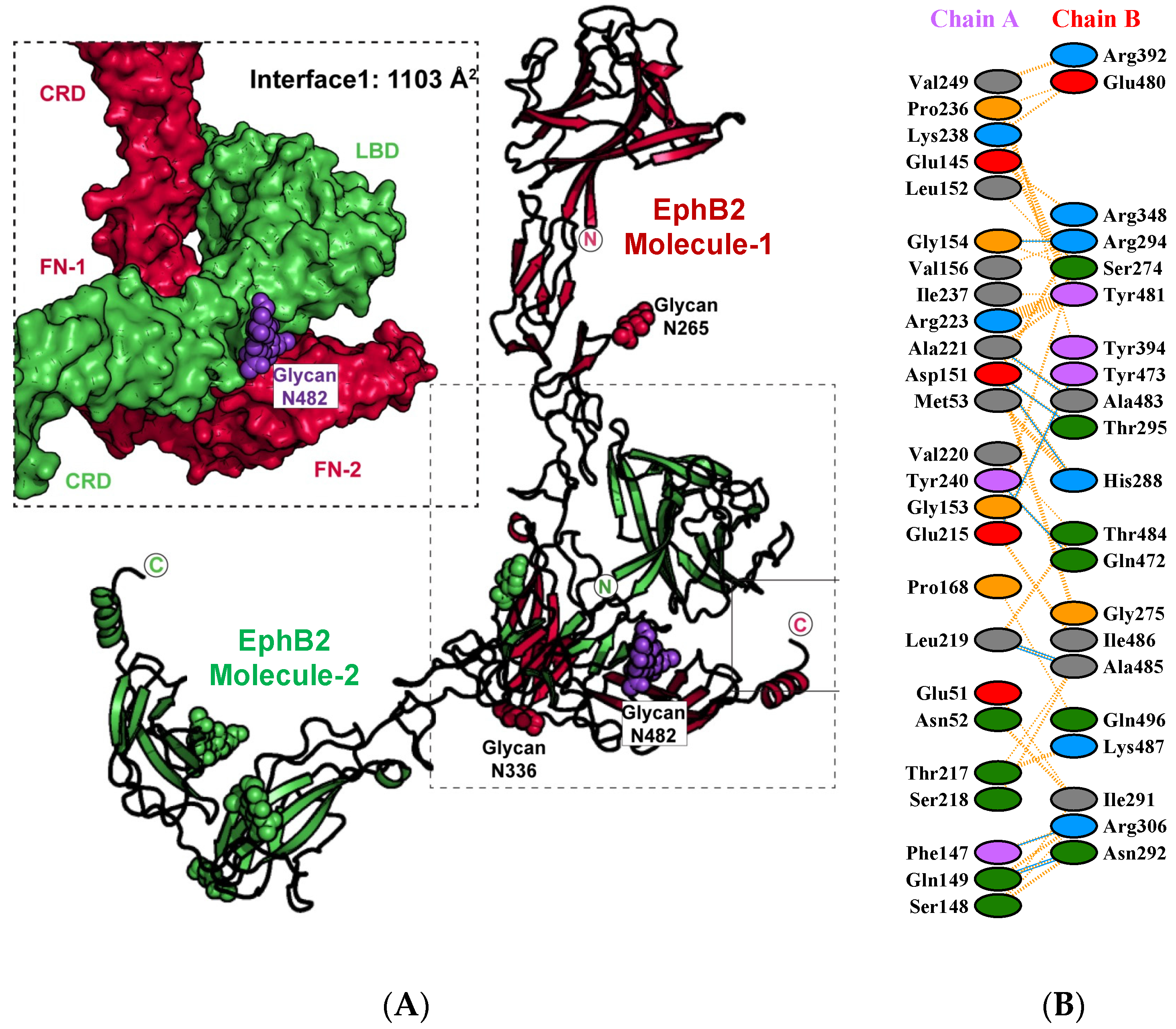
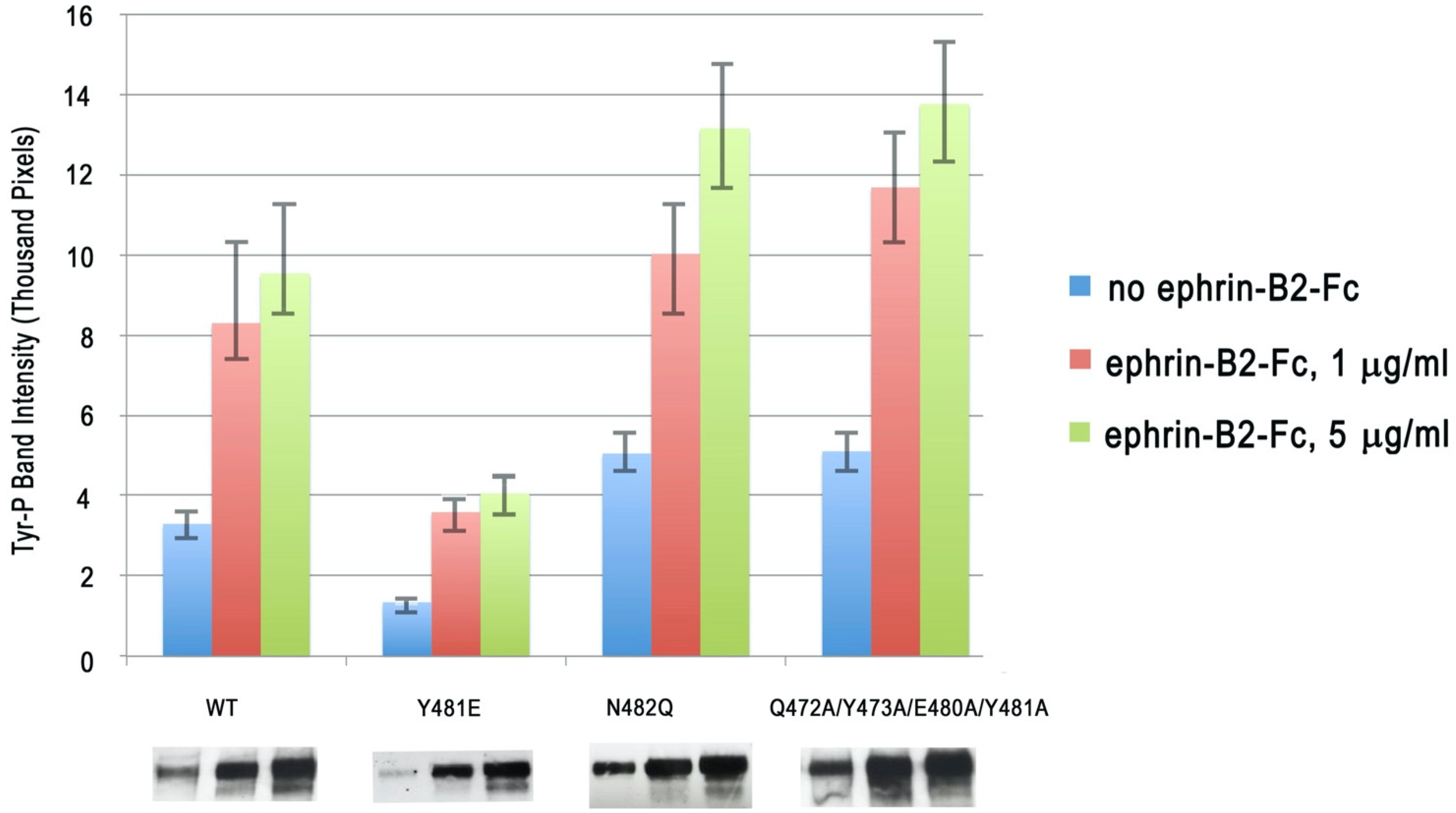
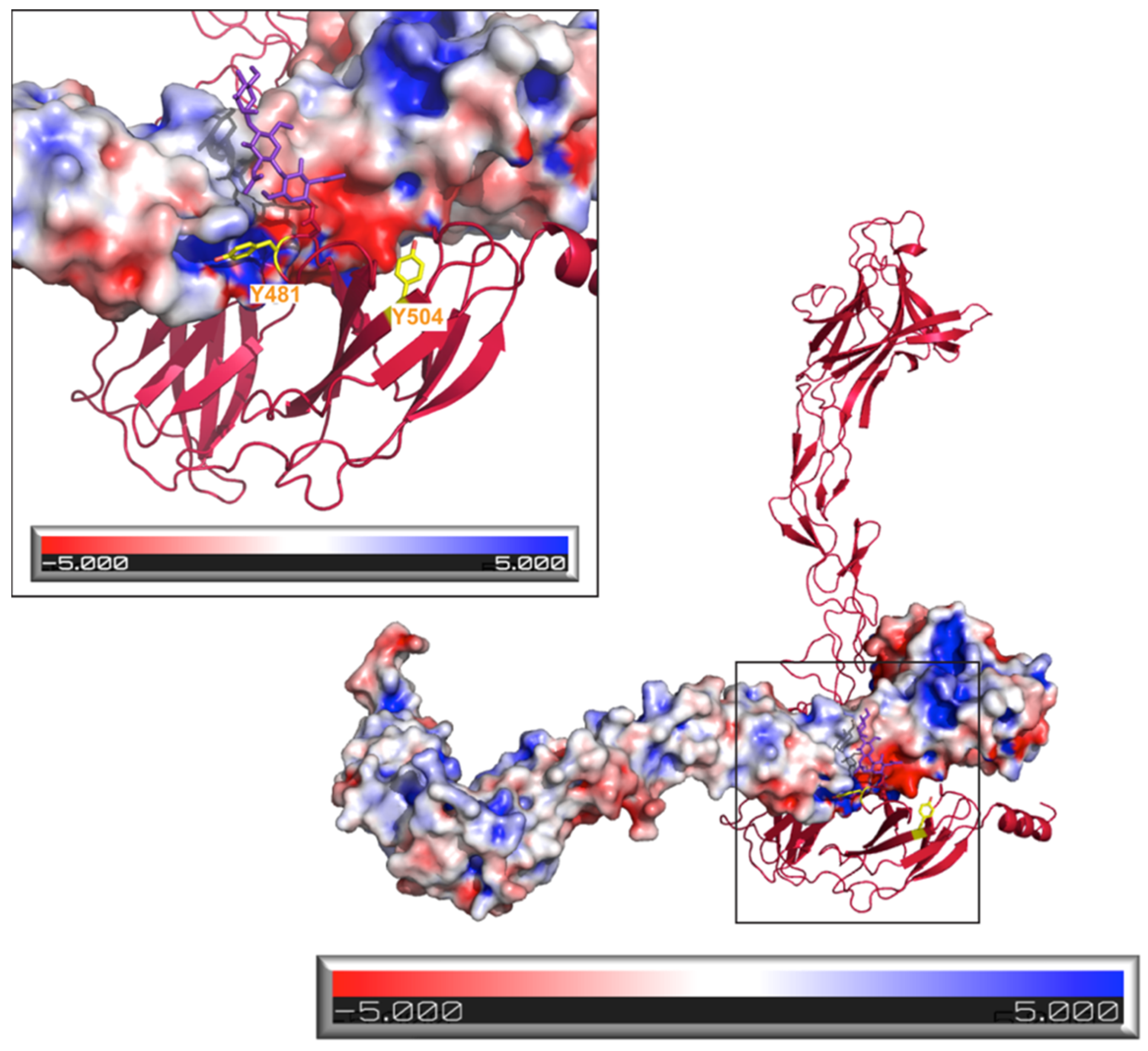
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Cloning and Mutagenesis
3.2. Protein Expression and Crystallization
3.3. Cell Manipulations and Transfections
3.4. Cell-Based EphB2 Kinase Activation Assay
3.5. Illustrations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boyd, A.W.; Ward, L.D.; Wicks, I.P.; Simpson, R.J.; Salvaris, E.; Wilks, A.; Welch, K.; Loudovaris, M.; Rockman, S.; Busmanis, I.; et al. Isolation and characterization of a novel re-ceptor-type protein tyrosine kinase (hek) from a human pre-B cell line. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 3262–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, N.W.; Holland, S.J.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Flenniken, A.; Pan, L.; Ryan, T.E.; Henkemeyer, M.; Strebhardt, K.; Hirai, H.; Wilkinson, D.; et al. Eph Receptors and Ligands Comprise Two Major Specificity Subclasses and Are Reciprocally Compartmentalized during Embryogenesis. Neuron 1996, 17, 9–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, J.-P.; Nikolov, D.B. Eph signaling: A structural view. Trends Neurosci. 2003, 26, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cowan, C.A.; Henkemeyer, M. The SH2/SH3 adaptor Grb4 transduces B-ephrin reverse signals. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 413, 174–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egea, J.; Klein, R. Bidirectional Eph–ephrin signaling during axon guidance. Trends Cell Biol. 2007, 17, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, E.B. Eph–ephrin promiscuity is now crystal clear. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 417–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.G. Multiple roles of eph receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 2, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquale, E.B. Eph receptor signalling casts a wide net on cell behaviour. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 6, 462–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, E.B. Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: Bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, P.W.; Adikari, S.; Lackmann, M. Eph/ephrin signalling and function in oncogenesis: Lessons from embryonic develop-ment. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2008, 8, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, P.W.; Slape, C.I.; Farnsworth, R.H.; Atapattu, L.; Scott, A.M.; Vail, M.E. EphA3 biology and cancer. Growth Factors 2014, 32, 176–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisabeth, E.M.; Falivelli, G.; Pasquale, E.B. Eph Receptor Signaling and Ephrins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genander, M.; Halford, M.M.; Xu, N.J.; Eriksson, M.; Yu, Z.; Qiu, Z.; Frisén, J. Dissociation of EphB2 signaling pathways mediating pro-genitor cell proliferation and tumor suppression. Cell 2009, 139, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cissé, M.; Halabisky, B.; Harris, J.; Devidze, N.; Dubal, D.B.; Sun, B.; Orr, A.; Lotz, G.; Kim, D.H.; Hamto, P.; et al. Reversing EphB2 depletion rescues cognitive functions in Alzheimer model. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 469, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijken, I.; van der Vlag, M.; Flores Hernandez, R.; Ross, A. Perspectives on Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Closer Look into EphB2 Depletion. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 11296–11297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, K.; Zhang, R.; Luan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gou, X. Therapeutic Strategies Targeting Amyloid-beta Receptors and Transporters in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2021, 79, 1429–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, J.-P.; Saha, N.; Nikolov, D.B. Cell–cell signaling via Eph receptors and ephrins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2007, 19, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, J.-P.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Lackmann, M.; Cowan, C.A.; Henkemeyer, M.; Nikolov, D.B. Crystal structure of an Eph receptor–ephrin complex. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 414, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, J.P.; Goldgur, Y.; Miao, H.; Myshkin, E.; Guo, H.; Buck, M.; Nguyen, M.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Wang, B.; Nikolov, D.B. Ligand recognition by A-class Eph receptors: Crystal structures of the EphA2 ligand-binding domain and the EphA2/ephrin-A1 complex. EMBO Rep. 2009, 10, 722–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrencik, J.E.; Brooun, A.; Kraus, M.L.; Recht, M.I.; Kolatkar, A.R.; Han, G.W.; Seifert, J.M.; Widmer, H.; Auer, M.; Kuhn, P. Structural and Biophysical Characterization of the EphB4·EphrinB2 Protein-Protein Interaction and Receptor Specificity. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28185–28192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himanen, J.P. Ectodomain structures of Eph receptors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vearing, C.J.; Lackmann, M. Eph receptor signalling; dimerisation just isn’t enough. Growth Factors 2005, 23, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J.; Ferguson, K.M. The EGFR Family: Not So Prototypical Receptor Tyrosine Kinases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a020768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, P.; Nievergall, E.; Lackmann, M. Concepts and consequences of Eph receptor clustering. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaupp, A.; Sabet, O.; Dudanova, I.; Ponserre, M.; Bastiaens, P.; Klein, R. The composition of EphB2 clusters determines the strength in the cellular repulsion response. J. Cell Biol. 2014, 204, 409–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lackmann, M.; Oates, A.C.; Dottori, M.; Smith, F.M.; Do, C.; Power, M.; Kravets, L.; Boyd, A.W. Distinct Subdomains of the EphA3 Receptor Mediate Ligand Binding and Receptor Dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 20228–20237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himanen, J.P.; Yermekbayeva, L.; Janes, P.; Walker, J.R.; Xu, K.; Atapattu, L.; Rajashankar, K.R.; Mensinga, A.; Lackmann, M.; Nikolov, D.B.; et al. Architecture of Eph receptor clusters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 10860–10865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiradake, E.; Harlos, K.; Sutton, G.; Aricescu, A.R.; Jones, E.Y. An extracellular steric seeding mechanism for Eph-ephrin signaling platform assembly. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, D.B.; Xu, K.; Himanen, J.P. Eph/ephrin recognition and the role of Eph/ephrin clusters in signaling initiation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Proteins Proteom. 2013, 1834, 2160–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, W.A.; Dalton, A.C.; Seegar, T.C.M.; Himanen, J.P.; Nikolov, D.B. Tie2 and Eph Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Activation and Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lackmann, M.; Boyd, A.W. Eph, a Protein Family Coming of Age: More Confusion, Insight, or Complexity? Sci. Signal. 2008, 1, re2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Tzvetkova-Robev, D.; Xu, Y.; Goldgur, Y.; Chan, Y.P.; Himanen, J.P.; Nikolov, D.B. Insights into Eph receptor tyrosine kinase activa-tion from crystal structures of the EphA4 ectodomain and its complex with ephrin-A5. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 14634–14639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolov, D.B.; Xu, K.; Himanen, J.P. Homotypic receptor-receptor interactions regulating Eph signaling. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2014, 8, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Yamashita, Y.; Noda, H.; Okafuji, T.; Go, M.J.; Tanaka, H. EphA receptor tyrosine kinases interact with co-expressed ephrin-A ligands in cis. Neurosci. Res. 2004, 48, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, R.F.; Beutler, M.; Marler, K.J.; Knoll, B.; Becker-Barroso, E.; Heintzmann, R.; Ng, T.; Drescher, U. Silencing of EphA3 through a cis interac-tion with ephrinA5. Nat. Neurosci. 2006, 9, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimmer-Kleikamp, S.H.; Janes, P.; Squire, A.; Bastiaens, P.I.; Lackmann, M. Recruitment of Eph receptors into signaling clusters does not require ephrin contact. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 661–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janes, P.W.; Griesshaber, B.; Atapattu, L.; Nievergall, E.; Hii, L.L.; Mensinga, A.; Lackmann, M. Eph receptor function is modulated by het-erooligomerization of A and B type Eph receptors. J. Cell. Biol. 2011, 195, 1033–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noren, N.K.; Yang, N.; Silldorff, M.; Mutyala, R.; Pasquale, E.B. Ephrin-independent regulation of cell substrate adhesion by the EphB4 receptor. Biochem. J. 2009, 422, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, E.O.; Goldgur, Y.; Robev, D.; Freywald, A.; Nikolov, D.B.; Himanen, J.P. Structure of the EphB6 receptor ectodomain. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0247335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Himanen, J.-P.; Chumley, M.J.; Lackmann, M.; Li, C.; Barton, W.A.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Vearing, C.; Geleick, D.; Feldheim, D.A.; Boyd, A.W.; et al. Repelling class discrimination: Ephrin-A5 binds to and activates EphB2 receptor signaling. Nat. Neurosci. 2004, 7, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Qiu, H. The Mechanistic Impact of N-Glycosylation on Stability, Pharmacokinetics, and Immunogenicity of Therapeutic Proteins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 108, 1366–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, R.M.; Ravetch, J.V. A Novel Role for the IgG Fc Glycan: The Anti-inflammatory Activity of Sialylated IgG Fcs. J. Clin. Immunol. 2010, 30, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferluga, S.; Hantgan, R.; Goldgur, Y.; Himanen, J.P.; Nikolov, D.B.; Debinski, W. Biological and Structural Characterization of Glycosylation on Ephrin-A1, a Preferred Ligand for EphA2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 18448–18457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanamura, K.; Washburn, H.R.; Sheffler-Collins, S.I.; Xia, N.L.; Henderson, N.; Tillu, D.V.; Hassler, S.; Spellman, D.S.; Zhang, G.; Neubert, T.A.; et al. Extracellular phosphorylation of a receptor tyrosine kinase controls synaptic localization of NMDA receptors and regulates pathological pain. PLoS Biol. 2017, 15, e2002457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldgur, Y.; Susi, P.; Karelehto, E.; Sanmark, H.; Lamminmaki, U.; Oricchio, E.; Himanen, J.P. Generation and characterization of a sin-gle-chain anti-EphA2 antibody. Growth Factors 2014, 32, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmsaz, S.; Al-Ejeh, F.; Yeadon, T.M.; Miller, K.J.; Smith, F.M.; Stringer, B.; Moore, A.; Lee, F.-T.; Cooper, L.T.; Stylianou, C.; et al. EphA3 as a target for antibody immunotherapy in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, W.; Luis, E.; Ross, S.; Silva, J.; Tan, C.; Crowley, C.; Chui, C.; Franz, G.; Senter, P.; Koeppen, H.; et al. EphB2 as a therapeutic antibody drug target for the treatment of colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 781–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Lamminmäki, U.; Nikolov, D.; Himanen, J. Eph Receptors as Drug Targets: Single-Chain Antibodies and Beyond. Curr. Drug Targets 2015, 16, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otwinowski, Z.; Minor, W. Processing of X-ray diffraction data collected in oscillation mode. In Methods in Enzymology: Mac-Romolecular Crystallography Part A; Carter, C.W., Jr., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1997; pp. 307–326. ISBN 0076-6879. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, A.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; Adams, P.D.; Winn, M.D.; Storoni, L.C.; Read, R.J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 658–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, P.D.; Afonine, P.V.; Bunkóczi, G.; Chen, V.B.; Davis, I.W.; Echols, N.; Headd, J.J.; Hung, L.-W.; Kapral, G.J.; Grosse-Kunstleve, R.W.; et al. PHENIX: A comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2019, 66, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emsley, P.; Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2004, 60, 2126–2132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| EphB2-ECD (PDB ID: 7S7K) | |
|---|---|
| Resolution range (Å) | 48.4–3.14 (3.32–3.14) |
| Space group | P 21 21 21 |
| Unit cell | 73.843 111.142 156.877 90 90 90 |
| Total reflections | 73,799 |
| Unique reflections | 22,498 |
| Multiplicity | 3.3 (3.4) |
| Completeness (%) | 97.26 (98.52) |
| Mean I/Sigma(I) | 18 (1.5) |
| Wilson B-factor | 116.94 |
| R-merge | 0.041 (0.792) |
| R-work | 0.1913 (0.3053) |
| R-free | 0.2469 (0.3427) |
| Number of atoms | 4167 |
| Macromolecules | 4072 |
| Ligands | 95 |
| Water | 0 |
| Protein residues | 532 |
| RMS (bonds) | 0.010 |
| RMS (angles) | 1.43 |
| Ramachandran favoured (%) | 95 |
| Ramachandran outliers (%) | 0.19 |
| Clash-score | 12.64 |
| Average B-factor | 48.50 |
| Macromolecules | 47.10 |
| Ligands | 109.90 |
| h-EphB1 | (469) iryyekehnefnssm-ar (485) |
| h-EphB2 | (471) lqyyekelseynata-ik (487) |
| h-EphB3 | (488) mkyfek--segiast-vt (502) |
| h-EphB4 | (443) vkyhekgaegpssvrflk (460) |
| h-EphB6 | (508) lryydqaedeshsftmts (525) |
| h-EphA1 | (469) vkyhekgaegpssv-vle (485) |
| h-EphA2 | (443) vtyrkkgdsnsynv-rrt (459) |
| h-EphA3 | (472) vkyyekqeqetsyti-lr (488) |
| h-EphA4 | (476) vkyyekdqnersyri-vr (492) |
| h-EphA5 | (504) ikyfekdq-etsyti-ik (519) |
| h-EphA6 | (477) tkyyekeheqltyss-tr (493) |
| h-EphA7 | (443) ikyyekdqrertyst-lk (459) |
| h-EphA8 | (475) ikyyekdkemqsyst-lk (491) |
| h-EphA10 | (492) iryyekgqseqtysmvkt (509) |
| EphB2 | |
| Human | (471) lqyyekelseynat |
| Mouse | (471) lqyyekelseynat |
| Rat | (471) lqyyekelseynat |
| Chicken | (479) lqyyeknlselnst |
| Macaque | (448) lqyyekelseynat |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, Y.; Robev, D.; Saha, N.; Wang, B.; Dalva, M.B.; Xu, K.; Himanen, J.P.; Nikolov, D.B. The Ephb2 Receptor Uses Homotypic, Head-to-Tail Interactions within Its Ectodomain as an Autoinhibitory Control Mechanism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910473
Xu Y, Robev D, Saha N, Wang B, Dalva MB, Xu K, Himanen JP, Nikolov DB. The Ephb2 Receptor Uses Homotypic, Head-to-Tail Interactions within Its Ectodomain as an Autoinhibitory Control Mechanism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910473
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Yan, Dorothea Robev, Nayanendu Saha, Bingcheng Wang, Matthew B. Dalva, Kai Xu, Juha P. Himanen, and Dimitar B. Nikolov. 2021. "The Ephb2 Receptor Uses Homotypic, Head-to-Tail Interactions within Its Ectodomain as an Autoinhibitory Control Mechanism" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910473
APA StyleXu, Y., Robev, D., Saha, N., Wang, B., Dalva, M. B., Xu, K., Himanen, J. P., & Nikolov, D. B. (2021). The Ephb2 Receptor Uses Homotypic, Head-to-Tail Interactions within Its Ectodomain as an Autoinhibitory Control Mechanism. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10473. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910473






