Abstract
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) signalling is crucial in modulating stress responses in plants, and NADPH oxidases (NOXs) are an important component of signal transduction under salt stress. The goal of this research was to investigate whether the regulation of NOX-dependent signalling during mild and severe salinity differs between the halophyte Eutrema salsugineum and the glycophyte Arabidopsis thaliana. Gene expression analyses showed that salt-induced expression patterns of two NOX genes, RBOHD and RBOHF, varied between the halophyte and the glycophyte. Five days of salinity stimulated the expression of both genes in E. salsugineum leaves, while their expression in A. thaliana decreased. This was not accompanied by changes in the total NOX activity in E. salsugineum, while the activity in A. thaliana was reduced. The expression of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes in E. salsugineum leaves was induced by abscisic acid (ABA) and ethephon spraying. The in silico analyses of promoter sequences of RBOHD and RBOHF revealed multiple cis-acting elements related to hormone responses, and their distribution varied between E. salsugineum and A. thaliana. Our results indicate that, in the halophyte E. salsugineum, the maintenance of the basal activity of NOXs in leaves plays a role during acclimation responses to salt stress. The different expression patterns of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes under salinity in E. salsugineum and A. thaliana point to a modified regulation of these genes in the halophyte, possibly through ABA- and/or ethylene-dependent pathways.
1. Introduction
Soil salinity is one of the major environmental factors that restrict crop productivity and the functioning of plants in natural ecosystems [1,2]. A common reaction of plants to salt-triggered osmotic stress and ionic imbalance is to increase the levels of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [3,4]. These reactive species include superoxide (O2•−), hydroxyl radical (OH•), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and singlet oxygen (1O2) and are generated constantly as products of normal cell metabolism. For a long time, ROS were thought to have primarily negative effects on the cells, such as lipid peroxidation, protein denaturation, and DNA damage [5]. However, more recently, ROS have been perceived as universal signalling metabolites regulating plant growth, development, and defence against biotic and abiotic stresses [6,7,8]. ROS are generated in several cellular compartments, such as chloroplasts, mitochondria, and peroxisomes. In the plasma membrane, ROS are synthesised by NADPH oxidases (NOXs), also termed respiratory burst oxidase homologs (RBOHs) [9]. These enzymes with homology to the NADPH oxidase from mammalian phagocytes can use NADPH as an electron donor to reduce O2 molecules and to generate O2•− in the apoplast. The resulting O2•− can be converted into H2O2 spontaneously or enzymatically by superoxide dismutase (SOD) [9,10]. NADPH oxidases in plants constitute a multigene family and the Arabidopsis thaliana genome contains 10 genes, RBOHA-J, which exhibit a different pattern of expression during ontogenesis and in response to stress stimuli [11,12]. The results of extensive studies confirmed that ROS produced by NOXs regulate many physiological processes, such as seed germination [13], stomatal opening [14], root growth [15], and pollen tube elongation [16]. RBOH-dependent ROS also appear to play an important role in signalling networks enabling acclimation to various stresses, including heat [17], wounding [18], drought [19], and salinity [20,21].
The regulatory mechanisms of NOXs are still under extensive research and their activity is controlled by different factors, such as calcium and protein kinases [22,23]. A link has been established between phytohormones and the regulation of NADPH oxidases. Abscisic acid (ABA) induced the expression of two RBOH genes in A. thaliana guard cells [14], and the overexpression of the ABA biosynthesis gene in tobacco resulted in salt-tolerance associated with NOX-dependent ROS production [24].
The two pleiotropic NOX genes in A. thaliana, RBOHD and RBOHF, are the main NADPH oxidases associated with acclimation to salinity [20]. It has been shown that an early response to salt stress is a calcium wave, which depends on the ROS produced by RBOHD and which then propagates the systemic response to salt [25]. The analyses of A. thaliana mutants enables linking the ROS produced by RBOHD and RBOHF with the regulation of Na+/K+ homeostasis under salinity, which relates to salt resistance [20,26]. The RBOHD- and RBOHF-related ROS also enhanced the accumulation of proline, an osmolyte associated with salinity tolerance [27].
Salt stress is harmful to most plants except for some species, termed halophytes, which can grow and reproduce in high salinity environments [28]. Halophytes activate protective mechanisms to prevent high Na+ accumulation in the cytosol and to maintain photosynthesis [29,30,31]. The salt-tolerance of halophytes seems to be linked with their ability to control the redox balance [3,32,33]. The comparison of two close relatives, the glycophyte Arabidopsis thaliana and the halophyte Eutrema salsugineum, showed that the latter was capable of enhancing the production of H2O2 under control and stress conditions [34,35]. This suggests a different regulation of ROS formation in these two species. The effect of H2O2 signalling depends not only on its type but also on the site of its origin in the cell, as shown for A. thaliana [36]; therefore, precise control of ROS formation may contribute to the outcome of the plant stress responses.
The goal of this research was to investigate whether the regulation of NOX-dependent signalling under salinity differs between the glycophyte A. thaliana and the halophyte E. salsugineum. We aimed to characterise the expression patterns of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes and total NADPH oxidase activity in A. thaliana and E. salsugineum during five days of salinity treatment. To gain insight into possible hormonal regulation mechanisms of RBOHD and RBOHF, we monitored the gene expression in response to ABA and ethephon and performed an in silico search for cis-acting promoter elements.
2. Results
The E. salsugineum genome was searched using the available genome sequences of RBOHD and RBOHF in A. thaliana, and one homolog of each gene was found. The conserved domains characteristic of the RBOH family [37] were searched after aligning the amino acid sequences of RBOHD and RBOHF in E. salsugineum with the homologs in A. thaliana. The C-terminal region included the FAD-binding domain and ferric reductase NAD binding domain (Supplementary Figure S1). The N-terminal regions of the predicted EsRBOHD and EsRBOHF proteins contained the respiratory burst NADPH oxidase domain and putative Ca2+-binding EF hands.
To establish whether the RBOHD and RBOHF genes in leaves of E. salsugineum respond to short (between 6 and 48 h) and prolonged (5 days) salinity conditions, the expression patterns were examined under moderate and severe NaCl stress and compared with the response of homologous genes in A. thaliana. The first significant changes in the expression of RBOHD in E. salsugineum were detected after 24 h of salt-stress. At this time, mild salinity suppressed the accumulation of the EsRBOHD transcripts (Figure 1A). Mild and severe salt treatment downregulated the RBOHD in this halophyte after 2 days, and the suppression was stronger under 300 mM NaCl. After 5 days of salinity conditions, the expression of the RBOHD gene increased (over 2-fold) regardless of the salt concentration used. Only under severe salt stress, 600 mM NaCl, was RBOHF in E. salsugineum upregulated at 12 h (less than 2-fold) and at 24 h (less than 2.5-fold) (Figure 1B). The EsRBOHF transcript also accumulated after 5 days of salinity but at a slightly higher level in response to 600 mM NaCl conditions (over 3.5-fold increase) than to 300 mM NaCl (over 2.5-fold increase).
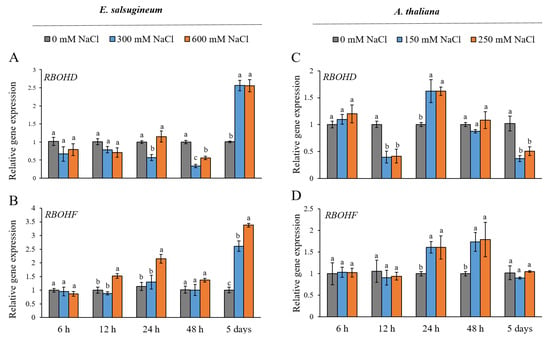
Figure 1.
Gene expression patterns of RBOHD (A,C) and RBOHF (B,D) in leaves of E. salsugineum and A. thaliana under NaCl stress conditions. E. salsugineum plants were exposed to 0, 300, or 600 mM NaCl and A. thaliana plants were exposed to 0, 150, or 250 mM NaCl for 6, 12, 24, or 48 h or 5 days. Data represent mean ± SE (n = 3). Different letters illustrate significant differences at p ≤ 0.05.
In A. thaliana, a 12-h exposure to moderate and severe salinity suppressed the expression of the AtRBOHD gene, but at 24 h, a slight upregulation was observed (less than 2-fold) (Figure 1C). After 5 days of mild and severe salt stress, the level of the RBOHD transcripts was significantly lower in relation to respective controls. Under both salinity treatments, the upregulation of AtRBOHF (less than 2-fold) was observed after 24 and 48 h (Figure 1D). The level of the AtRBOHF transcripts was not different from control samples after 5 days of salinity conditions.
Next, we aimed to verify whether changes in the transcript levels of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes in E. salsugineum and A. thaliana leaves under salinity translated to the activity of the enzymes; therefore, the total activity of NOXs in the leaf microsomal fraction was analysed. In E. salsugineum, the activity was decreased at 24 and 48 h of 300 mM NaCl conditions by 35.6 % and 11.3 %, respectively (Figure 2A). The activity of NADPH oxidase in the halophyte was not different from the control after 5 days of salinity, whereas in A. thaliana, changes in the activity of NOX were detected after 5 days of mild and severe salinity. The activity decreased by 27 % in plants treated with 150 mM NaCl and by 17.6 % in plants treated with 250 mM NaCl (Figure 2B).
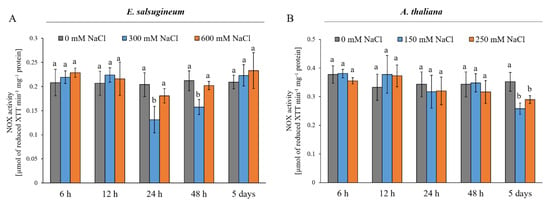
Figure 2.
Total activity of NOX in leaves of E. salsugineum (A) and A. thaliana (B) plants under NaCl stress conditions. E. salsugineum plants were exposed to 0, 300, or 600 mM NaCl and A. thaliana were exposed to 0, 150, or 250 mM NaCl for 6, 12, 24, or 48 h or 5 days. Data represent mean ± SD (n = 3). Different letters illustrate significant differences at p ≤ 0.05.
To evaluate the response of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes in E. salsugineum to exogenously applied stress hormones, the leaves were sprayed with ABA or ethephon, which quickly converts to ethylene [38]. As shown in Figure 3A, RBOHD was slightly induced by ABA after 7 h (less than 2-fold). The RBOHD transcripts were increased (less than 2-fold) at 3 and 7 h after the ethephon treatment. Both ABA and ethephon induced the expression of RBOHF by more than 2-fold at 3 h and by over 3-fold at 7 h after spraying of the leaves (Figure 3B).
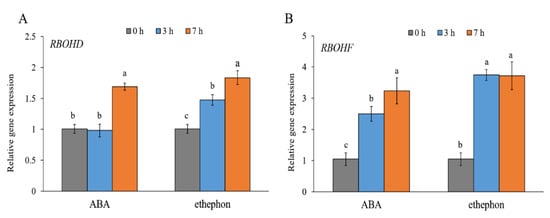
Figure 3.
Gene expression patterns of RBOHD (A) and RBOHF (B) in E. salsugineum leaves sprayed with ABA or ethephon. Data represent mean ± SE (n = 3). Different letters illustrate significant differences at p ≤ 0.05.
To gain an insight into possible transcriptional regulation of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes in A. thaliana and E. salsugineum, their promoter sequences were scanned using the PLACE database to predict possible cis-acting regulatory elements. Considering that the influence of stress-mediating hormones on the expression of the RBOH genes in plants has been reported earlier [14,39], we focused on the presence of cis-elements related to hormone signalling in 1500 bp upstream region from the transcription start site. The promoters of RBOHD and RBOHF were enriched in cis-elements responsive to salicylic acid, ethylene, cytokinins, auxins, gibberellins, and ABA (Table 1). However, the distribution of most identical sites varied between E. salsugineum and its homologs in A. thaliana. In all analysed promoters, multiple motifs involved in responses to ABA and gibberellins were localised. Conversely, only one motif was predicted for ethylene (ERELEE4) and cytokinins (CPBCSPOR) in all the promoters. The ABA responsive cis-element, LTRECOREATCOR15, was predicted only in AtRBOHD and AtRBOHF, while another ABA responsive motif, RYREPEATVFLEB4, was limited to EsRBOHF. Additionally, one auxin responsive motif, CATATGGMSAUR, was observed only in EsRBOHD.

Table 1.
Putative hormone cis-acting regulatory elements in EsRBOHD, EsRBOHF, AtRBOHD, and AtRBOHF promoters using the PLACE database.
3. Discussion
Salt-sensitive and salt-tolerant plant species use generally the same basic mechanisms of adaptation to salinity; therefore, it has been postulated that the differences in salt tolerance are most probably based on specific regulatory mechanisms [40]. As ROS signalling is a crucial component modulating stress responses in plants [3,7,41], it is reasonable to speculate that differences in the regulation of its components, such as NOXs, might influence stress tolerance. To verify this hypothesis, we compared the expression profiles of two NOX genes important in ROS signalling under salt-stress, RBOHD and RBOHF, in the halophyte E. salsugineum and the glycophyte A. thaliana. Our results showed that short-time NaCl conditions, up to 48 h, were accompanied by the increased activity of RBOHF in both species. Thus, in E. salsugineum, similar to A. thaliana, RBOHF might be involved in the early acclimation of leaves to salinity. However, in our studies, in contrast with A. thaliana, the early transcriptional changes of the RBOHF gene in E. salsugineum were dependent on NaCl concentrations since only severe salinity triggered the gene expression at 12 and 24 h of exposure to salt. A similar observation was made for the expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase genes, where high salt concentrations were required to trigger the defence mechanisms in E. salsugineum compared with A. thaliana [42]. In A. thaliana, the RBOHD and RBOHF genes were previously assigned to play a role in the primary responses to NaCl, since the stimulation of their expression was observed in seedlings within a few hours of the stress treatment [20,43]. In agreement with this view, we also detected the salinity-induced activation of AtRBOHD after 24 h of the stress treatment. Salinity conditions lasting for 5 days stimulated an expression of RBOH genes in E. salsugineum, which stood in contrast to A. thaliana. This suggests that, in the leaves of the halophyte, the RBOHD and RBOHF genes might be involved in the late acclimation response to ionic and osmotic stress.
We demonstrated that the total activity of NADPH oxidases in E. salsugineum was not affected by severe salt stress. Prolonged mild salinity also did not trigger changes in the enzyme activity despite an initial decline. It may be concluded from the activity measurements that the acclimation to salinity was associated with maintaining the basal activity of NOXs in the halophytic E. salsugineum, while the activity declined in A. thaliana. These observations are in agreement with Srivastava et al. [44] who showed that the total NADPH oxidase activity in the halophyte Sesuvium portulacastrum was unaffected, while it decreased significantly in the glycophyte Brassica juncea. The discrepancy of the EsRBOHD and EsRBOHF transcript level and enzyme activities after 5 days of salinity may result from post-transcriptional regulation of the RBOH proteins. Such a phenomenon was reported earlier for NOXs in cucumber [45]. The molecular mechanisms of NOXs activation are complex, which might explain the lack of stimulation in the in vitro activity assays. It is known that these enzymes are subjected to activation depending on Ca2+ and phosphatidic acid and are modified by various kinases [22,23,46].
The ABA and ethylene signalling pathways have been associated with the acclimation of plants to salinity [47,48]. In our studies, the EsRBOHD and EsRBOHF genes were induced by ABA and ethephon, which indicates a regulation of NOXs in E. salsugineum through the ABA- and ethylene-dependent pathways. In A. thaliana, the ABA caused a suppression of the RBOHD gene, whereas RBOHF was suppressed by ethylene [12,49]. Our observations contrast these results. These differences between species in the regulation of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes might influence their responses to the salt treatment. Earlier studies documented that the ethylene precursor was increased due to salinity in E. salsugineum and A. thaliana [35,50]. A significant increase in ABA was detected only in A. thaliana leaves as a result of exposure to salinity, while only a slight or no increase in ABA levels was observed in E. salsugineum [35,51,52].
The in silico analyses of cis-acting elements in promoters of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes in E. salsugineum and A. thaliana indicated a possible regulation by stress-related hormones (ABA, ethylene, salicylic acid, and jasmonic acid) and by growth-stimulating hormones (auxins, cytokinins, and gibberellins). It is in agreement with earlier studies, where multiple cis-acting elements related to hormonal regulation were predicted in promoters of the RBOH genes in A. thaliana and rice, including ethylene, ABA, auxins, and salicylic acid [12]. Our studies showed that the number of predicted cis-acting elements varied between the analysed homologs, which points to differences in the promoter architecture and possibly promoter activity.
4. Methods
4.1. Plant Material, Growth Conditions, and Treatments
The seeds of Eutrema salsugineum (earlier Thellungiella salsuginea) ecotype Shandong and Arabidopsis thaliana ecotype Columbia were obtained from Nottingham Arabidopsis Stock Centre (University of Nottingham, Loughborough, UK). The plants were individually grown in 100 mL pots containing market available soil (pH 5.5–6.5, NaCl < 1.9 g dm−3; Verve, Greenyard Horticulture, Pasłęk, Poland) and were irrigated with tap water (the water quality parameters are listed in Supplementary Table S1). Both species were cultivated in a growth chamber at photoperiod 10/14 h, an irradiance of about 120 μmol m−2 s−1, temperatures of 23/20 °C day/night, and 55–65% relative humidity. Plants with fully developed rosette leaves were used for salt stress and hormone treatment. The salt stress was applied by daily irrigation with 20 ml of the NaCl solution (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA). Taking into consideration different salt sensitivities of the species used in this study, the concentration of NaCl was different for E. salsugineum and A. thaliana. To induce mild stress, 300 mM NaCl was used for the former and 150 mM NaCl was used for the latter species. To induce severe salt stress, 600 mM NaCl was used for E. salsugineum and 250 mM NaCl was used for A. thaliana. Plants irrigated with 20 ml of water were treated as the control. The leaves were collected at 6, 12, 24, 48 h, and 5 days after the onset of NaCl treatment, used immediately or frozen in liquid nitrogen, and kept at −80 °C for further analysis. For spraying the leaves of E. salsugineum, 400 mM ABA (Sigma-Aldrich) [49] or 7 mM ethephon (Sigma-Aldrich) [38] dissolved in ethanol was used. Mock-treated plants were sprayed with 1 % ethanol solution. The leaves were collected 3 and 7 h after the spraying, immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and kept at −80 °C for further analysis.
4.2. Database Search and Prediction of Cis-Acting Regulatory Elements
The sequences of the EsRBOHD and EsRBOHF genes were retrieved from the Phytozome v12.1 database (http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/; accessed on 23 February 2018) after the genome of Eutrema salsugineum was searched using the Arabidopsis thaliana RBOHD (At5g47910) and RBOHF (At1g64060) sequences as queries. The Phytozome ID were Thhalv10003619m for EsRBOHD and Thhalv100023240m for EsRBOHF.
The PLACE online tool [53] was used to predict cis-acting regulatory elements in the promoter region (1500 bp upstream region from transcription start site) of RBOHD and RBOHF in A. thaliana and E. salsugineum.
4.3. Gene Expression Analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the frozen leaf tissue according to Valenzuela-Avendaño et al. [54]. RNA purity and quantity were determined by Biospec-Nano (SHIMADZU, Kyoto, Japan). The integrity of the RNA samples was assessed on a 2.0 % (w/v) agarose gel. RNA samples were treated with DNase I (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) to remove any traces of DNA. To produce a single-stranded cDNA population, 2 μg of total RNA were reversely transcribed with a RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific), using the oligo (dT)18 primer technique according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Relative quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) was performed with Maxima SYBR Green Master Mix (Thermo Fisher Scientific) using a CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection System (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Each qPCR analysis was performed for three samples of each variant and three technical replicates of each sample. The transcript levels were normalised to adenine phosphoribosyl transferase 1 (APT1) in the case of E. salsugineum and ubiquinol-cytochrome C reductase iron-sulphur subunit (AT5G) in the case of A. thaliana [21]. The gene sequences were obtained from the Phytozome database as described above. The primers used are listed in Supplementary Table S2. The probability of secondary structure folding in resulting target sequences was predicted with the M-fold webserver [55]. Reaction efficiency was tested by serial dilutions of cDNAs with gene-specific primers and the primer specificities were confirmed with the melting-curve analysis after amplification during the subsequent qPCR analysis. The expression was calculated according to Pfaffl [56], with water-treated plants serving as the calibrator.
4.4. Membrane Protein Extraction
Freshly harvested leaves were homogenised in a protein extraction buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl, 0.25 M sucrose, 2.5 mM dithiothreitol, and 0.1 mM MgCl2 under chilled conditions. The homogenate was filtered through a cheesecloth and centrifuged at 10,000× g for 15 min at 4 °C. The microsomal fraction was separated from the supernatant by centrifugation at 80,000× g for 45 min at 4 °C, according to the procedure described by Janeczko et al. [57]. The protein content was measured according to the method of Bradford [58] using BSA as a standard. All chemicals used were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich.
4.5. NADPH Oxidase (NOX) Activity
The total NOX activity was determined by measuring the reduction of 2,3-bis(2-methoxy-4-nitro-5-sulfophenyl)-2H-tetrazolium-5-carboxanilide inner salt (XTT; BioShop, Burlington, ON, Canada) by O2•− radicals at 470 nm [59,60]. The reaction mixture contained 50 mM Tris-HCl (Sigma-Aldrich) pH 7.5, 0.5 mM XTT, 0.6 mM NADPH (Sigma-Aldrich), and 5 µg of membrane proteins. The reaction was started by the addition of the NADPH solution. Measurements of absorbance changes in the presence and absence of 50 U SOD (Sigma-Aldrich) were carried out at 470 nm (for XTT ɛ = 2.16 × 104 M−1 cm−1) using an xMark™ Microplate Absorbance Spectrophotometer (Bio-Rad). Enzyme activity was defined as 1 μmol of XTT reduced by 1 mg of membrane proteins per minute.
4.6. Statistical Analysis
All data presented were expressed as mean ± standard error (SE) or standard deviation (SD). The differences between means (p ≤ 0.05) were determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Duncan test post hoc using SigmaPlot 12 (Systat Software, Inc, Palo Alto, CA, USA).
5. Conclusions
Our results suggest that the maintenance of the basal activity of NOXs in the leaves of the halophytic E. salsugineum plays a role in late acclimation responses to salt stress. The different expression patterns of the RBOHD and RBOHF genes under salinity in E. salsugineum and A. thaliana point to a modified regulation of these genes in the halophytic E. salsugineum, possibly through the ABA- and/or ethylene-dependent pathways.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/ijms221910341/s1, Figure S1: The multiple alignment of RBOHD and RBOHF amino acids in Arabidopsis thaliana and Eutrema salsugineum constructed using the EMBL-EBI Clustal OMEGA tool (www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/; accessed on 20 March 2020). Table S1: Selected parameters of tap water used for irrigation according to the information provided by the Kraków waterworks. Table S2: PCR primers used for quantitative RT-PCR.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, funding acquisition, investigation, formal analysis, data curation, visualisation, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing, M.P.; conceptualisation, and writing—review and editing, D.B.; writing—review and editing, E.N. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
MP acknowledges a fellowship from the Polish National Science Centre (MINIATURA, Project No. 2017/01/X/NZ3/00293), which supported her research stay at the Institute of Molecular Physiology and Biotechnology of Plants (IMBIO), University of Bonn, Germany.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data of this article are available within the manuscript and its Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
References
- Pan, T.; Liu, M.; Kreslavski, V.D.; Zharmukhamedov, S.K.; Nie, C.; Yu, M.; Kuznetsov, V.V.; Allakhverdiev, S.I.; Shabala, S. Non-stomatal limitation of photosynthesis by soil salinity. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 51, 791–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhang, H.; Song, C.; Zhu, J.K.; Shabala, S. Mechanisms of plant responses and adaptation to soil salinity. Innovation 2020, 1, 100017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, J.; Rodrigo-Moreno, A.; Shabala, S. ROS homeostasis in halophytes in the context of salinity stress tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 1241–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Khare, T.; Sharma, M.; Wani, S.H. ROS-induced signaling and gene expression in crops under salinity stress. In Reactive Oxygen Species and Antioxidant Systems in Plants: Role and Regulation under Abiotic Stress; Khan, M.I.R., Khan, N.A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2017; pp. 159–184. [Google Scholar]
- Møller, I.M.; Jensen, P.E.; Hansson, A. Oxidative modifications to cellular components in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2007, 58, 459–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foyer, C.H.; Ruban, A.V.; Noctor, G. Viewing oxidative stress through the lens of oxidative signaling rather than damage. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 877–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Czarnocka, W.; Karpiński, S. Friend or foe? Reactive oxygen species production, scavenging and signaling in plant response to environmental stresses. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2018, 122, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fichman, Y.; Mittler, R. Rapid systemic signaling during abiotic and biotic stresses: Is the ROS wave master of all trades? Plant J. 2020, 102, 887–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, G.; Guruprasad, K.; Temple, B.R.; Shirvanyants, D.G.; Dokholyan, N.V.; Pati, P.K. Structural complexity and functional diversity of plant NADPH oxidases. Amino Acids. 2018, 50, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, N.; Miller, G.; Morales, J.; Shulaev, V.; Torres, M.A.; Mittler, R. Respiratory burst oxidases: The engines of ROS signaling. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2011, 14, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagi, M.; Fluhr, R. Production of reactive oxygen species by plant NADPH oxidases. Plant Physiol. 2006, 141, 336–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaur, G.; Pati, P.K. Analysis of cis-acting regulatory elements of respiratory burst oxidase homolog (Rboh) gene families in Arabidopsis and rice provides clues for their diverse functions. Comput Biol. Chem. 2016, 62, 104–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Carstens, A.C.; Linkies, A.; Torres, M.A.; Leubner-Metzger, G. The NADPH-oxidase AtrbohB plays a role in Arabidopsis seed after-ripening. New Phytol. 2009, 184, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kwak, J.M.; Mori, I.C.; Pei, Z.M.; Leonhardt, N.; Torres, M.A.; Dangl, J.L.; Bloom, R.E.; Bodde, S.; Jones, J.D.; Schroeder, J.I. NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF genes function in ROS-dependent ABA signaling in Arabidopsis. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 2623–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monshausen, G.B.; Bibikova, T.N.; Messerli, M.A.; Shi, C.; Gilroy, S. Oscillations in extracellular pH and reactive oxygen species modulate tip growth of Arabidopsis root hairs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 20996–21001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Potocký, M.; Jones, M.A.; Bezvoda, R.; Smirnoff, N.; Žárský, V. Reactive oxygen species produced by NADPH oxidase are involved in pollen tube growth. New Phytol. 2007, 174, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkindale, J.; Hall, J.D.; Knight, M.R.; Vierling, E. Heat stress phenotypes of Arabidopsis mutants implicate multiple signaling pathways in the acquisition of thermotolerance. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 882–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, G.; Schlauch, K.; Tam, R.; Cortes, D.; Torres, M.A.; Shulaev, V.; Dangl, J.L.; Mittler, R. The plant NADPH oxidase RbohD mediates rapid systemic signaling in response to diverse stimuli. Sci. Signal. 2009, 2, ra45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, M.M.; Wang, Y.J.; Gao, Y.T.; Li, R.; Wang, G.F.; Li, V.Q.; Liu, W.T.; Chen, K.M. The plasma membrane NADPH oxidase OsRbohA plays a crucial role in developmental regulation and drought-stress response in rice. Physiol. Plant. 2016, 156, 421–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Zhang, H.; Sun, L.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, G.; Miao, C.; Hao, F. NADPH oxidase AtrbohD and AtrbohF function in ROS dependent regulation of Na+/K+ homeostasis in Arabidopsis under salt stress. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 305–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejeb, K.B.; Benzarti, M.; Debez, A.; Bailly, C.; Savouré, A.; Abdelly, C. NADPH oxidase-dependent H2O2 production is required for salt-induced antioxidant defense in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Plant Physiol. 2015, 174, 5–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogasawara, Y.; Kaya, H.; Hiraoka, G.; Yumoto, F.; Kimura, S.; Kadota, Y.; Hishinuma, H.; Senzaki, E.; Yamagoe, S.; Nagata, K.; et al. Synergistic activation of the Arabidopsis NADPH oxidase AtrbohD by Ca2+ and phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 8885–8892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Li, M.; Yu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Liang, X.; Liu, Z.; Cai, G.; Gao, L.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; et al. The FLS2-associated kinase BIK1 directly phosphorylates the NADPH oxidase RbohD to control plant immunity. Cell Host Microbe. 2014, 15, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Tan, J.; Guo, Z.; Lu, S.; He, S.; Shu, W.; Zhou, B. Increased abscisic acid levels in transgenic tobacco over-expressing 9 cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase influence H2O2 and NO production and antioxidant defences. Plant Cell Environ. 2009, 32, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; Choi, W.G.; Gilroy, S.; Morris, R.J. A ROS-assisted calcium wave dependent on the AtRBOHD NADPH oxidase and TPC1 cation channel propagates the systemic response to salt stress. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 1771–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.S.; Zhu, J.K.; Bressan, R.A.; Hasegawa, P.M.; Shi, H. Reactive oxygen species mediate Na+-induced SOS1 mRNA stability in Arabidopsis. Plant J. 2008, 53, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ben Rejeb, K.B.; Vos, D.L.; Disquet, I.L.; Leprince, A.; Bordenave, M.; Maldiney, R.; Jdey, A.; Abdelly, C.; Savouré, A. Hydrogen peroxide produced by NADPH oxidases increases proline accumulation during salt or mannitol stress in Arabidopsis thaliana. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Grigore, M.N. Defining halophytes: A conceptual and historical approach in an ecological frame. In Halophytes and Climate Change: Adaptive Mechanisms and Potential Uses; Hasanuzzaman, M., Shabala, S., Fujita, M., Eds.; CABI: Boston, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 3–18. [Google Scholar]
- Niewiadomska, E.; Wiciarz, M. Adaptations of chloroplastic metabolism in halophytic plants. In Progress in Botany; Lüttge, U., Beyschlag, W., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 177–193. [Google Scholar]
- Bose, J.; Munns, R.; Shabala, S.; Gilliham, M.; Pogson, B.; Tyerman, S.D. Chloroplast function and ion regulation in plants growing on saline soils: Lessons from halophytes. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 3129–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazachkova, Y.; Eshel, G.; Pantha, P.; Cheeseman, J.M.; Dassanayake, M.; Barak, S. Halophytism: What have we learnt from Arabidopsis thaliana relative model systems? Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 972–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozgur, R.; Uzilday, B.; Sekmen, A.H.; Turkan, I. Reactive oxygen species regulation and antioxidant defence in halophytes. Funct. Plant Biol. 2013, 40, 832–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surówka, E.; Latowski, D.; Libik-Konieczny, M.; Miszalski, Z. ROS Signalling, and Antioxidant Defence Network in Halophytes. In Halophytes and Climate Change: Adaptive Mechanisms and Potential Uses; Hasanuzzaman, M., Shabala, S., Fujita, M., Eds.; CABI: Boston, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 179–195. [Google Scholar]
- Wiciarz, M.; Gubernator, B.; Kruk, J.; Niewiadomska, E. Enhanced chloroplastic generation of H2O2 in stress-resistant Thellungiella salsuginea in comparison to Arabidopsis thaliana. Physiol. Plant. 2015, 153, 467–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pilarska, M.; Wiciarz, M.; Jajić, I.; Kozieradzka-Kiszkurno, M.; Dobrev, P.; Vanková, R.; Niewiadomska, E. A different pattern of production and scavenging of reactive oxygen species in halophytic Eutrema salsugineum (Thellungiella salsuginea) plants in comparison to Arabidopsis thaliana and its relation to salt stress signaling. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sewelam, N.; Jaspert, N.; Van Der Kelen, K.; Tognetti, V.B.; Schmitz, J.; Frerigmann, H.; Stahl, E.; Zeier, J.; Van Breusegem, F.; Maurino, V.G. Spatial H2O2 signaling specificity: H2O2 from chloroplasts and peroxisomes modulates the plant transcriptome differentially. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1191–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Torres, M.A.; Onouchi, H.; Hamada, S.; Machida, C.; Hammond-Kosack, K.E.; Jones, J.D. Six Arabidopsis thaliana homologues of the human respiratory burst oxidase (gp91phox). Plant J. 1998, 14, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wen, C.K. Preparation of ethylene gas and comparison of ethylene responses induced by ethylene, ACC, and ethephon. Plant Physiol. Bioch. 2010, 48, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Xu, X.; Gao, M.; Li, J.; Guo, C.; Song, J.; Wang, X. Genome-wide analysis of respiratory burst oxidase homologs in grape (Vitis vinifera L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 24169–24186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.-K. Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Rahman, A.; Skalicky, M.; Alabdallah, N.; Waseem, M.; Jahan, M.; Ahammed, G.; El-Mogy, M.; El-Yazied, A.; Ibrahim, M.; et al. Ozone Induced Stomatal Regulations, MAPK and Phytohormone Signaling in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Bartels, D. Comparative study of the aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) gene superfamily in the glycophyte Arabidopsis thaliana and Eutrema halophytes. Ann. Bot. 2014, 115, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xie, Y.J.; Xu, S.; Han, B.; Wu, M.Z.; Yuan, X.X.; Han, Y.; Gu, Q.; Xu, D.K.; Yang, Q.; Shen, W.B. Evidence of Arabidopsis salt acclimation induced by up-regulation of HY1 and the regulatory role of RbohD-derived reactive oxygen species synthesis. Plant J. 2011, 66, 280–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.K.; Srivastava, S.; Lokhande, V.H.; D’souza, S.F.; Suprasanna, P. Salt stress reveales differential antioxidant and energetics responses in, glycophyte (Brassica juncea L.) and halophyte (Sesuvium portulacastrum L.). Front. Environ. Sci. 2015, 3, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jakubowska, D.; Janicka-Russak, M.; Kabała, K.; Migocka, M.; Reda, M. Modification of plasma membrane NADPH oxidase activity in cucumber seedling roots in response to cadmium stress. Plant Sci. 2015, 234, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.; Yan, M.; Wang, R.; Wang, L.; Welti, R.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X. Phospholipase Da1 and phosphatidic acid regulate NADPH oxidase activity and production of reactive oxygen species in ABA-mediated stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 2357–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Smith, J.A.C.; Harberd, N.P.; Jiang, C. The regulatory roles of ethylene and reactive oxygen species (ROS) in plant salt stress responses. Plant Mol. Biol. 2016, 91, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Duan, X.; Luo, L.; Dai, S.; Ding, Z.; Xia, G. How plant hormones mediate salt stress responses. Trends Plant Sci. 2020, 25, 1117–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sewelam, N.; Kazan, K.; Thomas-Hall, S.R.; Kidd, B.N.; Manners, J.M.; Schenk, P.M. Ethylene response factor 6 is a regulator of reactive oxygen species signaling in Arabidopsis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellouzi, H.; Ben Hamed, K.; Hernández, I.; Cela, J.; Müller, M.; Magné, C.; Abdelly, C.; Munné-Bosch, S. A comparative study of the early osmotic, ionic, redox and hormonal signaling response in leaves and roots of two halophytes and a glycophyte to salinity. Planta 2014, 240, 1299–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbona, V.; Argamasilla, R.; Gómez-Cadenas, A. Common and divergent physiological, hormonal and metabolic responses of Arabidopsis thaliana and Thellungiella halophila to water and salt stress. J. Plant. Physiol. 2010, 167, 1342–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prerostova, S.; Dobrev, P.I.; Gaudinova, A.; Hosek, P.; Soudek, P.; Knirsch, V.; Vankova, R. Hormonal dynamics during salt stress responses of salt-sensitive Arabidopsis thaliana and salt-tolerant Thellungiella salsuginea. Plant Sci. 2017, 264, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higo, K.; Ugawa, Y.; Iwamoto, M.; Korenaga, T. Plant cis-acting regulatory DNA elements (PLACE) database: 1999. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Valenzuela-Avendaño, J.; Mota, I.E.; Uc, G.; Perera, R.; Valenzuela-Soto, E.; Aguilar, J.Z. Use of a simple method to isolate intact RNA from partially hydrated Selaginella lepidophylla plants. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2005, 23, 199–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuker, M. Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfaffl, M.W. A new mathematical model for relative quantification in real-time RT–PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, e45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeczko, A.; Budziszewska, B.; Skoczowski, A.; Dybała, M. Specific binding sites for progesterone and 17ß-estradiol in cells of Triticum aestivum L. Acta Biochem. Pol. 2008, 55, 708–711. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of proteindye- binding. Anal. Biochem. 1975, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Able, A.; Guest, D.; Sutherland, M. Use of a new tetrazolium-based assay to study the production of superoxide radicals by tobacco cell cultures challenged with avirulent zoospores of Phytophthora parasitica var nicotianae. Plant Physiol. 1998, 117, 491–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Potocký, M.; Pejchar, P.; Gutkowska, M.; Jiménez-Quesada, M.J.; Potocká, A.; de Dios, A.J.; Kost, B.; Žárský, V. NADPH oxidase activity in pollen tubes is affected by calcium ions, signaling phospholipids and Rac/Rop GTPases. J. Plant Physiol. 2012, 169, 1654–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).