Sex-Specific Differences in Lysine, 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Acetic Acid in Offspring Exposed to Maternal and Postnatal High Linoleic Acid Diet, Independent of Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
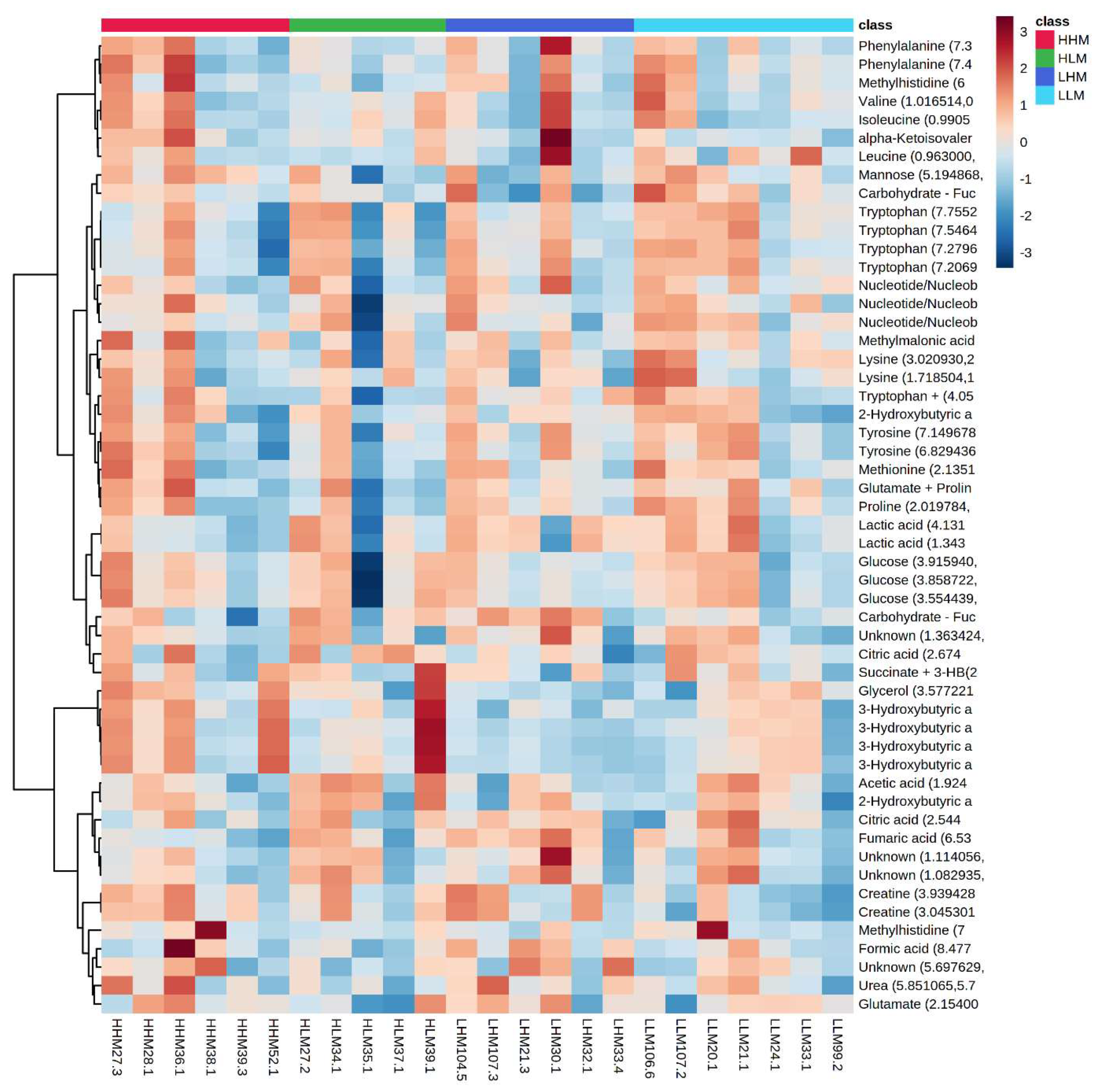
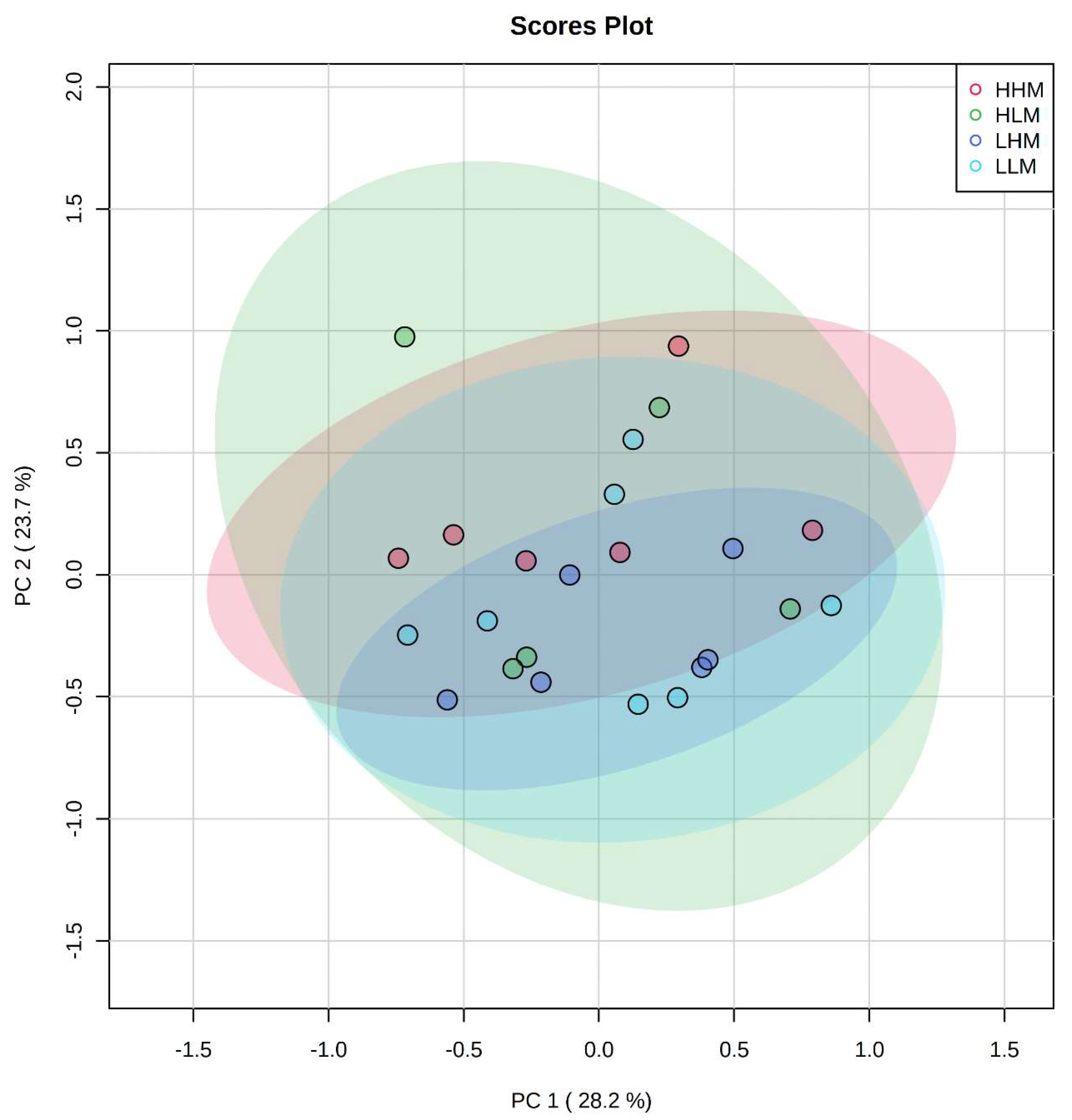
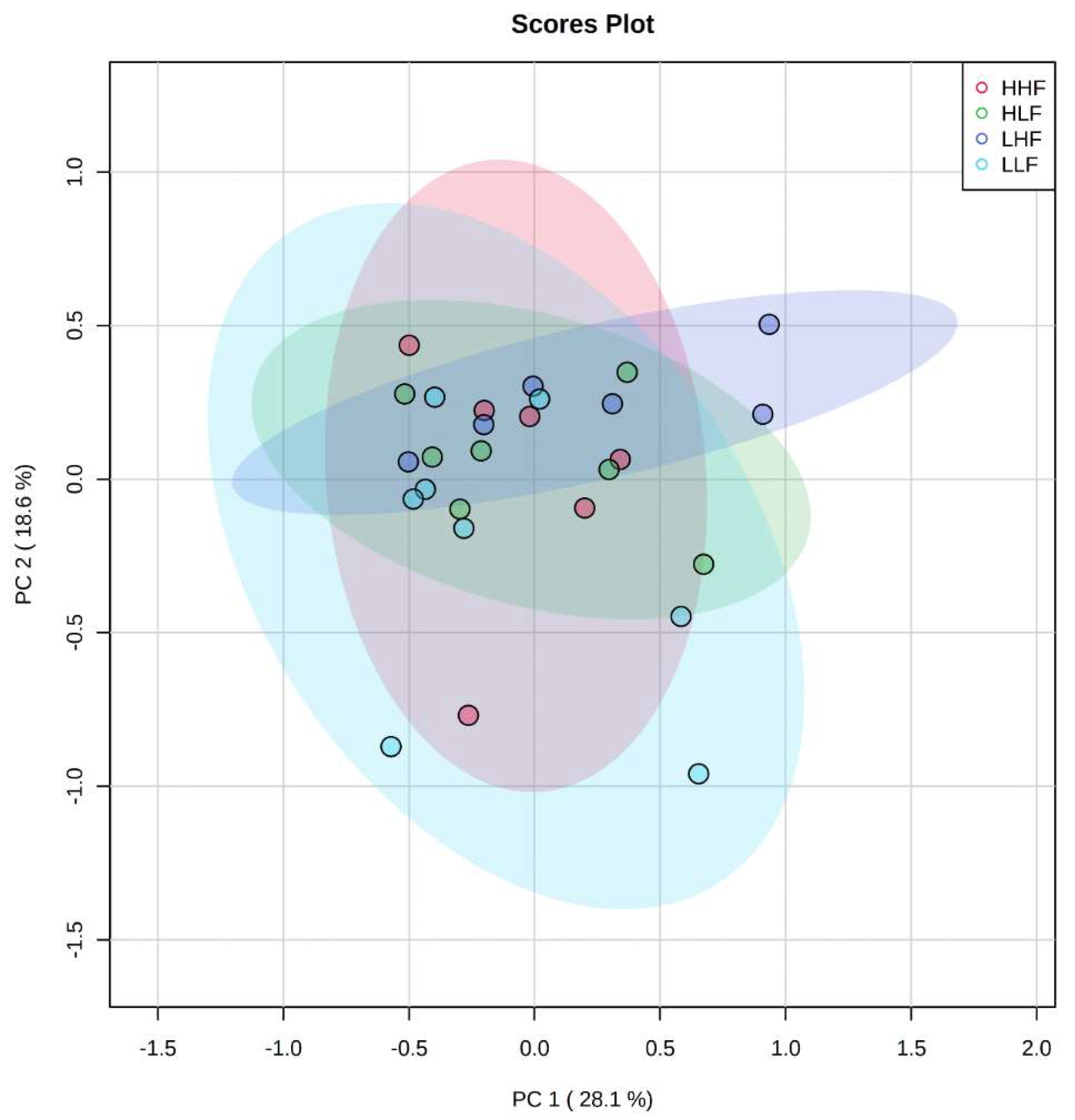
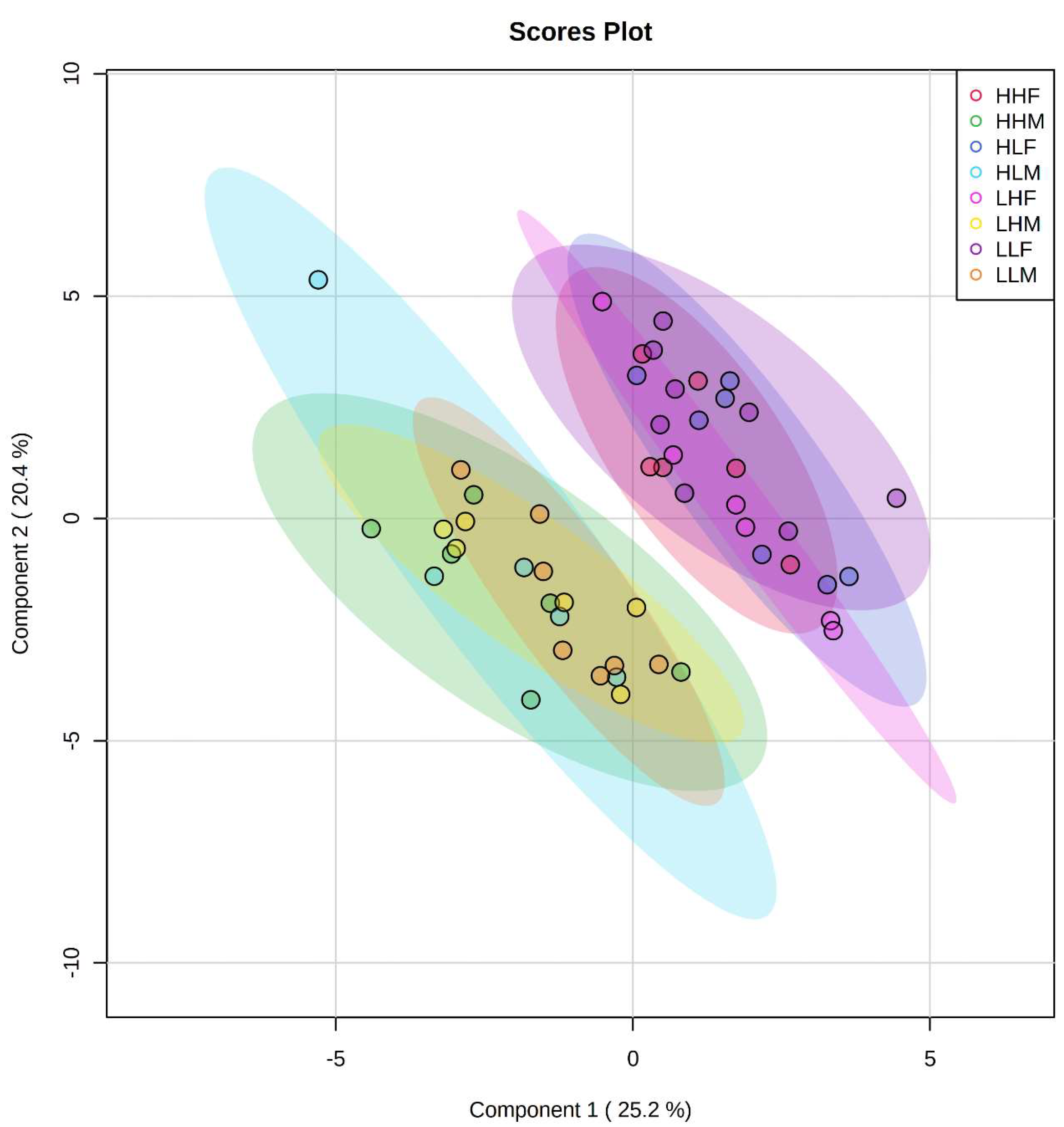
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Maternal and Postnatal High Linoleic Acid Diet on Plasma Metabolites in Adult Offspring
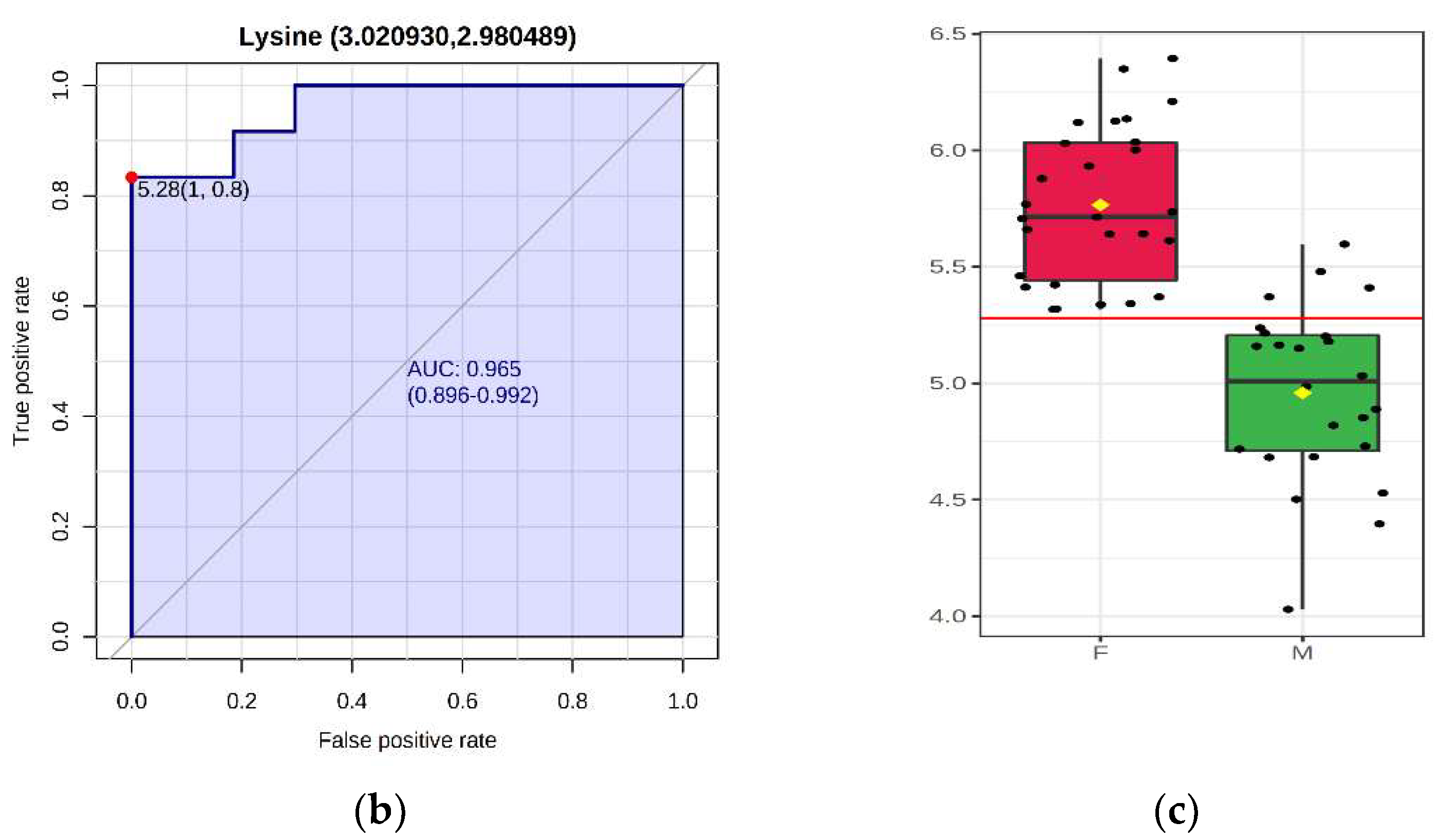
2.2. Clustering among Male and Female Offspring
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animal Model and Diet
4.2. Sample Analysis
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, G.; Bazer, F.W.; Cudd, T.A.; Meininger, C.J.; Spencer, T.E. Maternal nutrition and fetal development. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 2169–2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correia-Branco, A.; Keating, E.; Martel, F. Maternal undernutrition and fetal developmental programming of obesity: The glucocorticoid connection. Reprod. Sci. 2015, 22, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Xiao, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, M.; Zheng, J.; Deng, M. Maternal Exercise Improves High-Fat Diet-Induced Metabolic Abnormalities and Gut Microbiota Profiles in Mouse Dams and Offspring. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.L.; Nakamura, M.T.; Ma, D.W.L. Differentiating the biological effects of linoleic acid from arachidonic acid in health and disease. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2018, 135, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simopoulos, A.P. The importance of the omega-6/omega-3 fatty acid ratio in cardiovascular disease and other chronic diseases. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, S.S.; Mathai, M.L.; Hryciw, D.H.; McAinch, A.J. Linoleic acid and the pathogenesis of obesity. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2016, 125, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naughton, S.S.; Mathai, M.L.; Hryciw, D.H.; McAinch, A.J. Australia’s nutrition transition 1961–2009: A focus on fats. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsden, C.E.; Ringel, A.; Feldstein, A.E.; Taha, A.Y.; MacIntosh, B.A.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Majchrzak-Hong, S.F.; Faurot, K.; Rapoport, S.I.; Cheon, Y.; et al. Lowering dietary linoleic acid reduces bioactive oxidized linoleic acid metabolites in humans. Prostaglandins Leukot. Essent. Fat. Acids 2012, 87, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alvheim, A.R.; Torstensen, B.E.; Lin, Y.H.; Lillefosse, H.H.; Lock, E.-J.; Madsen, L.; Frøyland, L.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Malde, M.K. Dietary linoleic acid elevates the endocannabinoids 2-AG and anandamide and promotes weight gain in mice fed a low fat diet. Lipids 2014, 49, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S.; O’Connell, J.F.; Carlson, O.D.; González-Mariscal, I.; Kim, Y.; Moaddel, R.; Ghosh, P.; Egan, J.M. Linoleic acid in diets of mice increases total endocannabinoid levels in bowel and liver: Modification by dietary glucose. Obes. Sci. Pract. 2019, 5, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodrigues, H.G.; Vinolo, M.A.; Magdalon, J.; Fujiwara, H.; Cavalcanti, D.M.H.; Farsky, S.H.P.; Calder, P.; Hatanaka, E.; Curi, R. Dietary free oleic and linoleic acid enhances neutrophil function and modulates the inflammatory response in rats. Lipids 2010, 45, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsden, C.E.; Zamora, D.; Majchrzak-Hong, S.; Faurot, K.; Broste, S.K.; Frantz, R.; Davis, J.M.; Ringel, A.; Suchindran, C.M.; Hibbeln, J.R. Re-evaluation of the traditional diet-heart hypothesis: Analysis of recovered data from Minnesota Coronary Experiment (1968–1973). BMJ 2016, 353, i1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramsden, C.E.; Zamora, D.; Leelarthaepin, B.; Majchrzak-Hong, S.F.; Faurot, K.; Suchindran, C.M.; Ringel, A.; Davis, J.M.; Hibbeln, J.R. Use of dietary linoleic acid for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease and death: Evaluation of recovered data from the Sydney Diet Heart Study and updated meta-analysis. BMJ 2013, 346, e8707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, N.; Sleep, S.; Helman, T.; Holland, O.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Perkins, A.V.; McAinch, A.J.; Headrick, J.P.; Hryciw, D.H. Maternal diet high in linoleic acid alters offspring fatty acids and cardiovascular function in a rat model. Br. J. Nutr. 2021, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, N.; Vidimce, J.; Holland, O.; Cuffe, J.; Beck, B.; Perkins, A.; McAinch, A.; Hryciw, D. Maternal and Postnatal High Linoleic Acid Diet Impacts Lipid Metabolism in Adult Rat Offspring in a Sex-Specific Manner. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newgard, C.B. Metabolomics and Metabolic Diseases: Where Do We Stand? Cell Metab. 2017, 25, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ott, R.; Pawlow, X.; Weiß, A.; Hofelich, A.; Herbst, M.; Hummel, N.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Römisch-Margl, W.; Kastenmüller, G.; et al. Intergenerational Metabolomic Analysis of Mothers with a History of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Their Offspring. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gall, W.E.; Beebe, K.; Lawton, K.A.; Adam, K.-P.; Mitchell, M.; Nakhle, P.J.; Ryals, J.A.; Milburn, M.V.; Nannipieri, M.; Camastra, S.; et al. alpha-hydroxybutyrate is an early biomarker of insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in a nondiabetic population. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobb, J.; Eckhart, A.; Motsinger-Reif, A.; Carr, B.; Groop, L.; Ferrannini, E. α-Hydroxybutyric Acid Is a Selective Metabolite Biomarker of Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 988–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hellmuth, C.; Uhl, O.; Kirchberg, F.F.; Harder, U.; Peissner, W.; Koletzko, B.; Nathanielsz, P. Influence of moderate maternal nutrition restriction on the fetal baboon metabolome at 0.5 and 0.9 gestation. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2016, 26, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lowe, W.L., Jr.; Bain, J.R.; Nodzenski, M.; Reisetter, A.C.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Ilkayeva, O.R.; Lowe, L.P.; Metzger, B.E.; Newgard, C.B.; et al. Maternal BMI and Glycemia Impact the Fetal Metabolome. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bellissimo, M.P.; Ziegler, T.R.; Jones, D.P.; Liu, K.H.; Fernandes, J.; Roberts, J.L.; Weitzmann, M.N.; Pacifici, R.; Alvarez, J.A. Plasma high-resolution metabolomics identifies linoleic acid and linked metabolic pathways associated with bone mineral density. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senizza, A.; Rocchetti, G.; Callegari, M.L.; Lucini, L.; Morelli, L. Linoleic acid induces metabolic stress in the intestinal microorganism Bifidobacterium breve DSM 20213. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fotiou, M.; Michaelidou, A.M.; Athanasiadis, A.P.; Menexes, G.; Symeonidou, M.; Koulourida, V.; Ganidou, M.; Theodoridis, T.D.; Tarlatzis, B.C. Second trimester amniotic fluid glucose, uric acid, phosphate, potassium, and sodium concentrations in relation to maternal pre-pregnancy BMI and birth weight centiles. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal. Med. 2015, 28, 910–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graça, G.; Duarte, I.; Barros, A.; Goodfellow, B.; Diaz, S.D.O.; Carreira, I.M.; Couceiro, A.B.; Galhano, E.; Gil, A. (1)H NMR based metabonomics of human amniotic fluid for the metabolic characterization of fetus malformations. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 4144–4150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwong, W.Y.; Wild, A.E.; Roberts, P.; Willis, A.C.; Fleming, T.P. Maternal undernutrition during the preimplantation period of rat development causes blastocyst abnormalities and programming of postnatal hypertension. Development 2000, 127, 4195–4202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, L.L.; Ingelfinger, J.R.; Rasch, R. Modest maternal protein restriction fails to program adult hypertension in female rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 289, R1131–R1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Campesi, I.; Franconi, F.; Seghieri, G.; Meloni, M. Sex-gender-related therapeutic approaches for cardiovascular complications associated with diabetes. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 119, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoppolo, M.; Caterino, M.; Albano, L.; Pecce, R.; Di Girolamo, M.G.; Crisci, D.; Costanzo, M.; Milella, L.; Franconi, F.; Campesi, I. Targeted metabolomic profiling in rat tissues reveals sex differences. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnerie, S.; Comte, B.; Ziegler, D.; Morais, J.A.; Pujos-Guillot, E.; Gaudreau, P. Metabolomic and Lipidomic Signatures of Metabolic Syndrome and its Physiological Components in Adults: A Systematic Review. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, S.; Sadanala, K.C.; Kim, E.K. A Metabolomic Approach to Understanding the Metabolic Link between Obesity and Diabetes. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandre-Gouabau, M.-C.; Courant, F.; Le Gall, G.; Moyon, T.; Darmaun, D.; Parnet, P.; Coupé, B.; Antignac, J.-P. Offspring metabolomic response to maternal protein restriction in a rat model of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR). J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3292–3302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeating, D.R.; Clifton, V.L.; Hurst, C.P.; Fisher, J.J.; Bennett, W.W.; Perkins, A.V. Elemental Metabolomics for Prediction of Term Gestational Outcomes Utilising 18-Week Maternal Plasma and Urine Samples. Biol. Trace. Elem. Res. 2021, 199, 26–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertram, C.E.; Hanson, M.A. Animal models and programming of the metabolic syndrome. Br. Med. Bull. 2001, 60, 103–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Darst, B.F.; Koscik, R.L.; Hogan, K.J.; Johnson, S.C.; Engelman, C.D. Longitudinal plasma metabolomics of aging and sex. Aging 2019, 11, 1262–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.J.; Batch, B.C.; Svetkey, L.P.; Bain, J.R.; Turer, C.B.; Haynes, C.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Stevens, R.D.; Newgard, C.B.; Shah, S.H. Race and sex differences in small-molecule metabolites and metabolic hormones in overweight and obese adults. Omics 2013, 17, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- O’Doherty, P.J.; Lyons, V.; Tun, N.M.; Rogers, P.J.; Bailey, T.D.; Wu, M.J. Transcriptomic and biochemical evidence for the role of lysine biosynthesis against linoleic acid hydroperoxide-induced stress in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Free Radic. Res. 2014, 48, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.E.; Hennebelle, M.; Schuster, S.; Keyes, G.S.; Johnson, C.D.; Kirpich, I.A.; Dahlen, J.E.; Horowitz, M.S.; Zamora, D.; Feldstein, A.E.; et al. Effects of diets enriched in linoleic acid and its peroxidation products on brain fatty acids, oxylipins, and aldehydes in mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 2018, 1863, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, S.L.; Fausto, A.; Jänne, O.A.; Avioli, L.V. Regulation of ornithine decarboxylase by parathyroid hormone in osteoblastic cell systems. Calcif. Tissue Int. 1992, 51, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miggiels, P.; Wouters, B.; van Westen, G.; Dubbelman, A.-C.; Hankemeier, T. Novel technologies for metabolomics: More for less. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 120, 115323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadórniga-Valiño, C.; Grummer, R.R.; Armentano, L.E.; Donkin, S.S.; Bertics, S.J. Effects of fatty acids and hormones on fatty acid metabolism and gluconeogenesis in bovine hepatocytes. J. Dairy Sci. 1997, 80, 646–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Depczynski, B.; Lee, A.T.K.; Varndell, W.; Chiew, A.L. The Significance of an Increased Beta-Hydroxybutyrate at Presentation to the Emergency Department in Patients with Diabetes in the Absence of a Hyperglycemic Emergency. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 7387128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Halkes, C.; van Dijk, H.; Verseyden, C.; de Jaegere, P.; Plokker, H.; Meijssen, S.; Erkelens, D.; Cabezas, M.C. Gender differences in postprandial ketone bodies in normolipidemic subjects and in untreated patients with familial combined hyperlipidemia. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 1875–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, N.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Holland, O.; Bulmer, A.C.; Hill, M.; Perkins, A.V.; Muhlhausler, B.S.; McAinch, A.J.; Hryciw, D.H. Elevated maternal linoleic acid reduces circulating leptin concentrations, cholesterol levels and male fetal survival in a rat model. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 3349–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melvin, S.D.; Lanctôt, C.M.; Doriean, N.J.C.; Carroll, A.R.; Bennett, W.W. Untargeted NMR-based metabolomics for field-scale monitoring: Temporal reproducibility and biomarker discovery in mosquitofish (Gambusia holbrooki) from a metal(loid)-contaminated wetland. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melvin, S.D.; Leusch, F.D.L.; Carroll, A.R. Metabolite profiles of striped marsh frog (Limnodynastes peronii) larvae exposed to the anti-androgenic fungicides vinclozolin and propiconazole are consistent with altered steroidogenesis and oxidative stress. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 199, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melvin, S.D.; Lanctôt, C.M.; Doriean, N.J.C.; Bennett, W.W.; Carroll, A.R. NMR-based lipidomics of fish from a metal(loid) contaminated wetland show differences consistent with effects on cellular membranes and energy storage. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 654, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Vosegaard, T.; Guo, Z. Applications of nuclear magnetic resonance in lipid analyses: An emerging powerful tool for lipidomics studies. Prog. Lipid Res. 2017, 68, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mika, A.; Kaczyński, Z.; Stepnowski, P.; Kaczor, M.; Proczko-Stepaniak, M.; Kaska, L.; Sledzinski, T. Potential Application of (1)H NMR for Routine Serum Lipidome Analysis -Evaluation of Effects of Bariatric Surgery. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, Z.; Chong, J.; Zhou, G.; Morais, D.A.D.L.; Chang, L.; Barrette, M.; Gauthier, C.; Jacques, P.; Li, S.; Xia, J. MetaboAnalyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W388–W396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shrestha, N.; Melvin, S.D.; McKeating, D.R.; Holland, O.J.; Cuffe, J.S.M.; Perkins, A.V.; McAinch, A.J.; Hryciw, D.H. Sex-Specific Differences in Lysine, 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Acetic Acid in Offspring Exposed to Maternal and Postnatal High Linoleic Acid Diet, Independent of Diet. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910223
Shrestha N, Melvin SD, McKeating DR, Holland OJ, Cuffe JSM, Perkins AV, McAinch AJ, Hryciw DH. Sex-Specific Differences in Lysine, 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Acetic Acid in Offspring Exposed to Maternal and Postnatal High Linoleic Acid Diet, Independent of Diet. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(19):10223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910223
Chicago/Turabian StyleShrestha, Nirajan, Steven D Melvin, Daniel R. McKeating, Olivia J. Holland, James S. M. Cuffe, Anthony V. Perkins, Andrew J. McAinch, and Deanne H. Hryciw. 2021. "Sex-Specific Differences in Lysine, 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Acetic Acid in Offspring Exposed to Maternal and Postnatal High Linoleic Acid Diet, Independent of Diet" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 19: 10223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910223
APA StyleShrestha, N., Melvin, S. D., McKeating, D. R., Holland, O. J., Cuffe, J. S. M., Perkins, A. V., McAinch, A. J., & Hryciw, D. H. (2021). Sex-Specific Differences in Lysine, 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid and Acetic Acid in Offspring Exposed to Maternal and Postnatal High Linoleic Acid Diet, Independent of Diet. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(19), 10223. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910223








