Characterization of Glycosphingolipids in the Human Parathyroid and Thyroid Glands
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation of Glycosphingolipids from Human Parathyroid and Thyroid Glands
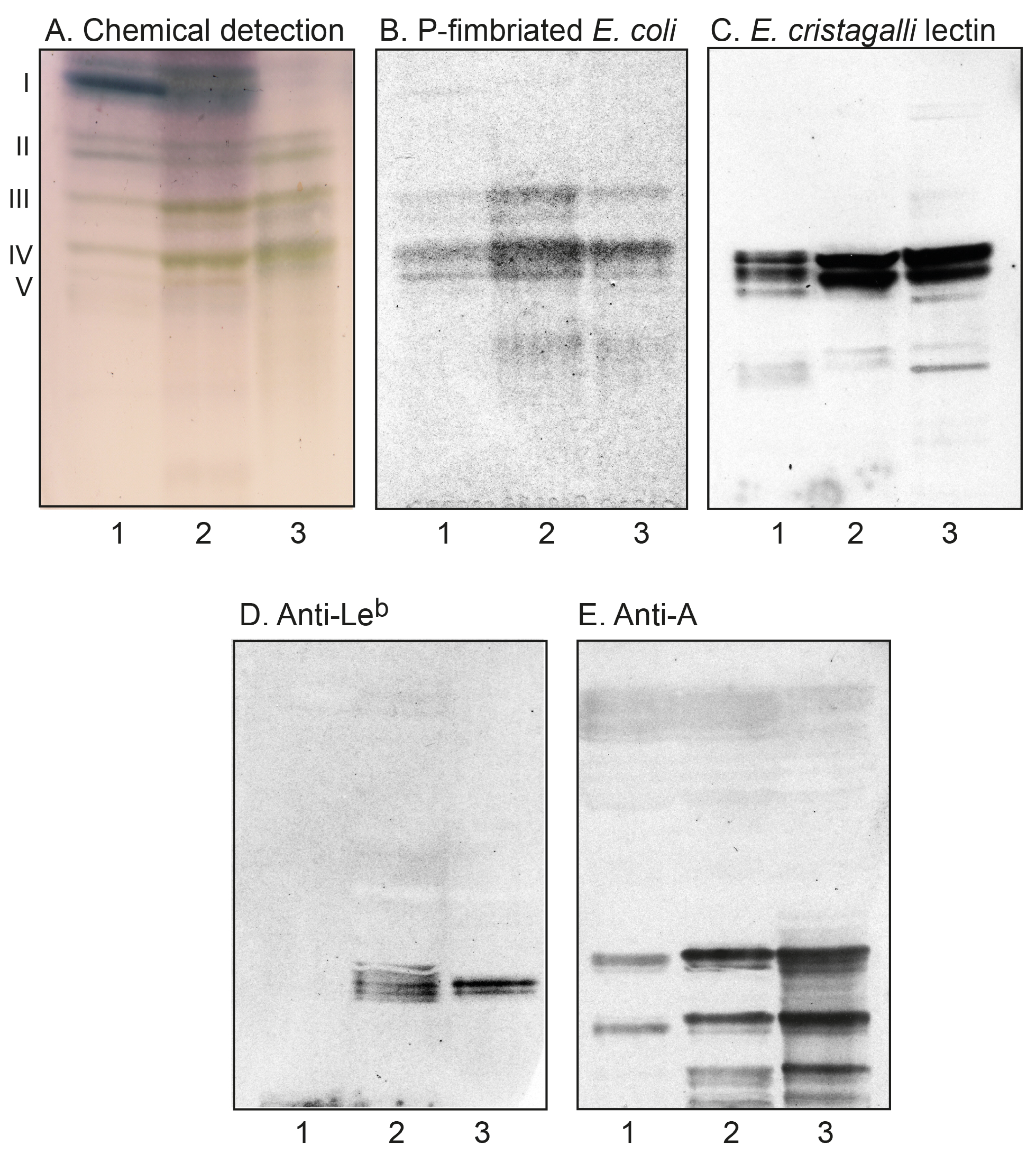
2.2. Characterization of the Non-Acid Glycosphingolipids from Human Parathyroid and Thyroid Glands
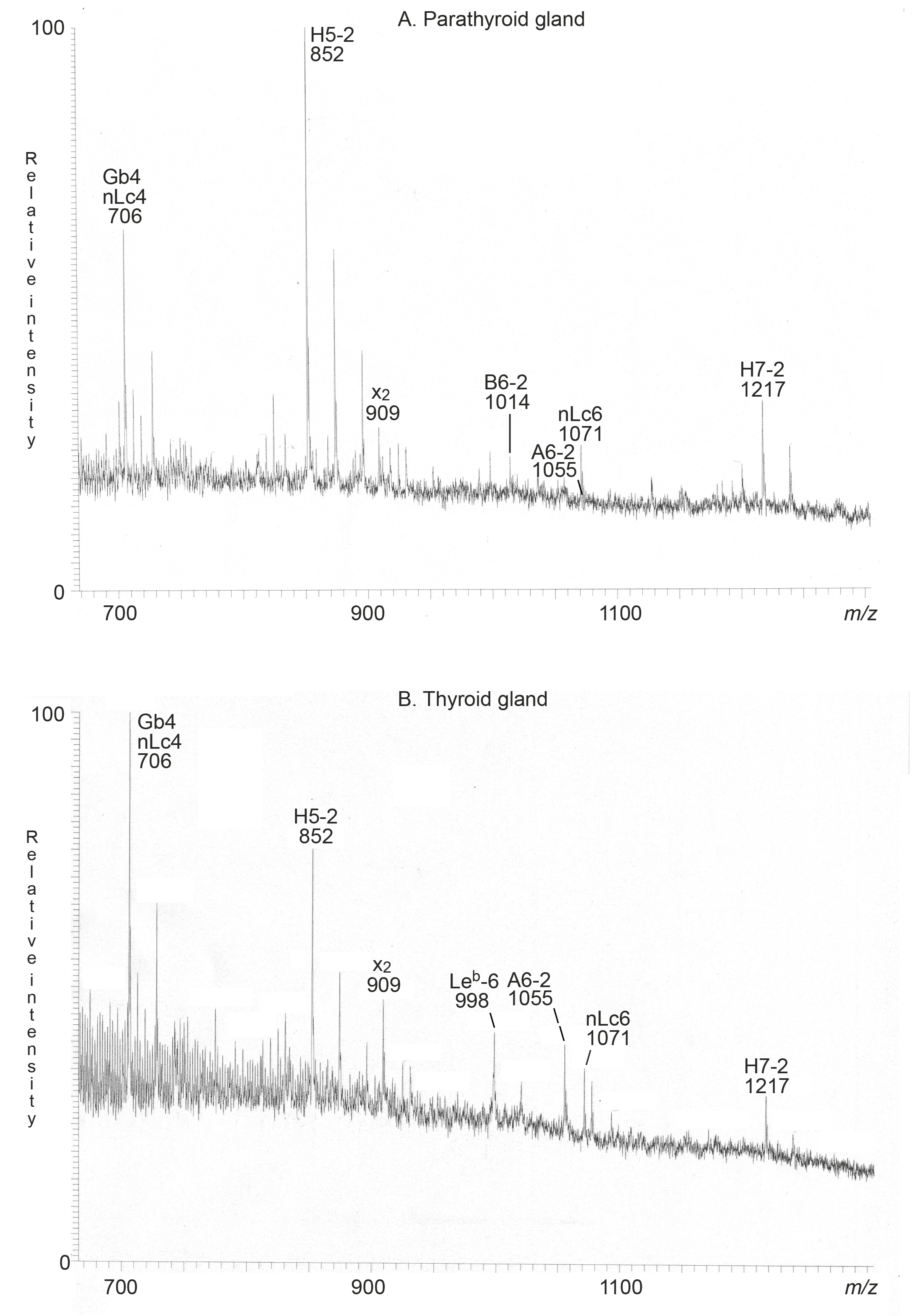
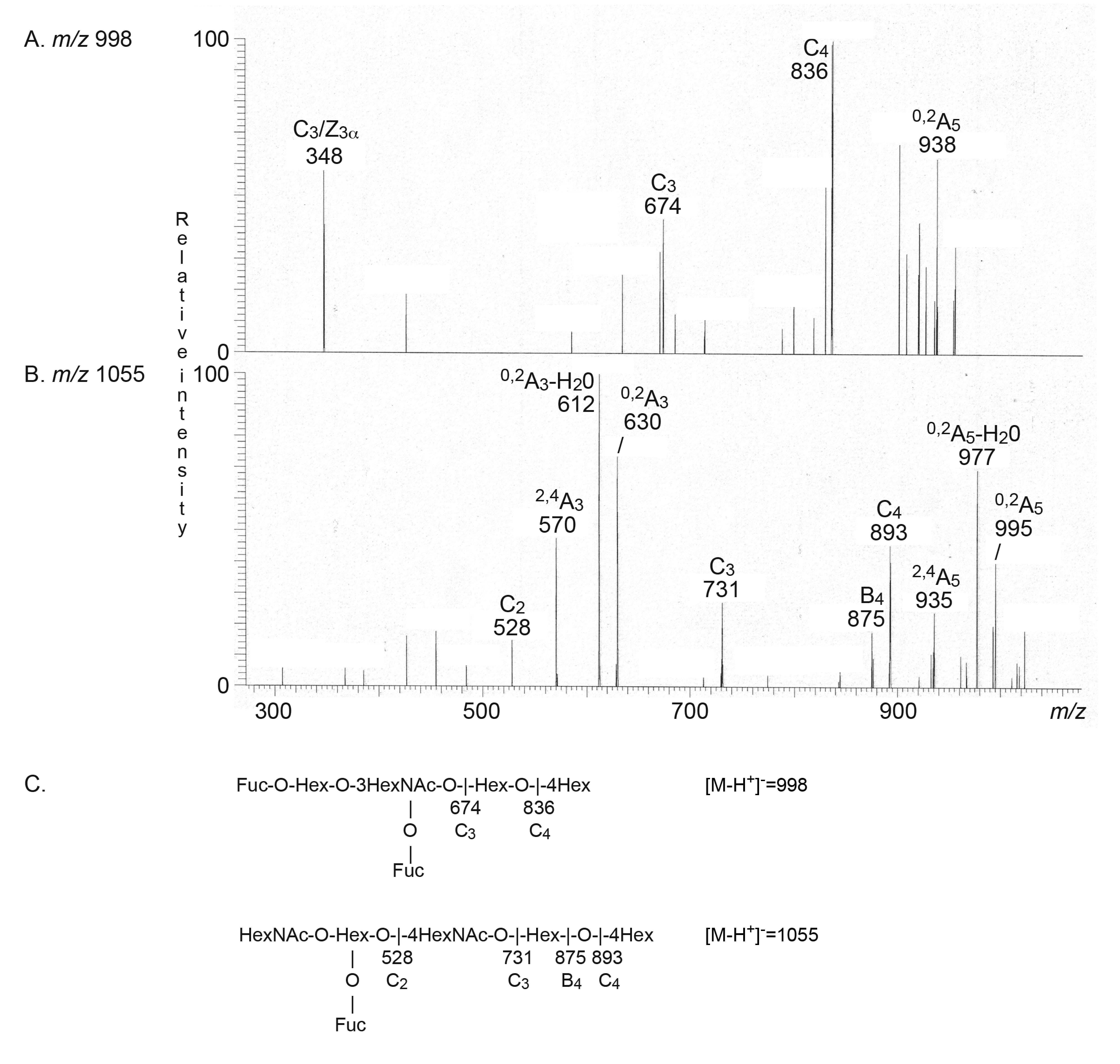
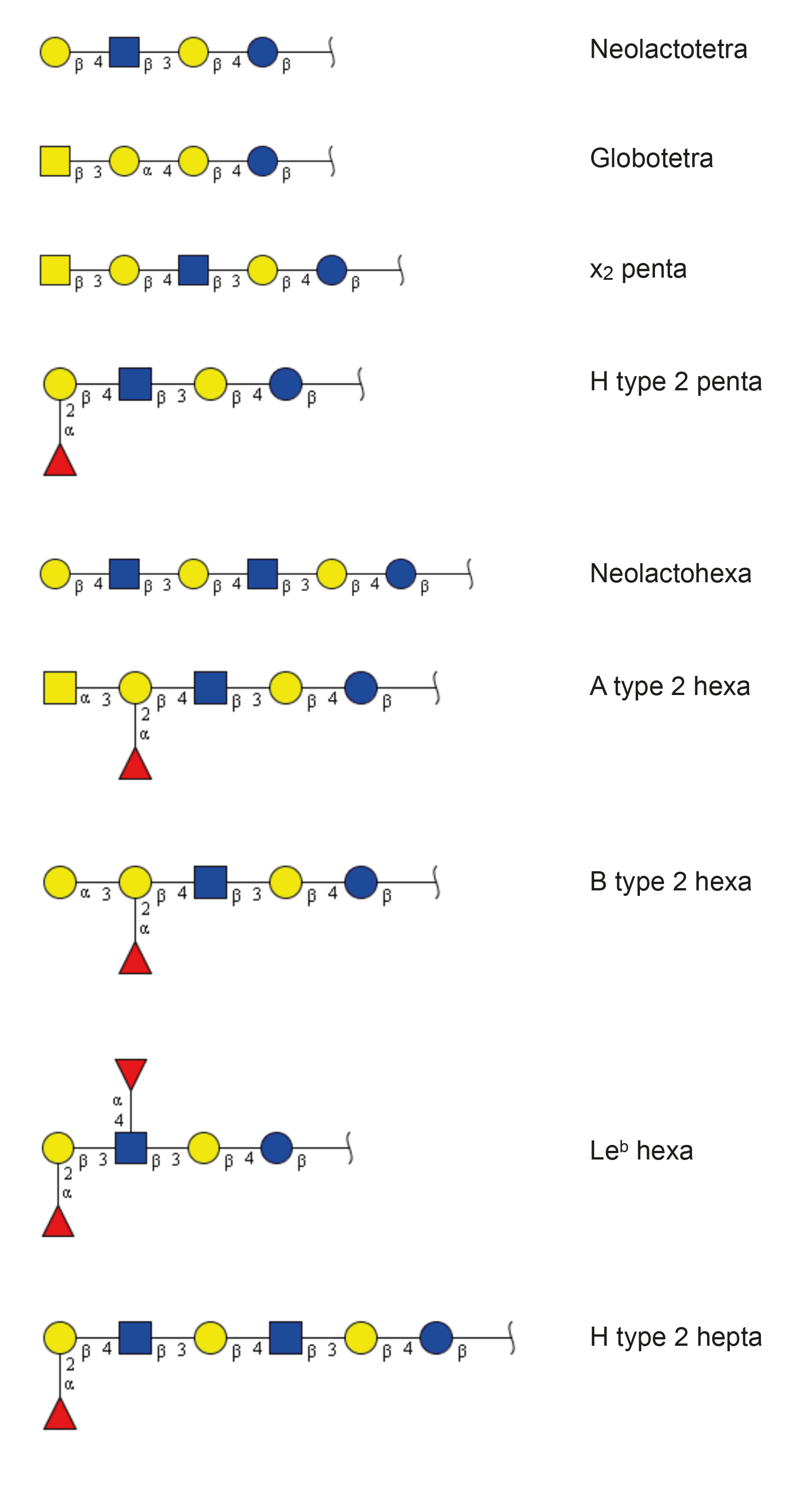
2.2.1. Mass Spectrometry
2.2.2. Chromatogram Binding Assays
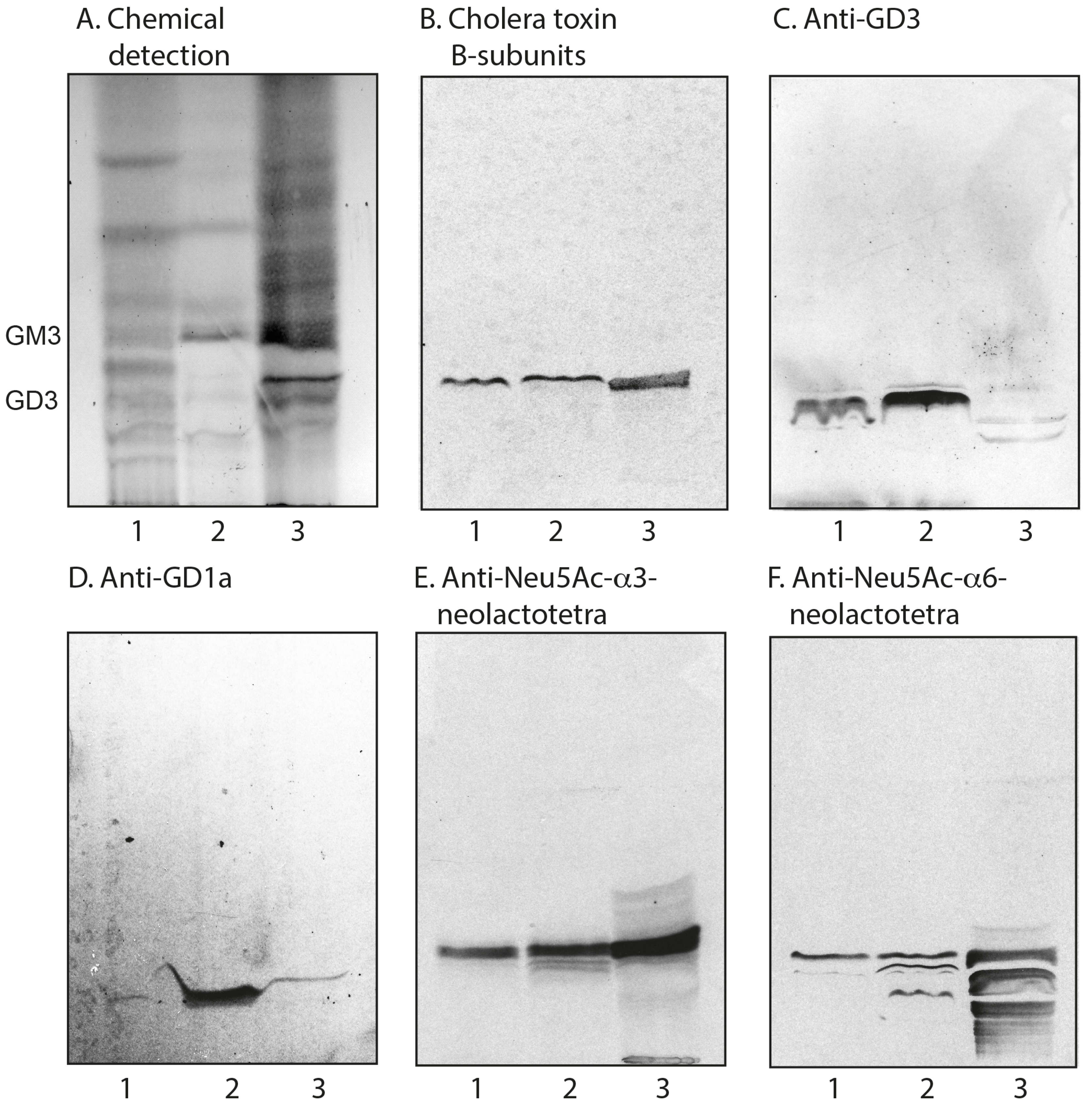
2.3. Characterization of the Acid Glycosphingolipids from Human Parathyroid and Thyroid Glands
2.3.1. Mass Spectrometry
2.3.2. Chromatogram Binding Assays
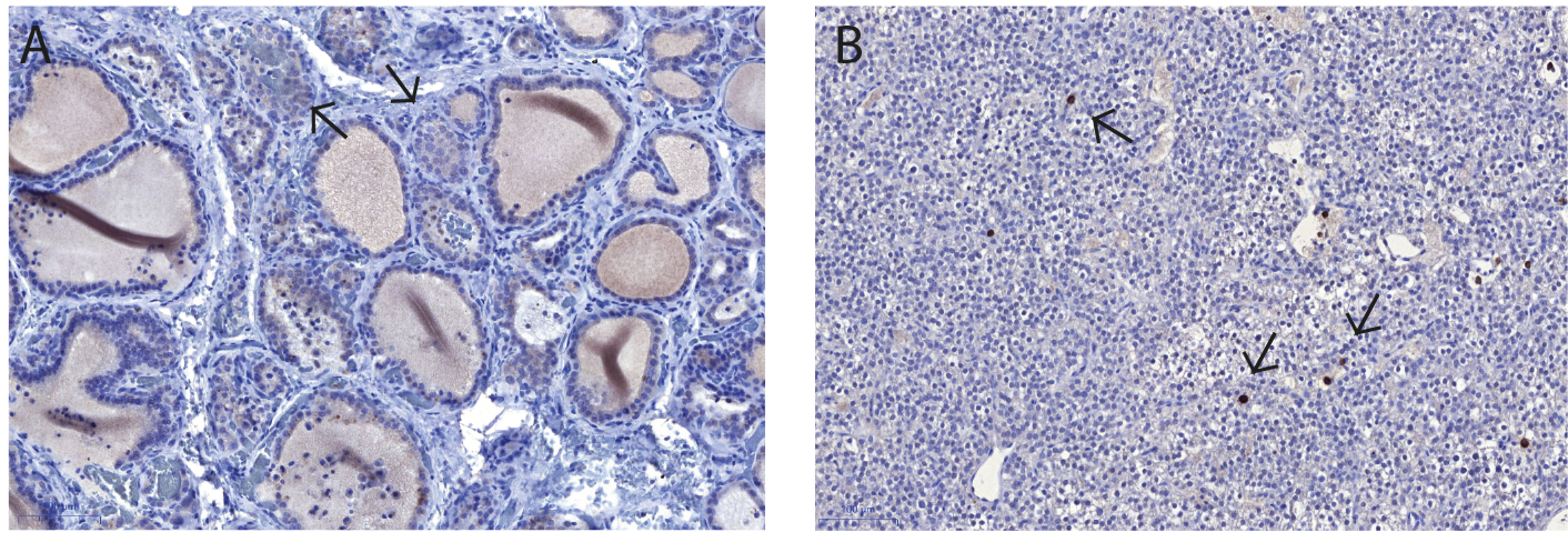
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Glycosphingolipid Preparations
4.2. Reference Glycosphingolipids
4.3. Thin-Layer Chromatography
4.4. Chromatogram Binding Assays
4.5. Endoglycoceramidase Digestion and LC-ESI/MS
4.6. LC-ESI/MS of Native Acid Glycosphingolipids
4.7. Immunohistochemistry
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Bilezikian, J.P.; Cusano, N.E.; Khan, A.A.; Liu, J.M.; Marcocci, C.; Bandeira, F. Primary hyperparathyroidism. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Norlén, O.; Wang, K.C.; Tay, Y.K.; Johnson, W.R.; Grodski, S.; Yeung, M.; Serpell, J.; Sidhu, S.; Sywak, M.; Delbridge, L. No need to abandon focused parathyroidectomy: A multicenter study of long-term outcome after surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism. Ann. Surg. 2015, 261, 991–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghadam, R.N.; Amlelshahbaz, A.P.; Nnamiranian, N.; Sobhan-Arkedani, M.; Emami-Meybodi, M.; Dehgan, A.; Rahmanian, M.; Razavi-Ratki, S.K. Comparative diagnostic performance of ultrasonography and 99mTc-sestamibi scintigraphy for parathyroid adenoma in primary hyperparathyroidism; systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 3195–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kluijfhout, W.P.; Pasternak, J.D.; Beninato, T.; Thurston Drake, F.; Gosnell, J.E.; Shen, W.T.; Duh, Q.-Y.; Allen, I.E.; Vriens, M.R.; de Keizer, B.; et al. Diagnostic performance of computed tomography for parathyroid adenoma localization; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Radiol. 2017, 88, 117–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karli, N.J.; Lewis, G.M. Glycosphingolipids of human thyroid. Lipids 1974, 9, 819–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouchon, B.; Portoukalian, J.; Bornet, H. Major gangliosides in normal and pathological thyroids. Biochem. Int. 1985, 10, 531–538. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bouchon, B.; Portoukalian, J.; Bornet, H. Sex-specific difference of the galabiosylceramide level in the glycosphingolipids of human thyroid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 836, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svennerholm, L. Gangliosides of human thyroid gland. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 835, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, A.; Di Carlo, A.; Macchia, P.E.; Pisano, G.; Parmeggiani, U.; Macchia, V. Gangliosides and phospholipids in human thyroids responsive and unresponsive to thyrotropin. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 1990, 13, 817–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, H.; Halim, A.; Teneberg, S. Differentiation of glycosphingolipid-derived glycan structural isomers by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chai, W.; Piskarev, V.; Lawson, A.M. Negative-ion electrospray mass spectrometry of neutral underivatized oligosaccharides. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 651–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varki, A.; Cummings, R.D.; Aebi, M.; Packer, N.H.; Seeberger, P.H.; Esko, J.D.; Stanley, P.; Hart, G.; Darvill, A.; Kinoshita, T.; et al. Symbol nomenclature for graphical representations of glycans. Glycobiology 2015, 25, 1323–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neelamegham, S.; Aoki-Kinoshita, K.; Bolton, E.; Frank, M.; Lisacek, F.; Lütteke, T.; O’Boyle, N.; Packer, N.H.; Stanley, P.; Toukach, P.; et al. The SNFG Discussion Group. Updates to the symbol nomenclature for glycans guidelines. Glycobiology 2019, 29, 620–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, F.-F.; Turk, J. Studies on sulfatides by quadrupole ion-trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization: Structural characterization and the fragmentation processes that include an unusual internal galactose residue loss and the classical charge-remote fragmentation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 15, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Larena, A.; Vierbuchen, M.; Fischer, R. Blood group antigen expression in malignant tumors of the thyroid: A parallel between medullary and nonmedullary carcinomas. Langenbecks Arch. Chir. 1995, 380, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Cámpora, R.; García-Sanatana, J.A.; Jordà i Heras, M.M.; Salaverri, C.O.; Vázquez-Ramírez, F.J.; Argueta-Manzano, O.E.; Galera-Davidson, H. Blood group antigens in differentiated thyroid neoplasms. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1998, 122, 957–965. [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto, F. ABO blood group system—ABH oligosaccharide antigens, anti-A and ant-B, A and B glycosyltransferases, and ABO genes. Immunohematology 2020, 20, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondeson, A.G.; Bondeson, L.; Busch, G.; Grimelius, L.; Ljungberg, O. ABO blood group antigens in parathyroid adenoma and hyperplasia. Surgery 1989, 105, 734–736. [Google Scholar]
- Woltering, E.A.; Emmott, R.C.; Javapour, N.; Marx, S.J.; Brennan, M.F. ABO(H) cell surface antigens in parathyroid adenoma and hyperplasia. Surgery 1981, 90, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Kielczynski, W.; Leedman, P.J.; Harrison, L.C. Association of ganglioside with the TSH receptor. Trends Glycosci. Glycotechnol. 1990, 2, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielczynski, W.; Harrison, L.C.; Leedman, P.J. Direct evidence that ganglioside is an integral component of the thyrotropin receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 1991–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kielczynski, W.; Bartholomeusz, R.K.; Harrison, L.C. Characterization of ganglioside associated with the thyrotropin receptor. Glycobiology 1994, 4, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Latif, R.; Ando, T.; Daniel, S.; Davies, T.F. Localization and regulation of thyrotropin receptors within lipid rafts. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 4724–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Latif, R.; Ando, T.; Davies, T.F. Lipid rafts as triage centers for multimeric and monomeric thyrotropin receptor regulation. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 3164–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossi, M.; Taddei, A.R.; Fasciani, I.; Maggio, R.; Giorgi, F. The cell biology of the thyroid-disrupting mechanism of dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT). J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2018, 41, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, K.A. Preparation of total non-acid glycolipids for overlay analysis of receptors for bacteria and viruses and for other studies. Meth. Enzymol. 1987, 138, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsson, B.E.; Pimlott, W.; Karlsson, K.A. Mass spectrometry of mixtures of intact glycosphingolipids. Meth. Enzymol. 1990, 193, 623–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koerner, T.A.W., Jr.; Prestegard, J.H.; Demou, P.C.; Yu, R.K. High-resolution proton NMR studies of gangliosides. 1. Use of homonuclear spin-echo J-correlated spectroscopy for determination of residue composition and anomeric configurations. Biochemistry 1983, 22, 2676–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldi, D. Sprühreagentien für die dünnschicht-chromatographie. In Dünnschicht-Chromatographie; Stahl, E., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1962; pp. 496–515. [Google Scholar]
- Barone, A.; Benktander, J.; Ångström, J.; Aspegren, A.; Björquist, P.; Teneberg, S.; Breimer, M.E. Structural complexity of non-acid glycosphingolipids in human embryonic stem cells grown under feeder-free conditions. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 10035–10050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Barone, A.; Säljö, K.; Benktander, J.; Blomqvist, M.; Månsson, J.-E.; Johansson, B.R.; Mölne, J.; Aspegren, A.; Björquist, P.; Breimer, M.E.; et al. Sialyl-lactotetra: A novel cell surface marker of undifferentiated human pluripotent stem cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18846–18859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Svennerholm, L.; Rynmark, B.M.; Vilbersson, G.; Fredman, P.; Gottfries, J.; Månsson, J.-E.; Percy, A. Gangliosides in human fetal brain. J. Neurochem. 1991, 56, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, O.; Lindholm, L.; Holmgren, J. and Svennerholm, L. Monoclonal antibodies raised against NeuAc alpha 2-6neolactotetraosylceramide detect carcinoma-associated gangliosides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 835, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roche, N.; Ilver, D.; Ångström, J.; Barone, S.; Telford, J.L.; Teneberg, S. Human gastric glycosphingolipid receptors for Helicobacter pylori vacuolating cytotoxin VacA. Microbes Infect. 2007, 9, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teneberg, S.; Jovall, P.-Å.; Ångström, J.; Karlsson, K.-A. Characterization of binding of Galβ4GlcNAc-specific lectins from Erythrina christagalli and Erythrina corallodendron to glycosphingolipids. Detection, isolation and characteriztion of a novel glycosphingolipid of bovine buttermilk. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 8554–8563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ångström, J.; Bäckström, M.; Berntsson, A.; Karlsson, N.; Holmgren, J.; Karlsson, K.-A.; Teneberg, S. Novel carbohydrate binding site recognizing blood group A and B determinants in a cholera toxin/heat-labile enterotoxin B-subunit hybrid. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 3231–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johansson, M.M.; Dedic, B.; Lundholm, K.; Branzell, F.B.; Barone, A.; Benktander, J.; Teneberg, S. Characterization of moose intestinal glycosphingolipids. Glycoconj. J. 2015, 32, 393–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
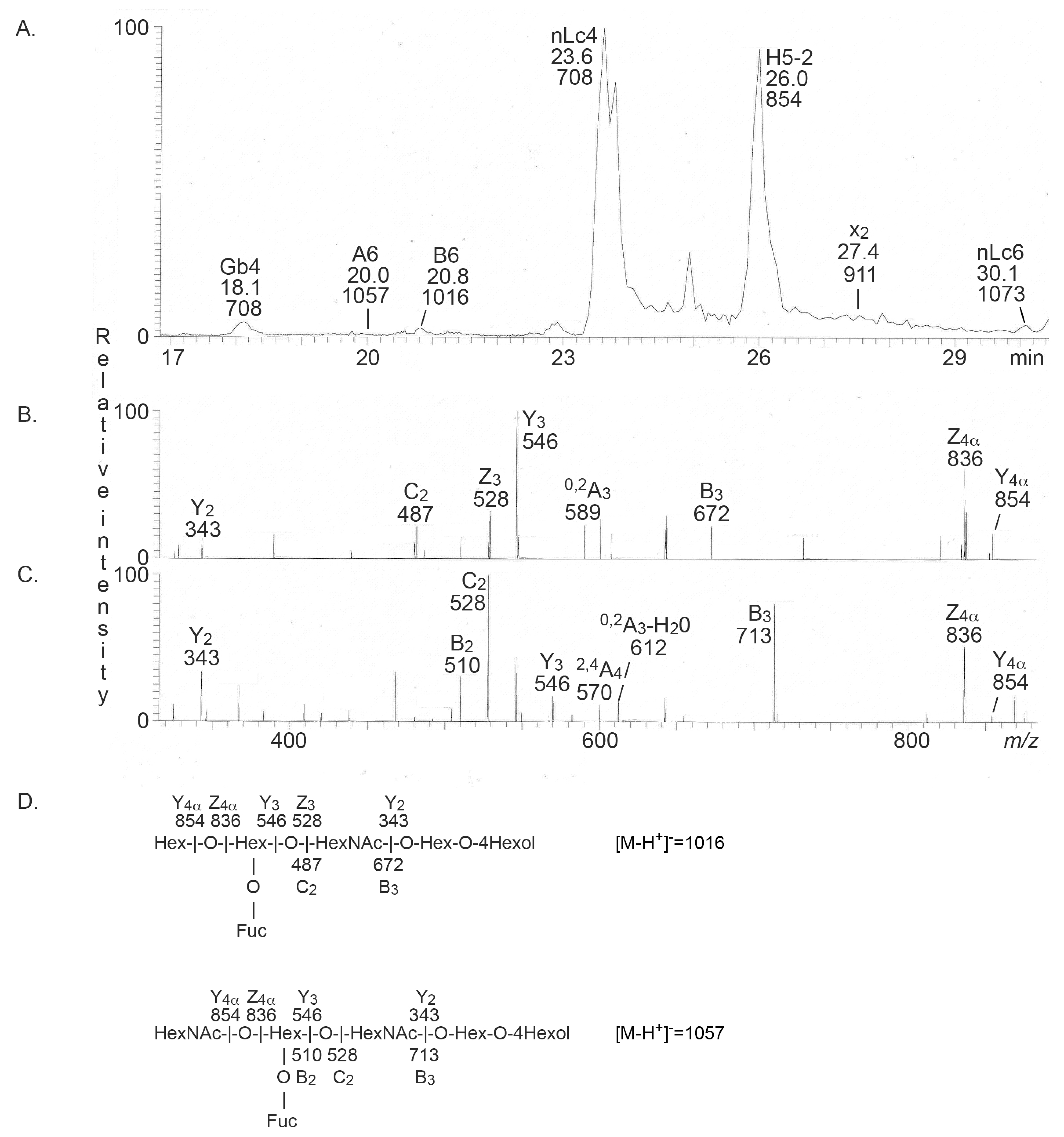

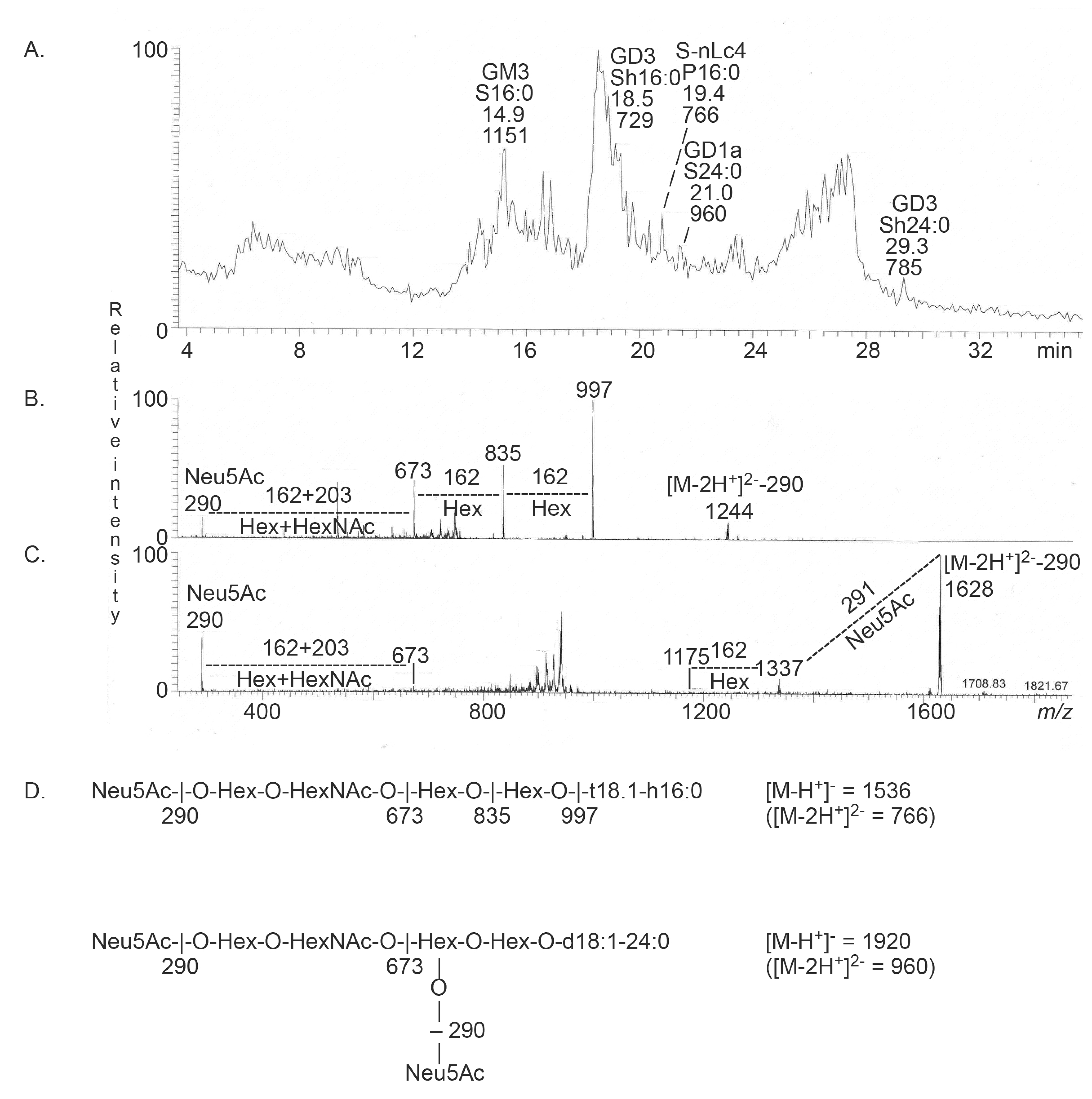


| Dry Weight | Total Acid Glycosphingolipids | Total Non-Acid Glycosphingolipids | mg Acid Glycosphingolipids/g Dry Weight | mg Non-Acid Glycosphingolipids/g Dry Weight | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parathyroid gland | 4.6 g | 5.0 mg | 19.1 mg | 1.1 | 4.1 |
| Thyroid gland | 5.2 g | 10.2 mg | 12.8 mg | 2.0 | 2.5 |
| Trivial Name | Structure | Parathyroid Gland | Thyroid Gland |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neolactotetra (nLc4) | Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glc | + | + |
| Globotetra (Gb4) | GalNAcβ3Galα4Galβ4Glc | + | + |
| x2 penta (x2) | GalNAcβ3Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glc | + | + |
| H type 2 penta (H5-2) | Fucα2Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glc | + | + |
| Neolactohexa (nLc6) | Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glc | + | + |
| A type 2 hexa (A6-2) | GalNAcα3(Fucα2)Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glc | + | + |
| B type 2 hexa (B6-2) | Galα3(Fucα2)Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glc | + | - |
| Leb hexa (Leb-6) | Fucα2Galβ3(Fucα4)GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glc | - | + |
| H type 2 hepta (H7-2) | Fucα2Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glc | + | + |
| Trivial Name | Structure | Parathyroid Gland | Thyroid Gland |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfatide | SO3-3Galβ1Cer | + | + |
| Neu5Ac-GM3 | Neu5Acα3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer | + | + |
| Neu5Ac-GD3 | Neu5Acα8Neu5Acα3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer | + | + |
| Neu5Ac-nLc4 | Neu5Acα3Galβ4GlcNAcβ3Galβ4Glcβ1Cer | + | + |
| Neu5Ac-GM1 | Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu5Acα3)Galβ4Glcβ1Cer | + | + |
| Neu5Ac-GD1a | Neu5Acα3Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu5Acα3)Galβ4Glcβ1Cer | + | - |
| Neu5Ac-GD1b | Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu5Acα8Neu5Acα3)Galβ4Glcβ1Cer | - | + |
| Neu5Ac-GT1b | Neu5Acα3Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu5Acα8Neu5Acα3)Galβ4Glcβ1Cer | - | + |
| Ligand | Clone | Manufacturer | Dilution | Binding Specificity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cholera toxin B-subunits | - | List Labs | - | Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu5Acα3)Galβ4Glc |
| Anti-GD3 | MB3.6 | BD Biosciences | 1:100 | Neu5Acα8Neu5Acα3Galβ4Glc |
| Anti-GD1a | GD1a-1 | Sigma-Aldrich | 1:100 | Neu5Acα3Galβ3GalNAcβ4(Neu5Acα3)Galβ4Glc |
| Anti-Neu5Acα3-nL4 | LM1:1a | [32] | 1:1000 | Neu5Acα3Galβ4GlcNAc |
| Anti-Neu5Acα6-nL4 | LM4:2 | [33] | 1:100 | Neu5Acα6Galβ4GlcNAc |
| P-fimbriated E. coli | - | [34] | - | Galα4Gal |
| E. cristagalli lectin | Sigma-Aldrich | - | Galβ4GlcNAc/Fucα2Galβ4GlcNAc | |
| Anti-Lewis b | BG-6/T218 | Signet/Covance | 1:100 | Fucα2Galβ3(Fucα4)GlcNAc |
| Anti-blood group A | HE-195 | Sigma-Aldrich | 1:500 | GalNAcα3(Fucα2)Gal |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Säljö, K.; Thornell, A.; Jin, C.; Stålberg, P.; Norlén, O.; Teneberg, S. Characterization of Glycosphingolipids in the Human Parathyroid and Thyroid Glands. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137044
Säljö K, Thornell A, Jin C, Stålberg P, Norlén O, Teneberg S. Characterization of Glycosphingolipids in the Human Parathyroid and Thyroid Glands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(13):7044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137044
Chicago/Turabian StyleSäljö, Karin, Anders Thornell, Chunsheng Jin, Peter Stålberg, Olov Norlén, and Susann Teneberg. 2021. "Characterization of Glycosphingolipids in the Human Parathyroid and Thyroid Glands" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 13: 7044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137044
APA StyleSäljö, K., Thornell, A., Jin, C., Stålberg, P., Norlén, O., & Teneberg, S. (2021). Characterization of Glycosphingolipids in the Human Parathyroid and Thyroid Glands. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 7044. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22137044









