The Odorant-Binding Proteins of the Spider Mite Tetranychus urticae
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
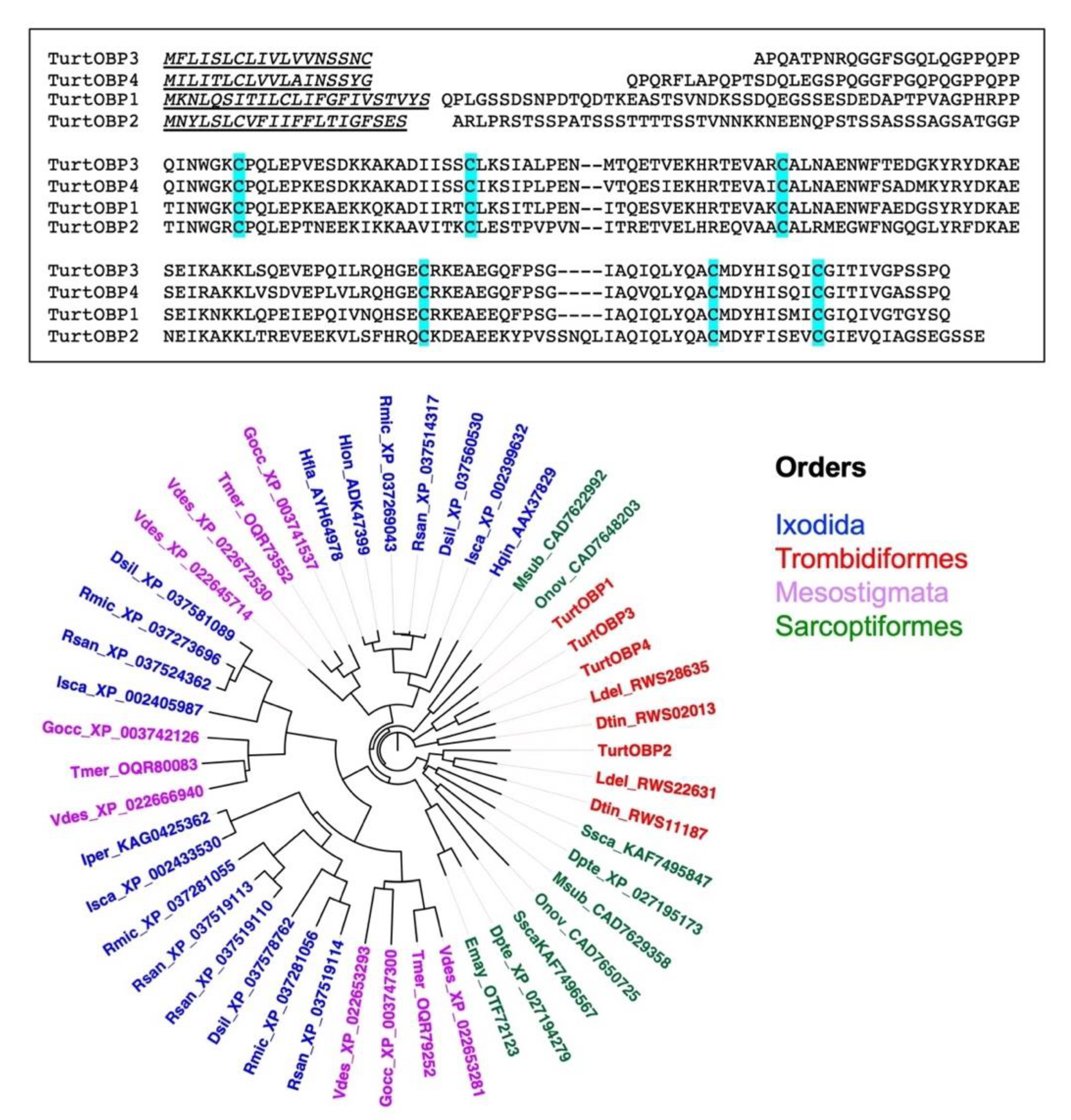
2.1. Protein Sequence Analysis
2.2. Proteomic Analysis
2.3. Protein Expression and Purification
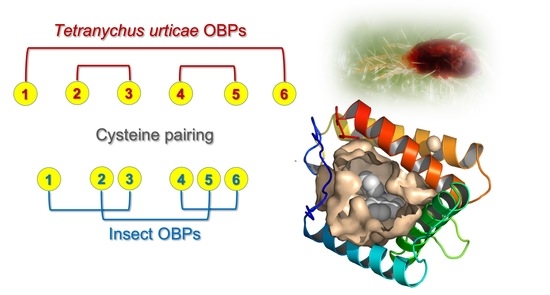
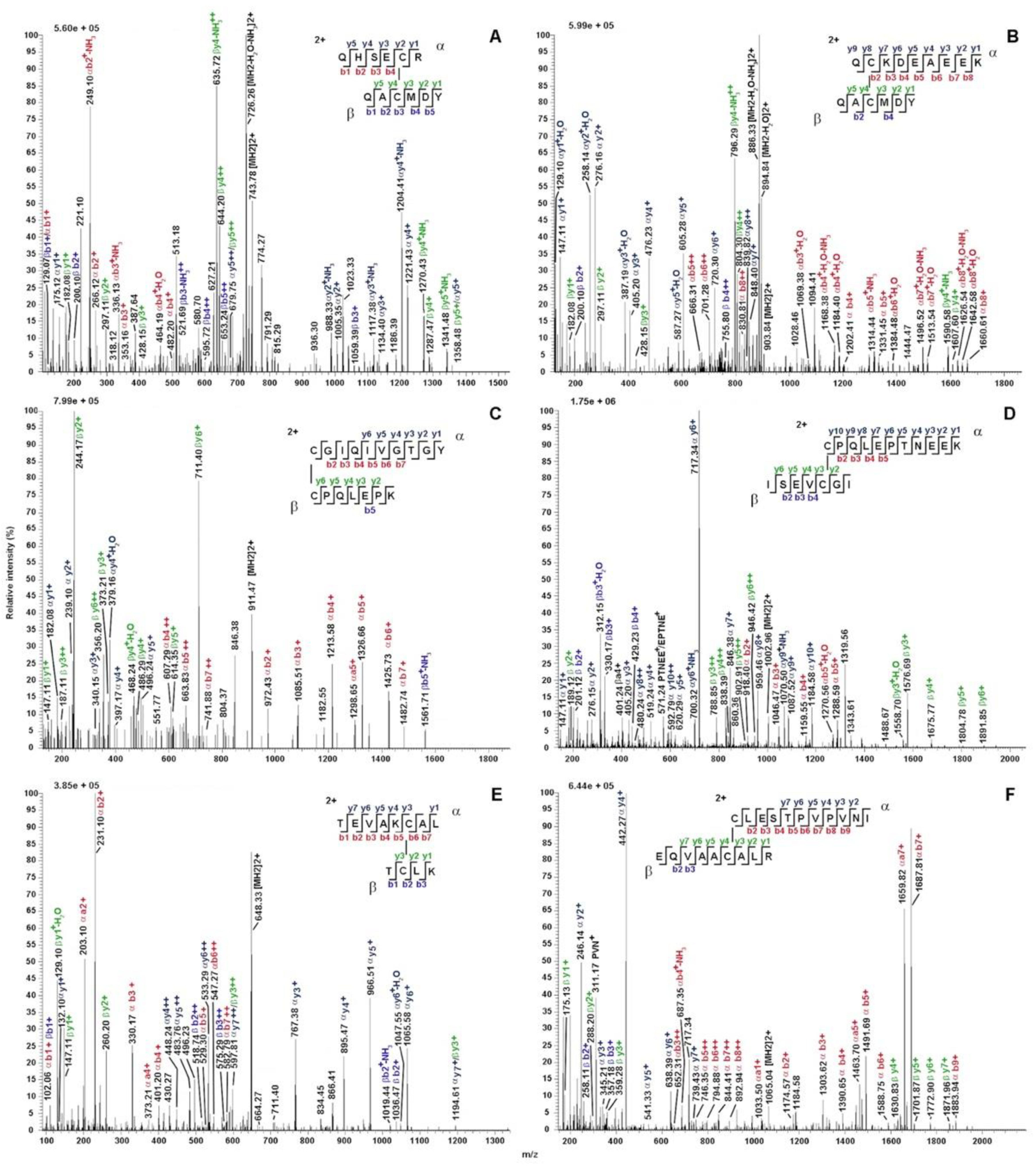
2.4. Cysteine Pairing Assignment
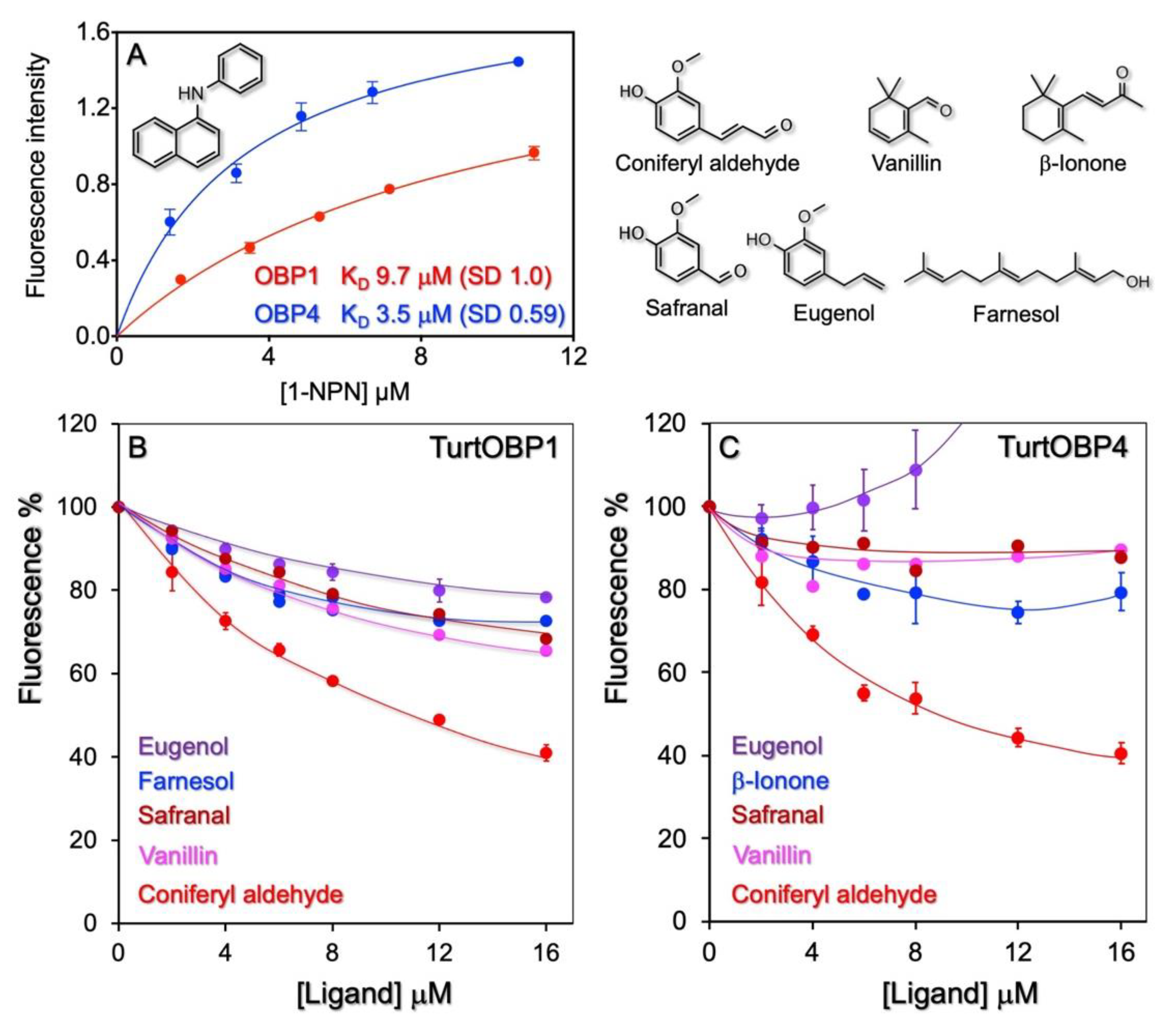
2.5. Ligand-Binding Experiments
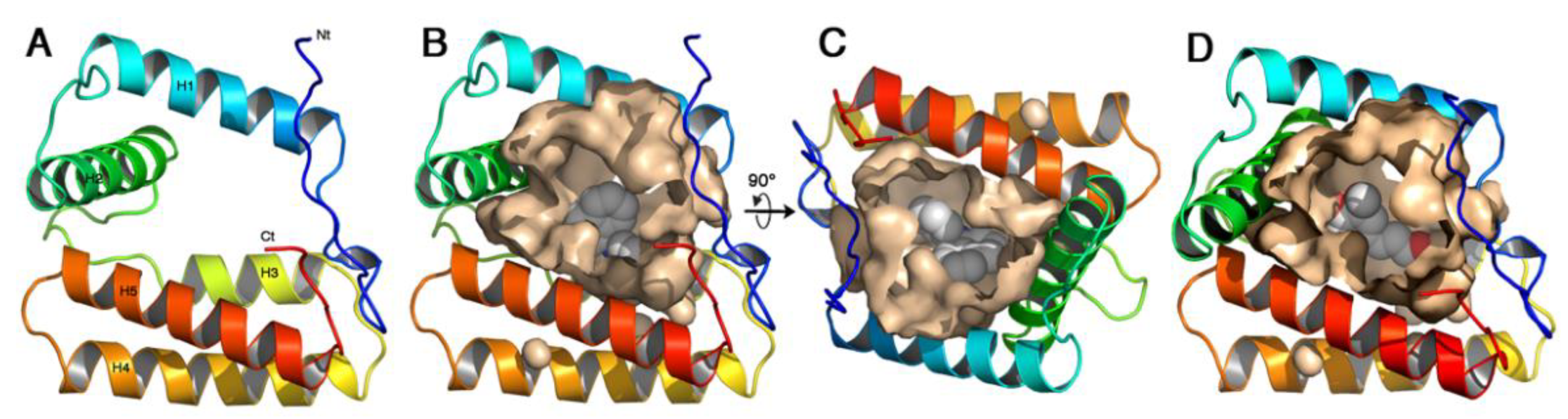
2.6. Three-Dimensional Folding
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mites
4.2. Chemicals
4.3. RNA Extraction, cDNA Synthesis, Cloning, and Sequencing
4.4. Proteomic Analysis
4.5. Protein Expression and Purification
4.6. Disulfide Assignment
4.7. Ligand-Binding Assays
4.8. Secondary Structure Analysis
4.9. Model Building
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eisen, R.J.; Eisen, L. The Blacklegged Tick, Ixodes scapularis: An Increasing Public Health Concern. Trends Parasitol. 2018, 34, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulia-Nuss, M.; Nuss, A.B.; Meyer, J.M.; Sonenshine, D.E.; Roe, R.M.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Sattelle, D.B.; De la Fuente, J.; Ribeiro, J.M.; Megy, K.; et al. Genomic insights into the Ixodes scapularis tick vector of Lyme disease. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornman, R.S.; Schatz, M.C.; Johnston, J.S.; Chen, Y.-P.; Pettis, J.; Hunt, G.; Bourgeois, L.; Elsik, C.; Anderson, D.; Grozinger, C.M.; et al. Genomic Survey of the Ectoparasitic Mite Varroa destructor, a Major Pest of the Honey Bee Apis mellifera. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decourtye, A.; Alaux, C.; Le Conte, Y.; Henry, M. Toward the protection of bees and pollination under global change: Present and future perspectives in a challenging applied science. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 35, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, A.L.; Roe, M. Acarine attractants: Chemoreception, bioassay, chemistry and control. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2016, 131, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, W.S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Nakano, Y.; Nakao, H.; Suzuki, T. 2(E)-(4-Mcthyl-3-Pentenyl)-Butenedial, α-Acaridial, a Novel Monoterpene from the Acarid Mite Tyrophagus perniciosus (Acarina, Acaridae). Agric. Biol. Chem. 1989, 53, 1193–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leal, W.S.; Kuwahara, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Kurosa, K. β-Acaridial, the Sex Pheromone of the Acarid Mite Caloglyphus polyphyllae: Pheromone Study of Acarid Mites. XXI. Naturwissenschaften 1989, 76, 332–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizoguchi, A.; Mori, N.; Nishida, R.; Kuwahara, Y. α-Acaridial a Female Sex Pheromone from an Alarm Pheromone Emitting Mite Rhizoglyphus robini. J. Chem. Ecol. 2003, 29, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Sato, M.; Koshii, T.; Suzuki, T. Chemical Ecology of Astigmatid Mites XXXII.2-Hydroxy-6-Methyl-Benzaldehyde, the Sex Pheromone of the Brown-Legged Grain Mite Aleuroglyphus ovatus (TROUPEAU)(Acarina:Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1992, 27, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regev, S.; Cone, W.W. Analyses of Pharate Female Twospotted Spider Mites for Nerolidol and Geraniol: Evaluation for Sex 2 Attraction of Males. Environ. Entomol. 1976, 5, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regev, S.; Cone, W.W. Evidence of Farnesol as a Male Sex Attractant of the Twospotted Spider Mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acarina: Tetranychidae) 1. Environ. Entomol. 1975, 4, 307–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regev, S.; Cone, W.W. The Monoterpene Citronellol, as a Male Sex Attractant of the Twospotted Spider Mite, Tetranychus urticae (Acarina: Tetranychidae) 1. Environ. Entomol. 1980, 9, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Shimizu, N.; Mori, N.; Kuwahara, Y. Chemical Ecology of Astigmatid Mites. LXIV. The Alarm Pheromone Neral Functions as an Attractant in Schwiebea elongata (Banks)(Acari: Acaridae). Appl. Entomol. Zool. 2002, 37, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelton, A.C.; Cameron, M.M.; Pickett, J.A.; Birkett, M.A. Identification of Neryl Formate as the Airborne Aggregation Pheromone for the American House Dust Mite and the European House Dust Mite (Acari: Epidermoptidae). J. Med. Entomol. 2010, 47, 798–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Asami, N.; Morr, M.; Matsuyama, S.; Suzuki, T. Chemical Ecology of Astigmatid Mites XXXVIII Aggregation Pheromone and Kairomone Activity of Lardolure and Its Analogues against Lardoglyphus konoi and Carpoglyphus lactis. Appl. Entomol. Zool. 1994, 29, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schulz, S.; Fuhlendorff, J.; Steidle, J.L.M.; Collatz, J.; Franz, J.-T. Identification and Biosynthesis of an Aggregation Pheromone of the Storage Mite Chortoglyphus arcuatus. ChemBioChem 2004, 5, 1500–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, M.J.C.; Câmara, C.A.G.; Born, F.S.; Moraes, M.M.; Badji, C.A. Acaricidal Activity and Repellency of Essential Oil from Piper aduncum and Its Components against Tetranychus Urticae. Exp. Appl. Acarol. 2012, 57, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tak, J.-H.; Isman, M.B. Acaricidal and Repellent Activity of Plant Essential Oil-Derived Terpenes and the Effect of Binary Mixtures against Tetranychus urticae Koch (Acari: Tetranychidae). Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 108, 786–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Camara, C.A.G.; Akhtar, Y.; Isman, M.B.; Seffrin, R.C.; Born, F.S. Repellent Activity of Essential Oils from Two Species of Citrus against Tetranychus urticae in the Laboratory and Greenhouse. Crop Prot. 2015, 74, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, H.S.; Park, K.C.; Park, C.G. Repellent Effect of Santalol from Sandalwood Oil Against Tetranychus urticae (Acari: Tetranychidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2012, 105, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grbić, M.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Clark, R.M.; Rombauts, S.; Rouzé, P.; Grbić, V.; Osborne, E.J.; Dermauw, W.; Thi Ngoc, P.C.; Ortego, F.; et al. The Genome of Tetranychus urticae Reveals Herbivorous Pest Adaptations. Nature 2011, 479, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoy, M.A.; Waterhouse, R.M.; Wu, K.; Estep, A.S.; Ioannidis, P.; Palmer, W.J.; Pomerantz, A.F.; Simão, F.A.; Thomas, J.; Jiggins, F.M.; et al. Genome Sequencing of the Phytoseiid Predatory Mite Metaseiulus Occidentalis Reveals Completely Atomized Hox Genes and Superdynamic Intron Evolution. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 1762–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoc, P.C.T.; Greenhalgh, R.; Dermauw, W.; Rombauts, S.; Bajda, S.; Zhurov, V.; Grbić, M.; Van de Peer, Y.; Van Leeuwen, T.; Rouzé, P.; et al. Complex Evolutionary Dynamics of Massively Expanded Chemosensory Receptor Families in an Extreme Generalist Chelicerate Herbivore. Genome Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 3323–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosi, P.; Iovinella, I.; Felicioli, A.; Dani, F.R. Soluble Proteins of Chemical Communication: An Overview across Arthropods. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Guo, M.; Ban, L.; Song, L.-M.; Liu, Y.; Pelosi, P.; Wang, G. Niemann-Pick C2 Proteins: A New Function for an Old Family. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Tsuchiya, W.; Fujii, T.; Fujimoto, Z.; Miyazawa, M.; Ishibashi, J.; Matsuyama, S.; Ishikawa, Y.; Yamazaki, T. Niemann–Pick Type C2 Protein Mediating Chemical Communication in the Worker Ant. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 3847–3852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, S.-N.; Peng, Y.; Lu, Z.-Y.; Shan, S.; Yang, Y.-Q.; Li, R.-J.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Guo, Y.-Y. Functional Characterization of a Niemann–Pick Type C2 Protein in the Parasitoid Wasp Microplitis mediator. Insect Sci. 2018, 25, 765–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Bao, H.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y. Niemann-Pick Proteins Type C2 Are Identified as Olfactory Related Genes of Pardosa pseudoannulata by Transcriptome and Expression Profile Analysis. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2019, 29, 320–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovinella, I.; Ban, L.; Song, L.; Pelosi, P.; Dani, F.R. Proteomic Analysis of Castor Bean Tick Ixodes ricinus: A Focus on Chemosensory Organs. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2016, 78, 58–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Iannucci, A.; Dani, F.R.; Knoll, W.; Pelosi, P. Lipocalins in Arthropod Chemical Communication. Genome Biol. Evol. 2021, 13, evab091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renthal, R.; Manghnani, L.; Bernal, S.; Qu, Y.; Griffith, W.P.; Lohmeyer, K.; Guerrero, F.D.; Borges, L.M.F.; Pérez de León, A. The Chemosensory Appendage Proteome of Amblyomma americanum (Acari: Ixodidae) Reveals Putative Odorant-Binding and Other Chemoreception-Related Proteins. Insect Sci. 2017, 24, 730–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, M.P.; Hekmat-Scafe, D.S.; Gaines, P.; Carlson, J.R. Putative Drosophila Pheromone-Binding Proteins Expressed in a Subregion of the Olfactory System. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 16340–16347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliash, N.; Singh, N.K.; Thangarajan, S.; Sela, N.; Leshkowitz, D.; Kamer, Y.; Zaidman, I.; Rafaeli, A.; Soroker, V. Chemosensing of Honeybee Parasite, Varroa destructor : Transcriptomic Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliash, N.; Thangarajan, S.; Goldenberg, I.; Sela, N.; Kupervaser, M.; Barlev, J.; Altman, Y.; Knyazer, A.; Kamer, Y.; Zaidman, I.; et al. Varroa Chemosensory Proteins: Some Are Conserved across Arthropoda but Others Are Arachnid Specific. Insect Mol. Biol. 2019, 28, 321–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iovinella, I.; McAfee, A.; Mastrobuoni, G.; Kempa, S.; Foster, L.J.; Pelosi, P.; Dani, F.R. Proteomic Analysis of Chemosensory Organs in the Honey Bee Parasite Varroa destructor: A Comprehensive Examination of the Potential Carriers for Semiochemicals. J. Proteom. 2018, 181, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vizueta, J.; Rozas, J.; Sánchez-Gracia, A. Comparative Genomics Reveals Thousands of Novel Chemosensory Genes and Massive Changes in Chemoreceptor Repertories across Chelicerates. Genome Biol. Evol. 2018, 10, 1221–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Josek, T.; Walden, K.K.O.; Allan, B.F.; Alleyne, M.; Robertson, H.M. A Foreleg Transcriptome for Ixodes scapularis Ticks: Candidates for Chemoreceptors and Binding Proteins That Might Be Expressed in the Sensory Haller’s Organ. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2018, 9, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scaloni, A.; Monti, M.; Angeli, S.; Pelosi, P. Structural Analysis and Disulfide-Bridge Pairing of Two Odorant-Binding Proteins from Bombyx mori. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 266, 386–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, W.S.; Nikonova, L.; Peng, G. Disulfide Structure of the Pheromone Binding Protein from the Silkworm Moth, Bombyx Mori. FEBS Lett. 1999, 464, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaloni, A. Analysis of post-translational modifications in soluble proteins involved in chemical communication from mammals and insects. In Methods in Enzymology; Elsevier: Cambridge MA, USA, 2020; Volume 642, pp. 103–124. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.-L.; Meng, J.-M.; Cao, Y.; Yin, J.-L.; Fang, R.-Q.; Fan, S.-B.; Liu, C.; Zeng, W.-F.; Ding, Y.-H.; Tan, D.; et al. A High-Speed Search Engine PLink 2 with Systematic Evaluation for Proteome-Scale Identification of Cross-Linked Peptides. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amigues, B.; Zhu, J.; Gaubert, A.; Arena, S.; Renzone, G.; Leone, P.; Fischer, I.M.; Paulsen, H.; Knoll, W.; Scaloni, A.; et al. A New Non-Classical Fold of Varroa Odorant-Binding Proteins Reveals a Wide Open Internal Cavity. Sci. Rep. 2021, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdetskiy, A.; Cole, C.; Procter, J.; Barton, G.J. JPred4: A Protein Secondary Structure Prediction Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W389–W394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterhouse, A.; Bertoni, M.; Bienert, S.; Studer, G.; Tauriello, G.; Gumienny, R.; Heer, F.T.; De Beer, T.A.P.; Rempfer, C.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Homology Modelling of Protein Structures and Complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W296–W303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, I.W.; Leaver-Fay, A.; Chen, V.B.; Block, J.N.; Kapral, G.J.; Wang, X.; Murray, L.W.; Arendall III, W.B.; Snoeyink, J.; Richardson, J.S.; et al. MolProbity: All-atom contacts and structure validation for proteins and nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35 (Suppl.2), W375–W383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, L. DALI and the persistence of protein shape. Protein Sci. 2000, 29, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lartigue, A.; Gruez, A.; Rivière, S.; Brossut, R.; Tegoni, M.; Cambillau, C. The Crystal Structure of a Cockroach Pheromone Binding Protein Suggests a New Ligand Binding and Release Mechanism. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 30213–30218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tegoni, M.; Campanacci, V.; Cambillau, C. Structural Aspects of Sexual Attraction and Chemical Communication in Insects. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2004, 29, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rappsilber, J.; Mann, M.; Ishihama, Y. Protocol for Micro-Purification, Enrichment, Pre-Fractionation and Storage of Peptides for Proteomics Using StageTips. Nat. Protoc. 2007, 2, 1896–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Mann, M. MaxQuant enables high peptide identification rates, individualized p.p.b.-range mass accuracies and proteome-wide protein quantification. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 1367–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Arena, S.; Spinelli, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, G.; Wei, R.; Cambillau, C.; Scaloni, A.; Wang, G.; Pelosi, P. Reverse Chemical Ecology: Olfactory Proteins from the Giant Panda and Their Interactions with Putative Pheromones and Bamboo Volatiles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E9802–E9810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arena, S.; Renzone, G.; Scaloni, A. A Multi-Approach Peptidomic Analysis of Hen Egg White Reveals Novel Putative Bioactive Molecules. J. Proteom. 2020, 215, 103646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, S.; Scaloni, A. An Extensive Description of the Peptidomic Repertoire of the Hen Egg Yolk Plasma. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 3239–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corpet, F. Multiple Sequence Alignment with Hierarchical Clustering. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 10881–10890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, X.; Gouet, P. Deciphering Key Features in Protein Structures with the New ENDscript Server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W320–W324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinelli, S.; Lagarde, A.; Iovinella, I.; Legrand, P.; Tegoni, M.; Pelosi, P.; Cambillau, C. Crystal Structure of Apis mellifera OBP14, a C-Minus Odorant-Binding Protein, and Its Complexes with Odorant Molecules. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2012, 42, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, P.; Lohkamp, B.; Scott, W.G.; Cowtan, K. Features and Development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2010, 66, 486–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Tetranychus urticae OBP1 | ||||||||
| Assigned disulfide bridged-peptides | Position | MH22+ exp./theor. | MH33+ exp./theor. | MH44+ exp./theor. | Cys-Cys | MH+ exp./theor. | BioPharma Finder# | pLink# |
| [C§PQLEPK]-[HISMIC§GIQIVGTGY] | (57-63)-(170-184) | 801.7346/ 801.7341 | 57-175 | 2403.1882/ 2403.1868 | x | |||
| [C§PQLEPK]-[C§GIQIVGTGY]* | (57-63)-(175-184) | 911.4472/ 911.4476 | 607.9676/ 607.9676 | 57-175 | 1821.8867/ 1821.8873 | x | ||
| [TC§LK]-[C§ALNAENW] | (76-79)-(102-109) | 691.3147/ 691.3162 | 461.2124/ 461.2134 | 77-102 | 1381.6216/ 1381.6247 | x | ||
| [TC§LK]-[C§ALN(deam)AENW] | (76-79)-(102-109) | 691.8088/ 691.8078 | 461.5411/ 461.5418 | 77-102 | 1382.6097/ 1382.6078 | x | ||
| [TC§LK]-[TEVAKC§AL] | (76-79)-(97-104) | 648.3378/ 648.3388 | 432.5611/ 432.5617 | 77-102 | 1295.6678/ 1295.6697 | x | ||
| [QHSEC§R]-[QAC§MDY]* | (141-146)-(164-169) | 743.7794/ 743.7792 | 145-166 | 1486.5510/ 1486.5507 | x | |||
| [IVNQHSEC§R]-[QAC§MDY]* | (138-146)-(164-169) | 906.8789/ 906.8770 | 145-166 | 1812.7500/ 1812.7461 | x | |||
| [IVNQHSEC§R]-[QAC§M]* | (138-146)-(164-167) | 767.8320/ 767.8318 | 145-166 | 1534.6561/ 1534.6559 | x | |||
| Tetranychus urticae OBP2 | ||||||||
| Assigned disulfide bridged-peptides | Position | MH22+ exp./theor. | MH33+ exp./theor. | MH44+ exp./theor. | Cys-Cys | MH+ exp./theor. | BioPharma Finder# | pLink# |
| [C§PQLEPTNEEK]-[ISEVC§GIEV]* | (56-66)-(174-182) | 1117.0222/ 1117.0220 | 745.0174/ 745.0173 | 56-178 | 2233.0366/ 2233.0362 | x | x | |
| [C§PQLEPTNEEK]- [ISEVC§GIEVQIAGSEGSSE] | (56-66)-(174-192) | 1060.1510/ 1060.1519 | 795.3652/ 795.3659 | 56-178 | 3178.4373/ 3178.4401 | x | x | |
| [C§PQLEPTNEEK]-[FISEVC§GIEV]* | (56-66)-(173-182) | 1190.5564/ 1190.5562 | 794.0402/ 794.0401 | 56-178 | 2380.1051/ 2380.1046 | x | x | |
| [C§PQLEPTNEEK]-[FISEVC§GIEVQIAGSEGSSE] | (56-66)-(173-192) | 1109.1745/ 1109.1747 | 832.1328/ 832.1330 | 56-178 | 3325.5078/ 3325.5085 | x | x | |
| [C§PQLEPTNEEK]-[ISEVC§GI]* | (56-66)-(174-180) | 1002.9666/ 1002.9665 | 668.9803/ 668.9803 | 56-178 | 2004.9254/ 2004.9252 | x | ||
| [C§L]-[EQVAAC§ALR] | (76-77)-(96-104) | 596.7946/ 596.7948 | 398.1990/ 398.1991 | 76-101 | 1192.5815/ 1192.5818 | x | ||
| [C§L]-[EQVAAC§AL] | (76-77)-(96-103) | 518.7439/ 518.7443 | 76-101 | 1036.4800/ 1036.4808 | x | |||
| [C§LESTPVPVNITR]-[EQVAAC§ALR] | (76-88)-(96-104) | 796.0782/ 796.0791 | 597.3106/ 597.3112 | 76-101 | 2386.2189/ 2386.2216 | x | x | |
| [C§LESTPVPV]-[C§ALR]* | (76-84)-(101-104) | 702.3542/ 702.3550 | 76-101 | 1403.7005/ 1403.7021 | x | |||
| [C§LESTPVPVNI]-[C§ALR]* | (76-86)-(101-104) | 544.2818/ 544.2815 | 76-101 | 1630.8297/ 1630.8290 | x | |||
| [C§LESTPVPV]-[EQVAAC§ALR]* | (76-84)-(96-104) | 951.4754/ 951.4768 | 76-101 | 1901.9430/ 1901.9459 | x | |||
| [C§LESTPVPVNI]-[EQVAAC§ALR]* | (76-86)-(96-104) | 1065.0384/ 1065.0403 | 76-101 | 2129.0691/ 2129.0728 | x | |||
| [C§LESTPVPV]-[AC§ALR] ]* | (76-84)-(100-104) | 737.8720/ 737.8735 | 76-101 | 1474.7363/ 1474.7392 | x | |||
| [C§LESTPVPV]-[AAC§ALR]* | (76-84)-(99-104) | 773.3928/ 773.3920 | 76-101 | 1545.7779/ 1545.7763 | x | |||
| [QC§KDEAEEK]- [QAC§MDY] | (143-151)-(167-172) | 903.8514/ 903.8528 | 602.9036/ 602.9045 | 452.4296/ 452.4303 | 144-169 | 1806.6951/ 1806.6978 | x | x |
| [Q(pGlu)C§KDEAEEK]-[QAC§MDY] | (143-151)-(167-172) | 895.3404/ 895.3396 | 144-169 | 1789.6730/ 1789.6713 | x | |||
| [QC§KDEAEEK]-[QAC§MDYF] | (143-151)-(167-173) | 977.3867/ 977.3870 | 651.9271/ 651.9273 | 489.1972/ 489.1974 | 144-169 | 1953.7656/ 1953.7662 | x | x |
| [Q(pGlu)C§KDEAEEK]-[QAC§MDYF] | (143-151)-(167-173) | 968.8734/ 968.8738 | 144-169 | 1936.7390/ 1936.7397 | x | |||
| Tetranychus urticae OBP3 | ||||||||
| Assigned disulfide bridged-peptides | Position | MH22+ exp./theor. | MH33+ exp./theor. | MH44+ exp./theor. | Cys-Cys | MH+ exp./theor. | BioPharma Finder# | pLink# |
| [C§PQLEPVESDK]-[HISQIC§GITIV]* | (30-40)-(143-153) | 1213.1086/ 1213.1092 | 890.0750/ 890.0754 | 30-148 | 2425.2093/ 2425.2107 | x | ||
| [GKC§PQLEPVESDKK]-[HISQIC§GITIVGPSSPQ] | (30-41)-(143-159) | 1097.8973/ 1097.8958 | 30-148 | 3291.6762/ 3291.6719 | x | |||
| [C§PQLEPVESDKKA]-[HISQIC§GI]* | (30-42)-(143-150) | 1156.0734/ 1156.0749 | 30-148 | 2311.1390/ 2311.1420 | x | |||
| [C§PQL]-[HISQIC§GITIVGPSSPQ] | (30-33)-(143-159) | 732.0355/ 732.0383 | 30-148 | 2194.0910/ 2194.0994 | x | |||
| [C§PQL]-[HISQIC§GI]* | (30-33)-(143-150) | 443.2220/ 443.2217 | 30-148 | 1327.6504/ 1327.6496 | x | |||
| [ADIISSC§LK]-[C§AL] | (44-52)-(75-77) | 626.8176/ 626.8178 | 418.2143/ 418.2145 | 50-75 | 1252.6273/ 1252.6278 | x | ||
| [ADIISSC§LK]-[C§ALNAENW] | (44-52)-(75-82) | 933.9396/ 933.9401 | 50-75 | 1866.8713/ 1866.8724 | x | |||
| [ADIISSC§LK]-[C§ALNAENWFTEDGK] | (44-52)-(75-88) | 848.7293/ 848.7300 | 50-75 | 2544.1722/ 2544.1744 | x | |||
| [ADIISSC§LK]-[C§ALNAENWF] | (44-52)-(75-83) | 1007.4736/ 1007.4743 | 50-75 | 2013.9395/ 2013.9408 | x | |||
| [ADIISSC§L]-[C§AL] | (44-51)-(75-77) | 562.7696/ 562.7703 | 50-75 | 1124.5314/ 1124.5328 | x | |||
| [QHGEC§R]-[QAC§MDY] | (114-119)-(137-142) | 728.7732/ 728.7740 | 118-139 | 1456.5387/ 1456.5402 | x | x | ||
| [Q(pGlu)HGEC§R]-[QAC§MDY] | (114-119)-(137-142) | 720.2600/ 720.2607 | 118-139 | 1439.5121/ 1439.5136 | x | |||
| [Q(pGlu)HGEC§R]-[C§MDY]* | (114-119)-(139-142) | 620.7130/ 620.7128 | 118-139 | 1240.4181/ 1240.4179 | x | |||
| [QHGEC§R]-[YQAC§MDY] | (114-119)-(136-142) | 810.3044/ 810.3056 | 118-139 | 1619.6010/ 1619.6035 | x | |||
| Tetranychus urticae OBP4 | ||||||||
| Assigned disulfide bridged-peptides | Position | MH22+ exp./theor. | MH33+ exp./theor. | MH44+ exp./theor. | Cys-Cys | MH+ exp./theor. | BioPharma Finder# | pLink# |
| [C$PQLEPK]-[HISQIC$GITIV] | (41-47)-(154-164) | 998.0242/ 998.0240 | 665.6854/ 665.6852 | 499.5160/ 499.5159 | 41-159 | 1995.0406/ 1995.0401 | x | x |
| [C$PQLEPK]-[HISQIC$GITIVGASSPQ] | (41-47)-(154-170) | 841.4300/ 841.4299 | 631.3245/ 631.3244 | 41-159 | 2522.2745/ 2522.2740 | x | x | |
| [GKC$PQLEPK]-[HISQIC$GITIVGASSPQ] | (39-47)-(154-170) | 903.1358/ 903.1354 | 677.6038/ 677.6035 | 41-159 | 2707.3918/ 2707.3904 | x | x | |
| [C$PQLEPK]-[HISQIC$G]* | (41-47)-(154-160) | 784.8812/ 784.8819 | 523.5901/ 523.5905 | 41-159 | 1568.7546/ 1568.7559 | x | x | |
| [GKC$PQLEPK]-[HISQIC$GI]* | (39-47)-(154-161) | 933.9817/ 933.9821 | 622.9904/ 622.9907 | 41-159 | 1866.9556/ 1866.9564 | x | x | |
| [ADIISSC$IK]-[TEVAIC$AL] | (55-63)-(81-88) | 883.4575/ 883.4576 | 589.3076/ 589.3077 | 61-86 | 1765.9071/ 1765.9074 | x | x | |
| [ADIISSC$IK]-[AIC$AL] | (55-63)-(84-88) | 718.8783/ 718.8783 | 479.5881/ 479.5881 | 61-86 | 1436.7488/ 1436.7487 | x | x | |
| [ADIISSC$IK]-[HRTEVAIC$AL] | (55-63)-(79-88) | 1030.0382/ 1030.0376 | 515.5230/ 515.5227 | 61-86 | 2059.0686/ 2059.0674 | x | x | |
| [AKADIISSC$IK]-[HRTEVAIC$AL] | (53-63)-(79-88) | 753.4045/ 753.4050 | 565.3053/ 565.3057 | 61-86 | 2258.1979/ 2258.1994 | x | ||
| [AKADIISSC$IK]-[TEVAIC$AL] | (53-63)-(81-88) | 655.6853/ 655.6850 | 61-86 | 1965.0404/ 1965.0394 | x | |||
| [ADIISSC$IK]-[TEVAIC$A]* | (55-63)-(81-87) | 826.9151/ 826.9156 | 61-86 | 1652.8223/ 1652.8233 | x | x | ||
| [ADIISSC$IK]-[RTEVAIC$AL]* | (55-63)-(80-88) | 961.5079/ 961.5081 | 641.3412/ 641.3414 | 61-86 | 1922.0080/ 1922.0084 | x | x | |
| [QHGEC$R]-[YQAC$MDY] | (125-130)-(147-153) | 810.3057/ 810.3057 | 129-150 | 1619.6036/ 1619.6035 | x | x | ||
| [Q(pGlu)HGEC§R]-[YQAC§MDY] | (125-130)-(147-153) | 801.7920/ 801.7924 | 129-150 | 1602.5761/ 1602.5769 | x | |||
| [QHGEC$R]-[QAC$MDY] | (125-130)-(148-153) | 728.7728/ 728.7740 | 129-150 | 1456.5378/ 1456.5402 | x | x | ||
| [Q(pGlu)HGEC§R]-[QAC§MDY] | (125-130)-(148-153) | 720.2608/ 720.2607 | 129-150 | 1439.5138/ 1439.5136 | x | |||
| [QHGEC$R]-[AC$MDY]* | (125-130)-(149-153) | 664.7437/ 664.7447 | 129-150 | 1328.4796/ 1328.4816 | x | x | ||
| [Q(pGlu)HGEC§R]-[AC§MDY]* | (125-130)-(149-153) | 656.2314/ 656.2314 | 129-150 | 1311.4549/ 1311.4550 | x | |||
| [QHGEC$R]-[QAC$MDYHISQ]* | (125-130)-(148-157) | 961.3915/ 961.3908 | 129-150 | 1921.7751/ 1921.7737 | x | |||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, J.; Renzone, G.; Arena, S.; Dani, F.R.; Paulsen, H.; Knoll, W.; Cambillau, C.; Scaloni, A.; Pelosi, P. The Odorant-Binding Proteins of the Spider Mite Tetranychus urticae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136828
Zhu J, Renzone G, Arena S, Dani FR, Paulsen H, Knoll W, Cambillau C, Scaloni A, Pelosi P. The Odorant-Binding Proteins of the Spider Mite Tetranychus urticae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(13):6828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136828
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Jiao, Giovanni Renzone, Simona Arena, Francesca Romana Dani, Harald Paulsen, Wolfgang Knoll, Christian Cambillau, Andrea Scaloni, and Paolo Pelosi. 2021. "The Odorant-Binding Proteins of the Spider Mite Tetranychus urticae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 13: 6828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136828
APA StyleZhu, J., Renzone, G., Arena, S., Dani, F. R., Paulsen, H., Knoll, W., Cambillau, C., Scaloni, A., & Pelosi, P. (2021). The Odorant-Binding Proteins of the Spider Mite Tetranychus urticae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(13), 6828. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22136828