Nuclear Respiratory Factor-1, a Novel SMAD4 Binding Protein, Represses TGF-β/SMAD4 Signaling by Functioning as a Transcriptional Cofactor
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
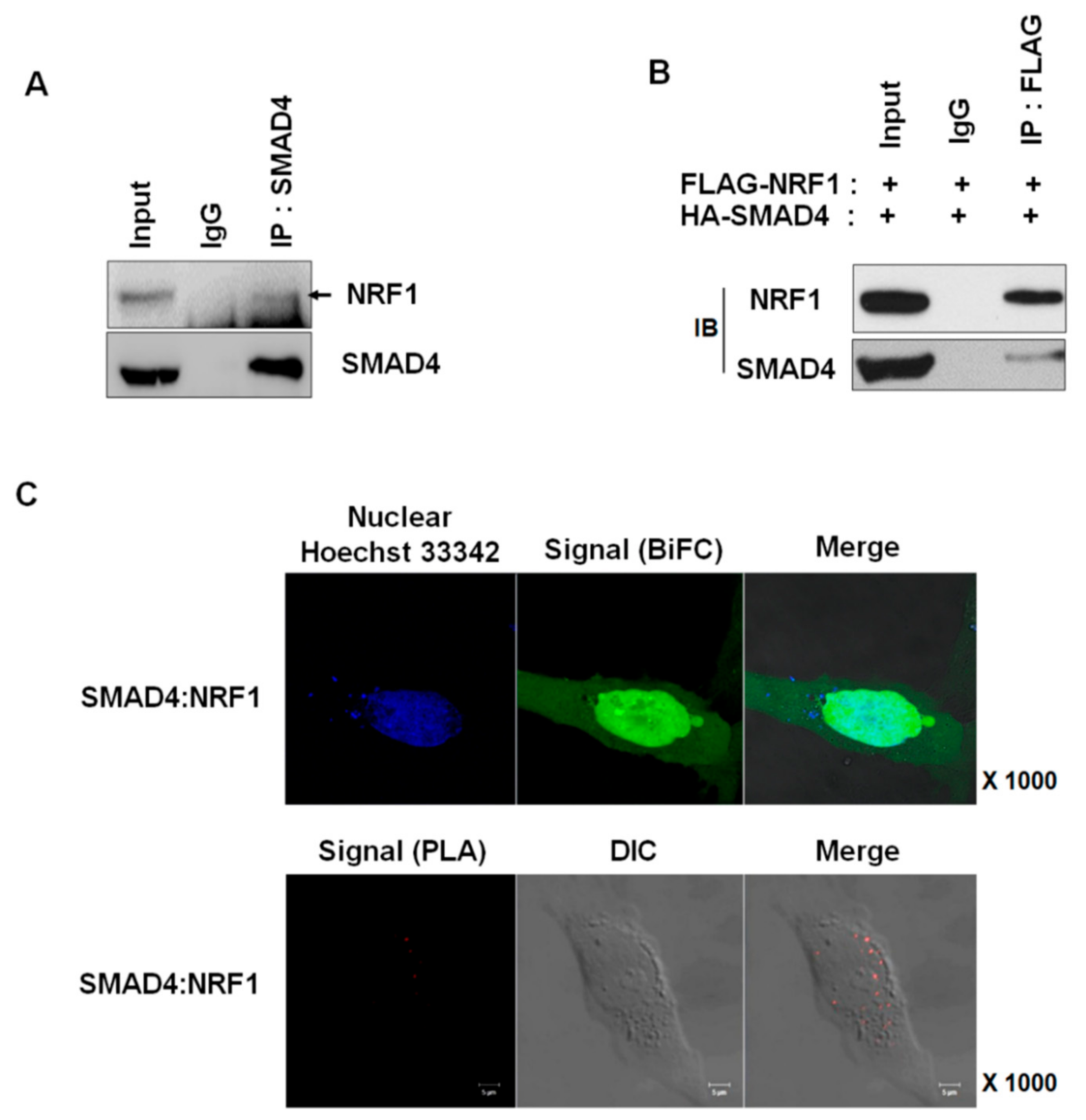
2.1. NRF1 Is a Novel SMAD4-Binding Partner
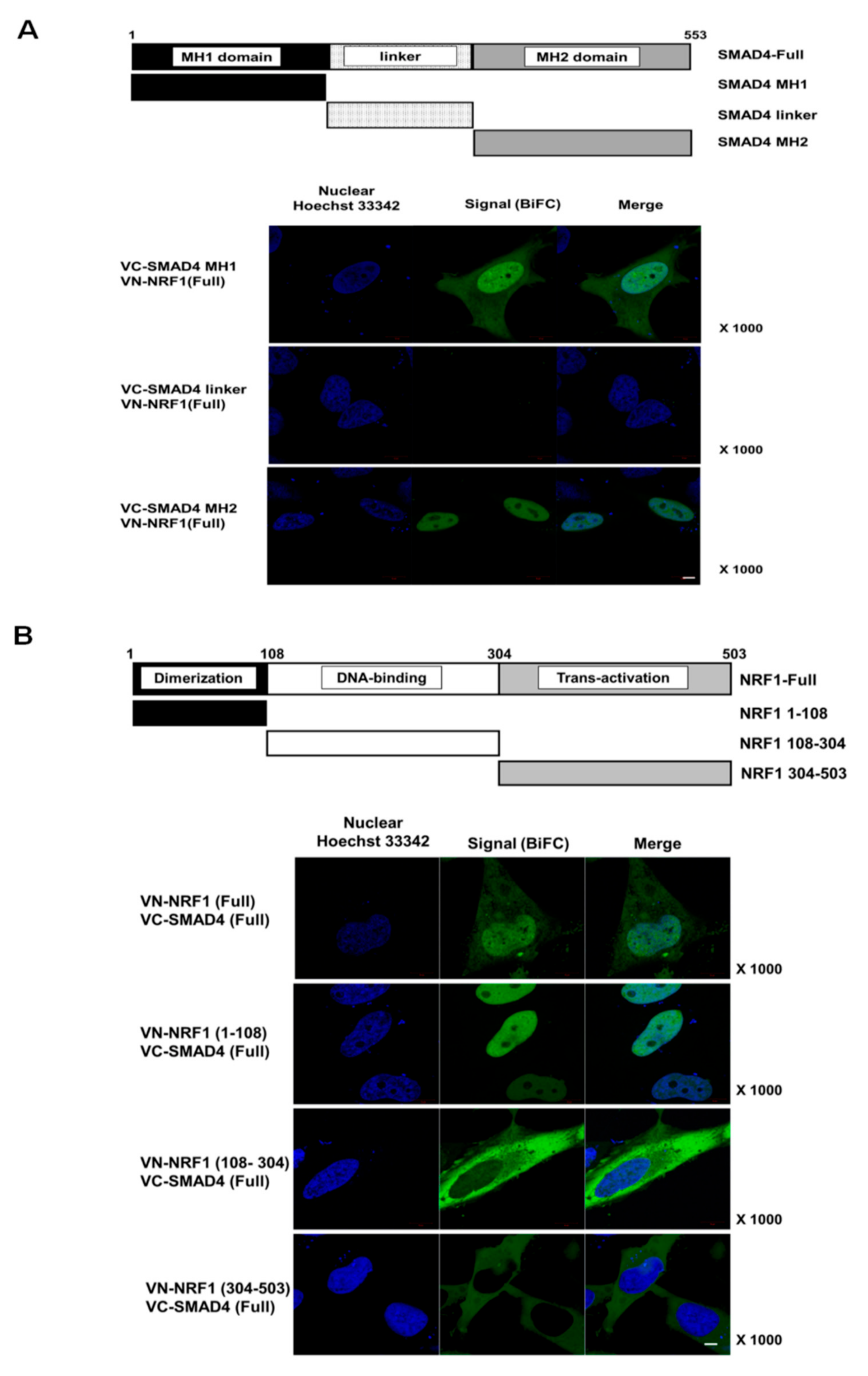
2.2. SMAD4 MH1 and MH2 Domains Interact with the NRF1 Dimerization Domain
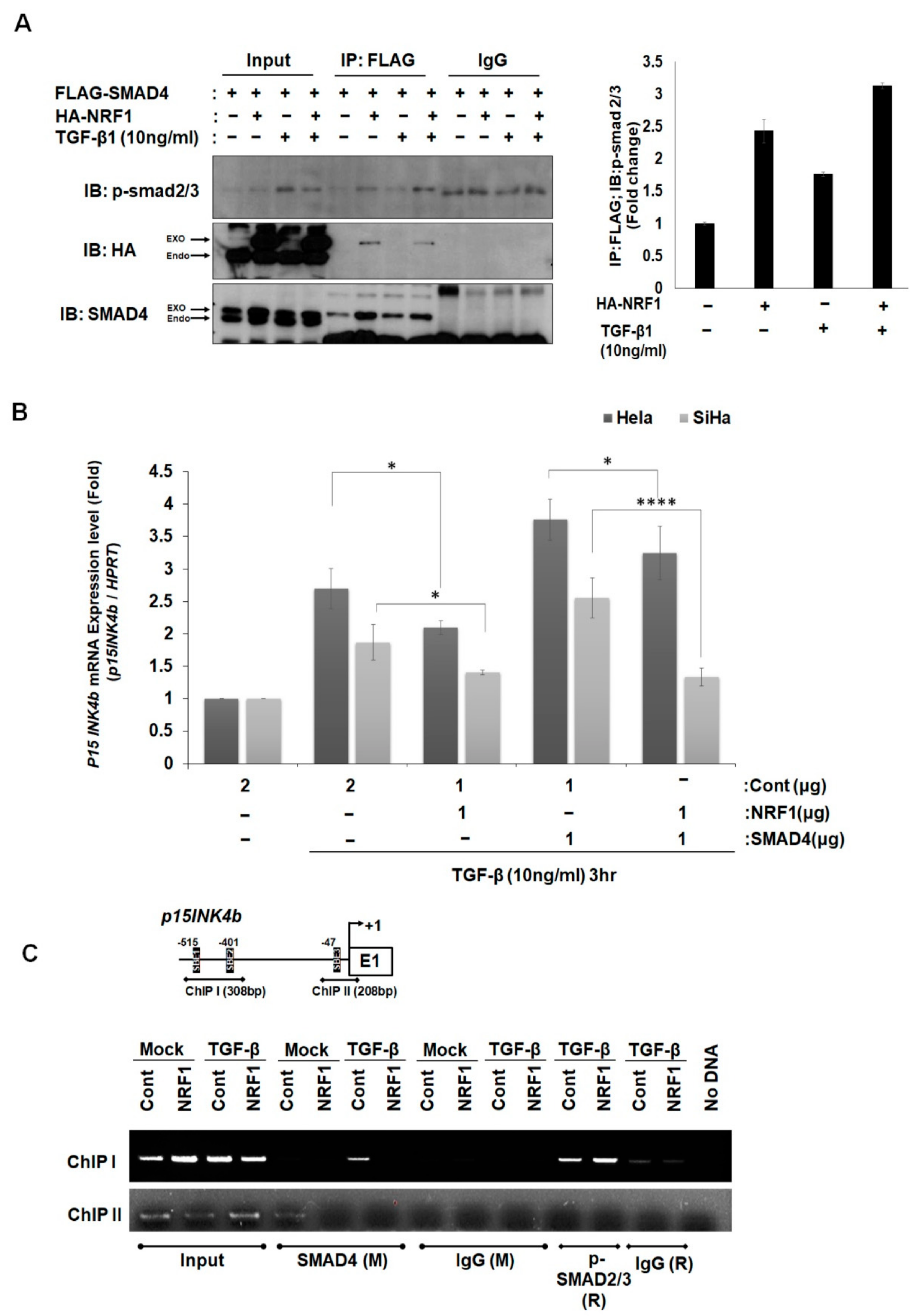
2.3. NRF1 Inhibits mRNA Expression of p15INK4b via SMAD4–NRF1 Interactions
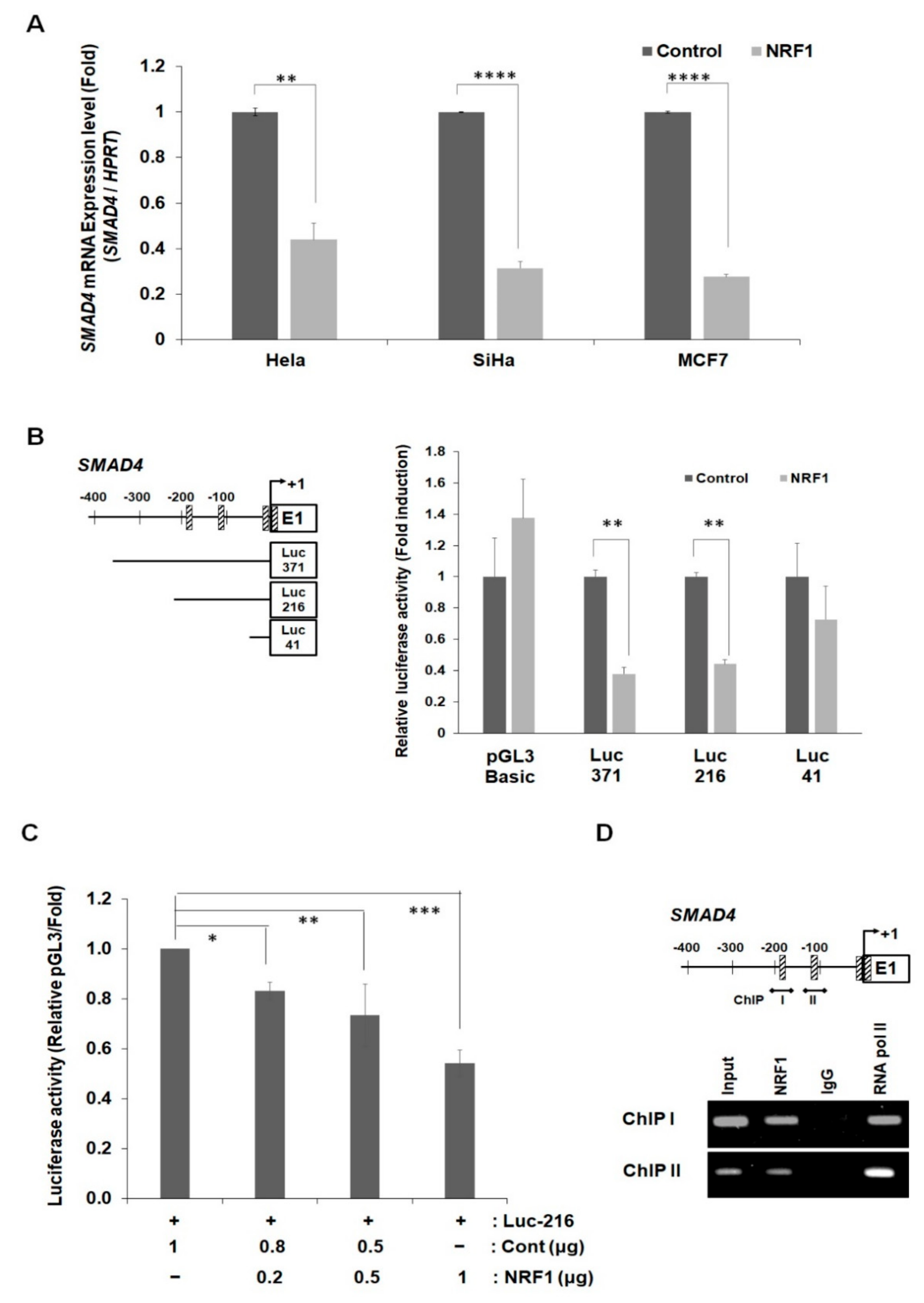
2.4. NRF1 Regulates SMAD4 Expression through Its Function as a Transcription Factor
3. Discussion and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture, Transient Transfection, and Treatments
4.2. Western Blotting Analysis
4.3. Immunoprecipitation (IP) Assay
4.4. Bimolecular Fluorescence Complementation (BiFC) Analysis
4.5. The Proximity Ligation (PLA) Assay
4.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR) Analysis
4.7. Luciferase Reporter Gene Assay
4.8. Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) Assays
4.9. Screening Analysis of Transcription Factor Binding Sites (TFBS)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Massague, J. TGFbeta in Cancer. Cell 2008, 134, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, S.A.; Schutte, M.; Hoque, A.T.; Moskaluk, C.A.; da Costa, L.T.; Rozenblum, E.; Weinstein, C.L.; Fischer, A.; Yeo, C.J.; Hruban, R.H.; et al. DPC4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene at human chromosome 18q21.1. Science 1996, 271, 350–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wotton, D.; Lo, R.S.; Lee, S.; Massague, J. A Smad transcriptional corepressor. Cell 1999, 97, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaki, M.; Kuroki, T. Role of Smad4 (DPC4) inactivation in human cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 306, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobuzio-Donahue, C.A.; Song, J.; Parmiagiani, G.; Yeo, C.J.; Hruban, R.H.; Kern, S.E. Missense mutations of MADH4: Characterization of the mutational hot spot and functional consequences in human tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 1597–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhao, M.; Mishra, L.; Deng, C.-X. The role of TGF-β/SMAD4 signaling in cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.J.; Scarpulla, R.C. Interaction of Nuclear Factors with Multiple Sites in the Somatic Cytochrome-C Promoter—Characterization of Upstream Nrf-1, Atf, and Intron Sp1 Recognition Sequences. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 14361–14368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virbasius, C.M.A.; Virbasius, J.V.; Scarpulla, R.C. Nrf-1, an Activator Involved in Nuclear-Mitochondrial Interactions, Utilizes a New DNA-Binding Domain Conserved in a Family of Developmental Regulators. Gene Dev. 1993, 7, 2431–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virbasius, J.V.; Scarpulla, R.C. Activation of the Human Mitochondrial Transcription Factor a Gene by Nuclear Respiratory Factors—A Potential Regulatory Link between Nuclear and Mitochondrial Gene-Expression in Organelle Biogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 1309–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleyzer, N.; Vercauteren, K.; Scarpulla, R.C. Control of mitochondrial transcription specificity factors (TFB1M and TFB2M) by nuclear respiratory factors (NRF-1 and NRF-2) and PGC-1 family coactivators. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 25, 1354–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, D.P.; Scarpulla, R.C. Transcriptional regulatory circuits controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and function. Gene Dev. 2004, 18, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpulla, R.C. Nuclear control of respiratory gene expression in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biochem. 2006, 97, 673–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cam, H.; Balciunaite, E.; Blais, A.; Spektor, A.; Scarpulla, R.C.; Young, R.; Kluger, Y.; Dynlacht, B.D. A common set of gene regulatory networks links metabolism and growth inhibition. Mol. Cell 2004, 16, 399–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Cuadrado, A.; Martin, M.; Noel, M.; Ruiz-Carrillo, A. Initiation binding repressor, a factor that binds to the transcription initiation site of the histone h5 gene, is a glycosylated member of a family of cell growth regulators [corrected]. Mol. Cell Biol. 1995, 15, 6670–6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhawe, K.; Felty, Q.; Yoo, C.; Ehtesham, Z.N.; Hasnain, S.E.; Singh, V.P.; Mohapatra, I.; Roy, D. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 (NRF1) transcriptional activity-driven gene signature association with severity of astrocytoma and poor prognosis of glioblastoma. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020, 57, 3827–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.J.; Felty, Q.; Poppiti, R.; Jackson, M.R.; Roy, D. Nuclear respiratory factor 1 acting as an oncoprotein drives estrogen-induced breast carcinogenesis. Cells 2018, 7, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cogswell, M.; Hixson, K.; Brooks-Kayal, A.R.; Russek, S.J. Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (NRF-1) controls the activity dependent transcription of the GABA-A receptor beta 1 subunit gene in neurons. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.D.; Handschin, C.; Spiegelman, B.M. Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell Metab. 2005, 1, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handschin, C.; Spiegelman, B.M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1 coactivators, energy homeostasis, and metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 728–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finck, B.N.; Kelly, D.P. PGC-1 coactivators: Inducible regulators of energy metabolism in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.P.; Lin, J.; Zack, D.J.; Qian, J.A. Computational analysis of tissue-specific combinatorial gene regulation: Predicting interaction between transcription factors in human tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 4925–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.D.; Chinenov, Y.; Kerppola, T.K. Visualization of interactions among bZIP and Rel family proteins in living cells using bimolecular fluorescence complementation. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerppola, T.K. Design and implementation of bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) assays for the visualization of protein interactions in living cells. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1278–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Lee, H.S.; Wu, C.F.; Kundu, J.; Park, S.G.; Kim, R.N.; Wang, L.H.; Erkin, O.C.; Choi, J.S.; Chae, S.W.; et al. SMAD4 suppresses AURKA-induced metastatic phenotypes via degradation of AURKA in a TGFbeta-independent manner. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1779–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.B.; Ji, P.; Anish, R.; Jacobson, R.H.; Takada, S. Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase 1 Interacts with Nuclear Respiratory Factor 1 (NRF-1) and Plays a Role in NRF-1 Transcriptional Regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8621–8632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Puigserver, P.; Andersson, U.; Zhang, C.; Adelmant, G.; Mootha, V.; Troy, A.; Cinti, S.; Lowell, B.; Scarpulla, R.C.; et al. Mechanisms controlling mitochondrial biogenesis and respiration through the thermogenic coactivator PGC-1. Cell 1999, 98, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cress, W.D.; Nevins, J.R. A role for a bent DNA structure in E2F-mediated transcription activation. Mol. Cell Biol. 1996, 16, 2119–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Seoane, J.; Pouponnot, C.; Staller, P.; Schader, M.; Eilers, M.; Massague, J. TGF beta influences Myc, Miz-1 and Smad to control the CDK inhibitor p15(INK4b). Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 400–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomis, R.R.; Alarcon, C.; Nadal, C.; Van Poznak, C.; Massague, J. C/EBP beta at the core of the TGF beta cytostatic response and its evasion in metastatic breast cancer cells. Cancer Cell 2006, 10, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staller, P.; Peukert, K.; Kiermaier, A.; Seoane, J.; Lukas, J.; Karsunky, H.; Moroy, T.; Bartek, J.; Massague, J.; Hanel, F.; et al. Repression of p15(INK4b) expression by Myc through association with Miz-1. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2001, 3, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.G.; Li, Z.P.; Lu, Y.N.; Du, R.L.; Katiyar, S.; Yang, J.G.; Fu, M.F.; Leader, J.E.; Quong, A.; Novikoff, P.M.; et al. Cyclin D1 repression of nuclear respiratory factor 1 integrates nuclear DNA synthesis and mitochondrial function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11567–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuezva, J.M.; Krajewska, M.; de Heredia, M.L.; Krajewski, S.; Santamaria, G.; Kim, H.; Zapata, J.M.; Marusawa, H.; Chamorro, M.; Reed, J.C. The bioenergetic signature of cancer: A marker of tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2002, 62, 6674–6681. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, D.J.; Nuyten, D.S.A.; Regev, A.; Lin, M.; Adler, A.S.; Segal, E.; van de Vijver, M.J.; Chang, H.Y. Revealing targeted therapy for human cancer by gene module maps. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbagallo, D.; Caponnetto, A.; Barbagallo, C.; Battaglia, R.; Mirabella, F.; Brex, D.; Stella, M.; Broggi, G.; Altieri, R.; Certo, F.; et al. The GAUGAA Motif Is Responsible for the Binding between circSMARCA5 and SRSF1 and Related Downstream Effects on Glioblastoma Multiforme Cell Migration and Angiogenic Potential. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broggi, G.; Salvatorelli, L.; Barbagallo, D.; Certo, F.; Altieri, R.; Tirrò, E.; Massimino, M.; Vigneri, P.; Guadagno, E.; Maugeri, G.; et al. Diagnostic Utility of the Immunohistochemical Expression of Serine and Arginine Rich Splicing Factor 1 (SRSF1) in the Differential Diagnosis of Adult Gliomas. Cancers 2021, 13, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.S.; Lee, H.S.; Hong, S.; Rajasekaran, N.; Wang, L.H.; Choi, J.S.; Shin, Y.K. Upregulation of SMAD4 by MZF1 inhibits migration of human gastric cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 272–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomis, R.R.; Alarcon, C.; He, W.; Wang, Q.; Seoane, J.; Lash, A.; Massague, J. A FoxO-Smad synexpression group in human keratinocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12747–12752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Gene Name | Protein Name | Z-Score | Molecular Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| CCDC149 | Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 149 | 19.86227 | none |
| TFEB | Transcription factor EB | 13.14539 | Transcription factor activity |
| FAM64A | Protein FAM64A | 11.54105 | none |
| VASH2 | Vasohibin-2 | 9.51351 | Positive regulation of Angiogenesis |
| ABT1 | Activator of basal transcription 1 | 8.0119 | Transcription factor activity |
| ROBO3 | ROBO3 protein | 7.69706 | Neuron migration |
| AEBP2 | Zinc finger protein AEBP2 | 6.16836 | Transcription factor activity |
| RNPC3 | RNA-binding protein 40 | 5.36746 | RNA splicing |
| TFE3 | Transcription factor E3 | 5.11651 | Transcription factor activity |
| AURKA | Aurora kinase A | 4.55737 | Positive regulation of mitosis |
| PHF7 | PHD finger protein 7 | 4.38257 | Zinc ion binding |
| ARHGAP15 | Rho GTPase-activating protein 15 | 4.14593 | small GTPase mediated signal transduction |
| MITF | Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor | 4.07745 | Multicellular organismal development |
| COIL | Coilin | 3.99107 | disulfide oxidoreductase activity |
| RAB24 | Ras-related protein Rab-24 | 3.43295 | small GTPase mediated signal transduction |
| ARHGEF5 | Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor 5 | 3.3522 | Regulation of Rho GTPase activity |
| UCHL3 | Ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L3 | 3.27706 | Ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process |
| IER3 | Radiation-inducible immediate-early gene IEX-1 | 3.0348 | Positive regulation of apoptotic process |
| EIF2S2 | EIF2S2 protein | 2.97858 | Translation initiation factor activity |
| NRF1 | Nuclear respiratory factor 1 | 2.87892 | Generation of precursor metabolites and energy |
| ANXA10 | Annexin A10 | 2.53086 | Calcium-dependent phospholipid binding |
| FN1 | FN1 protein | 2.52421 | None |
| SENP8 | Sentrin-specific protease 8 | 2.40973 | Cysteine-type peptidase activity |
| GNAI2 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-2 | 2.37446 | Signal transducer activity |
| ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | 2.15929 | ATP binding |
| MMAB | Methylmalonic aciduria type B protein | 2.11635 | cob(I)yrinic acid a,c-diamide adenosyltransferase activity |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rajasekaran, N.; Song, K.; Lee, J.-H.; Wei, Y.; Erkin, Ö.C.; Lee, H.; Shin, Y.-K. Nuclear Respiratory Factor-1, a Novel SMAD4 Binding Protein, Represses TGF-β/SMAD4 Signaling by Functioning as a Transcriptional Cofactor. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115595
Rajasekaran N, Song K, Lee J-H, Wei Y, Erkin ÖC, Lee H, Shin Y-K. Nuclear Respiratory Factor-1, a Novel SMAD4 Binding Protein, Represses TGF-β/SMAD4 Signaling by Functioning as a Transcriptional Cofactor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(11):5595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115595
Chicago/Turabian StyleRajasekaran, Nirmal, Kyoung Song, Jin-Hee Lee, Yun Wei, Özgür Cem Erkin, Hunseok Lee, and Young-Kee Shin. 2021. "Nuclear Respiratory Factor-1, a Novel SMAD4 Binding Protein, Represses TGF-β/SMAD4 Signaling by Functioning as a Transcriptional Cofactor" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 11: 5595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115595
APA StyleRajasekaran, N., Song, K., Lee, J.-H., Wei, Y., Erkin, Ö. C., Lee, H., & Shin, Y.-K. (2021). Nuclear Respiratory Factor-1, a Novel SMAD4 Binding Protein, Represses TGF-β/SMAD4 Signaling by Functioning as a Transcriptional Cofactor. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(11), 5595. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22115595







