Canonical and Interior Circular RNAs Function as Competing Endogenous RNAs in Psoriatic Skin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
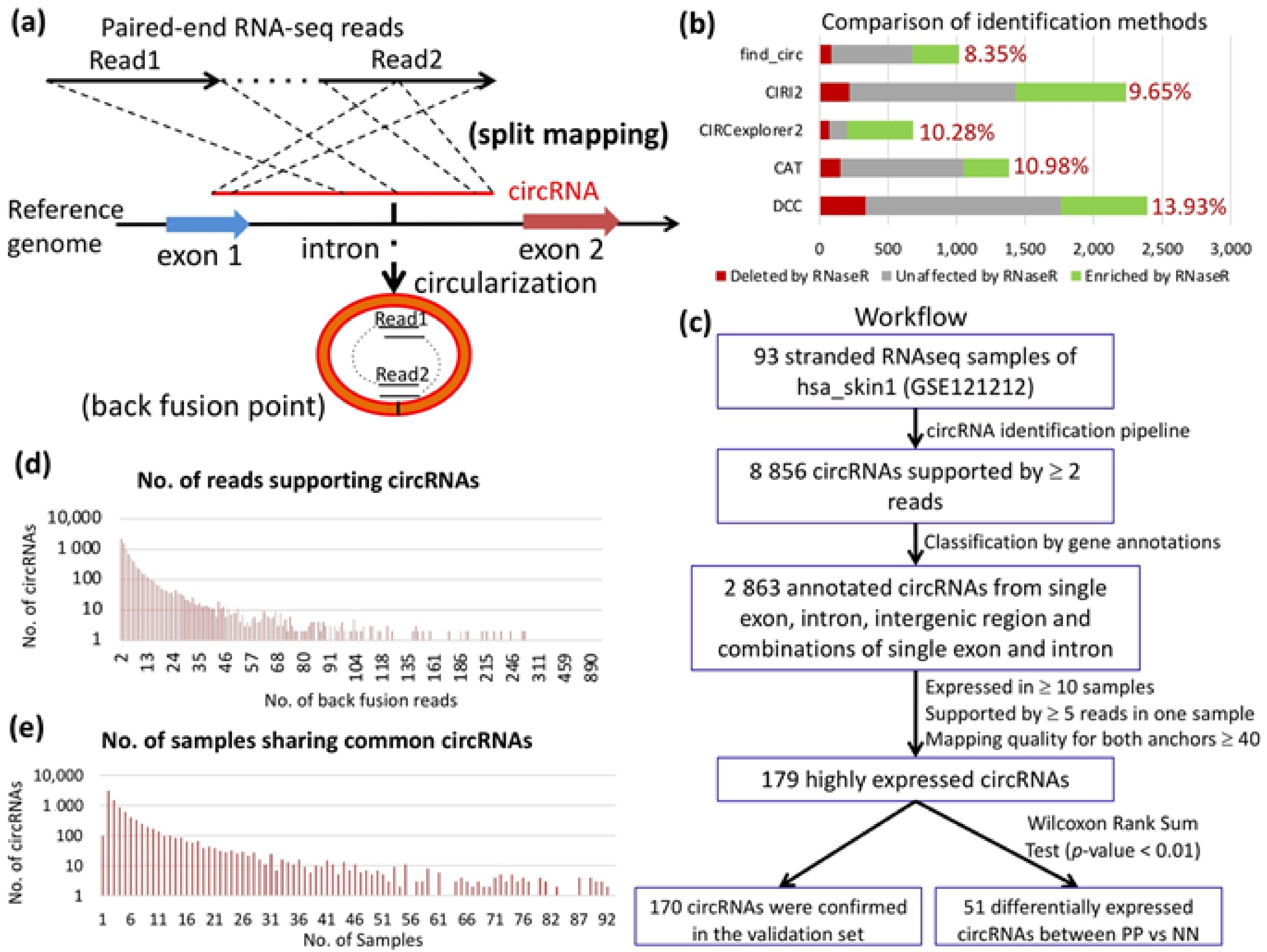
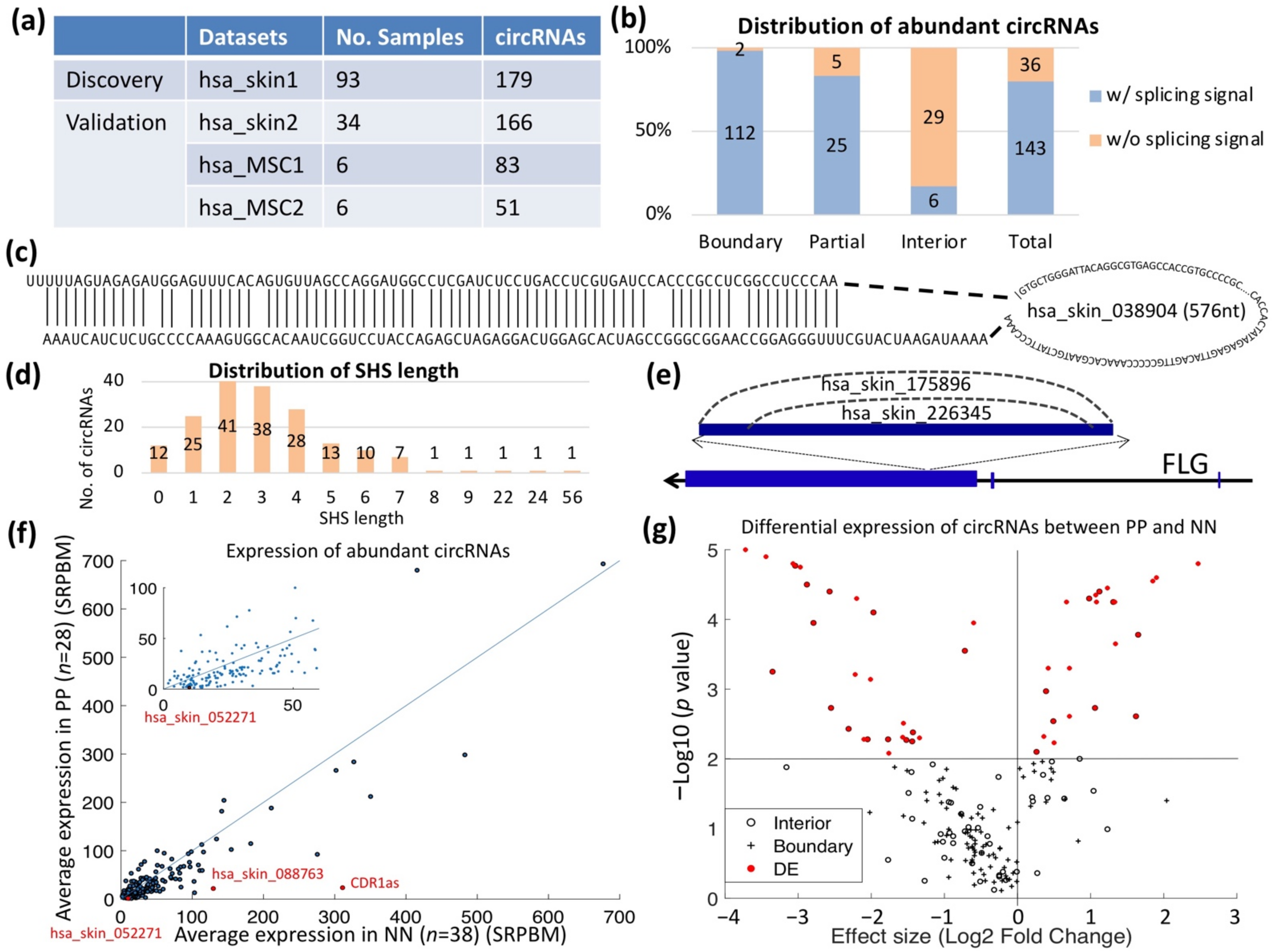
2.1. Detection and Profiling of circRNAs in PS
2.2. circRNAs in PS and their Characteristics
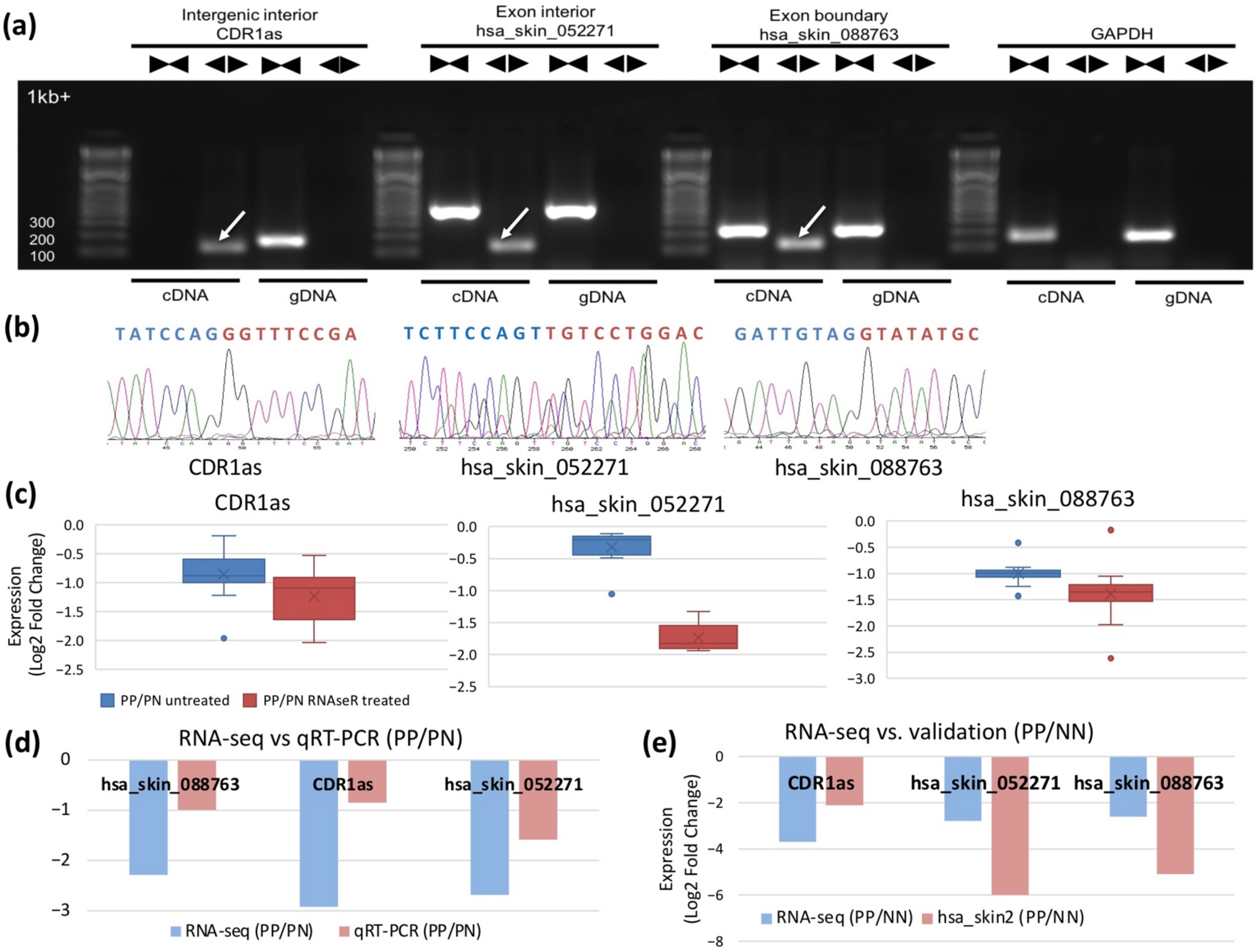
2.3. Aberrantly Expressed circRNAs in PS
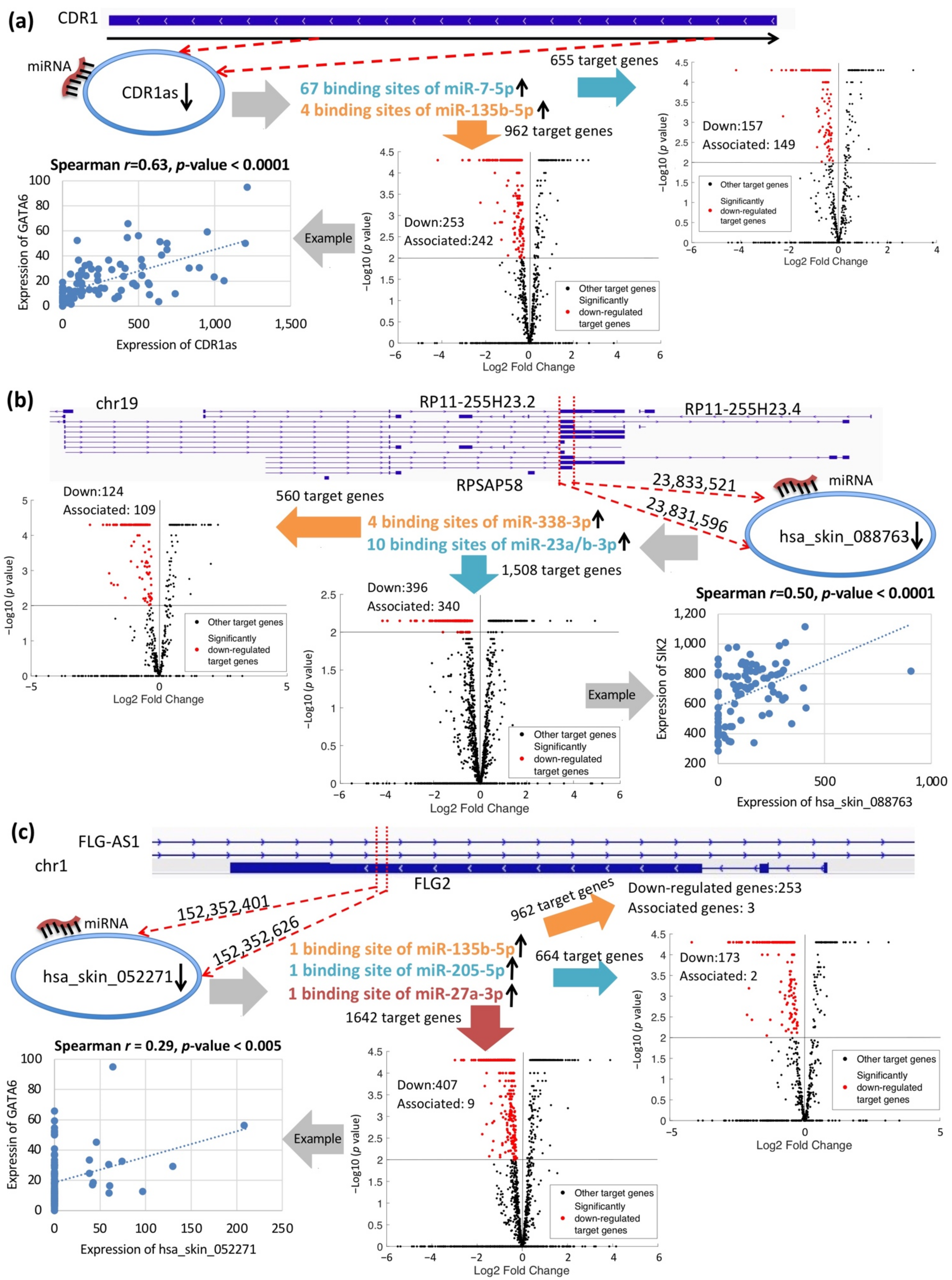
2.4. Putative circRNA Functions in PS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. RNA-seq Data
4.2. Psoriatic Skin Biopsy Samples and Cells for Validation
4.3. RNase R Digestion
4.4. PCR and Sanger Sequencing
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.6. Identification of circRNAs of All Types—The CAT Method
4.7. Identification of Differentially Expressed circRNAs
4.8. Identification of Differentially Expressed Genes
4.9. GO and KEGG Pathway Analyses
4.10. CircRNA-Associated Genes
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Harden, J.L.; Krueger, J.G.; Bowcock, A.M. The immunogenetics of psoriasis: A comprehensive review. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 64, 66–73. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. Global Report on Psoriasis; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Dommasch, E.D.; Shin, D.B.; Azfar, R.S.; Kurd, S.K.; Wang, X.; Troxel, A.B. The risk of stroke in patients with psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2411–2418. [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand, J.M.; Neimann, A.L.; Shin, D.B.; Wang, X.; Margolis, D.J.; Troxel, A.B. Risk of myocardial infarction in patients with psoriasis. JAMA 2006, 296, 1735–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Han, J.; Hu, F.B.; Curhan, G.C.; Qureshi, A.A. Psoriasis and risk of type 2 diabetes among women and men in the United States: A population-based cohort study. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sommer, D.M.; Jenisch, S.; Suchan, M.; Christophers, E.; Weichenthal, M. Increased prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2007, 298, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisondi, P.; Fostini, A.C.; Fossà, I.; Girolomoni, G.; Targher, G. Psoriasis and the metabolic syndrome. Clin. Dermatol. 2018, 36, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fuxench, Z.C.C.; Shin, D.B.; Beatty, A.O.; Gelfand, J.M. The risk of cancer in patients with psoriasis: A population-based cohort study in the health improvement network. JAMA Dermatol. 2016, 152, 282–290. [Google Scholar]
- Trafford, A.M.; Parisi, R.; Kontopantelis, E.; Griffiths, C.E.; Ashcroft, D.M. Association of Psoriasis With the Risk of Developing or Dying of Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol. 2019, 155, 1390–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, A.; Capon, F.; Spencer, C.C.; Knight, J.; Weale, M.E.; Allen, M.H.; Barton, A.; Band, G.; Bellenguez, C.; Bergboer, J.G. A genome-wide association study identifies new psoriasis susceptibility loci and an interaction between HLA-C and ERAP1. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 985. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Huang, W.; Yang, S.; Sun, L.-D.; Zhang, F.-Y.; Zhu, Q.-X.; Zhang, F.-R.; Zhang, C.; Du, W.-H.; Pu, X.-M. Psoriasis genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants within LCE gene cluster at 1q21. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 205. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Zhang, W. MicroRNAs in normal and psoriatic skin. Physiol. Genom. 2013, 46, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonkoly, E.; Wei, T.; Janson, P.C.; Sääf, A.; Lundeberg, L.; Tengvall-Linder, M.; Norstedt, G.; Alenius, H.; Homey, B.; Scheynius, A. MicroRNAs: Novel regulators involved in the pathogenesis of psoriasis? PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Joyce, C.E.; Bowcock, A.M.; Zhang, W. Noncanonical microRNAs and endogenous siRNAs in normal and psoriatic human skin. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 22, 737–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, C.E.; Zhou, X.; Xia, J.; Ryan, C.; Thrash, B.; Menter, A.; Zhang, W.; Bowcock, A.M. Deep sequencing of small RNAs from human skin reveals major alterations in the psoriasis miRNAome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4025–4040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Iyer, M.K.; Stuart, P.E.; Swindell, W.R.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Tejasvi, T.; Sarkar, M.K.; Li, B.; Ding, J.; Voorhees, J.J. Analysis of long non-coding RNAs highlights tissue-specific expression patterns and epigenetic profiles in normal and psoriatic skin. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meisgen, F.; Xu, N.; Wei, T.; Janson, P.C.; Obad, S.; Broom, O.; Nagy, N.; Kauppinen, S.; Kemény, L.; Ståhle, M. MiR-21 is up-regulated in psoriasis and suppresses T cell apoptosis. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 312–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Meisgen, F.; Butler, L.M.; Han, G.; Wang, X.-J.; Söderberg-Nauclér, C.; Ståhle, M.; Pivarcsi, A.; Sonkoly, E. MicroRNA-31 is overexpressed in psoriasis and modulates inflammatory cytokine and chemokine production in keratinocytes via targeting serine/threonine kinase 40. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkoly, E.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Pivarcsi, A.; Polyanka, H.; Kenderessy-Szabo, A.; Molnar, G.; Szentpali, K.; Bari, L.; Megyeri, K.; Mandi, Y. Identification and characterization of a novel, psoriasis susceptibility-related noncoding RNA gene, PRINS. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 24159–24167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Széll, M.; Danis, J.; Bata-Csörgő, Z.; Kemény, L. PRINS, a primate-specific long non-coding RNA, plays a role in the keratinocyte stress response and psoriasis pathogenesis. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2016, 468, 935–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, H.; Xie, N.; Tan, Z.; Banerjee, S.; Thannickal, V.J.; Abraham, E.; Liu, G. The human long noncoding RNA lnc-IL 7 R regulates the inflammatory response. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 2085–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Tang, Q.; Sharma, S.; Yu, F.; Escobar, T.M.; Muljo, S.A.; Zhu, J.; Zhao, K. Expression and regulation of intergenic long noncoding RNAs during T cell development and differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salzman, J.; Gawad, C.; Wang, P.L.; Lacayo, N.; Brown, P.O. Circular RNAs are the predominant transcript isoform from hundreds of human genes in diverse cell types. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30733. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Sun, X.; Li, N.; Wang, W.; Kuang, D.; Tong, P.; Han, Y.; Dai, J. CircRNAs in the tree shrew (Tupaia belangeri) brain during postnatal development and aging. Aging 2018, 10, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.L.; Bao, Y.; Yee, M.-C.; Barrett, S.P.; Hogan, G.J.; Olsen, M.N.; Dinneny, J.R.; Brown, P.O.; Salzman, J. Circular RNA is expressed across the eukaryotic tree of life. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.-L. The biogenesis, functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol. Cell 2018, 71, 428–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Wiklund, E.D.; Bramsen, J.B.; Villadsen, S.B.; Statham, A.L.; Clark, S.J.; Kjems, J. miRNA-dependent gene silencing involving Ago2-mediated cleavage of a circular antisense RNA. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4414–4422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, X.; Mo, Y.; Fan, C.; Xiong, F.; Ren, D.; Ye, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pamudurti, N.R.; Bartok, O.; Jens, M.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Stottmeister, C.; Ruhe, L.; Hanan, M.; Wyler, E.; Perez-Hernandez, D.; Ramberger, E. Translation of circRNAs. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 9–21.e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Fan, X.; Mao, M.; Song, X.; Wu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, Y.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.-L.; Wang, Y. Extensive translation of circular RNAs driven by N 6-methyladenosine. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legnini, I.; Di Timoteo, G.; Rossi, F.; Morlando, M.; Briganti, F.; Sthandier, O.; Fatica, A.; Santini, T.; Andronache, A.; Wade, M. Circ-ZNF609 is a circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 22–37.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukiw, W. Circular RNA (circRNA) in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Front. Genet. 2013, 4, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Alexandrov, P.; Jaber, V.; Lukiw, W. Deficiency in the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme UBE2A in Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is linked to deficits in a natural circular miRNA-7 sponge (circRNA; ciRS-7). Genes 2016, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.-B.; Huang, G.-X.; Fu, Q.; Han, B.; Lu, J.-J.; Chen, A.-M.; Zhu, L. circRNA. 33186 Contributes to the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis by Sponging miR-127-5p. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altesha, M.A.; Ni, T.; Khan, A.; Liu, K.; Zheng, X. Circular RNA in cardiovascular disease. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 5588–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Weng, X.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, W.; Gan, T.; Xu, D. Circular RNAs in cardiovascular disease: An overview. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.-H.; Sun, D.-W.; Hou, J.-C.; Ji, Z.-L. CircRNA: A novel type of biomarker for cancer. Breast Cancer 2018, 25, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, J.; Chen, K.; Dong, X.; Xu, X.; Jin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, W.; Han, Y.; Shao, L.; Gao, Y. Genome-wide identification of cancer-specific alternative splicing in circRNA. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.; Ding, J.; Yan, J.; Li, R.; Jiao, J.; Sun, Q. Circular RNA expression profile and analysis of their potential function in psoriasis. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 50, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Chang, W.; Li, J.; Cheng, Y.; Dang, E.; Yang, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, K. Mesenchymal stem cells in psoriatic lesions affect the skin microenvironment through circular RNA. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldovan, L.-I.; Hansen, T.B.; Venø, M.T.; Okholm, T.L.H.; Andersen, T.L.; Hager, H.; Iversen, L.; Kjems, J.; Johansen, C.; Kristensen, L.S. High-throughput RNA sequencing from paired lesional-and non-lesional skin reveals major alterations in the psoriasis circRNAome. BMC Med. Genom. 2019, 12, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Tian, C.; Tian, G.; He, M.; Gao, L.; Chen, L.; Li, T.; Peng, H.; et al. Interior circular RNA. RNA Biol. 2020, 17, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, F. Circular RNA identification based on multiple seed matching. Brief. Bioinform. 2018, 19, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-O.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.-L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.-L.; Yang, L. Diverse alternative back-splicing and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Metge, F.; Dieterich, C. Specific identification and quantification of circular RNAs from sequencing data. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1094–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.-S.; Wilusz, J.E. An improved method for circular RNA purification using RNase R that efficiently removes linear RNAs containing G-quadruplexes or structured 3’ ends. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 8755–8769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, T.B.; Venø, M.T.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Comparison of circular RNA prediction tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e58-e58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.-R.; Nam, K.-M.; Park, S.-J.; Kim, D.-S.; Huh, C.-H.; Park, W.-Y.; Park, K.-C. Suppression of miR135b increases the proliferative potential of normal human keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.-H.; Son, E.D.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, S.H.; Bae, I.-H.; Lee, T.R. EGR3 Is a Late Epidermal Differentiation Regulator that Establishes the Skin-Specific Gene Network. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 615–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanati, A.; Consales, V.; Orciani, M.; Giuliodori, K.; Ganzetti, G.; Bobyr, I.; Sorgentoni, G.; di Primio, R.; Offidani, A. Role of mesenchymal stem cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis: Current perspectives. Psoriasis 2017, 7, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rácz, E.; Kurek, D.; Kant, M.; Baerveldt, E.M.; Florencia, E.; Mourits, S.; de Ridder, D.; Laman, J.D.; van der Fits, L.; Prens, E.P. GATA3 expression is decreased in psoriasis and during epidermal regeneration; induction by narrow-band UVB and IL-4. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19806. [Google Scholar]
- Løvendorf, M.B.; Zibert, J.R.; Gyldenløve, M.; Røpke, M.A.; Skov, L. MicroRNA-223 and miR-143 are important systemic biomarkers for disease activity in psoriasis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 75, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Huang, J.; Zhao, X.; Lu, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.O.; Shi, Y.; Wang, X.; Lai, Y.; Dong, C. Interleukin-17 receptor D constitutes an alternative receptor for interleukin-17A important in psoriasis-like skin inflammation. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaau9657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundarrajan, S.; Lulu, S.; Arumugam, M. Insights into protein interaction networks reveal non-receptor kinases as significant druggable targets for psoriasis. Gene 2015, 566, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, T.; Mark, E.B.; Henriksson, R.; Hedman, H. Redistribution of LRIG proteins in psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1192–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundberg, T.B.; Liang, Y.; Wu, H.; Choi, H.G.; Kim, N.D.; Sim, T.; Johannessen, L.; Petrone, A.; Khor, B.; Graham, D.B. Development of chemical probes for investigation of salt-inducible kinase function in vivo. ACS Chem. Biol. 2016, 11, 2105–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilhar, A.; Yaniv, R.; Assy, B.; Serafimovich, S.; Ullmann, Y.; Kalish, R.S. Fas pulls the trigger on psoriasis. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 168, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J.; Damgaard, C.K. Circular RNA and miR-7 in cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5609–5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Yang, X.; Yuan, W.; Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Yang, H.; Li, P. CircRNA-Cdr1as exerts anti-oncogenic functions in bladder Cancer by sponging MicroRNA-135a. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1606–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Guo, S.; Li, W.; Yu, P. The circular RNA Cdr1as, via miR-7 and its targets, regulates insulin transcription and secretion in islet cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albanesi, C.; Madonna, S.; Gisondi, P.; Girolomoni, G. The interplay between keratinocytes and immune cells in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Gao, S.; Song, D.; Feng, Y. MiR-135b-5p promotes viability, proliferation, migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells by targeting Krüppel-like factor 4 (KLF4). Arch. Med Sci. AMS 2020, 16, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segre, J.A.; Bauer, C.; Fuchs, E. Klf4 is a transcription factor required for establishing the barrier function of the skin. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, C.Y.; Chen, L.; Liu, C.; Zhu, Q.H.; Fan, L. Widespread noncoding circular RNA s in plants. New Phytol. 2015, 208, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnerio, J.; Bezzi, M.; Jeong, J.C.; Paffenholz, S.V.; Berry, K.; Naldini, M.M.; Lo-Coco, F.; Tay, Y.; Beck, A.H.; Pandolfi, P.P. Oncogenic role of fusion-circRNAs derived from cancer-associated chromosomal translocations. Cell 2016, 165, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panda, A.C.; Gorospe, M. Detection and analysis of circular RNAs by RT-PCR. Bio-Protocol 2018, 8, e2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langmead, B.; Trapnell, C.; Pop, M.; Salzberg, S.L. Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences to the human genome. Genome Biol. 2009, 10, R25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, E.; Smith, C.P. RankProdIt: A web-interactive Rank Products analysis tool. BMC Res. Notes 2010, 3, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trapnell, C.; Roberts, A.; Goff, L.; Pertea, G.; Kim, D.; Kelley, D.R.; Pimentel, H.; Salzberg, S.L.; Rinn, J.L.; Pachter, L. Differential gene and transcript expression analysis of RNA-seq experiments with TopHat and Cufflinks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhou, B.; Pache, L.; Chang, M.; Khodabakhshi, A.H.; Tanaseichuk, O.; Benner, C.; Chanda, S.K. Metascape provides a biologist-oriented resource for the analysis of systems-level datasets. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths-Jones, S.; Grocock, R.J.; Van Dongen, S.; Bateman, A.; Enright, A.J. miRBase: microRNA sequences, targets and gene nomenclature. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, D140–D144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enright, A.J.; John, B.; Gaul, U.; Tuschl, T.; Sander, C.; Marks, D.S. MicroRNA targets in Drosophila. Genome Biol. 2003, 5, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Rodriguez, E.; Degenhardt, F.; Baurecht, H.; Wehkamp, U.; Volks, N.; Szymczak, S.; Swindell, W.R.; Sarkar, M.K.; Raja, K. Atopic Dermatitis Is an IL-13–Dominant Disease with Greater Molecular Heterogeneity Compared to Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, R.; Gupta, R.; Lai, K.; Chopra, N.; Arron, S.T.; Liao, W. Network analysis of psoriasis reveals biological pathways and roles for coding and long non-coding RNAs. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Ahn, R.; Lai, K.; Mullins, E.; Debbaneh, M.; Dimon, M.; Arron, S.; Liao, W. Landscape of long noncoding RNAs in psoriatic and healthy skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, X.; Frost, J.; Bowcock, A.; Zhang, W. Canonical and Interior Circular RNAs Function as Competing Endogenous RNAs in Psoriatic Skin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 5182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105182
Liu X, Frost J, Bowcock A, Zhang W. Canonical and Interior Circular RNAs Function as Competing Endogenous RNAs in Psoriatic Skin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021; 22(10):5182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105182
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Xiaoxin, Jacqueline Frost, Anne Bowcock, and Weixiong Zhang. 2021. "Canonical and Interior Circular RNAs Function as Competing Endogenous RNAs in Psoriatic Skin" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 22, no. 10: 5182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105182
APA StyleLiu, X., Frost, J., Bowcock, A., & Zhang, W. (2021). Canonical and Interior Circular RNAs Function as Competing Endogenous RNAs in Psoriatic Skin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(10), 5182. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22105182






