X-linked Retinitis Pigmentosa in Japan: Clinical and Genetic Findings in Male Patients and Female Carriers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Potentially Pathogenic Mutations in the Subjects
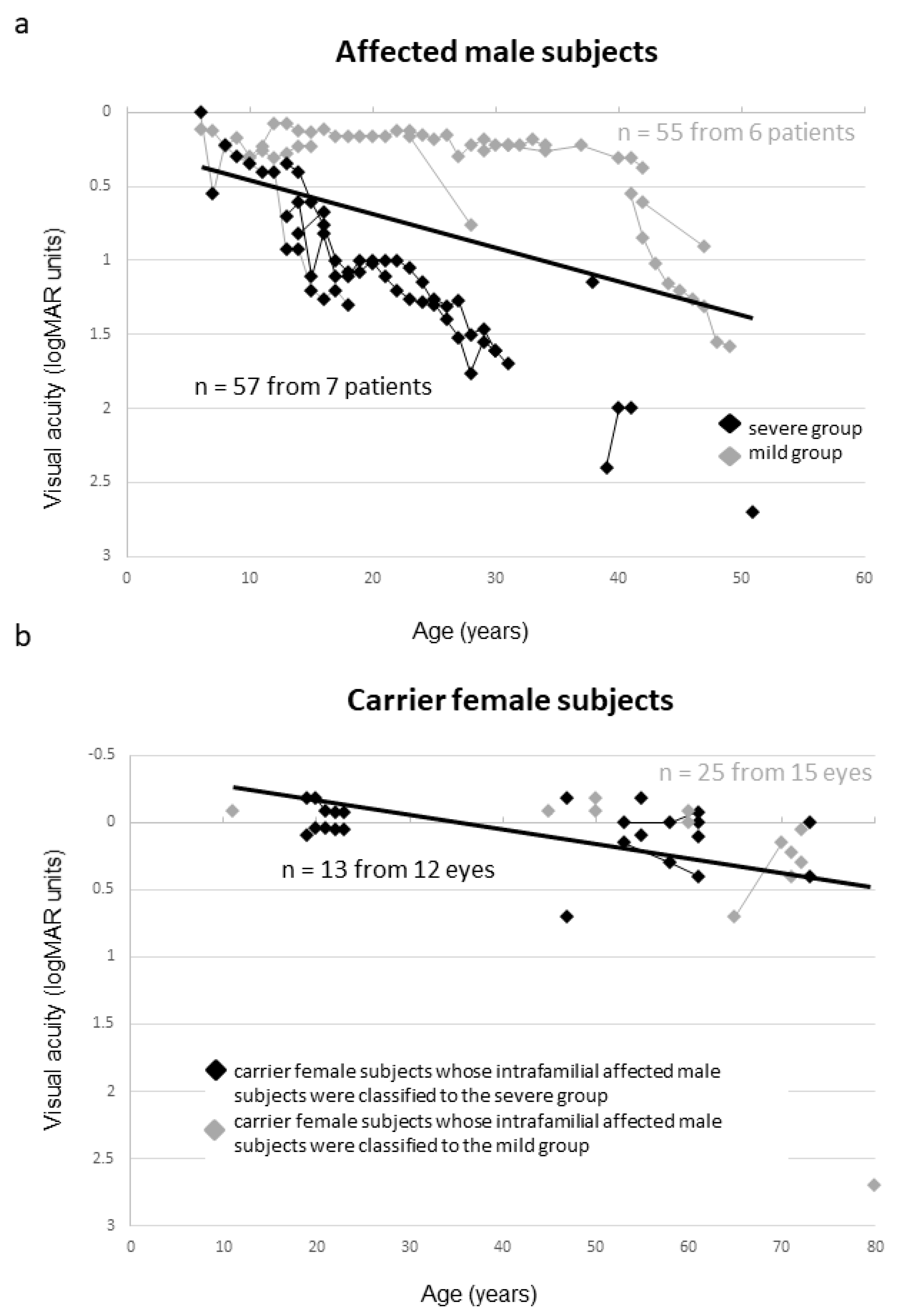
2.2. Clinical Findings of Affected Male Subjects
2.3. Clinical Findings of Female Carriers
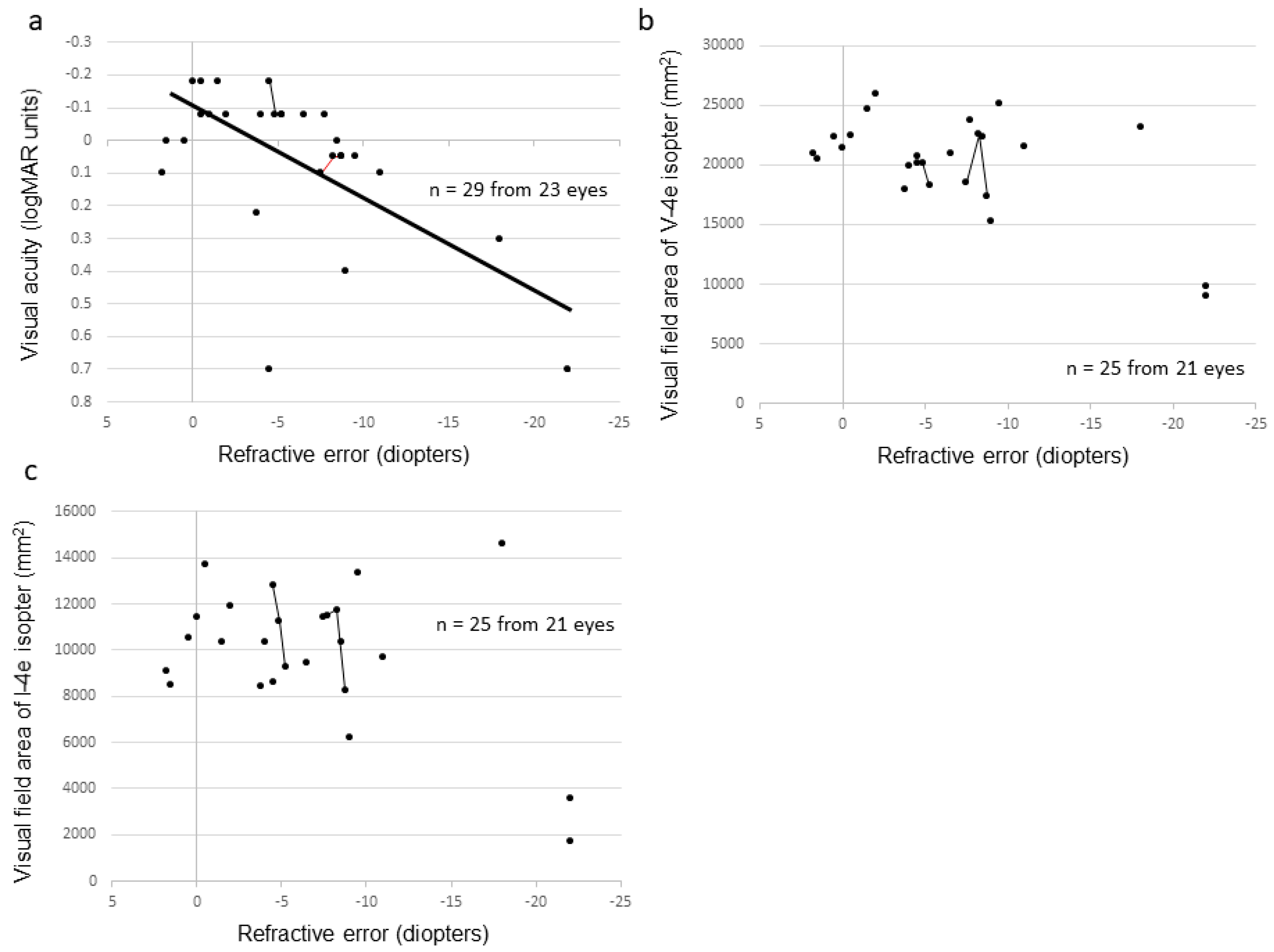
2.4. Phenotype-Genotype Correlation
2.5. Severity Among the Female Carriers
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethics Statement
4.2. Patient Recruitment
4.3. Clinical Examination
4.4. Statistical Analysis
4.5. TS and Bioinformatics Analysis
4.6. Sanger Sequencing
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chizzolini, M.; Galan, A.; Milan, E.; Sebastiani, A.; Costagliola, C.; Parmeggiani, F. Good epidemiologic practice in retinitis pigmentosa: From phenotyping to biobanking. Curr. Genomics 2011, 12, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Breuer, D.K.; Yashar, B.M.; Filippova, E.; Hiriyanna, S.; Lyons, R.H.; Mears, A.J.; Asaye, B.; Acar, C.; Vervoort, R.; Wright, A.F.; et al. A comprehensive mutation analysis of RP2 and RPGR in a North American cohort of families with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 70, 1545–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelletier, V.; Jambou, M.; Delphin, N.; Zinovieva, E.; Stum, M.; Gigarel, N.; Dollfus, H.; Hamel, C.; Toutain, A.; Dufier, J.L.; et al. Comprehensive survey of mutations in RP2 and RPGR in patients affected with distinct retinal dystrophies: Genotype-phenotype correlations and impact on genetic counseling. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vervoort, R.; Lennon, A.; Bird, A.C.; Tulloch, B.; Axton, R.; Miano, M.G.; Meindl, A.; Meitinger, T.; Ciccodicola, A.; Wright, A.F. Mutational hot spot within a new RPGR exon in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neidhardt, J.; Glaus, E.; Lorenz, B.; Netzer, C.; Li, Y.; Schambeck, M.; Wittmer, M.; Feil, S.; Kirschner-Schwabe, R.; Rosenberg, T.; et al. Identification of novel mutations in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa families and implications for diagnostic testing. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar]
- Hardcastle, A.J.; Thiselton, D.L.; Van Maldergem, L.; Saha, B.K.; Jay, M.; Plant, C.; Taylor, R.; Bird, A.C.; Bhattacharya, C. Mutations in the RP2 gene cause disease in 10% of families with familial X-linked retinitis pigmentosa assessed in this study. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 64, 1210–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branham, K.; Othman, M.; Brumm, M.; Karoukis, A.J.; Atmaca-Sonmez, P.; Yashar, B.M.; Schwartz, S.B.; Stover, N.B.; Trzupek, K.; Wheaton, D. Mutations in RPGR and RP2 account for 15% of male subjects with simplex retinal degenerative disease. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 8232–8237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berson, E.L.; Gouras, P.; Gunkel, R.D.; Myrianthopoulos, N.C. Rod and cone responses in sex-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1969, 81, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bird, A.C. X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1975, 59, 177–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talib, M.; van Schooneveld, M.J.; Van Cauwenbergh, C.; Wijnholds, J.; Ten Brink, J.B.; Florijn, R.J.; Schalij-Delfos, N.E.; Dagnelie, G.; van Genderen, M.M.; De Baere, E.; et al. The Spectrum of structural and functional abnormalities in female carriers of pathogenic variants in the RPGR. Gene Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2018, 59, 4123–4133. [Google Scholar]
- Sharon, D.; Sandberg, M.A.; Rabe, V.W.; Stillberger, M.; Dryja, T.P.; Berson, E.L. RP2 and RPGR mutations and clinical correlations in patients with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 73, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andréasson, S.; Breuer, D.K.; Eksandh, L.; Ponjavic, V.; Frennesson, C.; Hiriyanna, S.; Filippova, E.; Yashar, B.M.; Swaroop, A. Clinical studies of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa in three Swedish families with newly identified mutations in the RP2 and RPGR-ORF15 genes. Ophthalmic Genet. 2003, 24, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Yin, X.; Feng, L.; You, D.; Wu, L.; Chen, N.; Li, A.; Li, G.; Ma, Z. Novel mutations of RPGR in Chinese retinitis pigmentosa patients and the genotype-phenotype correlation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.B.; Liu, X.Q.; Hayakawa, M.; Murakami, A.; Nao-i, N. Mutational analysis of RPGR and RP2 genes in Japanese patients with retinitis pigmentosa: Identification of four mutations. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 1167–1174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Nakazawa, M.; Abe, T.; Tamai, M. A new Leu253Arg mutation in the RP2 gene in a Japanese family with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Oishi, M.; Oishi, A.; Gotoh, N.; Ogino, K.; Higasa, K.; Iida, K.; Makiyama, Y.; Morooka, S.; Matsuda, F.; Yoshimura, N. Comprehensive molecular diagnosis of a large cohort of Japanese retinitis pigmentosa and Usher syndrome patients by next-generation sequencing. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 7369–7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayakawa, M.; Fujiki, K.; Kanai, A.; Matsumura, M.; Honda, Y.; Sakaue, H.; Tamai, M.; Sakuma, T.; Tokoro, T.; Yura, T.; et al. Multicenter genetic study of retinitis pigmentosa in Japan: I. Genetic heterogeneity in typical retinitis pigmentosa. Jpn. J. Ophthalmol. 1997, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawlyk, B.S.; Bulgakov, O.V.; Sun, X.; Adamian, M.; Shu, X.; Smith, A.J.; Berson, E.L.; Ali, R.R.; Khani, S.; Wright, A.F.; et al. Photoreceptor rescue by an abbreviated human RPGR gene in a murine model of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Hiriyanna, S.; Qian, H.; Mookherjee, S.; Campos, M.M.; Gao, C.; Fariss, R.; Sieving, P.A.; Li, T.; Colosi, P.; et al. A long-term efficacy study of gene replacement therapy for RPGR-associated retinal degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 3956–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mookherjee, S.; Hiriyanna, S.; Kaneshiro, K.; Li, L.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Qian, H.; Li, T.; Khanna, H.; Colosi, P.; et al. Long-term rescue of cone photoreceptor degeneration in retinitis pigmentosa 2 (RP2)-knockout mice by gene replacement therapy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 6446–6458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosono, K.; Nishina, S.; Yokoi, T.; Katagiri, S.; Saitsu, H.; Kurata, K.; Miyamichi, D.; Hikoya, A.; Mizobuchi, K.; Nakano, T.; et al. Molecular diagnosis of 34 Japanese families with Leber congenital amaurosis using targeted next generation sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 8279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasundera, T.; Branham, K.E.; Othman, M.; Rhoades, W.R.; Karoukis, A.J.; Khanna, H.; Swaroop, A.; Heckenlively, J.R. RP2 phenotype and pathogenetic correlations in X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2010, 128, 915–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mears, A.J.; Gieser, L.; Yan, D.; Chen, C.; Fahrner, S.; Hiriyanna, S.; Fujita, R.; Jacobson, S.G.; Sieving, P.A.; Swaroop, A. Protein-truncation mutations in the RP2 gene in a North American cohort of families with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1999, 64, 897–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miano, M.G.; Testa, F.; Filippini, F.; Trujillo, M.; Conte, I.; Lanzara, C.; Millán, J.M.; De Bernardo, C.; Grammatico, B.; Mangino, M.; et al. Identification of novel RP2 mutations in a subset of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa families and prediction of new domains. Hum. Mutat. 2001, 18, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grover, S.; Fishman, G.A.; Anderson, R.J.; Lindeman, M. A longitudinal study of visual function in carriers of X-linked recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmology 2002, 109, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Xu, S.; Li, H.; Soens, Z.T.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Dong, F.; Chen, R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Diagnosis of a large Chinese Leber congenital amaurosis cohort. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 3642–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Sun, V.; Tuan, H.F.; Keser, V.; Wang, K.; Ren, H.; Lopez, I.; Zaneveld, J.E.; Siddiqui, S.; et al. Comprehensive molecular diagnosis of 179 Leber congenital amaurosis and juvenile retinitis pigmentosa patients by targeted next generation sequencing. J. Med. Genet. 2013, 50, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comander, J.; Weigel-DiFranco, C.; Sandberg, M.A.; Berson, E.L. Visual function in carriers of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 1899–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tzu, J.H.; Arguello, T.; Berrocal, A.M.; Berrocal, M.; Weisman, A.D.; Liu, M.; Hess, D.; Caputo, M.; Goldberg, J.L.; Feuer, W.J.; et al. Clinical and electrophysiologic characteristics of a large kindred with x-linked retinitis pigmentosa associated with the RPGR locus. Ophthalmic Genet. 2015, 36, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawada, A.; Tomidokoro, A.; Araie, M.; Iwase, A.; Yamamoto, T.; Tajimi Study Group. Refractive errors in an elderly Japanese population: The Tajimi study. Ophthalmology 2008, 115, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berson, E.L.; Rosen, J.B.; Simonoff, E.A. Electroretinographic testing as an aid in detection of carriers of X-chromosome-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1979, 87, 460–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegscheider, E.; Preising, M.N.; Lorenz, B. Fundus autofluorescence in carriers of X-linked recessive retinitis pigmentosa associated with mutations in RPGR, and correlation with electrophysiological and psychophysical data. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2004, 242, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogino, K.; Oishi, M.; Oishi, A.; Morooka, S.; Sugahara, M.; Gotoh, N.; Kurimoto, M.; Yoshimura, N. Radial fundus autofluorescence in the periphery in patients with X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2015, 9, 1467–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acton, J.H.; Greenberg, J.P.; Greenstein, V.C.; Marsiglia, M.; Tabacaru, M.; Theodore Smith, R.; Tsang, S.H. Evaluation of multimodal imaging in carriers of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Exp. Eye. Res. 2013, 113, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genead, M.A.; Fishman, G.A.; Lindeman, M. Structural and functional characteristics in carriers of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa with a tapetal-like reflex. Retina 2010, 30, 1726–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, S.G.; Yagasaki, K.; Feuer, W.J.; Román, A.J. Interocular asymmetry of visual function in heterozygotes of X-linked retinitis pigmentosa. Exp. Eye. Res. 1989, 48, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, C.; Feltgen, N.; Junker, B.; Schulze-Bonsel, K.; Bach, M. Resolving the clinical acuity categories “hand motion” and “counting fingers” using the Freiburg Visual Acuity Test (FrACT). Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 247, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Institutes of Health. ImageJ. Available online: http://rsbweb.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 6 October 2018).
- Daiger, S.D.; Sullivan, L.S.; Bowne, S.J. The Retinal Information Network. The University of Texas Health Science Center, USA. Available online: http://www.sph.uth.tmc.edu/Retnet/ (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- The Human Gene Mutation Database. Institute of Medical Genetics in Cardiff. Available online: http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/index.php (accessed on 16 October 2018).
- Kurata, K.; Hosono, K.; Hotta, Y. Clinical and genetic findings of a Japanese patient with RP1-related autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2018, 137, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, K.; Harada, Y.; Kurata, K.; Hikoya, A.; Sato, M.; Minoshima, S.; Hotta, Y. Novel GUCY2D gene mutations in Japanese male twins with Leber congenital amaurosis. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 2015, 693468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neveling, K.; Collin, R.W.; Gilissen, C.; van Huet, R.A.; Visser, L.; Kwint, M.P.; Gijsen, S.J.; Zonneveld, M.N.; Wieskamp, N.; de Ligt, J.; et al. Next-generation genetic testing for retinitis pigmentosa. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
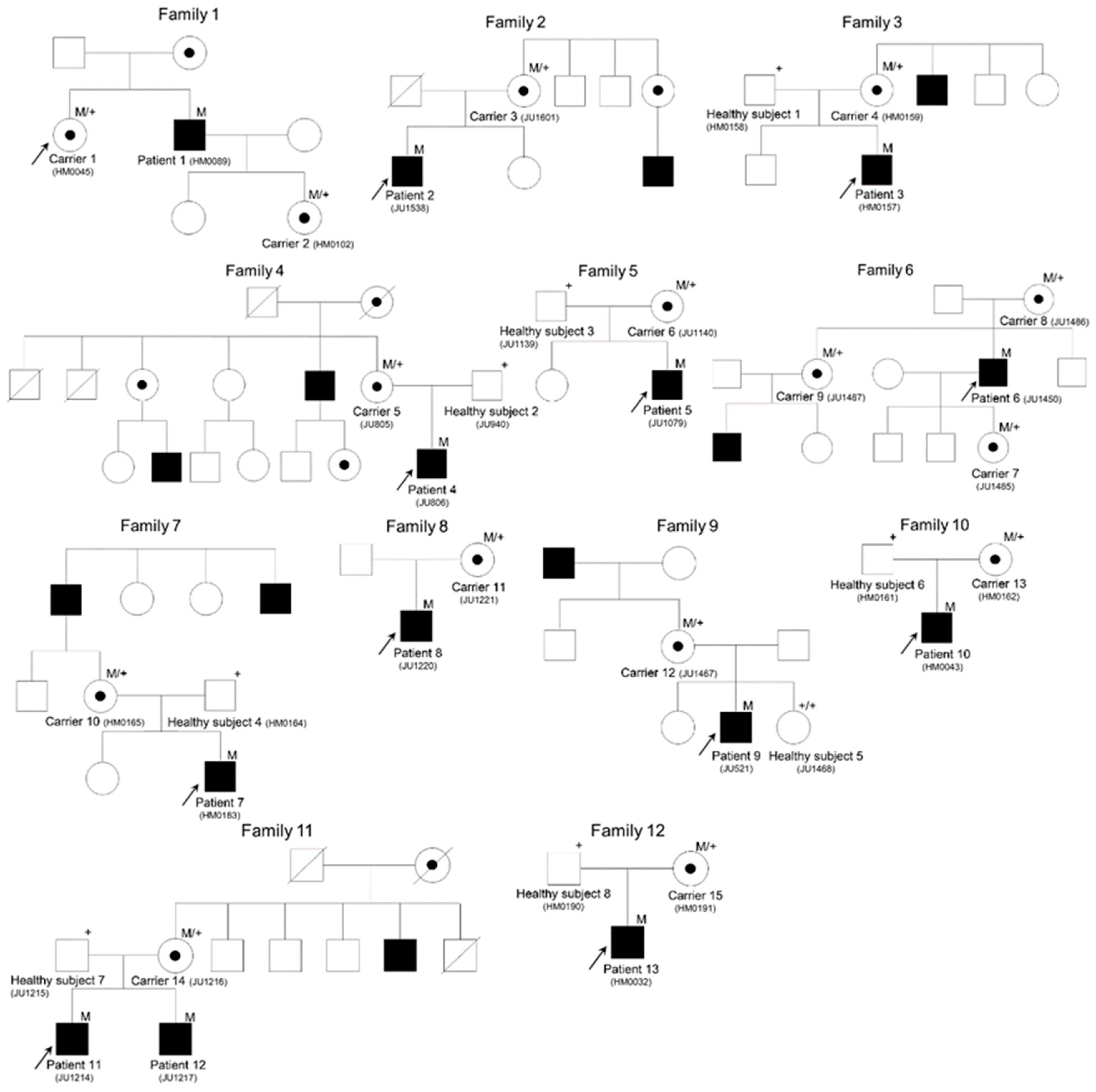
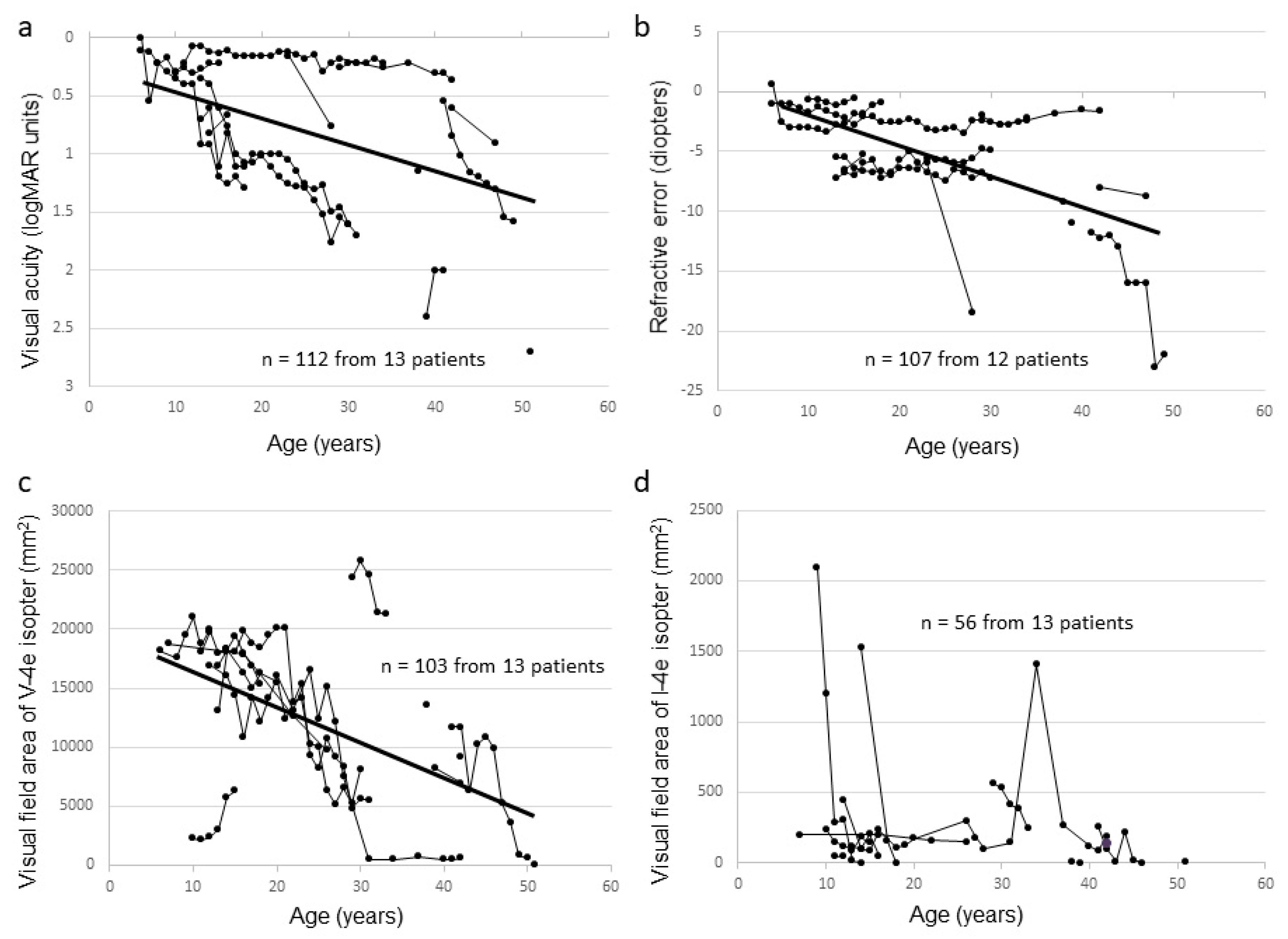
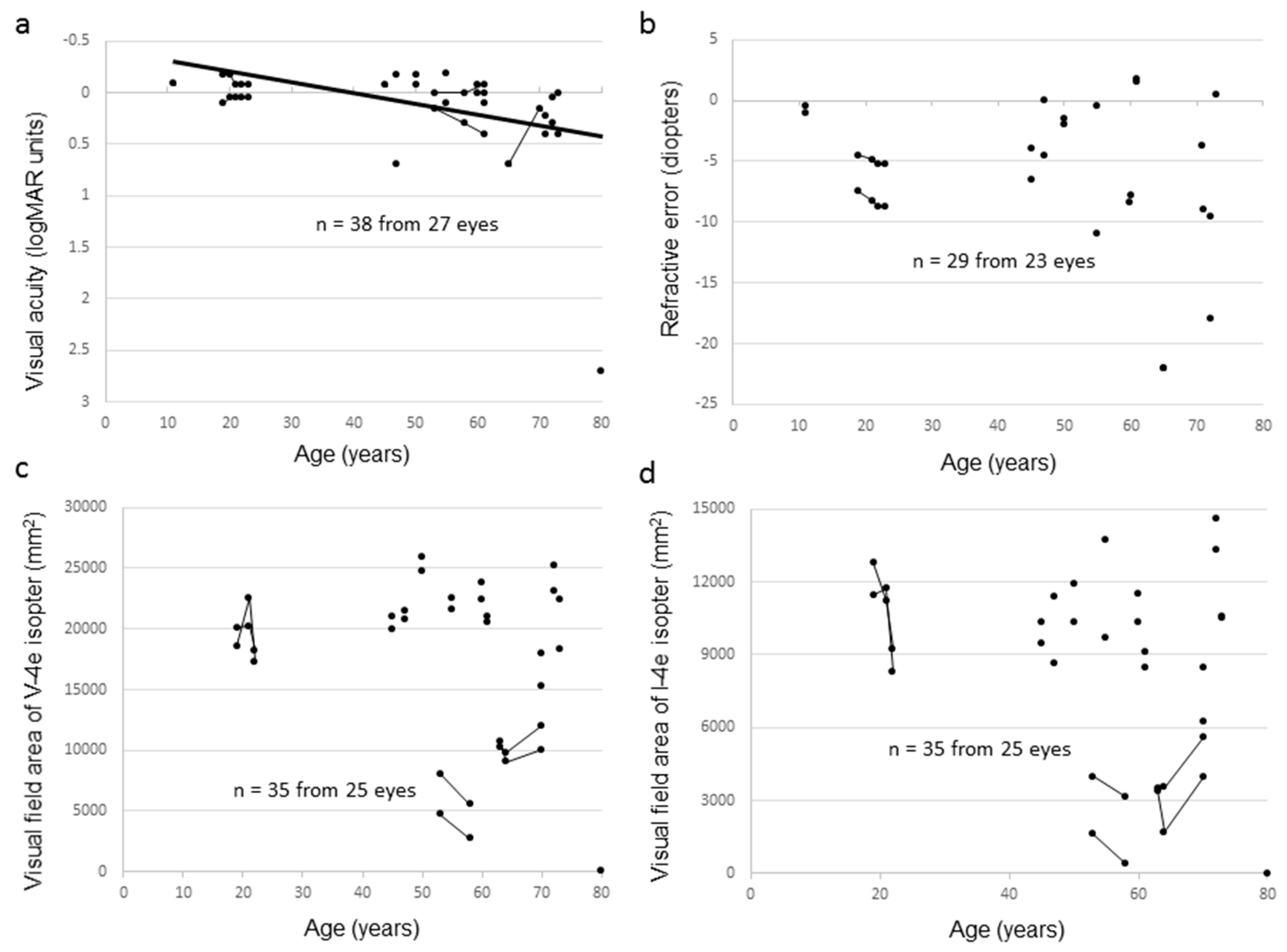

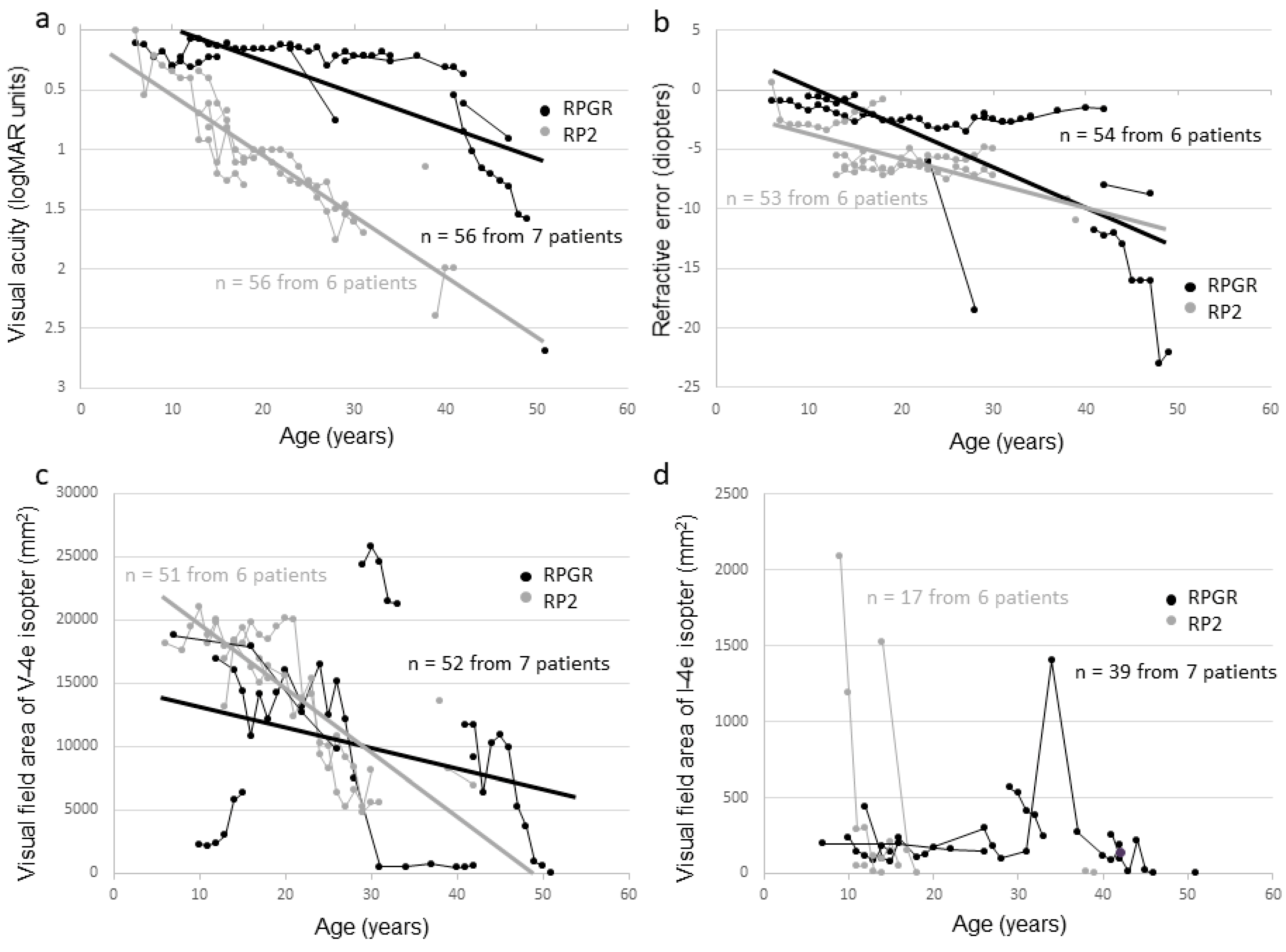
| Family Number | Subject Number | Gene | Accession Number | Mutation | Protein Change | Zygosity | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Patient 1 Carrier 1 | RPGR | NM_001034853.1 NM_000328.2 | c.469+1G>T c.469+1G>T | p.? p.? | Hemi Hetero | [16] |
| Carrier 2 | c.469+1G>T | p.? | Hetero | ||||
| 2 | Patient 2 | RPGR | c.492G>T | p.(W164C) | Hemi | Novel | |
| Carrier 3 | c.492G>T | p.(W164C) | Hetero | ||||
| 3 | Patient 3 | RPGR | c.830G>T | p.(G277V) | Hemi | Novel | |
| Healthy subject 1 | WT | ― | ― | ||||
| Carrier 4 | c.830G>T | p.(G277V) | Hetero | ||||
| 4 | Patient 4 | RPGR | c.1077T>A | p.(C359 *) | Hemi | Novel | |
| Healthy subject 2 | WT | ― | ― | ||||
| Carrier 5 | c.1077T>A | p.(C359 *) | Hetero | ||||
| 5 | Patient 5 | RPGR | c.1234C>T | p.(R412 *) | Hemi | [2] | |
| Healthy subject 3 | WT | ― | ― | ||||
| Carrier 6 | c.1234C>T | p.(R412 *) | Hetero | ||||
| 6 | Patient 6 | RPGR | c.1234C>T | p.(R412 *) | Hemi | [2] | |
| Carrier 7 | c.1234C>T | p.(R412 *) | Hetero | ||||
| Carrier 8 | c.1234C>T | p.(R412 *) | Hetero | ||||
| Carrier 9 | c.1234C>T | p.(R412 *) | Hetero | ||||
| 7 | Patient 7 | RPGR (ORF15) | NM_001034853.1 | c.2997_2998del | p.(E1000Gfs *78) | Hemi | [2] |
| Healthy subject 4 | WT | ― | ― | ||||
| Carrier 10 | c.2997_2998del | p.(E1000Gfs *78) | Hetero | ||||
| 8 | Patient 8 | RP2 | NM_006915.3 | c.102+1G>A | p.? | Hemi | [22] |
| Carrier 11 | c.102+1G>A | p.? | Hetero | ||||
| 9 | Patient 9 | RP2 | c.217del | p.(Y73Ifs *18) | Hemi | Novel | |
| Carrier 12 | c.217del | p.(Y73Ifs *18) | Hetero | ||||
| Healthy subject 5 | WT | ― | ― | ||||
| 10 | Patient 10 | RP2 | c.358C>T | p.(R120 *) | Hemi | [23] | |
| Healthy subject 6 | WT | ― | ― | ||||
| Carrier 13 | c.358C>T | p.(R120 *) | Hetero | ||||
| 11 | Patient 11 | RP2 | c.413A>G | p.(E138G) | Hemi | [24] | |
| Healthy subject 7 | WT | ― | ― | ||||
| Carrier 14 | c.413A>G | p.(E138G) | Hetero | ||||
| Patient 12 | c.413A>G | p.(E138G) | Hemi | ||||
| 12 | Patient 13 | RP2 | c.685C>T | p.(Q229 *) | Hemi | Novel | |
| Healthy subject 8 | WT | ― | ― | ||||
| Carrier 15 | c.685C>T | p.(Q229 *) | Hetero |
| All | Mutations in RPGR | Mutations in RP2 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of subjects | 13 | 7 | 6 | |
| Median age (range) | 34 (15–54) | 42 (15–54) | 30 (17–42) | 0.19 |
| Median onset age (range) | 6 (1–11) | 6 (1–9) | 7.5 (3–11) | 0.37 |
| Median refractive error (range), diopter | −5.8 (−24.0–−0.50) | −5.5 (−24.0–−0.50) | −5.8 (−10.0–+1.00) | 0.86 |
| Median decimal BCVA (range) | 0.08 (LP–0.7) | 0.2 (LP–0.7) | 0.03 (CF–0.3) | 0.15 |
| Median visual field area with V-4e (range), mm2 | 8089 (0–21,271) | 6302 (0–21,271) | 10814 (5528–20,048) | 0.25 |
| Median visual field area with I-4e (range), mm2 | 50 (0–244) | 142 (0–244) | 3 (0–52) | 0.08 |
| All | Mutations in RPGR | Mutations in RP2 | p Value | |
| Number of subjects | 15 | 10 | 5 | |
| Median age (range) | 59.5 (11–80) | 59.5 (11–80) | 58 (47–73) | 0.59 |
| Visual disturbance, n, (%) | 9/13 (69%) | 7/9 (78%) | 2/4 (50%) | 0.66 |
| Median refractive error (range), diopter | −3.88 (−22.0–+1.75) | −5.88 (−22.0–−0.50) | −0.25 (−11.0–+1.75) | 0.02 * |
| Median decimal BCVA (range) | 1.0 (LP–1.5) | 1.0 (LP–1.5) | 0.9 (0.2–1.5) | 0.87 |
| Median visual field area with V-4e (range), mm2 | 20,774 (38.1–25,947) | 18,247 (38.1–25,947) | 21,253 (18,339–22,501) | 0.32 |
| Median visual field area with I-4e (range), mm2 | 9448 (0–14,629) | 9256 (0–14,629) | 10,113 (8464–13,711) | 0.22 |
| Fundus grade, eyes, (%) | ||||
| Grade 0 | 4/27 (15%) | 2/19 (11%) | 2/8 (25%) | 0.58 |
| Grade 1 | 10/27 (37%) | 6/19 (31%) | 4/8 (50%) | 0.70 |
| Grade 2 | 4/27 (15%) | 2/19 (11%) | 2/8 (25%) | 0.58 |
| Grade 3 | 9/27 (33%) | 9/19 (47%) | 0/8 (0%) | 0.16 |
| Radial AF, eyes, (%) | 17/27 (63%) | 9/19 (47%) | 8/8 (100%) | 0.34 |
| 3.0 DA ERG patterns, eye, (%) | ||||
| No abnormalities | 2/25 (8%) | 0/17 (0%) | 2/8 (25%) | 0.13 |
| Subnormal | 9/25 (36%) | 7/17 (42%) | 2/8 (25%) | 0.69 |
| Reduced | 9/25 (36%) | 5/17 (29%) | 4/8 (50%) | 0.69 |
| Non-detectable | 5/25 (20%) | 5/17 (29%) | 0/8 (0%) | 0.29 |
| Grade 0 | Grade 1 | Grade 2 | Grade 3 | J-T Test | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 53.0 | 35.7 | 62.6 | 67.6 | p = 0.001 ** |
| BCVA (logMAR unit) | −0.015 | −0.079 | 0.20 | 0.47 | p = 0.005 ** |
| Refractive error (diopters) | −1.81 | −3.29 | −5.06 | −14.04 | p = 0.001 ** |
| Visual field area (mm2) | |||||
| V-4e isopter | 20,619 | 22,716 | 21,540 | 12,439 | p = 0.046 * |
| I-4e isopter | 9343 | 11,443 | 10,312 | 6198 | p = 0.062 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kurata, K.; Hosono, K.; Hayashi, T.; Mizobuchi, K.; Katagiri, S.; Miyamichi, D.; Nishina, S.; Sato, M.; Azuma, N.; Nakano, T.; et al. X-linked Retinitis Pigmentosa in Japan: Clinical and Genetic Findings in Male Patients and Female Carriers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061518
Kurata K, Hosono K, Hayashi T, Mizobuchi K, Katagiri S, Miyamichi D, Nishina S, Sato M, Azuma N, Nakano T, et al. X-linked Retinitis Pigmentosa in Japan: Clinical and Genetic Findings in Male Patients and Female Carriers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061518
Chicago/Turabian StyleKurata, Kentaro, Katsuhiro Hosono, Takaaki Hayashi, Kei Mizobuchi, Satoshi Katagiri, Daisuke Miyamichi, Sachiko Nishina, Miho Sato, Noriyuki Azuma, Tadashi Nakano, and et al. 2019. "X-linked Retinitis Pigmentosa in Japan: Clinical and Genetic Findings in Male Patients and Female Carriers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061518
APA StyleKurata, K., Hosono, K., Hayashi, T., Mizobuchi, K., Katagiri, S., Miyamichi, D., Nishina, S., Sato, M., Azuma, N., Nakano, T., & Hotta, Y. (2019). X-linked Retinitis Pigmentosa in Japan: Clinical and Genetic Findings in Male Patients and Female Carriers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1518. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061518





