The First Report of Polymorphisms and Genetic Features of the prion-like Protein Gene (PRND) in a Prion Disease-Resistant Animal, Dog
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Investigation of Genetic Characteristics of the PRND Gene in the 207Dogs
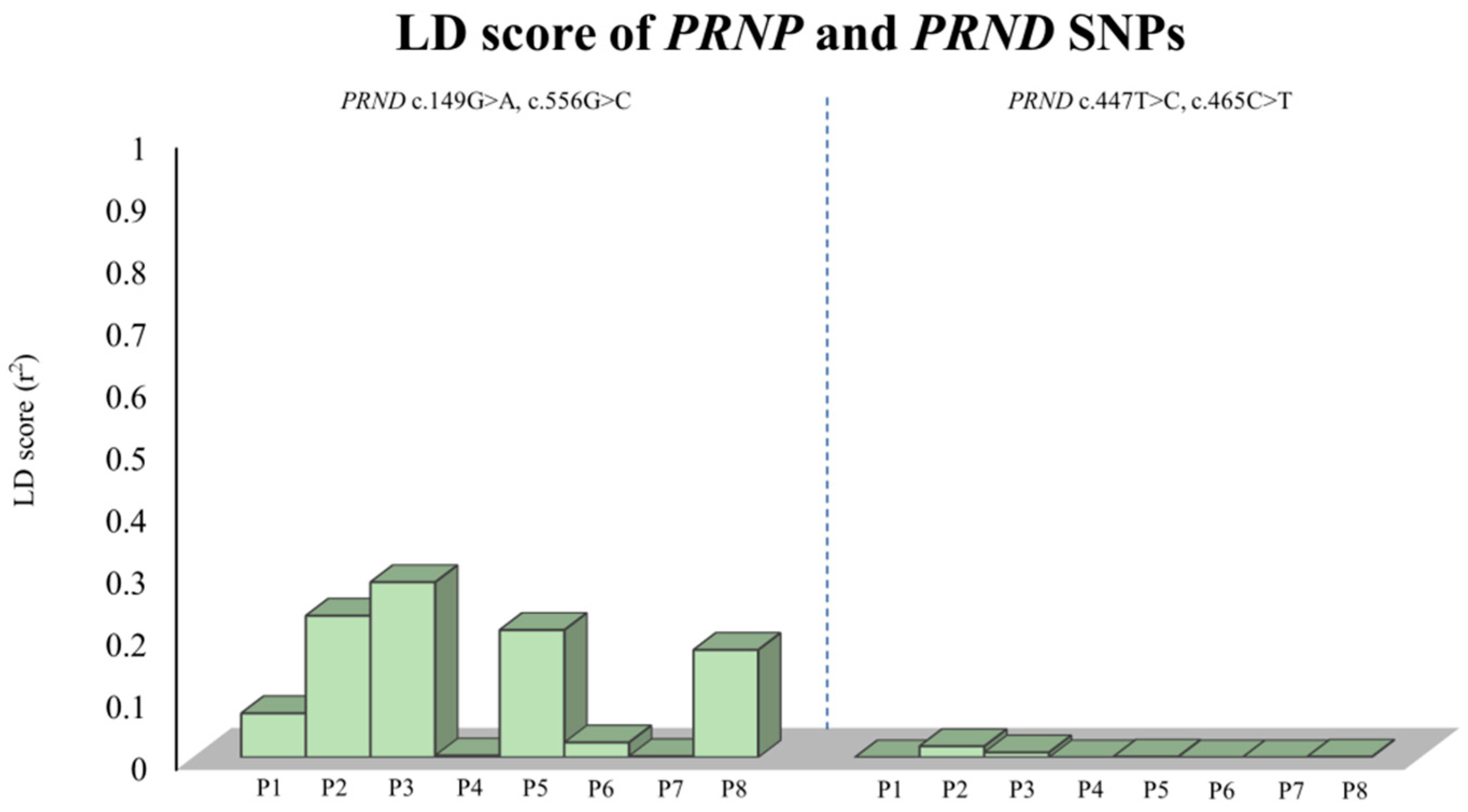
2.2. Analysis of the Genetic Linkage between SNPs of the PRNP and PRND Genes
2.3. Measurement of Protein Functional Alterations Induced by Nonsynonymous SNPs
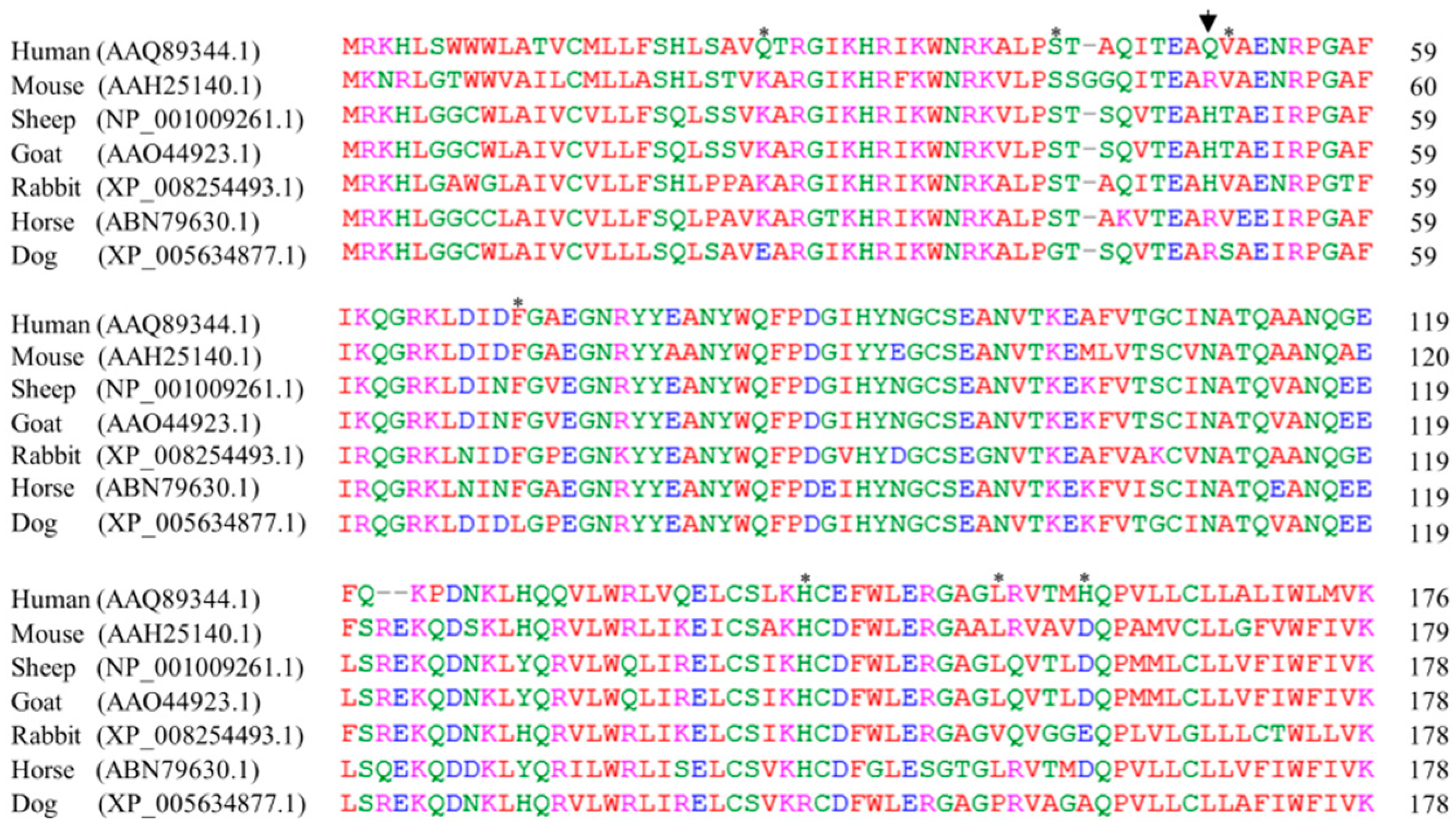
2.4. The Sequence Alignments of Doppel Protein among Several Species
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Ethical Statement
4.2. Genetic Analysis
4.3. Statistical Analysis
4.4. Analysis of the Genetic Linkage between SNPs of the PRNP and PRND Genes
4.5. The Sequence Alignments of Doppel Protein among Several Species
4.6. Measurement of Protein Functional Alterations Induced by Nonsynonymous SNPs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BSE | Bovine spongiform encephalopathy |
| CJD | Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease |
| CWD | Chronic wasting disease |
| FFI | Fatal familial insomnia |
| FSE | Feline spongiform encephalopathy |
| GSS | Gerstmann-Sträussler Scheinker syndrome |
| LD | Linkage disequilibrium |
| PRND | Prion-like protein gene |
| PRNP | Prion protein gene |
| SNPs | Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) |
| TME | Transmissible mink encephalopathy |
| TSEs | Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies |
References
- Zabel, M.D.; Reid, C. A brief history of prions. Pathog. Dis. 2015, 73, ftv087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B. The prion diseases. Brain Pathol. 1998, 8, 499–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prusiner, S.B. Prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 13363–13383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewell, J.E.; Conner, M.M.; Wolfe, L.L.; Miller, M.W.; Williams, E.S. Low frequency of PrP genotype 225SF among free-ranging mule deer (Odocoileus hemionus) with chronic wasting disease. J. Gen. Virol. 2005, 86, 2127–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, A.L.; Kelly, A.C.; Green, M.L.; Shelton, P.; Novakofski, J.; Mateus-Pinilla, N.E. Prion protein gene sequence and chronic wasting disease susceptibility in white-tailed deer (Odocoileus virginianus). Prion 2015, 9, 449–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monello, R.J.; Galloway, N.L.; Powers, J.G.; Madsen-Bouterse, S.A.; Edwards, W.H.; Wood, M.E.; O’Rourke, K.I.; Wild, M.A. Pathogen-mediated selection in free-ranging elk populations infected by chronic wasting disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 12208–12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perucchini, M.; Griffin, K.; Miller, M.W.; Goldmann, W. PrP genotypes of free-ranging wapiti (Cervus elaphus nelsoni) with chronic wasting disease. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 1324–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, B.; Doherr, M.G.; Seuberlich, T.; Drogemuller, C.; Dolf, G.; Nicken, P.; Schiebel, K.; Ziegler, U.; Groschup, M.H.; Zurbriggen, A.; et al. PRNP promoter polymorphisms are associated with BSE susceptibility in Swiss and German cattle. BMC Genet. 2007, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.H.; Jin, H.T.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE)-associated polymorphisms of the prion protein (PRNP) gene in Korean native cattle. Anim. Genet. 2013, 44, 356–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, R.F.; Hadlow, W.J. Transmissible mink encephalopathy. Rev. Sci. Tech. 1992, 11, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moennig, V. [Felinfo glossarium. Mad cow disease in the cat]. Tijdschr. Diergeneeskd. 1992, 117, 412–413. [Google Scholar]
- Baron, T.; Belli, P.; Madec, J.Y.; Moutou, F.; Vitaud, C.; Savey, M. Spongiform encephalopathy in an imported cheetah in France. Vet. Rec. 1997, 141, 270–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willoughby, K.; Kelly, D.F.; Lyon, D.G.; Wells, G.A. Spongiform encephalopathy in a captive puma (Felis concolor). Vet. Rec. 1992, 131, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurmi, M.H.; Bishop, M.; Strain, L.; Brett, F.; McGuigan, C.; Hutchison, M.; Farrell, M.; Tilvis, R.; Erkkila, S.; Simell, O.; et al. The normal population distribution of PRNP codon 129 polymorphism. Acta. Neurol. Scand. 2003, 108, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.H.; Kim, Y.S. Genetic studies in human prion diseases. J. Korean. Med. Sci. 2014, 29, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.H.; Lee, Y.J.; Kim, N.H.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S. Genotype distribution of the prion protein gene (PRNP) promoter polymorphisms in Korean cattle. Genome 2006, 49, 1539–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sander, P.; Hamann, H.; Drogemuller, C.; Kashkevich, K.; Schiebel, K.; Leeb, T. Bovine prion protein gene (PRNP) promoter polymorphisms modulate PRNP expression and may be responsible for differences in bovine spongiform encephalopathy susceptibility. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37408–37414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sailer, A.; Bueler, H.; Fischer, M.; Aguzzi, A.; Weissmann, C. No propagation of prions in mice devoid of PrP. Cell 1994, 77, 967–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Borges, N.; Parra, B.; Vidal, E.; Erana, H.; Sanchez-Martin, M.A.; de Castro, J.; Elezgarai, S.R.; Pumarola, M.; Mayoral, T.; Castilla, J. Unraveling the key to the resistance of canids to prion diseases. PloS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, N.; Foster, J.D.; Goldmann, W.; Stear, M.J.; Hope, J.; Bostock, C. Natural scrapie in a closed flock of Cheviot sheep occurs only in specific PrP genotypes. Arch. Virol. 1996, 141, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, J.J.; Kunkle, R.A.; Richt, J.A.; Nicholson, E.M.; Hamir, A.N. Lack of prion accumulation in lymphoid tissues of PRNP ARQ/ARR sheep intracranially inoculated with the agent of scrapie. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srithayakumar, V.; Mitchell, G.B.; White, B.N. Identification of amino acid variation in the prion protein associated with classical scrapie in Canadian dairy goats. BMC Vet. Res. 2016, 12, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortiz-Pelaez, A.; Georgiadou, S.; Simmons, M.M.; Windl, O.; Dawson, M.; Arnold, M.E.; Neocleous, P.; Papasavva-Stylianou, P. Allelic variants at codon 146 in the PRNP gene show significant differences in the risk for natural scrapie in Cypriot goats. Epidemiol. Infect. 2015, 143, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colussi, S.; Vaccari, G.; Maurella, C.; Bona, C.; Lorenzetti, R.; Troiano, P.; Casalinuovo, F.; Di Sarno, A.; Maniaci, M.G.; Zuccon, F.; et al. Histidine at codon 154 of the prion protein gene is a risk factor for Nor98 scrapie in goats. J. Gen. Virol. 2008, 89, 3173–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldmann, W.; Martin, T.; Foster, J.; Hughes, S.; Smith, G.; Hughes, K.; Dawson, M.; Hunter, N. Novel polymorphisms in the caprine PrP gene: A codon 142 mutation associated with scrapie incubation period. J. Gen. Virol. 1996, 77, 2885–2891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzalas, I.G.; Dovas, C.I.; Banos, G.; Papanastasopoulou, M.; Kritas, S.; Oevermann, A.; Papakostaki, D.; Evangelia, C.; Papadopoulos, O.; Seuberlich, T.; et al. Caprine PRNP polymorphisms at codons 171, 211, 222 and 240 in a Greek herd and their association with classical scrapie. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandel, J.P.; Preece, M.; Brown, P.; Croes, E.; Laplanche, J.L.; Agid, Y.; Will, R.; Alperovitch, A. Distribution of codon 129 genotype in human growth hormone-treated CJD patients in France and the UK. Lancet. 2003, 362, 128–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.H.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, N.H.; Jin, J.K.; Kim, J.I.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S. Association of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with homozygous genotypes at PRNP codons 129 and 219 in the Korean population. Neurogenetics 2005, 6, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Garcia, J.; Fernandez-Funez, P. D159 and S167 are protective residues in the prion protein from dog and horse, two prion-resistant animals. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 119, 11–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Garcia, J.; Jensen, K.; Zhang, Y.; Rincon-Limas, D.E.; Fernandez-Funez, P. A single amino acid (Asp159) from the dog prion protein suppresses the toxicity of the mouse prion protein in Drosophila. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 95, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polymenidou, M.; Trusheim, H.; Stallmach, L.; Moos, R.; Julius, C.; Miele, G.; Lenz-Bauer, C.; Aguzzi, A. Canine MDCK cell lines are refractory to infection with human and mouse prions. Vaccine 2008, 26, 2601–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, M.J.; Jeong, B.H. The first report of genetic variations in the chicken prion protein gene. Prion. 2018, 12, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, B.H. The first report of polymorphisms and genetic characteristics of the prion protein gene (PRNP) in horses. Prion. 2018, 12, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, A.; Bolea, R.; Hedman, C.; Fernández-Borges, N.; Marín, B.; López-Pérez, Ó.; Barrio, T.; Eraña, H.; Sánchez-Martín, M.A.; Monzón, M.; Badiola, J.J.; et al. An Amino Acid Substitution Found in Animals with Low Susceptibility to Prion Diseases Confers a Protective Dominant-Negative Effect in Prion-Infected Transgenic Mice. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6182–6192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, A.; Hedman, C.; Fernández-Borges, N.; Eraña, H.; Marín, B.; Monzón, M.; Sánchez-Martín, M.A.; Nonno, R.; Badiola, J.J.; Bolea, R.; et al. A Single Amino Acid Substitution, Found in Mammals with Low Susceptibility to Prion Diseases, Delays Propagation of Two Prion Strains in Highly Susceptible Transgenic Mouse Models. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, B.H.; Kim, N.H.; Choi, E.K.; Lee, C.; Song, Y.H.; Kim, J.I.; Carp, R.I.; Kim, Y.S. Polymorphism at 3’ UTR +28 of the prion-like protein gene is associated with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2005, 13, 1094–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peoc’h, K.; Guerin, C.; Brandel, J.P.; Launay, J.M.; Laplanche, J.L. First report of polymorphisms in the prion-like protein gene (PRND): Implications for human prion diseases. Neurosci. Lett. 2000, 286, 144–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, P.; Batista, M.; Marques, M.R.; Santos, I.C.; Pimenta, J.; Silva Pereira, M.; Carolino, I.; Santos Silva, F.; Oliveira Sousa, M.C.; Gama, L.T.; et al. Prion-like Doppel gene polymorphisms and scrapie susceptibility in Portuguese sheep breeds. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Croes, E.A.; Alizadeh, B.Z.; Bertoli-Avella, A.M.; Rademaker, T.; Vergeer-Drop, J.; Dermaut, B.; Houwing-Duistermaat, J.J.; Wientjens, D.P.; Hofman, A.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; et al. Polymorphisms in the prion protein gene and in the doppel gene increase susceptibility for Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 12, 389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, B.H. Bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE) associated polymorphisms of the prion-like protein gene (PRND) in Korean dairy cattle and Hanwoo. J. Dairy Res. 2018, 85, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, M.J.; Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, B.H. Prion-like protein gene (PRND) polymorphisms associated with scrapie susceptibility in Korean native black goats. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adzhubei, I.; Jordan, D.M.; Sunyaev, S.R. Predicting functional effect of human missense mutations using PolyPhen-2. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Chan, A.P. PROVEAN web server: A tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics. 2015, 31, 2745–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golaniska, E.; Flirski, M.; Liberski, P.P. Doppel: The prion’s double. Folia neuropathologica 2004, 42, 47–54. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, P.D.; Campbell, M.J.; Kejariwal, A.; Mi, H.; Karlak, B.; Daverman, R.; Diemer, K.; Muruganujan, A.; Narechania, A. PANTHER: A library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res. 2003, 13, 2129–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paisley, D.; Banks, S.; Selfridge, J.; McLennan, N.F.; Ritchie, A.M.; McEwan, C.; Irvine, D.S.; Saunders, P.T.; Manson, J.C.; Melton, D.W. Male infertility and DNA damage in Doppel knockout and prion protein/Doppel double-knockout mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2004, 164, 2279–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behrens, A.; Genoud, N.; Naumann, H.; Rulicke, T.; Janett, F.; Heppner, F.L.; Ledermann, B.; Aguzzi, A. Absence of the prion protein homologue Doppel causes male sterility. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 3652–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komar, A.A. Silent SNPs: Impact on gene function and phenotype. Pharmacogenomics 2007, 8, 1075–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimenta, J.; Domingos, A.; Santos, P.; Marques, C.C.; Cantante, C.; Santos, A.; Barbas, J.P.; Baptista, M.C.; Horta, A.E.; Viegas, A.; et al. Is prnt a pseudogene? Identification of ram Prt in testis and ejaculated spermatozoa. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mesquita, P.; Garcia, V.; Marques, M.R.; Santos Silva, F.; Oliveira Sousa, M.C.; Carolino, I.; Pimenta, J.; Fontes, C.M.; Horta, A.E.; Prates, J.A.; et al. The prion-related protein (testis-specific) gene (PRNT) is highly polymorphic in Portuguese sheep. Anim. Genet. 2016, 47, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, B.H. The first report of prion-related protein gene (PRNT) polymorphisms in goat. Acta. Vet. Hung. 2017, 65, 291–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Jeong, B.H. First report of prion-related protein gene (PRNT) polymorphisms in cattle. Vet. Rec. 2018, 182, 717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
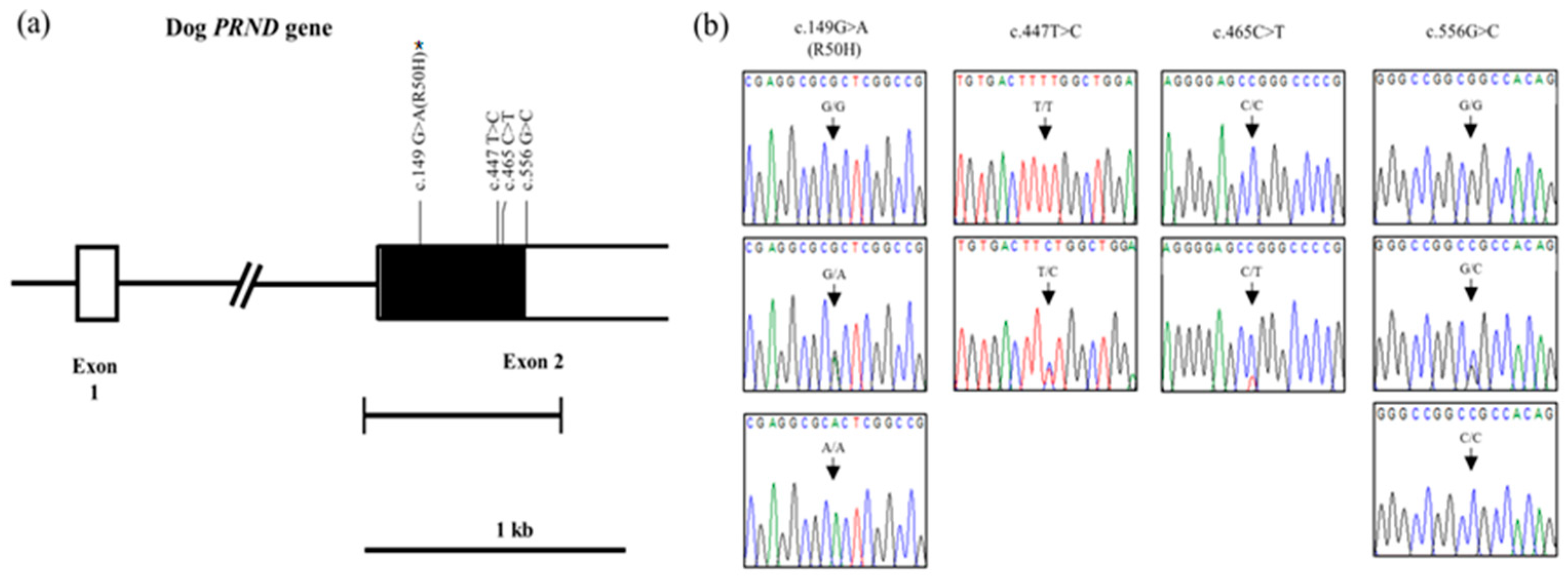
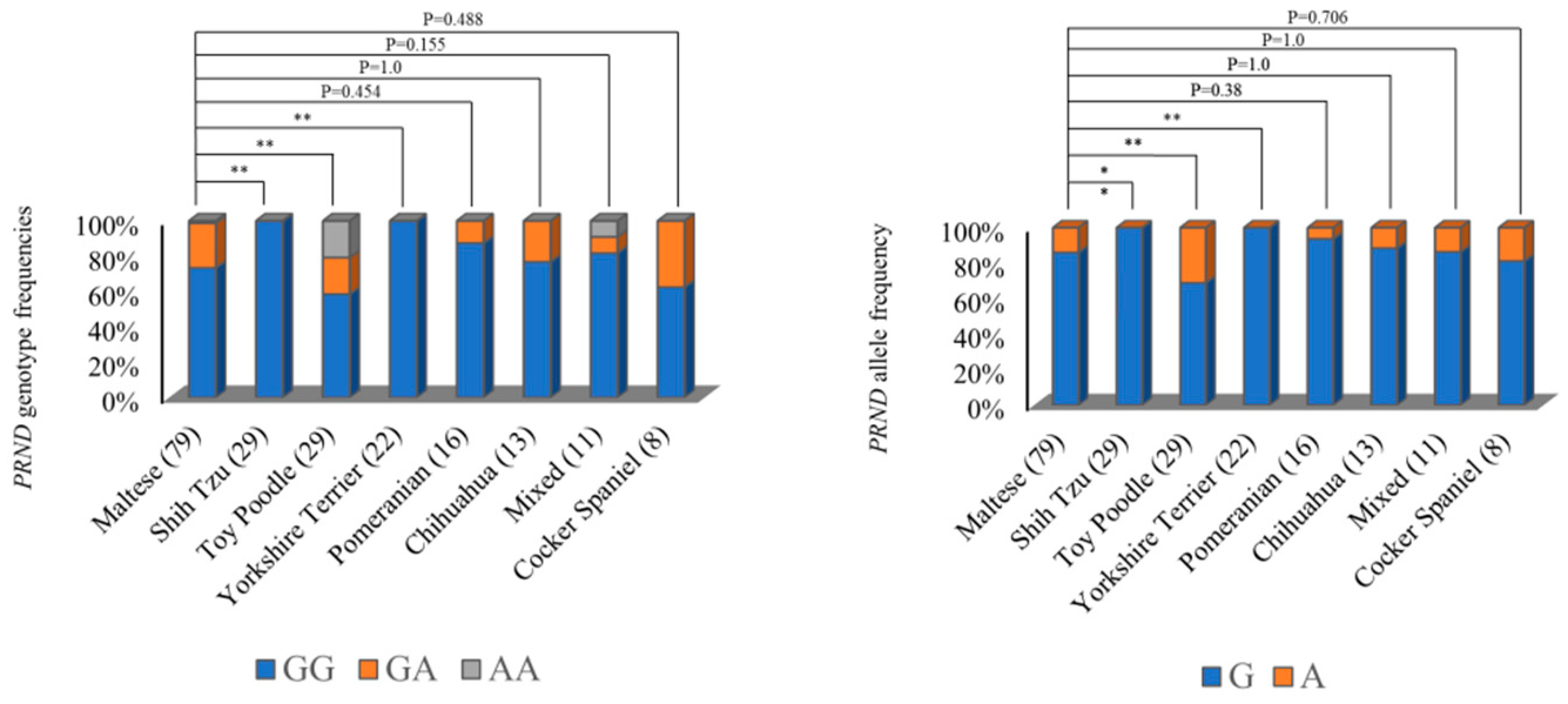
| Polymorphisms | Genotype Frequency, n (%) | Allele Frequency, n (%) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.149G>A (R50H) | GG 164 (79.2) | GA 35 (16.9) | AA 8 (3.9) | G 363 (87.7) | A 51 (12.3) |
| c.447T>C (F149F) | TT 206 (99.5) | TC 1 (0.5) | CC 0 (0) | T 413 (99.8) | C 1 (0.2) |
| c.465C>T (A155A) | CC 206 (99.5) | CT 1 (0.5) | TT 0 (0) | C 413 (99.8) | T 1 (0.2) |
| c.556G>C | GG 164 (79.2) | GC 35 (16.9) | CC 8 (3.9) | G 363 (87.7) | C 51 (12.3) |
| |D’| | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r2 | c.149G>A | c.447T>C | c.465C>T | c.556G>C |
| c.149G>A | - | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| c.447T>C | 0 | - | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| c.465C>T | 0 | 1.0 | - | 1.0 |
| c.556G>C | 1.0 | 0 | 0 | - |
| Haplotype | Dogs (n = 414) |
|---|---|
| GGTC | 362 (0.874) |
| ACTC | 51 (0.123) |
| Others | 1 (0.003) |
| Variation | Method | Score | Prediction |
|---|---|---|---|
| c.149G>A (R50H) | PolyPhen-2 | 0.051 | Benign |
| PROVEAN | −1.065 | Neutral | |
| PANTHER | 30 | Probably benign |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Won, S.-Y.; Kim, Y.-C.; Kim, K.; Kim, A.-D.; Jeong, B.-H. The First Report of Polymorphisms and Genetic Features of the prion-like Protein Gene (PRND) in a Prion Disease-Resistant Animal, Dog. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061404
Won S-Y, Kim Y-C, Kim K, Kim A-D, Jeong B-H. The First Report of Polymorphisms and Genetic Features of the prion-like Protein Gene (PRND) in a Prion Disease-Resistant Animal, Dog. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(6):1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061404
Chicago/Turabian StyleWon, Sae-Young, Yong-Chan Kim, Kiwon Kim, An-Dang Kim, and Byung-Hoon Jeong. 2019. "The First Report of Polymorphisms and Genetic Features of the prion-like Protein Gene (PRND) in a Prion Disease-Resistant Animal, Dog" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 6: 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061404
APA StyleWon, S.-Y., Kim, Y.-C., Kim, K., Kim, A.-D., & Jeong, B.-H. (2019). The First Report of Polymorphisms and Genetic Features of the prion-like Protein Gene (PRND) in a Prion Disease-Resistant Animal, Dog. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(6), 1404. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20061404






