Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose Metabolism
2.1. Possible Mechnisms for the Improvement of Glucose Metabolism by Adiponectin
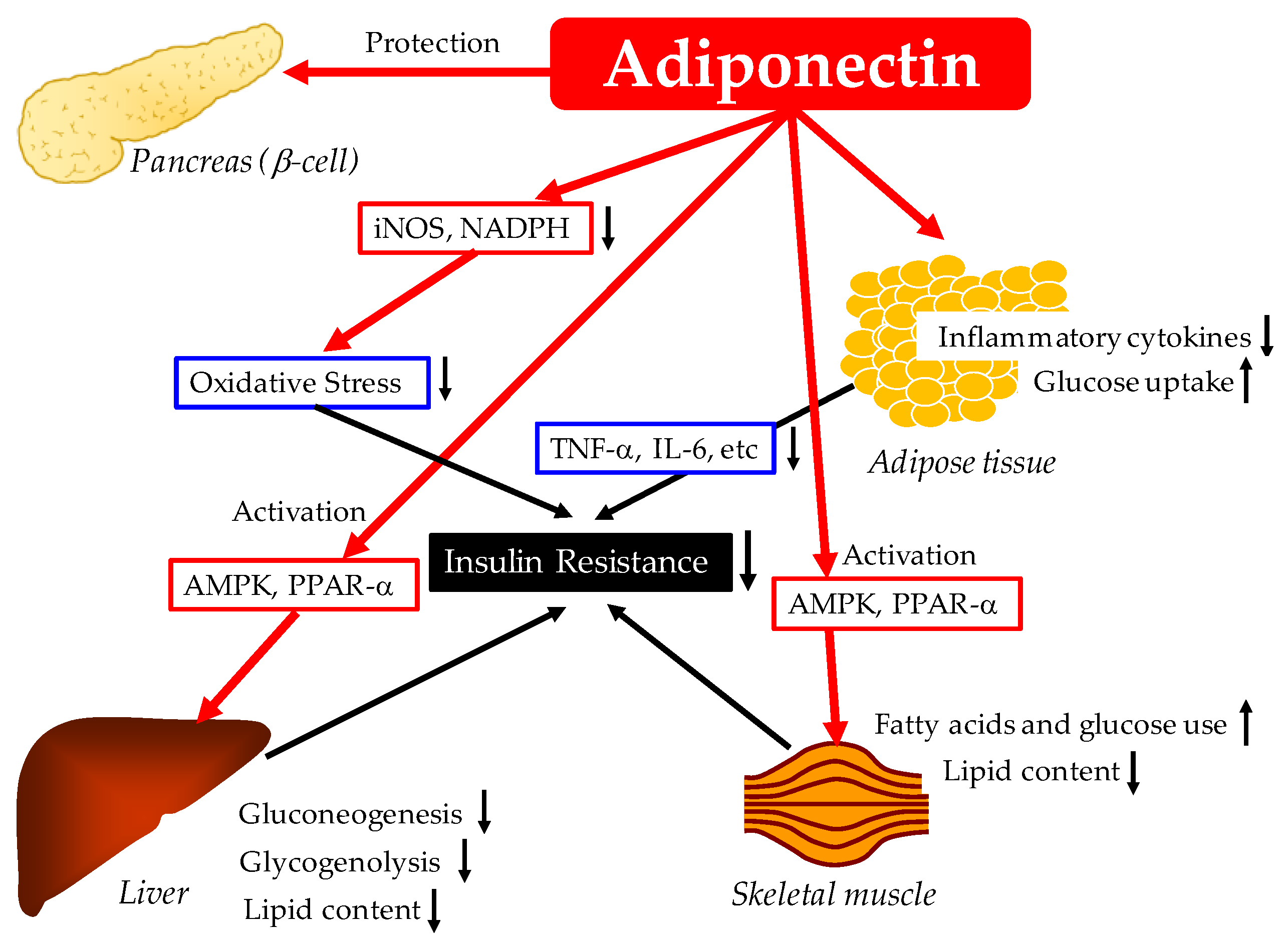
2.1.1. Reduction of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress and Improvement of Insulin Resistance by Adiponectin
2.1.2. Pancreatic β Cell Protective Effect of Adiponectin
2.1.3. Increase of Glucose Utilization and Fatty Acid Oxidation in Skeletal Muscles by Adiponectin
2.1.4. Adiponectin Reduces Hepatic Glucose Production
2.1.5. Adiponectin Increases Insulin-Stimulated Glucose Uptake by Adipocytes
2.1.6. Summary of Anti-Diabetic Effects of Adiponectin
2.2. Adiponectin and Development of Type 2 Diabetes
3. Effects of Adiponectin on Lipid Metabolism
3.1. Possible Mechanisms for the Improvement of Lipid Metabolism by Adiponectin
3.1.1. Possible Mechanism for the Increase of HDL by Adiponectin
3.1.2. Possible Mechanisms for TG reduction by Adiponectin
3.1.3. Effects of Adiponectin on LDL and Other Atherogenic Lipids
3.1.4. Summary of Mechanisms for the Improvement of Lipid Metabolism by Adiponectin.
4. Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects of Adiponectin
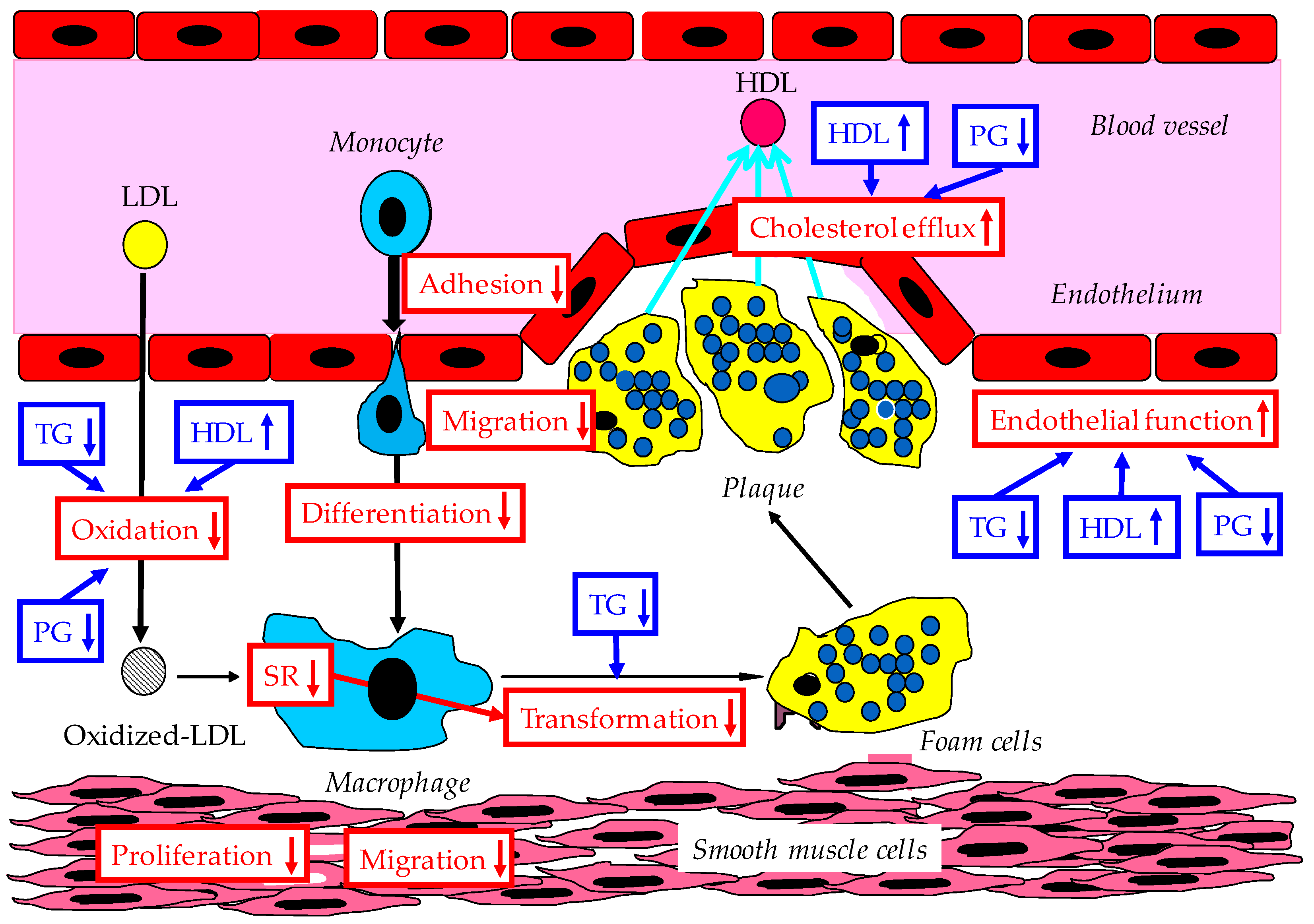
4.1. Improvement of Endothelial Function and Interaction Between Monocyte and Endothelium by Adiponectin
4.2. Inhibition of Smooth Muscle Proliferation by Adiponectin
4.3. Increase of Macrophage Cholesterol Efflux and Suppression of Foam Cell Formation
4.4. Putative Molecular Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects of Adiponectin
5. How can We Increase Adiponectin?
5.1. Weight Loss
5.2. Exercise
5.3. Nutritional Factors
5.3.1. Vitamins
5.3.2. Polyphenols
5.3.3. Carotenoids
5.3.4. Omega-3 FA
5.4. Anti-Diabetic Drugs
5.4.1. Thiazolidinediones
5.4.2. Metformin
5.4.3. α-Glycosidase Inhibitors
5.4.4. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP4i)
5.4.5. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogues
5.4.6. Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT-2i)
5.4.7. Sulfonyl Urea
5.5. Hypolipidemia Drugs
5.5.1. Statin
5.5.2. Ezetimibe
5.5.3. Fibrate
5.6. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs
Angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB)
5.7. Summary of Possible Factors Which Increase Circulating Adiponectin Levels
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCA1 | ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 |
| AMPK | adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| AOX | antioxidant |
| ARB | angiotensin II receptor blockers |
| BMI | body mass index |
| CAD | coronary artery disease |
| CI | confidence intervals |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| CVD | cardiovascular diseases |
| DPP4i | dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors |
| GLUT-4 | glucose transporter-4 |
| G6Pase | glucose-6-phosphatase |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| FA | fatty acid |
| FFA | free fatty acids |
| GLP-1 | glucagon-like peptide-1 |
| HDL | high-density lipoprotein |
| HMW | high-molecular weight |
| HL | hepatic lipase |
| HOMA-IR | homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance |
| HR | hazard ratio |
| HSL | hormone-sensitive lipase |
| IDL | intermediate-density lipoprotein |
| IL | interleukin |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| LDL | low-density lipoprotein |
| LPL | lipoprotein lipase |
| MCS | mixed-carotenoid supplementation |
| NADPH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| PCOS | polycystic ovary syndrome |
| PPAR | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| PEPCK | phosphoenolpyruvate carboxy kinase |
| RCTs | randomized controlled trials |
| S1P | sphingosine 1-phosphate |
| Sd-LDL | small dense LDL |
| SGLT-2i | sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors |
| SMCs | smooth muscle cells |
| SMD | standard mean difference |
| SR | scavenger receptor |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TG | triglycerides |
| VLDL | very low density lipoprotein |
| VLDL-R | very low density lipoprotein receptor |
| WMD | weighted mean difference |
References
- Maeda, K.; Okubo, K.; Shimomura, I.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Matsubara, K. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 221, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, T.; Oritani, K.; Takahashi, I.; Ishikawa, J.; Matsuyama, A.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Tenner, A.J.; Tomiyama, Y.; et al. Adiponectin, a new member of the family of soluble defense collagens, negatively regulates the growth of myelomonocytic progenitors and the functions of macrophages. Blood 2000, 96, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Nishida, M.; Matsuyama, A.; Okamoto, Y.; Ishigami, M.; Kuriyama, H.; Kishida, K.; Nishizawa, H.; et al. Adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, suppresses lipid accumulation and class A scavenger receptor expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Circulation 2001, 103, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waki, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Uchida, S.; Kita, S.; Hara, K.; Hada, Y.; Vasseur, F.; Froguel, P.; et al. Impaired multimerization of human adiponectin mutants associated with diabetes. Molecular structure and multimer formation of adiponectin. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40352–40363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pajvani, U.B.; Du, X.; Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Rajala, M.W.; Schulthess, T.; Engel, J.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. Structure-function studies of the adipocyte-secreted hormone Acrp30/adiponectin. Implications for metabolic regulation and bioactivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9073–9085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Ito, Y.; Tsuchida, A.; Yokomizo, T.; Kita, S.; Sugiyama, T.; Miyagishi, M.; Hara, K.; Tsunoda, M.; et al. Cloning of adiponectin receptors that mediate antidiabetic metabolic effects. Nature 2003, 423, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hug, C.; Wang, J.; Ahmad, N.S.; Bogan, J.S.; Tsao, T.S.; Lodish, H.F. T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10308–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achari, A.E.; Jain, S.K. Adiponectin, a Therapeutic Target for Obesity, Diabetes, and Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosen, E.D.; Spiegelman, B.M. Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 2006, 444, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghadge, A.A.; Diwan, A.G.; Harsulkar, A.M.; Kuvalekar, A.A. Gender dependent effects of fasting blood glucose levels and disease duration on biochemical markers in type 2 diabetics: A pilot study. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2017, 11, S481–S489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Maeda, K.; Miyagawa, J.; Hotta, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nakamura, T.; Miyaoka, K.; et al. Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 257, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funahashi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Shimomura, I.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Takahashi, M.; Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Matsuzawa, Y. Role of adipocytokines on the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis in visceral obesity. Intern. Med. 1999, 38, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuzawa, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Nakamura, T. Molecular mechanism of metabolic syndrome X: Contribution of adipocytokines adipocyte-derived bioactive substances. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 892, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, Y.; Arita, Y.; Nishida, M.; Muraguchi, M.; Ouchi, N.; Takahashi, M.; Igura, T.; Inui, Y.; Kihara, S.; Nakamura, T.; et al. An adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, adheres to injured vascular walls. Horm. Metab. Res. 2000, 32, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R. Adipocytokines: Mediators linking adipose tissue, inflammation and immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 772–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wang, N. Overexpression of adiponectin receptors potentiates the antiinflammatory action of sub-effective dose of globular adiponectin in vascular endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisberg, S.P.; McCann, D.; Desai, M.; Rosenbaum, M.; Leibel, R.L.; Ferrante, A.W., Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1796–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Barnes, G.T.; Yang, Q.; Tan, G.; Yang, D.; Chou, C.J.; Sole, J.; Nichols, A.; Ross, J.S.; Tartaglia, L.A.; et al. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1821–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, M.; Bai, W.; Nadler, J.L.; Natarajan, R. Molecular mechanisms of tumor necrosis factor alpha gene expression in monocytic cells via hyperglycemia-induced oxidant stress-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17728–17739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morohoshi, M.; Fujisawa, K.; Uchimura, I.; Numano, F. Glucose-dependent interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor production by human peripheral blood monocytes in vitro. Diabetes 1996, 45, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barzilay, J.I.; Abraham, L.; Heckbert, S.R.; Cushman, M.; Kuller, L.H.; Resnick, H.E.; Tracy, R.P. The relation of markers of inflammation to the development of glucose disorders in the elderly: The Cardiovascular Health Study. Diabetes 2001, 50, 2384–2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, D.J.; Norrie, J.; Caslake, M.J.; Gaw, A.; Ford, I.; Lowe, G.D.; O’Reilly, D.S.; Packard, C.J.; Sattar, N. C-reactive protein is an independent predictor of risk for the development of diabetes in the West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study. Diabetes 2002, 51, 1596–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, S.; Hossain, M.; Mathews, C.; Martinez, P.; Pino, P.; Gay, J.L.; Rentfro, A.; McCormick, J.B.; Fisher-Hoch, S.P. Type 2-diabetes is associated with elevated levels of TNF-alpha, IL-6 and adiponectin and low levels of leptin in a population of Mexican Americans: A cross-sectional study. Cytokine 2012, 57, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, A.G.; Burke, G.L.; Owusu, J.A.; Carnethon, M.R.; Vaidya, D.; Barr, R.G.; Jenny, N.S.; Ouyang, P.; Rotter, J.I. Inflammation and the incidence of type 2 diabetes: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA). Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marques-Vidal, P.; Schmid, R.; Bochud, M.; Bastardot, F.; von Känel, R.; Paccaud, F.; Glaus, J.; Preisig, M.; Waeber, G.; Vollenweider, P. Adipocytokines, hepatic and inflammatory biomarkers and incidence of type 2 diabetes. The CoLaus study. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi-Mamaeghani, M.; Mohammadi, S.; Arefhosseini, S.R.; Fallah, P.; Bazi, Z. Adiponectin as a potential biomarker of vascular disease. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2015, 11, 55–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Muraguchi, M.; et al. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-κB signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. Circulation 2000, 102, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin as an anti-inflammatory factor. Clin. Chim. Acta 2007, 380, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 1999, 100, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobashi, C.; Urakaze, M.; Kishida, M.; Kibayashi, E.; Kobayashi, H.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Takata, M.; Temaru, R.; Sato, A.; et al. Adiponectin inhibits endothelial synthesis of interleukin-8. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, A.M.; Wolf, D.; Rumpold, H.; Enrich, B.; Tilg, H. Adiponectin induces the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-1RA in human leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, L.; Gao, E.; Jiao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Li, S.; Christopher, T.A.; Lopez, B.L.; Koch, W.; Chan, L.; Goldstein, B.J.; et al. Adiponectin cardioprotection after myocardial ischemia/reperfusion involves the reduction of oxidative/nitrative stress. Circulation 2007, 115, 1408–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Roles of adiponectin and oxidative stress in obesity-associated metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, W.L.; Miller, R.A.; Wang, Z.V.; Sun, K.; Barth, B.M.; Bui, H.H.; Davis, K.E.; Bikman, B.T.; Halberg, N.; Rutkowski, J.M.; et al. Receptor-mediated activation of ceramidase activity initiates the pleiotropic actions of adiponectin. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakatzi, I.; Mueller, H.; Ritzeler, O.; Tennagels, N.; Eckel, J. Adiponectin counteracts cytokine- and fatty acid-induced apoptosis in the pancreatic beta-cell line INS-1. Diabetologia 2004, 47, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; van de Wall, E.; Laplante, M.; Azzara, A.; Trujillo, M.E.; Hofmann, S.M.; Schraw, T.; Durand, J.L.; Li, H.; Li, G.; et al. Obesity-associated improvements in metabolic profile through expansion of adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2621–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, C.; Sifuentes, A.; Holland, W.L. Regulation of glucose and lipid homeostasis by adiponectin: Effects on hepatocytes, pancreatic β cells and adipocytes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 28, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.A.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating amp-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruebis, J.; Tsao, T.S.; Javorschi, S.; Ebbets-Reed, D.; Erickson, M.R.S.; Yen, F.T.; Bihain, B.E.; Lodish, H.F. Proteolytic cleavage product of 30-kDa adipocyte complement-related protein increases fatty acid oxidation in muscle and causes weight loss in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2005–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, R.B.; Somwar, R.; Maida, A.; Fang, X.; Bikopoulos, G.; Sweeney, G. Globular adiponectin increases glut4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Obici, S.; Scherer, P.E.; Rossetti, L. Endogenous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein Acrp30. J. Clin. InvestIG. 2001, 108, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Mori, Y.; Ide, T.; Murakami, K.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shklyaev, S.; Aslanidi, G.; Tennant, M.; Prima, V.; Kohlbrenner, E.; Kroutov, V.; Campbell-Thompson, M.; Crawford, J.; Shek, E.W.; Scarpace, P.J.; et al. Sustained peripheral expression of transgene adiponectin offsets the development of diet-induced obesity in rats. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 14217–14222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.A.; Chu, Q.; Le Lay, J.; Scherer, P.E.; Ahima, R.S.; Kaestner, K.H.; Foretz, M.; Viollet, B.; Birnbaum, M.J. Adiponectin suppresses gluconeogenic gene expression in mouse hepatocytes independent of LKB1-AMPK signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 2518–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamic delivery of adiponectin and adiponectin receptor 2 gene blocks high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Combs, T.P.; Marliss, E.B. Adiponectin signaling in the liver. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Motoshima, H.; Mahadev, K.; Stalker, T.J.; Scalia, R.; Goldstein, B.J. Involvement of AMP-activated protein kinase in glucose uptake stimulated by the globular domain of adiponectin in primary rat adipocytes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1355–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Mao, X.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Wetzel, M.D.; Guan, K.L.; Dong, L.Q.; Liu, F. Adiponectin sensitizes insulin signaling by reducing p70 S6 kinase-mediated serine phosphorylation of IRS-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 7991–7996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saltiel, A.R.; Pessin, J.E. Insulin signaling pathways in time and space. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danielsson, A.; Ost, A.; Lystedt, E.; Kjolhede, P.; Gustavsson, J.; Nystrom, F.H.; Strålfors, P. Insulin resistance in human adipocytes occurs downstream of IRS1 after surgical cell isolation but at the level of phosphorylation of IRS1 in type 2 diabetes. FEBS J. 2005, 272, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, P.; Hanson, R.L.; Lee, Y.H.; Yang, X.; Kobes, S.; Permana, P.A.; Bogardus, C.; Baier, L.J. The role of insulin receptor substrate-1 gene (IRS1) in type 2 diabetes in Pima Indians. Diabetes 2003, 52, 3005–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsay, R.S.; Funahashi, T.; Hanson, R.L.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Tataranni, P.A.; Knowler, W.C.; Krakoff, J. Adiponectin and development of type 2 diabetes in the Pima Indian population. Lancet 2002, 360, 57–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorand, B.; Zierer, A.; Baumert, J.; Meisinger, C.; Herder, C.; Koenig, W. Associations between leptin and the leptin/adiponectin ratio and incident Type 2 diabetes in middle-aged men and women: Results from the MONICA/KORA Augsburg study 1984–2002. Diabet. Med. 2010, 27, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Feng, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Q.; Hua, M. Adiponectin, TNF-α and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cytokine 2016, 86, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, P.; Chen, S.; Sun, Q.; Zeng, Q.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Cao, X.H.; Ren, M.; Wang, J.K. The association of new inflammatory markers with type 2 diabetes mellitus and macrovascular complications: A preliminary study. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 1567–1572. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wannamethee, S.G.; Lowe, G.D.; Rumley, A.; Cherry, L.; Whincup, P.H.; Sattar, N. Adipokines and risk of type 2 diabetes in older men. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1200–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, S.H.; Harris, S.B.; Connelly, P.W.; Mamakeesick, M.; Gittelsohn, J.; Hegele, R.A.; Retnakaran, R.; Zinman, B.; Hanley, A.J. Adipokines and incident type 2 diabetes in an Aboriginal Canadian [corrected] population: The Sandy Lake Health and Diabetes Project. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1410–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, G.A.; Kiortsis, D.N. Adiponectin and lipoprotein metabolism. Obes. Rev. 2013, 14, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, Y.; Hirose, H.; Saito, I.; Tomita, M.; Taniyama, M.; Matsubara, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Ishii, T.; Nishikai, K.; Saruta, T. Correlation of the adipocyte-derived protein adiponectin with insulin resistance index and serum high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol, independent of body mass index, in the Japanese population. Clin. Sci. 2002, 103, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsubara, M.; Maruoka, S.; Katayose, S. Decreased plasma adiponectin concentrations in women with dyslipidemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 2764–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christou, G.A.; Tellis, K.C.; Elisaf, M.C.; Tselepis, A.D.; Kiortsis, D.N. High density lipoprotein is positively correlated with the changes in circulating total adiponectin and high molecular weight adiponectin during dietary and fenofibrate treatment. Hormones 2012, 11, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezenwaka, C.E.; Kalloo, R.; Uhlig, M.; Eckel, J. Relationship between adiponectin and metabolic variables in Caribbean offspring of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Horm. Metab. Res. 2004, 36, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kazumi, T.; Kawaguchi, A.; Hirano, T.; Yoshino, G. Serum adiponectin is associated with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, and low-density lipoprotein particle size in young healthy men. Metabolism 2004, 53, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, G.K.; Economides, P.A.; Horton, E.S.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Veves, A. Circulating adiponectin and resistin levels in relation to metabolic factors, inflammatory markers, and vascular reactivity in diabetic patients and subjects at risk for diabetes. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2450–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangas-Kontio, T.; Huotari, A.; Ruotsalainen, H.; Herzig, K.H.; Tamminen, M.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Savolainen, M.J.; Kakko, S. Genetic and environmental determinants of total and high-molecular weight adiponectin in families with low HDL-cholesterol and early onset coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, C.Y.; Park, S.; Kim, J.S.; Shin, D.J.; Ko, Y.G.; Kang, S.M.; Choi, D.; Ha, J.W.; Jang, Y.; Chung, N. Association of plasma retinol-binding protein 4, adiponectin, and high molecular weight adiponectin with insulin resistance in non-diabetic hypertensive patients. Yonsei Med. J. 2010, 51, 375–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, K.; Jung, S.H.; Choi, C.; Park, S.H. Reciprocal association between visceral obesity and adiponectin: In healthy premenopausal women. Int. J. Cardiol. 2005, 101, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, J.A.; Kim, S.H.; Lee, J.W.; Shim, J.Y.; Lee, H.R.; Lee, D.C. Association between hypoadiponectinemia and cardiovascular risk factors in nonobese healthy adults. Metabolism 2006, 55, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomono, Y.; Hiraishi, C.; Yoshida, H. Age and sex differences in serum adiponectin and its association with lipoprotein fractions. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 55, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Linthout, S.; Foryst-Ludwig, A.; Spillmann, F.; Peng, J.; Feng, Y.; Meloni, M.; Van Craeyveld, E.; Kintscher, U.; Schultheiss, H.P.; De Geest, B.; et al. Impact of HDL on adipose tissue metabolism and adiponectin expression. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 438–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oku, H.; Matsuura, F.; Koseki, M.; Sandoval, J.C.; Yuasa-Kawase, M.; Tsubakio-Yamamoto, K.; Masuda, D.; Maeda, N.; Ohama, T.; Ishigami, M.; et al. Adiponectin deficiency suppresses ABCA1 expression and ApoA-I synthesis in the liver. FEBS. Lett. 2007, 581, 5029–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, F.; Oku, H.; Koseki, M.; Sandoval, J.C.; Yuasa-Kawase, M.; Tsubakio-Yamamoto, K.; Masuda, D.; Maeda, N.; Tsujii, K.; Ishigami, M.; et al. Adiponectin accelerates reverse cholesterol transport by increasing high density lipoprotein assembly in the liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.; van der Westhuyzen, D.R.; Shao, J. Adiponectin reduces plasma triglyceride by increasing VLDL triglyceride catabolism. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1824–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubakio-Yamamoto, K.; Matsuura, F.; Koseki, M.; Oku, H.; Sandoval, J.C.; Inagaki, M.; Nakatani, K.; Nakaoka, H.; Kawase, R.; Yuasa-Kawase, M.; et al. Adiponectin prevents atherosclerosis by increasing cholesterol efflux from macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 390–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitajima, K.; Miura, S.; Yamauchi, T.; Uehara, Y.; Kiya, Y.; Rye, K.A.; Kadowaki, T.; Saku, K. Possibility of increasing cholesterol efflux by adiponectin and its receptors through the ATP binding cassette transporter A1 in HEK293T cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.G.; von Eynatten, M.; Schiekofer, S.; Nawroth, P.P.; Dugi, K.A. Low plasma adiponectin levels are associated with increased hepatic lipase activity in vivo. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2181–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarenbach, J.J.; Vega, G.L.; Adams-Huet, B.; Considine, R.V.; Ricks, M.; Sumner, A.E. Variability in postheparin hepatic lipase activity is associated with plasma adiponectin levels in African Americans. J. Investig. Med. 2007, 55, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, T.W.; Watts, G.F.; Farvid, M.S.; Chan, D.C.; Barrett, P.H. Adipocytokines and VLDL metabolism: Independent regulatory effects of adiponectin, insulin resistance, and fat compartments on VLDL apolipoprotein B-100 kinetics? Diabetes 2005, 54, 795–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, T.; Saito, E.; Kuromori, Y.; Miyashita, M.; Iwata, F.; Hara, M.; Harada, K. Relationship between serum adiponectin level and lipid composition in each lipoprotein fraction in adolescent children. Atherosclerosis 2006, 188, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhala, M.; Kumpula, L.S.; Soininen, P.; Kangas, A.J.; Ala-Korpela, M.; Kautiainen, H.; Mäntyselkä, P.; Saltevo, J. High serum adiponectin is associated with favorable lipoprotein subclass profile in 6.4-year follow-up. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 164, 549–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Hirowatari, Y.; Kurosawa, H.; Tada, N. Implications of decreased serum adiponectin for type IIb hyperlipidaemia and increased cholesterol levels of very-low-density lipoprotein in type II diabetic patients. Clin. Sci. 2005, 109, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.C.; Barrett, P.H.; Ooi, E.M.; Ji, J.; Chan, D.T.; Watts, G.F. Very low density lipoprotein metabolism and plasma adiponectin as predictors of high-density lipoprotein apolipoprotein A-I kinetics in obese and nonobese men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 989–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lapointe, A.; Tchernof, A.; Lamarche, B.; Piché, M.E.; Weisnagel, J.; Bergeron, J.; Lemieux, S. Plasma adiponectin concentration is strongly associated with VLDL-TG catabolism in postmenopausal women. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mead, J.R.; Irvine, S.A.; Ramji, D.P. Lipoprotein lipase: Structure, function, regulation, and role in disease. J. Mol. Med. 2002, 80, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Eynatten, M.; Schneider, J.G.; Humpert, P.M.; Rudofsky, G.; Schmidt, N.; Barosch, P.; Hamann, A.; Morcos, M.; Kreuzer, J.; Bierhaus, A.; et al. Decreased plasma lipoprotein lipase in hypoadiponectinemia: An association independent of systemic inflammation and insulin resistance. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 2925–2929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, J.; Kusunoki, M.; Murase, Y.; Kawashiri, M.; Higashikata, T.; Miwa, K.; Katsuda, S.; Takata, M.; Asano, A.; Nohara, A.; et al. Relationship of lipoprotein lipase and hepatic triacylglycerol lipase activity to serum adiponectin levels in Japanese hyperlipidemic men. Horm. Metab. Res. 2005, 37, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, T.P.; Pajvani, U.B.; Berg, A.H.; Lin, Y.; Jelicks, L.A.; Laplante, M.; Nawrocki, A.R.; Rajala, M.W.; Parlow, A.F.; Cheeseboro, L.; et al. A transgenic mouse with a deletion in the collagenous domain of adiponectin displays elevated circulating adiponectin and improved insulin sensitivity. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 367–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubakio-Yamamoto, K.; Sugimoto, T.; Nishida, M.; Okano, R.; Monden, Y.; Kitazume-Taneike, R.; Yamashita, T.; Nakaoka, H.; Kawase, R.; Yuasa-Kawase, M.; et al. Serum adiponectin level is correlated with the size of HDL and LDL particles determined by high performance liquid chromatography. Metabolism 2012, 61, 1763–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, D.C.; Watts, G.F.; Ng, T.W.; Uchida, Y.; Sakai, N.; Yamashita, S.; Barrett, P.H. Adiponectin and other adipocytokines as predictors of markers of triglyceride-rich lipoprotein metabolism. Clin. Chem. 2005, 51, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sztalryd, C.; Kraemer, F.B. Regulation of hormone-sensitive lipase in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Metabolism 1995, 44, 1391–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilz, S.; Horejsi, R.; Möller, R.; Almer, G.; Scharnagl, H.; Stojakovic, T.; Dimitrova, R.; Weihrauch, G.; Borkenstein, M.; Maerz, W.; et al. Early atherosclerosis in obese juveniles is associated with low serum levels of adiponectin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 4792–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kantartzis, K.; Rittig, K.; Balletshofer, B.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Porubska, K.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.U.; Stefan, N. The relationships of plasma adiponectin with a favorable lipid profile, decreased inflammation, and less ectopic fat accumulation depend on adiposity. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staiger, H.; Kaltenbach, S.; Staiger, K.; Stefan, N.; Fritsche, A.; Guirguis, A.; Péterfi, C.; Weisser, M.; Machicao, F.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Expression of adiponectin receptor mRNA in human skeletal muscle cells is related to in vivo parameters of glucose and lipid metabolism. Diabetes 2004, 53, 2195–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eckel, R.H.; Grundy, S.M.; Zimmet, P.Z. The metabolic syndrome. Lancet 2005, 365, 1415–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, M.; Kotur-Stevuljevic, J.; Berneis, K.; Spinas, G.; Rini, G.B.; Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V.; Vekic, J. Atherogenic dyslipidemia and oxidative stress: A new look. Transl. Res. 2009, 153, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Kugiyama, K. Triglycerides and remnant particles as risk factors for coronary artery disease. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2006, 8, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, D.; Yamashita, S. Postprandial Hyperlipidemia and Remnant Lipoproteins. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2017, 24, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Ohishi, M.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Nakamura, T.; Nagaretani, H.; Kumada, M.; Ohashi, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Nishizawa, H.; et al. Association of hypoadiponectinemia with impaired vasoreactivity. Hypertension 2003, 42, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimabukuro, M.; Higa, N.; Asahi, T.; Oshiro, Y.; Takasu, N.; Tagawa, T.; Ueda, S.; Shimomura, I.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y. Hypoadiponectinemia is closely linked to endothelial dysfunction in man. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 3236–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumada, M.; Kihara, S.; Sumitsuji, S.; Kawamoto, T.; Matsumoto, S.; Ouchi, N.; Arita, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Shimomura, I.; Hiraoka, H.; et al. Coronary artery disease. Association of hypoadiponectinemia with coronary artery disease in men. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I.; Sata, M.; Arita, Y.; Nishida, M.; Maeda, N.; Kumada, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Nagaretani, H.; Nishizawa, H.; et al. Role of adiponectin in preventing vascular stenosis. The missing link of adipo-vascular axis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37487–37491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, N.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, T.; Kumagai, H.; Itoh, S.; Satoh, H.; Yano, W.; Ogata, H.; Tokuyama, K.; Takamoto, I.; et al. Pioglitazone ameliorates insulin resistance and diabetes by both adiponectin-dependent and -independent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 8748–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torigoe, M.; Matsui, H.; Ogawa, Y.; Murakami, H.; Murakami, R.; Cheng, X.W.; Numaguchi, Y.; Murohara, T.; Okumura, K. Impact of the high-molecular-weight form of adiponectin on endothelial function in healthy young men. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 67, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouedraogo, R.; Wu, X.; Xu, S.Q.; Fuchsel, L.; Motoshima, H.; Mahadev, K.; Hough, K.; Scalia, R.; Goldstein, B.J. Adiponectin suppression of high-glucose-induced reactive oxygen species in vascular endothelial cells: Evidence for involvement of a cAMP signaling pathway. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1840–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyatani, Y.; Yasui, T.; Uemura, H.; Yamada, M.; Matsuzaki, T.; Kuwahara, A.; Tsuchiya, N.; Yuzurihara, M.; Kase, Y.; Irahara, M. Associations of circulating adiponectin with estradiol and monocyte chemotactic protein-1 in postmenopausal women. Menopause 2008, 15, 536–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; Dong, Y.; Zhong, J.; Cao, R.; Zhao, X.; Wen, G.; Liu, J. Adiponectin protects endothelial cells from the damages induced by the intermittent high level of glucose. Endocrine 2011, 40, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, M.; Maruhashi, T.; Matsumoto, T.; Iwamoto, Y.; Iwamoto, A.; Oda, N.; Kishimoto, S.; Matsui, S.; Aibara, Y.; Hidaka, T.; et al. Relationship between serum triglyceride levels and endothelial function in a large community-based study. Atherosclerosis 2016, 249, 70–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamwal, S.; Sharma, S. Vascular endothelium dysfunction: A conservative target in metabolic disorders. Inflamm. Res. 2018, 67, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Vanhoutte, P.M. Macro- and microvascular endothelial dysfunction in diabetes. J. Diabetes. 2017, 9, 434–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.; Xu, J.Y.; Lu, G.; Xu, L.Y.; Cooper, G.J.; Xu, A. Adiponectin inhibits cell proliferation by interacting with several growth factors in an oligomerization-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 18341–18347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arita, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Kumada, M.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; et al. Adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin acts as a platelet-derived growth factor-BB-binding protein and regulates growth factor-induced common postreceptor signal in vascular smooth muscle cell. Circulation 2002, 105, 2893–2898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marsche, G.; Zelzer, S.; Meinitzer, A.; Kern, S.; Meissl, S.; Pregartner, G.; Weghuber, D.; Almer, G.; Mangge, H. Adiponectin Predicts High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Efflux Capacity in Adults Irrespective of Body Mass Index and Fat Distribution. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 4117–4123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Xia, M. Adiponectin increases macrophages cholesterol efflux and suppresses foam cell formation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis 2013, 229, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, M.; Nakanishi, S.; Hirano, M.; Maeda, S.; Yoneda, M.; Awaya, T.; Yamane, K.; Kohno, N. Relationship between serum cholesterol efflux capacity and glucose intolerance in Japanese-Americans. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2014, 21, 1087–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yassine, H.N.; Belopolskaya, A.; Schall, C.; Stump, C.S.; Lau, S.S.; Reaven, P.D. Enhanced cholesterol efflux to HDL through the ABCA1 transporter in hypertriglyceridemia of type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2014, 63, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vries, R.; Groen, A.K.; Perton, F.G.; Dallinga-Thie, G.M.; van Wijland, M.J.; Dikkeschei, L.D.; Wolffenbuttel, B.H.; van Tol, A.; Dullaart, R.P. Increased cholesterol efflux from cultured fibroblasts to plasma from hypertriglyceridemic type 2 diabetic patients: Roles of pre beta-HDL, phospholipid transfer protein and cholesterol esterification. Atherosclerosis 2008, 196, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fournier, N.; Francone, O.; Rothblat, G.; Goudouneche, D.; Cambillau, M.; Kellner-Weibel, G.; Robinet, P.; Royer, L.; Moatti, N.; Simon, A.; et al. Enhanced efflux of cholesterol from ABCA1-expressing macrophages to serum from type IV hypertriglyceridemic subjects. Atherosclerosis 2003, 171, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosravi-Largani, M.; Nojomi, M.; Aghili, R.; Otaghvar, H.A.; Tanha, K.; Seyedi, S.H.S.; Mottaghi, A. Evaluation of all Types of Metabolic Bariatric Surgery and its Consequences: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obes. Surg. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincentis, A.; Pedone, C.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U.; Picardi, A.; Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P.; Sahebkar, A. Effect of Sibutramine on Plasma C-Reactive Protein, Leptin and Adipon ectin Concentrations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Contr olled Trials. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2017, 23, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi-Abargouei, A.; Izadi, V.; Azadbakht, L. The effect of low calorie diet on adiponectin concentration: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Horm. Metab. Res. 2015, 47, 549–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Ishikawa, T.; Suto, M.; Kurosawa, H.; Hirowatari, Y.; Ito, K.; Yanai, H.; Tada, N.; Suzuki, M. Effects of supervised aerobic exercise training on serum adiponectin and parameters of lipid and glucose metabolism in subjects with moderate dyslipidemia. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2010, 17, 1160–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinca, M.; Serban, M.C.; Sahebkar, A.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Toth, P.P.; Martin, S.S.; Blaha, M.J.; Blüher, M.; Gurban, C.; Penson, P.; et al. Does vitamin D supplementation alter plasma adipokines concentrations? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2016, 107, 360–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirico, F.; Bianco, A.; D’Alicandro, G.; Castaldo, C.; Montagnani, S.; Spera, R.; Di Meglio, F.; Nurzynska, D. Effects of Physical Exercise on Adiponectin, Leptin, and Inflammatory Markers in Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Child. Obes. 2018, 14, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.; Ruan, Y.; Gao, X.; Sun, J. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized, Controlled Trials on the Effect of Exercise on Serum Leptin and Adiponectin in Overweight and Obese Individuals. Horm. Metab. Res. 2017, 49, 164–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Hermoso, A.; Ceballos-Ceballos, R.J.; Poblete-Aro, C.E.; Hackney, A.C.; Mota, J.; Ramírez-Vélez, R. Exercise, adipokines and pediatric obesity: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Int. J. Obes. 2017, 41, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Hermoso, A.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Ramírez-Campillo, R.; Peterson, M.D.; Martínez-Vizcaíno, V. Concurrent aerobic plus resistance exercise versus aerobic exercise alone to improve health outcomes in paediatric obesity: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Sports Med. 2018, 52, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mousa, A.; Naderpoor, N.; Teede, H.; Scragg, R.; de Courten, B. Vitamin D supplementation for improvement of chronic low-grade inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutr. Rev. 2018, 76, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksomboon, N.; Poolsup, N.; Darli Ko Ko, H. Effect of vitamin K supplementation on insulin sensitivity: A meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2017, 10, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, E.; Arslan, A.K.K.; Yerer, M.B.; Bishayee, A. Resveratrol and diabetes: A critical review of clinical studies. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 95, 230–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi-Sartang, M.; Mazloom, Z.; Sohrabi, Z.; Sherafatmanesh, S.; Barati-Boldaji, R. Resveratrol supplementation and plasma adipokines concentrations? A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2017, 117, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishimoto, Y.; Yoshida, H.; Kondo, K. Potential Anti-Atherosclerotic Properties of Astaxanthin. Mar. Drugs 2016, 14, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Yanai, H.; Ito, K.; Tomono, Y.; Koikeda, T.; Tsukahara, H.; Tada, N. Administration of natural astaxanthin increases serum HDL-cholesterol and adiponectin in subjects with mild hyperlipidemia. Atherosclerosis 2010, 209, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canas, J.A.; Lochrie, A.; McGowan, A.G.; Hossain, J.; Schettino, C.; Balagopal, P.B. Effects of Mixed Carotenoids on Adipokines and Abdominal Adiposity in Children: A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 1983–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.F.; Chang, Y.Y.; Huang, H.C.; Wu, Y.C.; Yang, M.D.; Chao, P.M. Tomato juice supplementation in young women reduces inflammatory adipokine levels independently of body fat reduction. Nutrition 2015, 31, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llanos, A.A.; Peng, J.; Pennell, M.L.; Krok, J.L.; Vitolins, M.Z.; Degraffinreid, C.R.; Paskett, E.D. Effects of tomato and soy on serum adipokine concentrations in postmenopausal women at increased breast cancer risk: A cross-over dietary intervention trial. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben Amara, N.; Tourniaire, F.; Maraninchi, M.; Attia, N.; Amiot-Carlin, M.J.; Raccah, D.; Valéro, R.; Landrier, J.F.; Darmon, P. Independent positive association of plasma β-carotene concentrations with adiponectin among non-diabetic obese subjects. Eur. J. Nutr. 2015, 54, 447–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Inoue, T.; Hashimoto, S.; Ochiai, J.; Kusuhara, Y.; Ito, Y.; Hamajima, N. Association of serum carotenoids with high molecular weight adiponectin and inflammation markers among Japanese subjects. Clin. Chim. Acta 2010, 411, 1330–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwamoto, M.; Imai, K.; Ohta, H.; Shirouchi, B.; Sato, M. Supplementation of highly concentrated β-cryptoxanthin in a satsuma mandarin beverage improves adipocytokine profiles in obese Japanese women. Lipids Health Dis. 2012, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, H.K.; Bourguignon, C.M.; Weltman, A.L.; Vincent, K.R.; Barrett, E.; Innes, K.E.; Taylor, A.G. Effects of antioxidant supplementation on insulin sensitivity, endothelial adhesion molecules, and oxidative stress in normal-weight and overweight young adults. Metabolism 2009, 58, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, H.K.; Bourguignon, C.M.; Vincent, K.R.; Weltman, A.L.; Bryant, M.; Taylor, A.G. Antioxidant supplementation lowers exercise-induced oxidative stress in young overweight adults. Obesity 2006, 14, 2224–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.H.; Cahill, L.E.; Mozaffarian, D. Effect of fish oil on circulating adiponectin: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becic, T.; Studenik, C. Effects of Omega-3 Supplementation on Adipocytokines in Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Diabetes Metab. J. 2018, 42, 101–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.; Zeng, L.; Bao, T.; Ge, J. Effectiveness of Omega-3 fatty acid for polycystic ovary syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2018, 16, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahreini, M.; Ramezani, A.H.; Shishehbor, F.; Mansoori, A. The Effect of Omega-3 on Circulating Adiponectin in Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Can. J. Diabetes 2018, 42, 553–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farimani, A.R.; Hariri, M.; Azimi-Nezhad, M.; Borji, A.; Zarei, S.; Hooshmand, E. The effect of n-3 PUFAs on circulating adiponectin and leptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Acta Diabetol. 2018, 55, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyzos, S.A.; Mantzoros, C.S. Adiponectin as a target for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis with thiazolidinediones: A systematic review. Metabolism 2016, 65, 1297–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H. The Low-Dose (7.5 mg/day) Pioglitazone Therapy. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2017, 9, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutchman, G.; Modi, A.; Kleiner, D.E.; Promrat, K.; Heller, T.; Ghany, M.; Borg, B.; Loomba, R.; Liang, T.J.; Premkumar, A.; et al. The effects of discontinuing pioglitazone in patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2007, 46, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Niu, X.; Zeng, T.; Lu, M.; Chen, L. Impact of Treatment with Metformin on Adipocytokines in Patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.R.; Lu, Z.H.; Su, Y.; Zhao, N.; Dong, C.L.; Sun, L.; Zhao, S.F.; Li, Y. Relationship of Serum Adiponectin Levels and Metformin Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Horm. Metab. Res. 2016, 48, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimabukuro, M.; Higa, M.; Yamakawa, K.; Masuzaki, H.; Sata, M. Miglitol, α-glycosidase inhibitor, reduces visceral fat accumulation and cardiovascular risk factors in subjects with the metabolic syndrome: A randomized comparable study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 2108–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, H.; Kannno, S.; Ishimura, I.; Node, K. Miglitol increases the adiponectin level and decreases urinary albumin excretion in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2007, 56, 1458–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.S.; Lin, S.D.; Lee, W.J.; Su, S.L.; Lee, I.T.; Tu, S.T.; Tseng, Y.H.; Lin, S.Y.; Sheu, W.H. Effects of acarbose versus glibenclamide on glycemic excursion and oxidative stress in type 2 diabetic patients inadequately controlled by metformin: A 24-week, randomized, open-label, parallel-group comparison. Clin. Ther. 2011, 33, 1932–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimazu, T.; Inami, N.; Satoh, D.; Kajiura, T.; Yamada, K.; Iwasaka, T.; Nomura, S. Effect of acarbose on platelet-derived microparticles, soluble selectins, and adiponectin in diabetic patients. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 2009, 28, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochiai, H.; Ooka, H.; Shida, C.; Ishikawa, T.; Inoue, D.; Okazaki, R. Acarbose treatment increases serum total adiponectin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes. Endocr. J. 2008, 55, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Men, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhai, S.; Liu, G. Impact of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on serum adiponectin: A meta-analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frøssing, S.; Nylander, M.; Chabanova, E.; Frystyk, J.; Holst, J.J.; Kistorp, C.; Skouby, S.O.; Faber, J. Effect of liraglutide on ectopic fat in polycystic ovary syndrome: A randomized clinical trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, M.J.; Hull, D.; Guo, K.; Barton, D.; Hazlehurst, J.M.; Gathercole, L.L.; Nasiri, M.; Yu, J.; Gough, S.C.; Newsome, P.N.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1 decreases lipotoxicity in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, A.E.; Gaoatswe, G.; Lynch, L.; Corrigan, M.A.; Woods, C.; O’Connell, J.; O’Shea, D. Glucagon-like peptide 1 analogue therapy directly modulates innate immune-mediated inflammation in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, D.; Toyoda, M.; Kimura, M.; Miyauchi, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Sato, H.; Tanaka, E.; Kuriyama, Y.; Miyatake, H.; Abe, M.; et al. Effects of liraglutide, a human glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue, on body weight, body fat area and body fat-related markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Intern. Med. 2013, 52, 1029–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Adachi, H.; Moriyama, S.; Hirowatari, Y. Effects of Liraglutide, a Human Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analog, on Glucose/Lipid Metabolism, and Adipocytokines in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 1, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhu, J.; Yang, P.; Tang, X.; Yu, W.; Pan, C.; Shen, M.; Zhu, D.; Cheng, J.; Ye, X. Comparison of exenatide and acarbose on intra-abdominal fat content in patients with obesity and type-2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 11, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Hsieh, S.H.; Sun, J.H.; Tsai, J.S.; Huang, Y.Y. Glucose Variability and β- Cell Response by GLP-1 Analogue added-on CSII for Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Katsuyama, H.; Hamasaki, H.; Adachi, H.; Moriyama, S.; Yoshikawa, R.; Sako, A. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Possible Anti-Atherosclerotic Effects Beyond Glucose Lowering. J. Clin. Med. Res. 2016, 8, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomiyama, T.; Shimono, D.; Horikawa, T.; Fujimura, Y.; Ohsako, T.; Terawaki, Y.; Fukuda, T.; Motonaga, R.; Tanabe, M.; Yanase, T. Efficacy and safety of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor ipragliflozin on glycemic control and cardiovascular parameters in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus; Fukuoka Study of Ipragliflozin (FUSION). Endocr. J. 2018, 65, 859–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, S.; Jinnouchi, H.; Kurinami, N.; Hieshima, K.; Yoshida, A.; Jinnouchi, K.; Nishimura, H.; Suzuki, T.; Miyamoto, F.; Kajiwara, K.; et al. The SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Significantly Improves the Peripheral Microvascular Endothelial Function in Patients with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 2147–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, W.T.; Van Gaal, L.; Leiter, L.A.; Vijapurkar, U.; List, J.; Cuddihy, R.; Ren, J.; Davies, M.J. Effects of canagliflozin versus glimepiride on adipokines and inflammatory biomarkers in type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2018, 85, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobita, H.; Sato, S.; Miyake, T.; Ishihara, S.; Kinoshita, Y. Effects of Dapagliflozin on Body Composition and Liver Tests in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective, Open-label, Uncontrolled Study. Curr. Ther. Res. Clin. Exp. 2017, 87, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Fukui, T.; Nakanishi, N.; Yamamoto, S.; Tomoyasu, M.; Osamura, A.; Ohara, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Ito, Y.; Hirano, T. Dapagliflozin decreases small dense low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and increases high-density lipoprotein 2-cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes: Comparison with sitagliptin. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2017, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, H.; Yamaguchi, S.; Nakao, I.; Okitsu, A.; Asahina, S. Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as add-on therapy to insulin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (IOLITE): A multi-centre, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 1207–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, A.; Yokokawa, H.; Sanada, H.; Naito, T. Changes in Levels of Biomarkers Associated with Adipocyte Function and Insulin and Glucagon Kinetics during Treatment with Dapagliflozin among Obese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Drugs R D 2016, 16, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomoto, H.; Miyoshi, H.; Furumoto, T.; Oba, K.; Tsutsui, H.; Inoue, A.; Atsumi, T.; Manda, N.; Kurihara, Y.; Aoki, S. A Randomized Controlled Trial Comparing the Effects of Sitagliptin and Glimepiride on Endothelial Function and Metabolic Parameters: Sapporo Athero-Incretin Study 1 (SAIS1). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, M.; Yamaguchi, T.; Saiki, A.; Ban, N.; Kawana, H.; Nagumo, A.; Murano, T.; Shirai, K.; Tatsuno, I. Pioglitazone improves the cardio-ankle vascular index in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with metformin. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2014, 7, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sam, S.; Haffner, S.; Davidson, M.H.; D’Agostino, R., Sr.; Perez, A.; Mazzone, T. Pioglitazone-mediated changes in lipoprotein particle composition are predicted by changes in adiponectin level in type 2 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 97, E110–E114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfützner, A.; Schöndorf, T.; Tschöpe, D.; Lobmann, R.; Merke, J.; Müller, J.; Lehmann, U.; Fuchs, W.; Forst, T. PIOfix-study: Effects of pioglitazone/metformin fixed combination in comparison with a combination of metformin with glimepiride on diabetic dyslipidemia. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2011, 13, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P.; Ferrari, I.; Mereu, R.; Ragonesi, P.D.; Querci, F.; Franzetti, I.G.; Gadaleta, G.; Ciccarelli, L.; Piccinni, M.N.; et al. Effects of one year treatment of vildagliptin added to pioglitazone or glimepiride in poorly controlled type 2 diabetic patients. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 663–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forst, T.; Weber, M.M.; Löbig, M.; Lehmann, U.; Müller, J.; Hohberg, C.; Friedrich, C.; Fuchs, W.; Pfützner, A. Pioglitazone in addition to metformin improves erythrocyte deformability in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin. Sci. 2010, 119, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.J.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yu, D.M.; Zhang, Q.M. Adding glimepiride to current insulin therapy increases high-molecular weight adiponectin levels to improve glycemic control in poorly controlled type 2 diabetes. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2014, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Huang, Z.; Bi, M.; Xu, X.; Zhao, N. Effects of simvastatin on serum adiponectin: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Lipids Health Dis. 2017, 16, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chruściel, P.; Sahebkar, A.; Rembek-Wieliczko, M.; Serban, M.C.; Ursoniu, S.; Mikhailidis, D.P.; Jones, S.R.; Mosteoru, S.; Blaha, M.J.; Martin, S.S.; et al. Impact of statin therapy on plasma adiponectin concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 43 randomized controlled trial arms. Atherosclerosis 2016, 253, 194–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolezelova, E.; Stein, E.; Derosa, G.; Maffioli, P.; Nachtigal, P.; Sahebkar, A. Effect of ezetimibe on plasma adipokines: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 1380–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebkar, A.; Watts, G.F. Fibrate therapy and circulating adiponectin concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Atherosclerosis 2013, 230, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahebkar, A. Head-to-head comparison of fibrates versus statins for elevation of circulating adiponectin concentrations: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Metabolism 2013, 62, 1876–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, H.; Niwa, M.; Mizuno, Y.; Goto, S.N.; Umemoto, T. Telmisartan as a metabolic sartan: The first meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in metabolic syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2013, 7, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takagi, H.; Umemoto, T. Telmisartan increases adiponectin levels: A meta-analysis and meta-regression of randomized head-to-head trials. Int. J. Cardiol. 2012, 155, 448–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksomboon, N.; Poolsup, N.; Prasit, T. Systematic review of the effect of telmisartan on insulin sensitivity in hypertensive patients with insulin resistance or diabetes. Clin. Pharm. Ther. 2012, 37, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| 1. Weight Loss |
| Bariatric Surgery |
| Sibutramine |
| Low Calorie Diet |
| 2. Exercise |
| 3. Nutritional Factors |
| Resveratrol |
| Astaxanthin |
| Mixed-Carotenoid Supplementation (β-carotene, α-carotene, |
| Lutein, Zeaxanthin, Lycopene, Astaxanthin, γ-tocopherol) |
| Tomato Juice |
| β-carotene |
| β-cryptoxanthin |
| Antioxidant Supplementation (Vitamin E, Vitamin C, β-carotene) |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids |
| 4. Anti-Diabetic Drugs |
| Thiazolidinediones |
| Metformin |
| α-Glycosidase Inhibitors (Miglitol, Acarbose) |
| Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors |
| Glucagon-Like Peptide-1Analugues (Liraglutide < Exenatide) |
| Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors |
| 5. Hypolipidemia Drugs |
| Statin |
| Fibrate |
| 6. Anti-Hypertensive Drugs |
| Angiotensin II Receptor blockers (Telmisartan) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yanai, H.; Yoshida, H. Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051190
Yanai H, Yoshida H. Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(5):1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051190
Chicago/Turabian StyleYanai, Hidekatsu, and Hiroshi Yoshida. 2019. "Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 5: 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051190
APA StyleYanai, H., & Yoshida, H. (2019). Beneficial Effects of Adiponectin on Glucose and Lipid Metabolism and Atherosclerotic Progression: Mechanisms and Perspectives. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(5), 1190. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20051190





