Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-Mediated Competing Endogenous RNA Networks Provide Novel Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Colorectal Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
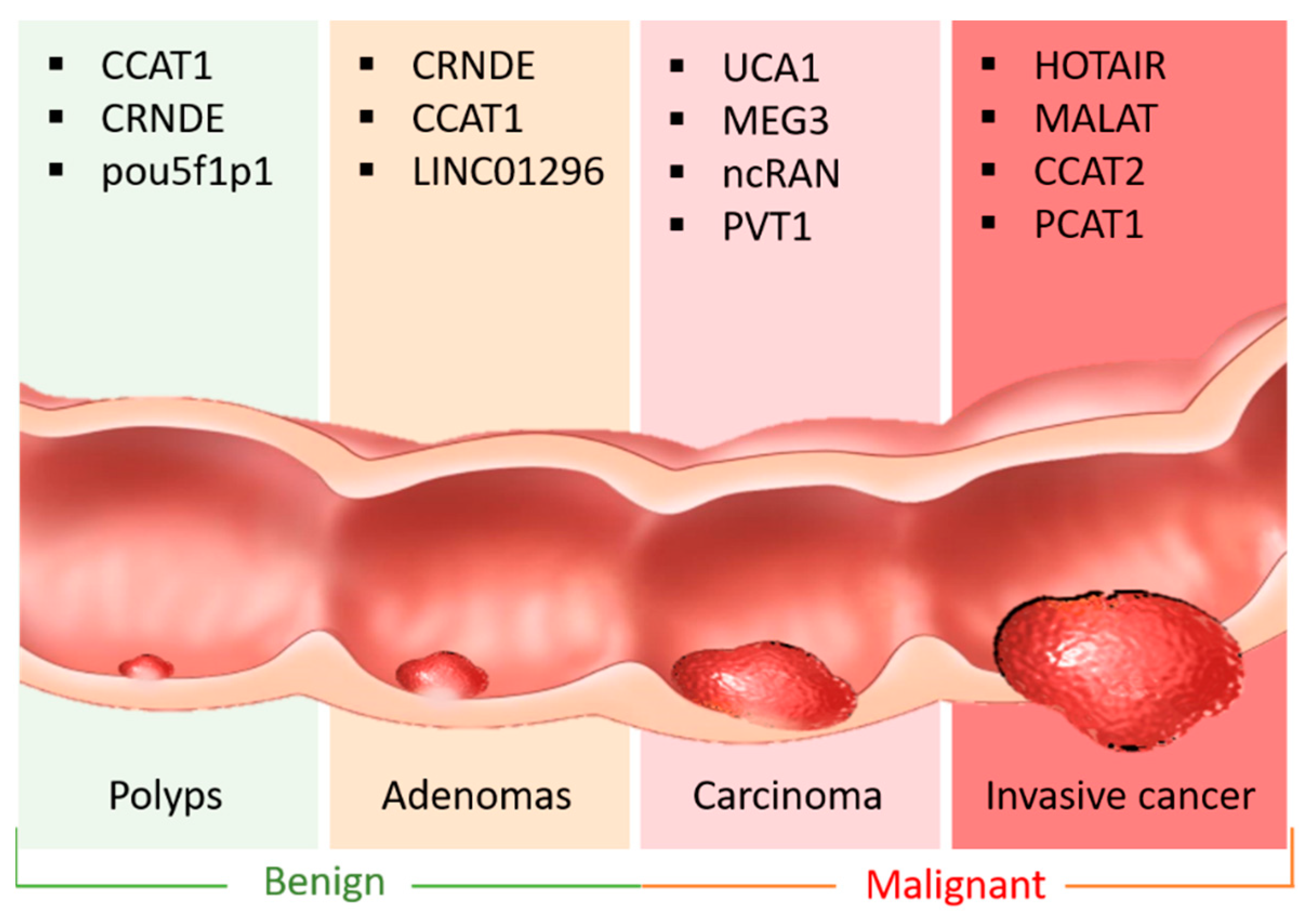
2. LncRNA in CRC
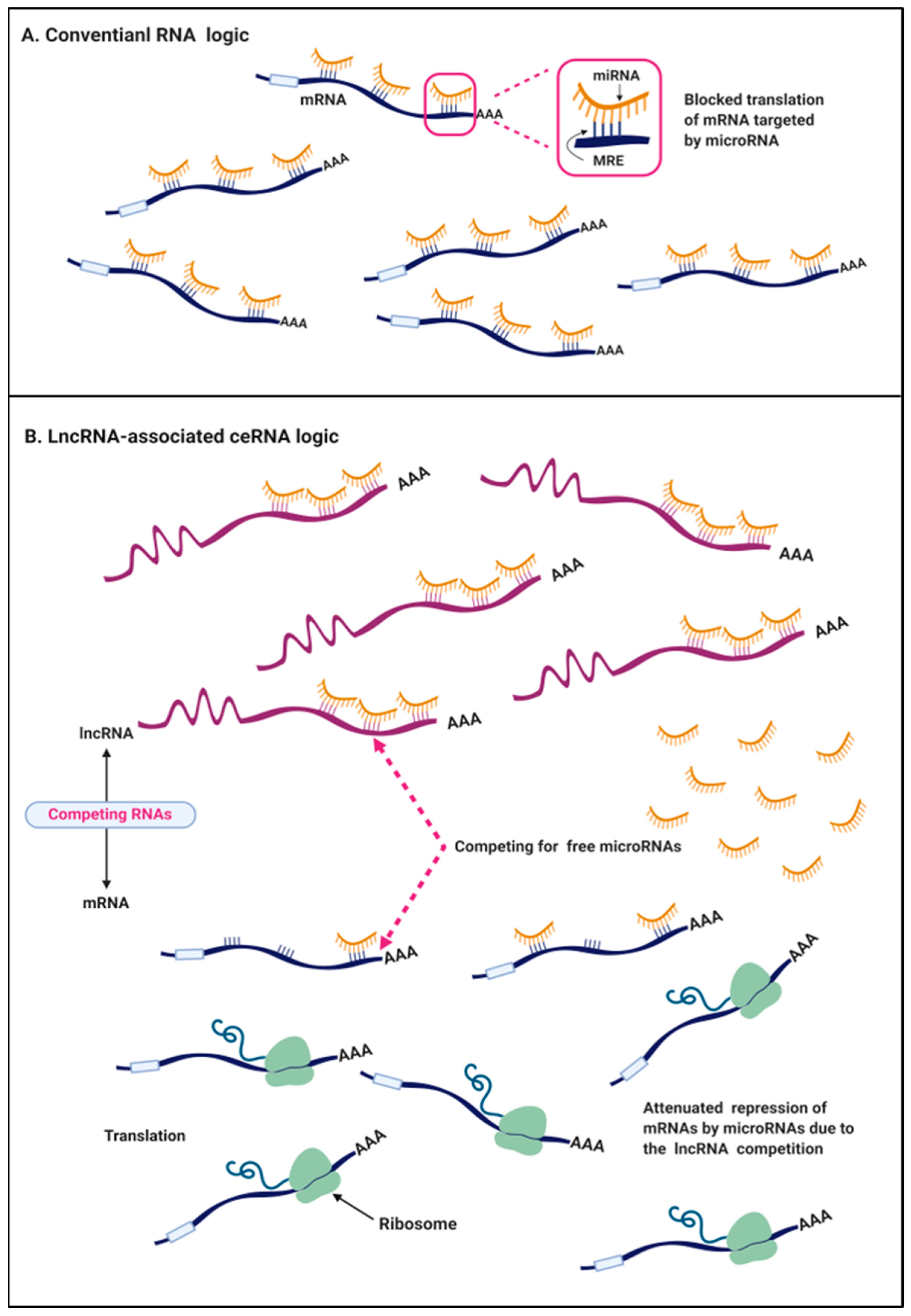
3. The ceRNA Hypothesis in Cancers
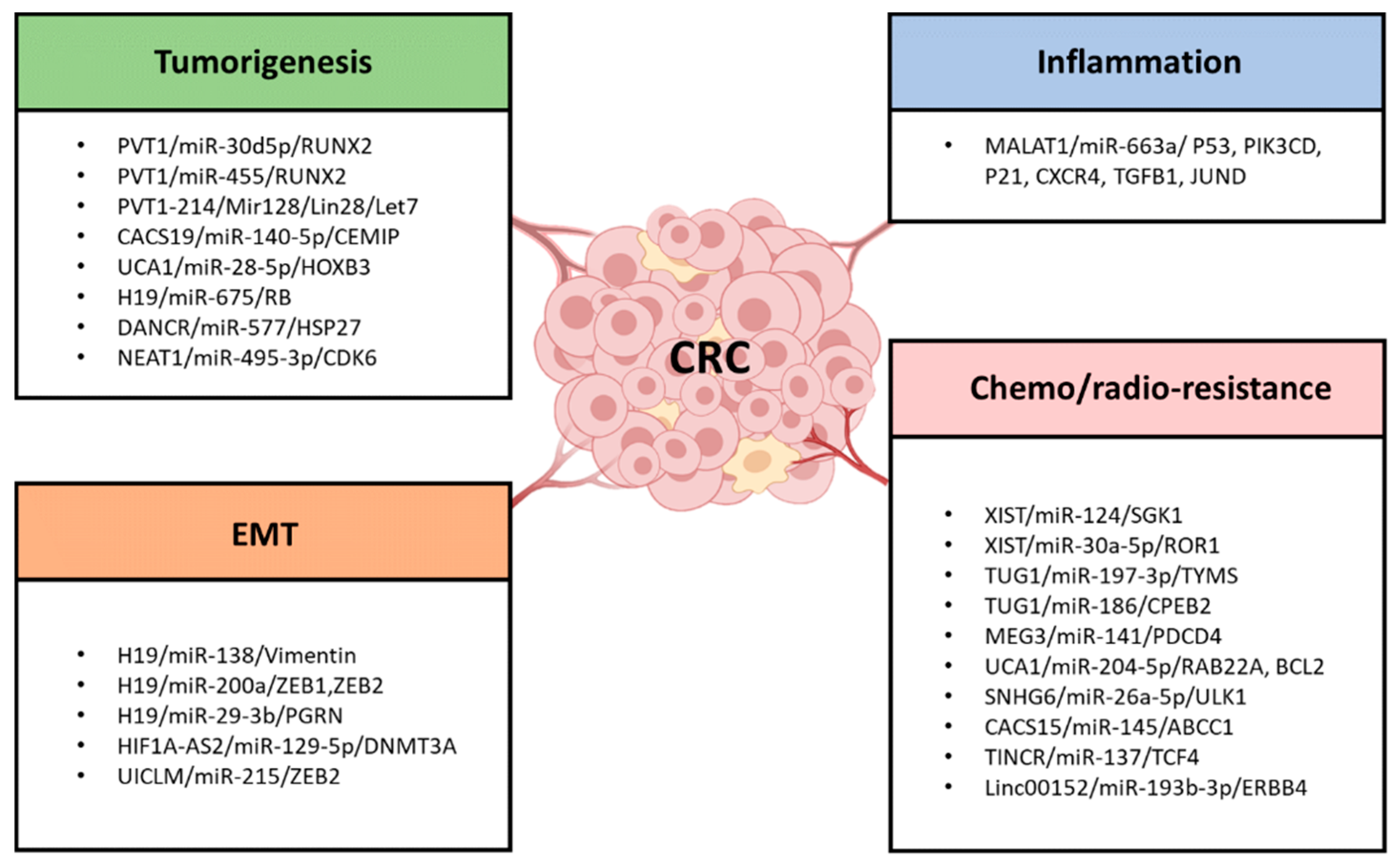
4. LncRNAs as ceRNA in CRC Tumorigenesis and Progression
4.1. PVT1/miR-30d-5p/RUNX2
4.2. PVT1/miR-455/RUNX2
4.3. PVT1-214/Mir128/Lin28/Let7
4.4. CACS19/miR-140-5p/CEMIP
4.5. UCA1/miR-28-5p/HOXB3
4.6. Other lncRNA/miRNA/mRNA Axis
5. LncRNAs as ceRNA in the EMT and Cell Stemness Formation in CRC
5.1. H19
5.1.1. H19/miR-138/Vimentin and H19/miR-200a/ZEB1, ZEB2
5.1.2. H19/miR-29-3b/PGRN
5.2. HIF1A-AS2/miR-129-5p/DNMT3A
5.3. UICLM/miR-215/ZEB2
6. LncRNA as ceRNA in the Inflammation Formation in CRC
7. LncRNA as ceRNA in Chemoresistance/Radioresistance of CRC
7.1. XIST
7.2. TUG1
7.3. MEG3
7.4. UCA1
7.5. Linc00152
7.6. SNHG6
7.7. CACS15
7.8. TINCR
8. Databases for the Prediction of lncRNA-Associated ceRNA Interactions
9. Conclusions and Future Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABCC1 | ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 1 |
| AKT | AKT Serine/Threonine Kinase 1 |
| BCAR4 | Breast Cancer Anti-Estrogen Resistance 4 |
| BCL2 | B-Cell CLL/Lymphoma 2 |
| CACS15 | Cancer Susceptibility 15 |
| CASC19 | Cancer Susceptibility 19 |
| CASC2 | Cancer Susceptibility 2 |
| CCAT1 | Colon Cancer Associated Transcript 1 |
| CCAT2 | Colon Cancer Associated Transcript 2 |
| CDC42 | Cell Division Cycle 42 |
| CDK1 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 1 |
| CDK6 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 6 |
| CDK9 | Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 9 |
| CEMIP | Cell Migration Inducing Hyaluronidase 1 |
| CPEB2 | Cytoplasmic Polyadenylation Element Binding Protein 2 |
| CRNDE | colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed |
| CXCR4 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 4 |
| CYTOR | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 152 |
| DANCR | Differentiation antagonizing non-protein noding RNA |
| DNMT3A | DNA Methyltransferase 3 Alpha |
| ERBB2 | Erb-B2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 4 |
| EZH2 | Enhancer of Zeste 2 Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 |
| FOXD2-AS1 | FOXD2 Antisense RNA 1 |
| FOXD3-AS1 | FOXD3 Antisense RNA 1 |
| GACAT3 | Gastric Cancer Associated Transcript 3 |
| HAND2-AS1 | HAND2 Antisense RNA 1 |
| HAGLROS | HAGLR opposite strand lncRNA |
| HIF1A-AS2 | HIF1A Antisense RNA 2 |
| HOTAIR | HOX Transcript Antisense RNA |
| HSP27 | Heat Shock Protein 27 |
| HULC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma Associated Transcript 1 |
| KCNQ1OT1 | KCNQ1 opposite strand/antisense transcript 1 |
| KIAA1199 | Cell Migration Inducing Hyaluronidase 1 |
| KLF14 | Kruppel-Like Factor 14 |
| KRAS | K-Ras |
| LGR5 | Leucine Rich Repeat Containing G Protein-Coupled Receptor 5 |
| LIMK2 | LIM Domain Kinase 2 |
| LINC00460 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 460 |
| LINC00668 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 668 |
| LINC00858 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 858 |
| LINC01234 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 1234 |
| LINC01296 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 1296 |
| LINC02418 | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA 2418 |
| LSD1 | Lysine Demethylase 1A |
| MACC1 | MET Transcriptional Regulator MACC1 |
| MALAT1 | Metastasis Associated Lung Adenocarcinoma Transcript 1 |
| MBNL1-AS1 | MBNL1 Antisense RNA 1 |
| MEG3 | Maternally Expressed 3 |
| MELK | Maternal Embryonic Leucine Zipper Kinase |
| MIAT | Myocardial Infarction Associated Transcript |
| MIR17HG | MIR17 Host Gene |
| MNX1-AS1 | MNX1 Antisense RNA 1 |
| MYL9 | Myosin Light Chain 9 |
| NEAT1 | Nuclear Paraspeckle Assembly Transcript 1 |
| OECC | Overexpressed in Colorectal Cancer lncRNA |
| PART-1 | Prostate Androgen-Regulated Transcript 1 |
| PCAT1 | prostate cancer associated transcript 1 |
| PDCD4 | Programmed Cell Death 4 |
| PDCD4 | Programmed Cell Death 4 |
| PGRN | Progranulin |
| PIAS3 | Protein Inhibitor Of Activated STAT 3 |
| PIK3CD | Phosphatidylinositol-4,5-Bisphosphate 3-Kinase Catalytic Subunit Delta |
| POU3F3 | POU class 3 homeobox 3 |
| POU5F1P1 | POU class 5 homeobox 1B |
| PRC2 | Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 |
| PTEN | Phosphatase And Tensin Homolog |
| PTEN | Phosphatase And Tensin Homolog |
| PVT1 | Plasmacytoma Variant Translocation 1 |
| RAB22A | Ras-Related Protein Rab-22A |
| ROR | Long Intergenic Non-Protein Coding RNA, Regulator Of Reprogramming |
| ROR1 | Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Like Orphan Receptor 1 |
| RTKN | Rhotekin |
| RUNX2 | Runt-Related Transcription Factor 2 |
| SEC61A1 | SEC61 Translocon Alpha 1 Subunit |
| SHMT2 | Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase 2 |
| SIRT1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| SNHG15 | Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 15 |
| SNHG16 | Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 16 |
| SNRHG6 | Small Nucleolar RNA Host Gene 6 |
| SP1 | Sp1 Transcription Factor |
| STAT3 | Signal Transducer And Activator Of Transcription 3 |
| TCF4 | Transcription Factor 4 |
| TGF-a | Transforming Growth Factor Alpha |
| TGFB1 | Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 |
| TINCR | Tissue Differentiation-Inducing Non-Protein Coding RNA |
| TOP2A | Topoisomerase (DNA) II Alpha |
| TP73-AS1 | lncRNA P73 antisense RNA 1T |
| TUG1 | Taurine Up-Regulated 1 |
| TUSC7 | Tumor Suppressor Candidate 7 |
| TYMS | Thymidylate Synthetase |
| UCA1 | Urothelial Cancer Associated 1 |
| UCC | A novel lincRNA termed upregulated in CRC |
| ULK1 | Unc-51 Like Autophagy Activating Kinase 1 |
| USP47 | Ubiquitin Specific Peptidase 47 |
| VEGFC | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C |
| XIST | X Inactive Specific Transcript |
| YWHAZ | Tyrosine 3-Monooxygenase/Tryptophan 5-Monooxygenase Activation Protein Zeta |
| ZDHHC8P1 | Zinc Finger DHHC-Type Containing 8 Pseudogene 1 |
| ZEB1 | Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 1 |
| ZEB2 | Zinc Finger E-Box Binding Homeobox 2 |
| ZFAS1 | ZNFX1 Antisense RNA 1 |
| ZNF148 | Zinc Finger Protein 148 |
| ZNFX1-AS1 | ZNFX1 Antisense RNA 1 |
References
- Macrae, F.A. Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Protective Factors. Available online: https://www.uptodate.com/contents/colorectal-cancer-epidemiology-risk-factors-and-protective-factors (accessed on 25 October 2019).
- Fearnhead, N.S.; Wilding, J.L.; Bodmer, W.F. Genetics of colorectal cancer: Hereditary aspects and overview of colorectal tumorigenesis. Br. Med. Bull. 2002, 64, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Yu, T.; Ding, L.; Laurini, E.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Weng, Y.; Lin, S.; Chen, P.; Marson, D.; et al. A Dual Targeting Dendrimer-Mediated siRNA Delivery System for Effective Gene Silencing in Cancer Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16264–16274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, A.; Miyata, K.; Kataoka, K. Recent progress in development of siRNA delivery vehicles for cancer therapy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 104, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsushima, K.; Natsume, A.; Ohka, F.; Shinjo, K.; Hatanaka, A.; Ichimura, N.; Sato, S.; Takahashi, S.; Kimura, H.; Totoki, Y.; et al. Targeting the Notch-regulated non-coding RNA TUG1 for glioma treatment. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xie, Z.; Xie, C.; Lu, W.; Gao, C.; Ren, H.; Ying, M.; Wei, X.; Gao, J.; Su, B.; et al. D-SP5 Peptide-Modified Highly Branched Polyethylenimine for Gene Therapy of Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Bioconj. Chem. 2015, 26, 1494–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lei, Y.; Xie, C.; Lu, W.; Wagner, E.; Xie, Z.; Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Yan, Z.; Liu, M. Retro-inverso CendR peptide-mediated polyethyleneimine for intracranial glioblastoma-targeting gene therapy. Bioconj. Chem. 2014, 25, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Lei, Y.; Xie, C.; Lu, W.; Yan, Z.; Gao, J.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, M. Targeted gene delivery to glioblastoma using a C-end rule RGERPPR peptide-functionalised polyethylenimine complex. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 458, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, J.J.; Tay, Y. Noncoding RNA: RNA Regulatory Networks in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orom, U.A.; Derrien, T.; Beringer, M.; Gumireddy, K.; Gardini, A.; Bussotti, G.; Lai, F.; Zytnicki, M.; Notredame, C.; Huang, Q.; et al. Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells. Cell 2010, 143, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.; Pichler, M.; Chen, M.; Calin, G.A.; Ling, H. To Wnt or Lose: The Missing Non-Coding Linc in Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.C.; Zhu, X.; Qiu, J.J.; Xu, J.; Wei, Y. Involvement of long non-coding RNA in colorectal cancer: From benchtop to bedside (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saus, E.; Brunet-Vega, A.; Iraola-Guzman, S.; Pegueroles, C.; Gabaldon, T.; Pericay, C. Long Non-Coding RNAs As Potential Novel Prognostic Biomarkers in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, M.; Lieberman, J.; Lal, A. Desperately seeking microRNA targets. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 1169–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, H. Redefining microRNA targets. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, 870–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selbach, M.; Schwanhausser, B.; Thierfelder, N.; Fang, Z.; Khanin, R.; Rajewsky, N. Widespread changes in protein synthesis induced by microRNAs. Nature 2008, 455, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y.; Jeyapalan, Z.; Fang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yee, A.Y.; Li, M.; Du, W.W.; Shatseva, T.; Yang, B.B. Expression of versican 3’-untranslated region modulates endogenous microRNA functions. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazalla, D.; Yario, T.; Steitz, J.A. Down-regulation of a host microRNA by a Herpesvirus saimiri noncoding RNA. Science 2010, 328, 1563–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Wu, H.; Ni, P.; Gu, Z.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, N.; Sun, F.; Fan, Q. CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA, HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver cancer. Nucl. Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5366–5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, Y.Y.; Moriarity, B.S.; Gong, W.; Akiyama, R.; Tiwari, A.; Kawakami, H.; Ronning, P.; Reuland, B.; Guenther, K.; Beadnell, T.C.; et al. PVT1 dependence in cancer with MYC copy-number increase. Nature 2014, 512, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, J.; He, Y. Long non-coding RNA PVT1 functions as an oncogene in human colon cancer through miR-30d-5p/RUNX2 axis. J. B.U.ON Off. J. Balk. Union Oncol. 2018, 23, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Gokulnath, M.; Partridge, N.C.; Selvamurugan, N. Runx2, a target gene for activating transcription factor-3 in human breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2015, 36, 1923–1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tandon, M.; Chen, Z.; Pratap, J. Runx2 activates PI3K/Akt signaling via mTORC2 regulation in invasive breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2014, 16, R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, J.; Shentu, Y.; Xie, X. MicroRNA-455 regulates migration and invasion of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting Runx2. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 3325–3332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, C.; Liu, X.; Ma, H.; Zhang, W.; Li, H. miR3383p suppresses tumor growth of ovarian epithelial carcinoma by targeting Runx2. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 2277–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, J.; Guo, D.; Ma, W.; Han, D.; Dong, W.; Guo, H.; Zhang, Y. A feedback loop consisting of RUNX2/LncRNA-PVT1/miR-455 is involved in the progression of colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 538–550. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.; Song, Z.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Yang, P.; Li, W.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, T.; Wang, F.; Wei, J.; et al. Long noncoding RNA PVT1-214 promotes proliferation and invasion of colorectal cancer by stabilizing Lin28 and interacting with miR-128. Oncogene 2019, 38, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.D.; Lu, J.; Lin, Y.S.; Gao, C.; Qi, F. Functional role of long non-coding RNA CASC19/miR-140-5p/CEMIP axis in colorectal cancer progression in vitro. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 1697–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banach, A.; Jiang, Y.P.; Roth, E.; Kuscu, C.; Cao, J.; Lin, R.Z. CEMIP upregulates BiP to promote breast cancer cell survival in hypoxia. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 4307–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Liu, W.; Xu, X.; Zhu, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, K.; He, S.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; et al. Downregulation of long noncoding RNA UCA1 enhances the radiosensitivity and inhibits migration via suppression of epithelialmesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 1554–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Yang, Y.N.; Yuan, H.H.; Zhang, T.T.; Sui, H.; Wei, X.L.; Liu, L.; Huang, P.; Zhang, W.J.; Bai, Y.X. UCA1, a long non-coding RNA up-regulated in colorectal cancer influences cell proliferation, apoptosis and cell cycle distribution. Pathology 2014, 46, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neve, B.; Jonckheere, N.; Vincent, A.; Van Seuningen, I. Epigenetic Regulation by lncRNAs: An Overview Focused on UCA1 in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2018, 10, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Jin, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Y.; Quan, C.; Hu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, H.; Fei, B.; Mao, Y.; et al. LncRNA-UCA1 enhances cell proliferation and 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting miR-204-5p. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 23892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, M.; Chen, M.; Shen, Z.; Wang, R.; Fang, X.; Song, B. LncRNA-UCA1 modulates progression of colon cancer through regulating the miR-28-5p/HOXB3 axis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, H.; Yao, B.; Xu, W.; Chen, J.; Zhou, X. lncRNA H19/miR-675 axis regulates cardiomyocyte apoptosis by targeting VDAC1 in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Wang, N.; Feng, J.; Zhang, J.; Luan, L.; Zhao, W.; Zeng, X. Long noncoding RNA DANCR promotes colorectal cancer proliferation and metastasis via miR-577 sponging. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.H.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.Z.; Hao, L.Q.; Liu, L.J.; Zhang, W. ZNF148 modulates TOP2A expression and cell proliferation via ceRNA regulatory mechanism in colorectal cancer. Medicine 2017, 96, e5845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Dang, J.; Song, A.; Cui, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhang, Z. NEAT1 promotes colon cancer progression through sponging miR-495-3p and activating CDK6 in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19582–19591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiwata, T. Cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Novel therapeutic targets for cancer. Pathol. Int. 2016, 66, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bates, R.C.; Pursell, B.M.; Mercurio, A.M. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and colorectal cancer: Gaining insights into tumor progression using LIM 1863 cells. Cells Tissues Organs 2007, 185, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bates, R.C. Colorectal cancer progression: Integrin alphavbeta6 and the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Cell Cycle (Georget. Tex.) 2005, 4, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, A.S. The morphogenetic role of cadherin cell adhesion molecules in human cancer: A thematic review. Cancer Investig. 1998, 16, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoreson, M.A.; Reynolds, A.B. Altered expression of the catenin p120 in human cancer: Implications for tumor progression. Differ. Res. Biol. Divers. 2002, 70, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez, M.G.; Kojima, S.; Goldman, R.D. Vimentin induces changes in cell shape, motility, and adhesion during the epithelial to mesenchymal transition. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2010, 24, 1838–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarkova, V.; Kralova, V.; Vitovcova, B.; Rudolf, E. Selected Aspects of Chemoresistance Mechanisms in Colorectal Carcinoma-A Focus on Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition, Autophagy, and Apoptosis. Cells 2019, 8, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeguchi, M.; Taniguchi, T.; Makino, M.; Kaibara, N. Reduced E-cadherin expression and enlargement of cancer nuclei strongly correlate with hematogenic metastasis in colorectal adenocarcinoma. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2000, 35, 839–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugli, A.; Zlobec, I.; Minoo, P.; Baker, K.; Tornillo, L.; Terracciano, L.; Jass, J.R. Prognostic significance of the wnt signalling pathway molecules APC, beta-catenin and E-cadherin in colorectal cancer: A tissue microarray-based analysis. Histopathology 2007, 50, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roca, F.; Mauro, L.V.; Morandi, A.; Bonadeo, F.; Vaccaro, C.; Quintana, G.O.; Specterman, S.; de Kier Joffe, E.B.; Pallotta, M.G.; Puricelli, L.I.; et al. Prognostic value of E-cadherin, beta-catenin, MMPs (7 and 9), and TIMPs (1 and 2) in patients with colorectal carcinoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2006, 93, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Z.; Zhou, M.; Tian, B.; Wu, B.; Li, J. Expression of lncRNA-CCAT1, E-cadherin and N-cadherin in colorectal cancer and its clinical significance. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2015, 8, 3707–3715. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shan, Z.Z.; Yan, X.B.; Yan, L.L.; Tian, Y.; Meng, Q.C.; Qiu, W.W.; Zhang, Z.; Jin, Z.M. Overexpression of Tbx3 is correlated with Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition phenotype and predicts poor prognosis of colorectal cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2015, 5, 344–353. [Google Scholar]
- Ying, L.; Chen, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Qiu, F. Upregulated MALAT-1 contributes to bladder cancer cell migration by inducing epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Mol. BioSyst. 2012, 8, 2289–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Mandal, S.S. LncRNA HOTAIR: A master regulator of chromatin dynamics and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1856, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.C.; Fu, W.M.; Wong, C.W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, W.M.; Hu, G.X.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, L.J.; Wan, D.C.; Zhang, J.F.; et al. The lncRNA H19 promotes epithelial to mesenchymal transition by functioning as miRNA sponges in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 22513–22525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Chen, Z. LncRNA H19 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by targeting miR-484 in human lung cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 4447–4457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Ye, X.L.; Xu, J.; Cao, M.G.; Fang, Z.Y.; Li, L.Y.; Guan, G.H.; Liu, Q.; Qian, Y.H.; Xie, D. The lncRNA H19 mediates breast cancer cell plasticity during EMT and MET plasticity by differentially sponging miR-200b/c and let-7b. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Nong, K.; Zhu, H.; Wang, W.; Huang, X.; Yuan, Z.; Ai, K. H19 promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis by derepressing let-7’s suppression on its target HMGA2-mediated EMT. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodev. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 9163–9169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.M.; Gaur, A.B.; Lengyel, E.; Peter, M.E. The miR-200 family determines the epithelial phenotype of cancer cells by targeting the E-cadherin repressors ZEB1 and ZEB2. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 894–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bert, A.G.; Paterson, E.L.; Barry, S.C.; Tsykin, A.; Farshid, G.; Vadas, M.A.; Khew-Goodall, Y.; Goodall, G.J. The miR-200 family and miR-205 regulate epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting ZEB1 and SIP1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Jin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Kolokythas, A.; Dai, Y.; Zhou, X. MicroRNA-138 suppresses epithelial-mesenchymal transition in squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Biochem. J. 2011, 440, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, L.; Huang, G.; Zhu, H.; Guo, Y.; Liu, Y.; Huo, J. Down-regulation of miR-138 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis via directly targeting TWIST2. J. Transl. Med. 2013, 11, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, D.; Feng, Z.; Mao, J.; Zhang, C.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Q.; Li, L. MicroRNA-138 modulates metastasis and EMT in breast cancer cells by targeting vimentin. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 77, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, D.; Fang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xiang, J. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitionassociated microRNAs in colorectal cancer and drug-targeted therapies (Review). Oncol. Rep. 2015, 33, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, C.; Chen, X.; He, J. H19 promotes the migration and invasion of colon cancer by sponging miR-138 to upregulate the expression of HMGA1. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1801–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, F.; Wang, T.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhou, S.; Ma, X.; Wang, S. HMGA1 exacerbates tumor growth through regulating the cell cycle and accelerates migration/invasion via targeting miR-221/222 in cervical cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Li, C.; Zhao, T.; Li, D.; Yang, L.; Zhang, B. LncRNA H19/miR-29b-3p/PGRN Axis Promoted Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition of Colorectal Cancer Cells by Acting on Wnt Signaling. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 423–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Jin, S.; Zheng, H.; Lin, J.; He, F.; Zhang, H.; Ma, S.; Mei, J.; et al. MiR-29b-3p promotes chondrocyte apoptosis and facilitates the occurrence and development of osteoarthritis by targeting PGRN. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2017, 21, 3347–3359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, T.; Yang, D.; Li, R.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kong, B.; Wang, L. PGRN promotes migration and invasion of epithelial ovarian cancer cells through an epithelial mesenchymal transition program and the activation of cancer associated fibroblasts. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2016, 100, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zhuang, C.; Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Dai, F.; Xia, M.; Zhan, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, Z.; He, A.; et al. Tetracycline-inducible shRNA targeting antisense long non-coding RNA HIF1A-AS2 represses the malignant phenotypes of bladder cancer. Cancer Lett. 2016, 376, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, M.; Mei, Z.; Cao, W.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wen, A. lncRNAs HIF1A-AS2 facilitates the up-regulation of HIF-1alpha by sponging to miR-153-3p, whereby promoting angiogenesis in HUVECs in hypoxia. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 96, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mineo, M.; Ricklefs, F.; Rooj, A.K.; Lyons, S.M.; Ivanov, P.; Ansari, K.I.; Nakano, I.; Chiocca, E.A.; Godlewski, J.; Bronisz, A. The Long Non-coding RNA HIF1A-AS2 Facilitates the Maintenance of Mesenchymal Glioblastoma Stem-like Cells in Hypoxic Niches. Cell Rep. 2016, 15, 2500–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.; Shi, Z.; Yu, Z.; He, Z. LncRNA HIF1A-AS2 positively affects the progression and EMT formation of colorectal cancer through regulating miR-129-5p and DNMT3A. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 98, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, J. DNA methyltransferases and their roles in tumorigenesis. Biomark. Res. 2017, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, A.E.; Arends, M.J.; Silva, A.L.; Wyllie, A.H.; Greger, L.; Ito, Y.; Vowler, S.L.; Huang, T.H.; Tavare, S.; Murrell, A.; et al. Sequential DNA methylation changes are associated with DNMT3B overexpression in colorectal neoplastic progression. Gut 2011, 60, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Steine, E.J.; Barrasa, M.I.; Hockemeyer, D.; Pawlak, M.; Fu, D.; Reddy, S.; Bell, G.W.; Jaenisch, R. Deletion of the de novo DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a promotes lung tumor progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18061–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, Q.; Cheng, J.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, J.; Fan, H. Depletion of DNMT3A suppressed cell proliferation and restored PTEN in hepatocellular carcinoma cell. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2010, 2010, 737535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathania, R.; Ramachandran, S.; Elangovan, S.; Padia, R.; Yang, P.; Cinghu, S.; Veeranan-Karmegam, R.; Arjunan, P.; Gnana-Prakasam, J.P.; Sadanand, F.; et al. DNMT1 is essential for mammary and cancer stem cell maintenance and tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.L.; Lu, Y.X.; Zhang, J.X.; Wei, X.L.; Wang, F.; Zeng, Z.L.; Pan, Z.Z.; Yuan, Y.F.; Wang, F.H.; Pelicano, H.; et al. Long non-coding RNA UICLM promotes colorectal cancer liver metastasis by acting as a ceRNA for microRNA-215 to regulate ZEB2 expression. Theranostics 2017, 7, 4836–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernstein, C.N.; Blanchard, J.F.; Kliewer, E.; Wajda, A. Cancer risk in patients with inflammatory bowel disease: A population-based study. Cancer 2001, 91, 854–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zacharopoulou, E.; Gazouli, M.; Tzouvala, M.; Vezakis, A.; Karamanolis, G. The contribution of long non-coding RNAs in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Dig. Liver Dis. 2017, 49, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Yao, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Pan, H.; Han, W. The role of autophagy in colitis-associated colorectal cancer. Sign. Transduct. Targ. Ther. 2018, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarani, R.; Mirza, A.H.; Kaur, S.; Pociot, F. The emerging role of lncRNAs in inflammatory bowel disease. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.Q.; Huang, M.L.; Xu, A.T.; Zhao, D.; Ran, Z.H.; Shen, J. LncRNA DQ786243 affects Treg related CREB and Foxp3 expression in Crohn’s disease. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Han, X.; Wittfeldt, A.; Sun, J.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; Gan, L.M.; Cao, H.; Liang, Z. Long non-coding RNA ANRIL regulates inflammatory responses as a novel component of NF-kappaB pathway. RNA Biol. 2016, 13, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Huang, Y.; Dong, F.; Kwon, J.H. Ulcerative Colitis-Associated Long Noncoding RNA, BC012900, Regulates Intestinal Epithelial Cell Apoptosis. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Wang, H.; Shen, Q.; Feng, L.; Jin, H. Long non-coding RNAs involved in autophagy regulation. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, M.; Aguilar-Medina, M.; Lizarraga-Verdugo, E.; Avendano-Felix, M.; Silva-Benitez, E.; Lopez-Camarillo, C.; Ramos-Payan, R. LncRNAs as Regulators of Autophagy and Drug Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, M.; Fang, X.; Wang, X. Autophagy and inflammation. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, C.; Li, D.; Yang, L.; Jin, J.; Zhang, B. lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 enhances the chemoresistance of oxaliplatin in colon cancer by targeting the miR-34a/ATG4B pathway. OncoTarg. Ther. 2019, 12, 2649–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, T.D.; Xu, J.H.; Yu, T.; Li, J.Y.; Zhao, L.N.; Ouyang, H.; Luo, S.; Lu, X.J.; Huang, C.Z.; Lan, Q.S.; et al. Knockdown of linc-POU3F3 suppresses the proliferation, apoptosis, and migration resistance of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 961–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Tan, K.; Huang, H. Long noncoding RNA HAGLROS regulates apoptosis and autophagy in colorectal cancer cells via sponging miR-100 to target ATG5 expression. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 3922–3933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Li, N.; Jiang, K.; Zhang, N.; Yao, L.L. MiR-100 up-regulation enhanced cell autophagy and apoptosis induced by cisplatin in osteosarcoma by targeting mTOR. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 5867–5873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.Y.; Shi, Q.; Zheng, Z.Y.; Gong, J.; Zeng, C.; Yang, J.; Zhuang, S.M. MicroRNA-100 promotes the autophagy of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting the expression of mTOR and IGF-1R. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 6218–6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Ji, L.; Song, X. Long non coding RNA UCA1 contributes to the autophagy and survival of colorectal cancer cells via sponging miR-185-5p to up-regulate the WISP2/β-catenin pathway. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 14160–14166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, W.; Du, Y.; Ma, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhou, J.; Deng, D. MALAT1-miR663a negative feedback loop in colon cancer cell functions through direct miRNA-lncRNA binding. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Liang, N.; Wang, M.; Fei, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, Y.; Guo, C.; Cao, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is a novel inflammatory regulator in human systemic lupus erythematosus. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 77400–77406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaille, J.J.; Piurowski, V.; Rigot, B.; Kelani, H.; Fortman, E.C.; Tili, E. MiR-663, a MicroRNA Linked with Inflammation and Cancer That Is under the Influence of Resveratrol. Medicines 2018, 5, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.C. The molecular mechanisms of chemoresistance in cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59950–59964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, L.; Liu, T.; Du, L.; Yang, Y.; Wang, C. MALAT1 Is Associated with Poor Response to Oxaliplatin-Based Chemotherapy in Colorectal Cancer Patients and Promotes Chemoresistance through EZH2. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Liu, H.; Yu, J.; Yu, H. Chemoresistance to doxorubicin induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition via upregulation of transforming growth factor beta signaling in HCT116 colon cancer cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhang, R.; Yang, D.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; Jin, K.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Shang, W.; et al. Knockdown of Long Non-Coding RNA XIST Inhibited Doxorubicin Resistance in Colorectal Cancer by Upregulation of miR-124 and Downregulation of SGK1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 51, 113–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talarico, C.; Dattilo, V.; D’Antona, L.; Menniti, M.; Bianco, C.; Ortuso, F.; Alcaro, S.; Schenone, S.; Perrotti, N.; Amato, R. SGK1, the New Player in the Game of Resistance: Chemo-Radio Molecular Target and Strategy for Inhibition. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 39, 1863–1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amato, R.; Menniti, M.; Agosti, V.; Boito, R.; Costa, N.; Bond, H.M.; Barbieri, V.; Tagliaferri, P.; Venuta, S.; Perrotti, N. IL-2 signals through Sgk1 and inhibits proliferation and apoptosis in kidney cancer cells. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 85, 707–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Wang, Z.; Yu, Q.; Shen, J.; He, W.; Zhou, D.; Yu, Q.; Fan, J.; Gao, S.; Duan, L. Atractylenolide II reverses the influence of lncRNA XIST/miR-30a-5p/ROR1 axis on chemo-resistance of colorectal cancer cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2019, 23, 3151–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, B.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Yu, J.; Widhopf, G.F., 2nd; Fecteau, J.F.; Rassenti, L.Z.; Kipps, T.J. Targeting ROR1 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3649–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.K.; Zheng, Y.Z.; Liu, X.S.; Gou, Q.; Ma, R.; Guo, C.L.; Croce, C.M.; Liu, L.; Peng, Y. ROR1 expression as a biomarker for predicting prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 32864–32872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.Y.; Guan, S.H.; Tang, R.N.; Tao, S.J.; Guo, D.A. Simultaneous determination of atractylenolide II and atractylenolide III by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry in rat plasma and its application in a pharmacokinetic study after oral administration of Atractylodes Macrocephala Rhizoma extract. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2012, 26, 1386–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longley, D.B.; Harkin, D.P.; Johnston, P.G. 5-fluorouracil: Mechanisms of action and clinical strategies. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Hu, H.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ma, T.; Qiao, T.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, H.; et al. Long non-coding RNA TUG1 mediates 5-fluorouracil resistance by acting as a ceRNA of miR-197-3p in colorectal cancer. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4603–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, R.; Li, M.C.; Spencer, D.B. Effect of methotrexate therapy upon choriocarcinoma and chorioadenoma. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1956, 93, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertino, J.R.; Goker, E.; Gorlick, R.; Li, W.W.; Banerjee, D. Resistance Mechanisms to Methotrexate in Tumors. Oncologist 1996, 1, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Ding, D. TUG1 mediates methotrexate resistance in colorectal cancer via miR-186/CPEB2 axis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 491, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Balibrea, E.; Martinez-Cardus, A.; Gines, A.; Ruiz de Porras, V.; Moutinho, C.; Layos, L.; Manzano, J.L.; Buges, C.; Bystrup, S.; Esteller, M.; et al. Tumor-Related Molecular Mechanisms of Oxaliplatin Resistance. Mol. Cancer ther. 2015, 14, 1767–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, S.; Peng, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Pan, H.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Zhao, Q. MEG3 is a prognostic factor for CRC and promotes chemosensitivity by enhancing oxaliplatin-induced cell apoptosis. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Yang, D. Overexpression of MEG3 sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to oxaliplatin through regulation of miR-141/PDCD4 axis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 106, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afonja, O.; Juste, D.; Das, S.; Matsuhashi, S.; Samuels, H.H. Induction of PDCD4 tumor suppressor gene expression by RAR agonists, antiestrogen and HER-2/neu antagonist in breast cancer cells. Evidence for a role in apoptosis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8135–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.H.; Ye, D.W.; Yao, X.D.; Zhang, S.L.; Dai, B.; Zhang, H.L.; Shen, Y.J.; Zhu, Y.; Zhu, Y.P.; Xiao, W.J.; et al. Involvement of microRNA-21 in mediating chemo-resistance to docetaxel in androgen-independent prostate cancer PC3 cells. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2010, 31, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiota, M.; Izumi, H.; Tanimoto, A.; Takahashi, M.; Miyamoto, N.; Kashiwagi, E.; Kidani, A.; Hirano, G.; Masubuchi, D.; Fukunaka, Y.; et al. Programmed cell death protein 4 down-regulates Y-box binding protein-1 expression via a direct interaction with Twist1 to suppress cancer cell growth. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3148–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, B.; Yu, X.; Guo, X.; Fan, X.; Yang, Z.; Wu, P.; Yuan, Z.; Deng, Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Increased urothelial cancer associated 1 is associated with tumor proliferation and metastasis and predicts poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Shen, B.; Tan, M.; Mu, X.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y. Long non-coding RNA UCA1 increases chemoresistance of bladder cancer cells by regulating Wnt signaling. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 1750–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, B.; Wang, W.; Fei, B.; Quan, C.; Zhang, J.; Song, M.; Bian, Z.; Wang, Q.; Ni, S.; et al. miR-204-5p inhibits proliferation and invasion and enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating RAB22A. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 6187–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; He, W.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y. Long non-coding RNA LINC00152 promotes tumorigenesis via sponging miR-193b-3p in osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 3630–3636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Tao, W. Long Noncoding RNA LINC00152 Facilitates the Leukemogenesis of Acute Myeloid Leukemia by Promoting CDK9 Through miR-193a. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Cai, D.; Liu, C.; Fang, C.; Yan, D. Linc00152 Functions as a Competing Endogenous RNA to Confer Oxaliplatin Resistance and Holds Prognostic Values in Colon Cancer. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2016, 24, 2064–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamoori, A.; Wahab, R.; Islam, F.; Lee, K.; Vider, J.; Lu, C.T.; Gopalan, V.; Lam, A.K. Clinical and biological significance of miR-193a-3p targeted KRAS in colorectal cancer pathogenesis. Hum. Pathol. 2018, 71, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.S.; Bernard, J.K.; Demory Beckler, M.; Almohazey, D.; Washington, M.K.; Smith, J.J.; Frey, M.R. ERBB4 is over-expressed in human colon cancer and enhances cellular transformation. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, M.; Feng, Y.; Yao, S.; Song, M.; Qi, X.; Fei, B.; Yin, Y.; Hua, D.; et al. Long non-coding RNA LINC00152 promotes cell proliferation, metastasis, and confers 5-FU resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting miR-139-5p. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Lan, Z.; He, J.; Lai, Q.; Yao, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Lai, H.; Gu, C.; Yan, Q.; et al. LncRNA SNHG6 promotes chemoresistance through ULK1-induced autophagy by sponging miR-26a-5p in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonioli, M.; Di Rienzo, M.; Piacentini, M.; Fimia, G.M. Emerging Mechanisms in Initiating and Terminating Autophagy. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2017, 42, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levy, J.M.M.; Towers, C.G.; Thorburn, A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2017, 17, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurley, J.H.; Young, L.N. Mechanisms of Autophagy Initiation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 225–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Guo, F.; Yu, Y.; Sun, T.; Ma, D.; Han, J.; Qian, Y.; Kryczek, I.; Sun, D.; Nagarsheth, N.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum Promotes Chemoresistance to Colorectal Cancer by Modulating Autophagy. Cell 2017, 170, 548–563.e516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Han, D.; Yuan, Z.; Hu, H.; Zhao, Z.; Yang, R.; Jin, Y.; Zou, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; et al. Long non-coding RNA H19 confers 5-Fu resistance in colorectal cancer by promoting SIRT1-mediated autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Fang, C.; Xu, J.; Tan, H.; Li, P.; Ma, L. LncRNA CACS15 contributes to oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer by positively regulating ABCC1 through sponging miR-145. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 663, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Zhan, T.; Li, M.; Yao, Y.; Jia, J.; Yi, H.; Qiao, M.; Xia, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, H.; et al. Enhancement of Sensitivity to Chemo/Radiation Therapy by Using miR-15b against DCLK1 in Colorectal Cancer. Stem Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 1506–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.; Jifu, E.; Guo, K.; Ma, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yu, E. Knockdown of long non-coding RNA TINCR decreases radioresistance in colorectal cancer cells. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 152622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Porath, I.; Thomson, M.W.; Carey, V.J.; Ge, R.; Bell, G.W.; Regev, A.; Weinberg, R.A. An embryonic stem cell-like gene expression signature in poorly differentiated aggressive human tumors. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Liu, S.; Zhou, H.; Qu, L.H.; Yang, J.H. starBase v2.0: Decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, D92–D97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Kostoulas, N.; Reczko, M.; Maragkakis, M.; Dalamagas, T.M.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-LncBase: Experimentally verified and computationally predicted microRNA targets on long non-coding RNAs. Nucl. Acids Res. 2013, 41, D239–D245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furio-Tari, P.; Tarazona, S.; Gabaldon, T.; Enright, A.J.; Conesa, A. spongeScan: A web for detecting microRNA binding elements in lncRNA sequences. Nucl. Acids Res. 2016, 44, W176–W180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ghosal, S.; Sen, R.; Chakrabarti, J. lnCeDB: Database of human long noncoding RNA acting as competing endogenous RNA. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Ping, Y.; Zhao, H.; Ning, S.; Xia, P.; Wang, W.; Wan, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Yu, L.; et al. LncNetP, a systematical lncRNA prioritization approach based on ceRNA and disease phenotype association assumptions. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 114603–114612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Bhattacharya, A.; Cui, Y. SomamiR 2.0: A database of cancer somatic mutations altering microRNA-ceRNA interactions. Nucl. Acids Res. 2016, 44, D1005–D1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zhi, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Guo, M.; Ning, S.; Li, X. miRSponge: A manually curated database for experimentally supported miRNA sponges and ceRNAs. Database J. Biol. Databases Curation 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Meng, X.; Li, X.; Illing, N.; Ingle, R.A.; Wang, J.; Chen, M. PceRBase: A database of plant competing endogenous RNA. Nucl. Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1009–D1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yan, Z.; Li, Y.; Sun, Z. Linc2GO: A human LincRNA function annotation resource based on ceRNA hypothesis. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2221–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, S.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Z.; Wang, M.; Zheng, X.; Xie, M. LncRNA BCAR4, targeting to miR-665/STAT3 signaling, maintains cancer stem cells stemness and promotes tumorigenicity in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, N.; Huang, T.; Guo, H.; Yang, J.; Li, M.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, Y. LncRNA CASC15 promotes colon cancer cell proliferation and metastasis by regulating the miR4310/LGR5/Wnt/betacatenin signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 18, 2269–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Wu, X.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Zhu, H.; Chen, X. The long noncoding RNA CASC2 functions as a competing endogenous RNA by sponging miR-18a in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Nangia-Makker, P.; Farhana, L.; Majumdar, A.P.N. A novel mechanism of lncRNA and miRNA interaction: CCAT2 regulates miR-145 expression by suppressing its maturation process in colon cancer cells. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wang, Q.; Xue, F.; Wu, Y. lncRNA-CYTOR Works as an Oncogene Through the CYTOR/miR-3679-5p/MACC1 Axis in Colorectal Cancer. DNA Cell Biol. 2019, 38, 572–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zou, Y.; Hu, G.; Lin, C.; Guo, Y.; Gao, K.; Wu, M. Facilitating colorectal cancer cell metastasis by targeted binding of long non-coding RNA ENSG00000231881 with miR-133b via VEGFC signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 509, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, B.; Sun, B.; Liu, C.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, D.; Yu, F.; Yan, D. Long non-coding RNA Fer-1-like protein 4 suppresses oncogenesis and exhibits prognostic value by associating with miR-106a-5p in colon cancer. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Qiao, L.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, N.; Wang, C.; Zhou, J. Long non-coding RNA FOXD2-AS1 contributes to colorectal cancer proliferation through its interaction with microRNA-185-5p. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2235–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Shi, M.; Meng, W.; Wang, Y.; Hui, P.; Ma, J. Long noncoding RNA FOXD3-AS1 promotes colon adenocarcinoma progression and functions as a competing endogenous RNA to regulate SIRT1 by sponging miR-135a-5p. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 21889–21902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Miao, Y.; Xing, R. Novel long noncoding RNA GACAT3 promotes colorectal cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration through miR-149. OncoTarg. Ther. 2018, 11, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wang, H.J.; Meng, T.; Lei, C.; Yang, X.H.; Wang, Q.S.; Jin, B.; Zhu, J.F. lncRNA GAS5 Inhibits Cell Migration and Invasion and Promotes Autophagy by Targeting miR-222-3p via the GAS5/PTEN-Signaling Pathway in CRC. Mol. Ther. Nucl. Acids 2019, 17, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Lin, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, F.; Xie, R. LncRNA HAND2-AS1 sponging miR-1275 suppresses colorectal cancer progression by upregulating KLF14. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 1848–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.L.; Zhao, X.J.; Wei, C.C.; Wu, J.W. LncRNA HOTAIR promotes colon cancer development by down-regulating miRNA-34a. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 5752–5761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Wei, M.-H.; Lu, J.-G.; Bi, C.-Y. Long non-coding RNA HULC interacts with miR-613 to regulate colon cancer growth and metastasis through targeting RTKN. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 2035–2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y. lncRNA LINC00460 promoted colorectal cancer cells metastasis via miR-939-5p sponging. Cancer Manag. Res. 2019, 11, 1779–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Yue, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Sun, M.; Gu, C.; Zeng, L. LINC00668 promotes tumorigenesis and progression through sponging miR-188–5p and regulating USP47 in colorectal cancer. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 858, 172464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Q.K.; Chen, L.; Xi, J.Z.; Song, H. Long non-coding RNA LINC00858 promotes cells proliferation, migration and invasion by acting as a ceRNA of miR-22-3p in colorectal cancer. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, Y. Long noncoding RNA LINC01234 promotes serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 expression and proliferation by competitively binding miR-642a-5p in colon cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, C.; Ning, X. Long Noncoding RNA LINC01296 Harbors miR-21a to Regulate Colon Carcinoma Proliferation and Invasion. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 541–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Du, T.; Du, L.; Li, P.; Li, J.; Duan, W.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C. Long noncoding RNA LINC02418 regulates MELK expression by acting as a ceRNA and may serve as a diagnostic marker for colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, L.; Li, S.; Yu, W. Long non-coding RNA MBNL1-AS1 regulates proliferation, migration, and invasion of cancer stem cells in colon cancer by interacting with MYL9 via sponging microRNA-412-3p. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Cai, H.; Hong, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, D.; Fan, Z. Long non-coding RNA MIAT promotes growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells through regulation of miR-132/Derlin-1 pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2018, 18, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, G.; Liu, B.; Han, W.; Zhao, D. LncRNA-MIR17HG mediated upregulation of miR-17 and miR-18a promotes colon cancer progression via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Transl. Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Gu, B.; Wang, Y.; Shen, S.; Huang, W. E2F1-mediated MNX1-AS1-miR-218-5p-SEC61A1 feedback loop contributes to the progression of colon adenocarcinoma. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 6145–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Wen, C.; Zhuansun, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, H. A novel long noncoding RNA OECC promotes colorectal cancer development and is negatively regulated by miR-143-3p. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 503, 2949–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Ma, Z.; He, Y.; Liu, W.; Su, Y.; Tang, Z. PART-1 functions as a competitive endogenous RNA for promoting tumor progression by sponging miR-143 in colorectal cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 490, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Sun, L.; Liu, D.; Liu, C.; Sun, L. Long Non-Coding RNA lincRNA-ROR Promotes the Progression of Colon Cancer and Holds Prognostic Value by Associating with miR-145. Pathol. Oncol. Res. POR 2016, 22, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Bai, Y.; Yang, C.; Hu, S.; Hou, Z.; Wang, G. Long noncoding RNA SNHG15 enhances the development of colorectal carcinoma via functioning as a ceRNA through miR-141/SIRT1/Wnt/beta-catenin axis. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 2536–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, D.; Wang, Q.; Ke, S.; Zou, L.; Wang, Q. Long-Non Coding RNA SNHG16 Supports Colon Cancer Cell Growth by Modulating miR-302a-3p/AKT Axis. Pathol. Oncol. Res. POR 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Peng, J.; Yang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, L.; Luo, D.; He, P. Long non-coding RNA TP73AS1 promotes colorectal cancer proliferation by acting as a ceRNA for miR103 to regulate PTEN expression. Gene 2019, 685, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Yan, P.; Zhang, G.; Yang, W.; Wang, H.; Cheng, X. Long non-coding RNA TP73-AS1 sponges miR-194 to promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion via up-regulating TGFalpha. Cancer Biomark. Sect. Dis. Mark. 2018, 23, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Hu, J.; Wang, G.; Yang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. LncRNA TUG1 promoted KIAA1199 expression via miR-600 to accelerate cell metastasis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, J. The Novel Long Noncoding RNA TUSC7 Inhibits Proliferation by Sponging MiR-211 in Colorectal Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 41, 635–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.T.; Chen, W.Y.; Gu, Z.Q.; Zhuang, Y.Y.; Li, C.Q.; Wang, L.Y.; Peng, J.F.; Zhu, Z.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.H.; et al. The novel long intergenic noncoding RNA UCC promotes colorectal cancer progression by sponging miR-143. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; He, X.; Li, S.; Xu, X.; Chen, X.; Zhu, H. Long Non-Coding RNA ucoo2kmd.1 Regulates CD44-Dependent Cell Growth by Competing for miR-211-3p in Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0151287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Liu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Q.; Jin, L.K. LncRNA-ZDHHC8P1 promotes the progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer by targeting miR-34a. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1476–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, D.; Liu, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, W. Long Non-coding RNA Zinc Finger Antisense 1 (ZFAS1) Regulates Proliferation, Migration, Invasion, and Apoptosis by Targeting MiR-7-5p in Colorectal Cancer. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2019, 25, 5150–5158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorenoor, N.; Faltejskova-Vychytilova, P.; Hombach, S.; Mlcochova, J.; Kretz, M.; Svoboda, M.; Slaby, O. Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 interacts with CDK1 and is involved in p53-dependent cell cycle control and apoptosis in colorectal cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 622–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hong, X.; Ba, L.; He, X.; Xiong, Y.; Ding, Q.; Yang, S.; Peng, G. Long non-coding RNA ZNFX1-AS1 promotes the tumor progression and metastasis of colorectal cancer by acting as a competing endogenous RNA of miR-144 to regulate EZH2 expression. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| LncRNA | Chromosome Location | Competitor mRNA | Shared miRNA | ceRNA Network | ceRNA Role | Related CRC Hallmark | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCAR4 | 16p13.13 | STAT3 | miR-665 | BCAR4/miR-655/STAT3 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration | [152] |
| CACS15 | 6p22.3 | LGR5 | miR-4310 | CACS15/miR-4310/LGR5 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, invasion, TNM stage, metastasis | [153] |
| CASC19 | 8q24.21 | CEMIP | miR-140-5p | CASC19/miR-140-5p/CEMIP | Oncogenic | Proliferation, invasion, migration, apoptosis, EMT | [33] |
| CASC2 | 10q26.11 | PIAS3 | miR-18a | CASC2/miR-18a/PIAS3/STAT3 | Tumor suppressive | Proliferation, tumor growth, G0/G1-S phase transition | [154] |
| CCAT2 | 8q24.21 | miR-145 | CCAT2/miR-145/miR-21 | Oncogenic | CSC proliferation and differentiation | [155] | |
| CYTOR | 2p11.2 | MACC1 | miR-3679-5p | CYTOR/miR-3679-5p/MACC1 | Oncogenic | TNM stage, perineural and venous invasions | [156] |
| ENSG00000-231881 | 6 | VEGFC | miR-133b | ENSG00000231881/miR-133b/VEGFC | Oncogenic | Metastasis | [157] |
| FER1L4 | 20q11.22 | miR-106a-5p | FER1L4/miR-106a-5p | Tumor suppressive | Proliferation, cell cycle | [158] | |
| FOXD2-AS1 | 1p33 | CDC42 | miR-185-5p | FOXD2-AS1/miR-185-5p/CDC42 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion | [159] |
| FOXD3-AS1 | 1p31.3 | SIRT1 | miR-135a-5p | FOXD3-AS1/miR-135a-5p/SIRT1 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion, cell cycle, apoptosis | [160] |
| GACAT3 | 2p24.3 | SP1, STAT3 | miR-149 | GACAT3/miR-149/SP1/STAT3 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, invasion, migration | [161] |
| GAS5 | 1q25.1 | PTEN | miR-222-3p | GAS5/miR-222-3p/PTEN | Tumor suppressive | Proliferation, migration, apoptosis | [162] |
| H19 | 11p15.5 | Vimentin, ZEB1, ZEB2 | miR-138, miR-200a | H19/miR-138/Vimentin, H19/miR-200a/ZEB1, H19/miR-200a/ZEB2 | Oncogenic | EMT progression | [58] |
| HAND2-AS1 | 4q34.1 | KLF14 | miR-1275 | HAND2-AS1/miR-1275/KLF14 | Tumor suppressive | Proliferation, invasion | [163] |
| HOTAIR | 12q13.13 | miR-34a | HOTAIR/miR-34a | Oncogenic | Metastasis | [164] | |
| HULC | 6p24.3 | RTKN | miR-613 | HULC/miR-613/RTKN | Oncogenic | Proliferation, metastasis | [165] |
| LINC00460 | 13q33.2 | LIMK2 | miR-939-5p | LINC00460/LIMK2/miR-939-5p | Oncogenic | Metastasis | [166] |
| LINC00668 | 18p11.31 | USP47 | miR-188–5p | LINC000668/miR-188-5p/USP47 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, metastasis | [167] |
| LINC00858 | 10q23.1 | YWHAZ | miR-22-3p | LINC00858/miR-22-3p/YWHAZ | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion | [168] |
| LINC01234 | 12q24.13 | SHMT2 | miR-642a-5p | LINC01234/miR-642a-5p/SHMT2 | Oncogenic | Proliferation | [169] |
| LINC01296 | 14q11.2 | PDCD4 | miR-21a | LINC01296/miR-21a/PDCD4 | Oncogenic | Proliferation | [170] |
| LINC02418 | 12q24.33 | MELK | miR-1273g-3p | LINC02418/miR-1273g-3p/MELK | Oncogenic | Proliferation, apoptosis | [171] |
| MALAT1 | 11q13.1 | p53 | miR-663a | MALAT1/miR-663a/p53 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis | [100] |
| MBNL1-AS1 | 3q25.1 | MYL9 | miR-412-3p | MBNL-AS1/miR-412-3p/MYL9 | Tumor suppressive | Proliferation, invasion | [172] |
| MIAT | 22q12.1 | Derlin-1 | miR-132 | MIAT/miR-132/Derlin-1 | Oncogenic | Tumor growth, metastasis | [173] |
| MIR17HG | 13q31.3 | Wnt, β-catenin | miR-17, miR-18a | MIR17HG-miR-17/18a-Wnt/ β-catenin | Oncogenic | Lymph node metastasis, TNM stage | [174] |
| MNX1-AS1 | 7q36.3 | SEC61A1 | miR-218-5p | MNX1-AS1/miR-218-5p/ SEC61A1 | Oncogenic | progression of colon adenocarcinoma | [175] |
| NEAT1 | 11q13.1 | CDK6 | miR-495-3p | NEAT1/miR-495-3p/CDK6 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion | [43] |
| OECC | 8q24 | NF-κB, p38MAPK | miR-143-3p | OECC/miR-143-3p/NF-κB/ p38 MAPK | Oncogenic | Proliferation, apoptosis, migration | [176] |
| PART-1 | 5q12.1 | DNMT3A | miR-143 | PART-1/miR-143/DNMT3A | Oncogenic | Proliferation, metastasis | [177] |
| PVT1 | 8q24.21 | RUNX2 | miR-30d-5p | PVT1/miR-30d-5p/RUNX2 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, metastasis | [26] |
| PVT1 | 8q24.21 | RUNX2 | miR-455 | PVT1/miR-455/RUNX2 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis | [31] |
| PVT1-214 | 8q24.21 | Lin28 | miR-128 | PVT1-214/miR-128/Lin28/let-7 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, invasion | [32] |
| ROR | 18q21.31 | miR-145 | ROR/miR-145 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion | [178] | |
| SNHG15 | 7p13 | SIRT1 | miR-141 | SNHG15/miR-141/SIRT1 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, apoptosis | [179] |
| SNHG16 | 17q25.1 | AKT | miR-302a-3p | SNHG16/miR-302a-3p/AKT | Oncogenic | Proliferation | [180] |
| TP73-AS1 | 1p36.32 | PTEN | miR-103 | TP73-AS1/miR-103/PTEN | Tumor suppressive | Proliferation | [181] |
| TP73-AS1 | 1p36.32 | TGF-a | miR-194 | TP73-AS1/miR-194/TGF-a | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion | [182] |
| TUG1 | 22q12.2 | KIAA1199 | miR-600 | TUG1/miR-600/KIAA1199 | Oncogenic | Metastasis, EMT | [183] |
| TUSC7 | 3q13.31 | CDK6 | miR-211-3p | TUSC7/miR-211-3p/CDK6 | Tumor suppressive | Proliferation | [184] |
| UCA1 | 19p13.12 | HOXB3 | miR-28-5p | UCA1/miR-28-5p/HOXB3 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration | [39] |
| UCC | 7p15.2 | KRAS | miR-143 | UCC/miR-143/KRAS | Oncogenic | Cell growth, invasion | [185] |
| ucoo2kmd.1 | 17q11.2 | CD44 | miR-211-3p | ucoo2lmd.1/miR-211-3p/CD44 | Oncogenic | Proliferation | [186] |
| ZDHHC8P1 | 22q11.23 | miR-34a | ZDHHC8P1/miRNA-34a | Oncogenic | Proliferation, metastasis | [187] | |
| ZFAS1 | 20q13.13 | miR-7-5p | ZFAS1/miR-7-5p | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion, apoptosis | [188] | |
| ZFAS1 | 20q13.13 | CDK1/ cyclinB1, p53 | miR-590-3p | ZFAS1/miR-590-3p | Oncogenic | Apoptosis, p53 dependent cell cycle control | [189] |
| ZNFX1-AS1 | 20q13.13 | EZH2 | miR-144 | ZNFX1-AS1/miR-144/EZH2 | Oncogenic | Proliferation, migration, invasion, metastasis | [190] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Cho, K.B.; Li, Y.; Tao, G.; Xie, Z.; Guo, B. Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-Mediated Competing Endogenous RNA Networks Provide Novel Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Colorectal Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225758
Wang L, Cho KB, Li Y, Tao G, Xie Z, Guo B. Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-Mediated Competing Endogenous RNA Networks Provide Novel Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225758
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liye, Kwang Bog Cho, Yan Li, Gabriel Tao, Zuoxu Xie, and Bin Guo. 2019. "Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-Mediated Competing Endogenous RNA Networks Provide Novel Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Colorectal Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225758
APA StyleWang, L., Cho, K. B., Li, Y., Tao, G., Xie, Z., & Guo, B. (2019). Long Noncoding RNA (lncRNA)-Mediated Competing Endogenous RNA Networks Provide Novel Potential Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets for Colorectal Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5758. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225758






