Development of SpyTag/SpyCatcher-Bacmid Expression Vector System (SpyBEVS) for Protein Bioconjugations Inside of Silkworms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
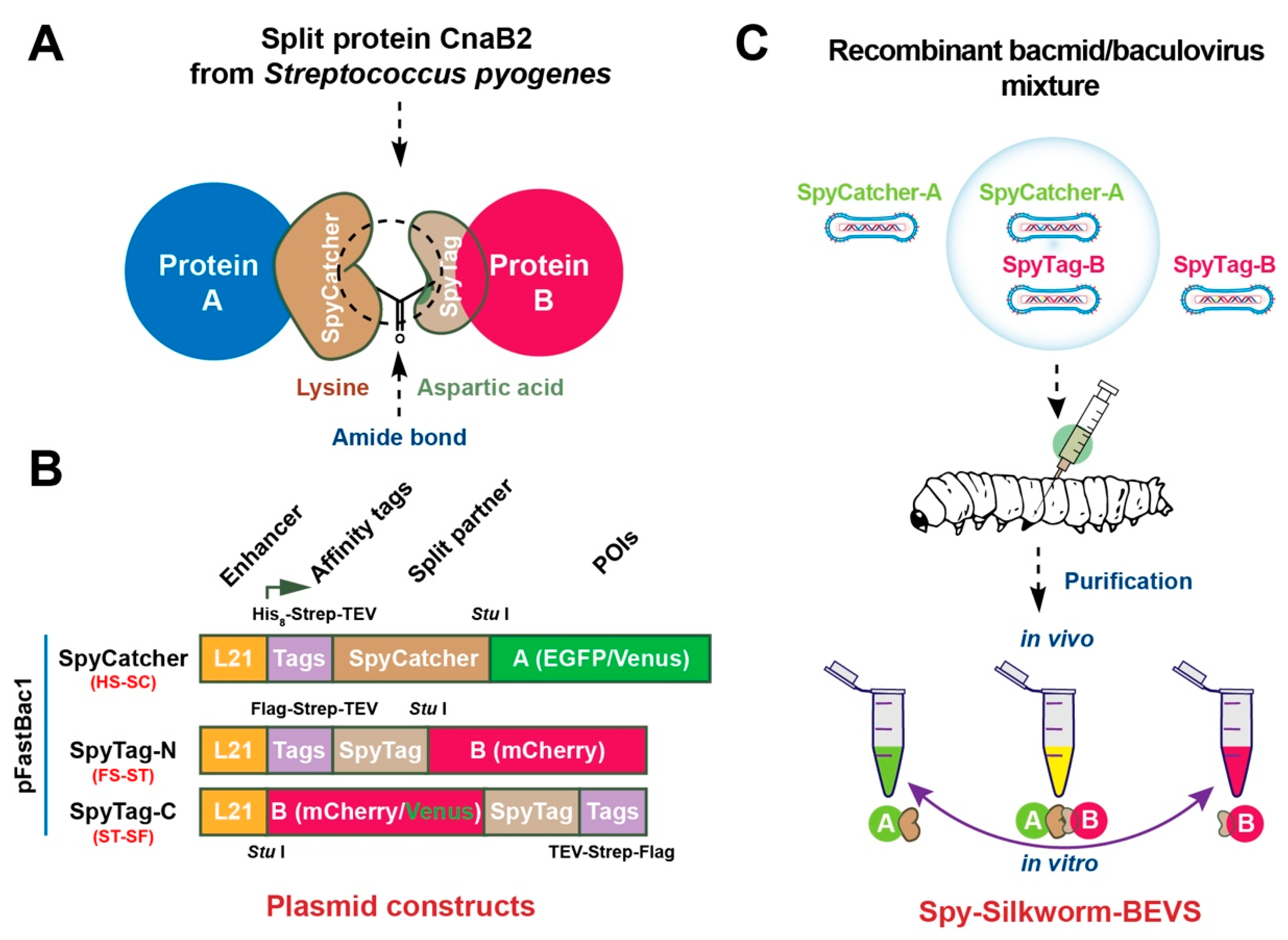
2.1. Establishment of ST/SC-Bacmid Expression Vector System (SpyBEVS)
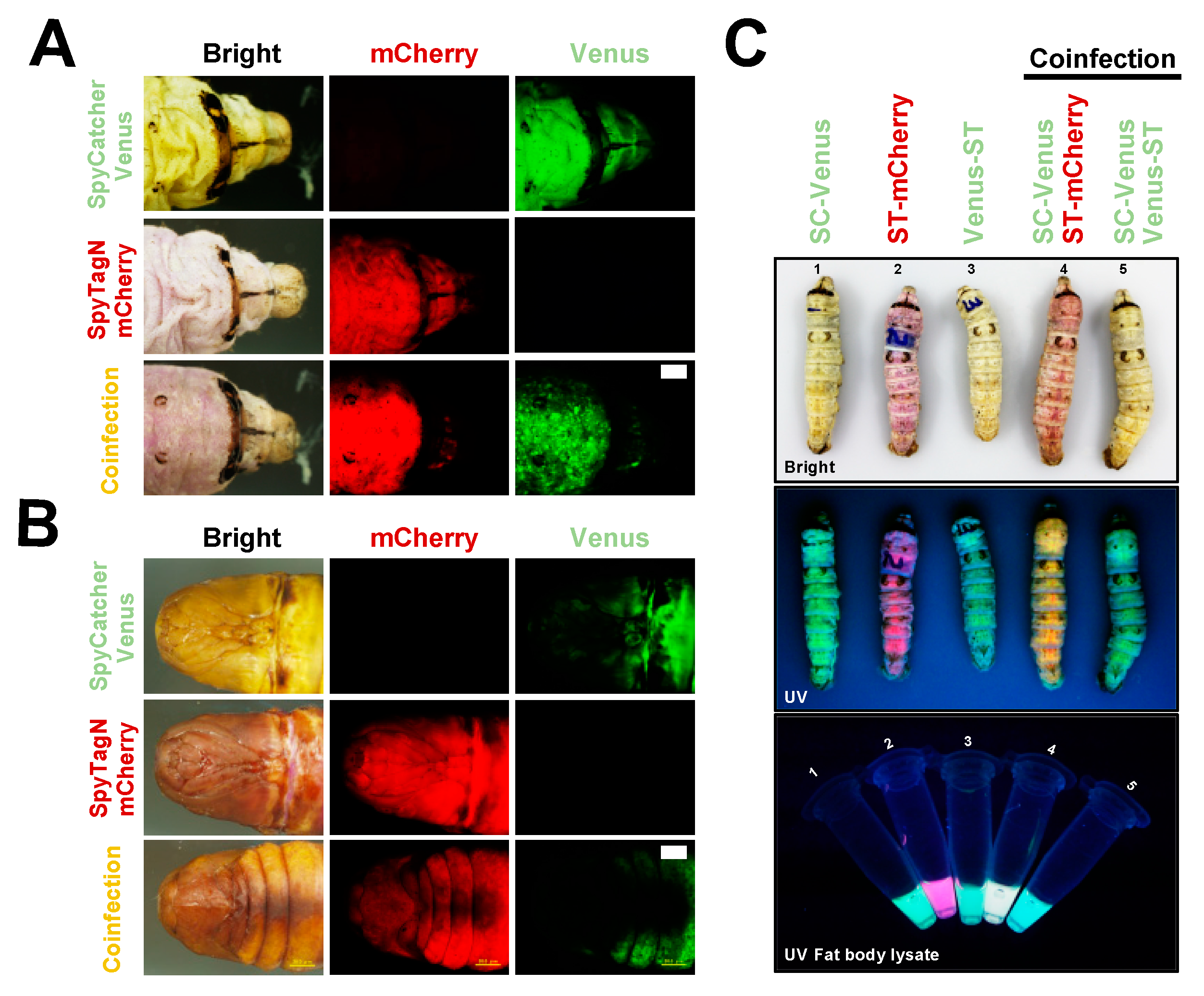
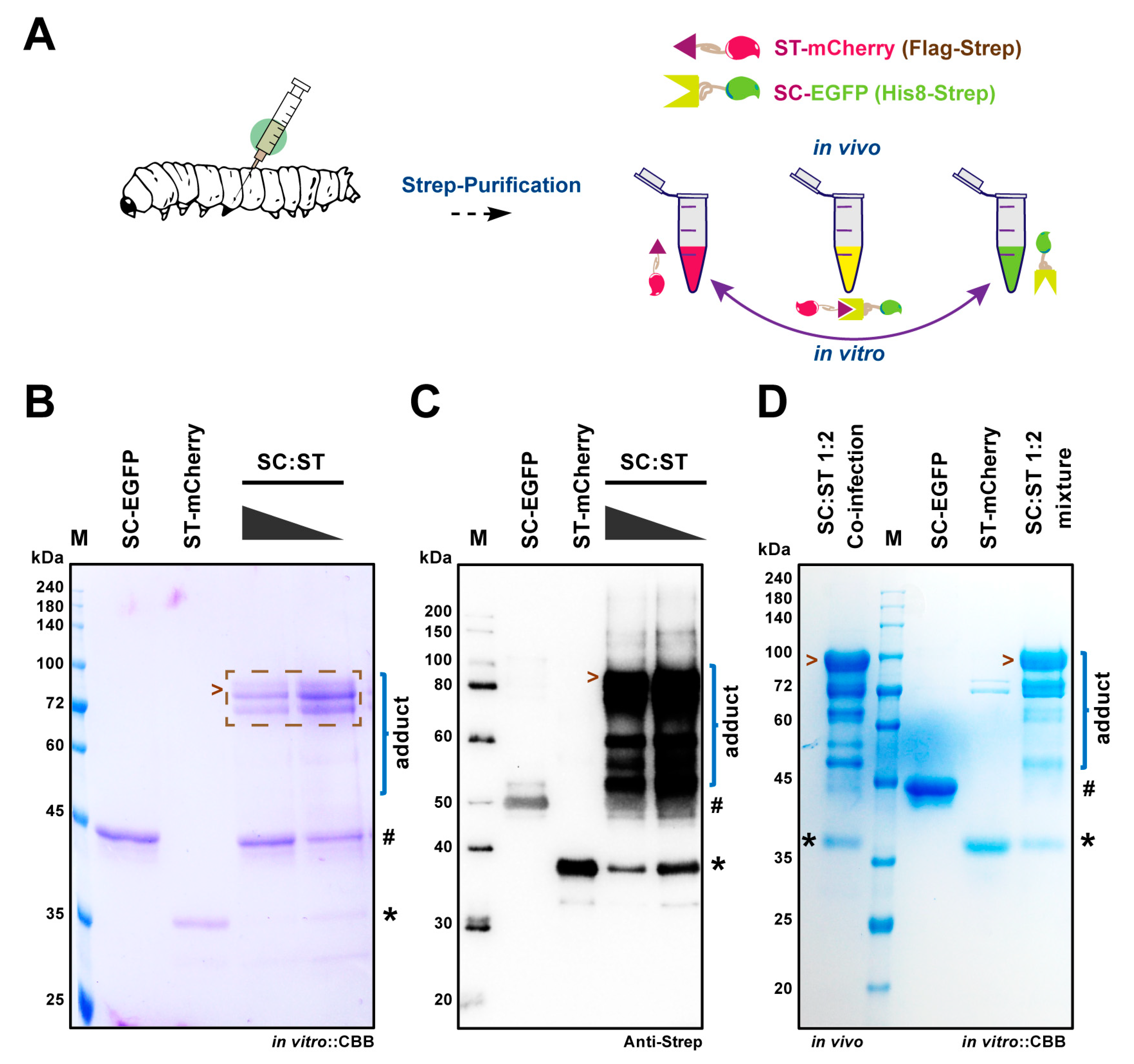
2.2. SpyBEVS Enables In Vitro and In Vivo Ligation of ST/SC Protein Pair
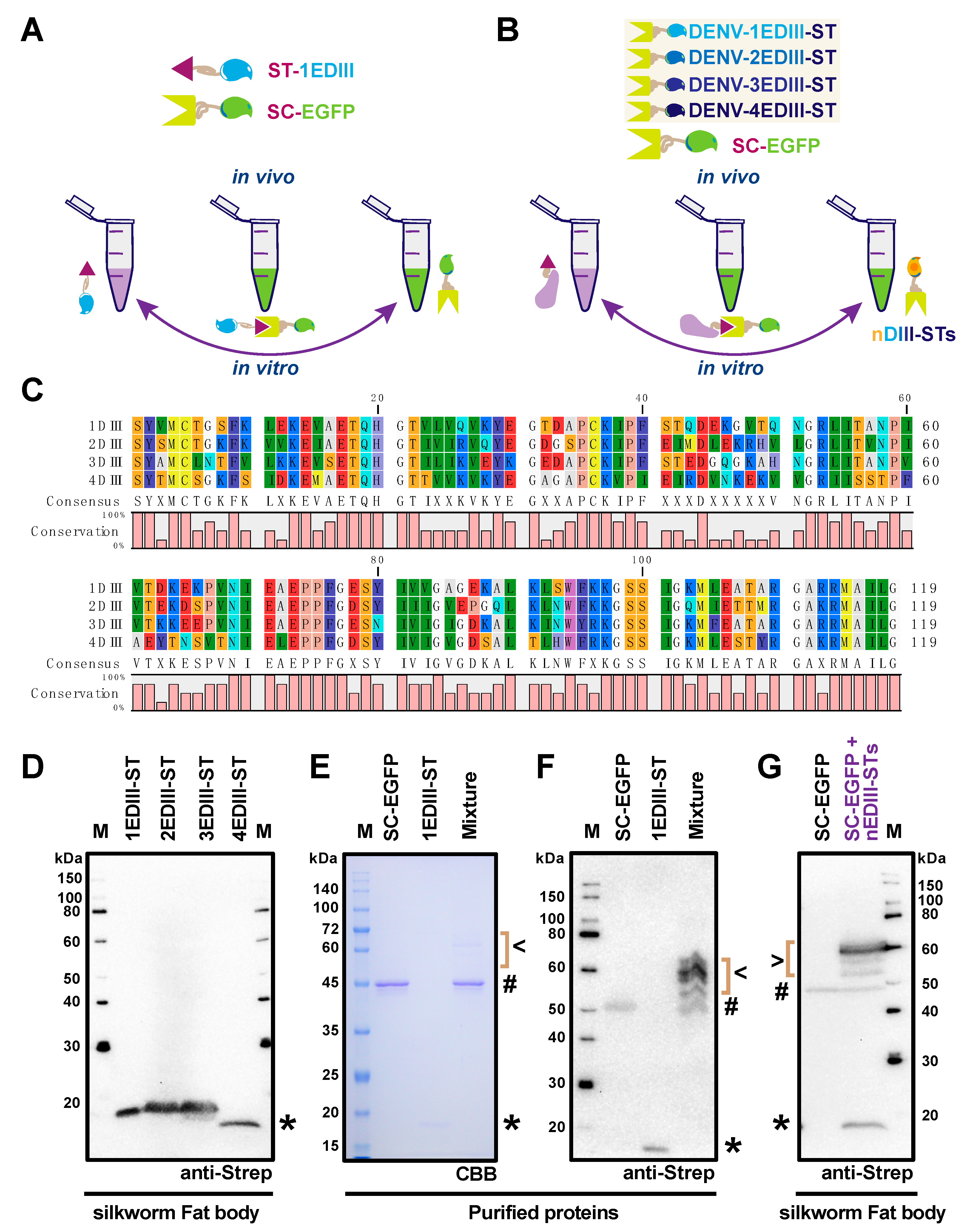
2.3. Application of SpyBEVS as a Post-Translational Protein Conjugation and Labeling Platform
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cultured Cells and Silkworms
4.2. Synthetic DNA for SpyTag/SpyCatcher Constructs
4.3. Generation of Recombinant Baculoviruses
4.4. In Vitro and In Vivo Ligation ST/SC Constructions in Cultured Silkworm Cells and Larvae
4.5. Protein Purification and In Vitro Protein Ligation Assay
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ST/SC | SpyTag/SpyCatcher |
| BEVS | Bacmid expression vector system |
| SpyBEVS | SpyTag/SpyCatcher-Bacmid expression vector system |
| FS | Flag-Strep-tag II |
| HS | His8-Strep-tag II |
| EDIII | Domain III of E dengue virus |
| POI | Protein of interest |
| DMRIE-C | 1,2-dimyristyloxypropyl-3-dimethyl-hydroxy ethyl ammonium bromide and cholesterol |
References
- Vijayachandran, L.S.; Viola, C.; Garzoni, F.; Trowitzsch, S.; Bieniossek, C.; Chaillet, M.; Schaffitzel, C.; Busso, D.; Romier, C.; Poterszman, A.; et al. Robots, pipelines, polyproteins: Enabling multiprotein expression in prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. J. Struct. Biol. 2011, 175, 198–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Oers, M.M.; Pijlman, G.P.; Vlak, J.M. Thirty years of baculovirus-insect cell protein expression: from dark horse to mainstream technology. J. Gen. Virol. 2015, 96, 6–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerrigan, J.J.; Xie, Q.; Ames, R.S.; Lu, Q. Production of protein complexes via co-expression. Protein Expr. Purif. 2011, 75, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, I.; Fitzgerald, D.J.; Richmond, T.J. Baculovirus expression system for heterologous multiprotein complexes. Nat. Biotechnol. 2004, 22, 1583–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Kajikawa, M.; Maenaka, K.; Park, E.Y. Silkworm expression system as a platform technology in life science. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 85, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morokuma, D.; Xu, J.; Mon, H.; Hirata, K.; Hino, M.; Kuboe, S.; Yamashita, M.; Kusakabe, T.; Lee, J.M. Human alpha 1-acid glycoprotein as a model protein for glycoanalysis in baculovirus expression vector system. J. Asia. Pac. Entomol. 2015, 18, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitsudome, T.; Xu, J.; Nagata, Y.; Masuda, A.; Iiyama, K.; Morokuma, D.; Li, Z.; Mon, H.; Lee, J.M.; Kusakabe, T. Expression, purification, and characterization of endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase H using baculovirus-mediated silkworm protein expression system. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 3978–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinoshita, Y.; Xu, J.; Masuda, A.; Minamihata, K.; Kamiya, N.; Mon, H.; Fujita, R.; Kusakabe, T.; Lee, J.M. Expression and purification of biologically active human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (hGM-CSF) using silkworm-baculovirus expression vector system. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 159, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, T.; Ishizaki, M.; Dohra, H.; Park, S.; Terzic, A.; Kato, T.; Kohsaka, T.; Park, E.Y. Insulin-like peptide 3 expressed in the silkworm possesses intrinsic disulfide bonds and full biological activity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez-Pena, C.; Kamen, A.A. RNA interference technology to improve the baculovirus-insect cell expression system. Biotechnol. Adv. 2018, 36, 443–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Nagata, Y.; Mon, H.; Li, Z.; Zhu, L.; Iiyama, K.; Kusakabe, T.; Lee, J.M. Soaking RNAi-mediated modification of Sf9 cells for baculovirus expression system by ectopic expression of Caenorhabditis elegans SID-1. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 5921–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mabashi-Asazuma, H.; Jarvis, D.L. CRISPR-Cas9 vectors for genome editing and host engineering in the baculovirus-insect cell system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 9068–9073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dundas, C.M.; Demonte, D.; Park, S. Streptavidin-biotin technology: improvements and innovations in chemical and biological applications. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 9343–9353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chivers, C.E.; Crozat, E.; Chu, C.; Moy, V.T.; Sherratt, D.J.; Howarth, M. A streptavidin variant with slower biotin dissociation and increased mechanostability. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 391–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddington, S.C.; Howarth, M. Secrets of a covalent interaction for biomaterials and biotechnology: SpyTag and SpyCatcher. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 29, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.J.; Baker, E.N. Intramolecular isopeptide bonds: Protein crosslinks built for stress? Trends Biochem. Sci. 2011, 36, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeri, B.; Fierer, J.O.; Celik, E.; Chittock, E.C.; Schwarz-Linek, U.; Moy, V.T.; Howarth, M. Peptide tag forming a rapid covalent bond to a protein, through engineering a bacterial adhesin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E690–E697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keeble, A.H.; Banerjee, A.; Ferla, M.P.; Reddington, S.C.; Anuar, I.N.A.K.; Howarth, M. Evolving accelerated amidation by spytag/spycatcher to analyze membrane dynamics. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2017, 56, 16521–16525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khairil Anuar, I.N.A.; Banerjee, A.; Keeble, A.H.; Carella, A.; Nikov, G.I.; Howarth, M. Spy&Go purification of SpyTag-proteins using pseudo-SpyCatcher to access an oligomerization toolbox. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-J.; Wu, X.-L.; Wang, X.-W.; Liu, D.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.-B. SpyCatcher-NTEV: A Circularly Permuted, Disordered SpyCatcher Variant for Less Trace Ligation. Bioconjug. Chem. 2018, 29, 1622–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.K.; El-Sayed, A.; Barreto, K.; Bernhard, W.; Fonge, H.; Geyer, C.R. Site-Specific Fluorescent Labeling of Antibodies and Diabodies Using SpyTag/SpyCatcher System for In Vivo Optical Imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 54–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van den Berg van Saparoea, H.B.; Houben, D.; de Jonge, M.I.; Jong, W.S.P.; Luirink, J. Display of recombinant proteins on bacterial outer membrane vesicles by using protein ligation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, K.D.; Leneghan, D.B.; Brian, I.J.; Ishizuka, A.S.; Bachmann, M.F.; Draper, S.J.; Biswas, S.; Howarth, M. Plug-and-Display: decoration of Virus-Like Particles via isopeptide bonds for modular immunization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, N.J.; Turner, K.B.; Daniele, M.A.; Oh, E.; Medintz, I.L.; Walper, S.A. Bacterial Nanobioreactors–Directing Enzyme Packaging into Bacterial Outer Membrane Vesicles. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24963–24972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Yang, Z.; Luo, J.; Hsing, I.-M.; Sun, F. B12-dependent photoresponsive protein hydrogels for controlled stem cell/protein release. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 5912–5917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, J.A.; Ruta, A.; Therien, A.M.; West, J.L. Cell-Compatible, Site-Specific Covalent Modification of Hydrogel Scaffolds Enables User-Defined Control over Cell-Material Interactions. Biomacromolecules 2019, 20, 2486–2493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasaraneni, N.; Chamoun-Emanuelli, A.M.; Wright, G.; Chen, Z. Retargeting Lentiviruses via SpyCatcher-SpyTag Chemistry for Gene Delivery into Specific Cell Types. mBio 2017, 8, e01860-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrane, S.; Janitzek, C.M.; Matondo, S.; Resende, M.; Gustavsson, T.; de Jongh, W.A.; Clemmensen, S.; Roeffen, W.; van de Vegte-Bolmer, M.; van Gemert, G.J.; et al. Bacterial superglue enables easy development of efficient virus-like particle based vaccines. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinrichsen, M.; Lenz, M.; Edwards, J.M.; Miller, O.K.; Mochrie, S.G.J.; Swain, P.S.; Schwarz-Linek, U.; Regan, L. A new method for post-translationally labeling proteins in live cells for fluorescence imaging and tracking. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2017, 30, 771–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, C.; Howarth, M.; Harwood, C.R.; Ellis, T. Extracellular Self-Assembly of Functional and Tunable Protein Conjugates from Bacillus subtilis. ACS Synth. Biol. 2017, 6, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sano, K.-I.; Maeda, K.; Oki, M.; Maéda, Y. Enhancement of protein expression in insect cells by a lobster tropomyosin cDNA leader sequence. FEBS Lett. 2002, 532, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renner, M.; Flanagan, A.; Dejnirattisai, W.; Puttikhunt, C.; Kasinrerk, W.; Supasa, P.; Wongwiwat, W.; Chawansuntati, K.; Duangchinda, T.; Cowper, A.; et al. Characterization of a potent and highly unusual minimally enhancing antibody directed against dengue virus. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 1248–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veggiani, G.; Nakamura, T.; Brenner, M.D.; Gayet, R.V.; Yan, J.; Robinson, C.V.; Howarth, M. Programmable polyproteams built using twin peptide superglues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brune, K.D.; Buldun, C.M.; Li, Y.; Taylor, I.J.; Brod, F.; Biswas, S.; Howarth, M. Dual Plug-and-Display Synthetic Assembly Using Orthogonal Reactive Proteins for Twin Antigen Immunization. Bioconjug. Chem. 2017, 28, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoene, C.; Fierer, J.O.; Bennett, S.P.; Howarth, M. SpyTag/SpyCatcher cyclization confers resilience to boiling on a mesophilic enzyme. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2014, 53, 6101–6104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, M.; Xu, Q.; Jiang, L.; Huang, H. Spytag/spycatcher cyclization enhances the thermostability of firefly luciferase. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Lee, J.M.; Tatsuke, T.; Ebihara, T.; Masuda, A.; Hino, M.; Morokuma, D.; Fujita, R.; Mon, H.; Kusakabe, T.; et al. Expression and Purification of Vaccinia Virus DNA Topoisomerase IB Produced in the Silkworm-Baculovirus Expression System. Mol. Biotechnol. 2019, 61, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsubokawa, D.; Lee, J.M.; Hatta, T.; Mikami, F.; Maruyama, H.; Arakawa, T.; Kusakabe, T.; Tsuji, N. Characterization of the RAGE-binding protein, Strongyloides venestatin, produced by the silkworm-baculovirus expression system. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019, 75, 103964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soejima, Y.; Lee, J.M.; Nagata, Y.; Mon, H.; Iiyama, K. Comparison of signal peptides for efficient protein secretion in the baculovirus-silkworm system. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2013, 8, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, J.O.; Veggiani, G.; Howarth, M. SpyLigase peptide-peptide ligation polymerizes affibodies to enhance magnetic cancer cell capture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E1176–E1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutherland, A.R.; Alam, M.K.; Geyer, C.R. Post-translational Assembly of Protein Parts into Complex Devices by Using SpyTag/SpyCatcher Protein Ligase. ChemBioChem 2019, 20, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motohashi, T.; Shimojima, T.; Fukagawa, T.; Maenaka, K.; Park, E.Y. Efficient large-scale protein production of larvae and pupae of silkworm by Bombyx mori nuclear polyhedrosis virus bacmid system. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 326, 564–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, T.; Arai, S.; Ichikawa, H.; Park, E.Y. Versatility of chitosan/BmNPV bacmid DNA nanocomplex as transfection reagent of recombinant protein expression in silkworm larvae. Biotechnol. Lett. 2016, 38, 1449–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| EGFP/Venus-Fw | gtgagcaagggcgaggagctg |
| EGFP/Venus-Rv-Stop | cccaagcttctacttgtacagctcgtccatg |
| EGFP/Venus-Rv-nStop | cccaagcttcttgtacagctcgtccatgcc |
| mCherry-Fw | gtgagcaagggcgaggaggat |
| mCherry-Rv-Stop | cccaagcttctacttgtacagctcgtccatg |
| mCherry-Rv-nStop | cccaagcttcttgtacagctcgtccatgcc |
| 1DIII-Fw | agttatgttatgtgcaccgg |
| 1DIII-Rv | gcccaaaatagccattcgcc |
| 2DIII-Fw | tcatactctatgtgcacagg |
| 2DIII-Rv | acctaaaatggccattctct |
| 3DIII-Fw | tcttatgctatgtgtttgaa |
| 3DIII-Rv | tcccaggatagccattcggc |
| 4DIII-Fw | tcgtacactatgtgttcagg |
| 4DIII-Rv | tcctagtattgccatacgct |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, J.; Kato, T.; Park, E.Y. Development of SpyTag/SpyCatcher-Bacmid Expression Vector System (SpyBEVS) for Protein Bioconjugations Inside of Silkworms. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174228
Xu J, Kato T, Park EY. Development of SpyTag/SpyCatcher-Bacmid Expression Vector System (SpyBEVS) for Protein Bioconjugations Inside of Silkworms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174228
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Jian, Tatsuya Kato, and Enoch Y. Park. 2019. "Development of SpyTag/SpyCatcher-Bacmid Expression Vector System (SpyBEVS) for Protein Bioconjugations Inside of Silkworms" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174228
APA StyleXu, J., Kato, T., & Park, E. Y. (2019). Development of SpyTag/SpyCatcher-Bacmid Expression Vector System (SpyBEVS) for Protein Bioconjugations Inside of Silkworms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4228. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174228







