Chondroitin-Sulfate-A-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Testing to Predict Their Colloidal Behavior in Biological Milieu
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
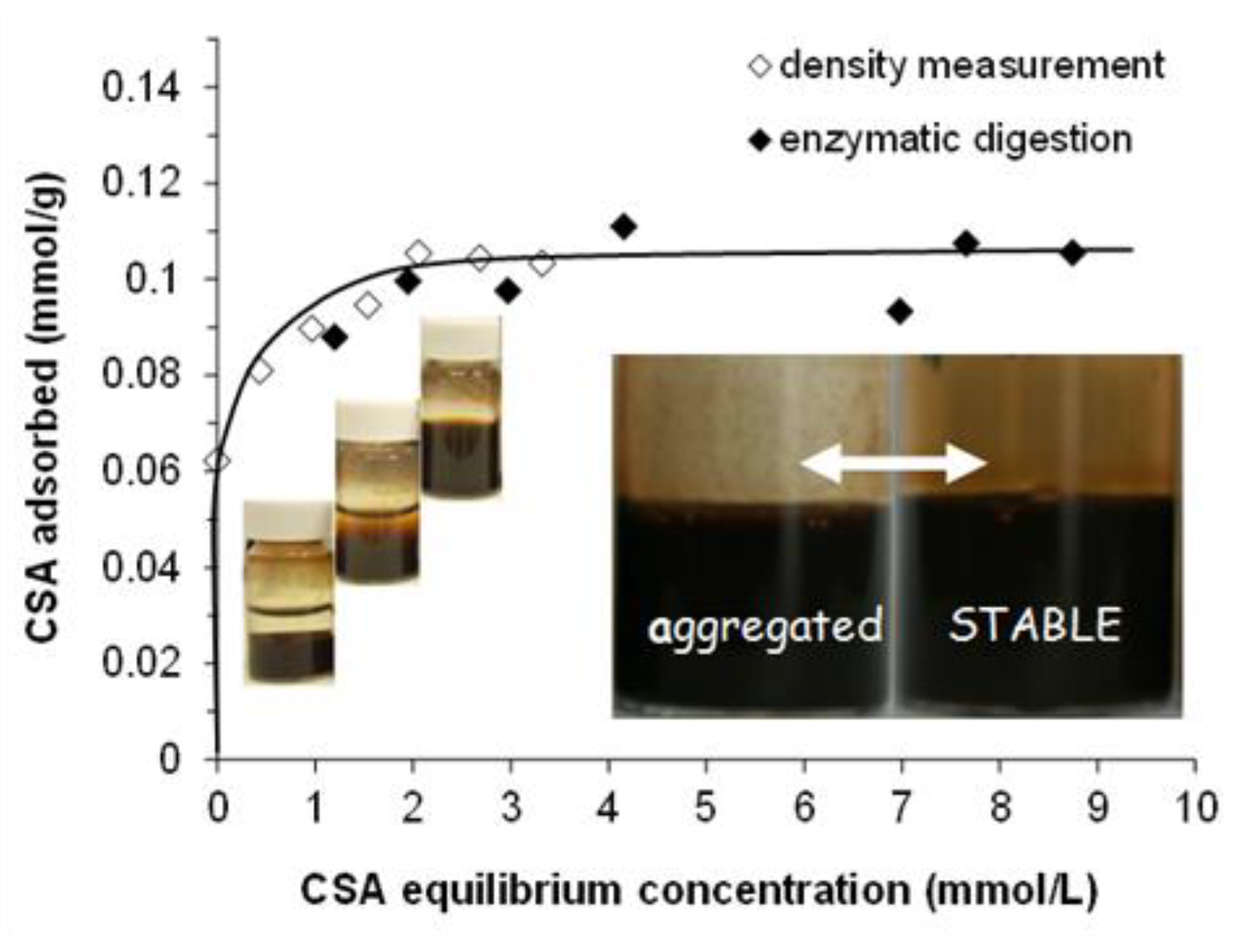
2.1. Adsorption of CSA on MNP
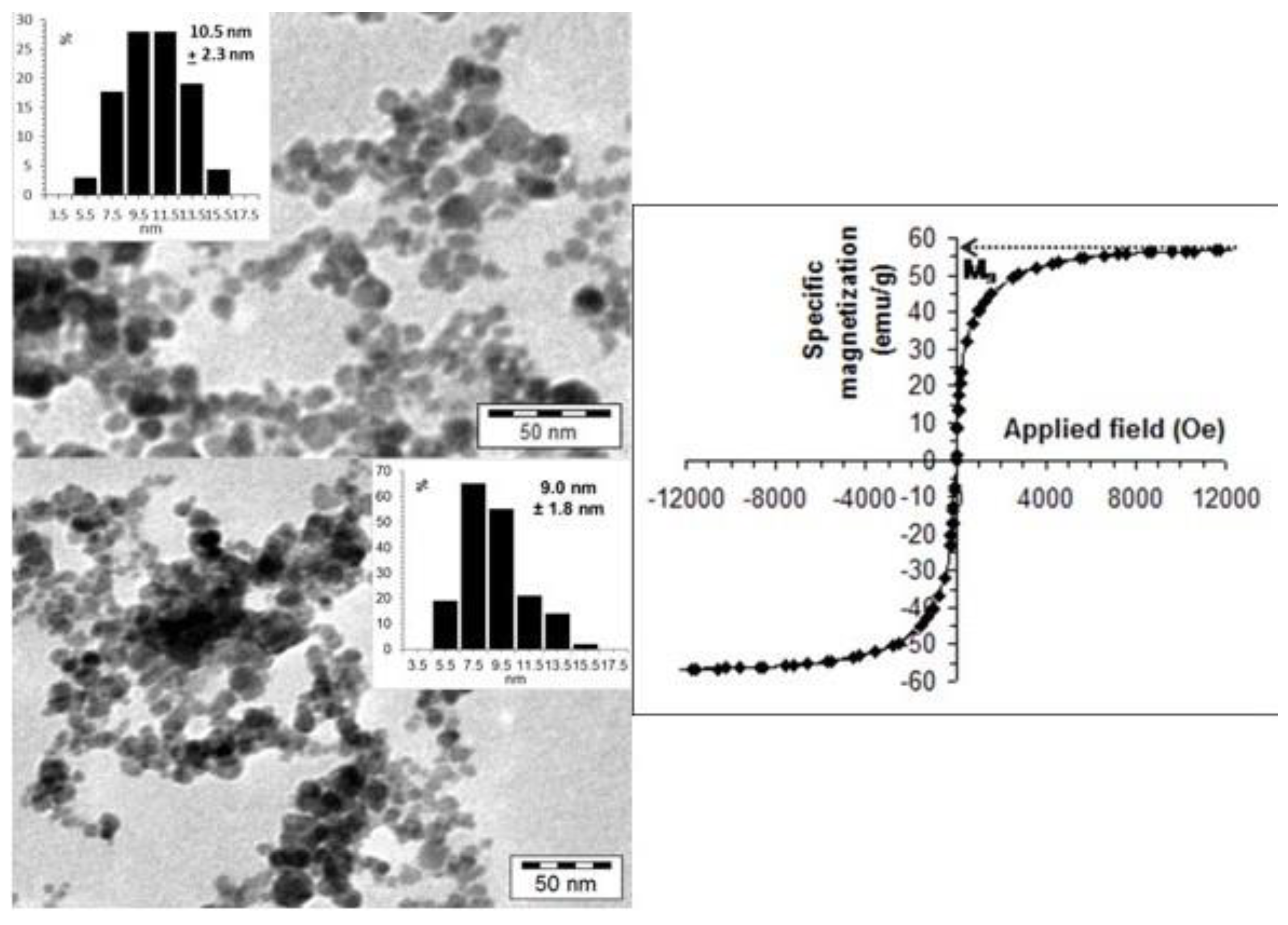
2.2. Size and Magnetic Property of Magnetic Core in CSA@MNP
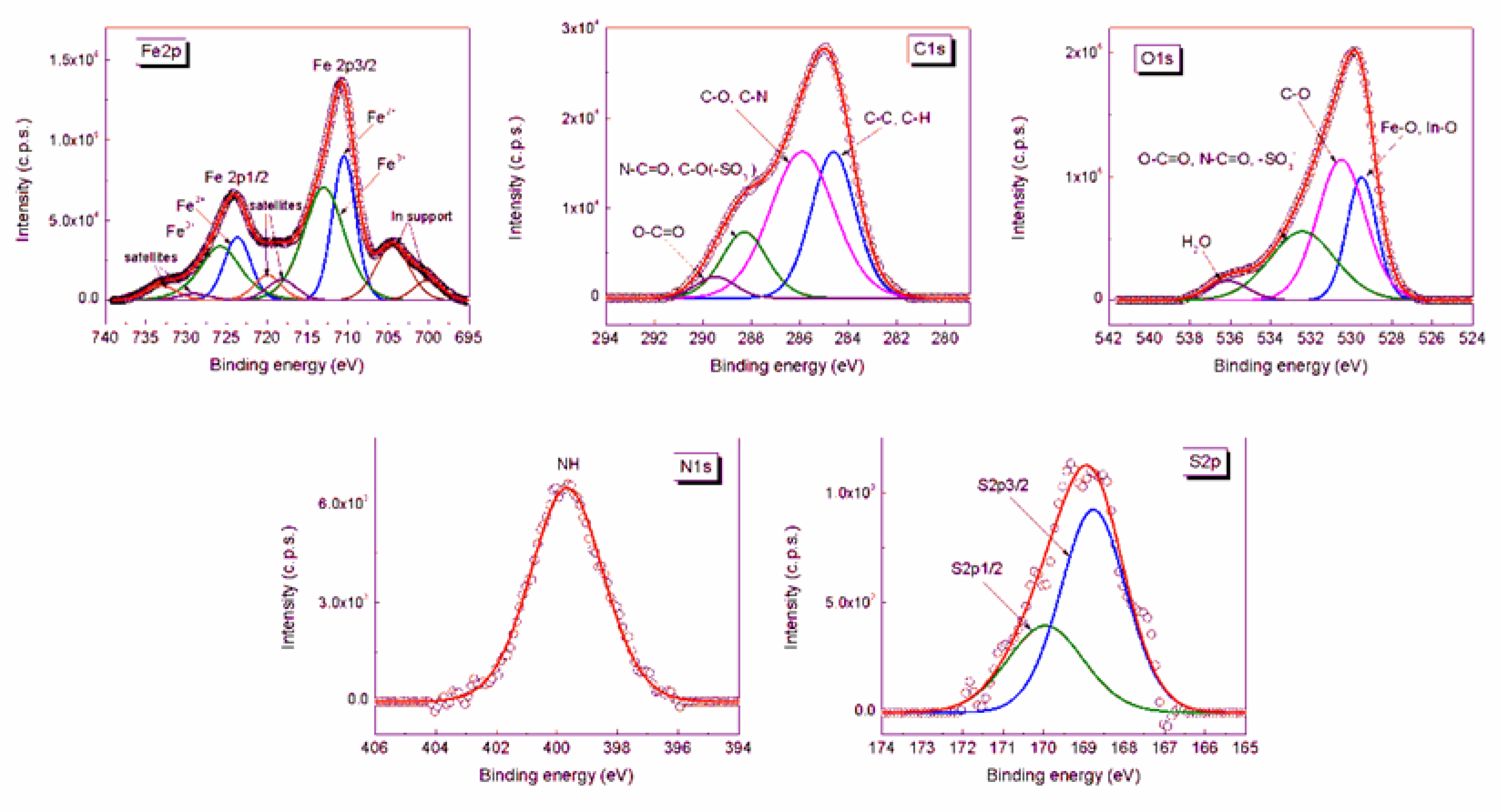
2.3. Binding of CSA on MNPs
2.4. The Effect of CSA Adsorption on the Charge State and Aggregation of MNPs
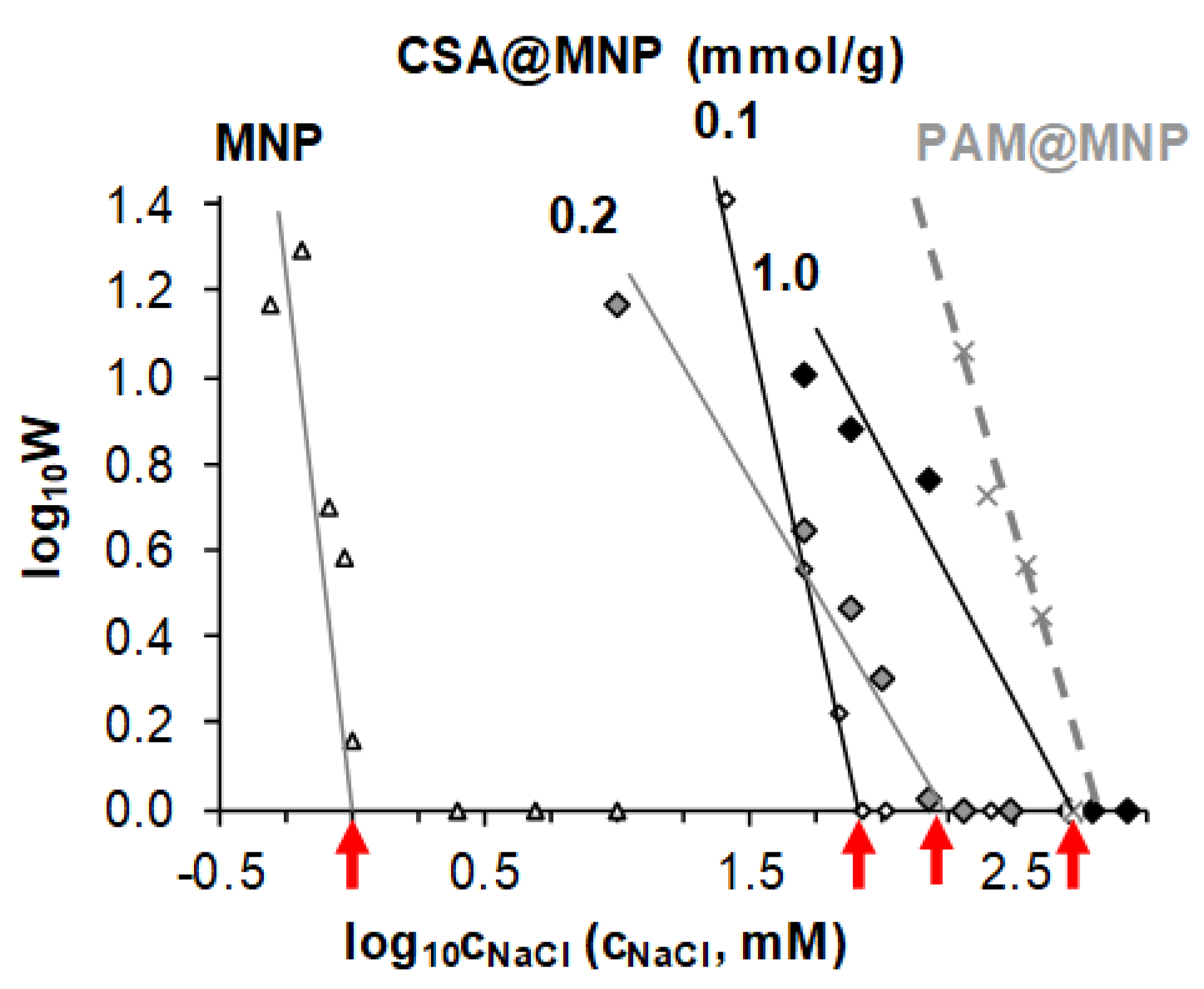
2.5. Salt Induced Aggregation of CSA@MNP at pH ~6.3
2.6. Chemical Stability of MNP Coated with CSA
2.7. Testing Toxicity of CSA@MNP
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Adsorption Experiment
3.3. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)
3.4. Magnetic Measurement (VSM)
3.5. Infrared Spectroscopy (FTIR-ATR)
3.6. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS)
3.7. Dynamic Light Scattering (DLS)
3.8. Electrophoresis Experiments
3.9. Coagulation Kinetics Experiments
3.10. Iron Dissolution Experiments
3.11. Anti-Proliferative Assays
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MNP | magnetite nanoparticle |
| MF | magnetic fluid |
| CSA | chondroitin-sulfate-A, chondroitin-4-sulfate |
| CSC | chondroitin-6-sulfate |
| CSA@MNP | CSA coated MNP |
| CS | Chondroitin-sulfate |
| CPCl | cetylpyridinium chloride |
| TEM | transmission electron microscopy |
| VSM | vibrating sample magnetometer |
| FTIR-ATR | Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy - attenuated total reflectance |
| XPS | X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| ICP | inductively coupled plasma |
| ICP-MS | inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry |
| MRI | magnetic resonance imaging |
| TG | thermogravimetry |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| CCC | critical coagulation concentration |
| MTT | a colorimetric assay for assessing cell metabolic activity |
References
- Revia, R.A.; Zhang, M. Magnetite nanoparticles for cancer diagnosis, treatment, and treatment monitoring: Recent advances. Mater. Today 2016, 19, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, K.; Sarkar, S.; Rao, K.J.; Paria, S. Core/shell nanoparticles in biomedical applications. Adv. Colloid Interfaces Sci. 2014, 209, 8–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ladj, R.; Bitar, A.; Eissa, M.M.; Fessi, H.; Mugnier, Y.; Le Dantec, R.; Elaissari, A. Polymer encapsulation of inorganic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 458, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, C.S.S.R.; Mohammad, F. Magnetic nanomaterials for hyperthermia-based therapy and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 789–808. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Saei, A.A.; Yazdani, M.; Lohse, S.E.; Bakhtiary, Z.; Serpooshan, V.; Ghavami, M.; Asadian, M.; Mashaghi, S.; Dreaden, E.C.; Mashaghi, A.; et al. Nanoparticle Surface Functionality Dictates Cellular and Systemic Toxicity. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 6578–6595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstad, E.; Textora, M.; Reimhult, E. Stabilization and functionalization of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2819–2843. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Figuerola, A.; Di Corato, R.; Manna, L.; Pellegrino, T. From iron oxide nanoparticles towards advanced iron-based inorganic materials designed for biomedical applications. Pharm. Res. 2010, 62, 126–143. [Google Scholar]
- Borbath, T.; Bica, D.; Potencz, I.; Vekas, L.; Boros, T. Magnetic nanofluids and magnetic composite fluids in rotating seal systems. Iop, C. Ser. Earth Env. 2010, 12, 012105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, T.K.; Richey, J.; Strand, M.; Leslie-Pelecky, D.L.; Flask, C.A.; Labhasetwar, V. Magnetic nanoparticles with dual functional properties: Drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4012–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munnier, E.; Cohen-Jonathan, S.; Linassier, C.; Douziech-Eyrolles, L.; Marchais, H.; Soucé, M.; Hervé, K.; Dubois, P.; Chourpa, I. Novel method of doxorubicin–SPION reversible association for magnetic drug targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 363, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3995–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odenbach, S. Ferrofluids-magnetically controlled suspensions. Colloid. Surf. A 2003, 217, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, M. Magnetic fluid and nanoparticle applications to nanotechnology. J. Nanopart. Res. 2001, 3, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochonski, W. Dynamic sealing with magnetic fluids. Wear 1989, 130, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soukup, D.; Moise, S.; Céspedes, E.; Dobson, J.; Telling, N.D. In situ measurement of magnetization relaxation of internalized nanoparticles in live cells. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corato, R.D.; Béalle, G.; Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Espinosa, A.; Clément, O.; Silva, A.K.A.; Ménager, C.; Wilhelm, C. Combining magnetic hyperthermia and photodynamic therapy for tumor ablation with photoresponsive magnetic liposomes. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 2904–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lartigue, L.; Hugounenq, P.; Alloyeau, D.; Clarke, S.P.; Lévy, M.; Bacri, J.C.; Bazzi, R.; Brougham, D.F.; Wilhelm, C.; Gazeau, F. Cooperative organization in iron oxide multi-core nanoparticles potentiates their efficiency as heating mediators and MRI contrast agents. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 10935–10949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankhurst, Q.A.; Connolly, J.; Jones, S.K.; Dobson, J. Applications of magnetic nanoparticles in biomedicine. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, R167–R181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, I.Y.; Illés, E.; Bauer, R.A.; Nesztor, D.; Szekeres, M.; Zupkó, I.; Tombácz, E. Designed polyelectrolyte shell on magnetite nanocore for dilution-resistant biocompatible magnetic fluids. Langmuir 2012, 28, 16638–16646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Vander-Elst, L.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations, and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombácz, E.; Tóth, I.Y.; Nesztor, D.; Illés, E.; Hajdú, A.; Szekeres, M.; Vékás, L. Adsorption of organic acids on magnetite nanoparticles, pH-dependent colloidal stability and salt tolerance. Colloid. Surf. A 2013, 435, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, M.; Tóth, I.Y.; Illés, E.; Hajdú, A.; Zupkó, I.; Farkas, K.; Oszlánczi, G.; Tiszlavicz, L.; Tombácz, E. Chemical and colloidal stability of carboxylated core-shell magnetite nanoparticles designed for biomedical applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14550–14574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bica, D.; Vékás, L.; Avdeev, M.V.; Marinica, O.; Socoliuc, V.; Balasoiu, M.; Garamus, V.M. Sterically stabilized water based magnetic fluids: Synthesis, structure and properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 2007, 311, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeev, M.V.; Feoktystov, A.V.; Kopcansky, P.; Lancz, G.; Garamus, V.M.; Willumeit, R.; Timko, M.; Koneracka, M.; Zavisova, V.; Tomasovicova, N.; et al. Structure of water-based ferrofluids with sodium oleate and polyethylene glycol stabilization by small-angle neutron scattering: Contrast-variation experiments. J. Appl. Cryst. 2010, 43, 959–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, H.; Ahmad, M.B.; Haron, M.J.; Namvar, F.; Nadi, B.; Rahman, M.Z.A.; Amin, J. Synthesis, surface modification and characterisation of biocompatible magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Molecules 2013, 18, 7533–7548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masoudi, A.; Hosseini, H.R.M.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Ahmadi, R.; Oghabian, M.A. The effect of poly(ethylene glycol) coating on colloidal stability of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as potential MRI contrast agent. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 433, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amici, J.; Celasco, E.; Allia, P.; Tiberto, P.; Sangermano, M. Poly(ethylene glycol)-coated magnetite nanoparticles: Preparation and characterization. Macromol. Chem. Physic. 2001, 212, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, R.J. Foundations of Colloid Science; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2001; Volume I, pp. 582–637. [Google Scholar]
- Ramos-Tejada, M.M.; Ontiveros, A.; Viota, J.L.; Durán, J.D.G. Interfacial and rheological properties of humic acid/hematite suspensions. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2003, 268, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyagi, M.; Sato, H.; Yagi, K.; Fukuda, N.; Nishimoto, S. Redox reactions of nitrite ions on the surface of colloidal magnetite particles coated with chondroitin sulfate. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2001, 279, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.L.; Lee, C.F.; Chiu, W.Y. Preparation and properties of poly(acrylic acid) oligomer stabilized superparamagnetic ferrofluid. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2005, 291, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, P. Manufacturing of size controlled magnetite nanoparticles potentially suitable for the preparation of aqueous magnetic fluids. Rom. Rep. Phys. 2006, 58, 269–272. [Google Scholar]
- Nanocrystalline magnetic iron oxide particles-method for preparation and use in medical diagnostics and therapy. US 5427767 A, 1995. Available online: http://www.google.com/patents/US5427767 (accessed on 16 June 2019).
- Lemarchanda, C.; Grefa, R.; Couvreu, P. Polysaccharide-decorated nanoparticles. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2004, 58, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Cheon, J. Nanoparticle contrast agents for molecular magnetic resonance imaging. In Nanobiotechnology II: More Concepts and Applications; Mirkin, C.A., Niemeye, C.M., Eds.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 321–346. [Google Scholar]
- Bae, K.H.; Park, M.; Do, M.J.; Lee, N.; Ryu, J.H.; Kim, G.W.; Kim, C.; Park, T.G.; Hyeon, T. Chitosan oligosaccharide-stabilized ferrimagnetic iron oxide nanocubes for magnetically modulated cancer hyperthermia. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 5266–5273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephen, Z.R.; Kievit, F.M.; Veiseh, O.; Chiarelli, P.A.; Fang, C.; Wang, K.; Hatzinger, S.J.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Silber, J.R.; Zhang, M. Redox-responsive magnetic nanoparticle for targeted convection-enhanced delivery of O6-benzylguanine to brain tumors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 10383–10395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallick, N.; Anwar, M.; Asfer, M.; Mehdi, S.H.; Rizvi, M.M.A.; Panda, A.K.; Talegaonkar, S.; Ahmad, F.J. Chondroitin sulfate-capped super-paramagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as potential carriers of doxorubicin hydrochloride. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauder, R.M. Chondroitin sulphate: A complex molecule with potential impacts on a wide range of biological systems. Complement. Med. 2009, 17, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bathe, M.; Rutledge, G.C.; Grodzinsky, A.J.; Tidor, B. A coarse-grained molecular model for glycosaminoglycans: Application to chondroitin, chondroitin sulfate, and hyaluronic acid. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 3870–3887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleland, R.L. Electrophoretic mobility of wormlike chains. I. experiment: Hyaluronate and chondroitin 4-sulfate. Macromolecules 1991, 24, 4386–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Loganathan, D.; Linhardt, R.J. Determination of the pKa of glucuronic acid and the carboxy groups of heparin by 13C-nuclear-magnetic-resonance spectroscopy. Biochem. J. 1991, 278, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimakopoulou, A.P.; Theocharis, A.D.; Tzanakakis, G.N.; Karamanos, N.K. The biological role of chondroitin sulfate in cancer and chondroitin-based anticancer agents. Vivo (AthensGreece) 2008, 22, 385–389. [Google Scholar]
- Kir’yanov, N.A.; Vasyukov, S.V.; Sukhanov, Y.S. Preparations based on salts of chondroitin sulfate for treating iron-deficiency anemia. Pharm. Chem. J. 1992, 26, 480–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dainippon Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. Overcoming challenges in a changing world. Annual report 2001. Available online: http://www.ds-pharma.com/ir/library/annual/pdf/2001/annual_report2001_mp.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2019).
- Aqueous preparation containing ashark-derived chondroitin iron sulfate colloid, EP 1 433 482 B1. Available online: https://data.epo.org/publication-server/rest/v1.0/publication-dates/20061220/patents/EP1433482NWB1/document.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2019).
- Martínez, A.M.; Benito, M.; Pérez, E.; Teijón, J.M.; Blanco, M.D. The role of anionic polysaccharides in the preparation of nanomedicines with anticancer applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2016, 22, 3364–3379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, L.M.R.; Paterno, L.G.; Chaves, N.L.; Gregurec, D.; Báo, S.N.; Moya, S.E.; Jain, M.; Azevedo, R.B.; Morais, P.C.; Soler, M.A.G. Biocompatible superparamagnetic carriers of chondroitin sulfate. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 066106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, I.Y.; Illés, E.; Szekeres, M.; Tombácz, E. Preparation and characterization of chondroitin-sulfate-A coated magnetite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2015, 380, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nel, A.E.; Madler, L.; Velegol, D.; Xia, T.; Hoek, E.M.V.; Somasundaran, P.; Klaessig, F.; Castranova, V.; Thompson, M. Understanding biophysicochemical interactions at the nano-bio interface. Nat. Mater. 2009, 8, 543–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombacz, E.; Farkas, K.; Foldesi, I.; Szekeres, M.; Illes, E.; Toth, I.Y.; Nesztor, D.; Szabo, T. Polyelectrolyte coating on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles as interface between magnetic core and biorelevant media. Interface Focus 2016, 6, 20160068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illés, E.; Tombácz, E. The effect of humic acid adsorption on pH-dependent surface charging and aggregation of magnetite nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2006, 295, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almond, A.; Sheehaman, J.K. Glycosaminoglycan conformation: Do aqueous molecular dynamics simulations agree with X-ray fiber diffraction? Glycobiology 2000, 10, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterk, H.; Braun, M.; Schmut, O.; Feichtinger, H. Investigation of the hyaluronic acid-copper complex by N.M.R. spectroscopy. Carbohyd. Res. 1985, 145, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, L.; Burger, K.; Kürti, J.; Korecz, L.; Kiricsi, I. Iron(III) complexes of sugar-type ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1986, 124, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Laskowski, J.S. The interactions between dextrin and metal hydroxides in aqueous solutions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 130, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, P.; Pierre, T.G.; Tombácz, E.; Webb, J. Rod-like iron(III) oxyhydroxide particles in iron(III)-polysaccharide solutions. J. Inorg. Biochem. 1995, 58, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnjanagoonchorn, W.; Wongekalak, L.; Engkagul, A. Determination of chondroitin sulfate from different sources of cartilage. Chem. Eng. Process. 2007, 46, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, M.A.; Rudd, T.R.; de Farias, E.H.C.; Ebner, L.F.; Gesteira, T.F.; de Souza, L.M.; Mendes, A.; Córdula, C.R.; Martins, J.R.M.; Hoppensteadt, D.; et al. A new approach for heparin standardization: Combination of scanning UV spectroscopy, nuclear magnetic resonance and principal component analysis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, J.D.; Premjee, M.M.; Buddhavarapu, S.; Hassib, A. A study of the partitioning of haloacetates into cetylpyridinium chloride micelles using semiequilibrium dialysis and ultrafiltration. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2013, 394, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.Y.; Oh, S.W.; Moon, S.D.; Kang, Y.S. Spectroscopic study on the precipitation of sodium alkyl sulfate with cetylpyridinium chloride. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2007, 314, 683–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tóth, I.Y.; Szekeres, M.; Turcu, R.; Sáringer, S.; Illés, E.; Nesztor, D.; Tombácz, E. Mechanism of in-situ surface polymerization of gallic acid in an environmental-inspired preparation of carboxylated core-shell magnetite nanoparticles. Langmuir 2014, 30, 15451–15461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, R.D.; Rivas, J.; Vaqueiro, P.; López-Quintela, M.A.; Caeiro, D. Particle size effects on magnetic properties of yttrium iron garnets prepared by a sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 247, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merce, A.L.R.; Carrera, L.C.M.; Romanholi, L.K.S.; Recio, M.A.L. Aqueous and solid complexes of iron(III) with hyaluronic acid: Potentiometric titrations and infrared spectroscopy studies. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2002, 89, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurti, G.S.R.; Huang, P.M. Influence of citrate on the kinetics of Fe(II) oxidation and the formation of iron oxyhydroxides. Clay. Clay Min. 1991, 39, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-S.; Church, J.S.; Woodhead, A.L. Infrared and Raman spectroscopic studies on iron oxide magnetic nano-particles and their surface modifications. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2012, 324, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Chen, Y.; Ding, C.; Li, G. Interaction study in homogeneous collagen/chondroitin sulfate blends by two-dimensional infrared spectroscopy. Carbohyd. Polym. 2012, 89, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, X.; He, D.; Liu, F.; Liu, R. Preparation and characterization of hydroxyapatite/chondroitin sulfate composites by biomimetic synthesis. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 112, 838–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchisawa, H.; Okuzaki, B.; Ichita, J.; Matsue, H. Binding between calcium ions and chondroitin sulfate chains of salmon nasal cartilage glycosaminoglycan. Int. Congr. Ser. 2001, 1223, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Dan, N.; Xiao, S.; Ye, Y.; Dan, W. Preparation and characterization of collagen–chitosan–chondroitin sulfate composite membranes. J. Membr. Biol. 2012, 245, 707–716. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.; Xiong, G.; Roguin, A.; Teoh, S.H.; Choong, C. Amelioration of blood compatibility and endothelialization of polycaprolactone substrates by surface-initiated atom transfer radical polymerization. Chapter 7. In Advances in Biomaterials Science and Biomedical Applications; Pignatello, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2013; pp. 177–205. [Google Scholar]
- Elimelech, M.; Gregory, J.; Jia, X.; Williams, R.A. Particle Deposition and Aggregation: Measurement, Modelling and Simulation; Butterworths: Oxford, UK, 1995; pp. 263–289. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, D.J. Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry, 4th ed.; Butterworth: Burlington, NJ, USA, 1992; pp. 210–241. [Google Scholar]
- Valko, M.; Morris, H.; Cronin, M.T.D. Metals, toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr. Med. Chem. 2005, 12, 1161–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, K.M. Biomedical nanomagnetics: A spin through possibilities in imaging, diagnostics, and therapy. IEEE T. Magn. 2010, 46, 2523–2558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soenen, S.J.H.; Himmelreich, U.; Nuytten, N.; Pisanic II, T.R.; Ferrari, A.; de Cuyper, M. Intracellular nanoparticle coating stability determines nanoparticle diagnostics efficacy and cell functionality. Small 2010, 6, 2136–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornell, R.M.; Schwertmann, U. The Iron Oxides, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2003; pp. 172–177. [Google Scholar]
- Enzymatic assay of chondroitinase ABC (EC 4.2.2.4.). Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/content/dam/sigma-aldrich/docs/Sigma/Enzyme_Assay/c2905enz.pdf (accessed on 16 June 2019).
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
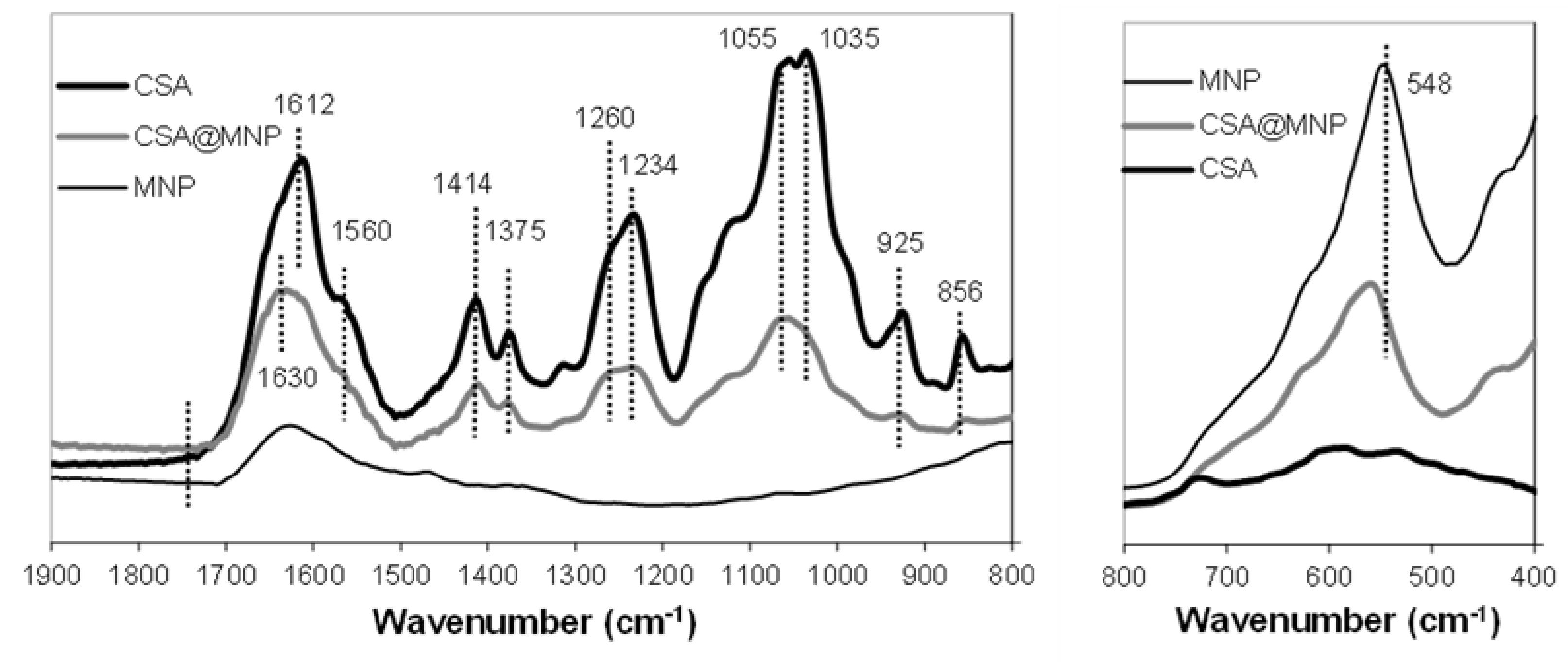



| MNP | CSA | CSA@MNP | Δν * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe–O (≡Fe–OH) | 548 | 559 | 11 | |
| C = O (–COOH) | - | - | - | |
| C–O (sym., –COO−) | 1375 | 1379 | 4 | |
| C–O (asym., –COO−) | 1612 | 1630 | 18 | |
| C–O–S (–O–SO3−) | 856 | 856 | 0 | |
| S = O (–O–SO3−) | 1260 | 1260 | 0 |
| Peak Name | Position (eV) | fwhm (eV) | Atomic Conc (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fe2+ 2p3/2 | 710.46 | 3.410 | 5.629 |
| Fe3+ 2p3/2 | 712.98 | 6.000 | 7.950 |
| Fe2+ 2p1/2 | 723.66 | 3.882 | 5.450 |
| Fe3+ 2p1/2 | 725.78 | 6.000 | 7.697 |
| Fe3+ satellite 2p3/2 | 719.92 | 4.075 | 1.184 |
| Fe2+ satellite 2p3/2 | 718.19 | 4.374 | 1.038 |
| Fe3+ satellite 2p1/2 | 733.06 | 4.627 | 1.507 |
| Fe2+ satellite 2p1/2 | 729.03 | 4.649 | 0.690 |
| C 1s; C‒C, C‒H | 284.61 | 2.147 | 6.221 |
| C 1s; C‒O, C‒N | 285.90 | 3.121 | 9.037 |
| C 1s; N‒C = O, C‒O(‒SO3‒) | 288.29 | 2.218 | 2.935 |
| C 1s; O‒C = O | 289.48 | 1.929 | 0.794 |
| O 1s; Fe‒O, In‒O | 529.49 | 1.746 | 11.066 |
| O 1s; C‒O | 530.51 | 2.802 | 20.488 |
| O 1s; O‒C = O, N‒C = O, ‒SO3‒ | 532.43 | 3.838 | 13.709 |
| O 1s; H2O | 536.11 | 2.356 | 2.342 |
| N 1s; N‒H | 399.67 | 2.814 | 1.717 |
| S 2p3/2; ‒SO3‒ | 169.95 | 2.230 | 0.271 |
| S 2p1/2; ‒SO3‒ | 168.77 | 1.909 | 0.277 |
| CSA-Loading (mmol/g) | pH of IEP | pH-Range of Aggregation |
|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | ~8 | ~5 ‒ ~10 |
| 0.05 | ~6 | ~3 ‒ ~10 |
| 0.10 | ~4 | < ~5 |
| 0.20 | < 3 | < ~3.5 |
| 0.40 | < 3 | < ~3 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tóth, I.Y.; Illés, E.; Szekeres, M.; Zupkó, I.; Turcu, R.; Tombácz, E. Chondroitin-Sulfate-A-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Testing to Predict Their Colloidal Behavior in Biological Milieu. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174096
Tóth IY, Illés E, Szekeres M, Zupkó I, Turcu R, Tombácz E. Chondroitin-Sulfate-A-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Testing to Predict Their Colloidal Behavior in Biological Milieu. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174096
Chicago/Turabian StyleTóth, Ildikó Y., Erzsébet Illés, Márta Szekeres, István Zupkó, Rodica Turcu, and Etelka Tombácz. 2019. "Chondroitin-Sulfate-A-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Testing to Predict Their Colloidal Behavior in Biological Milieu" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174096
APA StyleTóth, I. Y., Illés, E., Szekeres, M., Zupkó, I., Turcu, R., & Tombácz, E. (2019). Chondroitin-Sulfate-A-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization and Testing to Predict Their Colloidal Behavior in Biological Milieu. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4096. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174096






