Immunoglobulin Binding Protein 1 as a Potential Urine Biomarker in Patients with Lupus Nephritis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Baseline Characteristics of the SLE Patients
2.2. Urinary IGBP1 Level was Increased in Patients with Lupus Nephritis
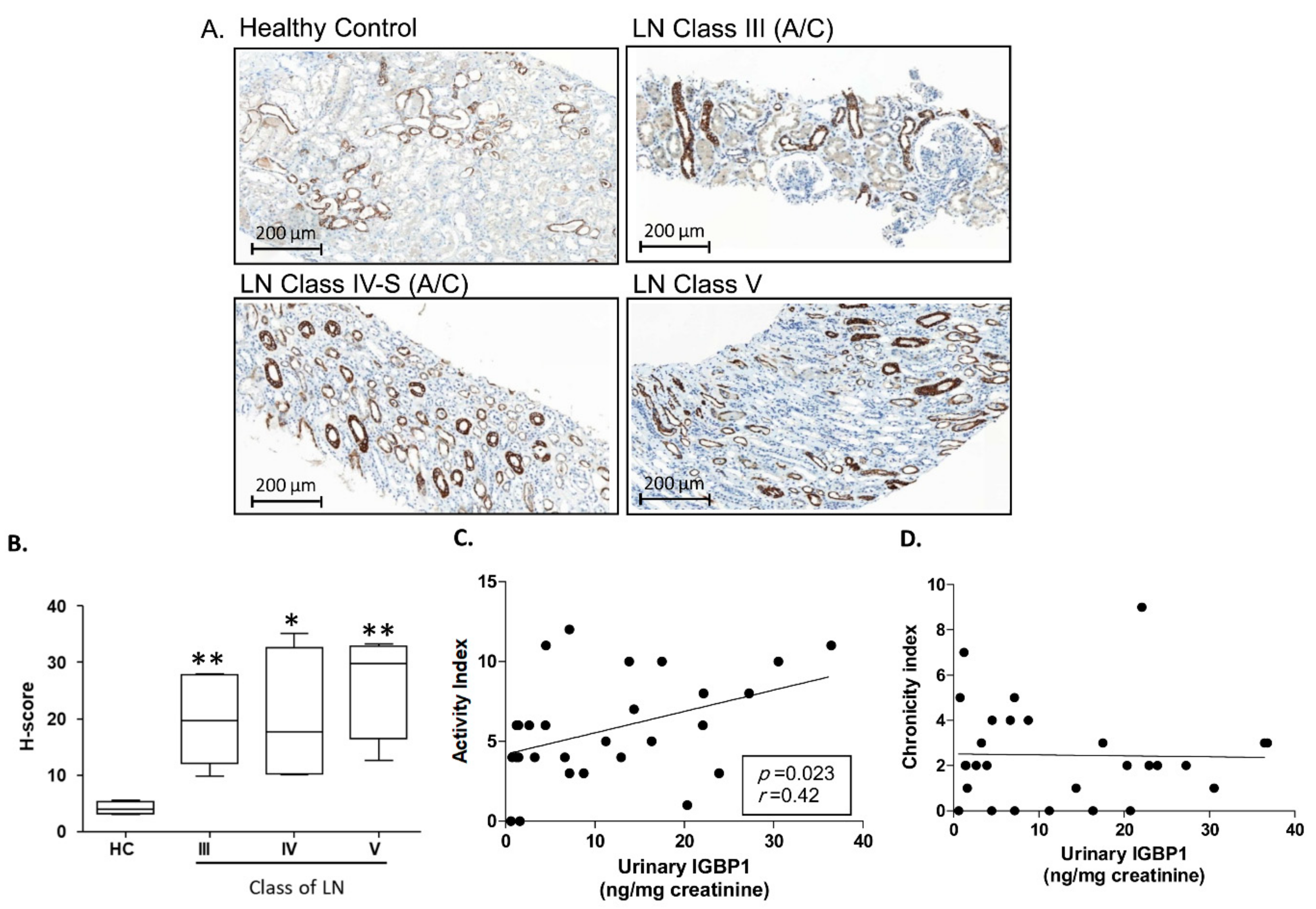
2.3. Tubular Expression of IGBP1 in Renal Pathology
2.4. Microarray Analysis in IGBP1 siRNA Transfected HK-2 Cells
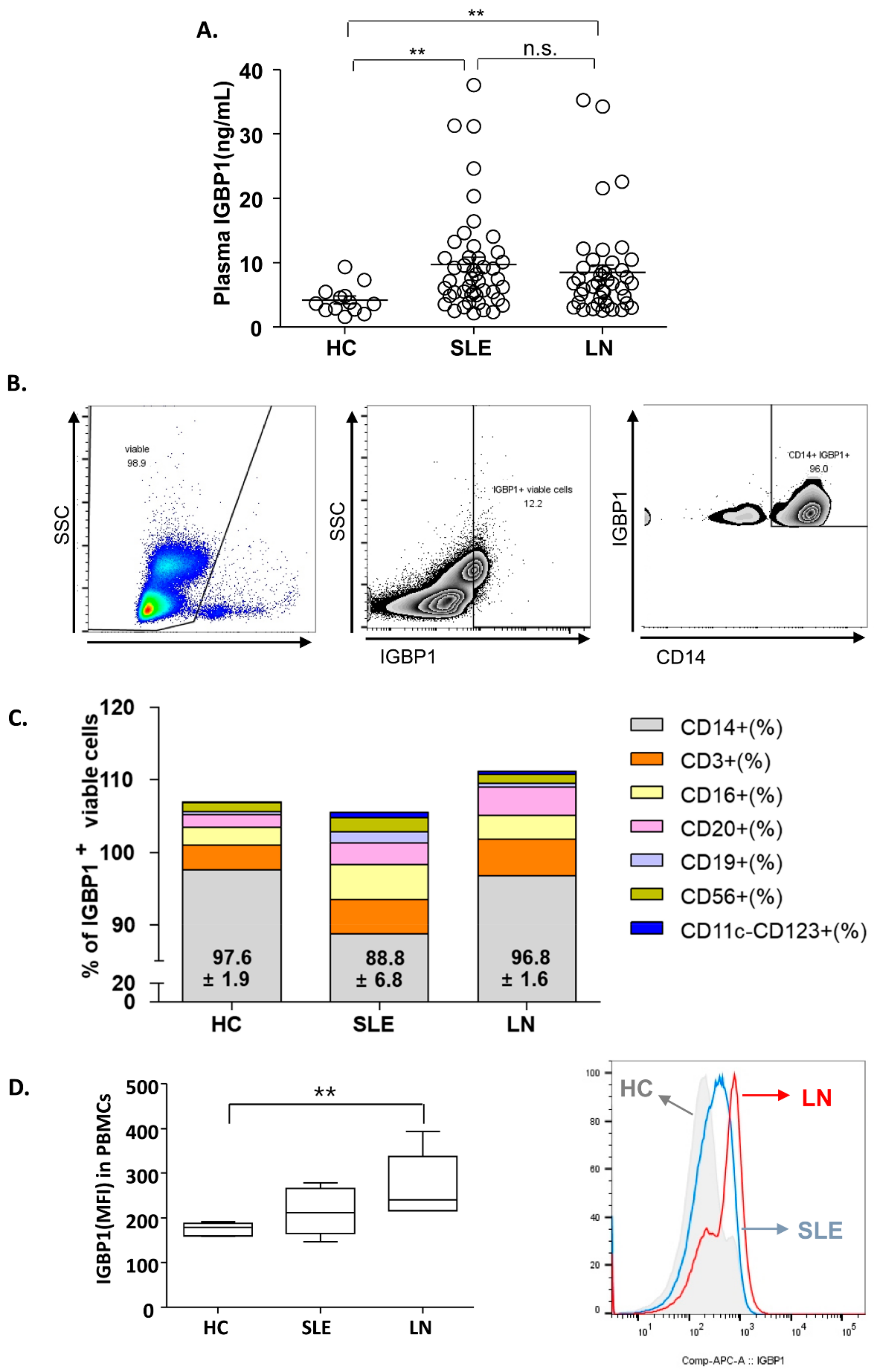
2.5. Increased Plasma IGBP1 in SLE Patients and Distribution of IGBP1 in PBMCs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients Selection and Estimation of IGBP1 Concentration
4.2. Lupus Nephritis Activity and Chronicity Index Assessment
4.3. Immunohistochemistry
4.4. Silencing IGBP1 in HK-2 Cells
4.5. Microarray Analysis
4.5.1. RNA Isolation and Gene Expression Profiling
4.5.2. Data Analysis
4.6. Surface and Intracellular Staining and Flow Cytometry
4.7. Statistical Analyses
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BCR | B cell receptor |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| ESR | Erythrocyte sedimentation rate |
| LN | Lupus nephritis |
| MHC | Major histocompatibility complex |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
References
- Cameron, J.S. Lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 413–424. [Google Scholar]
- Bevc, S.; Mohorko, E.; Kolar, M.; Brglez, P.; Holobar, A.; Kniepeiss, D.; Podbregar, M.; Piko, N.; Hojs, N.; Knehtl, M.; et al. Measurement of breath ammonia for detection of patients with chronic kidney disease. Clin. Nephrol. 2017, 88, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, C.; Bratu, A.M.; Matei, C.; Cernat, R.; Popescu, A.; Dumitras, D.C. Qualitative and quantitative determination of human biomarkers by laser photoacoustic spectroscopy methods. Laser Physics. 2011, 21, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esdaile, J.M.; Joseph, L.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Li, Y.; Danoff, D.; Clarke, A.E. Routine immunologic tests in systemic lupus erythematosus: Is there a need for more studies? J. Rheumatol. 1996, 23, 1891–1896. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Thomas, J.; Blanco, I.; Putterman, C. Urinary biomarkers in lupus nephritis. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2011, 40, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balow, J.E. Clinical presentation and monitoring of lupus nephritis. Lupus 2005, 14, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malvar, A.; Pirruccio, P.; Alberton, V.; Lococo, B.; Recalde, C.; Fazini, B.; Nagaraja, H.; Indrakanti, D.; Rovin, B.H. Histologic versus clinical remission in proliferative lupus nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2017, 32, 1338–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Xie, C.; Wang, H.W.; Zhou, X.J.; Schwartz, N.; Calixto, S.; Mackay, M.; Aranow, C.; Putterman, C.; Mohan, C. Elevated urinary VCAM-1, P-selectin, soluble TNF receptor-1, and CXC chemokine ligand 16 in multiple murine lupus strains and human lupus nephritis. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 7166–7175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, N.; Su, L.; Burkly, L.C.; Mackay, M.; Aranow, C.; Kollaros, M.; Michaelson, J.S.; Rovin, B.; Putterman, C. Urinary TWEAK and the activity of lupus nephritis. J. Autoimmun. 2006, 27, 242–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, N.; Rubinstein, T.; Burkly, L.C.; Collins, C.E.; Blanco, I.; Su, L.; Hojaili, B.; Mackay, M.; Aranow, C.; Stohl, W.; et al. Urinary TWEAK as a biomarker of lupus nephritis: A multicenter cohort study. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2009, 11, R143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, P.; Radhakrishnan, J. B lymphocytes and lupus nephritis: New insights into pathogenesis and targeted therapies. Kidney Int. 2008, 73, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nashi, E.; Wang, Y.; Diamond, B. The role of B cells in lupus pathogenesis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holdsworth, S.R.; Gan, P.Y.; Kitching, A.R. Biologics for the treatment of autoimmune renal diseases. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2016, 12, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwata, S.; Tanaka, Y. B-cell subsets, signaling and their roles in secretion of autoantibodies. Lupus 2016, 25, 850–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, D.L.; Sheng, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhu, Z.; Tombleson, P.; Chen, L.; Cunninghame Graham, D.S.; Bentham, J.; Roberts, A.L.; et al. Genome-wide association meta-analysis in Chinese and European individuals identifies ten new loci associated with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 940–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teruel, M.; Alarcon-Riquelme, M.E. The genetic basis of systemic lupus erythematosus: What are the risk factors and what have we learned. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 74, 161–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, S.; Saito, K.; Hirata, S.; Ohkubo, N.; Nakayamada, S.; Nakano, K.; Hanami, K.; Kubo, S.; Miyagawa, I.; Yoshikawa, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of anti-CD20 antibody rituximab for patients with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2018, 27, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, Y.; Takeuchi, T.; Miyasaka, N.; Sumida, T.; Mimori, T.; Koike, T.; Endo, K.; Mashino, N.; Yamamoto, K. Efficacy and safety of rituximab in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis who are refractory to conventional therapy. Mod. Rheumatol. 2016, 26, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, R.J.; Sangle, S.R.; Jordan, N.P.; Aslam, L.; Lewis, M.J.; Wedgwood, R.; D’Cruz, D.P. Rituximab in the treatment of resistant lupus nephritis: Therapy failure in rapidly progressive crescentic lupus nephritis. Lupus 2013, 22, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwahara, K.; Matsuo, T.; Nomura, J.; Igarashi, H.; Kimoto, M.; Inui, S.; Sakaguchi, N. Identification of a 52-kDa molecule (p52) coprecipitated with the Ig receptor-related MB-1 protein that is inducibly phosphorylated by the stimulation with phorbol myristate acetate. J. Immunol. 1994, 152, 2742–2752. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, M.; Ditsworth, D.; Lindsten, T.; Thompson, C.B. Alpha4 is an essential regulator of PP2A phosphatase activity. Mol. Cell 2009, 36, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanahoshi, M.; Tsujishita, Y.; Tokunaga, C.; Inui, S.; Sakaguchi, N.; Hara, K.; Yonezawa, K. Alpha4 protein as a common regulator of type 2A-related serine/threonine protein phosphatases. FEBS Lett. 1999, 446, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juang, Y.T.; Rauen, T.; Wang, Y.; Ichinose, K.; Benedyk, K.; Tenbrock, K.; Tsokos, G.C. Transcriptional activation of the cAMP-responsive modulator promoter in human T cells is regulated by protein phosphatase 2A-mediated dephosphorylation of SP-1 and reflects disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1795–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiari, C.G.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Juang, Y.T.; Tsokos, G.C. Protein phosphatase 2A is a negative regulator of IL-2 production in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 3193–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juang, Y.T.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Peng, H.B.; Ergin, S.; Finnell, M.; Magilavy, A.; Kyttaris, V.C.; Tsokos, G.C. PP2A dephosphorylates Elf-1 and determines the expression of CD3zeta and FcRgamma in human systemic lupus erythematosus T cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3658–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Li, M.; Yang, Y.; Guo, Z.; Sun, Y.; Shao, C.; Li, M.; Sun, W.; Gao, Y. A comprehensive analysis and annotation of human normal urinary proteome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pieper, R.; Gatlin, C.L.; McGrath, A.M.; Makusky, A.J.; Mondal, M.; Seonarain, M.; Field, E.; Schatz, C.R.; Estock, M.A.; Ahmed, N.; et al. Characterization of the human urinary proteome: A method for high-resolution display of urinary proteins on two-dimensional electrophoresis gels with a yield of nearly 1400 distinct protein spots. Proteomics 2004, 4, 1159–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, E.R.; Cai, M.M.; McMahon, L.P.; Wright, D.A.; Holt, S.G. The value of simultaneous measurements of urinary albumin and total protein in proteinuric patients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, O.C.; Park, Y.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, J.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Lee, C.K.; Yoo, B.; Hong, S. Non-albumin proteinuria as a parameter of tubulointerstitial inflammation in lupus nephritis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2019, 38, 235–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, S.; Tsang, R.C.; Sun, Y.; Leung, J.K.; Chan, T.M. Effect of human anti-DNA antibodies on proximal renal tubular epithelial cell cytokine expression: Implications on tubulointerstitial inflammation in lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 3281–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhingra, S.; Qureshi, R.; Abdellatif, A.; Gaber, L.W.; Truong, L.D. Tubulointerstitial nephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus: Innocent bystander or ominous presage. Histol. Histopathol. 2014, 29, 553–565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yap, D.Y.; Yung, S.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, C.; Chan, T.M. Serum level of proximal renal tubular epithelial cell-binding immunoglobulin G in patients with lupus nephritis. Lupus 2016, 25, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yung, S.; Ng, C.Y.; Ho, S.K.; Cheung, K.F.; Chan, K.W.; Zhang, Q.; Chau, M.K.; Chan, T.M. Anti-dsDNA antibody induces soluble fibronectin secretion by proximal renal tubular epithelial cells and downstream increase of TGF-beta1 and collagen synthesis. J. Autoimmun. 2015, 58, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, K.A. The tubulointerstitium in progressive renal disease. Kidney Int. 1998, 54, 992–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, R.E.; Cooper, M.E. The tubulointerstitium in progressive diabetic kidney disease: More than an aftermath of glomerular injury? Kidney Int. 1999, 56, 1627–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, S.A.; Rauen, T.; Hedrich, C.M.; Tsokos, G.C.; Crispin, J.C. Protein phosphatase 2A enables expression of interleukin 17 (IL-17) through chromatin remodeling. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26775–26784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozo, C.; Chinenov, Y.; Maharaj, R.K.; Gupta, S.; Leuenberger, L.; Kirou, K.A.; Bykerk, V.P.; Goodman, S.M.; Salmon, J.E.; Pernis, A.B. Targeting the RhoA-ROCK pathway to reverse T-cell dysfunction in SLE. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 740–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.P.; Wang, X.R.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhang, C.; Wang, D.G. Increased Serum Levels of Soluble B7-H4 in Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Iran. J. Immunol. 2019, 16, 43–52. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, C.; Xie, Z.; Zou, L.; Ruan, Z.; Zhang, X.; Tang, Y.; Fei, L.; Jia, Z.; Wu, Y. Expression of the novel co-stimulatory molecule B7-H4 by renal tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 2092–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badot, V.; Luijten, R.K.; van Roon, J.A.; Depresseux, G.; Aydin, S.; Van den Eynde, B.J.; Houssiau, F.A.; Lauwerys, B.R. Serum soluble interleukin 7 receptor is strongly associated with lupus nephritis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 453–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvaro-Benito, M.; Morrison, E.; Wieczorek, M.; Sticht, J.; Freund, C. Human leukocyte antigen-DM polymorphisms in autoimmune diseases. Open Biol. 2016, 6, 160165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morel, J.; Simoes Cda, S.; Avinens, O.; Sany, J.; Combe, B.; Eliaou, J.F. Polymorphism of HLA-DMA and DMB alleles in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J. Rheumatol. 2003, 30, 1485–1490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, M.L.; Katsumata, K.; Atsumi, T.; Romero, F.I.; Bertolaccini, M.L.; Funke, A.; Amengual, O.; Kondeatis, E.; Vaughan, R.W.; Cox, A.; et al. Association of HLA-DM polymorphism with the production of antiphospholipid antibodies. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2004, 63, 1645–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nowling, T.K.; Mather, A.R.; Thiyagarajan, T.; Hernandez-Corbacho, M.J.; Powers, T.W.; Jones, E.E.; Snider, A.J.; Oates, J.C.; Drake, R.R.; Siskind, L.J. Renal glycosphingolipid metabolism is dysfunctional in lupus nephritis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1402–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundararaj, K.; Rodgers, J.I.; Marimuthu, S.; Siskind, L.J.; Bruner, E.; Nowling, T.K. Neuraminidase activity mediates IL-6 production by activated lupus-prone mesangial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 314, F630–F642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vezzoli, M.; Sciorati, C.; Campana, L.; Monno, A.; Doglio, M.G.; Rigamonti, E.; Corna, G.; Touvier, T.; Castiglioni, A.; Capobianco, A.; et al. The clearance of cell remnants and the regeneration of the injured muscle depend on soluble pattern recognition receptor PTX3. Mol. Med. 2017, 22, 809–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirestam, L.; Enocsson, H.; Skogh, T.; Eloranta, M.L.; Ronnblom, L.; Sjowall, C.; Wettero, J. Interferon-alpha coincides with suppressed levels of pentraxin-3 (PTX3) in systemic lupus erythematosus and regulates leucocyte PTX3 in vitro. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 189, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.; Fox, C.J.; Mu, J.; Solt, L.; Xu, A.; Cinalli, R.M.; Birnbaum, M.J.; Lindsten, T.; Thompson, C.B. The PP2A-Associated protein alpha 4 is an essential inhibitor of apoptosis. Science 2004, 306, 695–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffer, L.; Bethunaickan, R.; Ramanujam, M.; Huang, W.; Schiffer, M.; Tao, H.; Madaio, M.P.; Bottinger, E.P.; Davidson, A. Activated renal macrophages are markers of disease onset and disease remission in lupus nephritis. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 1938–1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, M.C. Updating the American college of rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1997, 40, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weening, J.J.; D’Agati, V.D.; Schwartz, M.M.; Seshan, S.V.; Alpers, C.E.; Appel, G.B.; Balow, J.E.; Bruijn, J.A.; Cook, T.; Ferrario, F.; et al. The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 521–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, H.A., 3rd; Muenz, L.R.; Joyce, K.M.; Antonovych, T.A.; Kullick, M.E.; Klippel, J.H.; Decker, J.L.; Balow, J.E. Prognostic factors in lupus nephritis. Contribution of renal histologic data. Am. J. Med. 1983, 75, 382–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, M.J.; Johnson, G.; Kirk, J.; Fuerstenberg, S.M.; Zager, R.A.; Torok-Storb, B. HK-2: An immortalized proximal tubule epithelial cell line from normal adult human kidney. Kidney Int. 1994, 45, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| SLE without Nephritis (n = 30) | Lupus Nephritis (n = 39) | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female (N, %) | 29 (96.7%) | 38 (97.4%) | >0.999 |
| Age (years, mean ± SD) | 39.4 ± 8.5 | 39.1 ± 11.0 | 0.903 |
| Disease duration (years, median, range) | 6.2 (3.2–10.7) | 7.7 (2.1–10.9) | 0.410 |
| Laboratory data | |||
| Serum creatinine (mg/dl, median) | 0.70 (0.63–0.80) | 0.80 (0.70–1.10) | 0.019 |
| C3 (mg/dl, mean ± SD) | 77.3 ± 24.3 | 81.3 ± 24.8 | 0.523 |
| C4 (mg/dl, median) | 11.7 (9.1–15.1) | 14.0 (8.1–21.0) | 0.037 |
| Anti-dsDNA (IU/mL, median) | 7.5 (5.3–20.0) | 14.2 (7.7–78.8) | 0.037 |
| ESR (mm/hr, mean ± SD) | 27.1 ± 13.8 | 33.2 ± 19.0 | 0.125 |
| CRP (mg/dl, median) | 0.10 (0.10–0.20) | 0.11 (0.10–0.31) | 0.129 |
| Urine protein/creatinine ratio (mg/g, median) | NA | 1009.5 (155.4–2275.6) | NA |
| Microscopic hematuria (N, %) # | 1 (3.3%) | 19 (48.7%) | <0.001 |
| Organ involvement (N, %) | |||
| Renal | 0 (0.0%) | 39 (100.0%) | <0.001 |
| Neurologic | 2 (6.7%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0.576 |
| Musculoskeletal | 6 (20.0%) | 8 (20.5%) | 0.958 |
| Mucocutaneous | 4 (13.3%) | 6 (15.4%) | >0.999 |
| Serositis | 2 (6.7%) | 1 (2.6%) | 0.576 |
| SLEDAI-2K (mean ± SD) | 4.48 ± 0.73 | 12.18 ±1.16 | <0.001 |
| Medications | |||
| Glucocorticoids (mg/d, median) * | 0.0 (0.0–10.0) | 15.0 (6.3–20.0) | 0.001 |
| Hydroxychloroquine (N, %) | 29 (96.7%) | 31 (79.5%) | 0.067 |
| Mycophenolate mofetil (N, %) | 0 (0.0%) | 12 (30.8%) | 0.001 |
| Cyclophosphamide (N, %) | 0 (0.0%) | 10 (26.3%) | 0.002 |
| Azathioprine (N, %) | 2 (6.7%) | 7 (17.9%) | 0.281 |
| Methotrexate (N, %) | 1 (3.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.435 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, E.-J.; Kwon, O.C.; Ghang, B.; Lim, D.-H.; Kim, D.H.; Hong, S.; Lee, C.-K.; Yoo, B.; Kim, Y.-G. Immunoglobulin Binding Protein 1 as a Potential Urine Biomarker in Patients with Lupus Nephritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102606
Lee E-J, Kwon OC, Ghang B, Lim D-H, Kim DH, Hong S, Lee C-K, Yoo B, Kim Y-G. Immunoglobulin Binding Protein 1 as a Potential Urine Biomarker in Patients with Lupus Nephritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102606
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Eun-Ju, Oh Chan Kwon, Byeongzu Ghang, Doo-Ho Lim, Do Hoon Kim, Seokchan Hong, Chang-Keun Lee, Bin Yoo, and Yong-Gil Kim. 2019. "Immunoglobulin Binding Protein 1 as a Potential Urine Biomarker in Patients with Lupus Nephritis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102606
APA StyleLee, E.-J., Kwon, O. C., Ghang, B., Lim, D.-H., Kim, D. H., Hong, S., Lee, C.-K., Yoo, B., & Kim, Y.-G. (2019). Immunoglobulin Binding Protein 1 as a Potential Urine Biomarker in Patients with Lupus Nephritis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2606. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102606






