Recombinant Leucine-Rich Repeat Flightless-Interacting Protein-1 Improves Healing of Acute Wounds through Its Effects on Proliferation Inflammation and Collagen Deposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
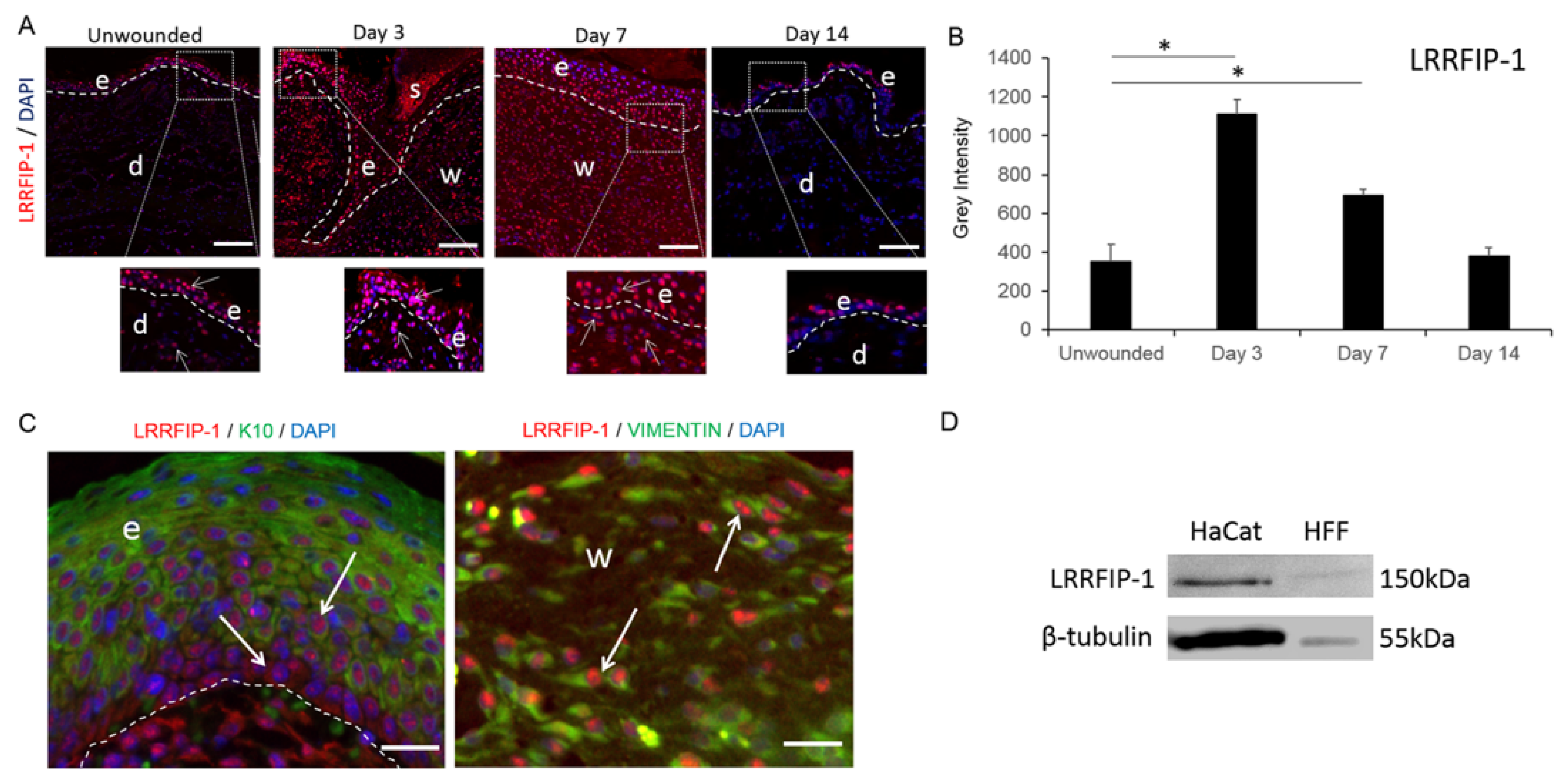
2.1. LRRFIP-1 Is Upregulated in Response to Wounding
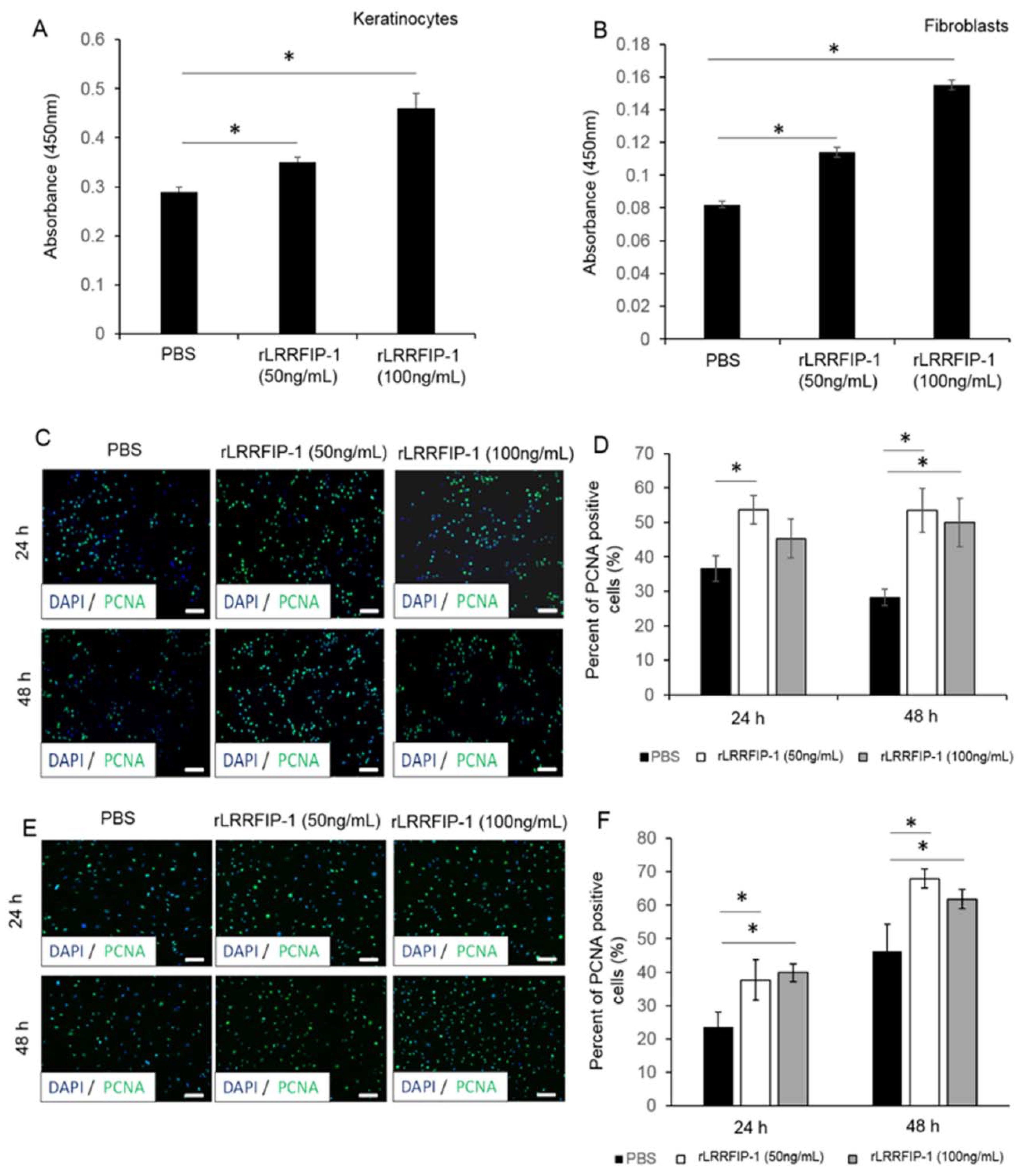
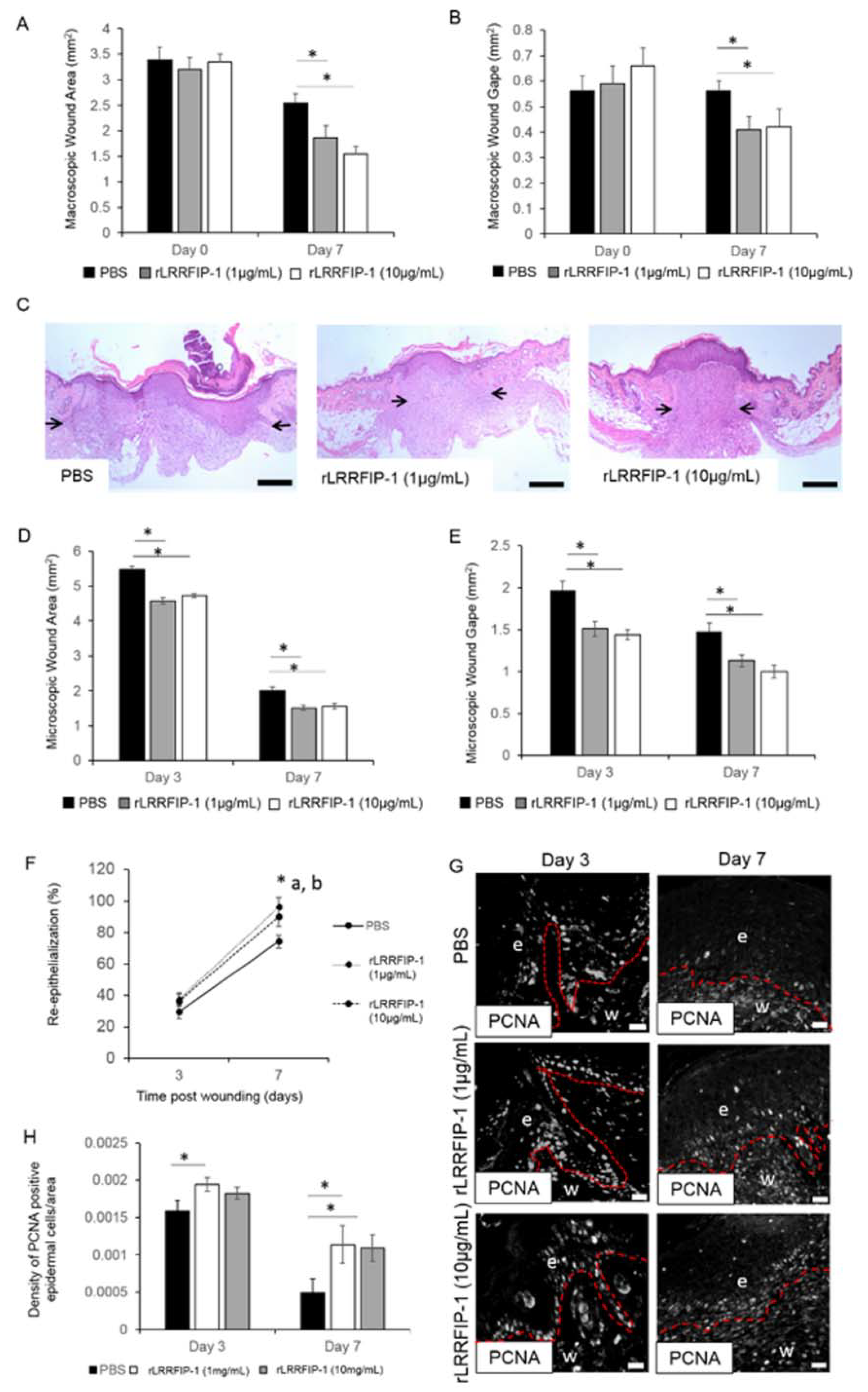
2.2. rLRRFIP-1 Increases Cell Proliferation and Improves Wound Healing
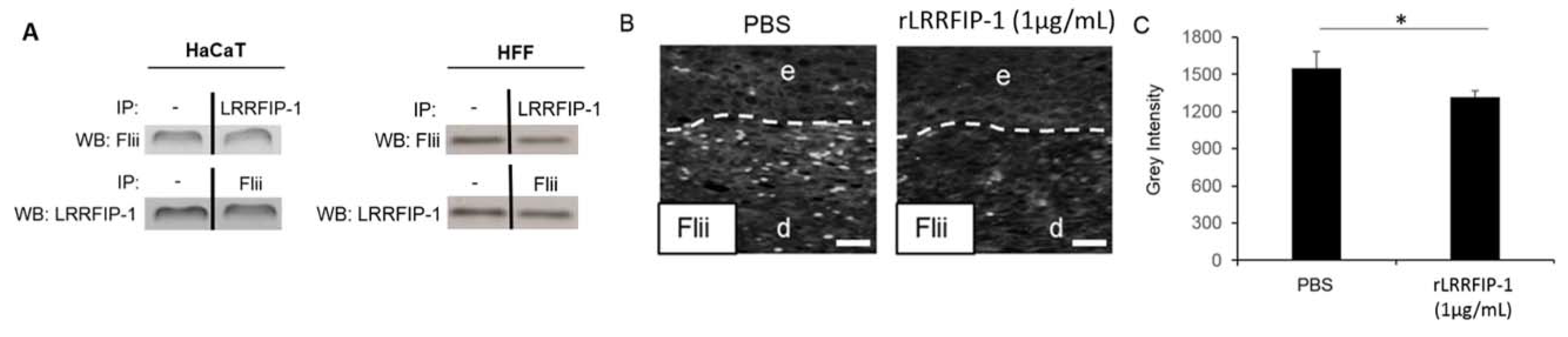
2.3. LRRFIP-1 Directly Associates with Flii Reducing Its Activity in Wounds In Vivo
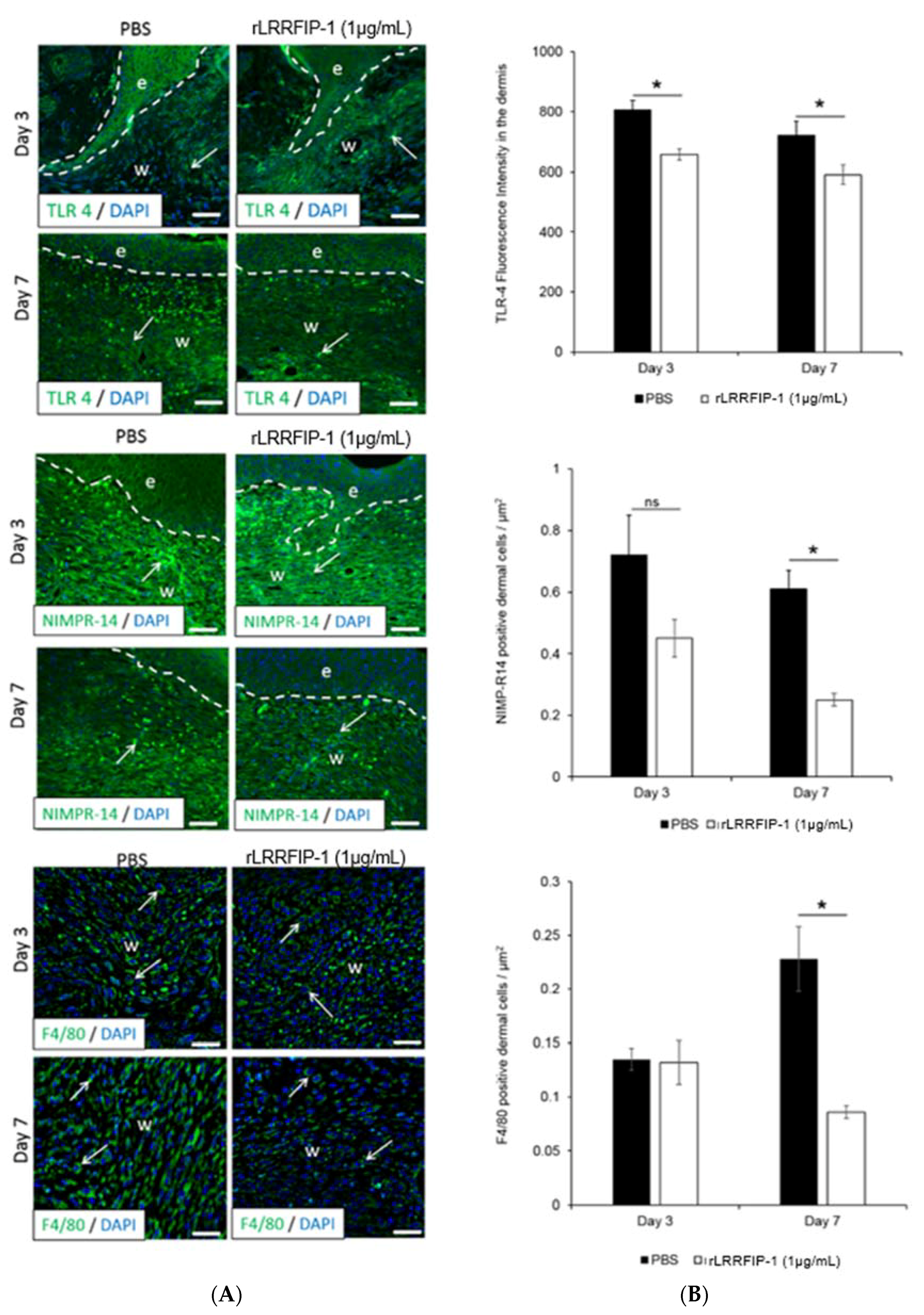
2.4. Inflammation Is Decreased in rLRRFIP-1-Treated Wounds
2.5. Treatment of Acute Wounds with rLRRFIP-1 Affects TGF-β Signalling and Collagen Deposition in Wounds In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Studies
4.2. Murine Surgery Techniques, Histology, and Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
4.4. Coimmunoprecipitation
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| rLRRFIP-1 | Recombinant Leucine-Rich Repeat Flightless-Interacting Protein-1 |
| Flii | Flightless I |
| PCNA | Proliferating Cell Nuclear Antigen |
| NIMP-R14 | Neutrophil Marker Antibody |
| F4/80 | Macrophage Marker Antibody |
References
- Wang, T.; Chuang, T.H.; Ronni, T.; Gu, S.; Du, Y.C.; Cai, H.; Sun, H.Q.; Yin, H.L.; Chen, X. Flightless I homolog negatively modulates the tlr pathway. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 1355–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowin, A.J.; Adams, D.H.; Strudwick, X.L.; Chan, H.; Hooper, J.A.; Sander, G.R.; Rayner, T.E.; Matthaei, K.I.; Powell, B.C.; Campbell, H.D. Flightless I deficiency enhances wound repair by increasing cell migration and proliferation. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 572–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowin, A.J.; Lei, N.; Franken, L.; Ruzehaji, N.; Offenhauser, C.; Kopecki, Z.; Murray, R.Z. Lysosomal secretion of flightless I upon injury has the potential to alter inflammation. Commun. Integr. Biol. 2012, 5, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H.; Stallcup, M.R. Interplay of fli-i and flap1 for regulation of beta-catenin dependent transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 5052–5059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbe, P.; Faure, E.; Lecointe, S.; Le Scouarnec, S.; Kyndt, F.; Marrec, M.; Le Tourneau, T.; Offmann, B.; Duplaa, C.; Zaffran, S.; et al. The alternatively spliced lrrfip1 isoform-1 is a key regulator of the wnt/beta-catenin transcription pathway. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1864, 1142–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.L.; Gu, L.J.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.Y.; Sun, B.S.; Li, Z.; Sung, C.K. Effect of wnt signaling pathway on wound healing. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 378, 149–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douchi, D.; Ohtsuka, H.; Ariake, K.; Masuda, K.; Kawasaki, S.; Kawaguchi, K.; Fukase, K.; Oikawa, M.; Motoi, F.; Naitoh, T.; et al. Silencing of lrrfip1 reverses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition via inhibition of the wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Lett. 2015, 365, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.P.; Cao, N.X.; Jiang, R.T.; He, S.J.; Huang, T.M.; Wu, B.; Chen, D.F.; Ma, P.; Chen, L.; Zhou, S.F.; et al. Knockdown of gcf2/lrrfip1 by rnai causes cell growth inhibition and increased apoptosis in human hepatoma hepg2 cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 2753–2758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; An, H.; Liu, X.; Wen, M.; Zheng, Y.; Rui, Y.; Cao, X. The cytosolic nucleic acid sensor lrrfip1 mediates the production of type i interferon via a beta-catenin-dependent pathway. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stout, A.J.; Gresser, I.; Thompson, W.D. Inhibition of wound healing in mice by local interferon alpha/beta injection. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 1993, 74, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dai, P.; Jeong, S.Y.; Yu, Y.; Leng, T.; Wu, W.; Xie, L.; Chen, X. Modulation of tlr signaling by multiple myd88-interacting partners including leucine-rich repeat fli-i-interacting proteins. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 3450–3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suriano, A.R.; Sanford, A.N.; Kim, N.; Oh, M.; Kennedy, S.; Henderson, M.J.; Dietzmann, K.; Sullivan, K.E. Gcf2/lrrfip1 represses tumor necrosis factor alpha expression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 9073–9081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Song, L.; Fitzgerald, M.; Maurer, K.; Bagashev, A.; Sullivan, K.E. Noncoding rnas and lrrfip1 regulate tnf expression. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 3057–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashcroft, G.S.; Jeong, M.J.; Ashworth, J.J.; Hardman, M.; Jin, W.; Moutsopoulos, N.; Wild, T.; McCartney-Francis, N.; Sim, D.; McGrady, G.; et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) is a therapeutic target for impaired cutaneous wound healing. Wound Repair Regen. 2012, 20, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, T.; Funato, Y.; Terabayashi, T.; Morinaka, A.; Sakamoto, R.; Ichise, H.; Fukuda, H.; Yoshida, N.; Miki, H. Nucleoredoxin negatively regulates toll-like receptor 4 signaling via recruitment of flightless-i to myeloid differentiation primary response gene(88). J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18586–18593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, H.T.; Yang, G.N.; Sidhu, S.; Ibbetson, J.; Kopecki, Z.; Cowin, A.J. Reducing flightless I expression decreases severity of psoriasis in an imiquimod-induced murine model of psoriasiform dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, J.E.; Kopecki, Z.; Adams, D.H.; Cowin, A.J. Flii neutralizing antibodies improve wound healing in porcine preclinical studies. Wound Repair Regen. 2012, 20, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzehaji, N.; Kopecki, Z.; Melville, E.; Appleby, S.L.; Bonder, C.S.; Arkell, R.M.; Fitridge, R.; Cowin, A.J. Attenuation of flightless I improves wound healing and enhances angiogenesis in a murine model of type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruzehaji, N.; Mills, S.J.; Melville, E.; Arkell, R.; Fitridge, R.; Cowin, A.J. The influence of flightless I on toll-like-receptor-mediated inflammation in a murine model of diabetic wound healing. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 389792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecki, Z.; Luchetti, M.M.; Adams, D.H.; Strudwick, X.; Mantamadiotis, T.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Gabrielli, A.; Ramsay, R.G.; Cowin, A.J. Collagen loss and impaired wound healing is associated with c-myb deficiency. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecki, Z.; O’Neill, G.M.; Arkell, R.; Cowin, A.J. Regulation of focal adhesions by flightless I involves inhibition of paxillin phosphorylation via a rac1-dependent pathway. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecki, Z.; Arkell, R.; Powell, B.C.; Cowin, A.J. Flightless i regulates hemidesmosome formation and integrin-mediated cellular adhesion and migration during wound repair. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2009, 129, 2031–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kopecki, Z.; Stevens, N.E.; Yang, G.N.; Melville, E.; Cowin, A.J. Recombinant Leucine-Rich Repeat Flightless-Interacting Protein-1 Improves Healing of Acute Wounds through Its Effects on Proliferation Inflammation and Collagen Deposition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072014
Kopecki Z, Stevens NE, Yang GN, Melville E, Cowin AJ. Recombinant Leucine-Rich Repeat Flightless-Interacting Protein-1 Improves Healing of Acute Wounds through Its Effects on Proliferation Inflammation and Collagen Deposition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072014
Chicago/Turabian StyleKopecki, Zlatko, Natalie E. Stevens, Gink N. Yang, Elizabeth Melville, and Allison J. Cowin. 2018. "Recombinant Leucine-Rich Repeat Flightless-Interacting Protein-1 Improves Healing of Acute Wounds through Its Effects on Proliferation Inflammation and Collagen Deposition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072014
APA StyleKopecki, Z., Stevens, N. E., Yang, G. N., Melville, E., & Cowin, A. J. (2018). Recombinant Leucine-Rich Repeat Flightless-Interacting Protein-1 Improves Healing of Acute Wounds through Its Effects on Proliferation Inflammation and Collagen Deposition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 2014. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072014






