Isolation and Characterization of a Green-Tissue Promoter from Common Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression Pattern of OrGSE in Common Wild Rice
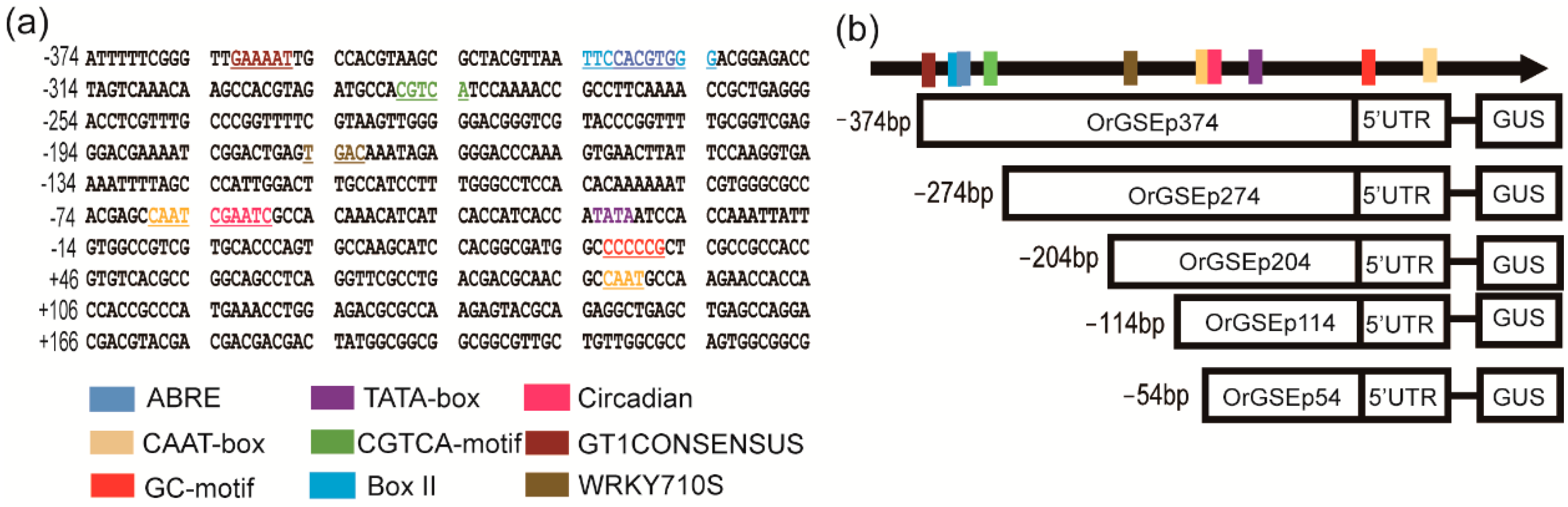
2.2. Cloning and Sequence Analysis of the OrGSE Promoter (OrGSEp-374)
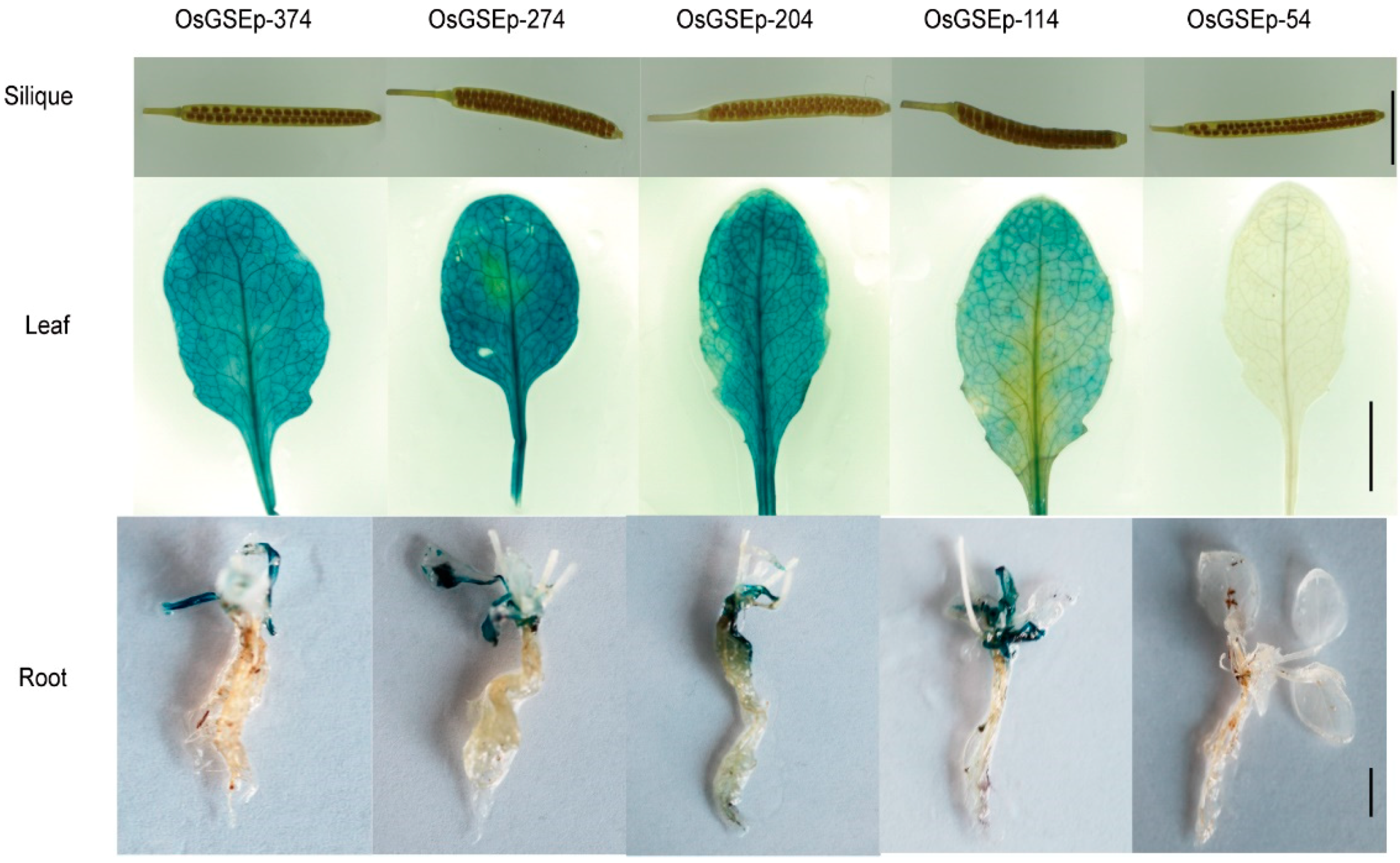
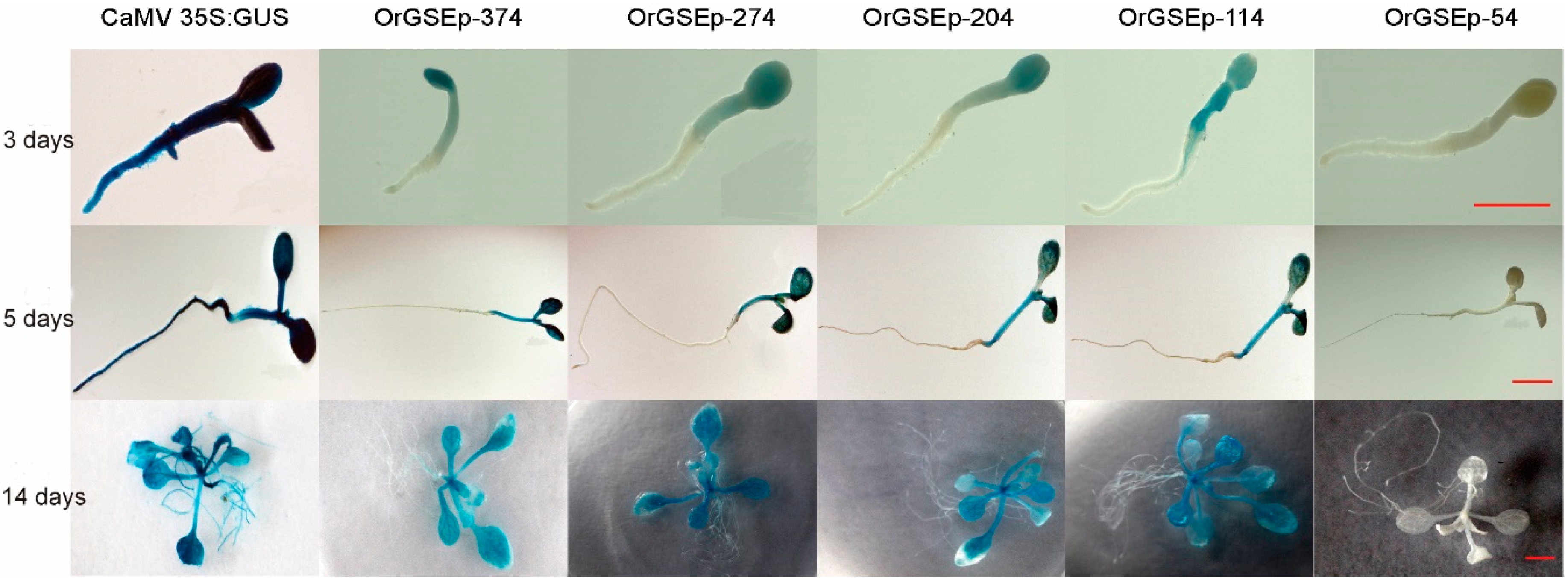
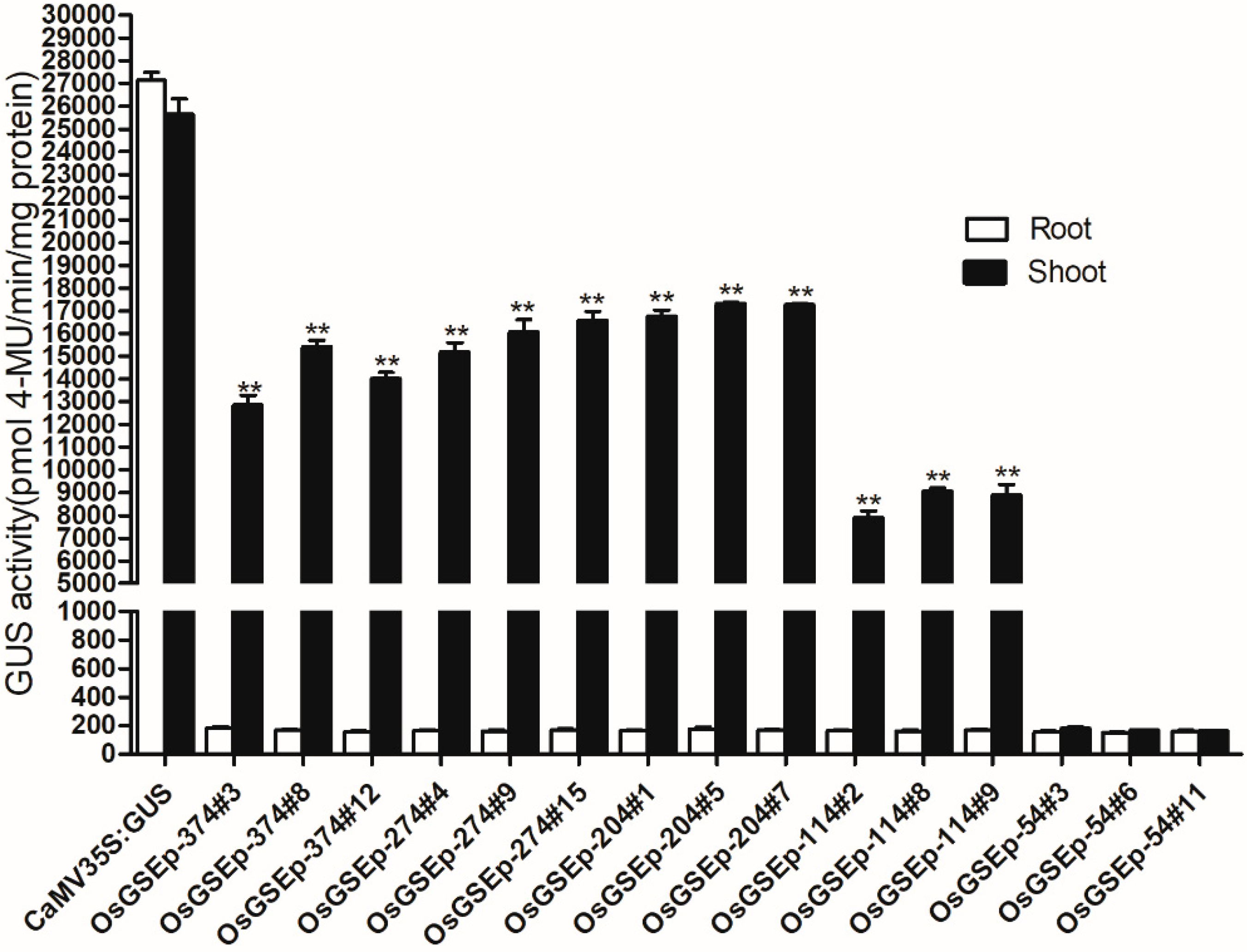
2.3. Spatiotemporal Expression Patterns of OrGSEp-374 and 5’-Deletion Fragments in Arabidopsis
2.4. OrGSEp-374 Confers Light-Responsive Expression
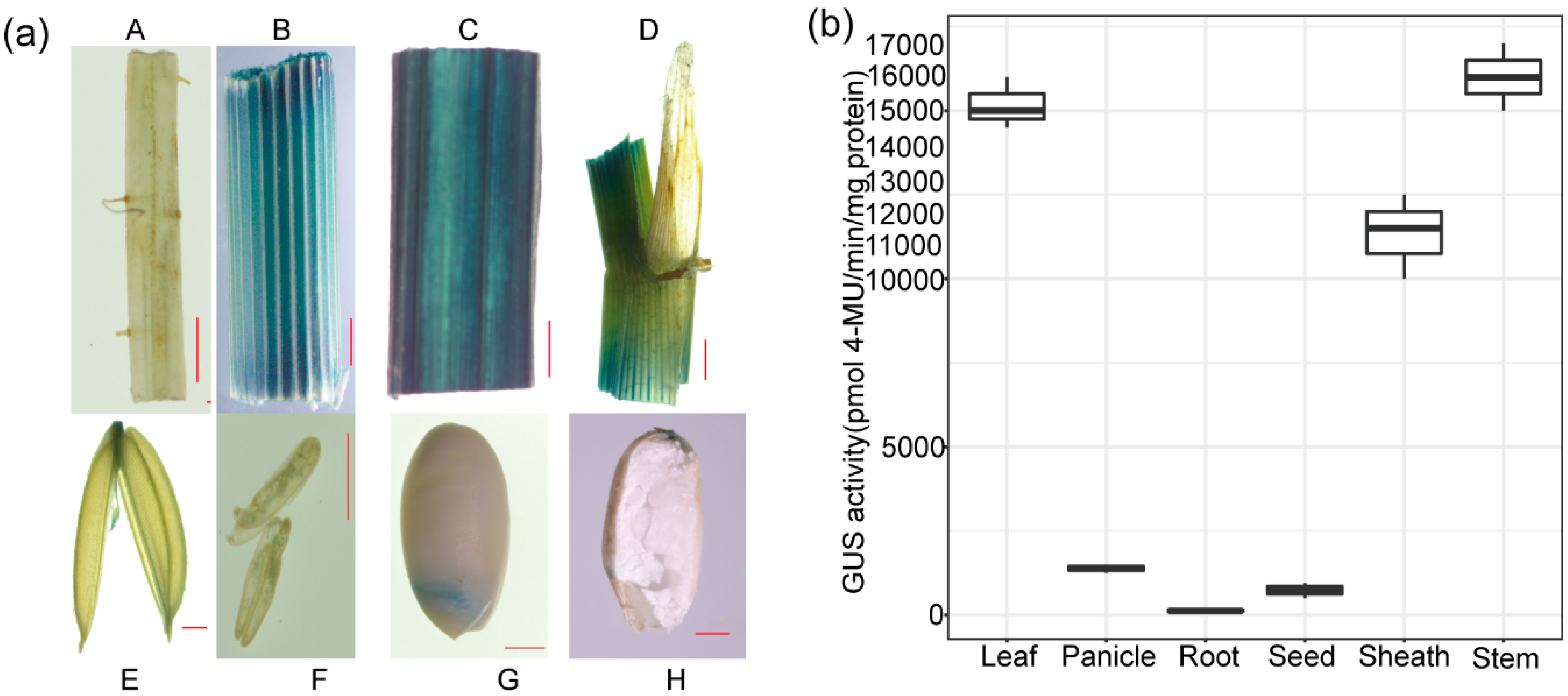
2.5. The Expression Pattern of OrGSEp-374 in Rice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Growth Conditions
4.2. Screening of Green Tissue-Specific Genes and Expression Analysis
4.3. Cloning of the OrGSE Promoter and Sequence Analysis
4.4. PCR Amplification of 5’-Deletion Fragments of the OrGSE Promoter
4.5. Detection of the Expression Pattern of the OrGSEp Promoter and 5’-Deletion Fragments in Different Organs
4.6. Inducible Activity Analysis of the OrGSEp Promoter and 5’-Deletion Fragments
4.7. GUS Histochemical and Fluorometric Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Q.C.; Kang, J.M.; Zhang, T.J.; Gruber, M.Y.; Fang, F. Cloning and function analysis of an alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) zinc finger protein promoter MsZPP. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 8559–8569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, G.L.; Gou, W.; Han, X.L.; Qin, C.; Zhang, L.X.; Abomohra, A.E.; Ashraf, M. Cloning and functional analysis of phosphoethanolamine methyltransferase promoter from maize (Zea mays L.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pih, K.T.; Yoo, J.; Fosket, D.E.; Han, I.S. A comparison of the activity of three cauliflower mosaic virus 35s promoters in rice seedlings and tobacco (by-2) protoplasts by analysis of gus reporter gene transient expression. Plant. Sci. 1996, 114, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McElroy, D.; Blowers, A.D.; Jenes, B.; Wu, R. Construction of expression vectors based on the rice actin 1 (act1) 5' region for use in monocot transformation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1991, 231, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christensen, A.H.; Quail, P.H. Ubiquitin promoter-based vectors for high-level expression of selectable and/or screenable marker genes in monocotyledonous plants. Transgenic Res. 1996, 5, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eva, C.; Teglas, F.; Zelenyanszki, H.; Tamas, C.; Juhasz, A.; Meszaros, K.; Tamas, L. Cold inducible promoter driven cre-lox system proved to be highly efficient for marker gene excision in transgenic barley. J. Biotechnol. 2018, 265, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, D.; Song, Y.; Li, W.M.; Pei, X.W.; Wang, Z.X.; Jia, S.R.; Zhang, Y.Q. Isolation and characterization of the organ-specific and light-inducible promoter of the gene encoding rubisco activase in potato (Solanum tuberosum). Genet. Mol. Res. 2011, 10, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, B.; Graciet, E.; Wellmer, F. Inducible promoter systems for gene perturbation experiments in Arabidopsis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1629, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Ding, X.; Chen, J.; Shen, Y.; Kong, L.; Li, N.; Chu, Z. Functional analysis of the GRMZM2g174449 promoter to identify rhizoctonia solani-inducible cis-elements in maize. BMC Plant. Biol. 2017, 17, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, S.I.; Lee, B.H. Generation of a stress-inducible luminescent Arabidopsis and its use in genetic screening for stress-responsive gene deregulation mutants. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1631, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Qin, R.; Xu, R.; Li, H.; Yang, Y.; Li, L.; Wei, P.; Yang, J. Isolation and identification of five cold-inducible promoters from Oryza sativa. Planta 2017, 247, 99–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jing, R.; Mao, X. Functional characterization of Tasnrk2.8 promoter in response to abiotic stresses by deletion analysis in transgenic Arabidopsis. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakrana, A.; Kumar, A.; Satheesh, V.; Abdin, M.Z.; Subramaniam, K.; Bhattacharya, R.C.; Srinivasan, R.; Sirohi, A.; Jain, P.K. Identification, validation and utilization of novel nematode-responsive root-specific promoters in Arabidopsis for inducing host-delivered RNAi mediated root-knot nematode resistance. Front. Plant. Sci. 2017, 8, 2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanjareddy, K.; Arthikala, M.K.; Aguirre, A.L.; Gomez, B.M.; Lara, M. Plant promoter analysis: Identification and characterization of root nodule specific promoter in the common bean. J. Vis. Exp. 2017, 23, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavez-Barcenas, A.T.; Valdez-Alarcon, J.J.; Martinez-Trujillo, M.; Chen, L.; Xoconostle-Cazares, B.; Lucas, W.J.; Herrera-Estrella, L. Tissue-specific and developmental pattern of expression of the rice SPS1 gene. Plant. Physiol. 2000, 124, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, H.J.; Jung, Y.J.; Kang, K.K.; Tyagi, W.; Kovach, M.; Sweeney, M.; McCouch, S.; Cho, Y.G. Functional properties of an alternative, tissue-specific promoter for rice nadph-dependent dihydroflavonol reductase. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panguluri, S.K.; Sridhar, J.; Jagadish, B.; Sharma, P.C.; Kumar, P.A. Isolation and characterization of a green tissue-specific promoter from pigeonpea [Cajanus cajan (L.) millsp.]. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 43, 369–372. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Liu, W.; Ye, R.; Mazarei, M.; Huang, D.; Zhang, X.; Stewart, C.N., Jr. A profilin gene promoter from switchgrass (Panicum virgatum L.) directs strong and specific transgene expression to vascular bundles in rice. Plant. Cell. Rep. 2018, 37, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, M.A.; O’Leary, S.J.; Wu, S.; Chabot, D.; Gleddie, S.; Laroche, A.; Eudes, F.; Robert, L.S. Investigating triticeae anther gene promoter activity in transgenic brachypodium distachyon. Planta 2017, 245, 385–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, J.; Xu, R.; Qin, R.; Song, F.; Li, L.; Wei, P.; Yang, J. Isolation of five rice non-endosperm tissue-expressed promoters and evaluation of their activities in transgenic rice. Plant. Biotechnol. J. 2017, 16, 1138–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Fowler, T.J.; Tierney, M.L. Deletion analysis and localization of SbPRP1, a soybean cell wall protein gene, in roots of transgenic tobacco and cowpea. Plant. Mol. Biol. 1993, 21, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Jiang, B.; Wu, C.; Sun, S.; Hou, W.; Han, T. GmPRP2 promoter drives root-preferential expression in transgenic Arabidopsis and soybean hairy roots. BMC Plant. Biol. 2014, 14, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Fan, M.; Wang, G.; Zhang, C.; Shi, L.; Wei, Z.; Ma, W.; Chang, J.; Huang, S.; Lin, F. Isolation and characterization of a novel pollen-specific promoter in maize (Zea mays L.). Genome 2017, 60, 485–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; El-Mezawy, A.; Shah, S. A seed coat outer integument-specific promoter for Brassica napus. Plant. Cell. Rep. 2011, 30, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, A.; Khan, A.; Mishra, D.R.; Bhuyan, K.; Sahoo, B.; Maiti, I.B.; Dey, N. WRKY71 and TGA1A physically interact and synergistically regulate the activity of a novel promoter isolated from petunia vein-clearing virus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1861, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Sun, L.; Li, L.; Jin, S.; Zhang, X. Transgenic Bt cotton driven by the green tissue-specific promoter shows strong toxicity to lepidopteran pests and lower Bt toxin accumulation in seeds. Sci. China Life Sci. 2016, 59, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manikandan, R.; Balakrishnan, N.; Sudhakar, D.; Udayasuriyan, V. Development of leaffolder resistant transgenic rice expressing cry2ax1 gene driven by green tissue-specific rbcS promoter. World J. Microb. Biot. 2016, 32, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menguer, P.K.; Sperotto, R.A.; Ricachenevsky, F.K. A walk on the wild side: Oryza species as source for rice abiotic stress tolerance. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40, 238–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, D.; Yu, L.; Chen, D.; Li, L.; Zhu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, D.; Chen, C. Multiple cold resistance loci confer the high cold tolerance adaptation of dongxiang wild rice (Oryza rufipogon) to its high-latitude habitat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Long, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, W.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Pei, X. De novo transcriptome assembly of common wild rice (Oryza rufipogon griff.) and discovery of drought-response genes in root tissue based on transcriptomic data. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Civan, P.; Svec, M. Genome-wide analysis of rice (Oryza sativa L. Subsp. Japonica) tata box and y patch promoter elements. Genome 2009, 52, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, T.R.; Park, S.C.; Kwon, H.B.; Peng, H.P.; Shih, M.C. Characterization of cis-acting elements in light regulation of the nuclear gene encoding a subunit of chloroplast isozymes of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1994, 14, 2525–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.Q.; Lu, X.; Zhao, F.Y.; Li, Q.T.; Niu, S.L.; Wei, W.; Zhang, W.K.; Ma, B.; Chen, S.Y.; Zhang, J.S. Soybean GmDREBl increases lipid content in seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Wang, R.X.; Qian, Q.; Yan, M.X.; Meng, X.B.; Fu, Z.M.; Yan, C.Y.; Jiang, B.; Su, Z.; Li, J.Y.; et al. DWARF27, an Iron-Containing Protein Required for the Biosynthesis of Strigolactones, Regulates Rice Tiller Bud Outgrowth. Plant Cell 2009, 21, 1512–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, M.T.; Brewer, P.B.; Bussell, J.D.; SmitSh, S.M.; Beveridge, C.A. The Arabidopsis ortholog of rice dwarf27 acts upstream of max1 in the control of plant development by strigolactones. Plant. Physiol. 2012, 159, 1073–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, R.; Zhou, F.; Lin, Y. Two novel positive cis-regulatory elements involved in green tissue-specific promoter activity in rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp.). Plant. Cell. Rep. 2012, 31, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eberhard, S.; Finazzi, G.; Wollman, F.A. The dynamics of photosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2008, 42, 463–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, N.; Tamoi, M.; Shigeoka, S. The sweet potato RbcS gene (IbRbcS1) promoter confers high-level and green tissue-specific expression of the gus reporter gene in transgenic Arabidopsis. Gene 2015, 567, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karmakar, S.; Molla, K.A.; Chanda, P.K.; Sarkar, S.N.; Datta, S.K.; Datta, K. Green tissue-specific co-expression of chitinase and oxalate oxidase 4 genes in rice for enhanced resistance against sheath blight. Planta 2016, 243, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghasimi Hagh, Z.; Rahnama, H.; Panahandeh, J.; Baghban Kohneh Rouz, B.; Arab Jafari, K.M.; Mahna, N. Green-tissue-specific, c(4)-pepc-promoter-driven expression of Cry1ab makes transgenic potato plants resistant to tuber moth (phthorimaea operculella, zeller). Plant. Cell. Rep. 2009, 28, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lescot, M.; Dehais, P.; Thijs, G.; Marchal, K.; Moreau, Y.; Van de Peer, Y.; Rouze, P.; Rombauts, S. Plantcare, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clough, S.J.; Bent, A.F. Floral dip: A simplified method for agrobacterium-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant. J. 1998, 16, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Zhu, M.; Ye, R.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, F.; Chen, H.; Lin, Y. Novel green tissue-specific synthetic promoters and cis-regulatory elements in rice. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, M.; Long, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, G.; Huang, K.; Zhang, T.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Pei, X. Isolation and Characterization of a Green-Tissue Promoter from Common Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072009
Xue M, Long Y, Zhao Z, Huang G, Huang K, Zhang T, Jiang Y, Yuan Q, Pei X. Isolation and Characterization of a Green-Tissue Promoter from Common Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072009
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Mande, Yan Long, Zhiqiang Zhao, Gege Huang, Ke Huang, Tianbao Zhang, Ying Jiang, Qianhua Yuan, and Xinwu Pei. 2018. "Isolation and Characterization of a Green-Tissue Promoter from Common Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072009
APA StyleXue, M., Long, Y., Zhao, Z., Huang, G., Huang, K., Zhang, T., Jiang, Y., Yuan, Q., & Pei, X. (2018). Isolation and Characterization of a Green-Tissue Promoter from Common Wild Rice (Oryza rufipogon Griff.). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 2009. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072009




