Changes of Microrna Levels in Plasma of Patients with Rectal Cancer during Chemoradiotherapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
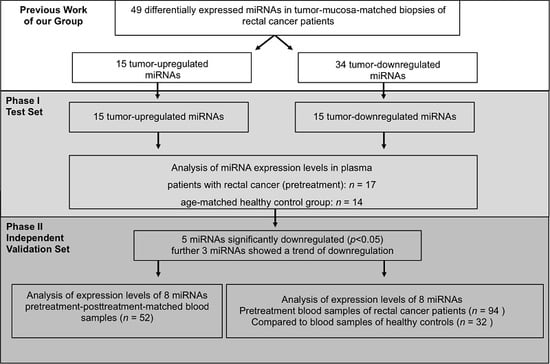
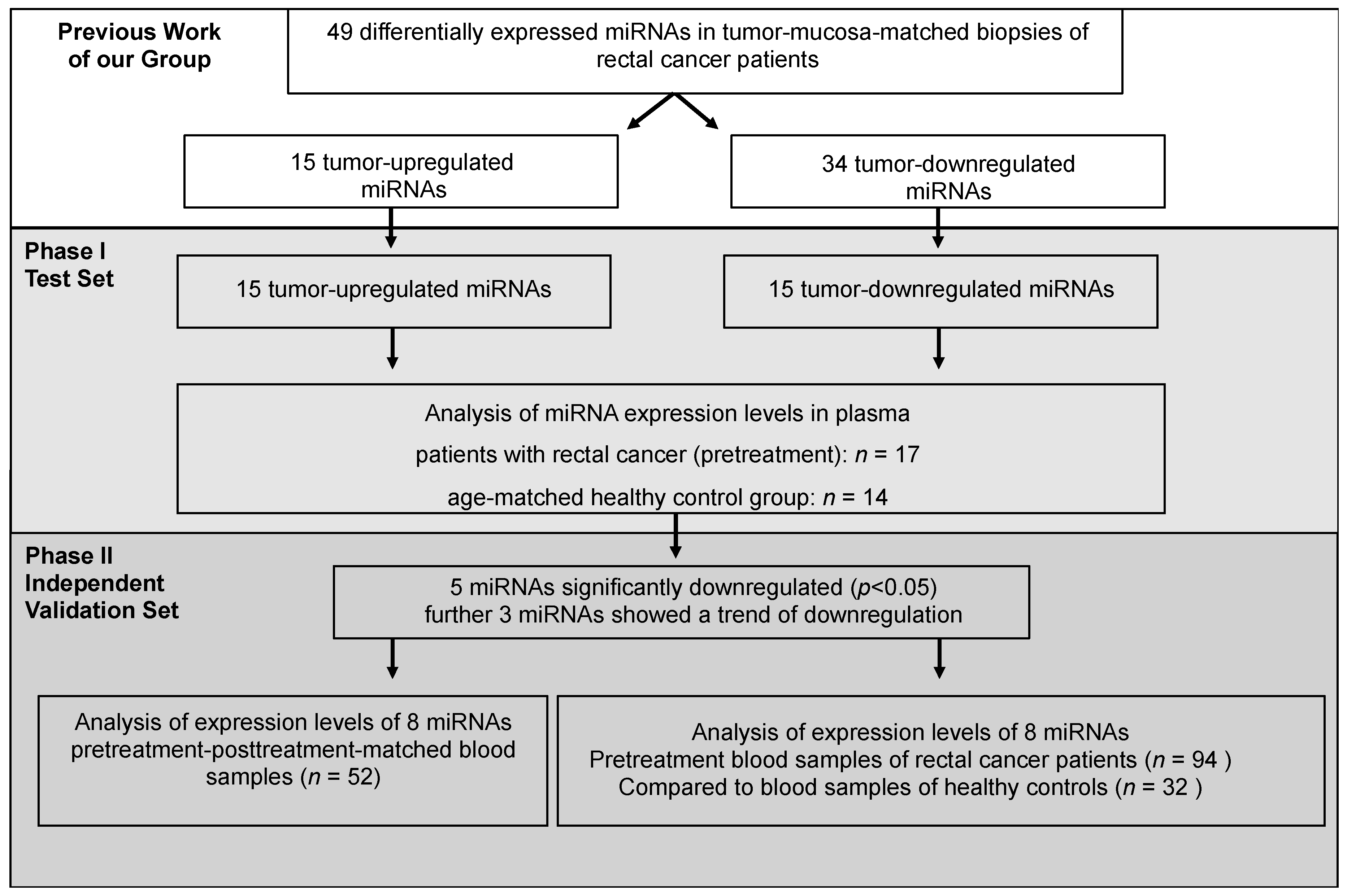
2.1. Initial Selection of Differentially Regulated miRNAs in Rectal Cancer Patients Compared to Controls—Phase I
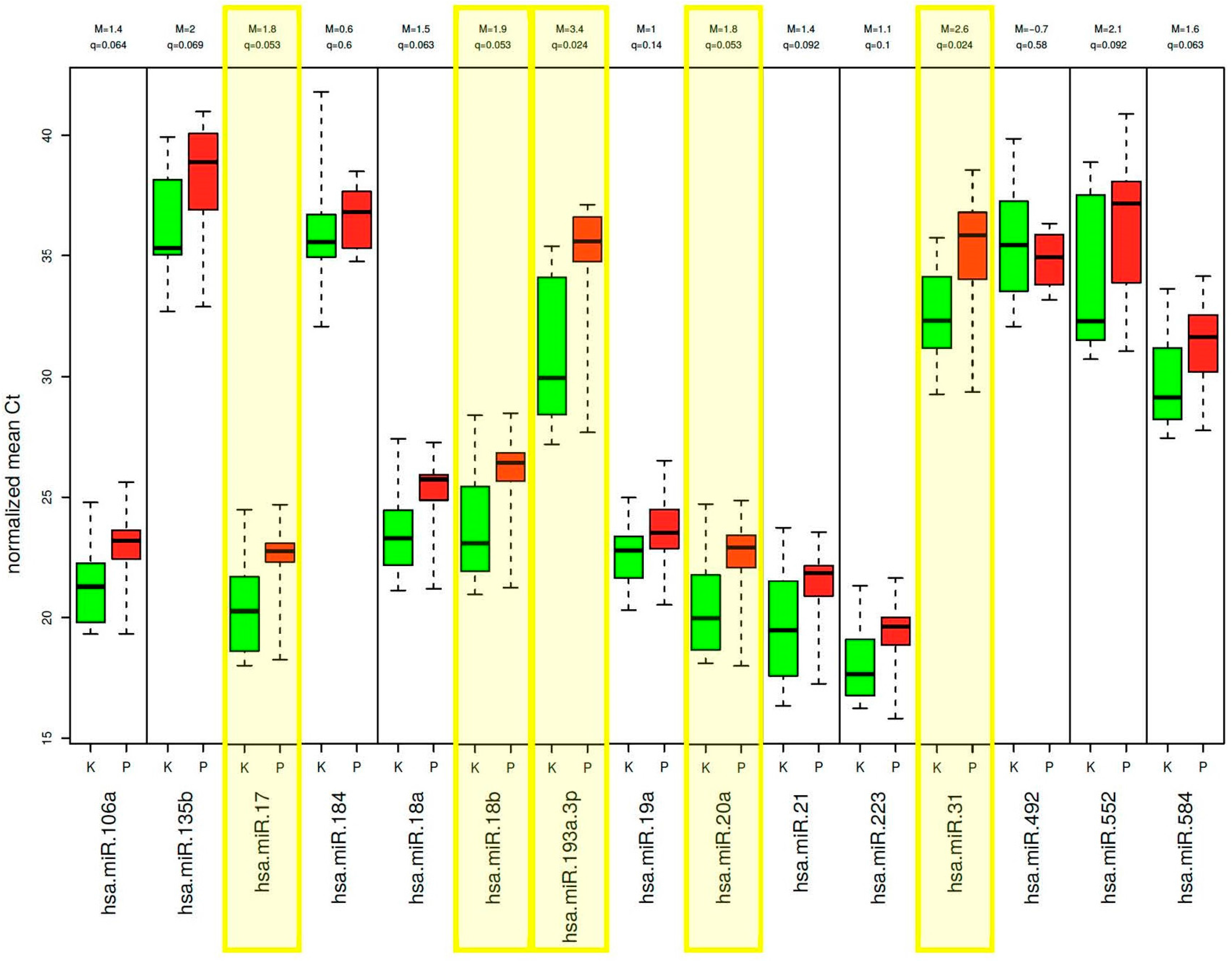
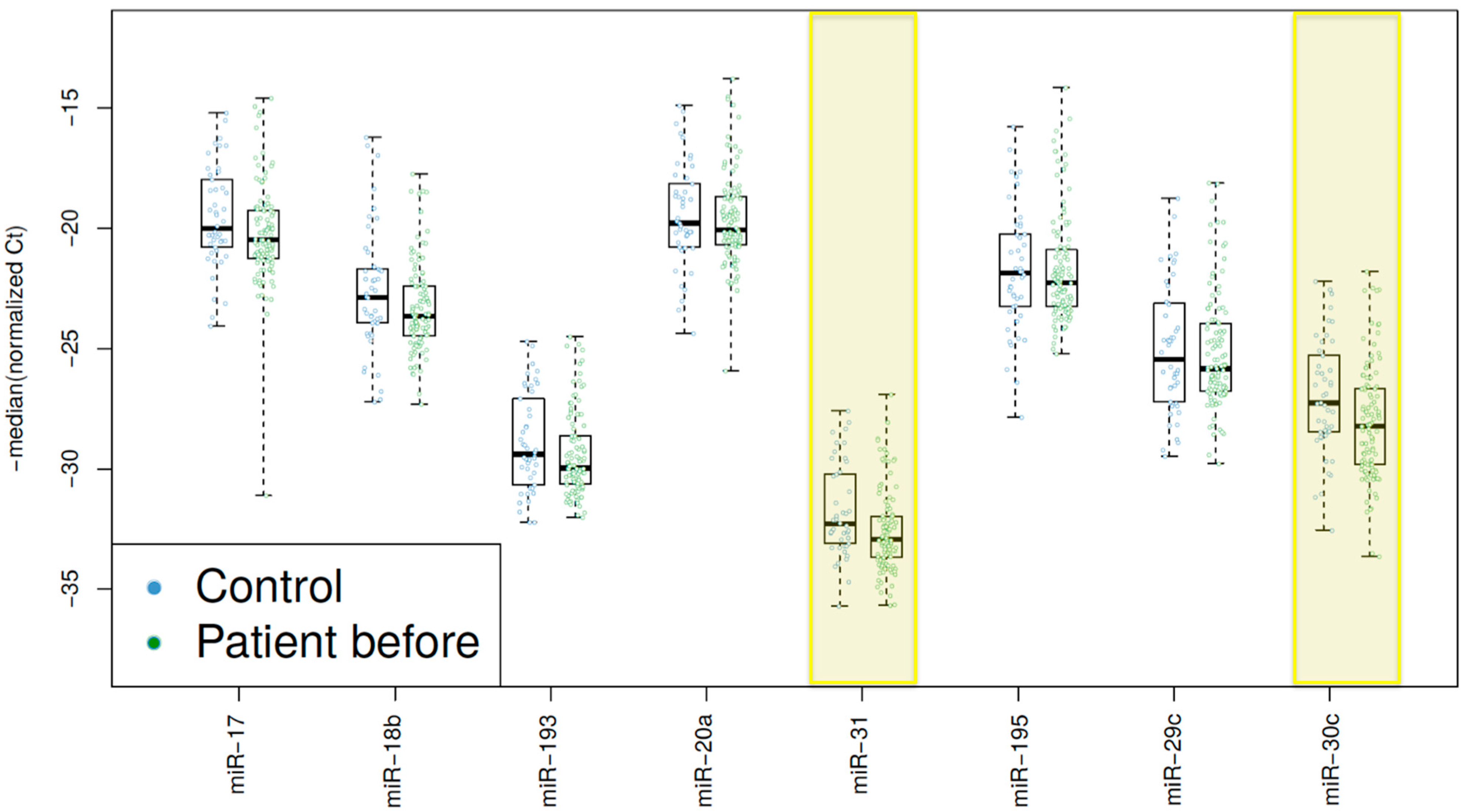
2.2. Validation of Differentially Expressed miRNAs—Phase I
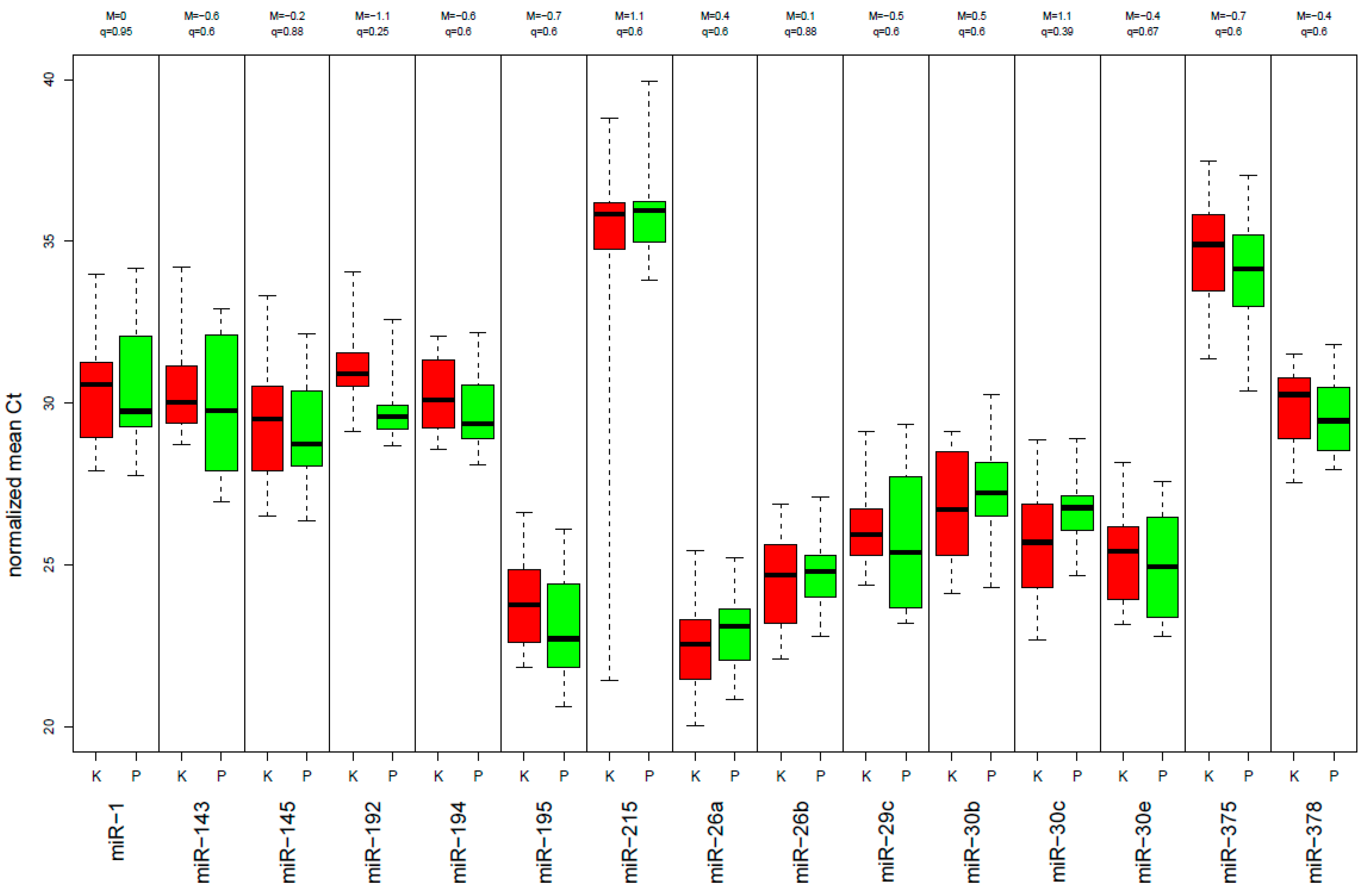
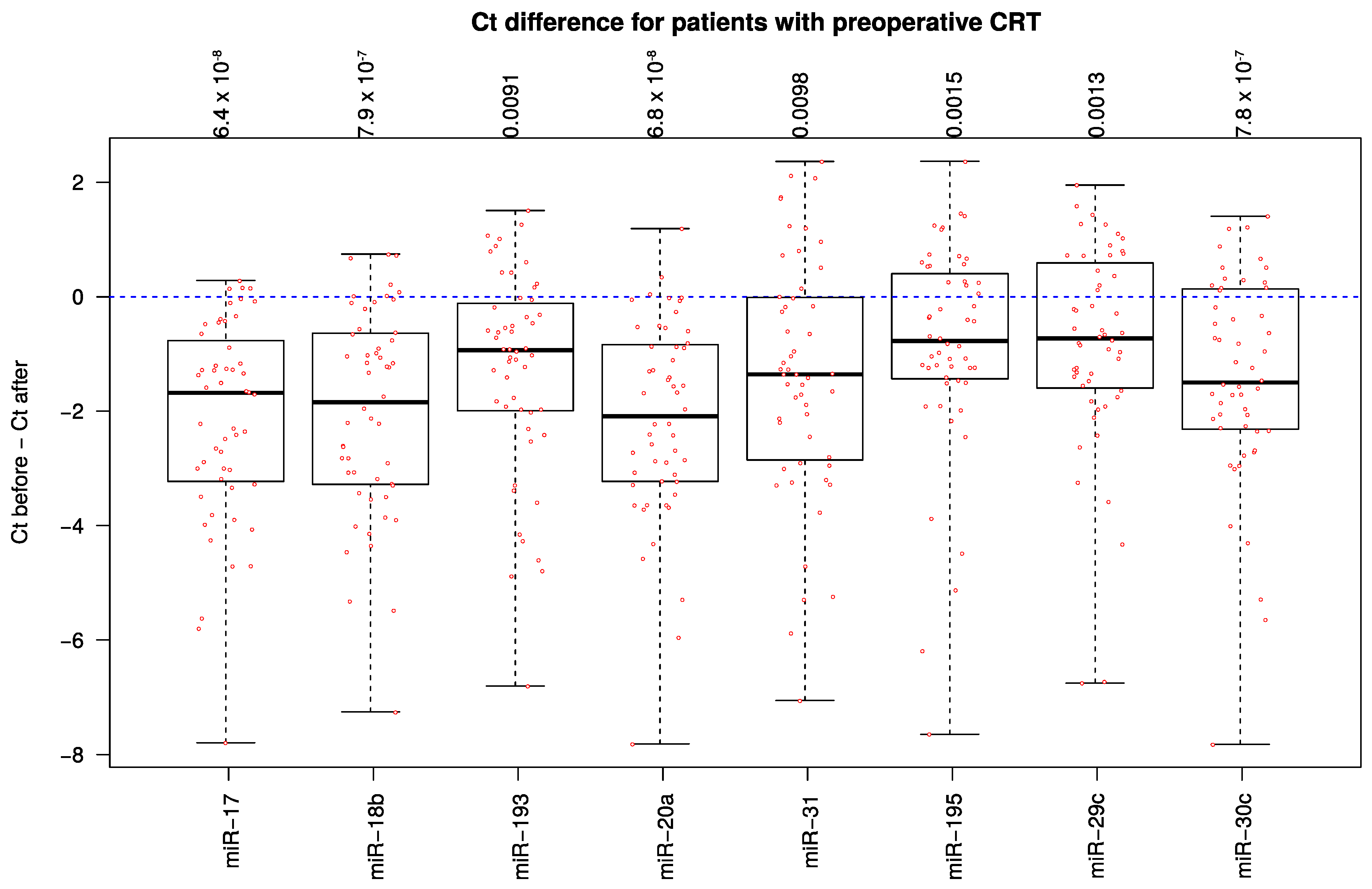
2.3. miRNA Expression-Level Changes during Multimodal Therapy
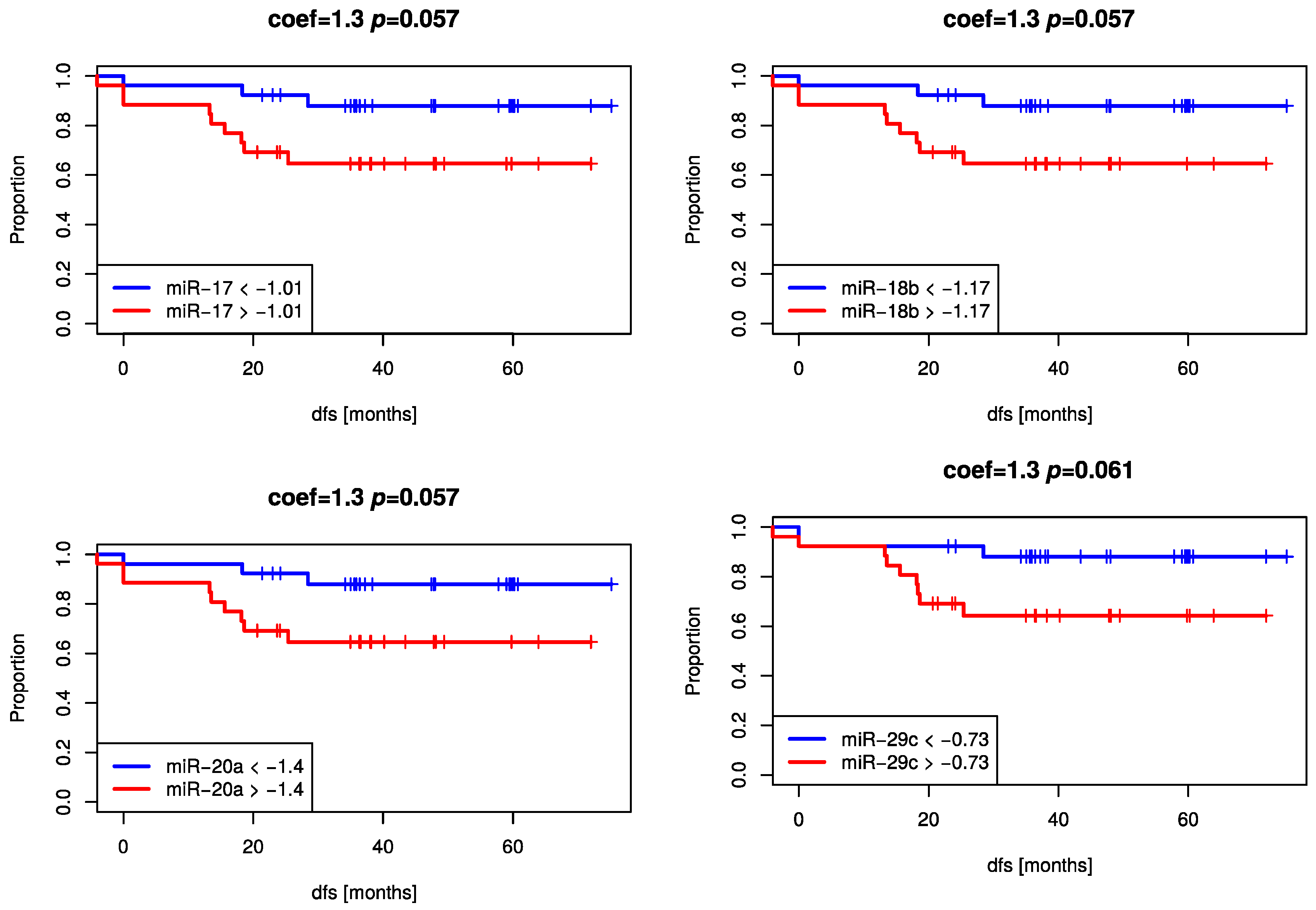
2.4. High Decrease of miRNA Expression Reveals A Trend for Better Prognosis
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients, Patient Treatment and Control Group
4.2. Study-Design
4.3. Plasma Preparation and Total RNA Isolation
4.4. Semi-Quantitative Real-Time PCR Analysis
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CEA | carcinoembryonic antigen |
| CT | chemotherapy |
| CRT | chemoradiotherapy |
| DFS | disease-free-survival |
| DNA | deoxyribonucleic acid |
| f | female |
| m | male |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| OS | overall-survival |
| pCR | pathologic complete response |
| PCR | polymerase chain reaction |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| TME | total mesorectal excision |
| TRG | tumor regression grade |
| ypN | post-chemoradiotherapy nodal status |
References
- Sauer, R.; Becker, H.; Hohenberger, W.; Rödel, C.; Wittekind, C.; Fietkau, R.; Martus, P.; Tschmelitsch, J.; Hager, E.; Hess, C.F.; et al. Preoperative versus postoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1731–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dworak, O.; Keilholz, L.; Hoffmann, A. Pathological features of rectal cancer after preoperative radiochemotherapy. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 1997, 12, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodel, C.; Martus, P.; Papadoupolos, T.; Füzesi, L.; Klimpfinger, M.; Fietkau, R.; Liersch, T.; Hohenberger, W.; Raab, R.; Sauer, R.; et al. Prognostic significance of tumor regression after preoperative chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 8688–8696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Overman, M.J.; Modak, J.; Kopetz, S.; Murthy, R.; Yao, J.C.; Hicks, M.E.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Tam, A.L. Use of research biopsies in clinical trials: Are risks and benefits adequately discussed? J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdhoff, M.; Schmidt, K.; Donehower, R.; Diaz, L.A., Jr. Analysis of circulating tumor DNA to confirm somatic KRAS mutations. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2009, 101, 1284–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, P.; König, A.; Schirmer, M.; Kitz, J.; Conradi, L.C.; Azizian, A.; Bernhardt, M.; Wolff, H.A.; Grade, M.; Ghadimi, M.; et al. Heterogeneity of KRAS Mutation Status in Rectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, P.; Nietert, M.; Gusky, L.; Kitz, J.; Conradi, L.C.; Müller-Dornieden, A.; Schüler, P.; Wolff, H.A.; Rüschoff, J.; Ströbel, P.; et al. Neoadjuvant Therapy in Rectal Cancer-Biobanking of Preoperative Tumor Biopsies. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siravegna, G.; Marsoni, S.; Siena, S.; Bardelli, A. Integrating liquid biopsies into the management of cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locker, G.Y.; Hamilton, S.; Harris, J.; Jessup, J.M.; Kemeny, N.; Macdonald, J.S.; Somerfield, M.R.; Hayes, D.F.; Bast, R.C., Jr. ASCO update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in gastrointestinal cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 5313–5327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldulaymi, B.; Christensen, I.J.; Soletormos, G.; Jess, P.; Nielsen, S.E.; Laurberg, S.; Brunner, N.; Nielsen, H.J. Chemoradiation-induced changes in serum CEA and plasma TIMP-1 in patients with locally advanced rectal cancer. Anticancer 2010, 30, 4755–4759. [Google Scholar]
- Restivo, A.; Zorcolo, L.; Cocco, I.M.; Manunza, R.; Margiani, C.; Marongiu, L.; Casula, G. Elevated CEA levels and low distance of the tumor from the anal verge are predictors of incomplete response to chemoradiation in patients with rectal cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2013, 20, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.S.; Lin, J.K.; Wang, L.W.; Liang, W.Y.; Lin, C.C.; Lan, Y.T.; Wang, H.S.; Yang, S.H.; Jiang, J.K.; Chen, W.S.; et al. Assessment of the value of carcinoembryonic antigen reduction ratio as a prognosis factor in rectal cancer. Am. J. Surg. 2014, 208, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotta, T.; Takifuji, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Matsuda, K.; Oku, Y.; Nasu, T.; Ieda, J.; Yamamoto, N.; Iwamoto, H.; Takei, Y.; et al. Impact of the post/preoperative serum CEA ratio on the survival of patients with rectal cancer. Surg. Today 2014, 44, 2106–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garland, M.L.; Vather, R.; Bunkley, N.; Pearse, M.; Bissett, I.P. Clinical tumour size and nodal status predict pathologic complete response following neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy for rectal cancer. Int. J. Colorectal. Dis. 2014, 29, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.J.; Chung, S.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Ryu, M.R. Prognostic significance of serum carcinoembryonic antigen normalization on survival in rectal cancer treated with preoperative chemoradiation. Cancer Res. Treat 2013, 45, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallin, U.; Rothenberger, D.; Lowry, A.; Luepker, R.; Mellgren, A. CEA: A predictor for pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant therapy for rectal cancer. Dis. Colon. Rectum 2013, 56, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalady, M.F.; de Campos-Lobato, L.F.; Stocchi, L.; Geisler, D.P.; Dietz, D.; Lavery, I.C.; Fazio, V.W. Predictive factors of pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemoradiation for rectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, A.; Jewell, D.A.; Liang, Y.; Ridzon, D.; Moore, J.H.; Chen, C.; Ambros, V.R.; Israel, M.A. Characterization of microRNA expression levels and their biological correlates in human cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2456–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarotto, E.; Secchiero, P.; Dasgupta, A.; Fortina, P.; Calin, G.A.; Hyslop, T. MicroRNAs as new players in the genomic galaxy and disease puzzles. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2008, 1, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaedcke, J.; Grade, M.; Camps, J.; Søkilde, R.; Kaczkowski, B.; Schetter, A.J.; Difilippantonio, M.J.; Harris, C.C.; Ghadimi, B.M.; Møller, S.; et al. The rectal cancer microRNAome - microRNA expression in rectal cancer and matched normal mucosa. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 4919–4930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salendo, J.; Spitzner, M.; Kramer, F.; Zhang, X.; Jo, P.; Wolff, H.A.; Kitz, J.; Kaulfuß, S.; Beißbarth, T.; Dobbelstein, M.; et al. Identification of a microRNA expression signature for chemoradiosensitivity of colorectal cancer cells, involving miRNAs-320a, -224, -132 and let7g. Radiother. Oncol. 2013, 108, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.H.; Yu, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, X.Y.; Wang, S.; Ding, Y.Q. Elevated microRNA-31 expression regulates colorectal cancer progression by repressing its target gene SATB2. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanutto, S.; Pizzamiglio, S.; Ghilotti, M.; Bertan, C.; Ravagnani, F.; Perrone, F.; Leo, E.; Pilotti, S.; Verderio, P.; Gariboldi, M.; et al. Circulating miR-378 in plasma: A reliable, haemolysis-independent biomarker for colorectal cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Li, M.; Wang, M.; Yan, D.; Feng, G.; An, G. The expression of microRNA-375 in plasma and tissue is matched in human colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulfken, L.M.; Moritz, R.; Ohlmann, C.; Holdenrieder, S.; Jung, V.; Becker, F.; Herrmann, E.; Walgenbach-Brünagel, G.; von Ruecker, A.; Müller, S.C.; et al. MicroRNAs in renal cell carcinoma: Diagnostic implications of serum miR-1233 levels. PLoS ONE 2011, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigati, L.; Yaddanapudi, S.C.; Iyengar, R.; Kim, D.J.; Hearn, S.A.; Danforth, D.; Hastings, M.L.; Duelli, D.M. Selective release of microRNA species from normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Huang, S.K.; Zhao, M.; Yang, M.; Zhong, J.L.; Gu, Y.Y.; Peng, H.; Che, Y.Q.; Huang, C.Z. Identification of a circulating microRNA signature for colorectal cancer detection. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e87451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Miao, Y.; Xiao, B.; Huan, R.; Jiang, Z.; Meng, D.; Wang, Y. Differential expression of microRNA species in human gastric cancer versus non-tumorous tissues. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2009, 24, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaconstantinou, I.G.; Manta, A.; Gazouli, M.; Lyberopoulou, A.; Lykoudis, P.M.; Polymeneas, G.; Voros, D. Expression of microRNAs in patients with pancreatic cancer and its prognostic significance. Pancreas 2013, 42, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.J.; Stratmann, J.; Zhou, Z.G.; Sun, X.F. Suppression of microRNA-31 increases sensitivity to 5-FU at an early stage, and affects cell migration and invasion in HCT-116 colon cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Yu, F.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, R.; Chen, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, C.Y.; Chen, J.; Zhang, J. MicroRNA-31 activates the RAS pathway and functions as an oncogenic MicroRNA in human colorectal cancer by repressing RAS p21 GTPase activating protein 1 (RASA1). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 9508–9518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynam-Lennon, N.; Reynolds, J.V.; Marignol, L.; Sheils, O.M.; Pidgeon, G.P.; Maher, S.G. MicroRNA-31 modulates tumour sensitivity to radiation in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 90, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Yu, L.; Qin, D.; Huang, R.; Jiang, X.; Zou, C.; Tang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Wang, G.; Wang, X.; et al. Role of microRNA-30c targeting ADAM19 in colorectal cancer. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0120698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Tang, Q.; Qin, D.; Yu, L.; Huang, R.; Lv, G.; Zou, Z.; Jiang, X.C.; Zou, C.; Liu, W.; et al. Role of microRNA 30a targeting insulin receptor substrate 2 in colorectal tumorigenesis. Mol. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 988–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Huang, F.; Zhang, D.; Ju, J.; Wu, X.B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Nie, M.; Li, Z.; et al. Heterochromatin protein HP1γ promotes colorectal cancer progression and is regulated by miR-30a. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 4593–4604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Wang, X.; Huo, Q.; Sun, M.; Cai, C.; Liu, Z.; Hu, G.; Yang, Q. MicroRNA-30a suppresses breast tumor growth and metastasis by targeting metadherin. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3119–3128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Li, F.; Tang, S. MiR-30a upregulates BCL2A1, IER3 and cyclin D2 expression by targeting FOXL2. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akat, K.M.; Moore-McGriff, D.; Morozov, P.; Brown, M.; Gogakos, T.; Correa Da Rosa, J.; Mihailovic, A.; Sauer, M.; Ji, R.; Ramarathnam, A.; et al. Comparative RNA-sequencing analysis of myocardial and circulating small RNAs in human heart failure and their utility as biomarkers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11151–11156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Ma, J.; Wang, Y.; Biswal, S. Plasma miRNA as biomarkers for assessment of total-body radiation exposure dosimetry. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner-Ecker, M.; Schwager, C.; Wirkner, U.; Abdollahi, A.; Huber, P.E. MicroRNA expression after ionizing radiation in human endothelial cells. Radiat. Oncol. 2010, 5, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchida, A.; Ohno, S.; Wu, W.; Borjigin, N.; Fujita, K.; Aoki, T.; Ueda, S.; Takanashi, M.; Kuroda, M. miR-92 is a key oncogenic component of the miR-17-92 cluster in colon cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011, 102, 2264–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodel, C.; Liersch, T.; Becker, H.; Fietkau, R.; Hohenberger, W.; Hothorn, T.; Graeven, U.; Arnold, D.; Lang-Welzenbach, M.; Raab, H.R.; et al. Preoperative chemoradiotherapy and postoperative chemotherapy with fluorouracil and oxaliplatin versus fluorouracil alone in locally advanced rectal cancer: Initial results of the German CAO/ARO/AIO-04 randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brase, J.C.; Johannes, M.; Schlomm, T.; Fälth, M.; Haese, A.; Steuber, T.; Beissbarth, T.; Kuner, R.; Sültmann, H. Circulating miRNAs are correlated with tumor progression in prostate cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyth, G.K. Linear models and empirical bayes methods for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Stat. Appl. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2004, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, D.R.; Oakes, D. Analysis of Survival Data 1984; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Stat Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jo, P.; Azizian, A.; Salendo, J.; Kramer, F.; Bernhardt, M.; Wolff, H.A.; Gruber, J.; Grade, M.; Beißbarth, T.; Ghadimi, B.M.; et al. Changes of Microrna Levels in Plasma of Patients with Rectal Cancer during Chemoradiotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061140
Jo P, Azizian A, Salendo J, Kramer F, Bernhardt M, Wolff HA, Gruber J, Grade M, Beißbarth T, Ghadimi BM, et al. Changes of Microrna Levels in Plasma of Patients with Rectal Cancer during Chemoradiotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061140
Chicago/Turabian StyleJo, Peter, Azadeh Azizian, Junius Salendo, Frank Kramer, Markus Bernhardt, Hendrik A. Wolff, Jens Gruber, Marian Grade, Tim Beißbarth, B. Michael Ghadimi, and et al. 2017. "Changes of Microrna Levels in Plasma of Patients with Rectal Cancer during Chemoradiotherapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061140
APA StyleJo, P., Azizian, A., Salendo, J., Kramer, F., Bernhardt, M., Wolff, H. A., Gruber, J., Grade, M., Beißbarth, T., Ghadimi, B. M., & Gaedcke, J. (2017). Changes of Microrna Levels in Plasma of Patients with Rectal Cancer during Chemoradiotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061140