The Estrogen Receptor-β Expression in De Quervain’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. The Expression of Estrogen Receptor (ER)-β Was Associated with the Severity of De Quervain’s Disease
| Patient Number | Age at Surgery (Years) | Gender | Side | Duration (Months) | Corticosteroid Injection | Age at Menopause (Years) | Grade I | Grade II | Grade III |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 61 | F | L | 4 | No | 50 | No | Yes | Yes |
| 2 | 53 | F | L | 7 | No | 53 | No | Yes | Yes |
| 3 | 64 | F | L | 3 | No | 53 | No | Yes | No |
| 4 | 50 | F | L | 5 | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| 5 | 38 | M | R | 6 | 1 | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 6 | 73 | F | R | 16 | 1 | 56 | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 7 | 51 | F | R | 4 | No | 49 | Yes | Yes | No |
| 8 | 68 | F | R | 3 | No | 51 | No | Yes | No |
| 9 | 54 | F | R | 5 | No | 49 | Yes | Yes | No |
| 10 | 53 | M | R | 7 | No | No | Yes | Yes | No |
| 11 | 54 | F | L | 12 | 1 | 52 | Yes | Yes | No |
| 12 | 44 | F | L | 18 | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| 13 | 52 | F | L | 3 | No | 50 | No | Yes | Yes |
| 14 | 53 | F | L | 8 | No | 53 | No | Yes | No |
| 15 | 57 | F | L | 14 | 1 | 50 | No | Yes | Yes |
| 16 | 65 | F | L | 12 | No | 50 | No | Yes | Yes |
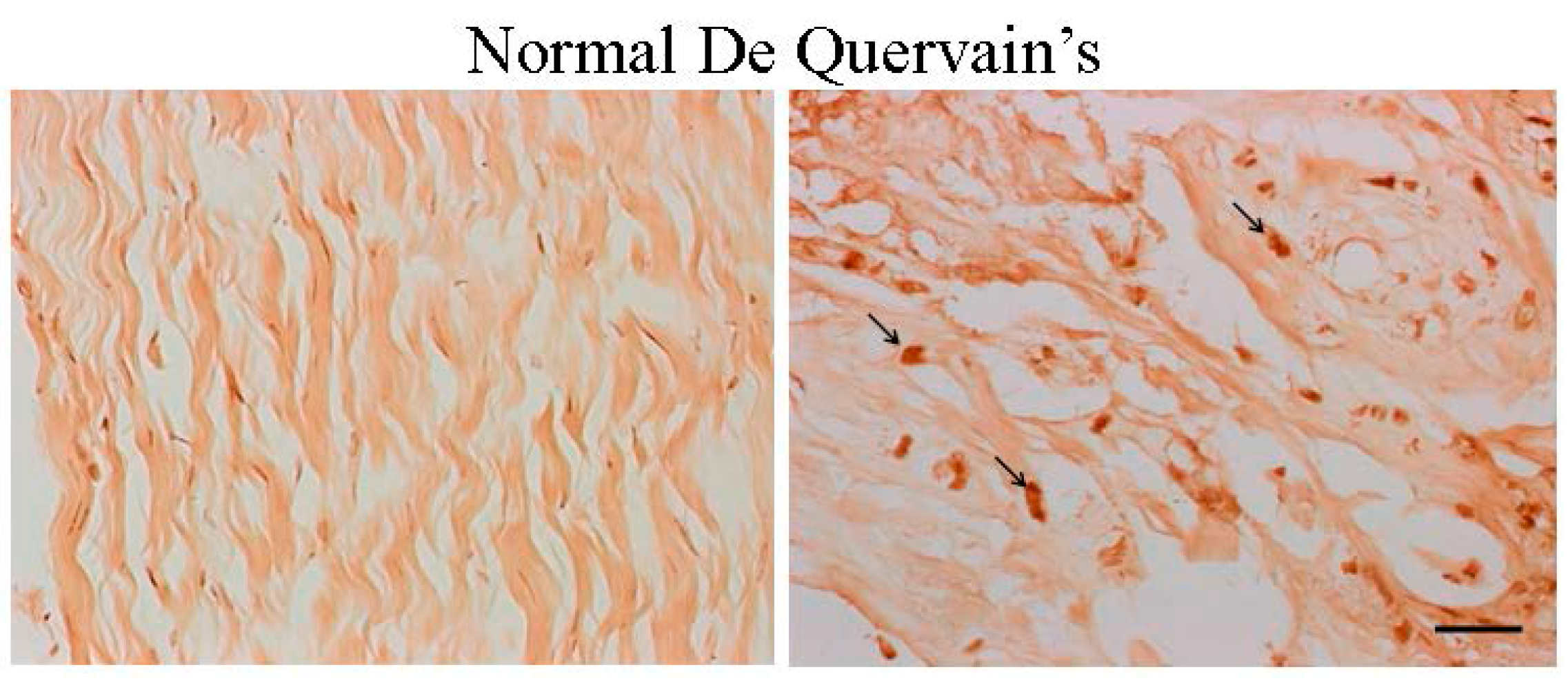
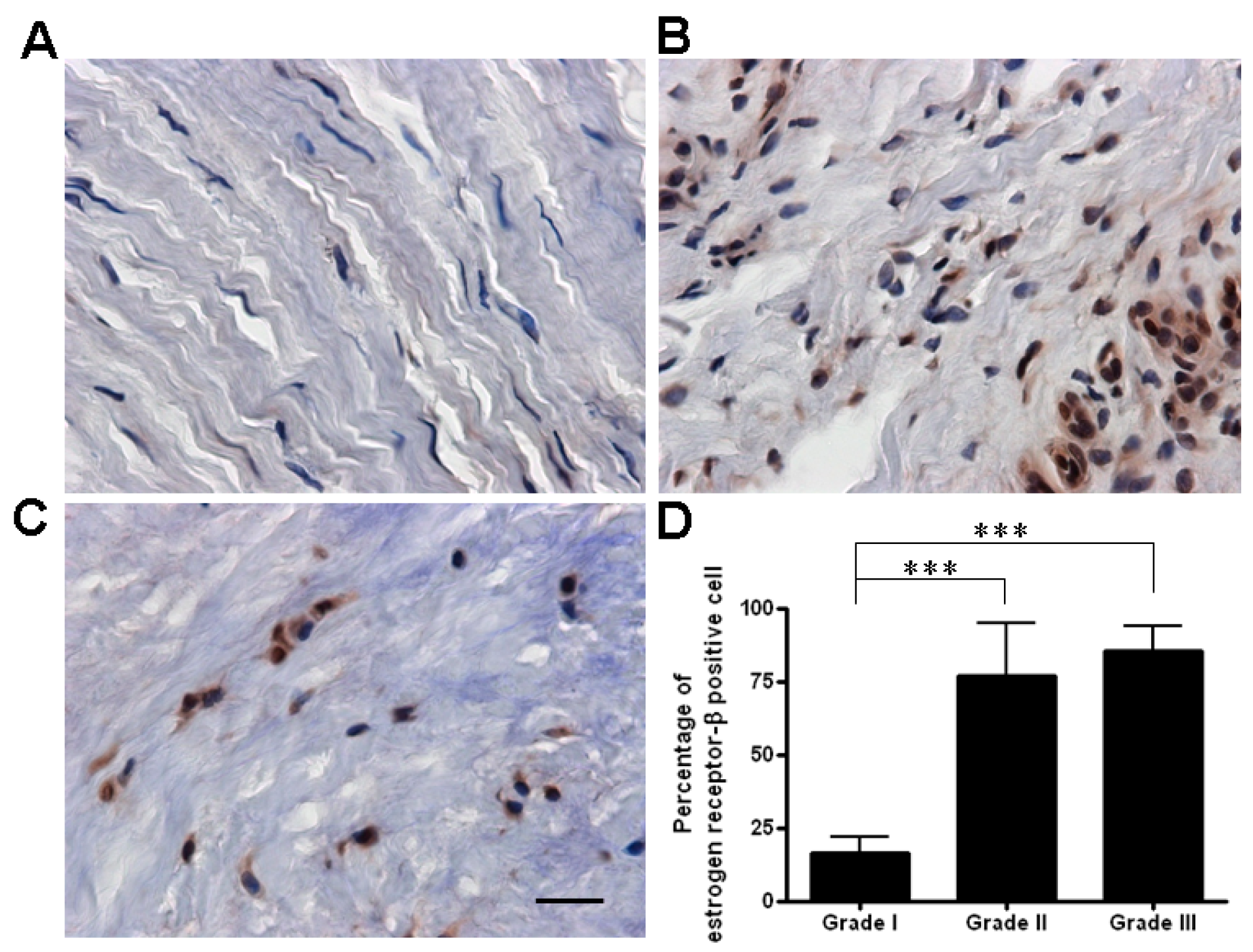
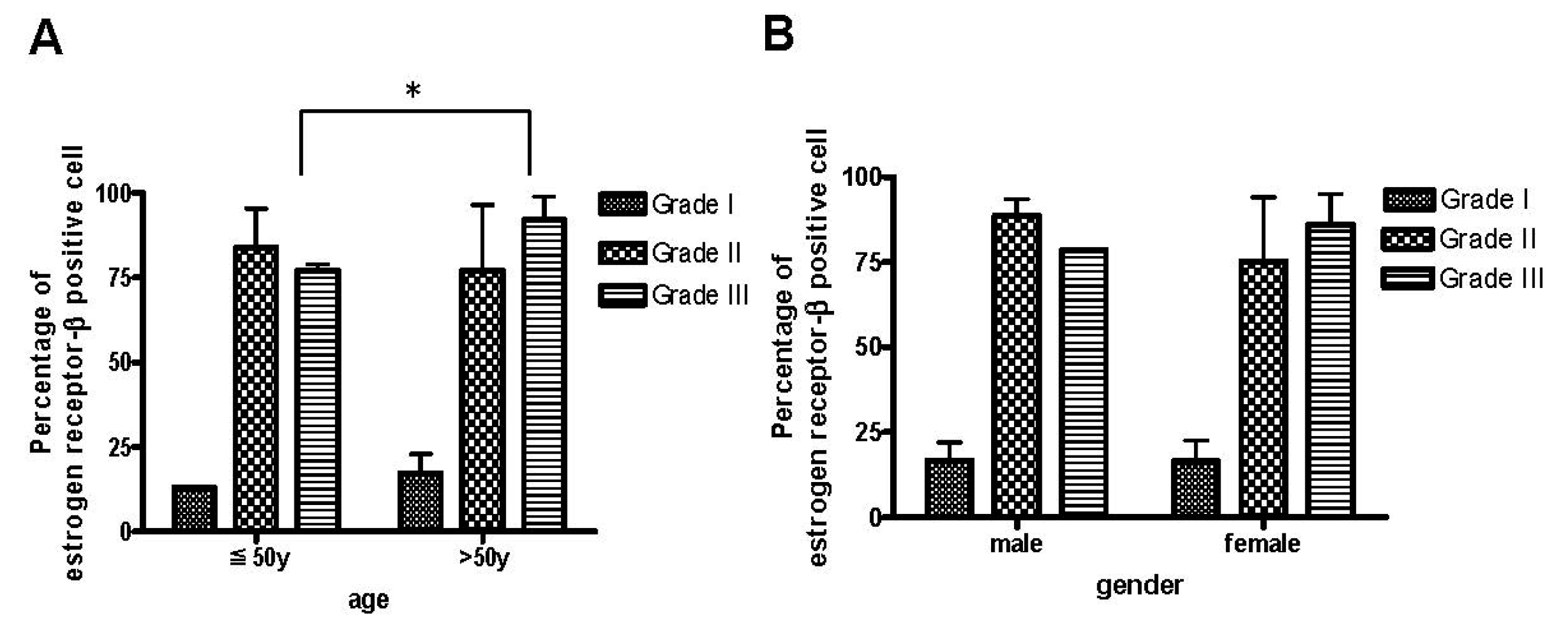
2.2. The Age Was Related to the Degree of ER-β Expression and Disease Severity
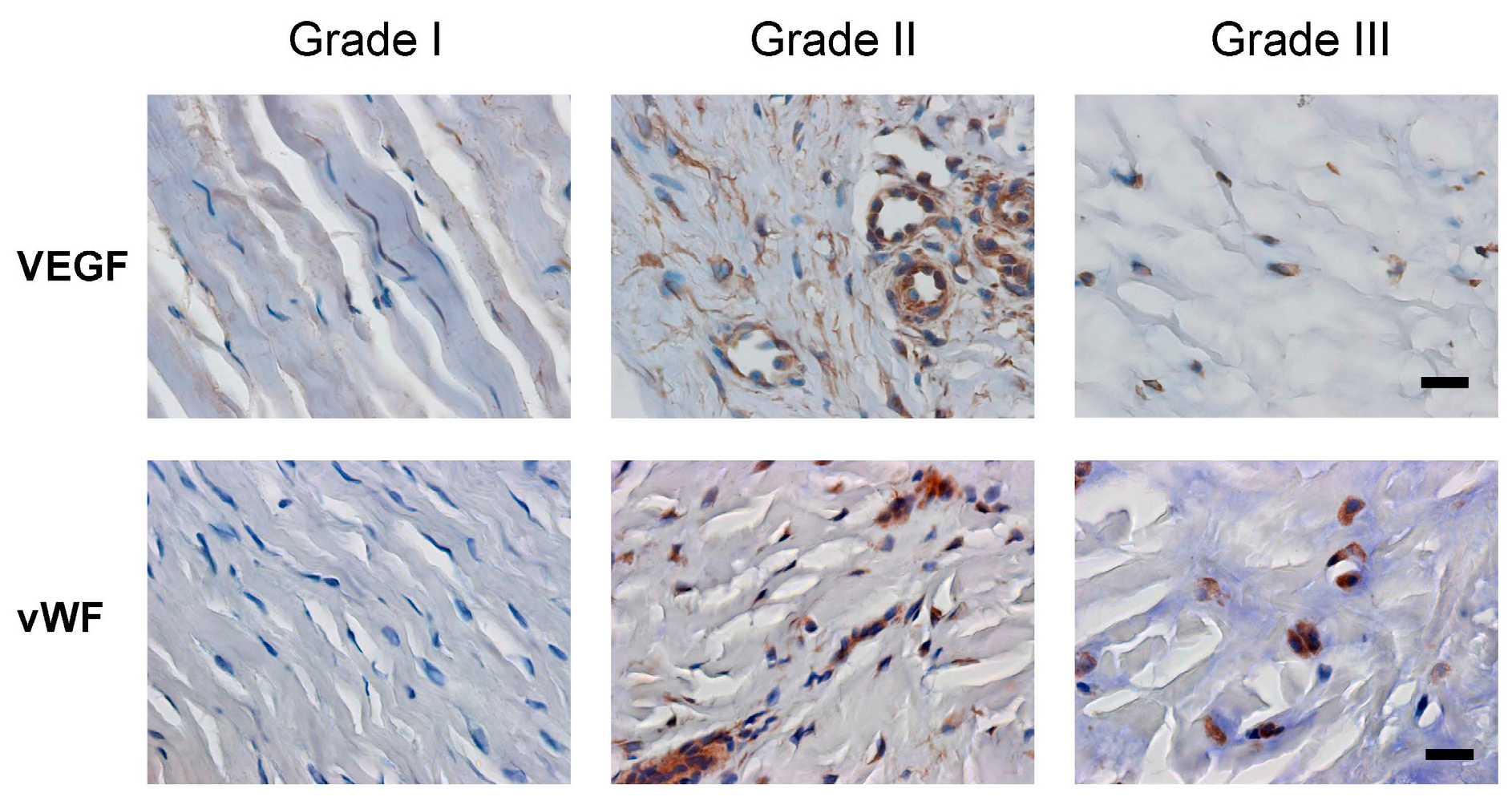
2.3. Inflammation and Angiogenesis Occurred and Increased along with Disease Progression
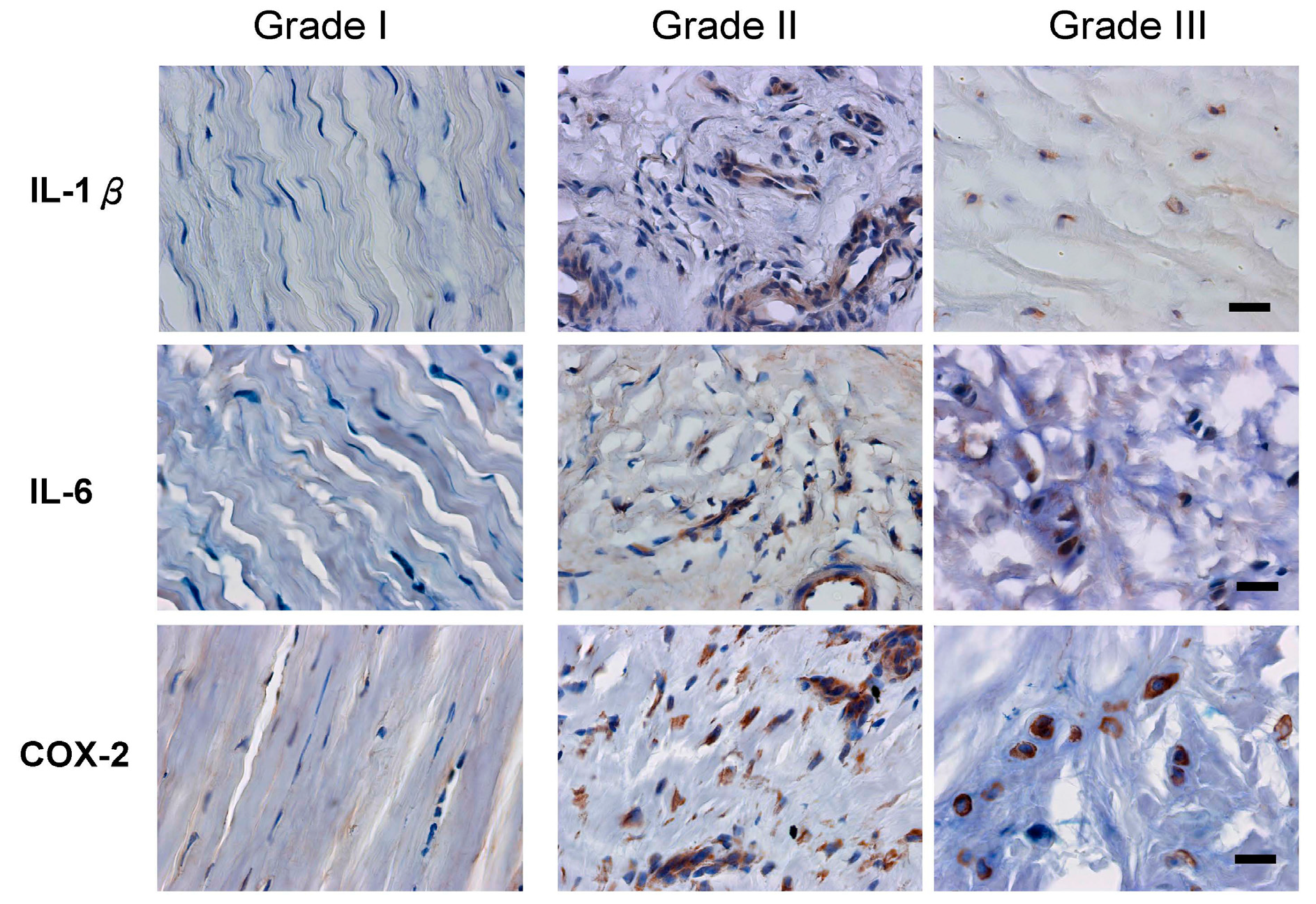
| Factors | Grade I | Grade II | Grade III |
|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1β | 13.08% ± 5.75% | 67.65% ± 16.17% *** | 89.43% ± 8.53% *** |
| IL-6 | 12.29% ± 8.72% | 67.23% ± 17.63% *** | 84.16% ± 10.41% *** |
| COX-2 | 8.81% ± 6.87% | 92.69% ± 5.51% *** | 87.07% ± 7.64% *** |
| VEGF | 12.33% ± 4.60% | 75.78% ± 17.70% *** | 90.63% ± 4.45% *** |
| vWF | 5.96% ± 0.10% | 48.99% ± 23.15% | 70.21% ± 15.54% * |
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. The Disease Diagnosis
4.2. Tissue Collection and Section Evaluation
4.3. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.4. Cell Counting
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Quervain, F. On a form of chronic tendovaginitis by Dr. Fritz de Quervain in la Chaux-de-Fonds. 1895. Am. J. Orthop. 1997, 26, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.S. De Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Stenosing tenosynovitis of the first dorsal compartment. J. Occup. Environ. Med. 1997, 39, 990–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilyas, A.M.; Ast, M.; Schaffer, A.A.; Thoder, J. De quervain tenosynovitis of the wrist. J. Am. Acad. Orthop. Surg. 2007, 15, 757–764. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peters-Veluthamaningal, C.; van der Windt, D.A.; Winters, J.C.; Meyboom-de Jong, B. Corticosteroid injection for de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 8, CD005616. [Google Scholar]
- Di Sante, L.; Martino, M.; Manganiello, I.; Tognolo, L.; Santilli, V. Ultrasound-guided corticosteroid injection for the treatment of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 92, 637–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laoopugsin, N.; Laoopugsin, S. The study of work behaviours and risks for occupational overuse syndrome. Hand Surg. 2012, 17, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, H.S.; Hooper, G.; Davie, R. Histological appearances in post-partum de Quervain’s disease. J. Hand Surg. Br. 2000, 25, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.A. Occurrence of de Quervain’s disease in postpartum women. J. Fam. Pract. 1991, 32, 325–327. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tendon Trouble in the Hands: De Quervain’s Tenosynovitis and Trigger Finger. Women are more likely than men to develop these painful conditions. Harv. Women Health Watch 2010, 17, 4–5.
- Wolf, J.M.; Sturdivant, R.X.; Owens, B.D. Incidence of de Quervain’s tenosynovitis in a young, active population. J. Hand Surg. Am. 2009, 34, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petit Le Manac’h, A.; Roquelaure, Y.; Ha, C.; Bodin, J.; Meyer, G.; Bigot, F.; Veaudor, M.; Descatha, A.; Goldberg, M.; Imbernon, E. Risk factors for de Quervain’s disease in a French working population. Scand. J. Work Environ. Health 2011, 37, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual, E.; Giner, V.; Arostegui, A.; Conill, J.; Ruiz, M.T.; Pico, A. Higher incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome in oophorectomized women. Br. J. Rheumatol. 1991, 30, 60–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hakim, A.J.; Cherkas, L.; el Zayat, S.; MacGregor, A.J.; Spector, T.D. The genetic contribution to carpal tunnel syndrome in women: A twin study. Arthritis Rheum. 2002, 47, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toesca, A.; Pagnotta, A.; Zumbo, A.; Sadun, R. Estrogen and progesterone receptors in carpal tunnel syndrome. Cell Biol. Int. 2008, 32, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Hann, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, J.S. The expression of estrogen receptors in the tenosynovium of postmenopausal women with idiopathic carpal tunnel syndrome. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 28, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavao, M.; Traish, A.M. Estrogen receptor antibodies: Specificity and utility in detection, localization and analyses of estrogen receptor α and β. Steroids 2001, 66, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clegg, D.J. Minireview: The year in review of estrogen regulation of metabolism. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1957–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, S.; Walter, P.; Kumar, V.; Krust, A.; Bornert, J.M.; Argos, P.; Chambon, P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: Sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature 1986, 320, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, G.G.; Enmark, E.; Pelto-Huikko, M.; Nilsson, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 5925–5930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosselman, S.; Polman, J.; Dijkema, R. ERβ: Identification and characterization of a novel human estrogen receptor. FEBS Lett. 1996, 392, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, Y.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Kuo, L.C.; Wu, P.T.; Shao, C.J.; Wu, K.C.; Wu, T.T.; Jou, I.M. Inflammation is present in de Quervain disease-correlation study between biochemical and histopathological evaluation. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2015, 74, S146–S151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.T.; Lyall, H.A.; Grant, J.W.; Matthewson, M.H. The histopathology of de Quervain’s disease. J. Hand Surg. Br. 1998, 23, 732–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, H.; Fujimoto, J.; Aoki, I.; Tamaya, T. Expression of estrogen receptor α and β in myometrium of premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Steroids 2003, 68, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandenberger, A.W.; Lebovic, D.I.; Tee, M.K.; Ryan, I.P.; Tseng, J.F.; Jaffe, R.B.; Taylor, R.N. Oestrogen receptor (ER)-α and ER-β isoforms in normal endometrial and endometriosis-derived stromal cells. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1999, 5, 651–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujimoto, J.; Sakaguchi, H.; Aoki, I.; Toyoki, H.; Tamaya, T. Clinical implications of the expression of estrogen receptor-α and -β in primary and metastatic lesions of uterine endometrial cancers. Oncology 2002, 62, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swedenborg, E.; Power, K.A.; Cai, W.; Pongratz, I.; Rüegg, J. Regulation of estrogen receptor β activity and implications in health and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 3873–3894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulun, S.E.; Monsavais, D.; Pavone, M.E.; Dyson, M.; Xue, Q.; Attar, E.; Tokunaga, H.; Su, E.J. Role of estrogen receptor-β in endometriosis. Semin. Reprod. Med. 2012, 30, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Q.; Lin, Z.; Cheng, Y.H.; Huang, C.C.; Marsh, E.; Yin, P.; Milad, M.P.; Confino, E.; Reierstad, S.; Innes, J.; et al. Promoter methylation regulates estrogen receptor 2 in human endometrium and endometriosis. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 681–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trukhacheva, E.; Lin, Z.; Reierstad, S.; Cheng, Y.H.; Milad, M.; Bulun, S.E. Estrogen receptor (ER) β regulates ERα expression in stromal cells derived from ovarian endometriosis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 94, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galal, N.; El-Beialy, W.R.; Deyama, Y.; Yoshimura, Y.; Suzuki, K.; Totsuka, Y. Novel effect of estrogen on RANK and c-fms expression in RAW 264.7 cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, M.; Honma, N. Estrogen receptor β. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2011, 135, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monica, V.; Longo, M.; Felice, B.; Scagliotti, G.V.; Papotti, M.; Novello, S. Role of hormone receptor expression in patients with advanced-stage lung cancer treated with chemotherapy. Clin. Lung Cancer 2012, 13, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, M.; Dahlman-Wright, K.; Gustafsson, J.Å. Estrogen receptor α and β in health and disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tam, A.; Wadsworth, S.; Dorscheid, D.; Man, S.F.; Sin, D.D. Estradiol increases mucus synthesis in bronchial epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e100633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, I.; Chuang, K.L.; Slavin, S.; Da, J.; Lim, W.X.; Pang, S.T.; O’Brien, J.H.; Yeh, S. Suppression of ERβ signaling via ERβ knockout or antagonist protects against bladder cancer development. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 651–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, P.C.; Lu, C.S.; Shiau, A.L.; Lee, C.H.; Jou, I.M.; Hsieh, J.L. Lentiviral small hairpin RNA knockdown of macrophage inflammatory protein-1γ ameliorates experimentally induced osteoarthritis in mice. Hum. Gene Ther. 2013, 24, 871–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, J.L.; Shen, P.C.; Shiau, A.L.; Jou, I.M.; Lee, C.H.; Wang, C.R.; Teo, M.L.; Wu, C.L. Intraarticular gene transfer of thrombospondin-1 suppresses the disease progression of experimental osteoarthritis. J. Orthop. Res. 2010, 28, 1300–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.H.; Al-Shaikh, R.A.; Panossian, V.; Finerman, G.A.; Lane, J.M. Estrogen affects the cellular metabolism of the anterior cruciate ligament. A potential explanation for female athletic injury. Am. J. Sports Med. 1997, 25, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, W.D.; Panossian, V.; Hatch, J.D.; Liu, S.H.; Finerman, G.A. Combined effects of estrogen and progesterone on the anterior cruciate ligament. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2001, 383, 268–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadimitriou, K.; Kountourakis, P.; Morakis, E.; Vassiliou, V.; Barbounis, V.; Ardavanis, A. Bilateral de Quervain syndrome after aromatase inhibitor administration: A case report and review of the literature. Case Rep. Med. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pavone, M.E.; Bulun, S.E. Clinical review: The use of aromatase inhibitors for ovulation induction and superovulation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 1838–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bearoff, F.; Case, L.K.; Krementsov, D.N.; Wall, E.H.; Saligrama, N.; Blankenhorn, E.P.; Teuscher, C. Identification of genetic determinants of the sexual dimorphism in CNS autoimmunity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, W.J.; Olsen, N.J. Sexual dimorphism of RA manifestations: Genes, hormones and behavior. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2011, 7, 307–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saijo, K.; Collier, J.G.; Li, A.C.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Glass, C.K. An ADIOL-ERβ-CtBP transrepression pathway negatively regulates microglia-mediated inflammation. Cell 2011, 145, 584–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kok, H.S.; van Asselt, K.M.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; Peeters, P.H.; Wijmenga, C. Genetic studies to identify genes underlying menopausal age. Hum. Reprod. Update 2005, 11, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Movin, T.; Gad, A.; Reinholt, F.P.; Rolf, C. Tendon pathology in long-standing achillodynia. Biopsy findings in 40 patients. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1997, 68, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, A.; Xu, J.; Zheng, M. In chronic lateral epicondylitis, apoptosis and autophagic cell death occur in the extensor carpi radialis brevis tendon. J. Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010, 19, 355–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ImageJ. Image Processing and analysis in Java. Available online: http://imagej.nih.gov/ij/ (accessed on 31 October 2015).
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, P.-C.; Wang, P.-H.; Wu, P.-T.; Wu, K.-C.; Hsieh, J.-L.; Jou, I.-M. The Estrogen Receptor-β Expression in De Quervain’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26452-26462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125968
Shen P-C, Wang P-H, Wu P-T, Wu K-C, Hsieh J-L, Jou I-M. The Estrogen Receptor-β Expression in De Quervain’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2015; 16(11):26452-26462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125968
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Po-Chuan, Ping-Hui Wang, Po-Ting Wu, Kuo-Chen Wu, Jeng-Long Hsieh, and I-Ming Jou. 2015. "The Estrogen Receptor-β Expression in De Quervain’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16, no. 11: 26452-26462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125968
APA StyleShen, P.-C., Wang, P.-H., Wu, P.-T., Wu, K.-C., Hsieh, J.-L., & Jou, I.-M. (2015). The Estrogen Receptor-β Expression in De Quervain’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 16(11), 26452-26462. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161125968





