An Improved MLVF Method and Its Comparison with Traditional MLVF, spa Typing, MLST/SCCmec and PFGE for the Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
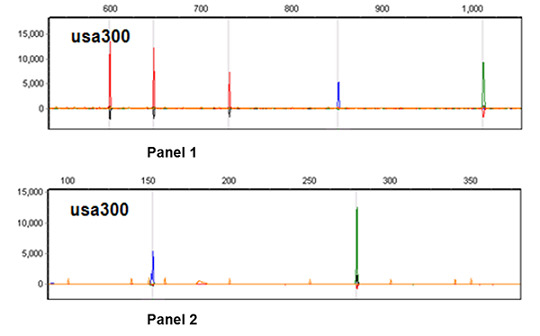
2.1. Multiplex PCRs Design and Pattern Profile Definition
2.2. CGE/MLVF Typeability
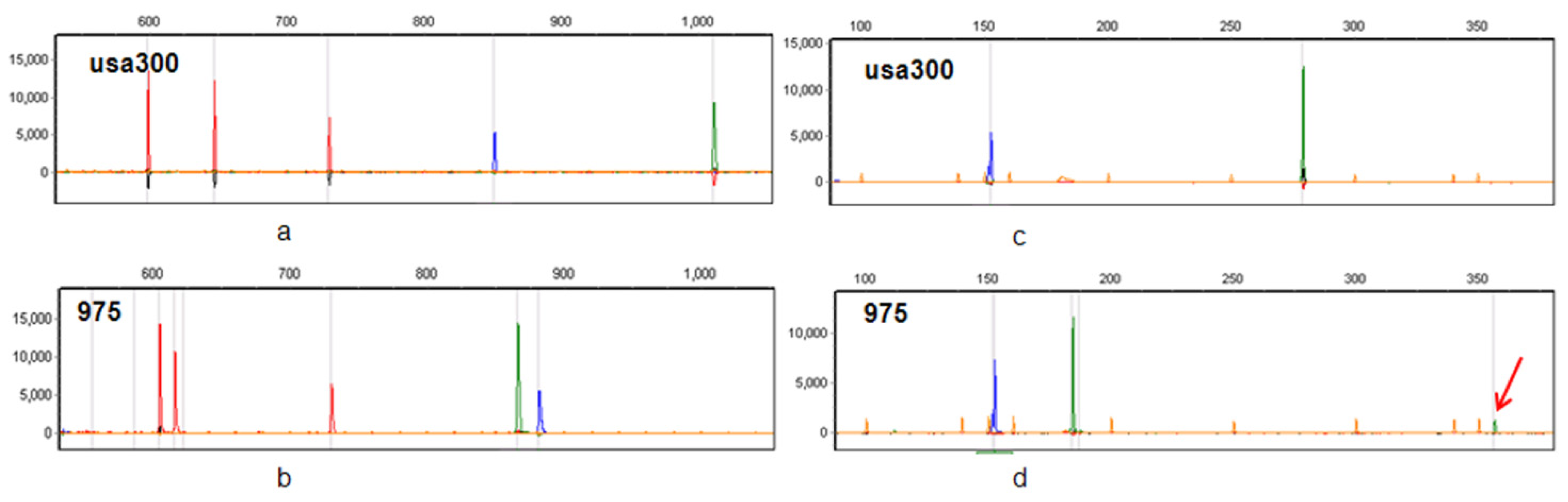
2.3. The Resolution of CGE/MLVF against Well-Characterized MRSA Strains
2.3.1. CGE/MLVF Compared to Traditional MLVF
2.4. Evaluation on Clinical MRSA Isolates
2.4.1. Discriminatory Power
2.4.2. CGE/MLVF
2.4.3. Traditional MLVF
2.4.4. Spa Typing
2.4.5. MLST/SCCmec
2.4.6. PFGE
2.5. Reproducibility of All the Typing Methods
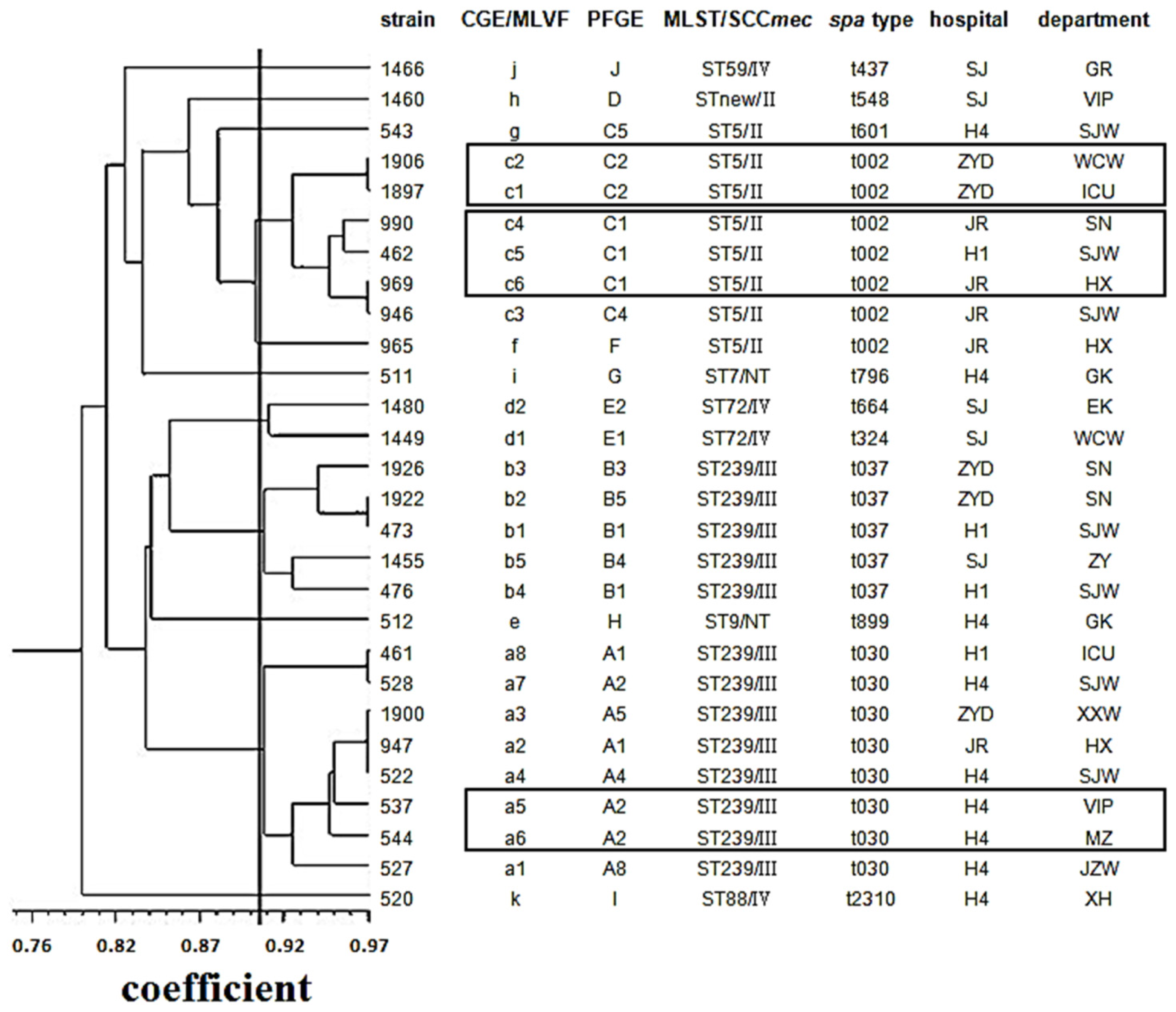
2.6. Criteria for Defining CGE/MLVF Clusters
2.7. Concordance between CGE/MLVF, spa Typing, MLST/SCCmec and PFGE
2.8. CGE/MLVF Can Distinguish Isolates Belonging to the Identical Epidemic Clone in China
2.9. CGE/MLVF Can Distinguish Isolates with Identical PFGE Patterns
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Bacterial Isolates
4.2. Extraction of Total DNA for PCR
4.3. Traditional MLVF
4.4. CGE/MLVF
4.4.1. Multiplex PCRs
4.4.2. Single PCR Verifying spa Locus
4.5. Spa Typing
4.6. MLST and SCCmec
4.7. PFGE
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Information
ijms-15-00725-s001.pdfAcknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, C.; Sun, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Hu, B.; Yu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Chu, Y.; Cao, B.; Liao, K.; et al. Antimicrobial resistance trends among 5608 clinical Gram-positive isolates in China: Results from the Gram-Positive Cocci Resistance Surveillance program (2005–2010). Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis 2012, 73, 174–181. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Sun, H.; Xu, Y.; Xie, X.; Chen, M. In vitro activity of ceftobiprole, linezolid, tigecycline, and 23 other antimicrobial agents against Staphylococcus aureus isolates in China. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis 2008, 62, 226–229. [Google Scholar]
- Grundmann, H.; Aanensen, D.M.; van den Wijngaard, C.C.; Spratt, B.G.; Harmsen, D.; Friedrich, A.W. European Staphylococcal Reference Laboratory Working Group. Geographic distribution of Staphylococcus aureus causing invasive infections in Europe: A molecular-epidemiological analysis. PLoS Med 2010, 7, e1000215. [Google Scholar]
- Struelens, M.J.; Hawkey, P.M.; French, G.L.; Witte, W.; Tacconelli, E. Laboratory tools and strategies for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus screening, surveillance and typing: State of the art and unmet needs. Clin. Microbiol. Infect 2009, 15, 112–119. [Google Scholar]
- El Helali, N.; Carbonne, A.; Naas, T.; Kerneis, S.; Fresco, O.; Giovangrandi, Y.; Fortineau, N.; Nordmann, P.; Astagneau, P. Nosocomial outbreak of staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in neonates: Epidemiological investigation and control. J. Hosp. Infect 2005, 61, 130–138. [Google Scholar]
- Enright, M.C.; Robinson, D.A.; Randle, G.; Feil, E.J.; Grundmann, H.; Spratt, B.G. The evolutionary history of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 7687–7692. [Google Scholar]
- Bosch, T.; Verkade, E.; van Luit, M.; Pot, B.; Vauterin, P.; Burggrave, R.; Savelkoul, P.; Kluytmans, J.; Schouls, L. High resolution typing by whole genome mapping enables discrimination of LA-MRSA (CC398) strains and identification of transmission events. PLoS One 2013, 8, e66493. [Google Scholar]
- Te Witt, R.; Vaessen, N.; Melles, D.C.; Lekkerkerk, W.S.; van der Zwaan, E.A.; Zandijk, W.H.; Severin, J.A.; Vos, M.C. Good performance of the SpectraCellRA system for typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol 2013, 51, 1434–1438. [Google Scholar]
- O’Sullivan, M.V.; Zhou, F.; Sintchenko, V.; Gilbert, G.L. Prospective genotyping of hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates by use of a novel, highly discriminatory binary typing system. J. Clin. Microbiol 2012, 50, 3513–3519. [Google Scholar]
- Hirvonen, J.J.; Pasanen, T.; Tissari, P.; Salmenlinna, S.; Vuopio, J.; Kaukoranta, S.S. Outbreak analysis and typing of MRSA isolates by automated repetitive-sequence-based PCR in a region with multiple strain types causing epidemics. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis 2012, 31, 2935–2942. [Google Scholar]
- Malachowa, N.; Sabat, A.; Gniadkowski, M.; Krzyszton-Russjan, J.; Empel, J.; Miedzobrodzki, J.; Kosowska-Shick, K.; Appelbaum, P.C.; Hryniewicz, W. Comparison of multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis, spa typing, and multilocus sequence typing for clonal characterization of Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol 2005, 43, 3095–3100. [Google Scholar]
- Harmsen, D.; Claus, H.; Witte, W.; Rothganger, J.; Claus, H.; Turnwald, D.; Vogel, U. Typing of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in a university hospital setting by using novel software for spa repeat determination and database management. J. Clin. Microbiol 2003, 41, 5442–5448. [Google Scholar]
- Sabat, A.; Krzyszton-Russjan, J.; Strzalka, W.; Filipek, R.; Kosowska, K.; Hryniewicz, W.; Travis, J.; Potempa, J. New method for typing Staphylococcus aureus strains: Multiple-locus variable-number tandem repeat analysis of polymorphism and genetic relationships of clinical isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol 2003, 41, 1801–1804. [Google Scholar]
- Holmes, A.; Edwards, G.F.; Girvan, E.K.; Hannant, W.; Danial, J.; Fitzgerald, J.R.; Templeton, K.E. Comparison of two multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat methods and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis for differentiating highly clonal methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol 2010, 48, 3600–3607. [Google Scholar]
- Karynski, M.; Sabat, A.J.; Empel, J.; Hryniewicz, W. Molecular surveillance of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus by multiple-locus variable number tandem repeat fingerprinting (formerly multiple-locus variable number tandem repeat analysis) and spa typing in a hierarchic approach. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis 2008, 62, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Sabat, A.; Malachowa, N.; Miedzobrodzki, J.; Hryniewicz, W. Comparison of PCR-based methods for typing Staphylococcus aureus isolates. J. Clin. Microbiol 2006, 44, 3804–3807. [Google Scholar]
- Glasner, C.; Sabat, A.J.; Dreisbach, A.; Larsen, A.R.; Friedrich, A.W.; Skov, R.L.; van Dijl, J.M. Rapid and high-resolution distinction of community-acquired and nosocomial Staphylococcus aureus isolates with identical pulsed-field gel electrophoresis patterns and spa types. Int. J. Med. Microbiol 2013, 303, 70–75. [Google Scholar]
- Sabat, A.J.; Chlebowicz, M.A.; Grundmann, H.; Arends, J.P.; Kampinga, G.; Meessen, N.E.; Friedrich, A.W.; van Dijl, J.M. Microfluidic-chip-based multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat fingerprinting with new primer sets for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol 2012, 50, 2255–2262. [Google Scholar]
- Schouls, L.M.; Spalburg, E.C.; van Luit, M.; Huijsdens, X.W.; Pluister, G.N.; van Santen-Verheuvel, M.G.; van der Heide, H.G.; Grundmann, H.; Heck, M.E.; de Neeling, A.J. Multiple-locus variable number tandem repeat analysis of Staphylococcus aureus: Comparison with pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and spa-typing. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5082. [Google Scholar]
- Pourcel, C.; Hormigos, K.; Onteniente, L.; Sakwinska, O.; Deurenberg, R.H.; Vergnaud, G. Improved multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat assay for Staphylococcus aureus genotyping, providing a highly informative technique together with strong phylogenetic value. J. Clin. Microbiol 2009, 47, 3121–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Rivero-Perez, B.; Perez-Roth, E.; Mendez-Alvarez, S. Evaluation of multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis for typing a polyclonal hospital-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus population in an area where such infections are endemic. J. Clin. Microbiol 2010, 48, 2991–2994. [Google Scholar]
- Luczak-Kadlubowska, A.; Sabat, A.; Tambic-Andrasevic, A.; Payerl-Pal, M.; Krzyszton-Russjan, J.; Hryniewicz, W. Usefulness of multiple-locus VNTR fingerprinting in detection of clonality of community- and hospital-acquired Staphylococcus aureus isolates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 2008, 94, 543–553. [Google Scholar]
- Moser, S.A.; Box, M.J.; Patel, M.; Amaya, M.; Schelonka, R.; Waites, K.B. Multiple-locus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis of meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus discriminates within USA pulsed-field gel electrophoresis types. J. Hosp. Infect 2009, 71, 333–339. [Google Scholar]
- Conceicao, T.; Aires de Sousa, M.; de Lencastre, H. Staphylococcal interspersed repeat unit typing of Staphylococcus aureus: Evaluation of a new multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis typing method. J. Clin. Microbiol 2009, 47, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Yuan, W.; Zeng, F.; Hu, Q.; Shang, W.; Tang, D.; Xue, W.; Fu, J.; Liu, J.; Liu, N.; et al. Molecular and phenotypic evidence for the spread of three major methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus clones associated with two characteristic antimicrobial resistance profiles in China. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 2013, 68, 2453–2457. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Mao, L.L.; Brown, M.; Yu, Y.S.; O’Sullivan, M.V.; Kong, F.; Xu, Y.C. National surveillance of methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus in China highlights a still-evolving epidemiology with 15 novel emerging multilocus sequence types. J. Clin. Microbiol 2013, 51, 3638–3644. [Google Scholar]
- Aires-de-Sousa, M.; Boye, K.; de Lencastre, H.; Deplano, A.; Enright, M.C.; Etienne, J.; Friedrich, A.; Harmsen, D.; Holmes, A.; Huijsdens, X.W.; et al. High interlaboratory reproducibility of DNA sequence-based typing of bacteria in a multicenter study. J. Clin. Microbiol 2006, 44, 619–621. [Google Scholar]
- Enright, M.C.; Day, N.P.; Davies, C.E.; Peacock, S.J.; Spratt, B.G. Multilocus sequence typing for characterization of methicillin-resistant and methicillin-susceptible clones of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol 2000, 38, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar]
- Boye, K.; Bartels, M.D.; Andersen, I.S.; Moller, J.A.; Westh, H. A new multiplex PCR for easy screening of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus SCCmec types I–V. Clin. Microbiol. Infect 2007, 13, 725–727. [Google Scholar]
- Bannerman, T.L.; Hancock, G.A.; Tenover, F.C.; Miller, J.M. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis as a replacement for bacteriophage typing of Staphylococcus aureus. J. Clin. Microbiol 1995, 33, 551–555. [Google Scholar]
- Hunter, P.R.; Gaston, M.A. Numerical index of the discriminatory ability of typing systems: An application of Simpson’s index of diversity. J. Clin. Microbiol 1988, 26, 2465–2466. [Google Scholar]
- Grundmann, H.; Hori, S.; Tanner, G. Determining confidence intervals when measuring genetic diversity and the discriminatory abilities of typing methods for microorganisms. J. Clin. Microbiol 2001, 39, 4190–4192. [Google Scholar]
- Carrico, J.A.; Silva-Costa, C.; Melo-Cristino, J.; Pinto, F.R.; de Lencastre, H.; Almeida, J.S.; Ramirez, M. Illustration of a common framework for relating multiple typing methods by application to macrolide-resistant Streptococcus pyogenes. J. Clin. Microbiol 2006, 44, 2524–2532. [Google Scholar]


| Panel | VNTR | Primer 1 | Oligonucleotide sequences (5′ to 3′) 2 | Size range (bp) | Size (bp) of Mu50 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In NCBI database | |||||
| panel 1 | ClfA | ClfA-F | GATTCTGACCCAGGTTCAGA-H | 700–1500 | 1021 |
| ClfA-R | CTGTATCTGGTAATGGTTCTTT | ||||
| ClfB | ClfB-F | ATGGTGATTCAGCAGTAAATCC-F | 600–1000 | 832 | |
| ClfB-R | CATTATTTGGTGGTGTAACTCTT | ||||
| Sdr | SdrCDE-F | GTAACAATTACGGATCATGATG-R | 400–1000 | 670/748/580 | |
| SdrCDE-R | TACCTGTTTCTGGTAATGCTTT | ||||
| panel 2 | Spa | Spa-F1 | AGCACCAAAAGAGGAAGACAA-H | 100–400 | 284 |
| Spa-R1 | GTTTAACGACATGTACTCCGT | ||||
| SspA | SspA-F | ATCMATTTYGCMAAYGATGACCA-F | 100–200 | 173 | |
| SspA-R | TTGTCTGAATTATTGTTATCGCC | ||||
| Strain | MLST | SCC-mec | spa type | CGE/MLVF | CGE/MLVF profile(bp) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST | pattern | SspA | spa | sdrC&sdrD&sdrE | ClfB | ClfA | |||
| PC8 | 1 | IV | t127 | 1 | 180.1 | 208.0 | 575.4/677.5 */683.6 * | 903.5 | 1053.4 |
| FH | 1 | IV | t127 | 2 | 123.8 | 207.8 | 575.4/784.7 | 802.9 | 1053.4 |
| SJOG30 | 1 | IV | t127 | 1 | 180.0 | 208.0 | 575.6/677.5 */683.6 * | 903.9 | 1053.3 |
| RPH85 | 1 | IV | t127 | 3 | 180.0 | 207.5 | 575.4/677.5 */683.6 * | 903.7 | 765.3 |
| B827549 | 1 | new | t1784 | 4 | 180.0 | 134.7 | 575.6/677.5 | 696.0 | 1053.6 |
| SN39 | 1 | new | t127 | 5 | 180.1 | 207.9 | 450.5/575.4/677.3 | 695.8 | 1053.2 |
| RHH58 | 1 | IV | t127 | 6 | 162.0 | 207.9 | 659.9 | 886.1 | 1071.4 |
| RHH10 | 1 | IV | t127 | 6 | 162.0 | 207.9 | 659.2 | 885.9 | 1071.4 |
| MW2 | 1 | IV | t128 | 7 | 123.7 | 232.4 | 575.4/629.6/671.5 | 909.9 | 1053.6 |
| E804531 | 5 | IV | t002 | 8 | 170.7 | 279.5 | 611.1/725.0/760.8 | 820.8 | 1160.8 |
| BK2464 | 5 | II | t002 | 9 | 170.5 | 278.6 | 599.9/611.1/683.0 | 731.1 | 926.3 |
| MU3 | 5 | II | t002 | 10 | 170.6 | 279.0 | 575.3/665.3/742.7 | 820.4 | 1016.5 |
| MU50 | 5 | II | t002 | 10 | 170.6 | 279.1 | 575.4/665.4/742.8 | 820.4 | 1016.8 |
| B8-10 | 8 | IV | t711 | 11 | 123.8 | 233.1 | 599.3/647.6/731.1 | 833.3 | 999.3 |
| RPH2 | 8 | NT | t190 | 12 | 152.4 | 208.1 | 599.4/611.4/725.1 | 647.4 | 957.0 |
| IMVS67 | 8 | V | t008 | 13 | 152.6 | 278.8 | 599.9/647.5/802.5 | 851.1 | 999.1 |
| DEN-2988 | 8 | II | t008 | 14 | 152.8 | 279.0 | 492.0 | 933.9 | 1011.0 |
| USA300 | 8 | IV | t008 | 15 | 152.4 | 279.0 | 599.3/647.4/731.0 | 851.2 | 1011.2 |
| RPH81 | 239 | III | t037 | 16 | 152.5 | 208.5 | 563.3 */575.9 */730.8 | 991.0 * | 993.5 * |
| 14176-5710 | 239 | III | t1959 | 17 | 152.5 | 232.8 | 558.0/635.2/695.3 | 973.2 | 1011.4 |
| K704540 | 239 | III | t037 | 18 | 152.5 | 208.2 | 593.8/635.2/713.1 | 973.2 | 1011.5 |
| ANS46 | 239 | III | t037 | 18 | 152.4 | 208.0 | 593.7/635.1/713.0 | 972.8 | 1011.0 |
| K711532 | 239 | III | t037 | 19 | 152.5 | 208.4 | 593.8/617.2/713.1 | 972.9 | 1011.2 |
| AH13 | 239 | III | t037 | 20 | 152.5 | 208.4 | 569.7/724.7 | 991.0 * | 993.5 * |
| RPAH18 | 239 | III | t037 | 21 | 152.5 | 208.4 | 551.3/593.8/641.6 | 955.0 * | 957.3 * |
| RPAH15 | 239 | III | t037 | 22 | 152.4 | 208.3 | 551.5/594.0/713.3 * | 703.2 * | 1011.5 * |
| HDG2 | 239 | III | t421 | 23 | 152.5 | 184.5 | 563.4/730.9/814.7 | 990.9 * | 1011.0 * |
| HU25 | 239 | III | t138 | 24 | 152.7 | 184.5 | 575.9/635.2/730.9 | 991.3 * | 1011.4 * |
| AH1 | 128 | III | t037 | 16 | 152.5 | 208.2 | 563.4 */576.1 */731.0 | 991.4 * | 993.8 * |
| COL | 250 | I | t008 | 25 | 152.5 | 279.0 | 635.2 */647.8 */731.2 | 928.5 | 1011.4 |
| CH16 | 22 | IV | t032 | 26 | 207.1 | 419.5 | 611.3/712.7 | 881.9 | 1022.2 |
| CH69 | 22 | IV | t1963 | 27 | 188.8 | 326.4 | 611.3/712.7 | 881.9 | 1022.2 |
| PAH58 | 30 | IV | t019 | 28 | 216.1 | 233.0 | 617.1/693.7/718.8 | 990.8 | 1190.1 |
| PAH1 | 30 | IV | t019 | 29 | 216.1 | 233.0 | 521.8/599.1/693.8 | 990.8 | 1190.1 |
| E822485 | 36 | II | t018 | 30 | 216.0 | 301.9 | 563.3/603.9/683.1 | 810.3 | 1254.2 |
| RPH74 | 45 | V | t065 | 31 | 142.5 | 256.3 | 611.4/904.3 */915.9 * | 1160.2 | 1111.4 |
| J710566 | new | V | t065 | 32 | 142.5 | 256.3 | 611.5/695.2/719.1 | 1192.8 | 1129.5 |
| IP01M0181 | 59 | IV | t216 | 33 | 188.0 | 232.7 | 527.9/599.1/724.9 | 1037.0 | 1248.7 |
| C801535 | 78 | NT | t325 | 34 | 226.3 | 278.3 | 468.4/700.0/802.8 | 862.1 | 1070.7 |
| IP01M-2046 | 88 | IV | t1958 | 35 | 152.5 | 256.1 | 468.6/581.2/784.7 | 808.4 | 1143.2 |
| RBH98 | 93 | IV | t202 | 36 | 170.4 | 233.5 | 593.0/720.0/1012.3 | 965.5 | 1137.8 |
| 137924492 | 93 | IV | t202 | 36 | 170.4 | 233.3 | 592.9/720.0/1012.1 | 965.4 | 1137.2 |
| Total types/patterns | 15 | 7 | 20 | 36 | |||||
| Method | No. of clusters | No. of types/patterns | DIs | (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFGE | 10 | 28 | 0.854 | (0.818–0.89) |
| MLVF | 11 | 28 | 0.855 | (0.807–0.902) |
| CGE/MLVF | 11 | 28 | 0.855 | (0.807–0.902) |
| spa typing | 11 | 0.623 | (0.559–0.687) | |
| MLST/SCCmec | 8 | 0.517 | (0.449–0.585) |
| Typing method | Adjusted Rand’s coefficient | Wallace’s coefficient | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Spa type | MLST/ | PFGE | CGE/MLVF | Spa type | MLST/ | PFGE | CGE/MLVF | |
| SCCmec | pattern/CC (CI 84% 1) | pattern/CC (SC 0.905 2) | SCCmec | pattern/CC (CI 84% 1) | pattern/CC (SC 0.905 2) | |||
| Spa type | 0.786 | 0.441/0.977 | 0.438/0.988 | 1.000 | 0.388/0.986 | 0.385/0.986 | ||
| MLST/SCCmec | 0.31/0.786 | 0.308/0.776 | 0.78 | 0.303/0.781 | 0.301/0.77 | |||
| PFGE pattern | 0.384/0.449 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.472/1.000 | ||||
| PFGE CC (CI 84% 1) | 0.438/0.989 | 0.986 | 1.000 | 0.385/0.986 | ||||
| CGE/MLVF pattern | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.476/1.000 | |||||
| CGE/MLVF SC 0.905 2 | 1.000 | 1.000 | 0.393/1.000 | |||||
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Du, X.-F.; Xiao, M.; Liang, H.-Y.; Sun, Z.; Jiang, Y.-H.; Chen, G.-Y.; Meng, X.-Y.; Zou, G.-L.; Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.-L.; et al. An Improved MLVF Method and Its Comparison with Traditional MLVF, spa Typing, MLST/SCCmec and PFGE for the Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 725-742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010725
Du X-F, Xiao M, Liang H-Y, Sun Z, Jiang Y-H, Chen G-Y, Meng X-Y, Zou G-L, Zhang L, Liu Y-L, et al. An Improved MLVF Method and Its Comparison with Traditional MLVF, spa Typing, MLST/SCCmec and PFGE for the Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(1):725-742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010725
Chicago/Turabian StyleDu, Xue-Fei, Meng Xiao, Hong-Yan Liang, Zhe Sun, Yue-Hong Jiang, Guo-Yu Chen, Xiao-Yu Meng, Gui-Ling Zou, Li Zhang, Ya-Li Liu, and et al. 2014. "An Improved MLVF Method and Its Comparison with Traditional MLVF, spa Typing, MLST/SCCmec and PFGE for the Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 1: 725-742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010725
APA StyleDu, X.-F., Xiao, M., Liang, H.-Y., Sun, Z., Jiang, Y.-H., Chen, G.-Y., Meng, X.-Y., Zou, G.-L., Zhang, L., Liu, Y.-L., Zhang, H., Sun, H.-L., Jiang, X.-F., & Xu, Y.-C. (2014). An Improved MLVF Method and Its Comparison with Traditional MLVF, spa Typing, MLST/SCCmec and PFGE for the Typing of Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(1), 725-742. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010725