In Silico Discovery of Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Inhibitor Identification Using Virtual Screening
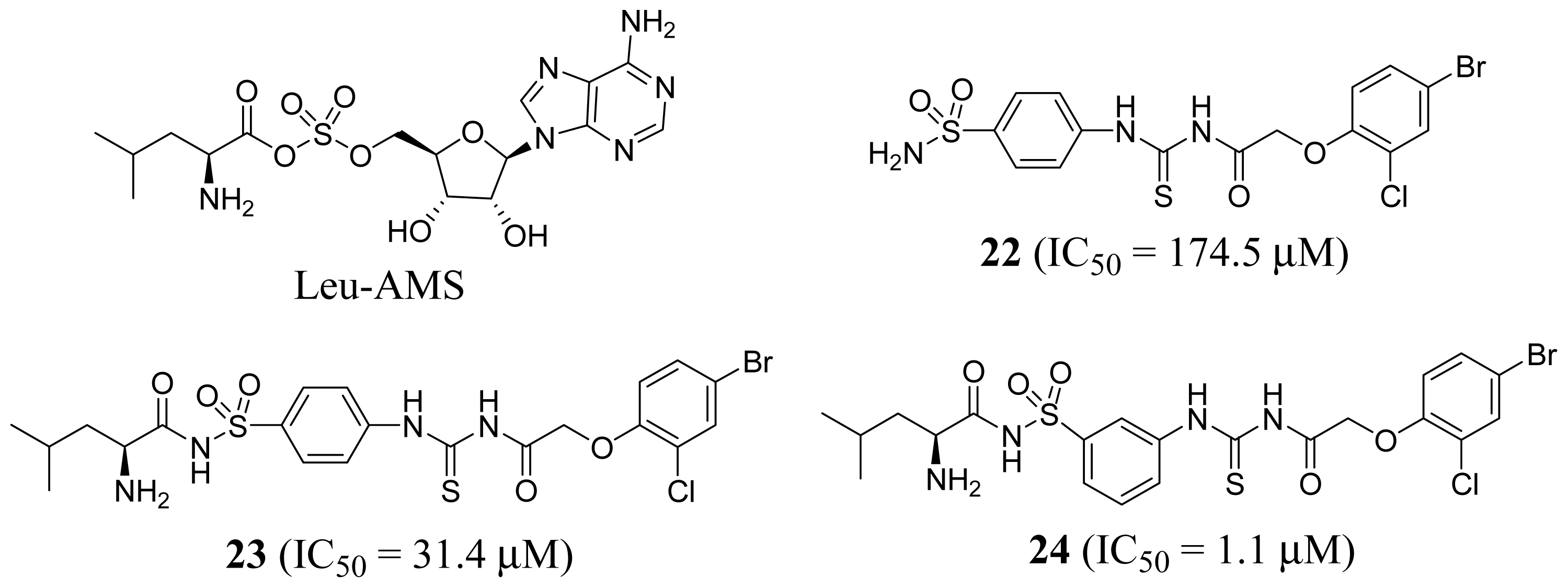
2.1. Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
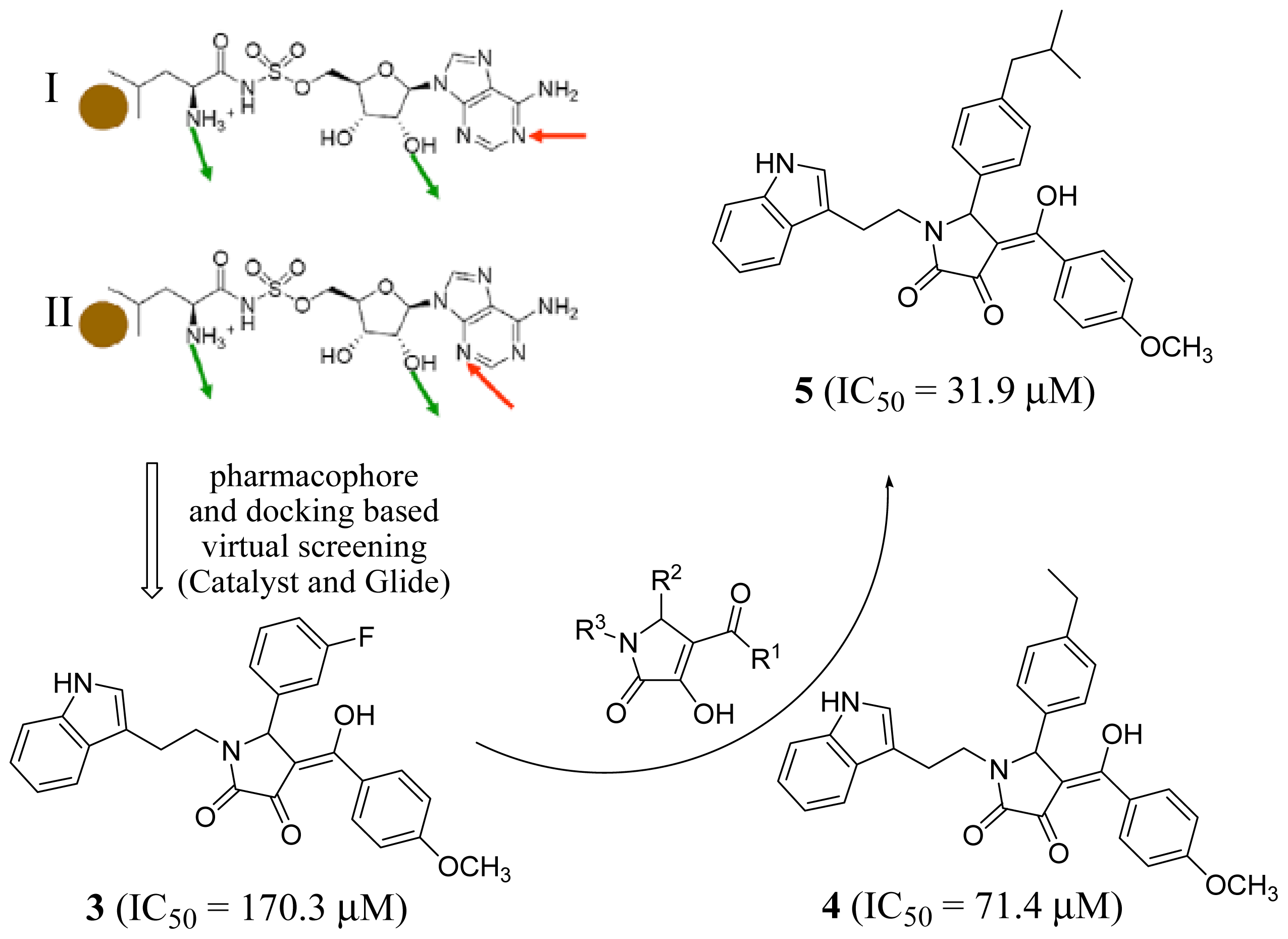
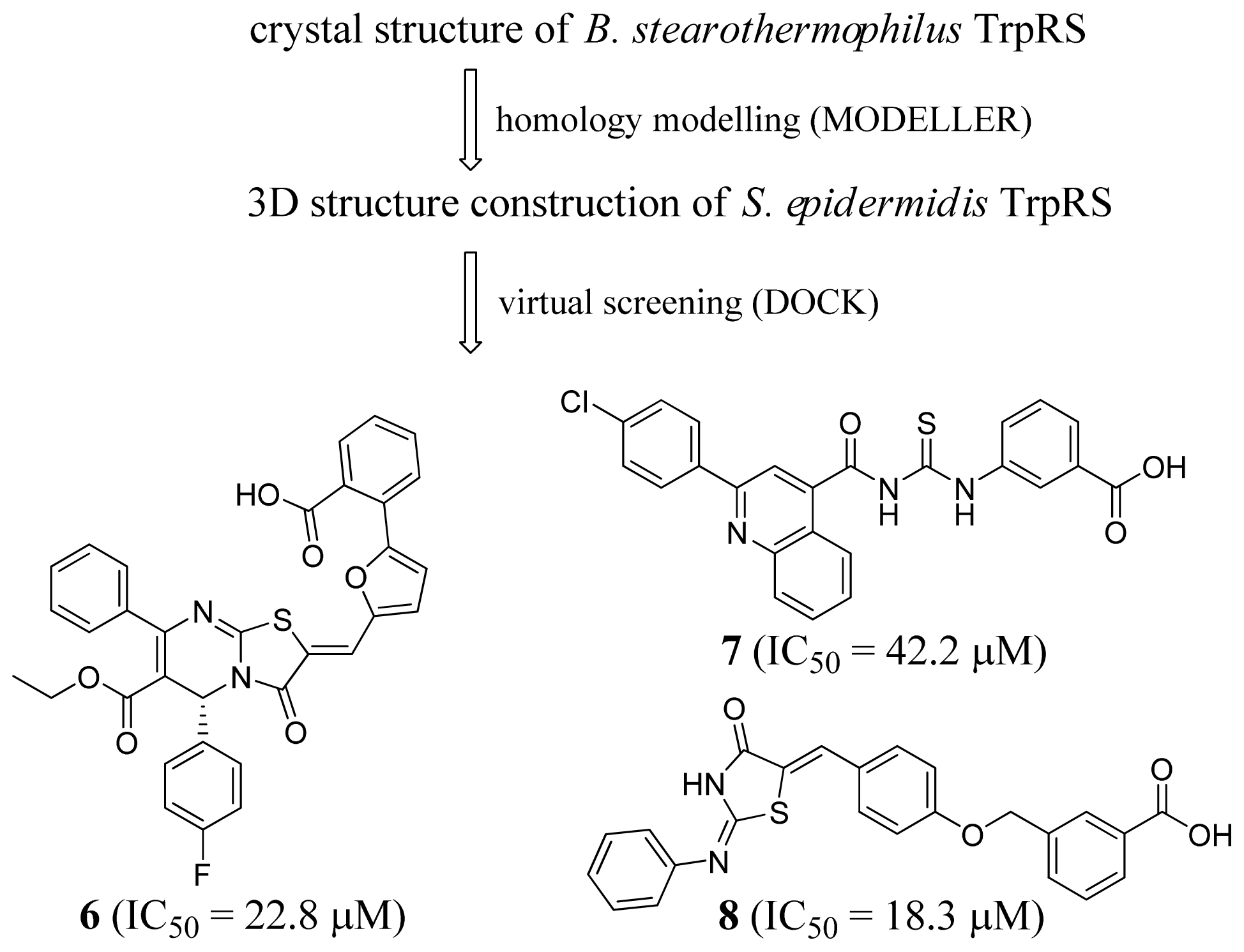
2.2. Tryptophanyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
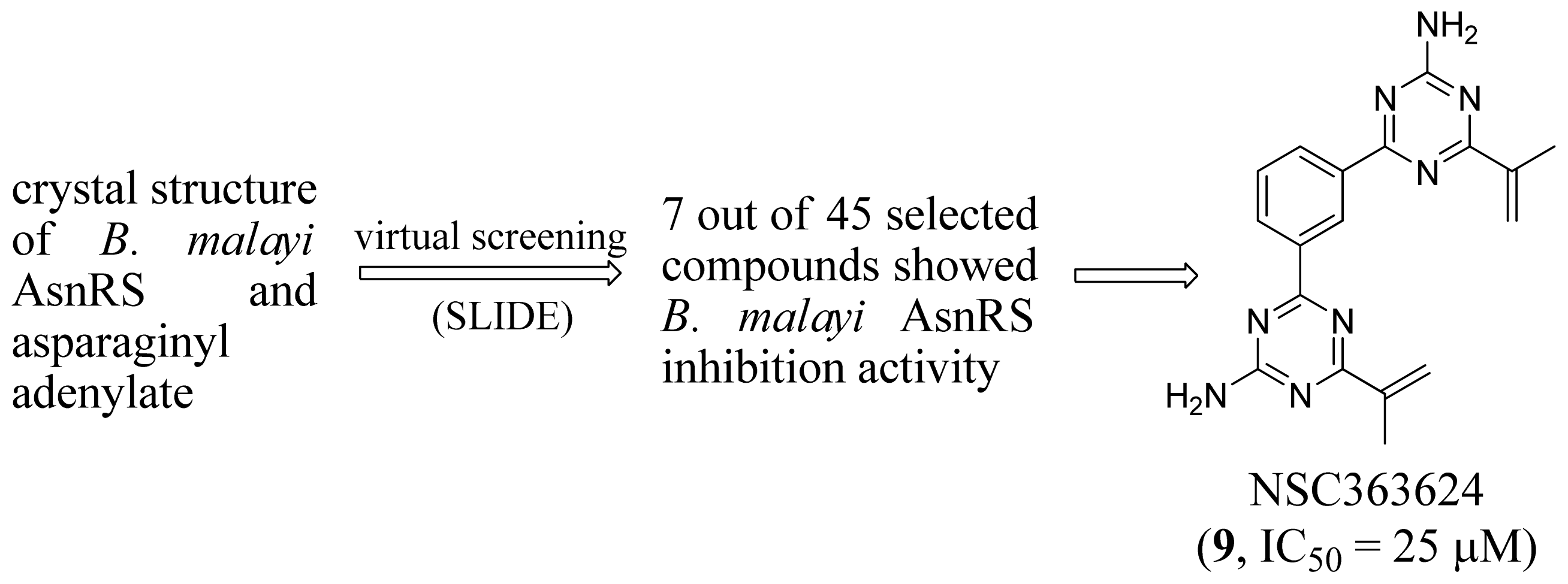
2.3. Asparaginyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
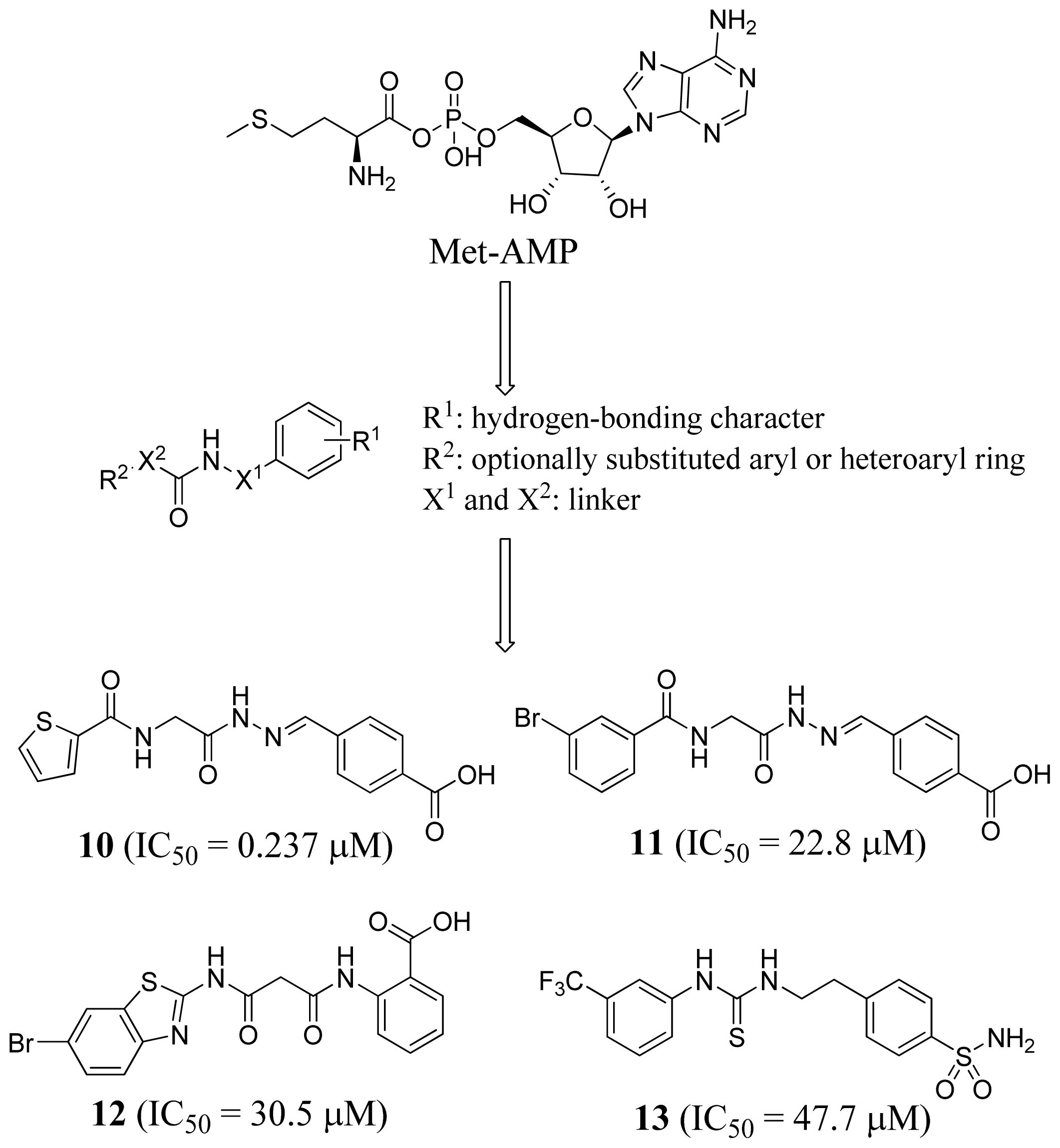
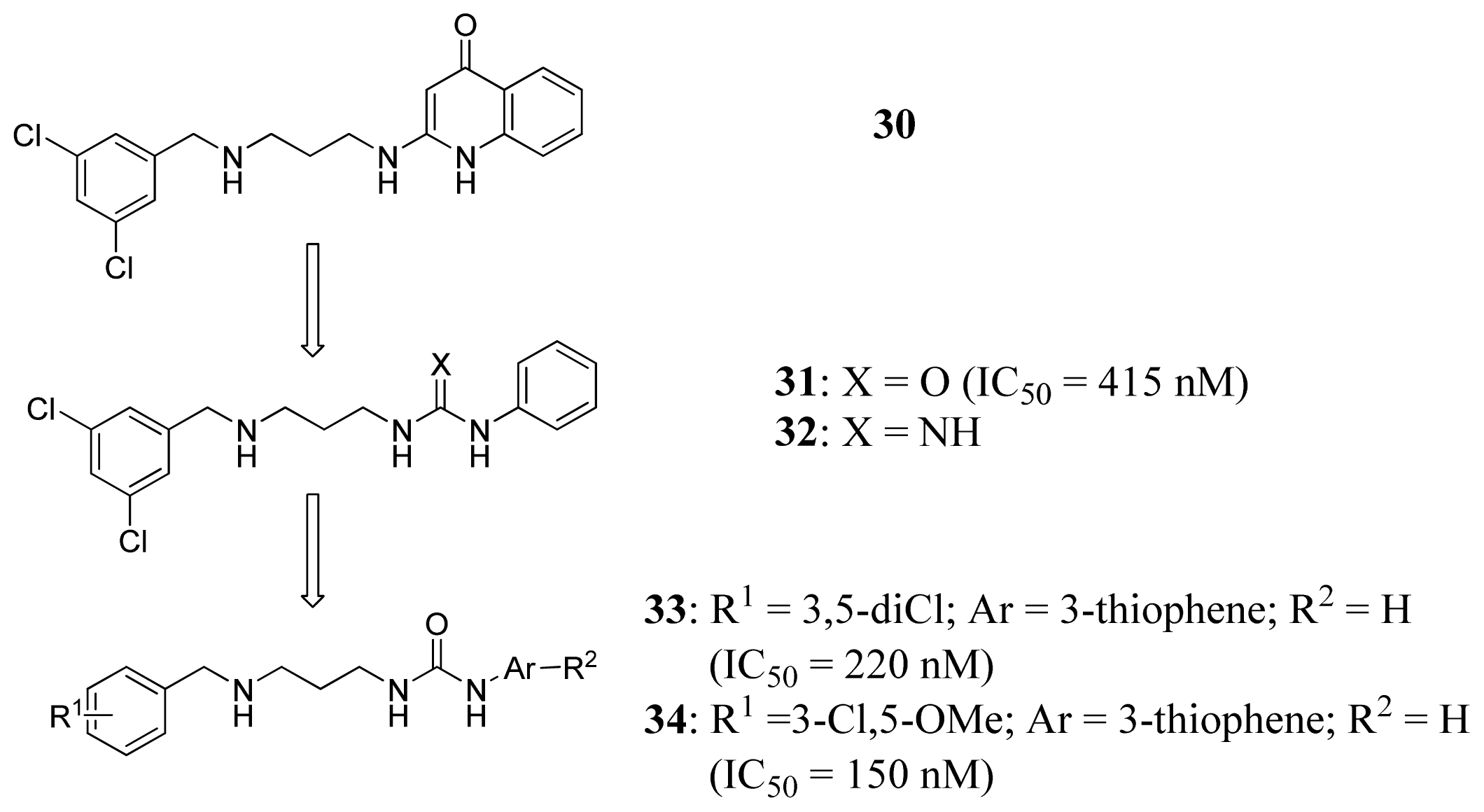
2.4. Methionyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
3. Inhibitor Identification Using Structure-Based Drug Design
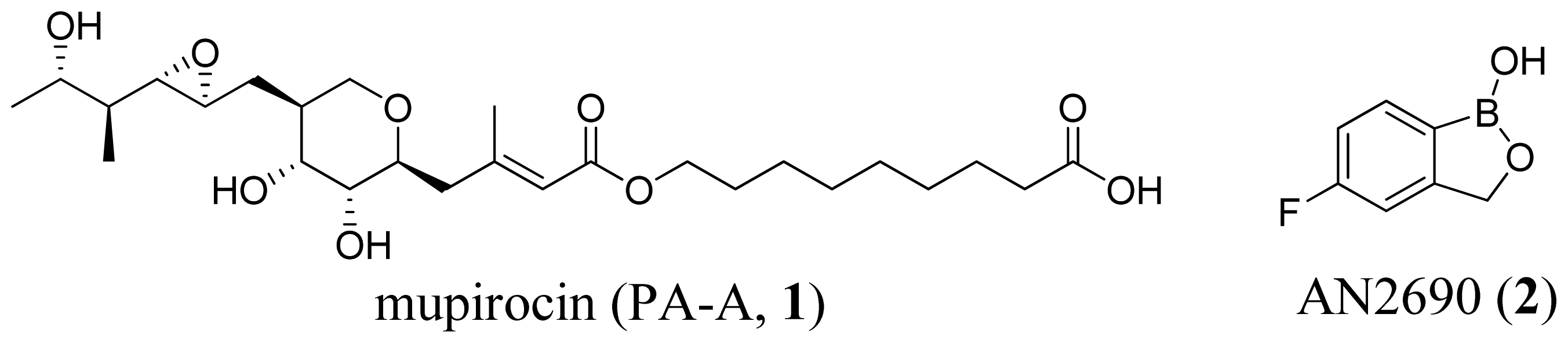
3.1. Leucyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
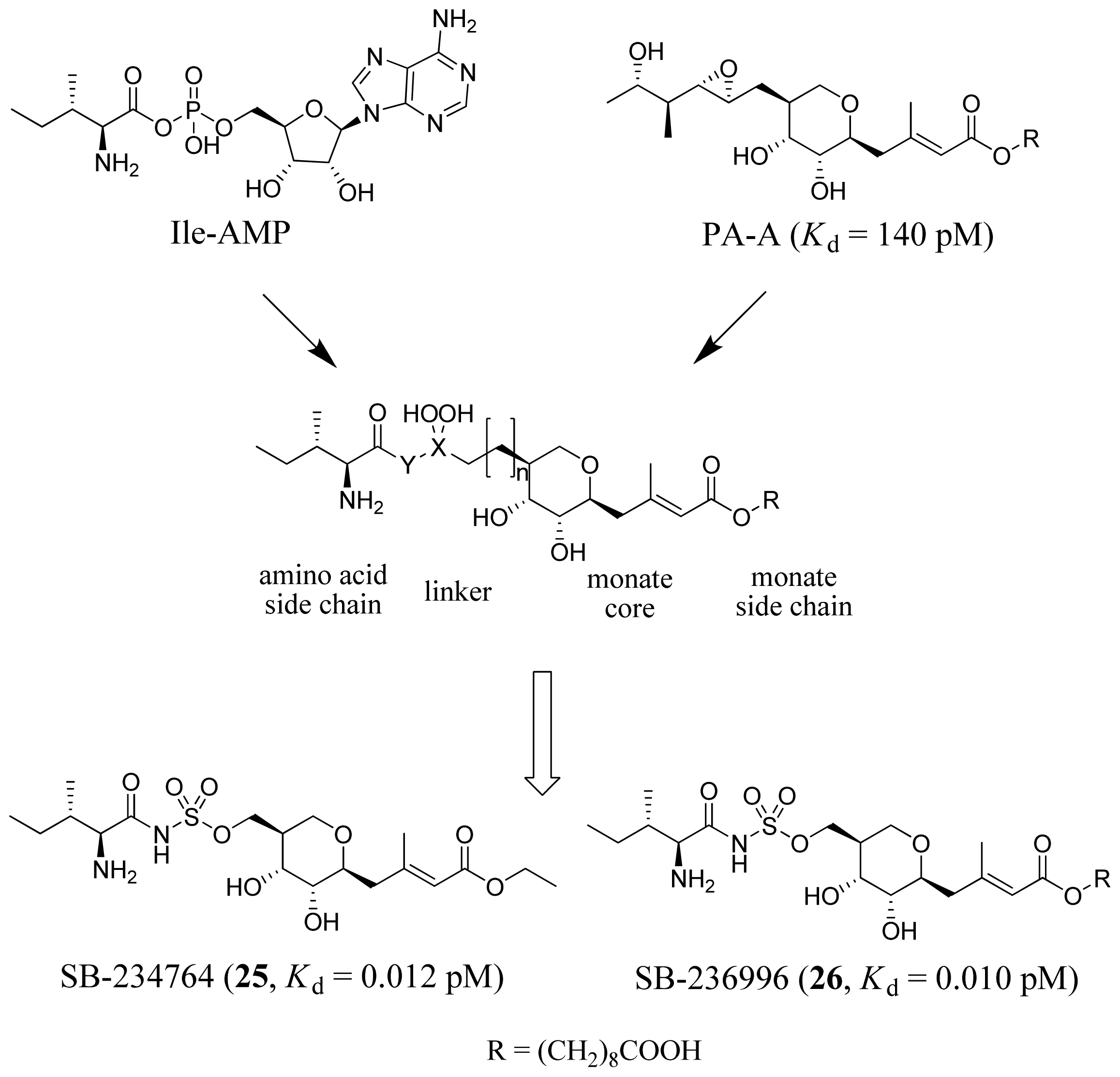
3.2. Isoleucyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
3.3. Threonyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
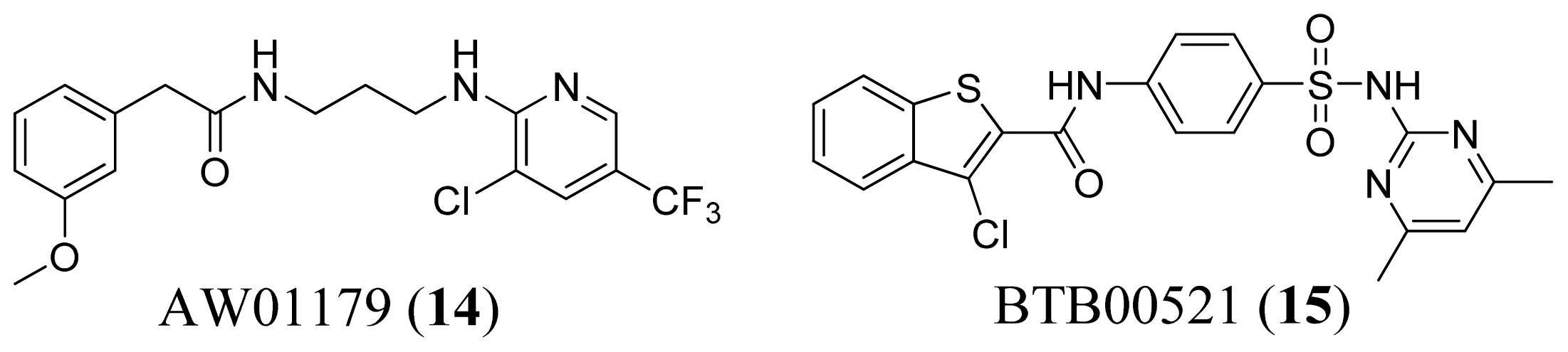
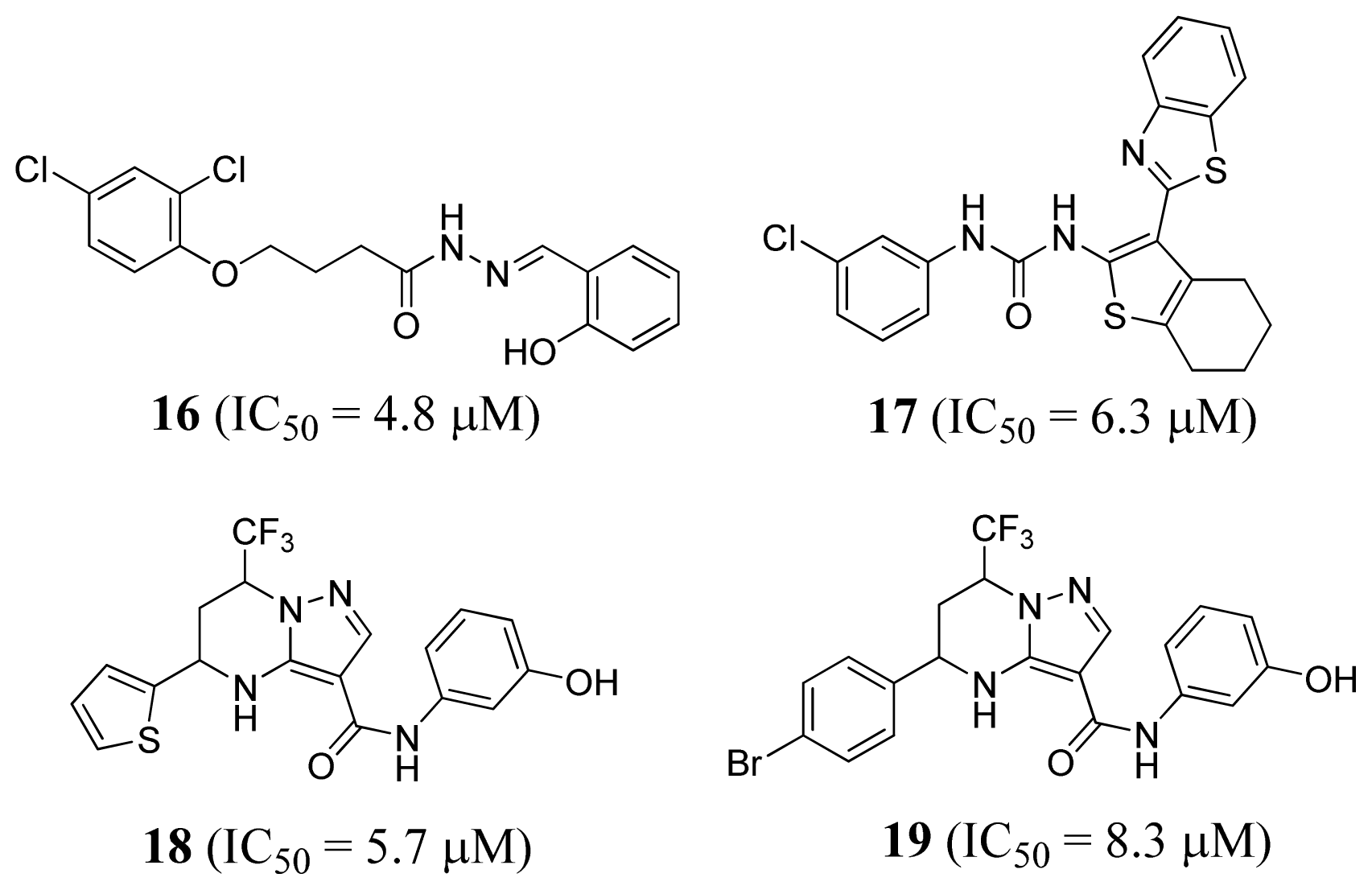
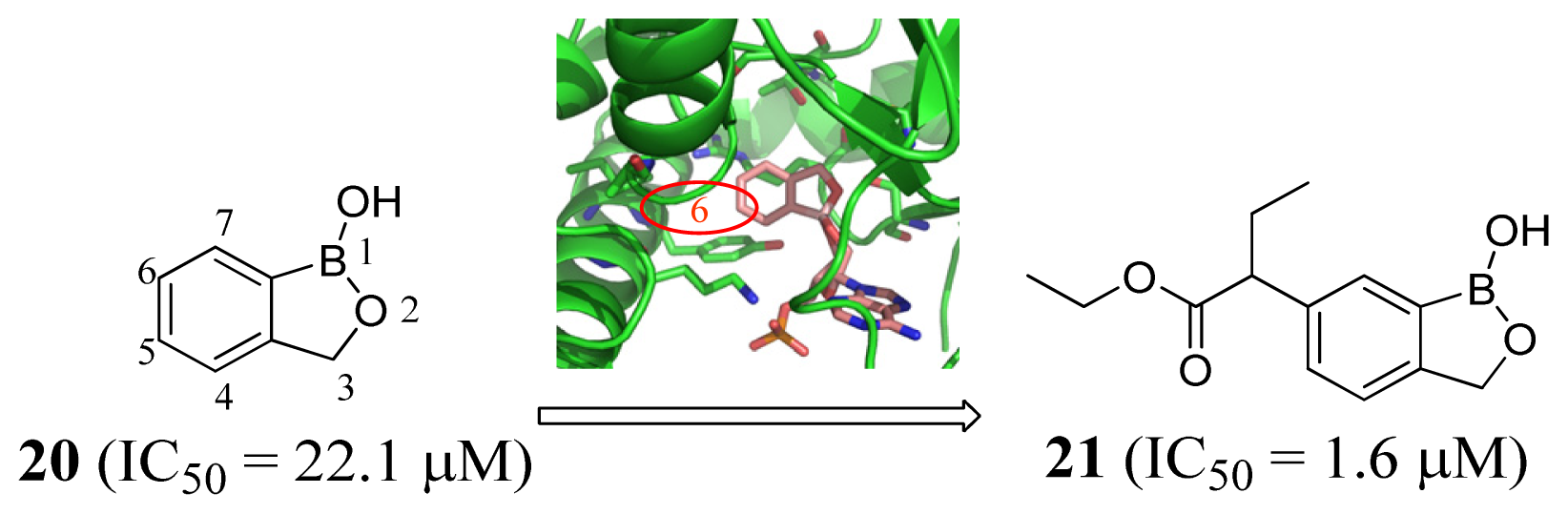
3.4. Methionyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ibba, M.; Soll, D. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem 2000, 69, 617–650. [Google Scholar]
- Eriani, G.; Delarue, M.; Poch, O.; Gangloff, J.; Moras, D. Partition of tRNA synthetases into two classes based on mutually exclusive sets of sequence motifs. Nature 1990, 347, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Arnez, J.G.; Moras, D. Structural and functional considerations of the aminoacylation reaction. Trends. Biochem. Sci 1997, 22, 211–216. [Google Scholar]
- Schimmel, P. Development of tRNA synthetases and connection to genetic code and disease. Protein Sci 2008, 17, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Lincecum, T.L., Jr.; Tukalo, M.; Yaremchuk, A.; Mursinna, R.S.; Williams, A.M.; Sproat, B.S.; van den Eynde, W.; Link, A.; van Calenbergh, S.; Grotli, M.; et al. Structural and mechanistic basis of pre- and posttransfer editing by leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 951–963. [Google Scholar]
- Jakubowski, H.; Goldman, E. Editing of errors in selection of amino acids for protein synthesis. Microbiol. Rev 1992, 56, 412–429. [Google Scholar]
- Beuning, P.J.; Musier-Forsyth, K. Hydrolytic editing by a class II aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 8916–8920. [Google Scholar]
- Dock-Bregeon, A.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Romby, P.; Caillet, J.; Springer, M.; Rees, B.; Francklyn, C.S.; Ehresmann, C.; Moras, D. Transfer RNA-mediated editing in threonyl-tRNA synthetase. The class II solution to the double discrimination problem. Cell 2000, 103, 877–884. [Google Scholar]
- Beaulieu, D.; Ohemeng, K.A. Patents on bacterial tRNA synthetase inhibitors: January 1996 to March 1999. Exp. Opin. Ther. Patents 1999, 9, 1021–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Seiradake, E.; Mao, W.; Hernandez, V.; Baker, S.J.; Plattner, J.J.; Alley, M.R.; Cusack, S. Crystal structures of the human and fungal cytosolic Leucyl-tRNA synthetase editing domains: A structural basis for the rational design of antifungal benzoxaboroles. J. Mol. Biol 2009, 390, 196–207. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Plattner, J.J.; Freund, Y.R.; Easom, E.E.; Zhou, Y.; Gut, J.; Rosenthal, P.J.; Waterson, D.; Gamo, F.J.; Angulo-Barturen, I.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of novel benzoxaboroles as a new class of antimalarial agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2011, 21, 644–651. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, D.; Meng, Q.; Gao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Nare, B.; Jacobs, R.; Rock, F.; Alley, M.R.; Plattner, J.J.; et al. Design, synthesis, and structure-activity relationship of Trypanosoma brucei leucyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors as antitrypanosomal agents. J. Med. Chem 2011, 54, 1276–1287. [Google Scholar]
- Chopra, S.; Palencia, A.; Virus, C.; Tripathy, A.; Temple, B.R.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Cusack, S.; Reader, J.S. Plant tumour biocontrol agent employs a tRNA-dependent mechanism to inhibit leucyl-tRNA synthetase. Nat. Commun 2013, 4, 1417. [Google Scholar]
- Van de Vijver, P.; Ostrowski, T.; Sproat, B.; Goebels, J.; Rutgeerts, O.; van Aerschot, A.; Waer, M.; Herdewijn, P. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors as potent and synergistic immunosuppressants. J. Med. Chem 2008, 51, 3020–3029. [Google Scholar]
- Ataide, S.F.; Ibba, M. Small molecules: Big players in the evolution of protein synthesis. ACS Chem. Biol 2006, 1, 285–297. [Google Scholar]
- Hurdle, J.G.; O’Neill, A.J.; Chopra, I. Prospects for aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors as new antimicrobial agents. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2005, 49, 4821–4833. [Google Scholar]
- Hurdle, J.G.; O’Neill, A.J.; Ingham, E.; Fishwick, C.; Chopra, I. Analysis of mupirocin resistance and fitness in Staphylococcus aureus by molecular genetic and structural modeling techniques. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2004, 48, 4366–4376. [Google Scholar]
- Nakama, T.; Nureki, O.; Yokoyama, S. Structural basis for the recognition of isoleucyl-adenylate and an antibiotic, mupirocin, by isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. J. Biol. Chem 2001, 276, 47387–47393. [Google Scholar]
- Rock, F.L.; Mao, W.; Yaremchuk, A.; Tukalo, M.; Crepin, T.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.K.; Hernandez, V.; Akama, T.; Baker, S.J.; et al. An antifungal agent inhibits an aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase by trapping tRNA in the editing site. Science 2007, 316, 1759–1761. [Google Scholar]
- Lavecchia, A.; di Giovanni, C. Virtual screening strategies in drug discovery: A critical review. Curr. Med. Chem 2013, 20, 2839–2860. [Google Scholar]
- Shoichet, B.K.; McGovern, S.L.; Wei, B.; Irwin, J.J. Lead discovery using molecular docking. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol 2002, 6, 439–446. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy, A.S.; Pati, S.P.; Kumar, P.P.; Pradeep, H.N.; Sastry, G.N. Virtual screening in drug discovery—A computational perspective. Curr. Protein. Pept. Sci 2007, 8, 329–351. [Google Scholar]
- Zoete, V.; Grosdidier, A.; Michielin, O. Docking, virtual high throughput screening and in silico fragment-based drug design. J. Cell. Mol. Med 2009, 13, 238–248. [Google Scholar]
- PDB. Available online: http://www.pdb.org (accessed on 6 December 2013).
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J. Med. Chem 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar]
- Halgren, T.A.; Murphy, R.B.; Friesner, R.A.; Beard, H.S.; Frye, L.L.; Pollard, W.T.; Banks, J.L. Glide: A new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J. Med. Chem 2004, 47, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, G.; Willett, P.; Glen, R.C.; Leach, A.R.; Taylor, R. Development and validation of a genetic algorithm for flexible docking. J. Mol. Biol 1997, 267, 727–748. [Google Scholar]
- Moustakas, D.T.; Lang, P.T.; Pegg, S.; Pettersen, E.; Kuntz, I.D.; Brooijmans, N.; Rizzo, R.C. Development and validation of a modular, extensible docking program: DOCK 5. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 2006, 20, 601–619. [Google Scholar]
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. J. Comput. Chem 2010, 31, 455–461. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.H.; Kim, N.D.; Seong, B.L. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening: A review of recent applications. Expert. Opin. Drug Discov 2010, 5, 205–222. [Google Scholar]
- Discovery Studio; Accelrys Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013.
- Phase; Schrödinger LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2013.
- Wolber, G.; Langer, T. LigandScout: 3-D pharmacophores derived from protein-bound ligands and their use as virtual screening filters. J. Chem. Inf. Model 2005, 45, 160–169. [Google Scholar]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Chen, Y.P. Structure-based drug design to augment hit discovery. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 831–839. [Google Scholar]
- Zurcher, M.; Diederich, F. Structure-based drug design: Exploring the proper filling of apolar pockets at enzyme active sites. J. Org. Chem 2008, 73, 4345–4361. [Google Scholar]
- Reich, S.H.; Melnick, M.; Davies, J.F.; Appelt, K.; Lewis, K.K.; Fuhry, M.A.; Pino, M.; Trippe, A.J.; Nguyen, D.; Dawson, H.; et al. Protein structure-based design of potent orally bioavailable, nonpeptide inhibitors of human immunodeficiency virus protease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 3298–3302. [Google Scholar]
- Von Itzstein, M.; Wu, W.Y.; Kok, G.B.; Pegg, M.S.; Dyason, J.C.; Jin, B.; van Phan, T.; Smythe, M.L.; White, H.F.; Oliver, S.W.; et al. Rational design of potent sialidase-based inhibitors of influenza virus replication. Nature 1993, 363, 418–423. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.U.; Lew, W.; Williams, M.A.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Swaminathan, S.; Bischofberger, N.; Chen, M.S.; Mendel, D.B.; Tai, C.Y.; et al. Influenza neuraminidase inhibitors possessing a novel hydrophobic interaction in the enzyme active site: Design, synthesis, and structural analysis of carbocyclic sialic acid analogues with potent anti-influenza activity. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1997, 119, 681–690. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, C.U.; Lew, W.; Williams, M.A.; Wu, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, X.; Escarpe, P.A.; Mendel, D.B.; Laver, W.G.; Stevens, R.C. Structure-activity relationship studies of novel carbocyclic influenza neuraminidase inhibitors. J. Med. Chem 1998, 41, 2451–2460. [Google Scholar]
- Fukunaqa, R.; Yokoyama, S. Crystal structure of leucyl-tRNA synthetase from the archaeon Pyrococcus horikoshii reveals a novel editing domain orientation. J. Mol. Biol 2005, 346, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Q.; Meng, Q.; Ding, D.; Yang, H.; Gao, G.; Li, D.; Zhu, W.; Zhou, H. Identification of Trypanosoma brucei leucyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors by pharmacophore- and docking-based virtual screening and synthesis. Bioorg. Med. Chem 2012, 20, 1240–1250. [Google Scholar]
- SPECS. Available online: http://www.specs.net (accessed on 6 December 2013).
- Wu, Y.; Yu, K.; Xu, B.; Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Mao, J.; Danchin, A.; Shen, X.; Qu, D.; Jiang, H. Potent and selective inhibitors of Staphylococcus epidermidis tr yptophanyl-tRNA synthetase. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 2007, 60, 502–509. [Google Scholar]
- Retailleau, P.; Huang, X.; Yin, Y.; Hu, M.; Weinreb, V.; Vachette, P.; Vonrhein, C.; Bricogne, G.; Roversi, P.; Ilyin, V.; et al. Interconversion of ATP binding and conformational free energies by tryptophanyl-tRNA synthetase: Structures of ATP bound to open and closed, pre-transition-state conformations. J. Mol. Biol 2003, 325, 39–63. [Google Scholar]
- Sukuru, S.C.; Crepin, T.; Milev, Y.; Marsh, L.C.; Hill, J.B.; Anderson, R.J.; Morris, J.C.; Rohatgi, A.; O’Mahony, G.; Grotli, M.; et al. Discovering new classes of Brugia malayi asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors and relating specificity to conformational change. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 2006, 20, 159–178. [Google Scholar]
- Crepin, T.; Peterson, F.; Haertlein, M.; Jensen, D.; Wang, C.; Cusack, S.; Kron, M. A hybrid structural model of the complete Brugia malayi cytoplasmic asparaginyl-tRNA synthetase. J. Mol. Biol 2011, 405, 1056–1069. [Google Scholar]
- Cambridge Structural Database. Available online: http://cds.dl.ac.uk/cds/datasets/crys/csd/csd.html (accessed on 6 December 2013).
- National Cancer Institute Plated Compounds Database. Available online: http://cactus.nci.nih.gov/download/nci/ (accessed on 6 December 2013).
- Kim, S.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kang, T.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Pharmacophore-based virtual screening: The discovery of novel methionyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2006, 16, 4898–4907. [Google Scholar]
- Bharatham, N.; Bharatham, K.; Lee, K.W. Pharmacophore identification and virtual screening for methionyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors. J. Mol. Graph. Model 2007, 25, 813–823. [Google Scholar]
- Maybridge. Available online: http://www.maybridge.com (accessed on 6 December 2013).
- Finn, J.; Stidham, M.; Hilgers, M.G.; C.K. Identification of novel inhibitors of methionyl-tRNA synthetase (MetRS) by virtual screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2008, 18, 3932–3937. [Google Scholar]
- ChemDiv. Available online: http://eu.chemdiv.com (accessed on 6 December 2013).
- Zhang, F.; Du, J.; Wang, Q.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ding, D.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, E.; Zhou, H. Discovery of N-(4-sulfamoylphenyl)thioureas as Trypanosoma brucei leucyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors. Org. Biomol. Chem 2013, 11, 5310–5324. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.J.; Mensah, L.M.; Doyle, M.L.; Broom, N.J.; Osbourne, N.; Forrest, A.K.; Richardson, C.M.; O’Hanlon, P.J.; Pope, A.J. Rational design of femtomolar inhibitors of isoleucyl tRNA synthetase from a binding model for pseudomonic acid-A. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 6003–6011. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, M.; Hilgers, M.T.; Cunningham, M.L.; Borchardt, A.; Locke, J.B.; Abraham, S.; Haley, G.; Kwan, B.P.; Hall, C.; Hough, G.W.; et al. Identification of bacteria-selective threonyl-tRNA synthetase substrate inhibitors by structure-based design. J. Med. Chem 2013, 56, 1748–1760. [Google Scholar]
- Sankaranarayanan, R.; Dock-Bregeon, A.C.; Rees, B.; Bovee, M.; Caillet, J.; Romby, P.; Francklyn, C.S.; Moras, D. Zinc ion mediated amino acid discrimination by threonyl-tRNA synthetase. Nat. Struct. Biol 2000, 7, 461–465. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, S.; Gillespie, J.R.; Kelley, A.M.; Napuli, A.J.; Zhang, Z.; Kovzun, K.V.; Pefley, R.M.; Lam, J.; Zucker, F.H.; Van Voorhis, W.C.; et al. Selective inhibitors of methionyl-tRNA synthetase have potent activity against Trypanosoma brucei infection in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2011, 55, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar]
- Shibata, S.; Gillespie, J.R.; Ranade, R.M.; Koh, C.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Laydbak, J.U.; Zucker, F.H.; Hol, W.G.; Verlinde, C.L.; Buckner, F.S.; et al. Urea-based inhibitors of Trypanosoma brucei methionyl-tRNA synthetase: Selectivity and in vivo characterization. J. Med. Chem 2012, 55, 6342–6351. [Google Scholar]
- Koh, C.Y.; Kim, J.E.; Shibata, S.; Ranade, R.M.; Yu, M.; Liu, J.; Gillespie, J.R.; Buckner, F.S.; Verlinde, C.L.; Fan, E.; et al. Distinct states of methionyl-tRNA synthetase indicate inhibitor binding by conformational selection. Structure 2012, 20, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar]
- Ranade, R.M.; Gillespie, J.R.; Shibata, S.; Verlinde, C.L.; Fan, E.; Hol, W.G.; Buckner, F.S. Induced resistance to methionyl-tRNA synthetase inhibitors in Trypanosoma brucei is due to overexpression of the target. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2013, 57, 3021–3028. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, R.; Green, L.; Sun, X.; Guiles, J.; Lorimer, D.; Burgin, A.; Janjic, N.; Jarvis, T.; Davies, D. Co-crystal structure of REP3123 bound to Clostridium difficile methionyl tRNA synthetase, poster F1−2114. Abstracts of the 47th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Proceedings of the 47th Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, Chicago, IL, USA, 17–20 September 2007; American Society for Microbiology: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
| Class | Subclass | aaRS |
|---|---|---|
| I | Ia | MetRS |
| ValRS | ||
| LeuRS | ||
| IleRS | ||
| CysRS | ||
| ArgRS | ||
| Ib | GluRS | |
| GlnRS | ||
| LysRS-I | ||
| Ic | TyrRS | |
| TrpRS | ||
| II | IIa | SerRS |
| ThrRS | ||
| AlaRS | ||
| GlyRS | ||
| ProRS | ||
| HisRS | ||
| IIb | AspRS | |
| AsnRS | ||
| LysRS-II | ||
| IIc | PheRS | |
| ID | MIC (μM) | |
|---|---|---|
| S. epidermidis ATCC 12228 | S. epidermidis ATCC 35984 | |
| 6 | 6.25 | 6.25 |
| 7 | 25 | 25 |
| 8 | 100 | 100 |
| ID | Structure | ThrRS Ki (nM) | Selectivity ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| E. coli | Human | Human/E.coli | ||
| 27 | 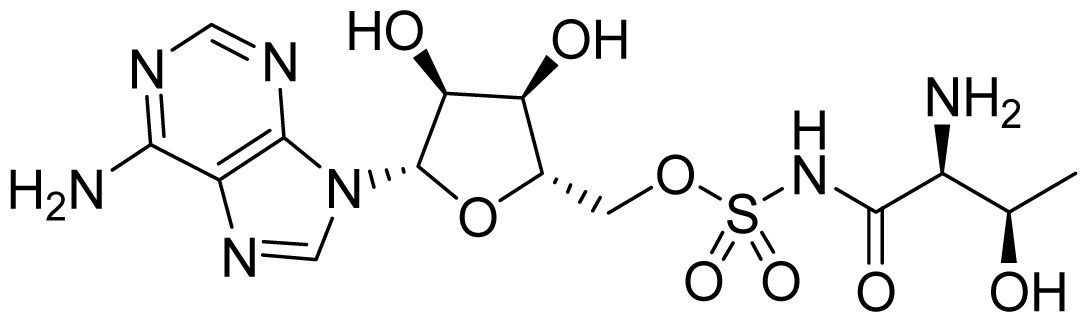 | 13.1 | 13.4 | 1 |
| 28 | 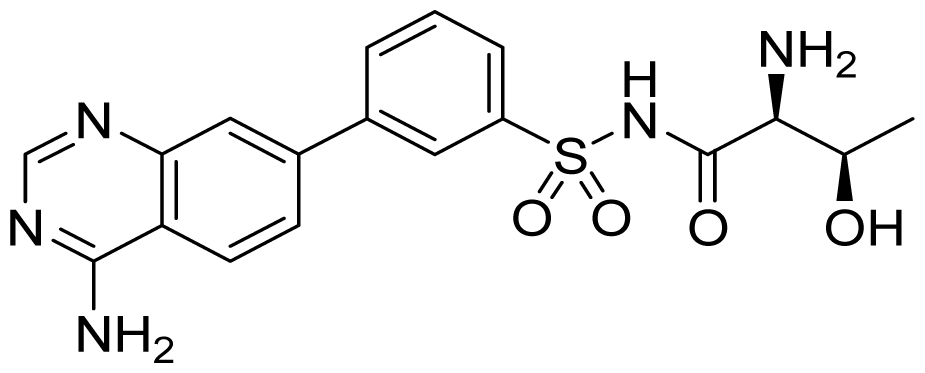 | 2.9 | 3.3 | 1.1 |
| 29 | 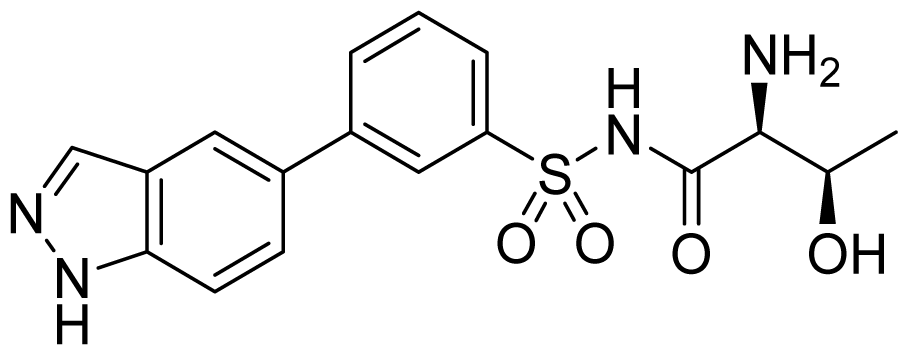 | 182 | >50,000 | >270 |
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y.; Meng, Q.; Bai, L.; Zhou, H. In Silico Discovery of Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1358-1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15011358
Zhao Y, Meng Q, Bai L, Zhou H. In Silico Discovery of Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(1):1358-1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15011358
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yaxue, Qingqing Meng, Linquan Bai, and Huchen Zhou. 2014. "In Silico Discovery of Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 1: 1358-1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15011358
APA StyleZhao, Y., Meng, Q., Bai, L., & Zhou, H. (2014). In Silico Discovery of Aminoacyl-tRNA Synthetase Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(1), 1358-1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15011358





