Effect and Mechanism of Mitomycin C Combined with Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Type II against Glioma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
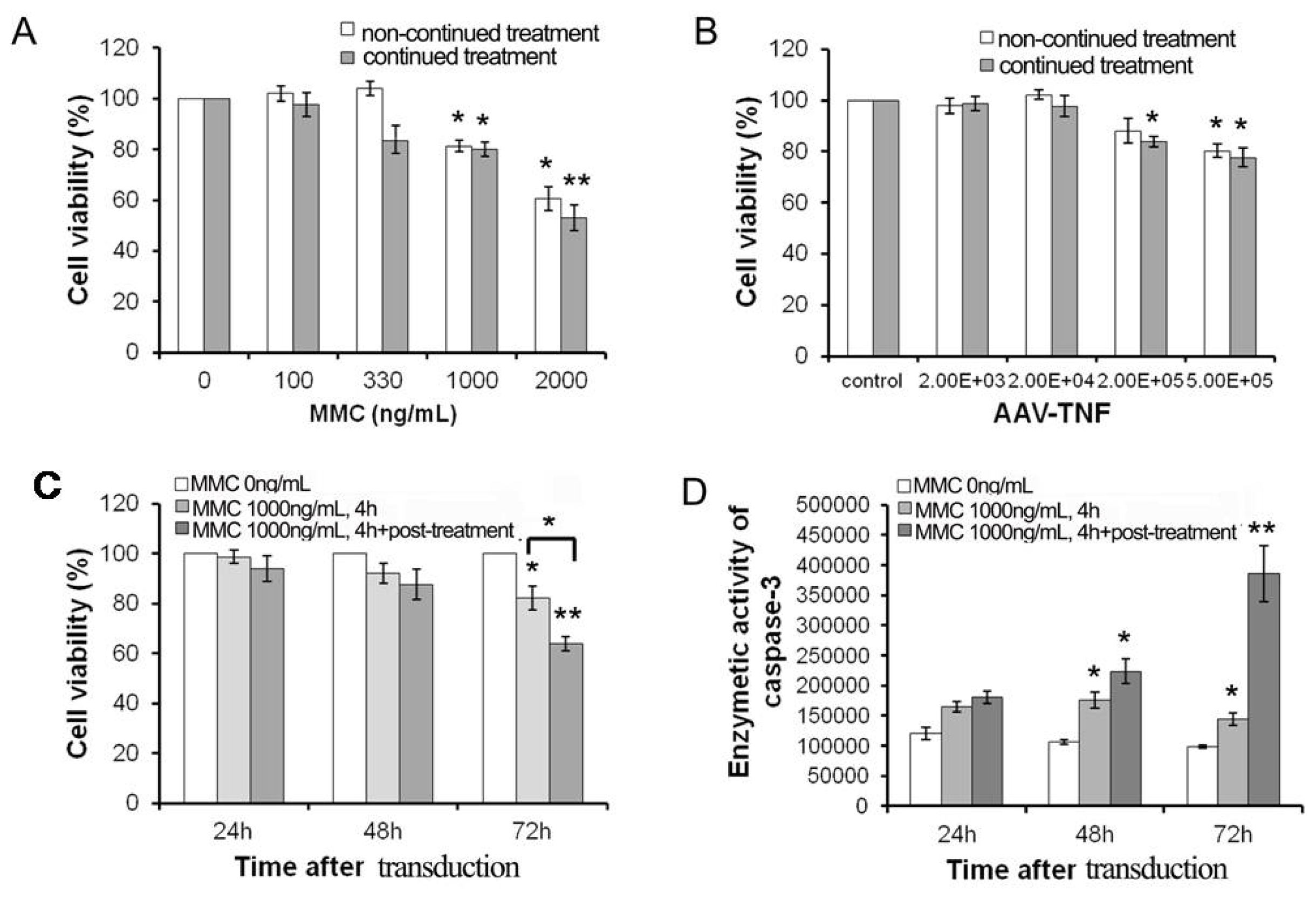
2.1. The Sensitivity of U251 Cell Line to MMC and rAAV-TNF in Vitro
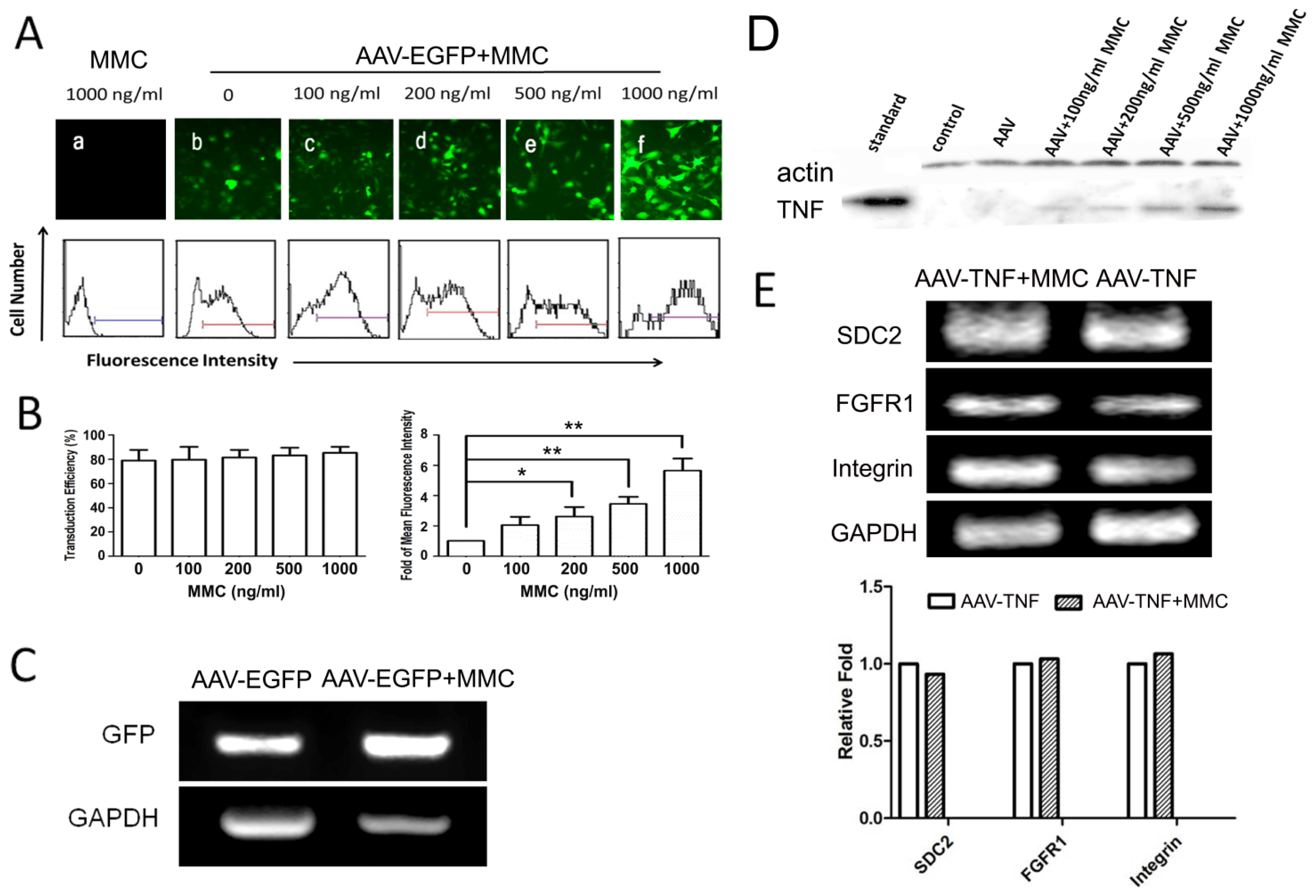
2.2. MMC Enhances rAAV-Mediated Transgene Expression but Does not Augment Transduction Efficiency
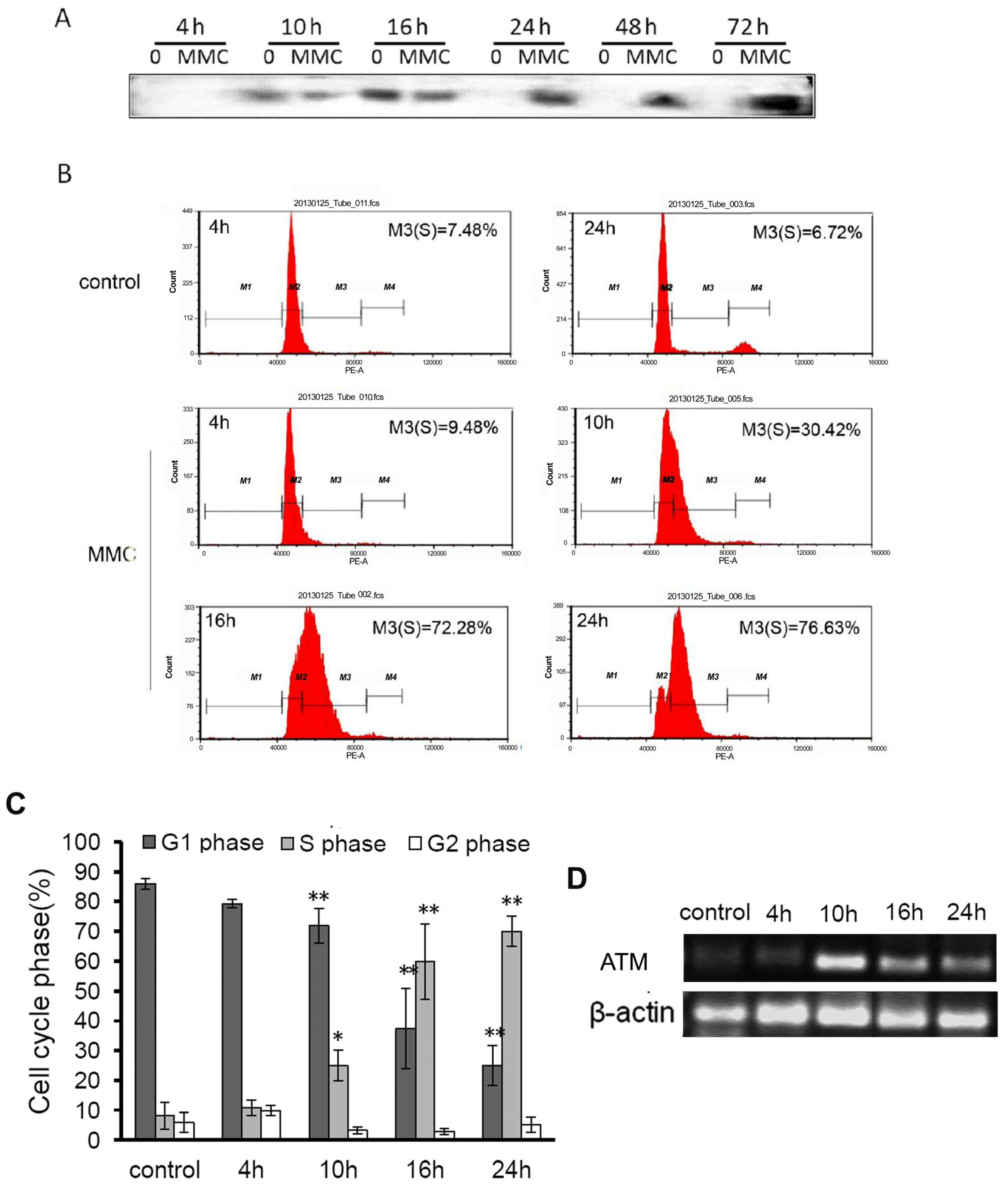
2.3. The Effect of MMC on the Genome of Targeted Cells Infected by rAAV
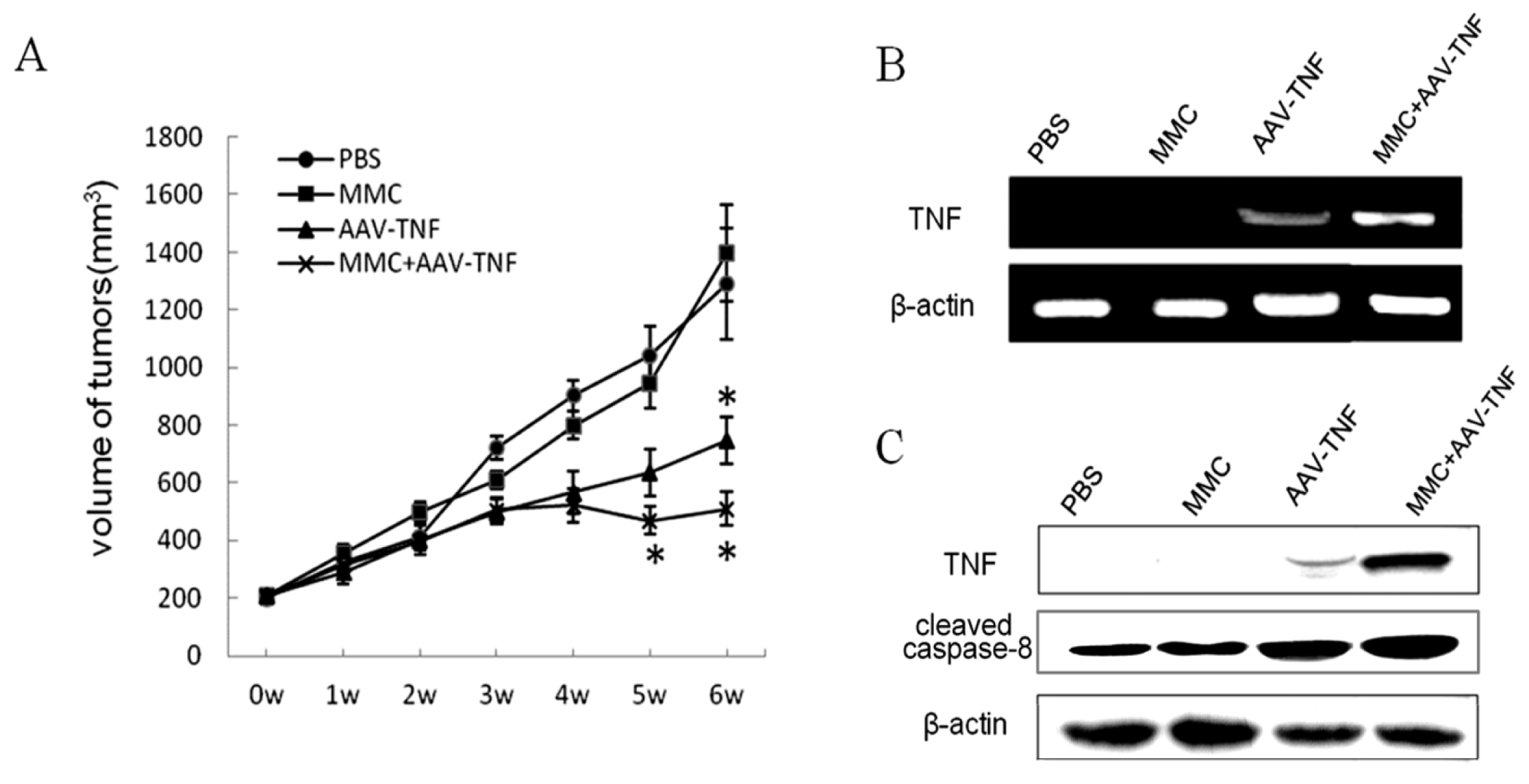
2.4. Improvement of rAAV-Mediated Gene Expression by MMC in Vivo
2.5. Killing Effect of AAV-TNF with MMC after Intratumoral Injections
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Cell Culture and Reagents
3.2. Cell Infection with rAAV and Treatment with MMC
3.3. FACS Assay
3.4. Western Blot Assay
3.5. RT-PCR Assay
3.6. Southern Blot Assay
3.7. Experimental Animal Model and Tumorigenic Assay
3.8. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bartlett, J.S.; Samulski, R.J.; McCown, T.J. Selective and rapid uptake of adeno-associated virus type 2 in brain. Hum. Gene Ther 1998, 9, 1181–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Manno, C.S.; Chew, A.J.; Hutchison, S.; Larson, P.J.; Herzog, R.W.; Arruda, V.R.; Tai, S.J.; Ragni, M.V.; Thompson, A.; Ozelo, M.; et al. AAV-mediated factor IX gene transfer to skeletal muscle in patients with severe hemophilia B. Blood 2003, 101, 2963–2972. [Google Scholar]
- Grieger, J.C.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-associated virus as a gene therapy vector: Vector development, production and clinical applications. Adv. Biochem. Eng. Biotechnol 2005, 99, 119–145. [Google Scholar]
- Summerford, C.; Samulski, R.J. Membrane-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycan is a receptor for adeno-associated virus type 2 virions. J. Virol 1998, 72, 1438–1445. [Google Scholar]
- Qing, K.; Mah, C.; Hansen, J.; Zhou, S.; Dwarki, V.; Srivastava, A. Human fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is a co-receptor for infection by adeno-associated virus 2. Nat. Med 1999, 5, 71–77. [Google Scholar]
- Summerford, C.; Bartlett, J.S.; Samulski, R.J. αVβ5 integrin: A co-receptor for adeno-associated virus type 2 infection. Nat. Med 1999, 5, 78–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.; Zhang, L.; Yan, Z.; Engelhardt, J. Intracellular trafficking of adeno-associated viral vectors. Gene Ther 2005, 12, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Faust, S.M.; Rabinowitz, J.E. The next step in gene delivery: Molecular engineering of adeno-associated virus serotypes. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol 2011, 50, 793–802. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Asokan, A.; Samulski, R.J. Adeno-associated virus serotypes: Vector toolkit for human gene therapy. Mol. Ther 2006, 14, 316–327. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, F.K.; Samulski, T.; Shenk, T.; Samulski, R.J. Second-strand synthesis is a rate-limiting step for efficient transduction by recombinant adeno-associated virus vectors. J. Virol 1996, 70, 3227–3234. [Google Scholar]
- Fisher, K.J.; Gao, G.P.; Weitzman, M.D.; DeMatteo, R.; Burda, J.F.; Wilson, J.M. Transduction with recombinant adeno-associated virus for gene therapy is limited by leading-strand synthesis. J. Virol 1996, 70, 520–532. [Google Scholar]
- Kume, A.; Nishino, H.; Monahan, J.; Kitamura, K.; Ichimura, K. Gamma-Rays enhance rAAV-mediated transgene expression and cytocidal effect of AAV-HSVtk/ganciclovir on cancer cells. Cancer Gene Ther 2001, 8, 99–106. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, I.E.; Russell, D.W.; Miller, A. DNA-damaging agents greatly increase the transduction of nondividing cells by adeno-associated virus vectors. J. Virol 1994, 68, 8282–8287. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Lo, C.; Lin, B.; Sibley, E.; Tang, S. Application of doxorubicin-induced rAAV2-p53 gene delivery in combined chemotherapy and gene therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Ther 2008, 7, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.H.; Liu, Z.; Xiang, Y.; Ma, H.; Liu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D. Synergistic antitumor effect of AAV-mediated TRAIL expression combined with cisplatin on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2011, 11, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, F.; Cai, H.; Wu, Y.; He, G.; Tan, W.S. The efficacy of combination therapy using adeno-associated virus-TRAIL targeting to telomerase activity and cisplatin in a mice model of hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin 2010, 136, 1827–1837. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Hu, J.; Ding, W.; Wang, X. Doxorubicin augments rAAV-2 transduction in rat neuronal cells. Neurochem. Int 2009, 55, 521–528. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Z.; Zak, R.; Zhang, Y.; Ding, W.; Godwin, S.; Munson, K.; Peluso, R.; Engelhardt, J.F. Distinct classes of proteasome-modulating agents cooperatively augment recombinant adeno-associated virus type 2 and type 5-mediated transduction from the apical surfaces of human airway epithelia. J. Virol 2004, 78, 2863–2874. [Google Scholar]
- Kanazawa, T.; Mizukami, H.; Okada, T.; Hanazono, Y.; Kume, A.; Nishino, H.; Takeuchi, K.; Kitamura, K.; Ichimura, K.; Ozawa, K. Suicide gene therapy using AAV-HSVtk/ganciclovir in combination with irradiation results in regression of human head and neck cancer xenografts in nude mice. Gene Ther 2003, 10, 51–58. [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, V.N.; Szybalski, W. A molecular mechanism of mitomycin action: Linking of complementary DNA strands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1963, 50, 355–362. [Google Scholar]
- Mitomycin, C. Health-Based Calculated Occupational Cancer Risk Values; Health Council of the Netherlands: The Hague, The Netherlands, 2004; Publication 2004/05OSH; ISBN 90-5549-536-0. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, V.W.; McCarty, D.M.; Samulski, R.J. Host cell DNA repair pathways in adeno-associated viral genome processing. J. Virol 2006, 80, 10346–10356. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, D.; Qian, C.; Sun, Y.; Barajas, M.A.; Prieto, J. Transduction of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) using recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV): In vitro and in vivo effects of genotoxic agents. J. Hepatol 2000, 32, 975–985. [Google Scholar]
- Sanlioglu, S.; Duan, D.; Engelhardt, J.F. Two independent molecular pathways for recombinant adeno-associated virus genome conversion occur after UV-C and E4orf6 augmentation of transduction. Hum. Gene Ther 1999, 10, 591–602. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, A.Y.; Chiba, T.; Truong, L.N.; Cheng, A.N.; Do, J.; Cho, M.J.; Chen, L.; Wu, X. Dbf4 is a direct downstream target of ATM and ATR to regulate the intra S-phase checkpoint. J. Biol. Chem 2012, 287, 2531–2543. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Kleckner, N.E.; Storlazzi, A.; Kim, K.P. Meiotic double-strand breaks occur once per pair of (sister) chromatids and, via Mec1/ATR and Tel1/ATM, once per quartet of chromatids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20036–20041. [Google Scholar]
- Mladenov, E.; Tsaneva, I.; Anachkova, B. Activation of the S phase DNA damage checkpoint by mitomycin C. J. Cell Physiol 2007, 211, 468–476. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, C.E.; Nienhuis, A.W.; Samulski, R.J.; Brown, M.G.; Miller, J.L.; Young, N.S.; Liu, J.M. Phenotypic correction of Fanconi Anemia in human hemotopoietic cells with a recombinant adeno-associated virus vector. J. Clin. Invest 1994, 94, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]

© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Han, C.; Lei, R.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Z.; Rao, L.; Qing, H.; Xiang, J.; et al. Effect and Mechanism of Mitomycin C Combined with Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Type II against Glioma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010001
Ma H, Zhang Y, Wang H, Han C, Lei R, Zhang L, Yang Z, Rao L, Qing H, Xiang J, et al. Effect and Mechanism of Mitomycin C Combined with Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Type II against Glioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2014; 15(1):1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010001
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Hong, Yunjia Zhang, Hailong Wang, Chuanhui Han, Runhong Lei, Lei Zhang, Zuye Yang, Ling Rao, Hong Qing, Jim Xiang, and et al. 2014. "Effect and Mechanism of Mitomycin C Combined with Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Type II against Glioma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15, no. 1: 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010001
APA StyleMa, H., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Han, C., Lei, R., Zhang, L., Yang, Z., Rao, L., Qing, H., Xiang, J., & Deng, Y. (2014). Effect and Mechanism of Mitomycin C Combined with Recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus Type II against Glioma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 15(1), 1-14. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms15010001



