Abstract
Quorum sensing is a cell density-dependent signaling phenomenon used by bacteria for coordination of population-wide phenotypes, such as expression of virulence genes, antibiotic resistance and biofilm formation. Lately, disruption of bacterial communication has emerged as an anti-virulence strategy with enormous therapeutic potential given the increasing incidences of drug resistance in pathogenic bacteria. The quorum quenching therapeutic approach promises a lower risk of resistance development, since interference with virulence generally does not affect the growth and fitness of the bacteria and, hence, does not exert an associated selection pressure for drug-resistant strains. With better understanding of bacterial communication networks and mechanisms, many quorum quenching methods have been developed against various clinically significant bacterial pathogens. In particular, Gram-negative bacteria are an important group of pathogens, because, collectively, they are responsible for the majority of hospital-acquired infections. Here, we discuss the current understanding of existing quorum sensing mechanisms and present important inhibitory strategies that have been developed against this group of pathogenic bacteria.
1. Introduction
Bacterial quorum sensing has attracted significant research interest since its initial discovery in the marine bacterium, Vibrio fischeri, almost four decades ago [1]. Recent progress includes the identification of new quorum sensing systems and a broader understanding of how bacteria organize collective action. One of the main reasons behind this gathered interest is the importance of quorum sensing in bacterial pathogenesis [2]. Quorum sensing regulates the expression of virulence genes through intercellular communication; this is mediated by quorum molecules and receptors in a density-dependent manner [3]. The apparent advantage of such interactions is the ability to coordinate population-wide phenotypes for effective host colonization and disease progression. Naturally, significant efforts have been focused on quorum sensing disruption, due to its role as a “master switch” in virulence control. Blocking communication can potentially prevent bacterial pathogenesis [4]. In terms of recent advancement, quorum sensing disruption is one of the emerging anti-virulence strategies against bacterial infections [5].
An anti-virulence approach is relevant in the current context, as antibiotics are losing their efficacy, and many bacteria are becoming multi-drug resistant (MDR) [6]. Although fundamentally effective against bacterial infections, antibiotics exert considerable selection pressure, as they target growth processes, such as nucleic acid replication and cell wall biosynthesis [7]. The eventual growth arrest and cell death can be followed by rapid expansion of resistant subpopulations, making subsequent treatment difficult or impossible [8]. However, it is the rate at which bacteria gain resistance that is alarming; these therapeutic agents were only in clinical use for just over half a century, and incidences of resistance have rapidly surfaced [9]. Over-prescription of antibiotics is the primary cause, as clinicians underestimated the long-term effects of these drugs. Faced with the risk of losing this treatment method, antibiotic prescription became better regulated and usage was often reserved for severe conditions [10]. Consequently, there are now limited treatment options for many infections, as bacterial evolution has outpaced drug development [11]. New anti-bacterial strategies are therefore required, and methods that aim to disable pathogenesis can prevent further development of drug resistance.
A quorum-based method can provide several approaches for virulence disruption (Figure 1). In general, this is achieved via impeding the interaction between a quorum molecule and its cognate receptor. More importantly, quorum sensing is not essential for growth; hence, its disruption is unlikely to affect primary metabolic pathways necessary for survival [4]. Since fitness is not compromised, there is no associated selection pressure for the bacteria to evolve and acquire resistance against such treatments [12]. This is an advantage over traditional antibiotic methods, as bacterial pathogenesis can be mitigated without running the risk of immunity development; in addition, targeting bacterial quorum sensing also results in the attenuation of bacterial biofilm formation and the associated resistance to antibiotics [13,14]. In such cases, disruption of this signaling event can interfere with inherent bacterial protective mechanisms. With the recent understanding that quorum sensing is present in most bacteria species, this method presents great promise in the fight against bacterial pathogens.
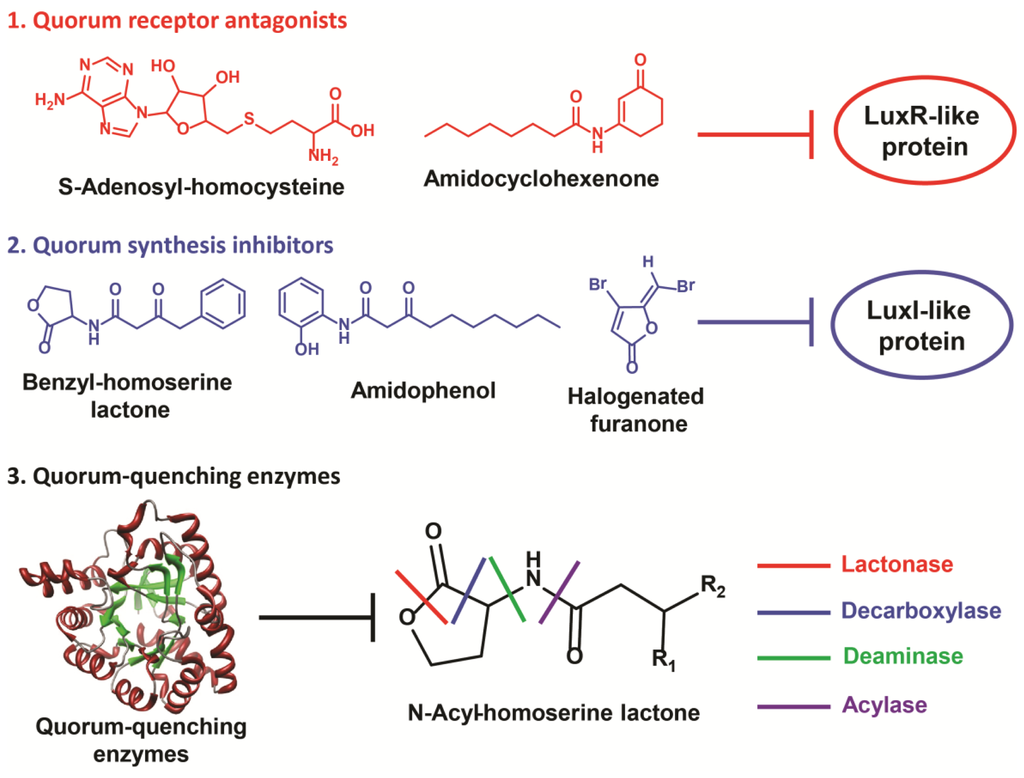
Figure 1.
Anti-virulence strategies to disrupt bacterial quorum circuits.
Gram-negative bacterial pathogens account for the majority of hospital-acquired infections, resulting in extensive mortality and burden on global healthcare systems [15]. Reports have indicated that hospital-acquired infections complicate treatments and lead to an increasing risk of death. In a study conducted on intensive care unit (ICU) patients, a higher risk of infection was associated with longer ICU stays, and the mortality of infected patients doubled as compared to uninfected patients [16]. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Klebsiella pneumoniae are known to be highly problematic in the ICU milieu, due to their affiliation with a multitude of nosocomial infections. More recently, some Enterobacter species, Escherichia coli and Acinetobacter baumannii, were added to this group as associated complications in bloodstream, surgical site and urinary tract infections continue to rise [17]. The severity of hospital-acquired infections is contributed by pathogens developing resistance against a wide variety of drugs. Certain strains of P. aeruginosa, K. pneumoniae and A. baumannii that are resistant to all antibiotics, also known as pan-drug resistant (PDR), have already been identified and are associated with considerable mortality [18]. Extended-spectrum β-lactamase (ESBL)-producing Enterobacter and E. coli are also proving very hard to treat, due to acquired resistance against broad spectrum drugs, such as cephalosporins, carbapenems and even non-β-lactams, such as fluoroquinolones [19,20]. Collectively, this group of Gram-negative bacterial pathogens account for the majority of nosocomial life-threatening infections; the challenge is on the research community to find new and more effective agents or methods to mediate the biomedical situation.
Given the current issue of antibiotic resistance and optimism in anti-virulence strategies, considerable work has been done to explore quorum sensing disruption in clinically important pathogens. This review focuses on Gram-negative bacterial pathogens and aims to provide a detailed account of quorum sensing regulation and strategies for the future advancement of anti-virulence therapeutic development.
2. Quorum Sensing in Gram-Negative Bacteria
2.1. Classical AHL- and AI-2-Mediated Quorum Sensing
The canonical quorum sensing system in bacteria consists of two main components: the quorum molecule and the receptor. N-Acyl homoserine lactones (AHLs) are the most common quorum molecules (Figure 2) used by Gram-negative bacteria, typically produced by synthases homologous to LuxI from V. fischeri. Chemical derivatives of AHLs vary in terms of acyl chain length and saturation state, as well as oxidation status at the third carbon position. A variety of acyl chains, ranging from four to 18 carbons in length, is linked to an invariant homoserine lactone ring via an amide bond. These quorum molecules, after synthesis, are mostly membrane permeable and are free to accumulate in both the intracellular and extracellular environment [21]. Since AHL concentrations are determined by diffusion, a high population cell density is required for sufficient intracellular accumulation [22]. Above a critical threshold concentration, AHLs binds to cognate receptors to form activated complexes.
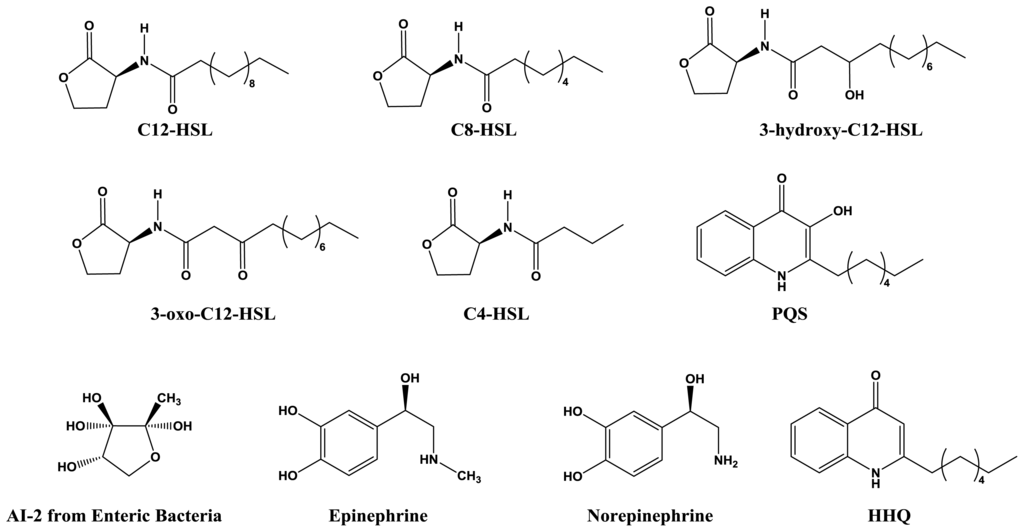
Figure 2.
Chemical structures of quorum molecules.
Homology is also observed in AHL receptors that belong to the LuxR family of transcriptional regulators. Briefly, AHL binding relieves an inhibitory effect on the DNA binding motif, and the receptor complex is mobilized to drive target gene expression [23]. In certain bacteria, such as Vibrio harveyi, AHLs can also mediate transcription through a signaling cascade. An accumulation of AHLs produced by the LuxM synthase is detected by the corresponding LuxN receptor located on the cell membrane; receptor-ligand interaction results in a change in the phosphorylation state of the receptor, leading to the expression of downstream transcriptional activators [24,25]. Meanwhile, bacteria can have more than one AHL synthase/receptor pair. In species with multiple quorum networks, each set may be associated with different virulence phenotypes, though there is a certain amount of redundancy [26]. In any case, AHLs are used only by Gram-negative bacteria for quorum signaling and could be important for intraspecies communication.
Autoinducer-2 (AI-2) is another class of quorum molecules utilized by Gram-negative bacteria for cell-to-cell communication. However, AI-2 is not unique to Gram-negative bacteria, and it is believed to be involved in interspecies communication [27]. Bacteria with the AI-2 quorum sensing pathways can respond to both native and exogenous quorum molecules, even those produced by Gram-positive bacteria. This is particularly evident in V. harveyi, where two sensor strains (coupled to the expression of bioluminescence) are commonly used to detect AI-2 from other species [28]. 5′-Methylthioadenosine/S-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase (MTAN or Pfs) and LuxS are two essential enzymes required for the sequential synthesis of the AI-2 precursor, 4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentanedione (DPD) [29]. Upon formation, DPD is energetically unstable and undergoes spontaneous chemical rearrangement to generate a variety of DPD derivatives. Subsequent cyclization reactions would give rise to an active pool of AI-2 compounds that can exist in equilibrium [30,31]. The AI-2 pathway exists in many bacteria; to date, LuxS homologues have been identified in 537 of the 1,402 bacterial genomes that have been sequenced [32].
In contrast, the identification and categorization of AI-2 receptors is less extensive and is limited to a handful of bacterial species. Currently, the two most well-characterized AI-2 receptors are LuxP from V. harveyi and LsrB from Salmonella typhimurium; the crystallographic structures of these receptors have been determined [33]. Using the AI-2 system in V. harveyi as an example, LuxP receptors are typically periplasmic binding proteins with an affinity for the membrane-associated sensor kinase LuxQ. The activated LuxPQ induces a transition from kinase to phosphatase activity and production of transcriptional activators is upregulated via a series of signal transduction events [34,35]. In addition, LsrB-type receptors have also been identified in members of the Enterobacteriaceae, Rhizobiaceae and Bacillaceae families, due to their AI-2 binding abilities [36]. Since non-LuxP and LsrB producing bacteria also exhibit responses towards AI-2, there must be alternative receptors present in these bacteria as yet to be discovered. From understanding of the current literature, AI-2 is implicated in a wide range of bacterial phenotypes, namely biofilm formation, cell motility, conjugation and virulence factor production [26,37]. However, its contribution may not be limited to pathogenesis, as AI-2 quorum sensing is also known to influence metabolism and bacterial fitness to various extents [38].
2.2. Alternative Quorum Sensing Pathways in Gram-Negative Bacteria
Other pathways (Table 1) that regulate quorum sensing in Gram-negative bacteria include the 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone (Pseudomonas quinolone signal [PQS]), 3-hydroxytridecan-4-one (cholera autoinducer-1 [CAI-1]), cis-11-methyl-2-dodecenoic acid (diffusible signal factor [DSF]) and autoinducer-3 (AI-3). The PQS pathway exists in P. aeruginosa and the operon, pqsABCDE, controls the initial production of the PQS precursor, 2-heptyl-4(1H)-hydroxyquinoline (HHQ), followed by a subsequent oxidative hydroxylation reaction by PqsH at the 3′ carbon position to convert HHQ to PQS [39,40]. Though PQS is used only by P. aeruginosa for quorum signaling, HHQ is used by other species in the Pseudomonas family and some species of Burkholderia for communication [41]. Both quorum molecules interact with the transcriptional regulator, PqsR, to mediate gene expression.

Table 1.
Quorum systems of selected Gram-negative bacteria.
In the CAI-1 pathway, CqsA in V. harveyi and Vibrio cholerae are responsible for quorum molecule biosynthesis, and the downstream effect is a consequence of interaction with the sensor kinase, CqsS [26,42]. Signals are passed through a relay cascade involving components of the previously described AI-2 system in Vibrio species. Interestingly, in V. cholerae, CAI-1 favors the production of virulence factors when present at low concentrations; at higher CAI-1 concentrations, the expression of virulence factors is repressed [56].
The DSF quorum sensing pathway was first described in the plant pathogen, Xanthomonas campestris pathovar campestris; quorum molecule production is dependent on RpfF, an enoyl-CoA hydratase-related protein, and RpfB, a long-chain fatty acyl CoA ligase [57]. In a typical two component signaling model, RpfC functions as the receptor and an activated regulator component, RpfG, is known to degrade the second messenger molecule cyclic di-GMP to low levels intracellularly; this results in the synthesis of virulence factors and motility [58]. Recent studies have identified rpf gene cluster homologs in others species of Xanthomonas, Xylella fastidiosa and the human pathogen, Stenotrophomonas maltophilia [59,60]. Variable forms of DSF were also detected in Burkholderia species, and B. cepacia utilizes more than one type of DSF [61]. Although the relevance of having multiple DSF in one organism is still undefined, it is believed to be involved in intraspecies or interspecies communication [62]. This was demonstrated in P. aeruginosa, whereby these non-DSF producing bacteria were able to sense DSF signals to modulate their own behavior [63].
The AI-3 quorum sensing pathway proposed by Sperandio et al. is probably the least characterized communication network in Gram-negative bacteria. From enteric microbial flora studies, the QseC/B two component system is recognized as the sensor for AI-3, though the structure and gene responsible for AI-3 production remain unknown [64,65]. Epinephrine and norepinephrine have been found to activate the QseC/B system; hence, it is likely that AI-3 could resemble these hormones. Currently, AI-3 signaling has been described in E. coli and S. typhimurium, while subsequent studies on gastrointestinal bacteria could reveal further details about this pathway [49].
2.3. Quorum Sensing Mechanisms Used by Clinically Relevant Gram-Negative Pathogens
2.3.1. Pseudomonas aeruginosa
P. aeruginosa is one of the most common human pathogen, and it is associated with a wide range of hospital-acquired infections, particularly with cystic fibrosis and burn patients. Due to the enormous clinical relevance of P. aeruginosa, its quorum sensing network is very well characterized and it is often used as a model organism for studies in the field [66]. Quorum sensing in P. aeruginosa generally exists as a complex hierarchical organization, where significant cross-talk between multiple pathways leads to a coordination of a significant number of genes [67]. To date, four quorum sensing systems have been described in the bacterium.
The las and rhl systems, identified much earlier, share similarities with the lux system from V. fischeri. AHL synthesis in both systems is mediated by LuxI-type synthases, LasI and RhlI, for production of N-(3-oxododecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12-HSL) and N-butanoyl-l-homoserine lactone (C4-HSL), respectively. These quorum molecules are recognized by their corresponding receptors, LasR and RhlR, when threshold quorum concentration is attained. In combination, the las and rhl systems regulate up to 353 genes or six percent of the P. aeruginosa genome; hence, a majority of P. aeruginosa quorum sensing research has focused on these two systems [43,68]. PQS is the third quorum molecule used by P. aeruginosa, and genomics studies have shown that 141 genes can be differentially controlled by the pqs system, suggesting a role in global regulation [69]. Production of PQS can be upregulated by the las system, although the rhl system mediates a negative effect [70]. In addition, the pqs system also auto-regulates its own production and promotes RhlIR expression [71,72]. Consequently, this results in a negative feedback loop that limits the synthesis of PQS. Likewise, both rhl and las systems mediate their own production, while the latter is also known to positively enhance the rhl system [73,74]. Despite its role as a positive regulator of adjacent pathways, the las system is not known to receive any feedback from both rhl and pqs systems.
In addition to the three quorum sensing systems, P. aeruginosa contains another LuxR-type receptor, QscR, for transcription modulation. The apparent distinction of QscR from the other two LuxR-type receptors is the lack of an associated synthase gene in the genome [44]. Without a cognate ligand pair, QscR is known to utilize 3-oxo-C12-HSL produced by LasI for signal activation [45]. The receptor also has an affinity for longer chain AHLs, and its promiscuity towards a variety of ligands indicates possible conduct in interspecies communication [75]. Based on earlier studies, QscR has a repressive effect on other quorum sensing systems, while the converse impact remains relatively uncharacterized [76]. From a transcription profiling study, QscR regulates overlapping genes with LasR and RhlR, though the “orphan” receptor also separately controls a distinct subset of genes [77].
2.3.2. Acinetobacter baumannii and Klebsiella pneumoniae
Along with P. aeruginosa, A. baumannii and K. pneumoniae are categorized as the “ESKAPE” bugs, a group of problematic nosocomial pathogens that have evolved to escape the lethal actions of antibiotics [17]. As the threat of these emerging pathogens escalates, new drugs are constantly being tested for suitable anti-bacterial properties. However, quorum sensing perspectives in these two pathogens are still rather limiting. In A. baumannii, N-(3-hydroxydodecanoyl)-l-homoserine lactone (3-hydroxy-C12-HSL) is the only quorum molecule identified, though mass spectrometry quantitation suggested that other AHL molecules are also present at significantly lower amounts [78]. AbaI is the LuxI-type synthase responsible for 3-hydroxy-C12-HSL production, and signal detection is by its cognate AbaR receptor [51]. In addition, the aba system influences biofilm formation in the bacterium, thereby reducing susceptibility to antibiotics and enhancing species survival [79]. More recently, interspecies interaction between A. baumannii and P. aeruginosa was investigated to determine the effects of co-location in hospital settings: biofilm formation, bacterial growth and virulence of A. baumannii were not affected by metabolites produced by P. aeruginosa. Instead, biofilm formation was augmented when a heterologous pool of AHLs from both species was used, suggesting that complementary quorum interactions were responsible for symbiotic co-existence [80].
In K. pneumoniae, two quorum sensing systems have been described in the literature. The AI-2 quorum molecule was, for many years, the only recognized regulator of cell-to-cell communication in the bacterium. Synthesis of AI-2 and maturation of biofilm, through upregulation of lipopolysaccharide production, were essentially luxS-dependent [55,81]. Likewise, luxS transcription is sensitive to pH, glucose and boracic acid concentrations in the environment [82]. As for the subsequent AHL-mediated mechanism, it was discovered more recently from a dorsal human tongue profiling study. High resolution mass spectrometry analyses revealed that N-octanoylhomoserine lactone (C8-HSL) and N-3-dodecanoyl-l-homoserine lactone (C12-HSL) are the AHL molecules produced by K. pneumoniae [54]. Unfortunately, the specific receptor component was not determined in both mechanisms. In addition, hypervirulent strains of K. pneumoniae can enhance inherent virulence characteristics by releasing a siderophore-related quorum molecule to fully exploit iron deposits in the surrounding environment [83].
2.3.3. Enterobacter spp. and Escherichia coli
Enterobacter spp. exists in the microbiota of soil, water, food and gastrointestinal tracts of animals and humans. Certain strains have gained resistance against antimicrobial agents and are recognized as increasingly important human pathogens in recent years. E. aerogenes and E. cloacae are among the two most prominent pathogens in the genus, with serious implications in respiratory and urinary tract infections [84]. Despite growing concerns with nosocomial and community risks, little is known about quorum control and pathogenesis in this group of bacteria. Outcomes of quorum sensing in Enterobacter spp. were mainly revealed through food-associated studies. Earlier reports have shown that Enterobacter spp. isolated from chilled salmon and raw milk can produce a detectable amount of AHLs [85,86]. The quorum molecule was confirmed to be C12-HSL by high resolution mass spectrometry in a subsequent dorsal human tongue study [52]. In species that do not produce AHLs, such as E. cloacae GS1, a LuxR homolog, SdiA, has been detected. Similar to the QscR receptor from P. aeruginosa, SdiA is an “orphan” receptor that functions as a transcriptional regulator. The SdiA receptor in E. cloacae GS1 is sensitive to exogenous AHLs, and it has been found to negatively regulate bacterial adhesion and biofilm formation [53]. This result was corroborated by another study using a different strain of E. cloacae [87]. Furthermore, AI-2-mediated quorum sensing has also been suggested to play a role in intercellular communication within Enterobacter spp. Although the AI-2 quorum molecules have yet to be identified, Lsr-type receptors have been found in strains of E. cancerogenus, E. cloacae and E. mori [47].
Three quorum sensing circuits have been described in E. coli strains, namely SdiA, AI-2 and AI-3-mediated systems. With the exception of the AI-3 system, the other two circuits have been relatively well characterized. As mentioned, SdiA is an “orphan” LuxR homologue without a corresponding LuxI synthase [46]. Nevertheless, the E. coli SdiA receptor binds AHLs produced by other bacterial species, and the activated complex is believed to coordinate cell division, virulence and antibiotic resistance [46,88–90]. Similar to Enterobacter spp., SdiA also downregulates biofilm formation in E. coli and could serve to antagonize the effects of other quorum regulators [91]. In the parallel AI-2 system, AI-2 synthesis is controlled by the luxS gene, while signal binding, transport and modulation are encoded by the lsr operon. Briefly, AI-2 is delivered into the cell via the Lsr transporter, followed by LsrK-mediated phosphorylation [48]. LsrR is a repressor of the lsr operon and itself, however, phosphor-AI-2 can bind specifically to LsrR as an antagonist [92]. Subsequently, phosphor-AI-2 can be modified by LsrF and LsrG to effect further downstream regulation [93]. Overall, the lsr operon can be stimulated by the cyclic AMP (cAMP)-cAMP receptor complex [94]. The third AI-3 system, the QseC/B system, is mainly described in enterohemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC), and structural analysis of AI-3 has suggested that it is an aromatic compound [49]. In the presence of AI-3 or its analogous activators, the QseC/B system is mobilized to promote flagella formation and motility in the bacterium [50].
With multiple quorum sensing systems in E. coli, it is unlikely that each exist independently without any interaction. Recently, an EAL domain protein was found to facilitate interaction between the SdiA and AI-2 systems through cAMP regulation. A knockdown of sdiA and ydiV (the gene encoding for the EAL domain protein) led to a decrease in intracellular cAMP levels and subsequent inhibition of the AI-2 system [95]. Although the nature of the specific interplay between the EAL domain protein and cAMP is still unknown, the possibility to effect indirect regulation of a parallel quorum sensing system using downstream response elements was clearly demonstrated. Besides, the AI-2 system can also influence cellular motility under the control of the AI-3 system. This cross-system effect was found to be mediated by the quorum sensing regulator, MqsR, which interacts with the adjacent QseC/B system [96].
3. Quorum Sensing Disruption Strategies in Gram-Negative Bacteria
There are three essential processes for bacterial quorum sensing: quorum molecule synthesis, extracellular accumulation of quorum molecules and ligand/receptor-mediated activation of downstream processes. Therefore, quorum disruption strategies generally adopt three common approaches: inhibition of quorum molecule synthesis, inhibition of quorum molecule/receptor interaction and degradation of quorum molecules (Figure 1). Though many quorum inhibitors were developed for broad spectrum effects, it is important to note that quorum sensing is largely unique to each bacterial species (Table 2). In some cases, there is more than one quorum sensing system present, and a combination of inhibition strategies may be necessary to prevent pathogenesis. In the next section, we will discuss quorum sensing disruption methods used in some clinically significant Gram-negative pathogens. The review is not meant to be exhaustive; instead, it is written to highlight the current important inhibitory developments against these pathogenic bacteria. P. aeruginosa will be used as an example for elaboration of inhibition methods, since such studies on the pathogen have been comprehensive. In pathogenic bacteria where quorum inhibition efforts are still lacking, possible approaches will be discussed.

Table 2.
Quorum sensing inhibitors.
3.1. Quorum Sensing Disruption in Pseudomonas aeruginosa
3.1.1. Inhibition of AHL Detection
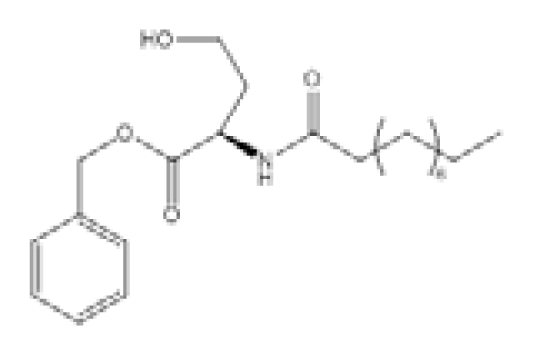
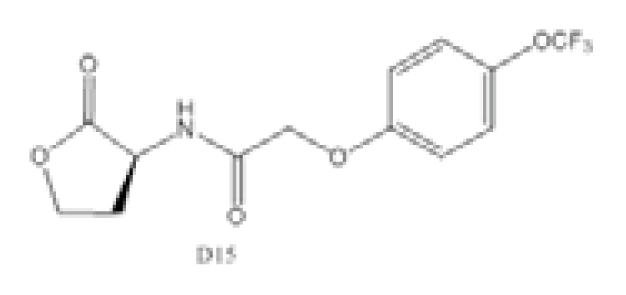
As a model organism for quorum sensing research, P. aeruginosa has been used extensively for various inhibition studies with modest success. Among the methods explored, interference with signal detection has been one of the most commonly reported strategies. Inhibitors and analogues of native quorum molecules can recognize and bind to receptor elements yet prevent subsequent signaling through the formation of an inactive ligand-receptor complex. For the AHL group of quorum molecules, the length and saturation state of the acyl tail can be critical for binding affinity and activity [105]. AHL molecules with a conserved lactone ring, but modified acyl tail, have been shown to exhibit preferential binding and antagonism with LasR receptor, and the presence of a 3-oxo moiety was noticed to favor LasR interaction [105]. In addition, other AHL molecules with variation at the lactone ring have also been synthesized and found to be inhibitory towards LasR and RhlR receptors [106]. Collectively, antagonists of LuxR-type receptors have included both natural and synthetic analogues of native quorum molecules. Screening of natural compounds is likely to be more unbiased, and selected antagonists may display greater structural diversity. Recently, Yang et al. identified a structural analogue of N-decanoyl-l-homoserine lactone (C10-HSL) with inhibitory effects against P. aeruginosa [97]. The compound, N-decanoyl-l-homoserine benzyl ester (C2), repressed transcription of las and rhl genes, while concomitantly downregulating production of rhamnolipid and swarming motility in the P. aeruginosa PAO1 strain. On the other hand, synthetic derivatives of quorum molecules are usually designed to be specific and retain considerable properties to the corresponding template compounds. Blackwell et al. have synthesized many non-native AHL analogues and systematically evaluated their inhibitory efficacies in several Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria over the years. Among a selection of potential antagonists, the compound, D15, with an aromatic substitution on the acyl chain, exhibited potent quorum sensing inhibition against P. aeruginosa [98]. The LasR receptor was the target in the study, and the addition of antagonists generally negated elastase B production. In a subsequent study by the same group, new antagonists that target the QscR receptor of P. aeruginosa have also been discovered [99]. The most potent antagonists were identified from compounds containing an N-benzoyl substitution on the acyl chain; however, the associated phenotypic response of the antagonism has yet to be elucidated. More recently, Morkunas et al. explored the strategy of using synthetic AHL mimics with significant feedback, suggesting that antagonists of P. aeruginosa LuxR-type receptors can originate from a diverse structural background [107].
Crystal structures of receptor bound to its quorum molecule can provide useful information on key interactions between the two components. In the case of P. aeruginosa, with the availability of 3D structural data, computational docking was used to screen for inhibitors against its LuxR-type receptors. Through this method, several compounds antagonistic to LasR and RhlR were successfully identified and their activity validated in vitro [108]. In addition, the crystal structure of LasR has facilitated the development of electrophilic probes that can target the ligand binding pocket of the receptor [100]. The probes bind covalently to the Cys79 residue within the pocket, specifically inhibiting the LasR receptor. The ability of an inhibitor to specifically target a pathogen is crucial in realizing its full therapeutic potential. Consequently, agonists or antagonists that are specific for certain receptors become therapeutic leads. Ganguly et al. exploited the specificity of C4-HSL analogues and showed that these compounds can be used to deliver covalently bound antibiotics to disrupt biofilm formation in P. aeruginosa [101]. Incidentally, C4-HSL is not exclusive to P. aeruginosa, and the antibiotic conjugate could be non-specific in mixed culture conditions. Similarly, LuxR-type receptors share significant homology; therefore, antagonists of the LasR, RhlR and QscR receptors can potentially have inhibitory effects on analogous receptors in other bacterial pathogens.
3.1.2. Inhibition of AHL Accumulation
Since quorum sensing is a density-dependent mechanism, prevention of signal accumulation is one of the most intuitive and viable approaches for disruption. Due to their catalytic prowess, enzymes have been postulated to be effective agents that degrade or inactivate quorum molecules (of Gram-negative bacteria). There are three groups of enzymes known to act on AHLs, namely acylases, lactonases and oxidoreductases. Acylases hydrolyze the amide bond in AHLs, releasing the homoserine lactone and fatty acyl chain, while lactonases target the hydrolysis of the ester bond in the lactone ring. Oxidoreductases, however, do not hydrolyze the quorum molecule, but rather modify it to an inactive form [109–111]. Each of these classes of enzyme has been shown to target AHLs produced by P. aeruginosa.
The AiiD protein isolated from Ralstonia strain is one of the first acylase used against AHLs; this enzyme was able to completely degrade 3-oxo-C8-HSL, 3-oxo-C10-HSL and 3-oxo-C12-HSL, respectively, within three hours of incubation [109]. When AiiD protein was expressed in P. aeruginosa PAO1, there was a corresponding decrease in elastase and pyocyanin production, as well as a reduction in swarming and nematode paralyzing ability. In a separate study, an AiiA homolog expressed in the same P. aeruginosa strain was able to prevent the accumulation of both AHLs secreted by the bacteria, thereby leading to a decrease in associated virulence factor production [112]. The AiiA protein, belonging to the metallo-β-lactamase superfamily, is the first lactonase found to degrade AHLs, although later studies have identified other members with similar activity. Likewise, the effect of using lactonases in combination with antibiotics was studied by means of biofilm microplate assays. Interestingly, the addition of lactonases increased antibiotic susceptibility: less gentamicin and ciprofloxacin were required for eradication of biofilms formed by MDR P. aeruginosa as compared to lactonase-free treatment [13]. In contrast, oxidoreductase activity against P. aeruginosa AHLs was characterized more recently. The protein bpiB09 was identified through metagenomic analysis as an NADP-dependent reductase, suggesting that AHLs are not the native substrates of the enzyme [113]. Nevertheless, bpiB09 was shown to act on 3-oxo-C12-HSL, and the ensuing quorum inhibition led to the reduction of pyocyanin and biofilm formation. In spite of P. aeruginosa’s susceptibility to AHL quenching enzymes, the bacterium is also capable of producing its own enzymatic quenchers. The P. aeruginosa associated PA0305 protein was identified to be an acylase with activity against long chain AHLs, including 3-oxo-C12-HSL, the cognate quorum sensing molecule in the bacteria [114]. In particular, PA0305 probably controls quorum molecule levels in the local environment. In addition, bacteria can be thought to produce quorum quenching enzymes to inactivate non-native signal molecules (from competing bacteria) for niche colonization [115].
Besides enzymes, antibody-mediated quorum inactivation has also been demonstrated. Using a monoclonal antibody XYD-11G2 fused to a hapten containing a squaric monoester monoamide motif, Marin et al. showed that the antibody was able to “neutralize” 3-oxo-C12-HSL and disrupt pyocyanin production in P. aeruginosa [116]. Furthermore, the hapten linker functions as mimic of the AHL acyl chain and can thus be developed for greater specificity. Antibodies can also sequester AHLs, rendering them inactive. Kaufmann et al. showed that (a stoichiometric amount of) monoclonal antibody RS2-1G9 can readily sequester 3-oxo-C12-HSL and protect macrophages from P. aeruginosa [117]. Overall, the immunopharmacotherapeutic approach is a promising strategy for the design and development of novel quorum inhibitors/quenchers to combat bacterial virulence.
3.1.3. Inhibition of the pqs System
As compared to the well-studied las and rhl systems, there are noticeably less reports on pqs inhibition studies. Nonetheless, inhibition of the pqs system is important for attenuation of quorum sensing and virulence in associated bacterial species. All three quorum inhibition approaches mentioned prior (inhibition of quorum molecule synthesis, inhibition of quorum molecule accumulation and inhibition of ligand/receptor interaction) have been explored for this system. Inhibition of quorum detection is probably the most direct approach, and Lu et al. were the first to discover antagonists against the receptor, PqsR, using a ligand-based drug design method. Antagonists 18 and 19 were particularly effective, as pyocyanin levels can be diminished with low micromolar concentrations of the compounds [102]. With the characterization of the PqsR X-ray crystallographic structure, crucial ligand-receptor interactions can be determined, paving the way for the future design of novel PqsR antagonists [118]. The structural similarity between PQS and a natural substrate, 3-hydroxy-2-methyl-4(1H)-quinolone, has prompted the use of a relevant dioxygenase enzyme (Hod) for quorum inhibition. As expected, the enzyme Hod was able to convert PQS to N-octanoylanthranilic acid and carbon monoxide, preventing the accumulation of PQS in P. aeruginosa cultures. Consequently, there was a decrease in PQS-regulated virulence determinants, lectin A, pyocyanin and rhamnolipids [119]. In addition to the first two approaches, inhibition of PQS synthesis can be achieved by using anthranilate analogues (incidentally, these analogues are precursors of PQS). Calfee et al. first reported inhibition of PQS synthesis using methyl anthranilate, with the resulting decrease in downstream elastase production in P. aeruginosa [120]. Subsequently, Lesic et al. also found that halogenated anthranilate had similar inhibitory effects, including a disruption of MvfR-dependent gene expression [121]. The MvfR pathway apparently plays an essential role in quorum sensing, as P. aeruginosa dissemination in the research model was significantly reduced. More importantly, these compounds restricted quorum sensing without affecting bacterial growth, hence decreasing the risk of resistance development.
3.1.4. Inhibition by Natural Compounds
Besides the prior-mentioned candidates, natural compound libraries serve as another source of quorum inhibitors/quenchers. Plants, in particular, are known to produce highly complex molecules with a variety of medicinal or therapeutic properties. Many of these molecules, however, may be very difficult to synthesize chemically, due to their complicated chemical scaffolds; hence, direct extraction would be the method-of-choice to obtain these products. A significant number of plant-extracted compounds have already been discovered with bacterial quorum quenching activity. Most recently, Plyuta et al. have found phenolic plant extracts that are able to inhibit biofilm formation in the P. aeruginosa PAO1 strain when applied at high concentrations [122]. However, at sub-inhibitory concentrations, these compounds have an opposite effect and supported biofilm growth instead. Some of these compounds included vanillin, 4-hydroxybenzoic and gallic acids, which do not resemble the prototypical structure of AHLs. In addition, ellagic acid derivatives from Terminalia chebula and aqueous extracts from Conocarpus erectus, Callistemon viminalis and Bucida buceras also had reported inhibitory effects on quorum sensing of P. aeruginosa [123,124]. Ellagic acid derivatives disrupted expression of LasR and RhlR, while concomitantly decreasing virulence factor production and enhancing the sensitivity of P. aeruginosa PAO1 biofilm towards tobramycin treatment. The later study was conducted in a Caenorhabditis elegans model, and the aqueous extracts prevented gut infection in 60% of nematodes and reduced mortality by 50%. Importantly, these extracts were effective without causing host toxicity and could be useful for further development as therapeutics. In addition to plant-derived compounds, natural compounds derived from insects and marine life have also been found, though these examples will not be elaborated in this review [125,126]. In view of the extensive ecological diversity in the natural world, many useful compounds have yet to be discovered, and studies into novel and uncharacterized natural extracts would undoubtedly expand the lexicon of effective compounds beyond the current known libraries.
3.2. Quorum Sensing Disruption in Escherichia coli
E. coli is a significant nosocomial pathogen, and as a model organism for life science research, its quorum sensing network is well described. Sufficient understanding of the quorum sensing architecture may be correlated to greater inhibition efforts, as this was evident when compared against species that are less studied. In E. coli, representative work has been done on the existing quorum sensing pathways. This part of the review will highlight some of the quorum sensing disruption efforts in each of the pathways described in this bacterium.
As mentioned earlier, MTAN is involved in the synthesis of the AI-2 precursor DPD by converting S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) to S-ribosylhomocysteine (SRH) in the SRH biosynthetic pathway [9]. Typically, MTAN inhibitors can disrupt SRH biosynthesis and, thus, prevent AI-2 formation. Gutierrez et al. have shown that transition analogues of MTAN (5′-Methylthio-DADMe-Immucillin-A, 5′-ethylthio-DADMe-Immucillin-A and 5′-butylthio-DADMe-Immucillin-A, respectively) can function as inhibitors of AI-2 synthesis, and their corresponding picomolar range dissociation constants indicated high binding affinity to the associated enzymes [127]. The study also highlighted the feasibility of blocking quorum molecule production and, at the same time, emphasized the importance of MTAN in AI-2 synthesis. On the other hand, analogues of DPD can also be used for quorum sensing inhibition in the bacterium. Guo et al. demonstrated that ester derivatives of DPD analogues introduced into E. coli can be hydrolyzed subsequently inside the cells to reveal a biologically active diol functional group for quorum sensing disruption [128]. Interestingly, when identical DPD analogues were delivered into S. typhimurium, a similar disruption effect was not observed, suggesting that selective quorum sensing modulation could possibly be achieved between closely related species using this type of ester-linked compound. The reason for such selectivity remains unclear; however, the authors suggested that it could be due to differential analogue permeation and esterase sensitivity. In addition to MTAN and DPD analogues, enzymatic quenching of the AI-2 signal is another method that can be used to disrupt this pathway. In the following enzyme-mediated example, the native bacterial phosphorylation machinery, LsrK, was retooled to inactivate its own AI-2 molecule [129]. Under native conditions, LsrK is the kinase responsible for phospho-AI-2 generation; phosphor-AI-2 then activates a series of lsr-controlled genes. When Roy et al. used LsrK to phosphorylate AI-2 molecules in vitro and added phospho-AI-2 exogenously to E. coli cultures, quorum sensing was significantly inhibited. This observation suggested an alternative function for LsrK: it could downregulate lsr-controlled genes when present in an extracellular context; this effect can also be attributed to the impermeability of membranes to phosphor-AI-2 molecules.
AI-3 related quorum sensing inhibition in E. coli has also been reported in the literature. Rasko et al. showed that a small organic molecule, N-phenyl-4-[(phenylamino)thioxomethyl]amino-benzenesulfonamide, termed LED209, was able to attenuate expression of QseC-associated genes to reduce virulence in EHEC strains [103]. More recently, Vikram et al. also described the use of isolimonic acid and ichangin as potent inhibitors of Type III secretion systems (TTSS) and biofilm formation in a QseC- and QseA-dependent manner [130]. In addition, there were further accounts of natural compounds that interfered with E. coli quorum sensing. Using Melia dubia seed extracts, Ravichandiran et al. found that the crude content was able to reduce biofilm and swarming motility in uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC) by targeting the SdiA-mediated quorum sensing pathway [131]. Notably, honey when delivered at low concentrations can also inhibit biofilm formation in EHEC. Sugar moieties in honey, such as glucose and fructose, were likely to be responsible for the observed inhibitions [132]. Biofilm reduction was attributed to the repression of AI-2 quorum sensing and virulence gene expression [133]. In other studies, halogenated furanones have been recognized as inhibitors of quorum sensing, due to their structural similarity to bacterial AHLs. Givskov et al. were one of the first groups to report the inhibitory effects of brominated furanones on bacterial species [134]. Later, the effects of brominated furanones were also shown in E. coli by means of a comparative gene expression study. The objective of investigation, however, focused on the AI-2-mediated pathway, and it was suggested that furanones can also alter AI-2 signaling post-transcriptionally to downregulate biofilm formation and motility phenotypes [135].
3.3. Quorum Sensing Disruption in Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter spp. and Acinetobacter baumannii
According to a report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii and Enterobacter spp. collectively accounted for more than 13 percent of hospital-acquired infections in the two-year period of 2009 to 2010 [136]. Moreover, highly resistant strains of these bacteria can kill up to 40% of infected patients, prompting the healthcare industry to revisit abandoned drugs for “last resort” treatments. Colistin, for example, is a polymyxin antibiotic useful against most Gram-negative bacilli; however, due to the associated risk of neurotoxicity and nephrotoxicity, the drug became obsolete 20 years ago. Yet, in the last decade, colistin prescription became more common against MDR pathogens, although some instances of resistance have already been reported [137,138]. Given the clinical importance, it is surprising that not much work has been done to address the virulence of these pathogens (vis-à-vis quorum inhibitions). Studies related to K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii and Enterobacter spp. have been limited, and the methods developed are unlikely to be useful for complete attenuation of quorum sensing in these bacteria. For example, Derakhshan et al. were the only group to show that essential oil from cumin seeds reduced biofilm formation in K. pneumoniae. From scanning electron microscopy images, it was evident that the capsular layer of K. pneumoniae was affected, possibly accounting for the observed two-fold decrease in biofilm formation [139]. However, there was no direct evidence to show that this reduction was mediated via quorum sensing pathways (although it is known that quorum sensing regulates the biofilm formation phenotype in the bacteria).
In the case of Enterobacter spp., Reis Ponce et al. have found that AiiA lactonase lowered cell numbers during early biofilm formation by Enterobacter cloacae [87]. The effect of quorum quenching enzymes was later corroborated by Kim et al. in an anti-biofouling study, which showed that Enterobacter microbial populations were reduced by half in treated membrane bioreactors (MBRs) [140]. Proteomic analysis further confirmed that flagellin and outer membrane protein expressions were downregulated, possibly resulting in a decrease in MBR biofilm mass. For A. baumannii, disruption of quorum sensing has been limited to the use of non-native AHLs and antagonists containing aromatic acyl groups [104]. Interestingly, non-native d-AHLs were also strong antagonists of the AbaR receptor, with increased potency against L-AHLs analogues, although d-AHLs are predicted to be less effective against LuxR-type receptors. In any case, the antagonists identified were successful in inhibiting AHL-mediated quorum sensing and its subsequent surface motility and biofilm formation. Most recently, Saroj et al. also found that streptomycin at sub-inhibitory concentrations is able to inhibit quorum sensing in A. baumannii [141]. Streptomycin (and not other antibiotics, such as gentamicin and myomycin) downregulated transcription of two quorum sensing genes, abaI and A1S_0112, resulting in the corresponding decrease in 3-oxo-C12-HSL production. It was proposed that streptomycin could act as an antagonist of AbaR and prevent positive feedback activation of abaI by functional 3-oxo-C12-HSL-AbaR complexes. In addition to this study, several others have also showed that sub-inhibitory concentrations of antibiotics can positively or negatively modulate quorum sensing, in contrast to bactericidal effects observed at high concentrations: tobramycin was found to induce biofilm formation in E. coli and P. aeruginosa when applied at concentrations three-fold below the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) [142]. It has been suggested that antibiotics could act as intermicrobial signaling agents, with roles in maintaining homeostasis in bacterial biofilm formation, motility and TTSS, instead of their widely regarded function as biological adversaries [143]. Such a hypothesis provides a refreshing evolutionary explanation for the observed relationship between antibiotics and quorum sensing in these bacteria.
In spite of the above-mentioned examples, studies related to quorum inhibition of K. pneumoniae, A. baumannii and Enterobacter spp. are still rather limited. The current lack of quorum inhibitors for clinically significant Gram-negative pathogens is a mounting concern, especially with the continued evolution of resistance mechanisms and the prevalence of MDR strains. When “last resort” drugs, such as colistin and tigecycline lose their efficacies, there will be even less treatment options available against MDR species. Fortunately, at least for the moment, we may not have to look beyond existing strategies, as many Gram-negative pathogens share similar quorum sensing mechanisms. Generic pathways and methods can be exploited and used against affiliated species. As mentioned, MTAN inhibitors were able to disrupt DPD formation and prevent AI-2 synthesis in E. coli strains. Since the AI-2 biosynthetic pathway is conserved in many bacterial species, inhibition of AI-2 production can target bacteria with the existing quorum sensing system [32]. In addition, MTAN is also involved in the synthesis of AHLs through the conversion of 5′-methylthioadenosine (MTA) to 5-methylthioribose (MTR). MTA is a by-product of polyamine synthesis from S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), and MTAN is important for the salvage of methionine for SAM regeneration [144]. Currently, potent MTAN inhibitors with picomolar range efficacies have been determined, and there is potential that MTAN inhibitors could be important anti-bacterial agents for suppression of AHL synthesis by disrupting SAM supply [145]. Alternatively, the enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (FabI), which is important for AHL acyl chain formation, can be a target of inhibition. The role of FabI in AHL synthesis was demonstrated by Hoang et al. using FabI mutants, and the group have further shown that triclosan at low concentrations successfully inhibited FabI by almost 50 percent [146]. It is palpable that such approaches can be applicable to pathogens that use LuxI-type of AHL synthases to potentially disrupt quorum sensing.
Quorum-quenching enzymes are another noteworthy group of quorum inhibitors, as many enzymes have already been characterized, and there is substantial literature coverage in terms of hydrolyzable AHLs. Furthermore, bacteria share many common AHLs; hence, enzymatic degradation of these signaling molecules might be useful in broad-spectrum control of virulence in various pathogenic bacteria [147]. Enzymes usually exhibit substrate preference, as seen in the case of AiiD acylase, where catalytic specificity is towards longer chain AHLs [109]. However, exceptions do exist among AHL acylases: the AiiC acylase from Anabaena sp. is promiscuous and is able to degrade AHLs ranging from four to 14 carbons in acyl chain length. In addition, the enzyme does not discriminate against any particular substitution group on the acyl chain, suggesting a probable involvement in broad range signal interference within a complex microbial community [148]. Likewise, there are also broad-spectrum quorum-quenching enzymes from the lactonase group. The QsdA lactonase from Rhodococcus erythropolis is a distinct example, where AHLs with acyl chain lengths ranging from six to 14 carbons can be inactivated [149]; similar to the reactivity of AiiC, the oxidation state at position three of the acyl chain is not discriminated against by the QsdA enzyme. In a more recent study, Chow et al. described an engineered GKL lactonase from Geobacillus kaustophilus with enhanced catalytic activity against AHLs ranging from six to 12 carbons in acyl chain length [150]. Notably, the engineered GKL has improved hydrolytic activity of up to 72-fold (catalytic efficiency, kcat/KM) against longer chained AHLs and a newly acquired C4-HSL activity (the wild-type enzyme had no detectable lactonase activity against C4-HSL). The improved lactonase was identified through directed evolution methods, illustrating the utility of this approach for engineering novel substrate specificities into existing quorum quenching enzyme scaffolds. The authors also demonstrated the translational potential of the study by using the engineered quorum-quenching lactonase to disrupt biofilm formation in A. baumannii (Figure 3). From crystal violet assays and confocal imaging results, the biomass of A baumannii-associated biofilms was significantly reduced; this work represents the first successful account of biofilm disruption using recombinant quorum-quenching enzymes [151]. The study also highlighted the utility of using enzymes with broad AHL specificity to treat infectious diseases associated with a variety of Gram-negative bacteria (including bacterial pathogens with multiple AHL quorum systems).
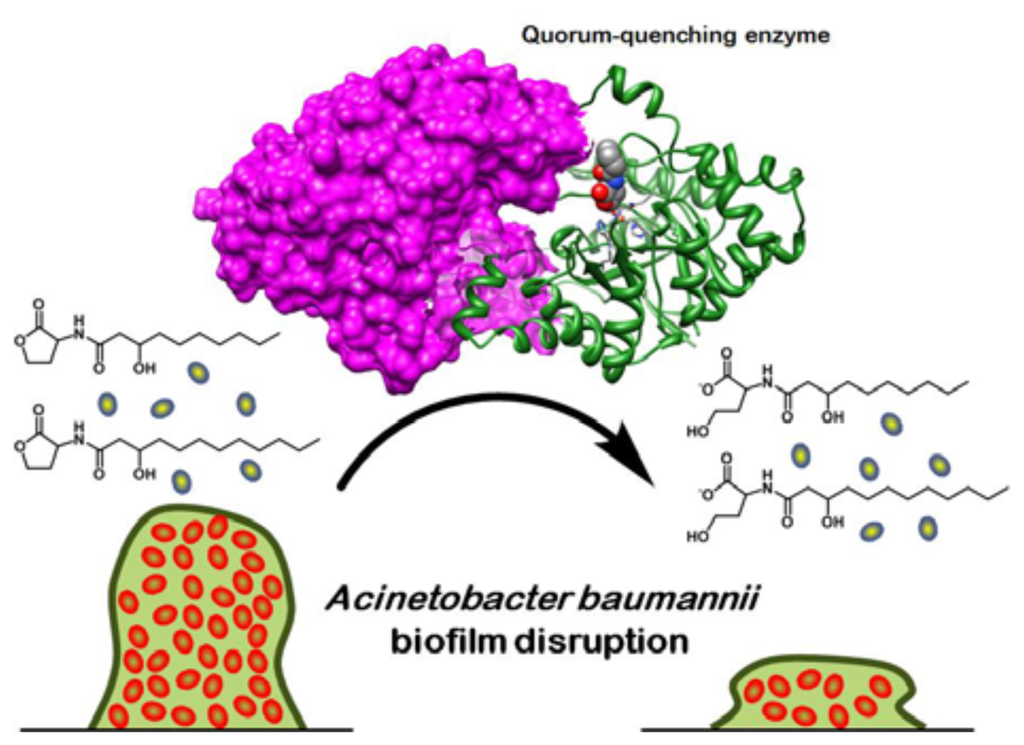
Figure 3.
Disruption of biofilm formation in Acinetobacter baumannii using engineered quorum-quenching lactonases.
4. Quorum-Quenching Considerations and Implications
Interference with bacterial virulence, via quorum-quenching, promises to be “tolerance-free”, as the approach is not bactericidal in nature [12]. Indeed, bacteria viability is usually not affected when quorum sensing is blocked, and there has been considerable success since interest gathered in the field almost a decade ago. Even though quorum sensing inhibitors have been shown to be effective in preventing virulence factor expression, reducing biofilm formation and altering membrane permeability, bacteria do persist after treatment. Therefore, to achieve their therapeutic potential, quorum sensing inhibitors may have to be used concurrently with antibiotics for both anti-virulence and anti-bacterial effects. Certain inhibitors are known to increase susceptibility to antibiotics, although the combined treatment was rarely tested [13]. In addition, due to the complexity of bacterial quorum circuits (some bacteria have more than one quorum sensing system) the disruption of one quorum system often does not effectively prevent the expression of virulence factors. There are four distinct quorum regulatory circuits in P. aeruginosa that are interconnected by regulator-mediated feedback mechanisms. Such redundancy allows for compensatory responses by other systems, and shutting down the entire complex network poses a great challenge: in the absence of a las system in P. aeruginosa, RhlR was still able to control LasR-specific functions, providing a testament to the difficulty in addressing quorum-mediated pathogenesis by the bacteria [152]. In addition, the production of 3-oxo-C12-HSL and PQS were not affected, indicating a complicated hierarchy in quorum circuitry in the human pathogen. On a different note, quorum sensing can negatively regulate virulence phenotypes, as evidenced by the SdiA-mediated system in E. cloacae GS1 [53]. Hence, the disruption of quorum sensing in such exceptional systems would instead increase bacterial virulence.
An anti-virulence approach represents an anticipated solution to PDR bacterial infections, yet such optimism has to be periodically reviewed and tempered with caution. Recently, Defoirdt et al. challenged the assumption that quorum sensing disruption is resistance-free and suggested that fitness of bacteria can be affected through variability in quorum sensing core genes [153]. In retrospect, support for this resistance-free concept was gathered through a credible research effort conducted in laboratory-based conditions. However, conditions could differ significantly in vivo, and it was highlighted by Martinez et al. that evaluation of fitness should be made in models that better reflect actual infection and treatment settings [154]. Certainly, bacteria within a host environment will be subjected to a very different set of selective pressures (such as those imposed by the host immune system). As mentioned earlier, bacteria can compensate for partial quorum sensing inhibition by using alternative or redundant circuits for virulence [152]. Similarly, quorum sensing-deficient mutants can also exploit signals and metabolites produced by quorum sensing-proficient variants for virulence, since quorum sensing is fundamentally a cooperative behavior that is beneficial to the community [155]. The emergence of social “cheaters” has already been reported by Sandoz et al. in their study where P. aeruginosa lasR mutants ceased production of quorum regulated factors and take advantage of those produced by their proficient neighbors [156]. Taking an alternative perspective, quorum sensing-insensitive mutants capable of producing quorum regulated factors can likewise interfere with quorum inhibition efforts. A proof-of-concept study was carried out by Mellbye et al. illustrating that inhibition-resistant subtypes (“cooperators”) were able to profiteer from inhibition-sensitive subtypes when the quorum regulated product was secreted into the extracellular milieu (“public goods”). More importantly, mutual sharing in this case does not necessarily lead to a selective advantage for “cooperators”, and the enrichment of resistant subtypes can be mitigated. Nevertheless, quorum-quenching efficiency will be compromised when resistant subtypes are present in the treatment population. On the other hand, if the quorum regulated product is intracellular (“private goods”), inhibition of quorum sensing could favorably select for resistant subtypes, as the “products” generally cannot be shared [157]. Essentially, this study highlighted an often neglected consideration in quorum inhibition research, in that the discrimination of “public” or “private” goods is crucial in preventing the emergence of bacterial resistance to quorum inhibitors.
5. Conclusions
Research efforts in the past few decades have contributed significantly to the understanding of the mechanisms of bacterial communication. Due to the rapid occurrence of antibiotic resistance, recent focus was placed on inhibitory studies to address the therapeutic potential for the healthcare industry. Disruption of quorum sensing is widely regarded as an attractive anti-virulence approach, as this strategy is non-bactericidal and, therefore, would not generate the unwanted selective pressure for resistance. A variety of quorum disruption strategies (with varied success) against pathogenic bacteria have been described, including the inhibition of quorum molecule synthesis, accumulation and detection. Gram-negative bacteria represent a significant group of human pathogens, as they are responsible for a majority of hospital-acquired infections. Despite successful efforts against some of the more common pathogens, there remain a number of less-studied (and understood) bacterial pathogens waiting for effective therapeutic intervention: there have been limited reports on quorum sensing disruption in pathogens, such as A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae and the Enterobacter species. Along with the studies on quorum inhibition, there is also concern about bacterial resistance against anti-virulence methods. In fact, there is increasing evidence of quorum quenching treatments leading to a rise in resistant bacterial phenotypes. Further studies are necessary to determine the molecular mechanisms of mutations that confer the resistant bacterial phenotypes and if the selection of such mutations is by chance and would confer advantages in fitness. Nevertheless, future studies in the therapeutic development of anti-virulence strategies should proceed with care and caution to avoid the undesired fate currently associated with antibiotic development.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Hastings, J.W.; Nealson, K.H. Bacterial bioluminescence. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 1977, 31, 549–595. [Google Scholar]
- Winzer, K.; Williams, P. Quorum sensing and the regulation of virulence gene expression in pathogenic bacteria. Int. J. Med. Microbiol 2001, 291, 131–143. [Google Scholar]
- Waters, C.M.; Bassler, B.L. Quorum sensing: Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 2005, 21, 319–346. [Google Scholar]
- LaSarre, B.; Federle, M.J. Exploiting quorum sensing to confuse bacterial pathogens. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 2013, 77, 73–111. [Google Scholar]
- Cegelski, L.; Marshall, G.R.; Eldridge, G.R.; Hultgren, S.J. The biology and future prospects of antivirulence therapies. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2008, 6, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Alanis, A.J. Resistance to antibiotics: Are we in the post-antibiotic era? Arch. Med. Res 2005, 36, 697–705. [Google Scholar]
- Walsh, C. Antibiotics: Actions, Origins, Resistance; Asm Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Werner, G.; Strommenger, B.; Witte, W. Acquired vancomycin resistance in clinically relevant pathogens. Future Microbiol 2008, 3, 547–562. [Google Scholar]
- Sengupta, S.; Chattopadhyay, M.K.; Grossart, H.P. The multifaceted roles of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Front. Microbiol 2013, 4, 47. [Google Scholar]
- Dellit, T.H.; Owens, R.C.; McGowan, J.E.; Gerding, D.N.; Weinstein, R.A.; Burke, J.P.; Huskins, W.C.; Paterson, D.L.; Fishman, N.O.; Carpenter, C.F.; et al. Infectious diseases society of america and the society for healthcare epidemiology of america guidelines for developing an institutional program to enhance antimicrobial stewardship. Clin. Infect. Dis 2007, 44, 159–177. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, P. Antibacterial discovery and development[mdash]the failure of success? Nat. Biotech 2006, 24, 1497–1503. [Google Scholar]
- Rasko, D.A.; Sperandio, V. Anti-virulence strategies to combat bacteria-mediated disease. Nature reviews. Drug Discov 2010, 9, 117–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kiran, S. Enzymatic quorum quenching increases antibiotic susceptibility of multidrug resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Irani. J. Microbiol 2011, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- McLean, R.J.C.; Whiteley, M.; Stickler, D.J.; Fuqua, W.C. Evidence of autoinducer activity in naturally occurring biofilms. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 1997, 154, 259–263. [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein, R.A.; Gaynes, R.; Edwards, J.R. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System Overview of nosocomial infections caused by gram-negative bacilli. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 41, 848–854. [Google Scholar]
- Vincent, J.L.; Rello, J.; Marshall, J.; Silva, E.; Anzueto, A.; Martin, C.D.; Moreno, R.; Lipman, J.; Gomersall, C.; Sakr, Y.; et al. International study of the prevalence and outcomes of infection in intensive care units. JAMA 2009, 302, 2323–2329. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, L.B. Federal funding for the study of antimicrobial resistance in nosocomial pathogens: No eskape. J. Infect. Dis 2008, 197, 1079–1081. [Google Scholar]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No eskape! An update from the infectious diseases society of america. Clin. Infect. Dis 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Ramphal, R.; Ambrose, P.G. Extended-spectrum β-lactamases and clinical outcomes: Current data. Clin. Infect. Dis 2006, 42, S164–S172. [Google Scholar]
- Tschudin-Sutter, S.; Frei, R.; Dangel, M.; Stranden, A.; Widmer, A.F. Rate of transmission of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing enterobacteriaceae without contact isolation. Clin. Infect. Dis 2012, 55, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan, H.B.; Greenberg, E.P. Diffusion of autoinducer is involved in regulation of the Vibrio fischeri luminescence system. J. Bacteriol 1985, 163, 1210–1214. [Google Scholar]
- Fuqua, C.; Winans, S.C.; Greenberg, E.P. Census and consensus in bacterial ecosystems: The luxr-luxi family of quorum-sensing transcriptional regulators. Annu. Rev. Microbiol 1996, 50, 727–751. [Google Scholar]
- Re, S.D.; Bertagnoli, S.; Fourment, J.; Reyrat, J.-M.; Kahn, D. Intramolecular signal transduction within the fixj transcriptional activator: In vitro evidence for the inhibitory effect of the phosphorylatable regulatory domain. Nucleic Acids Res 1994, 22, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Freeman, J.A.; Lilley, B.N.; Bassler, B.L. A genetic analysis of the functions of luxn: A two-component hybrid sensor kinase that regulates quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi. Mol. Microbiol 2000, 35, 139–149. [Google Scholar]
- Lenz, D.H.; Mok, K.C.; Lilley, B.N.; Kulkarni, R.V.; Wingreen, N.S.; Bassler, B.L. The small rna chaperone hfq and multiple small rnas control quorum sensing in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio cholerae. Cell 2004, 118, 69–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ni, N.; Li, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, B. Inhibitors and antagonists of bacterial quorum sensing. Med. Res. Rev 2009, 29, 65–124. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, K.B.; Bassler, B.L. Interference with ai-2-mediated bacterial cell-cell communication. Nature 2005, 437, 750–753. [Google Scholar]
- Rajamani, S.; Sayre, R.T. A sensitive fluorescence reporter for monitoring quorum sensing regulated protease production in Vibrio harveyi. J. Microbiol. Methods 2011, 84, 189–193. [Google Scholar]
- Schauder, S.; Shokat, K.; Surette, M.G.; Bassler, B.L. The luxs family of bacterial autoinducers: Biosynthesis of a novel quorum-sensing signal molecule. Mol. Microbiol 2001, 41, 463–476. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Schauder, S.; Potier, N.; Van Dorsselaer, A.; Pelczer, I.; Bassler, B.L.; Hughson, F.M. Structural identification of a bacterial quorum-sensing signal containing boron. Nature 2002, 415, 545–549. [Google Scholar]
- De Keersmaecker, S.C.J.; Varszegi, C.; van Boxel, N.; Habel, L.W.; Metzger, K.; Daniels, R.; Marchal, K.; de Vos, D.; Vanderleyden, J. Chemical synthesis of (S)-4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentanedione, a bacterial signal molecule precursor, and validation of its activity in Salmonella typhimurium. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 19563–19568. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, C.S.; Thompson, J.A.; Xavier, K.B. Ai-2-mediated signaling in bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev 2013, 37, 156–181. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, W.R.J.D.; Hodgkinson, J.T.; Bowden, S.D.; Welch, M.; Spring, D.R. Quorum sensing in gram-negative bacteria: Small-molecule modulation of ahl and ai-2 quorum sensing pathways. Chem. Rev 2010, 111, 28–67. [Google Scholar]
- Henke, J.M.; Bassler, B.L. Three parallel quorum-sensing systems regulate gene expression in vibrio harveyi. J. Bacteriol 2004, 186, 6902–6914. [Google Scholar]
- Neiditch, M.B.; Federle, M.J.; Miller, S.T.; Bassler, B.L.; Hughson, F.M. Regulation of luxpq receptor activity by the quorum-sensing signal autoinducer-2. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 507–518. [Google Scholar]
- Pereira, C.S.; de Regt, A.K.; Brito, P.H.; Miller, S.T.; Xavier, K.B. Identification of functional lsrb-like autoinducer-2 receptors. J. Bacteriol 2009, 191, 6975–6987. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, K.B.; Bassler, B.L. Luxs quorum sensing: More than just a numbers game. Curr. Opin. Microbiol 2003, 6, 191–197. [Google Scholar]
- Vendeville, A.; Winzer, K.; Heurlier, K.; Tang, C.M.; Hardie, K.R. Making ‘sense’ of metabolism: Autoinducer-2, luxs and pathogenic bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol 2005, 3, 383–396. [Google Scholar]
- Déziel, E.; Lépine, F.; Milot, S.; He, J.; Mindrinos, M.N.; Tompkins, R.G.; Rahme, L.G. Analysis of Pseudomonas aeruginosa 4-hydroxy-2-alkylquinolines (haqs) reveals a role for 4-hydroxy-2-heptylquinoline in cell-to-cell communication. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Pesci, E.C.; Milbank, J.B.J.; Pearson, J.P.; McKnight, S.; Kende, A.S.; Greenberg, E.P.; Iglewski, B.H. Quinolone signaling in the cell-to-cell communication system of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci 1999, 96, 11229–11234. [Google Scholar]
- Dubern, J.-F.; Diggle, S.P. Quorum sensing by 2-alkyl-4-quinolones in Pseudomonas aeruginosa and other bacterial species. Mol. BioSyst 2008, 4, 882–888. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, W.L.; Perez, L.J.; Wei, Y.; Kraml, C.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. Signal production and detection specificity in vibrio cqsa/cqss quorum-sensing systems. Mol. Microbiol 2011, 79, 1407–1417. [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert, K.B.; Kim, T.H.; Gupta, R.; Greenberg, E.P.; Schuster, M. Global position analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing transcription factor lasr. Mol. Microbiol 2009, 73, 1072–1085. [Google Scholar]
- Chugani, S.A.; Whiteley, M.; Lee, K.M.; D’Argenio, D.; Manoil, C.; Greenberg, E.P. Qscr, a modulator of quorum-sensing signal synthesis and virulence in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 2752–2757. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-H.; Lequette, Y.; Greenberg, E.P. Activity of purified qscr, a Pseudomonas aeruginosa orphan quorum-sensing transcription factor. Mol. Microbiol 2006, 59, 602–609. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.D.; de Boer, P.A.; Rothfield, L.I. A factor that positively regulates cell division by activating transcription of the major cluster of essential cell division genes of Escherichia coli. EMBO J 1991, 10, 3363–3372. [Google Scholar]
- Rezzonico, F.; Smits, T.H.M.; Duffy, B. Detection of ai-2 receptors in genomes of enterobacteriaceae suggests a role of type-2 quorum sensing in closed ecosystems. Sensors 2012, 12, 6645–6665. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Li, J.; March, J.C.; Valdes, J.J.; Bentley, W.E. Luxs-dependent gene regulation in Escherichia coli k-12 revealed by genomic expression profiling. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 8350–8360. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, M.; Sperandio, V. Quorum sensing in Escherichia coli and Salmonella. Int. J. Med. Microbiol 2006, 296, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Sperandio, V.; Torres, A.G.; Kaper, J.B. Quorum sensing Escherichia coli regulators b and c (qsebc): A novel two-component regulatory system involved in the regulation of flagella and motility by quorum sensing in e. Coli. Mol. Microbiol 2002, 43, 809–821. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, N.; Sharma, P.; Capalash, N. Quorum sensing in acinetobacter: An emerging pathogen. Crit. Rev. Microbiol 2010, 36, 349–360. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.-F.; Purmal, K.; Chin, S.; Chan, X.-Y.; Chan, K.-G. Long chain N-acyl homoserine lactone production by Enterobacter sp. isolated from human tongue surfaces. Sensors 2012, 12, 14307–14314. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, M.; Ponraj, P.; Illakkiam, D.; Rajendhran, J.; Gunasekaran, P. Inactivation of the transcriptional regulator-encoding gene sdia enhances rice root colonization and biofilm formation in Enterobacter cloacae gs1. J. Bacteriol 2013, 195, 39–45. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, W.-F.; Purmal, K.; Chin, S.; Chan, X.-Y.; Koh, C.-L.; Sam, C.-K.; Chan, K.-G. N-acyl homoserine lactone production by Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from human tongue surface. Sensors 2012, 12, 3472–3483. [Google Scholar]
- Balestrino, D.; Haagensen, J.A.J.; Rich, C.; Forestier, C. Characterization of type 2 quorum sensing in Klebsiella pneumoniae and relationship with biofilm formation. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 2870–2880. [Google Scholar]
- Higgins, D.A.; Pomianek, M.E.; Kraml, C.M.; Taylor, R.K.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. The major vibrio cholerae autoinducer and its role in virulence factor production. Nature 2007, 450, 883–886. [Google Scholar]
- Barber, C.E.; Tang, J.L.; Feng, J.X.; Pan, M.Q.; Wilson, T.J.G.; Slater, H.; Dow, J.M.; Williams, P.; Daniels, M.J. A novel regulatory system required for pathogenicity of Xanthomonas campestris is mediated by a small diffusible signal molecule. Mol. Microbiol 1997, 24, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Fouhy, Y.; Lucey, J.F.; Ryan, R.P.; Dow, J.M. Cell-cell signaling, cyclic di-gmp turnover and regulation of virulence in Xanthomonas campestris. Res. Microbiol 2006, 157, 899–904. [Google Scholar]
- Newman, K.L.; Almeida, R.P.P.; Purcell, A.H.; Lindow, S.E. Cell-cell signaling controls Xylella fastidiosa interactions with both insects and plants. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar]
- Fouhy, Y.; Scanlon, K.; Schouest, K.; Spillane, C.; Crossman, L.; Avison, M.B.; Ryan, R.P.; Dow, J.M. Diffusible signal factor-dependent cell-cell signaling and virulence in the nosocomial pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia. J. Bacteriol 2007, 189, 4964–4968. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, Y.; Wu, J.E.; Eberl, L.; Zhang, L.-H. Structural and functional characterization of diffusible signal factor family quorum-sensing signals produced by members of the Burkholderia cepacia complex. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2010, 76, 4675–4683. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, R.P.; Dow, J.M. Communication with a growing family: Diffusible signal factor (dsf) signaling in bacteria. Trends Microbiol 2011, 19, 145–152. [Google Scholar]
- Ryan, R.P.; Fouhy, Y.; Garcia, B.F.; Watt, S.A.; Niehaus, K.; Yang, L.; Tolker-Nielsen, T.; Dow, J.M. Interspecies signaling via the stenotrophomonas maltophilia diffusible signal factor influences biofilm formation and polymyxin tolerance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Microbiol 2008, 68, 75–86. [Google Scholar]
- Sperandio, V.; Torres, A.G.; Jarvis, B.; Nataro, J.P.; Kaper, J.B. Bacteria-host communication: The language of hormones. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci 2003, 100, 8951–8956. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, M.B.; Hughes, D.T.; Zhu, C.; Boedeker, E.C.; Sperandio, V. The qsec sensor kinase: A bacterial adrenergic receptor. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci 2006, 103, 10420–10425. [Google Scholar]
- Juhas, M.; Eberl, L.; Tümmler, B. Quorum sensing: The power of cooperation in the world of Pseudomonas. Environ. Microbiol 2005, 7, 459–471. [Google Scholar]
- Wilder, C.N.; Diggle, S.P.; Schuster, M. Cooperation and cheating in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The roles of the las, rhl and pqs quorum-sensing systems. ISME J 2011, 5, 1332–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, M.; Lostroh, C.P.; Ogi, T.; Greenberg, E.P. Identification, timing, and signal specificity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-controlled genes: A transcriptome analysis. J. Bacteriol 2003, 185, 2066–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Deziel, E.; Gopalan, S.; Tampakaki, A.P.; Lepine, F.; Padfield, K.E.; Saucier, M.; Xiao, G.; Rahme, L.G. The contribution of mvfr to Pseudomonas aeruginosa pathogenesis and quorum sensing circuitry regulation: Multiple quorum sensing-regulated genes are modulated without affecting lasri, rhlri or the production of N-acyl-l-homoserine lactones. Mol. Microbiol 2005, 55, 998–1014. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, S.; Wade, D.S.; Pesci, E.C. Dueling quorum sensing systems in Pseudomonas aeruginosa control the production of the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (pqs). FEMS Microbiol. Lett 2004, 230, 27–34. [Google Scholar]
- McKnight, S.L.; Iglewski, B.H.; Pesci, E.C. The Pseudomonas quinolone signal regulates rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol 2000, 182, 2702–2708. [Google Scholar]
- Wade, D.S.; Calfee, M.W.; Rocha, E.R.; Ling, E.A.; Engstrom, E.; Coleman, J.P.; Pesci, E.C. Regulation of Pseudomonas quinolone signal synthesis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 4372–4380. [Google Scholar]
- Pesci, E.C.; Pearson, J.P.; Seed, P.C.; Iglewski, B.H. Regulation of las and rhl quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol 1997, 179, 3127–3132. [Google Scholar]
- Pearson, J.P.; Pesci, E.C.; Iglewski, B.H. Roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa las and rhl quorum-sensing systems in control of elastase and rhamnolipid biosynthesis genes. J. Bacteriol 1997, 179, 5756–5767. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, C.; Park, S.J.; Im, S.J.; Lee, J.H. Interspecies signaling through qscr, a quorum receptor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol. Cells 2012, 33, 53–59. [Google Scholar]
- Ledgham, F.; Ventre, I.; Soscia, C.; Foglino, M.; Sturgis, J.N.; Lazdunski, A. Interactions of the quorum sensing regulator qscr: Interaction with itself and the other regulators of Pseudomonas aeruginosa lasr and rhlr. Mol. Microbiol 2003, 48, 199–210. [Google Scholar]
- Lequette, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Ledgham, F.; Lazdunski, A.; Greenberg, E.P. A distinct qscr regulon in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum-sensing circuit. J. Bacteriol 2006, 188, 3365–3370. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, C.; Clemmer, K.M.; Bonomo, R.A.; Rather, P.N. Isolation and characterization of an autoinducer synthase from Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Bacteriol 2008, 190, 3386–3392. [Google Scholar]
- Wand, M.E. Acinetobacter baumannii virulence is enhanced in Galleria mellonella following biofilm adaptation. J. Med. Microbiol 2012, 61, 470–477. [Google Scholar]
- Bhargava, N.; Sharma, P.; Capalash, N. N-acyl homoserine lactone mediated interspecies interactions between A. baumannii and P. aeruginosa. Biofouling 2012, 28, 813–822. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, H.-J.; Ning, S.-J.; Gao, Y.-L. A luxs-dependent transcript profile of cell-to-cell communication in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Mol. BioSyst 2011, 7, 3164–3168. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, H.J.; Ning, S.J.; Gao, Y.L. The response of type 2 quorum sensing in Klebsiella pneumoniae to a fluctuating culture environment. DNA Cell Biol 2012, 31, 455–459. [Google Scholar]
- Russo, T.A.; Shon, A.S.; Beanan, J.M.; Olson, R.; MacDonald, U.; Pomakov, A.O.; Visitacion, M.P. Hypervirulent k. Pneumoniae secretes more and more active iron-acquisition molecules than “classical” k. Pneumoniae thereby enhancing its virulence. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26734. [Google Scholar]
- Sanders, W.E.; Sanders, C.C. Enterobacter spp.: Pathogens poised to flourish at the turn of the century. Clin. Microbiol. Rev 1997, 10, 220–241. [Google Scholar]
- Pinto, U.M.; de Souza Viana, E.; Martins, M.L.; Vanetti, M.C.D. Detection of acylated homoserine lactones in gram-negative proteolytic psychrotrophic bacteria isolated from cooled raw milk. Food Control 2007, 18, 1322–1327. [Google Scholar]
- Gram, L.; Christensen, A.B.; Ravn, L.; Molin, S.; Givskov, M. Production of acylated homoserine lactones by psychrotrophic members of the Enterobacteriaceae isolated from foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 1999, 65, 3458–3463. [Google Scholar]
- Reis Ponce, A.; Martins, M.; Araujo, E.; Mantovani, H.; Vanetti, M. Aiia quorum-sensing quenching controls proteolytic activity and biofilm formation by Enterobacter cloacae. Curr. Microbiol 2012, 65, 758–763. [Google Scholar]
- Rahmati, S.; Yang, S.; Davidson, A.L.; Zechiedrich, E.L. Control of the acrab multidrug efflux pump by quorum-sensing regulator sdia. Mol. Microbiol 2002, 43, 677–685. [Google Scholar]
- Tavío, M.M.; Aquili, V.D.; Poveda, J.B.; Antunes, N.T.; Sánchez-Céspedes, J.; Vila, J. Quorum-sensing regulator sdia and mara overexpression is involved in in vitro-selected multidrug resistance of Escherichia coli. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 2010, 65, 1178–1186. [Google Scholar]
- Kanamaru, K.; Kanamaru, K.; Tatsuno, I.; Tobe, T.; Sasakawa, C. Sdia, an Escherichia coli homologue of quorum-sensing regulators, controls the expression of virulence factors in enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli o157:H7. Mol. Microbiol 2000, 38, 805–816. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Maeda, T.; Hong, S.H.; Wood, T.K. Reconfiguring the quorum-sensing regulator sdia of Escherichia coli to control biofilm formation via indole and n-acylhomoserine lactones. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2009, 75, 1703–1716. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, T.; Zhao, L.; Sun, H.; Zhou, X.; Sun, B. Lsrr-binding site recognition and regulatory characteristics in Escherichia coli ai-2 quorum sensing. Cell Res 2009, 19, 1258–1268. [Google Scholar]
- Xavier, K.B.; Miller, S.T.; Lu, W.; Kim, J.H.; Rabinowitz, J.; Pelczer, I.; Semmelhack, M.F.; Bassler, B.L. Phosphorylation and processing of the quorum-sensing molecule autoinducer-2 in enteric bacteria. ACS Chem. Biol 2007, 2, 128–136. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Hashimoto, Y.; Tsao, C.-Y.; Valdes, J.J.; Bentley, W.E. Cyclic amp (camp) and camp receptor protein influence both synthesis and uptake of extracellular autoinducer 2 in Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol 2005, 187, 2066–2076. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Meng, X.; Sun, B. An eal domain protein and cyclic amp contribute to the interaction between the two quorum sensing systems in Escherichia coli. Cell Res 2008, 18, 937–948. [Google Scholar]
- González Barrios, A.F.; Zuo, R.; Hashimoto, Y.; Yang, L.; Bentley, W.E.; Wood, T.K. Autoinducer 2 controls biofilm formation in Escherichia coli through a novel motility quorum-sensing regulator (mqsr, b3022). J. Bacteriol 2006, 188, 305–316. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.X.; Xu, Z.H.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Tian, J.; Weng, L.X.; Wang, L.H. A new quorum-sensing inhibitor attenuates virulence and decreases antibiotic resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Microbiol 2012, 50, 987–993. [Google Scholar]
- Geske, G.D.; O’Neill, J.C.; Miller, D.M.; Mattmann, M.E.; Blackwell, H.E. Modulation of bacterial quorum sensing with synthetic ligands: Systematic evaluation of n-acylated homoserine lactones in multiple species and new insights into their mechanisms of action. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 13613–13625. [Google Scholar]
- Mattmann, M.E.; Shipway, P.M.; Heth, N.J.; Blackwell, H.E. Potent and selective synthetic modulators of a quorum sensing repressor in Pseudomonas aeruginosa identified from second-generation libraries of N-acylated l-homoserine lactones. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 942–949. [Google Scholar]
- Amara, N.; Mashiach, R.; Amar, D.; Krief, P.; Spieser, S.A.H.; Bottomley, M.J.; Aharoni, A.; Meijler, M.M. Covalent inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 10610–10619. [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly, K.; Wu, R.; Ollivault-Shiflett, M.; Goodwin, P.M.; Silks, L.A.; Iyer, R. Design, synthesis, and a novel application of quorum-sensing agonists as potential drug-delivery vehicles. J. Drug Target 2010, 19, 528–539. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C.; Kirsch, B.; Zimmer, C.; de Jong, J.C.; Henn, C.; Maurer, C.K.; Müsken, M.; Häussler, S.; Steinbach, A.; Hartmann, R.W. Discovery of antagonists of pqsr, a key player in 2-alkyl-4-quinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem. Biol 2012, 19, 381–390. [Google Scholar]
- Rasko, D.A.; Moreira, C.G.; Li de, R.; Reading, N.C.; Ritchie, J.M.; Waldor, M.K.; Williams, N.; Taussig, R.; Wei, S.; Roth, M.; et al. Targeting qsec signaling and virulence for antibiotic development. Science 2008, 321, 1078–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Stacy, D.M.; Welsh, M.A.; Rather, P.N.; Blackwell, H.E. Attenuation of quorum sensing in the pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii using non-native N-acyl homoserine lactones. ACS Chem. Biol 2012, 7, 1719–1728. [Google Scholar]
- Passador, L.; Tucker, K.D.; Guertin, K.R.; Journet, M.P.; Kende, A.S.; Iglewski, B.H. Functional analysis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa autoinducer pai. J. Bacteriol 1996, 178, 5995–6000. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, K.M.; Bu, Y.; Suga, H. Induction and inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing by synthetic autoinducer analogs. Chem. Biol 2003, 10, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Morkunas, B.; Galloway, W.R.J.D.; Wright, M.; Ibbeson, B.M.; Hodgkinson, J.T.; O’Connell, K.M.G.; Bartolucci, N.; Valle, M.D.; Welch, M.; Spring, D.R. Inhibition of the production of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence factor pyocyanin in wild-type cells by quorum sensing autoinducer-mimics. Org. Biomol. Chem 2012, 10, 8452–8464. [Google Scholar]
- Annapoorani, A.; Umamageswaran, V.; Parameswari, R.; Pandian, S.; Ravi, A. Computational discovery of putative quorum sensing inhibitors against lasr and rhlr receptor proteins of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des 2012, 26, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Xu, J.-L.; Hu, J.; Wang, L.-H.; Ong, S.L.; Leadbetter, J.R.; Zhang, L.-H. Acyl-homoserine lactone acylase from ralstonia strain xj12b represents a novel and potent class of quorum-quenching enzymes. Mol. Microbiol 2003, 47, 849–860. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.-H.; Xu, J.-L.; Li, X.-Z.; Zhang, L.-H. Aiia, an enzyme that inactivates the acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing signal and attenuates the virulence of erwinia carotovora. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci 2000, 97, 3526–3531. [Google Scholar]
- Uroz, S.; Chhabra, S.R.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P.; Oger, P.; Dessaux, Y. N-acylhomoserine lactone quorum-sensing molecules are modified and degraded by rhodococcus erythropolis w2 by both amidolytic and novel oxidoreductase activities. Microbiology 2005, 151, 3313–3322. [Google Scholar]
- Reimmann, C.; Ginet, N.; Michel, L.; Keel, C.; Michaux, P.; Krishnapillai, V.; Zala, M.; Heurlier, K.; Triandafillu, K.; Harms, H.; et al. Genetically programmed autoinducer destruction reduces virulence gene expression and swarming motility in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pao1. Microbiology 2002, 148, 923–932. [Google Scholar]
- Bijtenhoorn, P.; Mayerhofer, H.; Müller-Dieckmann, J.; Utpatel, C.; Schipper, C.; Hornung, C.; Szesny, M.; Grond, S.; Thürmer, A.; Brzuszkiewicz, E.; et al. A novel metagenomic short-chain dehydrogenase/reductase attenuates Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and virulence on caenorhabditis elegans. PLoS One 2011, 6, e26278. [Google Scholar]
- Wahjudi, M.; Papaioannou, E.; Hendrawati, O.; van Assen, A.H.G.; van Merkerk, R.; Cool, R.H.; Poelarends, G.J.; Quax, W.J. Pa0305 of Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a quorum quenching acylhomoserine lactone acylase belonging to the ntn hydrolase superfamily. Microbiology 2011, 157, 2042–2055. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, K.-W.; Koh, C.-L.; Sam, C.-K.; Yin, W.-F.; Chan, K.-G. Quorum quenching revisited—from signal decays to signaling confusion. Sensors 2012, 12, 4661–4696. [Google Scholar]
- De Lamo Marin, S.; Xu, Y.; Meijler, M.M.; Janda, K.D. Antibody catalyzed hydrolysis of a quorum sensing signal found in gram-negative bacteria. BioOrg. Med. Chem. Lett 2007, 17, 1549–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann, G.F.; Park, J.; Mee, J.M.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Janda, K.D. The quorum quenching antibody rs2-1g9 protects macrophages from the cytotoxic effects of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing signaling molecule N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-homoserine lactone. Mol. Immunol 2008, 45, 2710–2714. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, N.; Yu, S.; Moniot, S.; Weyand, M.; Blankenfeldt, W. Crystallization and preliminary crystal structure analysis of the ligand-binding domain of pqsr (mvfr), the Pseudomonas quinolone signal (pqs) responsive quorum-sensing transcription factor of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Acta Crystallogr. Section F 2012, 68, 1034–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Pustelny, C.; Albers, A.; Büldt-Karentzopoulos, K.; Parschat, K.; Chhabra, S.R.; Cámara, M.; Williams, P.; Fetzner, S. Dioxygenase-mediated quenching of quinolone-dependent quorum sensing in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Chem. Biol 2009, 16, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar]
- Calfee, M.W.; Coleman, J.P.; Pesci, E.C. Interference with pseudomonas quinolone signal synthesis inhibits virulence factor expression by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci 2001, 98, 11633–11637. [Google Scholar]
- Lesic, B.; Lépine, F.; Déziel, E.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Padfield, K.; Castonguay, M.-H.; Milot, S.; Stachel, S.; Tzika, A.A.; et al. Inhibitors of pathogen intercellular signals as selective anti-infective compounds. PLoS Pathog 2007, 3, e126. [Google Scholar]
- Plyuta, V.; Zaitseva, J.; Lobakova, E.; Zagoskina, N.; Kuznetsov, A.; Khmel, I. Effect of plant phenolic compounds on biofilm formation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. APMIS 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adonizio, A.; Leal, S.M.; Ausubel, F.M.; Mathee, K. Attenuation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence by medicinal plants in a Caenorhabditis elegans model system. J. Med. Microbiol 2008, 57, 809–813. [Google Scholar]
- Sarabhai, S.; Sharma, P.; Capalash, N. Ellagic acid derivatives from Terminalia chebula retz. Downregulate the expression of quorum sensing genes to attenuate Pseudomonas aeruginosa pao1 virulence. PLoS One 2013, 8, e53441. [Google Scholar]
- Zimmer, K.R.; Macedo, A.J.; Nicastro, G.G.; Baldini, R.L.; Termignoni, C. Egg wax from the cattle tick Rhipicephalus(Boophilus) microplus inhibits Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm. Ticks Tick-Borne Dis. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skindersoe, M.; Ettinger-Epstein, P.; Rasmussen, T.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Nys, R.; Givskov, M. Quorum sensing antagonism from marine organisms. Mar. Biotechnol 2008, 10, 56–63. [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez, J.A.; Crowder, T.; Rinaldo-Matthis, A.; Ho, M.-C.; Almo, S.C.; Schramm, V.L. Transition state analogs of 5[prime]-methylthioadenosine nucleosidase disrupt quorum sensing. Nat. Chem. Biol 2009, 5, 251–257. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, M.; Gamby, S.; Nakayama, S.; Smith, J.; Sintim, H.O. A pro-drug approach for selective modulation of ai-2-mediated bacterial cell-to-cell communication. Sensors 2012, 12, 3762–3772. [Google Scholar]
- Roy, V.; Fernandes, R.; Tsao, C.-Y.; Bentley, W.E. Cross species quorum quenching using a native ai-2 processing enzyme. ACS Chem. Biol 2009, 5, 223–232. [Google Scholar]
- Vikram, A.; Jesudhasan, P.R.; Pillai, S.D.; Patil, B.S. Isolimonic acid interferes with Escherichia coli o157:H7 biofilm and ttss in qsebc and qsea dependent fashion. BMC Microbiol 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravichandiran, V.; Karthi, S.; Princy, S.A. Screening of sdia inhibitors from melia dubia seed extracts towards the hold back of uropathogenic E. coli quorum sensing-regulated factors. Med. Chem 2012, 8, 1190–1197. [Google Scholar]
- Allison, K.R.; Brynildsen, M.P.; Collins, J.J. Metabolite-enabled eradication of bacterial persisters by aminoglycosides. Nature 2011, 473, 216–220. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.H.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.A.; Neupane, G.P.; Cho, M.H.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J. Low concentrations of honey reduce biofilm formation, quorum sensing, and virulence in Escherichia coli o157:H7. Biofouling 2011, 27, 1095–1104. [Google Scholar]
- Givskov, M.; de Nys, R.; Manefield, M.; Gram, L.; Maximilien, R.; Eberl, L.; Molin, S.; Steinberg, P.D.; Kjelleberg, S. Eukaryotic interference with homoserine lactone-mediated prokaryotic signaling. J. Bacteriol 1996, 178, 6618–6622. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, D.; Bedzyk, L.A.; Ye, R.W.; Thomas, S.M.; Wood, T.K. Differential gene expression shows natural brominated furanones interfere with the autoinducer-2 bacterial signaling system of Escherichia coli. Biotechnol. Bioeng 2004, 88, 630–642. [Google Scholar]
- Sievert, D.M.; Ricks, P.P.; Edwards, J.R.; Schneider, A.; Patel, J.; Srinivasan, A.; Kallen, A.; Limbago, B.; Fridkin, S.; et al. National Healthcare Safety Network (NHSN) Team. Antimicrobial-resistant pathogens associated with healthcare-associated infections: Summary of data reported to the national healthcare safety network at the centers for disease control and prevention 2009–2010. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2013, 34, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Y.; Chai, D.; Wang, R.; Liang, B.; Bai, N. Colistin resistance of Acinetobacter baumannii: Clinical reports, mechanisms and antimicrobial strategies. J. Antimicrob. Chemother 2012, 67, 1607–1615. [Google Scholar]
- Falagas, M.E.; Kasiakou, S.K.; Saravolatz, L.D. Colistin: The revival of polymyxins for the management of multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis 2005, 40, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar]
- Derakhshan, S.; Sattari, M.; Bigdeli, M. Effect of cumin (cuminum cyminum) seed essential oil on biofilm formation and plasmid integrity of Klebsiella pneumoniae. Pharmacogn. Mag 2010, 6, 57–61. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.-W.; Oh, H.-S.; Kim, S.-R.; Lee, K.-B.; Yeon, K.-M.; Lee, C.-H.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.-K. Microbial population dynamics and proteomics in membrane bioreactors with enzymatic quorum quenching. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 4665–4675. [Google Scholar]
- Saroj, S.D.; Rather, P.N. Streptomycin inhibits quorum sensing in Acinetobacter baumannii. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 2013, 57, 1926–1929. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, L.R.; D’Argenio, D.A.; MacCoss, M.J.; Zhang, Z.; Jones, R.A.; Miller, S.I. Aminoglycoside antibiotics induce bacterial biofilm formation. Nature 2005, 436, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar]
- Linares, J.F.; Gustafsson, I.; Baquero, F.; Martinez, J.L. Antibiotics as intermicrobial signaling agents instead of weapons. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci 2006, 103, 19484–19489. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, V.; Evans, G.B.; Lenz, D.H.; Mason, J.M.; Clinch, K.; Mee, S.; Painter, G.F.; Tyler, P.C.; Furneaux, R.H.; Lee, J.E.; et al. Femtomolar transition state analogue inhibitors of 5′-methylthioadenosine/s-adenosylhomocysteine nucleosidase from Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem 2005, 280, 18265–18273. [Google Scholar]
- Schramm, V.L.; Gutierrez, J.A.; Cordovano, G.; Basu, I.; Guha, C.; Belbin, T.J.; Evans, G.B.; Tyler, P.C.; Furneaux, R.H. Transition state analogues in quorum sensing and sam recycling. Nucleic Acids Symp. Ser 2008, 52, 75–76. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, T.T.; Schweizer, H.P. Characterization of Pseudomonas aeruginosa enoyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (fabi): A target for the antimicrobial triclosan and its role in acylated homoserine lactone synthesis. J. Bacteriol 1999, 181, 5489–5497. [Google Scholar]
- Czajkowski, R.; Jafra, S. Quenching of acyl-homoserine lactone-dependent quorum sensing by enzymatic disruption of signal molecules. Acta Biochim. Pol 2009, 56, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Romero, M.; Diggle, S.P.; Heeb, S.; Cámara, M.; Otero, A. Quorum quenching activity in anabaena sp. Pcc 7120: Identification of aiic, a novel ahl-acylase. FEMS Microbiol. Lett 2008, 280, 73–80. [Google Scholar]
- Uroz, S.; Oger, P.M.; Chapelle, E.; Adeline, M.-T.; Faure, D.; Dessaux, Y. A rhodococcus qsda-encoded enzyme defines a novel class of large-spectrum quorum-quenching lactonases. Appl. Environ. Microbiol 2008, 74, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.Y.; Xue, B.; Lee, K.H.; Tung, A.; Wu, L.; Robinson, R.C.; Yew, W.S. Directed evolution of a thermostable quorum-quenching lactonase from the amidohydrolase superfamily. J. Biol. Chem 2010, 285, 40911–40920. [Google Scholar]
- Chow, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Tay, S.B.; Chua, K.L.; Yew, W.S. Disruption of biofilm formation by the human pathogen Acinetobacter baumannii using engineered quorum-quenching lactonases; National University of Singapore: Singapore, Unpublished work; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dekimpe, V.; Déziel, E. Revisiting the quorum-sensing hierarchy in Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The transcriptional regulator rhlr regulates lasr-specific factors. Microbiology 2009, 155, 712–723. [Google Scholar]
- Defoirdt, T.; Boon, N.; Bossier, P. Can bacteria evolve resistance to quorum sensing disruption? PLoS Pathog 2010, 6, e1000989. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, J.L.; Baquero, F.; Andersson, D.I. Predicting antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Micro 2007, 5, 958–965. [Google Scholar]
- Diggle, S.P.; Griffin, A.S.; Campbell, G.S.; West, S.A. Cooperation and conflict in quorum-sensing bacterial populations. Nature 2007, 450, 411–414. [Google Scholar]
- Sandoz, K.M.; Mitzimberg, S.M.; Schuster, M. Social cheating in Pseudomonas aeruginosa quorum sensing. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci 2007, 104, 15876–15881. [Google Scholar]
- Mellbye, B.; Schuster, M. The sociomicrobiology of antivirulence drug resistance: A proof of concept. MBio 2011, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).