The ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Is Involved in Sulfur Dioxide Preconditioning-Induced Protection against Cardiac Dysfunction in Isolated Perfused Rat Heart Subjected to Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
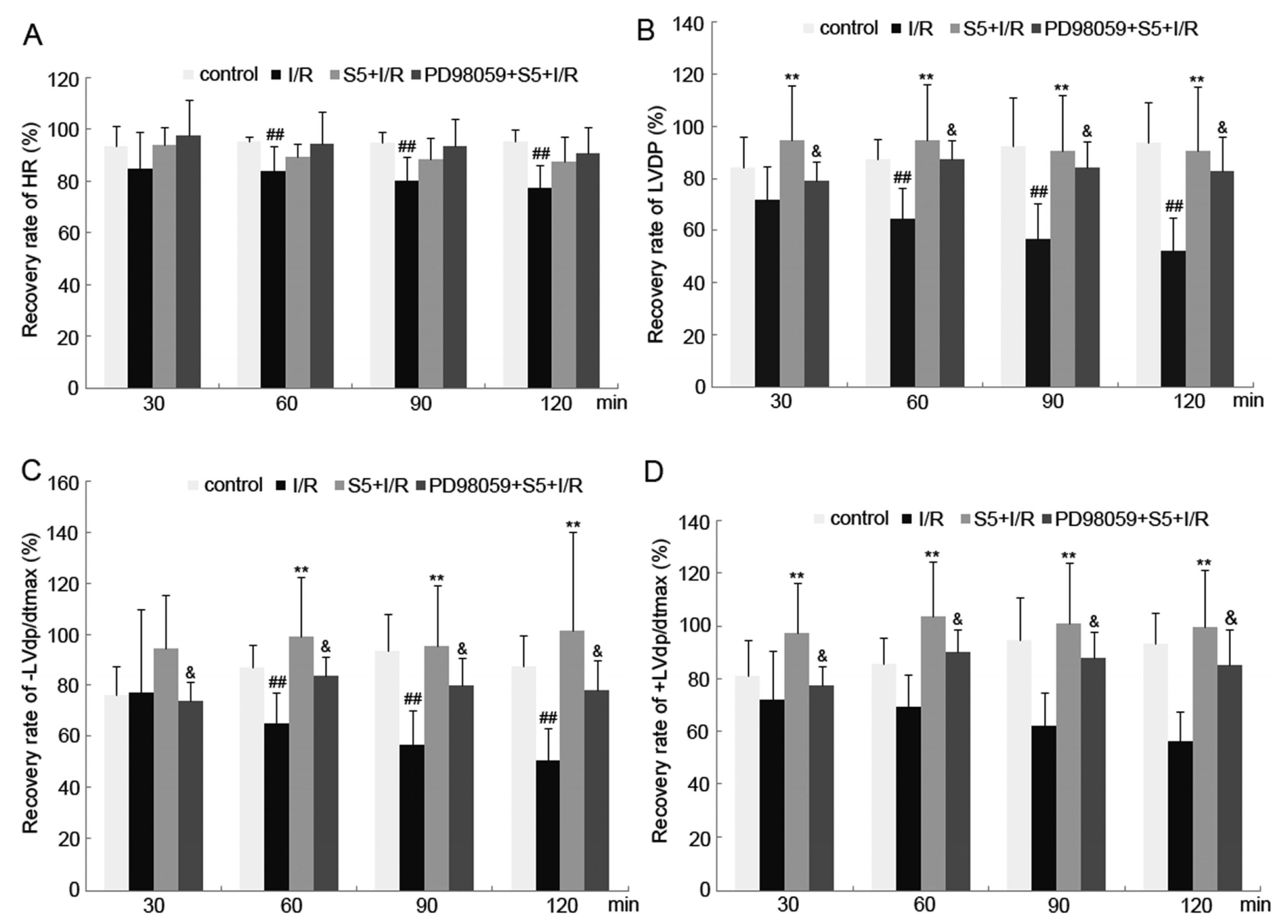
2.1. Ischemia/Reperfusion Resulted in Impaired Cardiac Function in Isolated Perfused Rat Heart
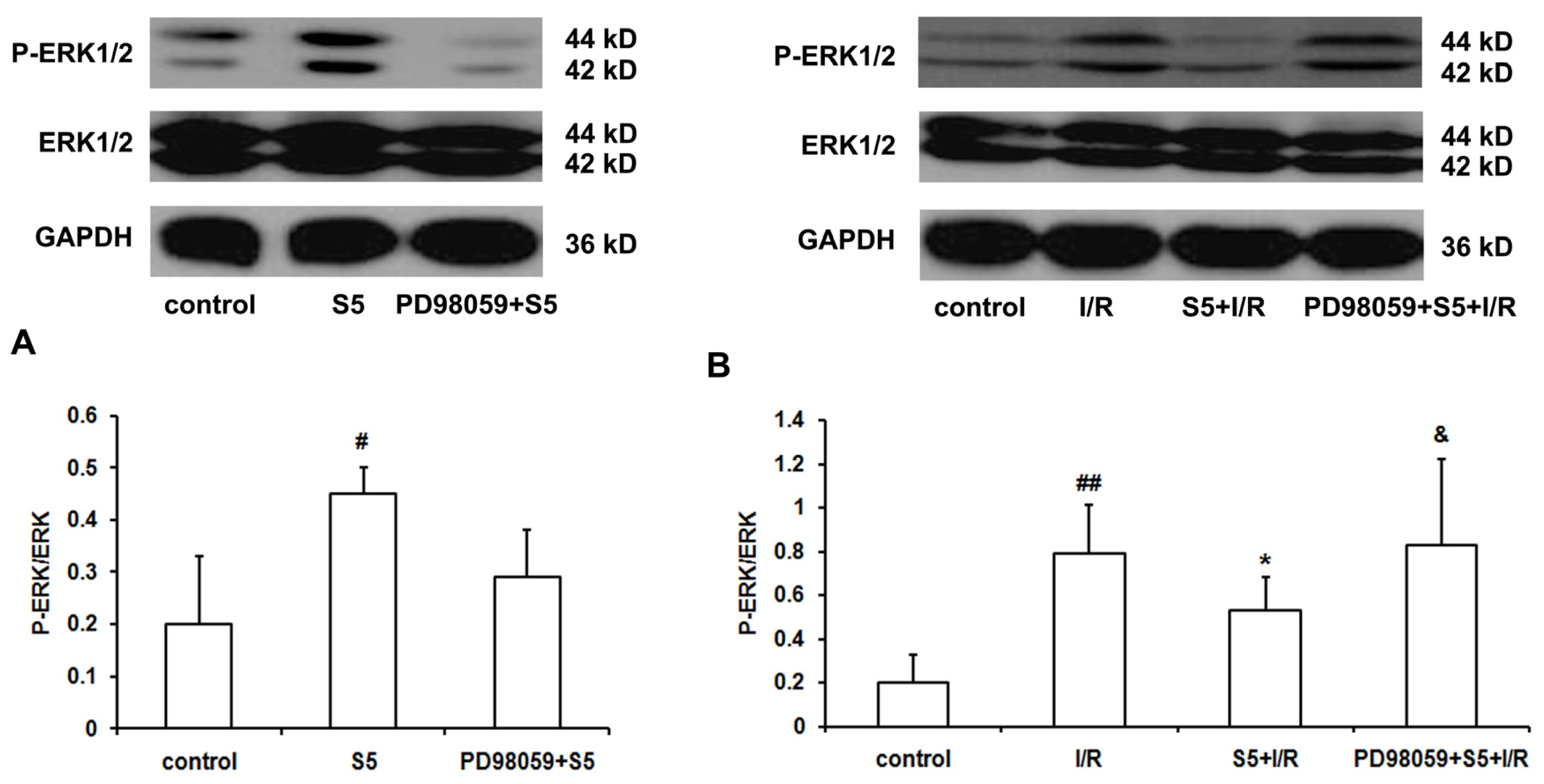
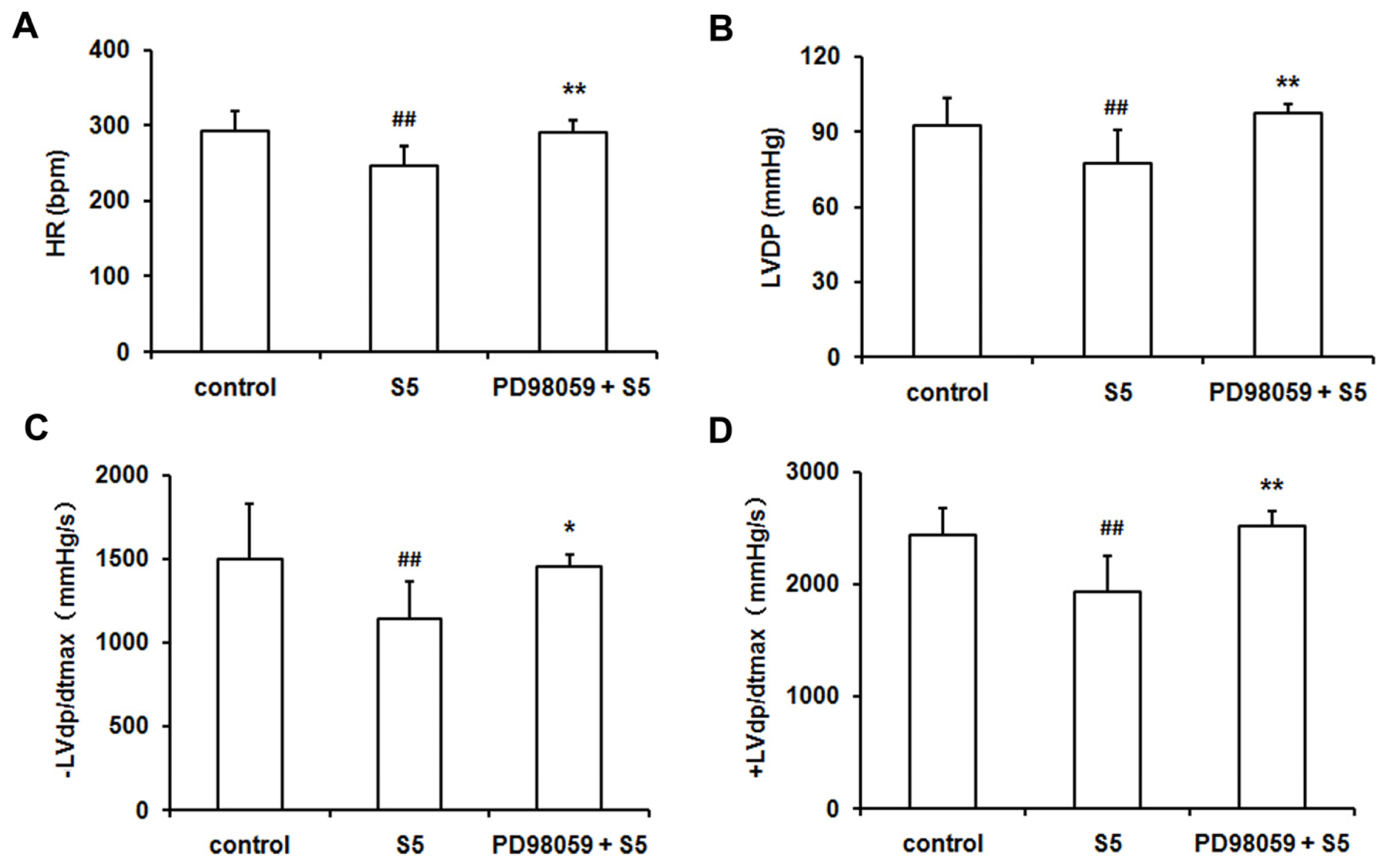
2.2. SO2 Induced Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 Protein and Depressed Cardiac Function in Isolated Perfused Rat Heart without Ischemia/Reperfusion
2.3. SO2 Preconditioning Inhibited the Excessively-Induced Myocardial Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 Protein Induced by Ischemia/Reperfusion
2.4. SO2 Preconditioning Improved the Myocardial Function in Isolated Perfused Rat Heart Subjected to Ischemia/Reperfusion, Which Could Be Abolished by Treatment with PD98059
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Animals
4.2. Reagents
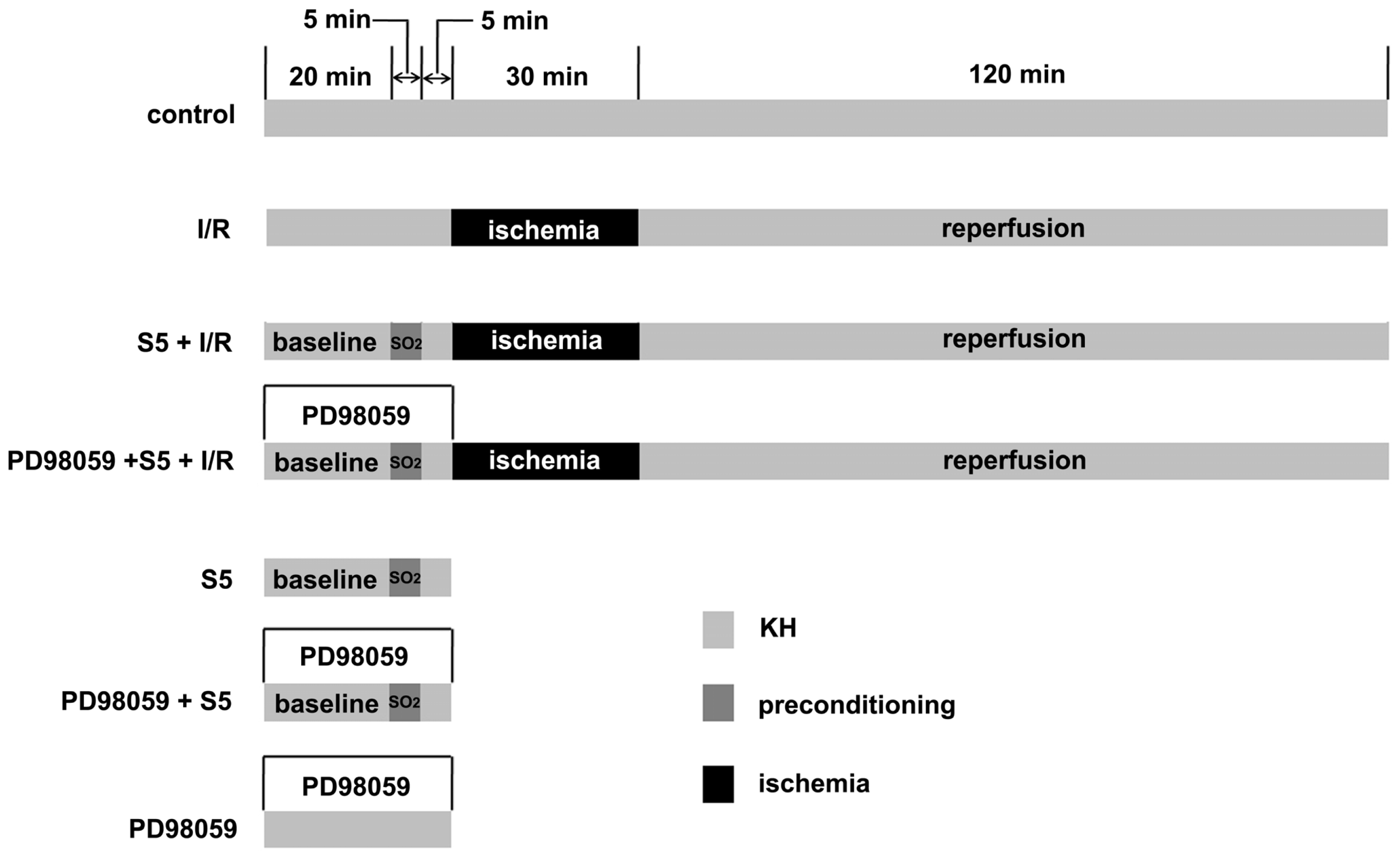
4.3. Animal Grouping
4.4. Heart Perfusion In Vitro and Cardiac Function Measurement
4.5. Measurement of CK and GOT Activity in CPF
4.6. Myocardial ERK and P-ERK Detection by Western Blotting
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
| Group | n | CK (U/L) | GOT (U/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 8 | 3.50 ± 1.85 | 3.25 ± 0.71 |
| I/R | 8 | 14.33 ± 8.34 ## | 6.50 ± 1.88 ## |
| S5 + I/R | 8 | 6.71 ± 4.23 * | 3.71 ± 1.25 ** |
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhao, H.X.; Wang, X.L.; Wang, Y.H.; Wu, Y.; Li, X.Y.; Lv, X.P.; Zhao, Z.Q.; Zhao, R.R.; Liu, H.R. Attenuation of myocardial injury by postconditioning: Role of hypoxia inducible factor-1α. Basic Res. Cardiol 2010, 105, 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Xiang, X.; Lin, H. Early protective effect of total hypoxic preconditioning on rats against systemic injury from hemorrhagic shock and resuscitation. J. Surg. Res 2012, 178, 842–850. [Google Scholar]
- Gruner, C.; Akkaya, E.; Kretschmar, O.; Roffi, M.; Corti, R.; Jenni, R.; Eberli, F.R. Pharmacologic preconditioning therapy prior to atrial septal defect closure in patients at high risk for acute pulmonary edema. J. Interv. Cardiol 2012, 25, 505–512. [Google Scholar]
- Du, S.X.; Jin, H.F.; Bu, D.F.; Zhao, X.; Geng, B.; Tang, C.S.; Du, J.B. Endogenously generated sulfur dioxide and its vasorelaxant effect in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin 2008, 29, 923–930. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, H.F.; Du, S.X.; Zhao, X.; Wei, H.L.; Wang, Y.F.; Liang, Y.F.; Tang, C.S.; Du, J.B. Effects of endogenous sulfur dioxide on monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin 2008, 29, 1157–1166. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Tian, Y.; Prabha, M.; Liu, D.; Chen, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, X.; Tang, C.; Tang, X.; Jin, H.; et al. Effects of sulfur dioxide on hypoxic pulmonary vascular structural remodeling. Lab. Invest 2010, 90, 68–82. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Meng, Z. The role of sulfur dioxide as an endogenous gaseous vasoactive factor in synergy with nitric oxide. Nitric Oxide 2009, 20, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, D.; Ochs, T.; Tang, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, S.; Geng, B.; Jin, H.; Du, J. Endogenous sulfur dioxide protects against isoproterenol-induced myocardial injury and increases myocardial antioxidant capacity in rats. Lab. Invest 2011, 91, 12–23. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, Z.; Zhang, H. The vasodilator effect and its mechanism of sulfur dioxide-derivatives on isolated aortic rings of rats. Inhal. Toxicol 2007, 19, 979–986. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.K.; Ren, A.J.; Yang, X.Q.; Wang, L.G.; Rong, W.F.; Tang, C.S.; Yuan, W.J.; Lin, L. Sulfur dioxide relaxes rat aorta by endothelium-dependent and independent mechanisms. Physiol. Res 2009, 58, 521–527. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Meng, Z. The vasodilator mechanism of sulfur dioxide on isolated aortic rings of rats: Involvement of the K+ and Ca2+ channels. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2009, 602, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Q.; Du, J.B.; Jin, H.F.; Li, W.; Liang, Y.F.; Geng, B.; Li, S.K.; Zhang, C.Y.; Tang, C.S. Endogenous sulfur dioxide aggravates myocardial injury in isolated rat heart with ischemia and reperfusion. Transplantation 2009, 87, 517–524. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.B.; Huang, X.M.; Ochs, T.; Li, X.Y.; Jin, H.F.; Tang, C.S.; Du, J.B. Effect of sulfur dioxide preconditioning on rat myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inducing endoplasmic reticulum stress. Basic Res. Cardiol 2011, 106, 865–878. [Google Scholar]
- Widmann, C.; Gibson, S.; Jarpe, M.B.; Johnson, G.L. Mitogen-activated protein kinase: Conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol. Rev 1999, 79, 143–180. [Google Scholar]
- Gerits, N.; Kostenko, S.; Moens, U. In vivo functions of mitogen-activated protein kinases: Conclusions from knock-in and knock-out mice. Transgenic Res 2007, 16, 281–314. [Google Scholar]
- Cargnello, M.; Roux, P.P. Activation and function of the MAPKs and their substrates, the MAPK-activated protein kinases. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev 2011, 75, 50–83. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, L.; Sawada, T.; Decker, S.J.; Saltiel, A.R. Inhibition of MAP kinase kinase blocks the differentiation of PC-12 cells induced by nerve growth factor. J. Biol. Chem 1995, 270, 13585–13588. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Song, K.H.; Ha, H. Fractalkine increases mesangial cell proliferation through reactive oxygen species and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Transpl. Proc 2012, 44, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.W.; Choi, R.J.; Seo, E.K.; Nam, J.W.; Dong, M.S.; Shin, E.M.; Guo, L.Y.; Kim, Y.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of Z-ligustilide through suppression of mitogen-activated protein kinases and nuclear factor-κB activation pathways. Arch. Pharm. Res 2012, 35, 723–732. [Google Scholar]
- Himaya, S.W.; Ryu, B.; Qian, Z.J.; Kim, S.K. Paeonol from Hippocampus kuda Bleeler suppressed the neuro-inflammatory responses in vitro via NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathways. Toxicol. Vitro 2012, 26, 878–887. [Google Scholar]
- McCarroll, J.A.; Phillips, P.A.; Park, S.; Doherty, E.; Pirola, R.C.; Wilson, J.S.; Apte, M.V. Pancreatic stellate cell activation by ethanol and acetaldehyde: Is it mediated by the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway? Pancreas 2003, 27, 150–160. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, D.; Fan, X.; Yin, P.; Wen, Q.; Yan, F.; Yuan, S.; Liu, B.; Zhuang, G.; Liu, Z. Ignification of decoy receptor 3 (DcR3) and external-signal regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) in gastric cancer patients. BMC Immunol 2012, 13, 28. [Google Scholar]
- Fujioka, N.; Nguyen, J.; Chen, C.; Li, Y.; Pasrija, T.; Niehans, G.; Johnson, K.N.; Gupta, V.; Kratzke, R.A.; Gupta, K. Morphine-induced epidermal growth factor pathway activation in non-small cell lung cancer. Anesth. Analg 2011, 113, 1353–1364. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattacharya, I.; Damjanović, M.; Dominguez, A.P.; Haas, E. Inhibition of activated ERK1/2 and JNKs improves vascular function in mouse aortae in the absence of nitric oxide. Eur. J. Pharmacol 2011, 658, 22–27. [Google Scholar]
- Punn, A.; Mockridge, J.W.; Farooqui, S.; Marber, M.S.; Heads, R.J. Sustained activation of p42/p44 mitogen-activated protein kinase during recovery from simulated ischaemia mediates adaptive cytoprotection in cardiomyocytes. Biochem. J 2000, 350, 891–899. [Google Scholar]
- Crews, C.M.; Alessandrini, A.; Erikson, R.L. The primary structure of MEK, a protein kinase that phosphorylates the ERK gene product. Science 1992, 258, 478–480. [Google Scholar]
- Cowley, S.; Paterson, H.; Kemp, P.; Marshall, C.J. Activation of MAP kinase kinase is necessary and sufficient for PC12 differentiation and for transformation of NIH 3T3 cells. Cell 1994, 77, 841–852. [Google Scholar]
- Dudley, D.T.; Pang, L.; Decker, S.J.; Bridges, A.J.; Saltiel, A.R. A synthetic inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 7686–7689. [Google Scholar]
- Alessi, D.R.; Saito, Y.; Campbell, D.G.; Cohen, P.; Sithanandam, G.; Rapp, U.; Ashworth, A.; Marshall, C.J.; Cowley, S. Identification of the sites in MAP kinase kinase-1 phosphorylated by p74raf-1. EMBO J 1994, 13, 1610–1619. [Google Scholar]
- Hausenloy, D.J.; Baxter, G.; Bell, R.; Botker, H.E.; Davidson, S.M.; Downey, J.; Heusch, G.; Kitakaze, M.; Lecour, S.; Mentzer, R.; et al. Translating novel strategies for cardioprotection: The hatter workshop recommendations. Basic Res. Cardiol 2010, 105, 677–686. [Google Scholar]
- Koca, V.; Ari, H. Angioplasty as early revascularization in acute myocardial infarction. Anadolu. Kardiyol. Derg 2008, 8, 77–83. [Google Scholar]
- Yavuz, S. Surgery as early revascularization after acute myocardial infarction. Anadolu. Kardiyol. Derg 2008, 8, 84–92. [Google Scholar]
- Murry, C.E.; Jennings, R.B.; Reimer, K.A. Preconditioning with ischemia: A delay of lethal cell injury in ischemic myocardium. Circulation 1986, 74, 1124–1136. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, J.; Meng, Z. Expression of apoptosis-related genes in livers from rats exposed to sulfur dioxide. Toxicology 2005, 216, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Balazy, M.; Abu-Yousef, I.A.; Harpp, D.N.; Park, J. Identification of carbonyl sulfide and sulfur dioxide in porcine coronary artery by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, possible relevance to EDHF. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 2003, 311, 728–734. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, T.L.; Wang, C.; Gu, J.L.; Ma, X.L.; Kumar, S.; Lee, J.C.; Feuerstein, G.Z.; Thomas, H.; Maleeff, B.; Ohlstein, E.H. Inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase enhances ischemia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in cultured cardiac myocytes and exaggerates reperfusion injury in isolated perfused heart. Circ. Res 2000, 86, 692–699. [Google Scholar]
- Lips, D.J.; Bueno, O.F.; Wilkins, B.J.; Purcell, N.H.; Kaiser, R.A.; Lorenz, J.N.; Voisin, L.; Saba-El-Leil, M.K.; Meloche, S.; Pouysségur, J.; et al. MEK1-ERK2 signaling pathway protects myocardium from ischemic injury in vivo. Circulation 2004, 109, 1938–1941. [Google Scholar]
- Das, A.; Salloum, F.N.; Xi, L.; Rao, Y.J.; Kukreja, R.C. ERK phosphorylation mediates sildenafil-induced myocardial protection against ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol 2009, 296, H1236–H1243. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.M.; Hu, F.; Cui, L.; Swingle, M.R.; Honkanen, R.E.; Soltani, P.; Tissier, R.; Cohen, M.V.; et al. Cardioprotection by mild hypothermia during ischemia involves preservation of ERK activity. Basic Res. Cardiol 2011, 106, 421–430. [Google Scholar]
- Johansen, D.; Ytrehus, K.; Baxter, G.F. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide (H2S) protects against regional myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury—Evidence for a role of KATP channels. Basic Res. Cardiol 2006, 101, 53–60. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, P.; Sun, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, S.; Liu, A.D.; Holmberg, L.; Huang, X.; Tang, C.; Du, J.; Jin, H. The ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Is Involved in Sulfur Dioxide Preconditioning-Induced Protection against Cardiac Dysfunction in Isolated Perfused Rat Heart Subjected to Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 22190-22201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122190
Huang P, Sun Y, Yang J, Chen S, Liu AD, Holmberg L, Huang X, Tang C, Du J, Jin H. The ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Is Involved in Sulfur Dioxide Preconditioning-Induced Protection against Cardiac Dysfunction in Isolated Perfused Rat Heart Subjected to Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(11):22190-22201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122190
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Pan, Yan Sun, Jinyan Yang, Siyao Chen, Angie Dong Liu, Lukas Holmberg, Xiaomei Huang, Chaoshu Tang, Junbao Du, and Hongfang Jin. 2013. "The ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Is Involved in Sulfur Dioxide Preconditioning-Induced Protection against Cardiac Dysfunction in Isolated Perfused Rat Heart Subjected to Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 11: 22190-22201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122190
APA StyleHuang, P., Sun, Y., Yang, J., Chen, S., Liu, A. D., Holmberg, L., Huang, X., Tang, C., Du, J., & Jin, H. (2013). The ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway Is Involved in Sulfur Dioxide Preconditioning-Induced Protection against Cardiac Dysfunction in Isolated Perfused Rat Heart Subjected to Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(11), 22190-22201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms141122190






