Synthesis of Bisindolylmethanes and Their Cytotoxicity Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
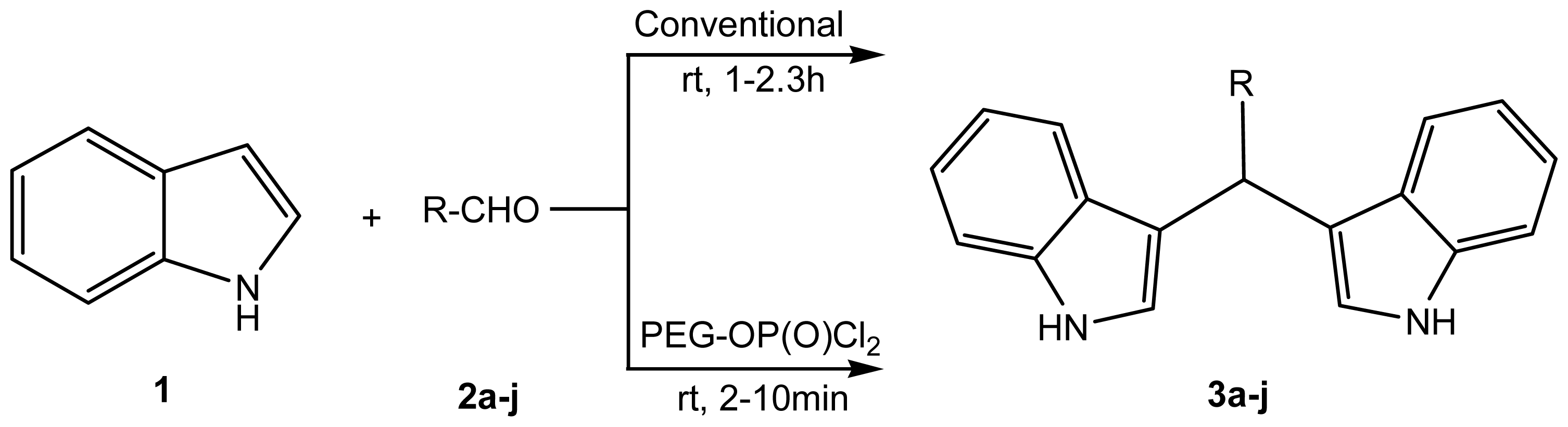
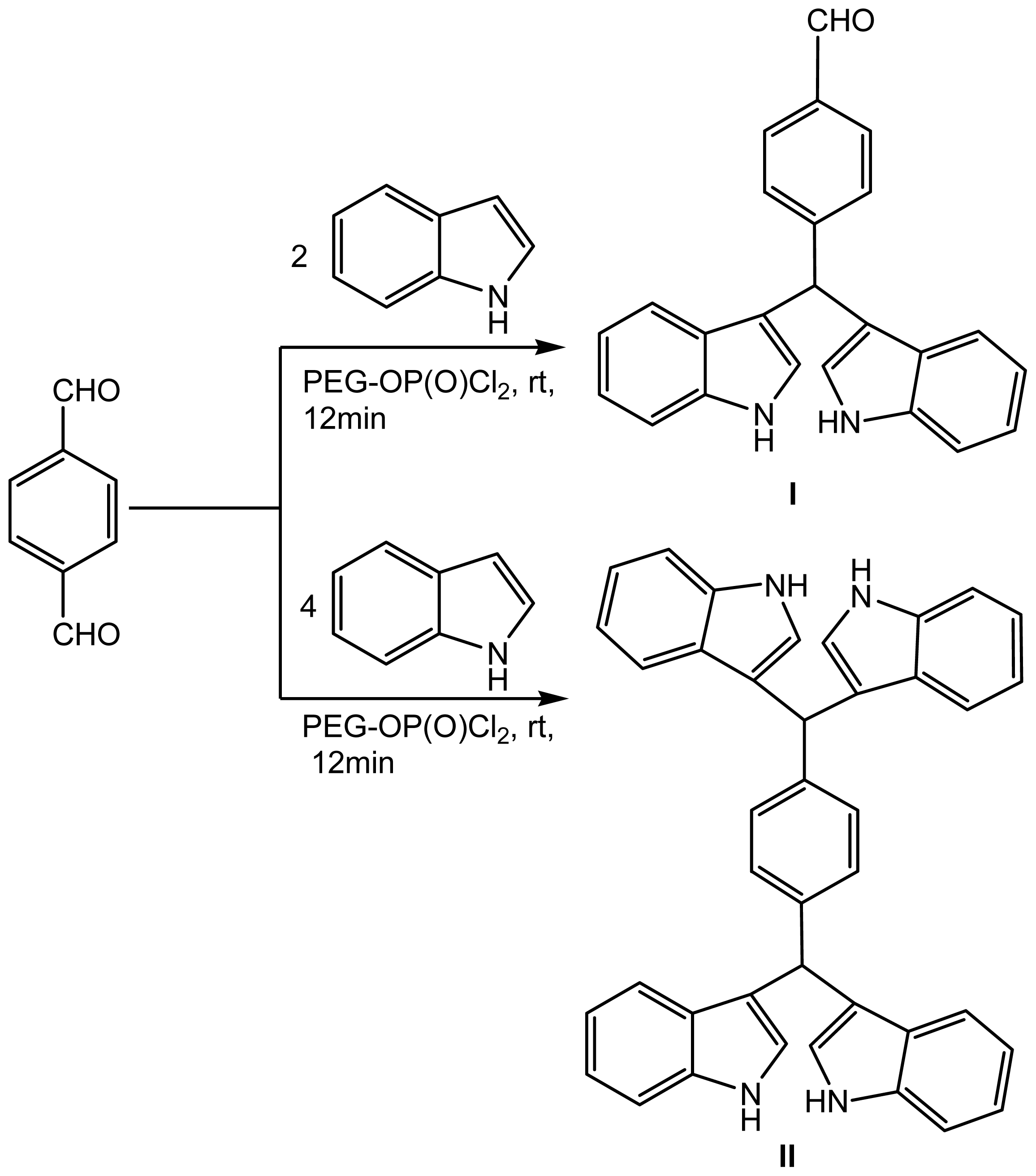
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biology
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General
3.2. Preparation of PEG-POCl2 Catalyst
3.3. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Bisindolylmethanes (3a–j)
3.3.1. Method A: Conventional
3.3.2. Method B: Catalytic Condition
3.4. Cell Lines and Culture
3.5. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Jemal, A.; Bray, F.; Center, M.M.; Ferlay, J.; Ward, E.F. Global cancer statistics. Cancer J. Clin 2011, 61, 69–90. [Google Scholar]
- Arulselvan, P.; Wen, C.C.; Lan, C.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Wei, W.C.; Yang, N.S. Dietary administration of scallion extract effectively inhibits colorectal tumor growth: Cellular and molecular mechanisms in mice. PLoS One 2012, 7, e44658. [Google Scholar]
- Halliwell, B. Oxidative stress and cancer. Biochem. J 2007, 401, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mostafa, Y.A.H.; Hussein, M.A.; Radwan, A.A.; Kfafy, A.E.H.N. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of certain new 1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine derivatives. Arch. Pharm. Res 2008, 31, 279–293. [Google Scholar]
- Habib, N.S.; Soliman, R.; El-Tombary, A.A.; El-Hawash, S.A.; Shaaban, O.G. Synthesis ofthiazolo[4,5-d]pyrimidine derivatives as potential antimicrobial agents. Arch. Pharm. Res 2007, 30, 1511–1520. [Google Scholar]
- Sundberg, R.J. The Chemistry of Indoles; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Sivaprasad, G.; Perumal, P.T.; Prabavathy, V.R.; Mathivanan, N. Synthesis antimicrobial activity of pyrazolylbisindoles. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett 2006, 16, 6302–6305. [Google Scholar]
- Kamal, A.; Khan, M.N.A.; Reddy, K.S.; Srikanth, Y.V.V.; Ahmed, S.K.; Kumar, K.P.; Murthy, U.S.N. An efficient synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem 2009, 24, 559–565. [Google Scholar]
- Sujatha, K.; Perumal, P.T.; Muralidharan, D.; Rajendran, M. Synthesis, analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of bis(indolyl)methanes. Indian J. Chem 2009, 48, 267–272. [Google Scholar]
- Benabadji, S.H.; Wen, R.; Zheng, J.; Dong, X.; Yuan, S. Anticarcinogenic and antioxidant activity of diindolylmethane derivatives. Acta Pharmacol. Sin 2004, 25, 666–671. [Google Scholar]
- Shiri, M.; Zolfigol, M.A.; Kruger, H.G.; Tanbakouchian, Z. Bis- and trisindolylmethanes. Chem. Rev 2010, 110, 2250–2293. [Google Scholar]
- Kirkus, M.; Tsai, M.H.; Grazulevicius, J.V.; Wu, C.C.; Chi, L.C.; Wong, K.T. New indole-carbazole hybrids as glass-forming high-triplet-energy materials. Synth. Met 2009, 159, 729–734. [Google Scholar]
- Stupnikova, T.V.; Reybenko, L.A.; Skorobogotova, Z.M.; Sheinkman, A.K. Tri(3-indolyl)-methyl perchlorates—New dyes of the triarylmethane series. Khim. Geterotsikl. Soedin 1978, 3, 314. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Hu, S.; Liu, K.; Guo, Y.; Xu, J.; Shao, S. Oxidized bis(indolyl)methane: A simple and efficient chromogenic-sensing molecule based on the proton transfer signaling mode. Org. Lett 2006, 8, 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Martinez, R.; Espinosa, A.; Tarraga, A.; Molina, P. Bis(indolyl)methane derivatives as highly selective colourimetric and ratiometric fluorescent molecular chemosensors for Cu2+ cations. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 2184–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, B.S.; Chen, J.T.; Liu, S.T. An efficient preparation of bis(indole)methanes catalyzed by tetrakis[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]borate salts in aqueous medium. Synthesis 2007, 20, 3125–3128. [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi-Yachide, T.; Tetsuhashi, M.; Aoyama, H.; Hashimoto, Y. Enhancement of chemically-induced HL-60 cell differentiation by 3,3′-diindolylmethane derivatives. Chem. Pharm. Bull 2009, 57, 536–540. [Google Scholar]
- Najmodin, A.; Lalleh, T.; Mohammad, R.S. Highly efficient synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes in water. J. Mol. Catal. A 2007, 275, 109–112. [Google Scholar]
- Najmadin, A.; Zohreh, M. Eutectic salts promote green synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes. Res. Chem. Intermed 2012, 38, 1495–1500. [Google Scholar]
- Mi, X.L.; Luo, S.Z.; He, J.Q.; Cheng, J.P. Dy(OTf)3 in ionic liquid: An efficient catalytic system for reactions of indole with aldehydes/ketones or imines. Tetrahedron Lett 2004, 45, 4567–4570. [Google Scholar]
- Samuel, R.M.; Samuel, T.; Margiani, P.F.; Filipe, P.; Eder, J.L.; Diego, A.; Gelson, P.; Raquel, G.J. Synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes using silica gel as an efficient and recyclable surface. Tetrahedron Lett 2012, 53, 5402–5406. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, B.W.; Qin, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.P. Amberlyst-catalyzed reaction of indole: Synthesis of bisindolylalkane. Synth. Commun 2005, 35, 1209–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, J.S.; Reddy, B.V.S.; Murthy, C.V.S.R.; Kumar, G.M.; Madan, C. Lithium perchlorate catalyzed reactions of indoles: An expeditious synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes. Synthesis 2001, 5, 783–787. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, R.; Perumal, P.T. InCl3 and In(OTf)3 catalyzed reactions: Synthesis of 3-acetyl indoles, bis-indolylmethane and indolylquinoline derivatives. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 1229–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, S.M.; Yu, S.C.; Peng, Z.H. Sc(OTf)3-catalyzed efficient synthesis of 1,1-bis(indolyl)ketones by the double indolylation of acetic acid 2-methylene-3-oxobutyl ester. Org. Biomol. Chem 2005, 3, 1933–1936. [Google Scholar]
- Bandgar, B.P.; Shaikh, K.A. Molecular iodine-catalyzed efficient and highly rapid synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes under mild conditions. Tetrahedron Lett 2003, 44, 1959–1961. [Google Scholar]
- Deb, W.L.; Bhuyan, P.J. An efficient and clean synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes in a protic solvent at room temperature. Tetrahedron Lett 2006, 47, 1441–1443. [Google Scholar]
- Nagawade, R.R.; Shinde, D.B. Synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes. Acta Chim. Slov 2006, 53, 210–213. [Google Scholar]
- Babu, G.; Sreedhar, N.; Perumal, P.T. A convenient method of synthesis of bis(indolyl)-methane indiumtrichloride catalyzed reactions of indole with aldehydes and schiff bases. Synth. Commun 2000, 30, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar]
- Firouzabadi, H.; Iranpoor, N.; Ali Jafari, A.A. Aluminumdodecatungstophosphate (AlPW12O40), a versatile and a highly water tolerant green lewis acid catalyzes efficient preparation of indole derivatives. J. Mol. Catal 2006, 244, 168–172. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, S.J.; Zhou, J.F.; Gu, D.G.; Wang, S.Y.; Loh, T.P. Efficient synthesis of bis(indolyl)methanes catalyzed by lewis acids in ionic liquids. Synlett 2003, 2077–2079. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.S.; Reddy, C.B.; Krishna, B.S.; Srinivasulu, K.; Reddy, C.S. Micelle promoted synthesis of bis-(indolyl)methanes. Lett. Org. Chem 2012, 9, 294–299. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Yu, J.L.; Ding, R.B.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.C. Microwave accelerated solvent-free synthesis of 1,3,4-oxadiazoles using polymer supported dehydration reagent. Synth. Commun 2004, 34, 2981–2986. [Google Scholar]
- Reddi Mohan Naidu, K.; Krishna, B.S.; Kumar, M.A.; Selvan, P.A.; Khalivulla, S.I.; Lasekan, O. Design, synthesis and antiviral potential of 14-aryl/heteroaryl-14H-dibenzo[a,j]xanthenes using an efficient polymer-supported catalyst. Molecules 2012, 17, 7543–7555. [Google Scholar]
- Reddi Mohan Naidu, K.; Dadapeer, E.; Bhupendra Reddy, C.; Janardhan Rao, A.; Suresh Reddy, C.; Naga Raju, C. Polyethylene glycol-promoted dialkyl, aryl/heteroaryl phosphonates. Synth. Commun 2011, 41, 3462–3468. [Google Scholar]
| Compound | R | Conventional method | PEG-POCl2 method | Melting point | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (h)/Yield (%) | Time (min)/Yield (%) | Found | Literature | ||
| 3a | 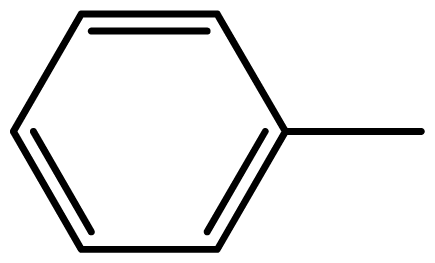 | 2/55 | 3/95 | 124–126 | 125–127 |
| 3b | 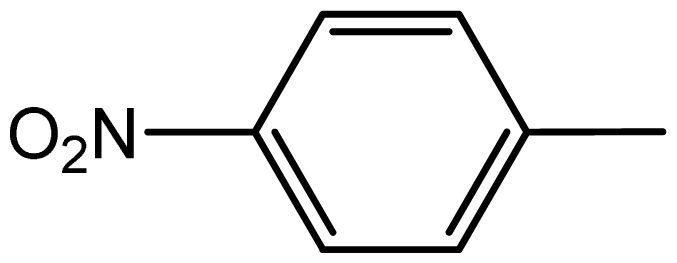 | 1.2/65 | 5.2/92 | 220–222 | 221–223 |
| 3c | 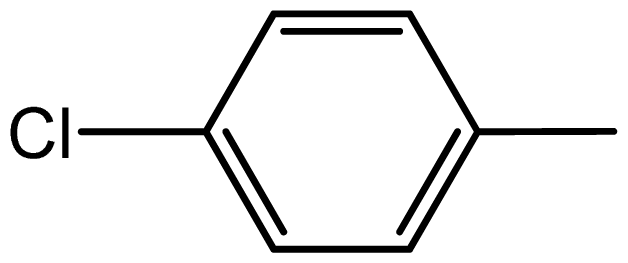 | 1.3/68 | 5.5/94 | 104–106 | 102–104 |
| 3d | 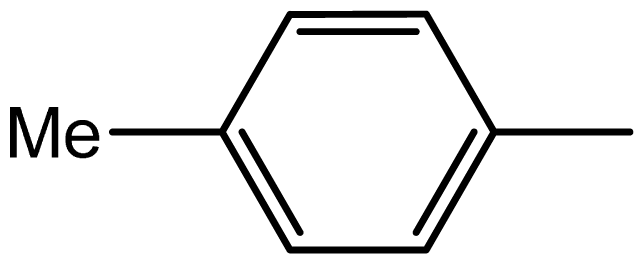 | 1.6/63 | 6/94 | 96–98 | 97–99 |
| 3e |  | 1.6/63 | 6/94 | 122–124 | 122–124 |
| 3f |  | 2.2/65 | 8/95 | 196–198 | - |
| 3g | 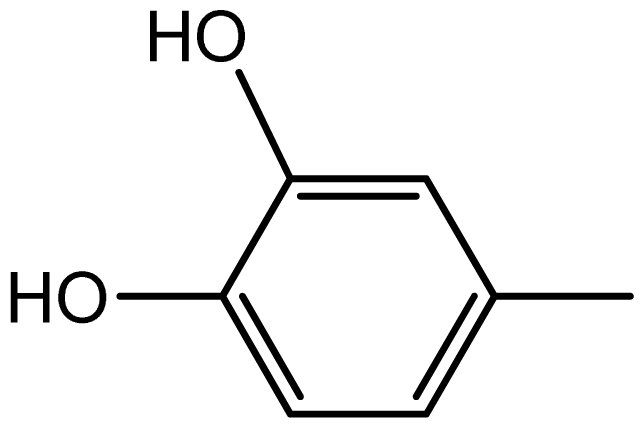 | 2.2/64 | 8/94 | 204–206 | - |
| 3h | 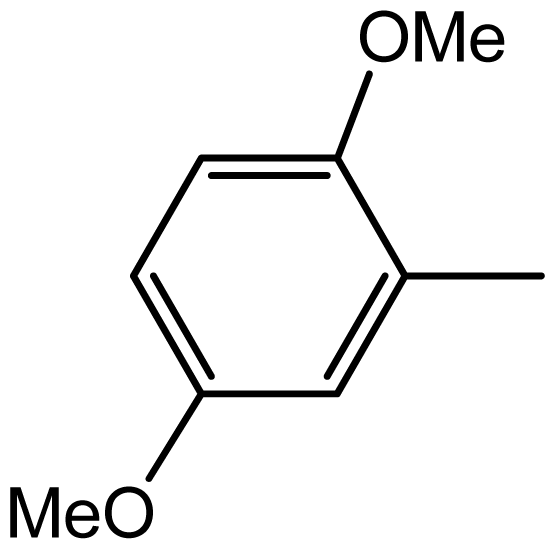 | 2/75 | 4/96 | 194–196 | - |
| 3i | 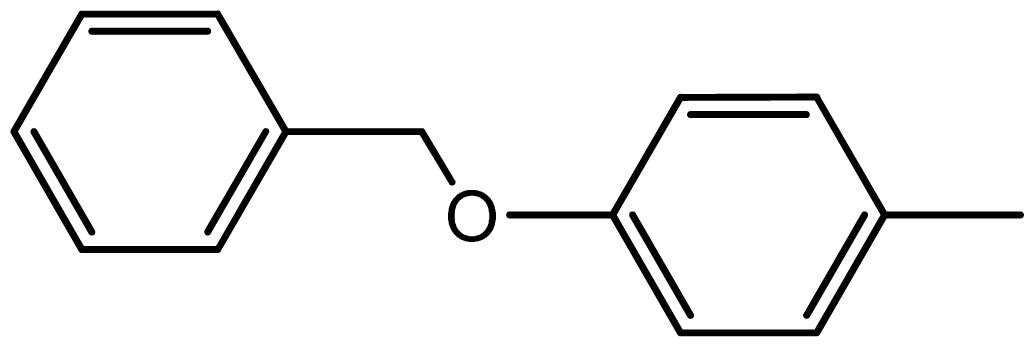 | 2.3/67 | 10/95 | 264–266 | 264–266 |
| 3j | 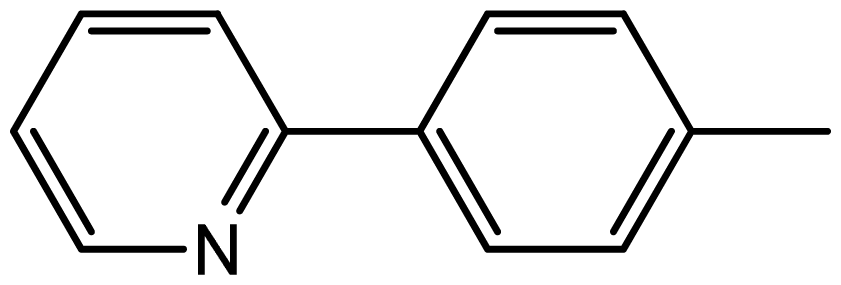 | 1.9/66 | 9/94 | 180–182 | 182–183 |
| Entry | Catalyst (Mole %) | Yield of the product |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1 | 72 |
| 2 | 0.2 | 86 |
| 3 | 0.5 | 95 |
| 4 | 1 | 95 |
| S.No. | Compound | Hela cells (μM) | HT 29 (μM) | MCF-7 (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3a | 86.3 | 62.3 | 138 |
| 2 | 3b | >150 | >150 | >150 |
| 3 | 3c | >150 | >150 | 136 |
| 4 | 3d | >150 | 91.7 | >150 |
| 5 | 3e | >150 | >150 | >150 |
| 6 | 3f | 95.4 | 128.3 | 145.8 |
| 7 | 3g | >150 | >150 | >150 |
| 8 | 3h | >150 | 142.7 | 149.3 |
| 9 | 3i | 129.5 | 98.4 | >150 |
| 10 | 3j | 139.3 | 89.7 | >150 |
© 2013 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Naidu, K.R.M.; Khalivulla, S.I.; Rasheed, S.; Fakurazi, S.; Arulselvan, P.; Lasekan, O.; Abas, F. Synthesis of Bisindolylmethanes and Their Cytotoxicity Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 1843-1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011843
Naidu KRM, Khalivulla SI, Rasheed S, Fakurazi S, Arulselvan P, Lasekan O, Abas F. Synthesis of Bisindolylmethanes and Their Cytotoxicity Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013; 14(1):1843-1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011843
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaidu, Kalla Reddi Mohan, Shaik Ibrahim Khalivulla, Syed Rasheed, Sharida Fakurazi, Palanisamy Arulselvan, Ola Lasekan, and Faridah Abas. 2013. "Synthesis of Bisindolylmethanes and Their Cytotoxicity Properties" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 14, no. 1: 1843-1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011843
APA StyleNaidu, K. R. M., Khalivulla, S. I., Rasheed, S., Fakurazi, S., Arulselvan, P., Lasekan, O., & Abas, F. (2013). Synthesis of Bisindolylmethanes and Their Cytotoxicity Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14(1), 1843-1853. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms14011843




