Hedyotis diffusa Willd Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth in Vivo via Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Preparation of Ethanol Extract from Hedyotis diffusa Willd
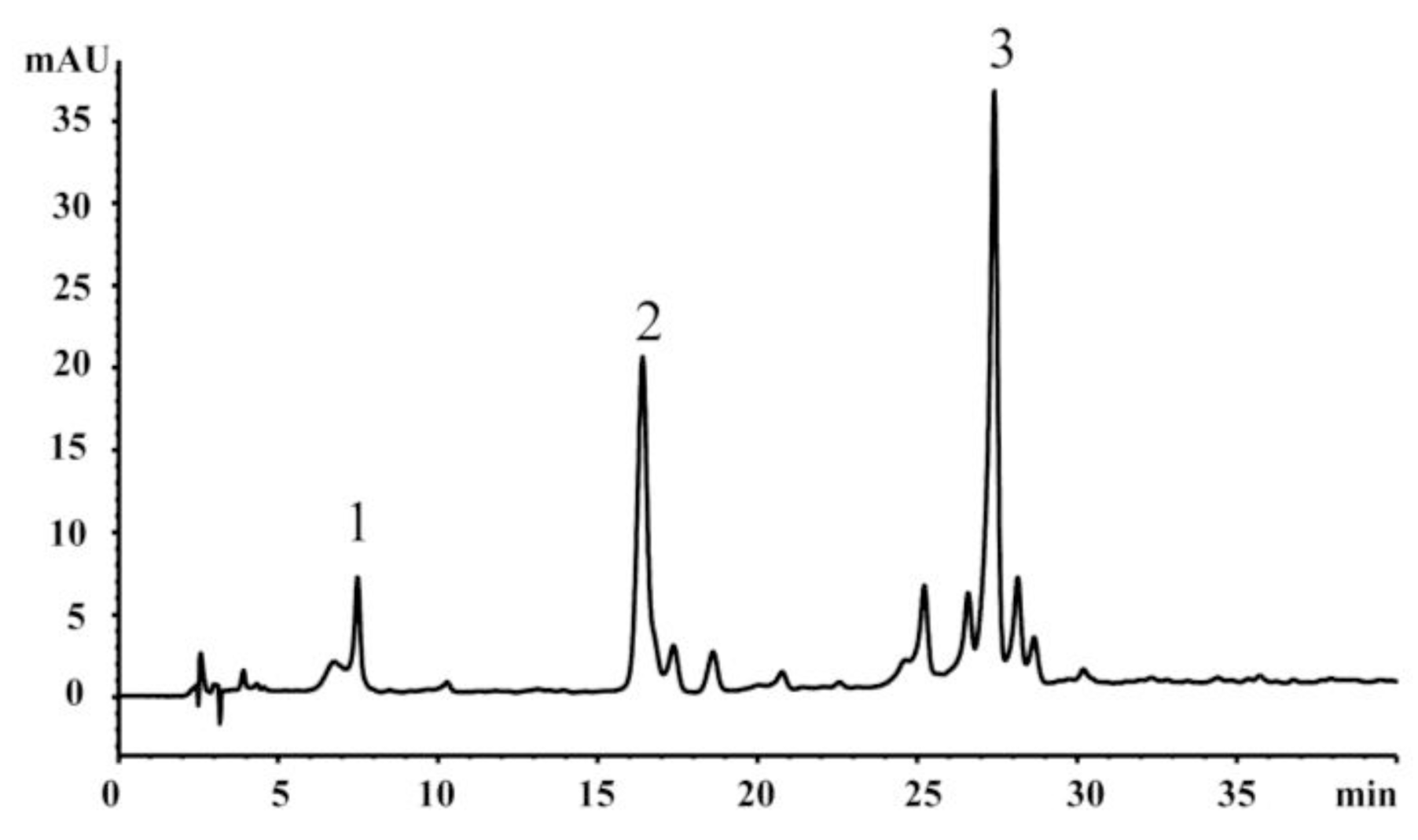
2.3. HPLC Analysis
2.4. Cell Culture
2.5. Animals
2.6. In Vivo Nude Mouse Xenograft Study
2.7. Immunohistochemical Staining for PCNA
2.8. In Situ Apoptosis Detection by TUNEL Staining
2.9. RNA Extraction and RT-PCR Analysis
2.10. Preparation of Tumor Homogenate and Western Immunoblotting
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
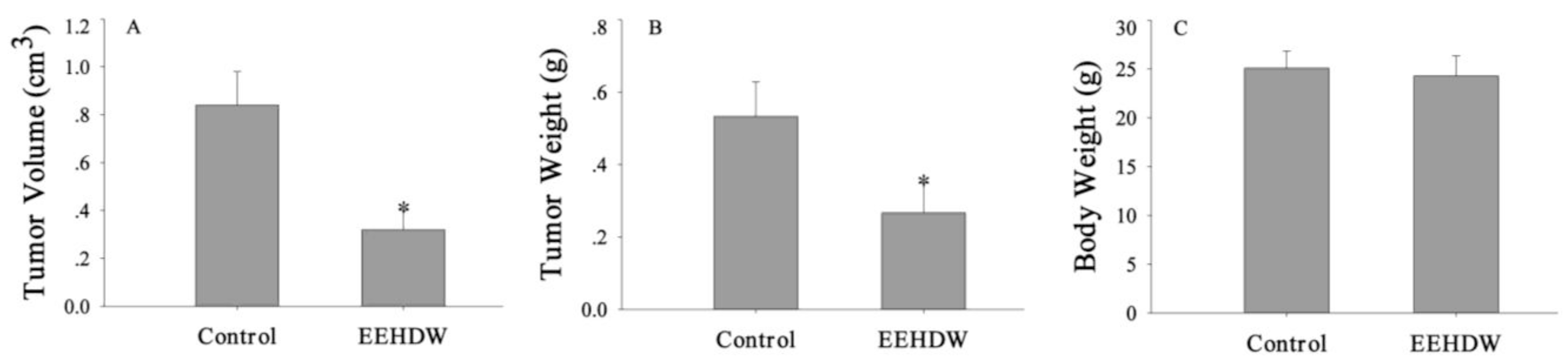
3.1. EEHDW Inhibits Tumor Growth in CRC Xenograft Mice
3.2. EEHDW Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in CRC Xenograft Mice
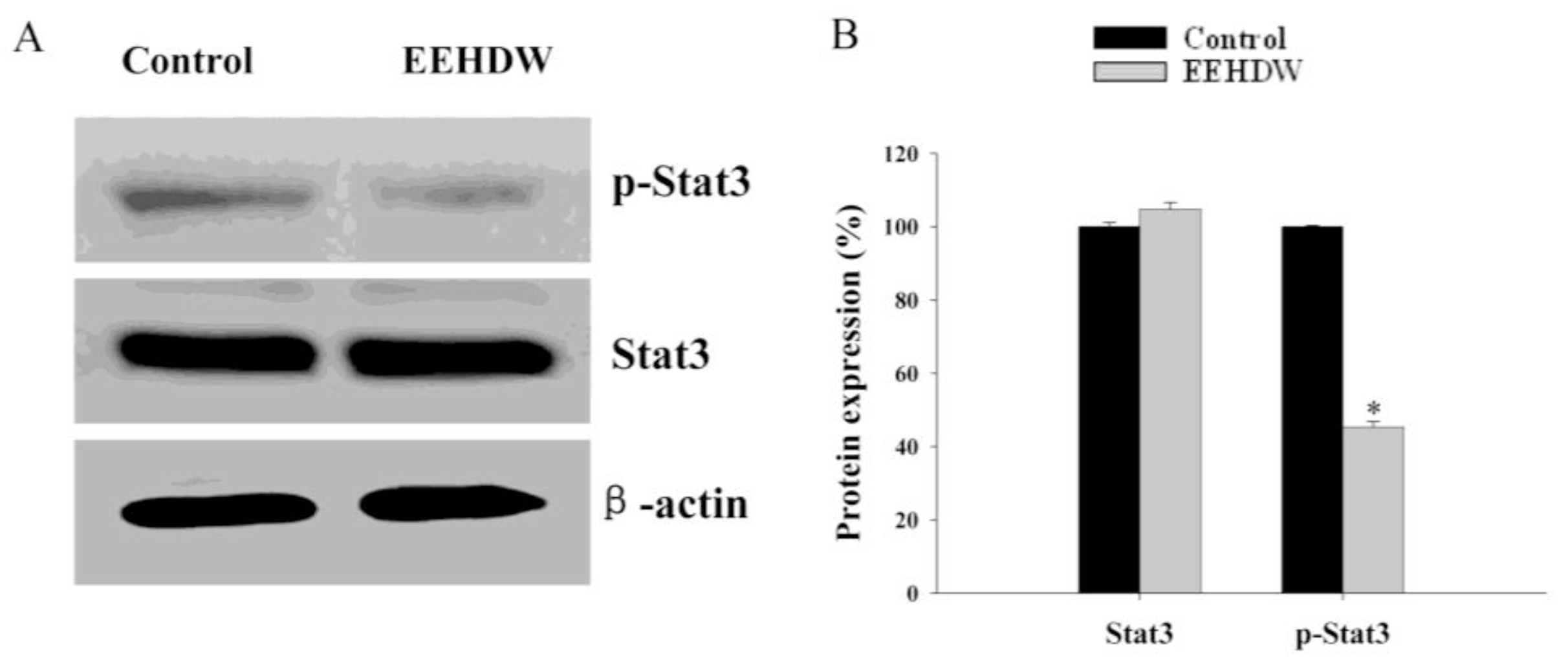
3.3. EEHDW Inhibits the Phosphorylation of STAT3 in CRC Xenograft Mice
3.4. EEHDW Regulates the Expression of Bcl-2, Bax, p21, Cyclin D1 and CDK4 in CRC Xenograft Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations
| CRC | colorectal cancer |
| STAT3 | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| EEHDW | ethanol extract of Hedyotis diffusa Willd |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| TCM | traditional Chinese medicine |
| TUNEL | terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick end labeling |
| PCNA | proliferating cell nuclear antigen |
References
- Jemal, A.; Siegel, R.; Ward, E.; Hao, Y.; Xu, J.; Murray, T.; Thun, M.J. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J. Clin 2008, 58, 71–96. [Google Scholar]
- Renehan, A.G.; Egger, M.; Saunders, M.P.; O’Dwyer, S.T. Impact on survival of intensive follow up after curative resection for colorectal cancer: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised trials. BMJ 2002, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prat, A.; Casado, E.; Cortés, J. New approaches in angiogenic targeting for colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol 2007, 13, 5857–5866. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Zhao, H.; Guo, Y.; Lin, F.; Tang, L.; Yao, Y. Clinical study of combining chemotherapy of oxaliplatin or 5-fluorouracil/leucovorin with hydroxycamptothecine for advanced colorectal cancer. Clin. Oncol. Cancer Res 2009, 6, 117–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Jiang, P.; Zhang, W. Molecular networks for the study of TCM Pharmacology. Brief. Bioinform 2010, 11, 417–430. [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg, J.; Darnell, J.E., Jr. The role of STATs in transcriptional control and their impact on cellular function. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2468–2473. [Google Scholar]
- Levy, D.E.; Lee, C. What does Stat3 do? J. Clin. Invest 2002, 109, 1143–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, M.; Jenkins, B.J. Acquiring signalling specificity from the cytokine receptor gp130. Trends Genet 2004, 20, 23–32. [Google Scholar]
- Kamimura, D.; Ishihara, K.; Hirano, T. IL-6 signal transduction and its physiological roles: The signal orchestration model. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol 2003, 149, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Darnell, J.E., Jr. STATs and gene regulation. Science 1997, 277, 1630–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Masuda, M.; Suzui, M.; Yasumatu, R.; Nakashima, T.; Kuratomi, Y.; Azuma, K.; Tomita, K.; Komiyama, S.; Weinstein, I.B. Constitutive activation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 correlates with cyclin D1 overexpression and may provide a novel prognostic marker in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 2002, 62, 3351–3355. [Google Scholar]
- Bromberg, J.; Wang, T.C. Inflammation and cancer: IL-6 and STAT3 complete the link. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 79–80. [Google Scholar]
- Darnell, J.E. Transcription factors as targets for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 740–749. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Q.; Lai, R.; Chirieac, L.R.; Li, C.; Thomazy, V.A.; Grammatikakis, I.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Zhang, W.; Fujio, Y.; Kunisada, K. Constitutive activation of JAK3/STAT3 in colon carcinoma tumors and cell lines: Inhibition of JAK3/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest of colon carcinoma cells. Am. J. Pathol 2005, 167, 969–980. [Google Scholar]
- Xiong, H.; Zhang, Z.G.; Tian, X.Q.; Sun, D.F.; Liang, Q.C.; Zhang, Y.J.; Lu, R.; Chen, Y.X.; Fang, J.Y. Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia 2008, 10, 287–297. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.; Ali, A.M.; Israf, D.A.; Ismail, N.H.; Shaari, K.; Lajis, N.H. Antioxidant, radical-scavenging, anti-inflammatory, cytotoxic and antibacterial activities of methanolic extracts of some Hedyotis species. Life Sci 2005, 76, 1953–1964. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.C.; Ng, L.T.; Yang, J.J.; Hsu, Y.F. Anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activity of peh-hue-juwa-chi-cao in male rats. Am. J. Chin. Med 2002, 30, 225–234. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, F.; Liu, G.; Zhang, L.; Niu, G. Studies on chemical constituents of Hedyotis diffusa Willd. Chin. Pharm. J 2005, 40, 502–504. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad, R.; Shaari, K.; Lajis, N.H.; Hamzah, A.S.; Ismail, N.H.; Kitajima, M. Anthraquinones from Hedyotis capitellata. Phytochemistry 2005, 66, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xue, X.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Q.; Ren, L.; Liang, X. Analysis of iridoid glucosides in Hedyotis diffusa by high-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2008, 48, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Chen, Y.; Wei, L.; Chen, X.; Xu, W.; Hong, Z.; Sferra, T.J.; Peng, J. Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract induces apoptosis via activation of the mitochondrion-dependent pathway in human colon carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol 2010, 37, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.; Wei, L.; Xu, W.; Hong, Z.; Liu, X.; Peng, J. Effect of Hedyotis diffusa Willd extract on tumor angiogenesis. Mol. Med. Rep 2011, 4, 1283–1288. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.H.; Li, S.J.; Hu, H.H.; Sun, L.R.; Das, M.; Gao, T.M. Neuroprotective effects of Xiao-Xu-Ming decoction against ischemic neuronal injury in vivo and in vitro. J. Ethnopharmacol 2010, 127, 38–46. [Google Scholar]
- Longley, D.B.; Allen, W.L.; Johnston, P.G. Drug resistance, predictive markers and pharmacogenomics in colorectal cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1766, 184–196. [Google Scholar]
- Gordaliza, M. Natural products as leads to anticancer drugs. Clin. Transl. Oncol 2007, 9, 767–776. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.R. Zhong Hua Ben Cao; Shanghai Science and Technology Press: Shanghai, China, 1999; p. 433. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Yao, Z. Clinical study of Hedyotis diffusa Willd injection in treating primary liver cancer (in Chinese). J. Med. Forum 2004, 25, 37–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, B.; Lin, N.; He, X.; Zhou, X. Analysis on the clinical application of Hedyotis diffusa Willd in the anti-cancer therapy. Chin. J. Chin. Mater. Med 2006, 31, 1550–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, J.; Cory, S. The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1324–1337. [Google Scholar]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar]
- Nurse, P. Ordering S phase and M phase in the cell cycle. Cell 1994, 79, 547–550. [Google Scholar]
- Morgan, D.O. Principles of CDK regulation. Nature 1995, 374, 131–134. [Google Scholar]
- Harakeh, S.; Abu-El-Ardat, K.; Diab-Assaf, M.; Niedzwiecki, A.; El-Sabban, M.; Rath, M. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in HTLV-1-positive and -negative leukemia cells. Med. Oncol 2008, 25, 30–39. [Google Scholar]
- Kessel, D.; Luo, Y. Cells in cryptophycin-induced cell-cycle arrest are susceptible to apoptosis. Cancer Lett 2000, 151, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Purohit, A.; Hejaz, H.A.M.; Walden, L.; MacCarthy-Morrogh, L.; Packham, G.; Potter, B.V.L.; Reed, M.J. The effect of 2-methoxyoestrone-3-O-sulphamate on the growth of breast cancer cells and induced mammary tumours. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 85, 584–589. [Google Scholar]
- Zafonte, B.T.; Hulit, J.; Amanatullah, D.F.; Albanese, C.; Wang, C.; Rosen, E.; Reutens, A.; Sparano, J.A.; Lisanti, M.P.; Pestell, R.G. Cell-cycle dysregulation in breast cancer: Breast cancer therapies targeting the cell cycle. Front. Biosci 2000, 5, D938–D961. [Google Scholar]
- Domagala, W.; Welcker, M.; Chosia, M.; Karbowniczek, M.; Harezga, B.; Bartkova, J.; Bartek, J.; Osborn, M. p21/WAF1/Cip1 expression in invasive ductal breast carcinoma: Relationship to p53, proliferation rate, and survival at 5 years. Virchows Arch 2001, 439, 132–140. [Google Scholar]
- Zushi, S.; Shinomura, Y.; Kiyohara, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Kondo, S.; Sugimachi, M.; Higashimoto, Y.; Kanayama, S.; Matsuzawa, Y. STAT3 mediates the survival signal in oncogenic ras-transfected intestinal epithelial cells. Int. J. Cancer 1998, 78, 326–330. [Google Scholar]



© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, Q.; Lin, J.; Wei, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhan, Y.; Zeng, J.; Xu, W.; Shen, A.; Hong, Z.; et al. Hedyotis diffusa Willd Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth in Vivo via Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 6117-6128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13056117
Cai Q, Lin J, Wei L, Zhang L, Wang L, Zhan Y, Zeng J, Xu W, Shen A, Hong Z, et al. Hedyotis diffusa Willd Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth in Vivo via Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(5):6117-6128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13056117
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Qiaoyan, Jiumao Lin, Lihui Wei, Ling Zhang, Lili Wang, Youzhi Zhan, Jianwei Zeng, Wei Xu, Aling Shen, Zhenfeng Hong, and et al. 2012. "Hedyotis diffusa Willd Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth in Vivo via Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 5: 6117-6128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13056117
APA StyleCai, Q., Lin, J., Wei, L., Zhang, L., Wang, L., Zhan, Y., Zeng, J., Xu, W., Shen, A., Hong, Z., & Peng, J. (2012). Hedyotis diffusa Willd Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Growth in Vivo via Inhibition of STAT3 Signaling Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(5), 6117-6128. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13056117



