Congenital Diarrheal Disorders: An Updated Diagnostic Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Contribution of Epidemiological Data to the Diagnostic Approach
3. The Initial Steps of Diagnostic Work Up
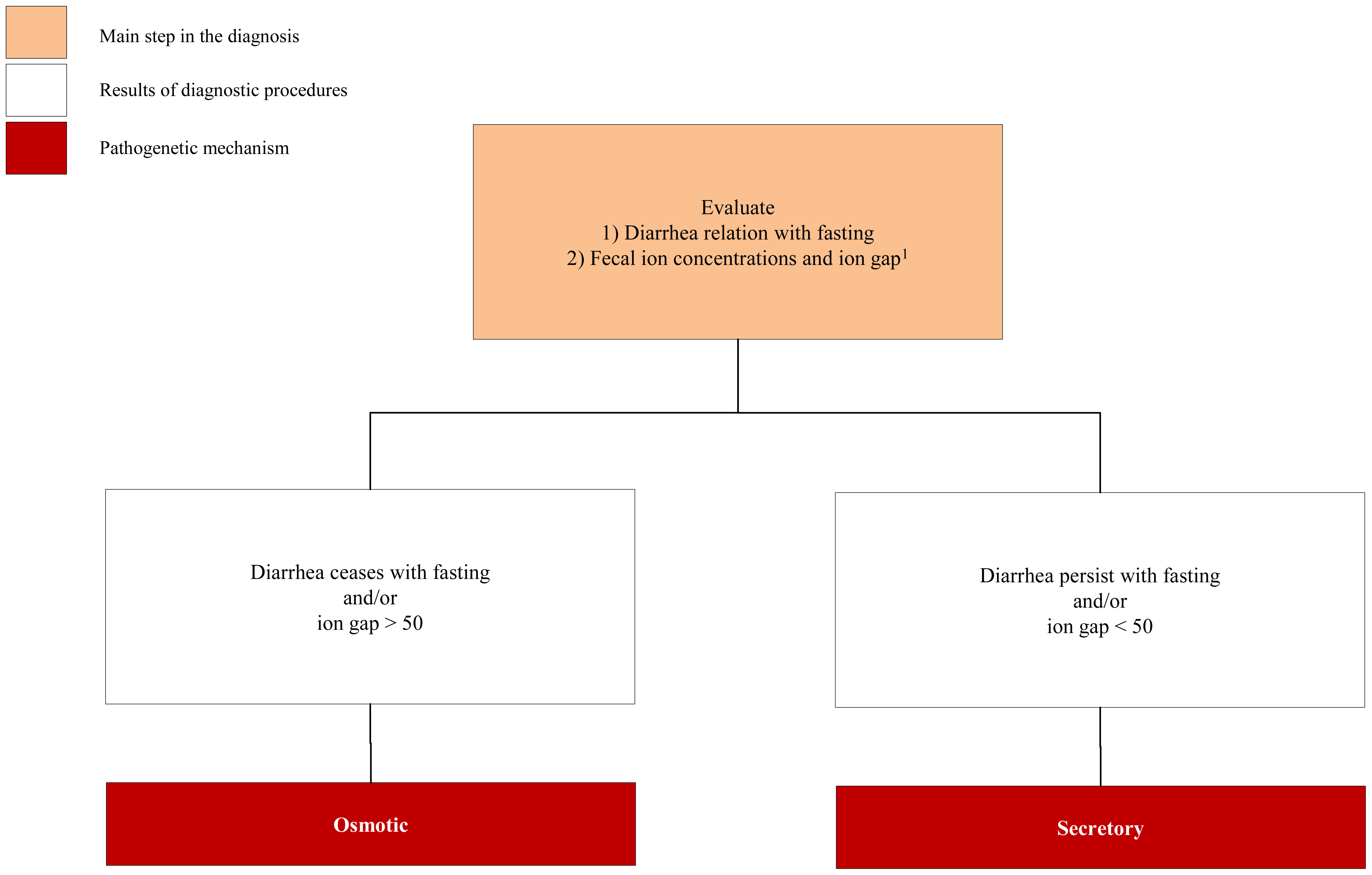
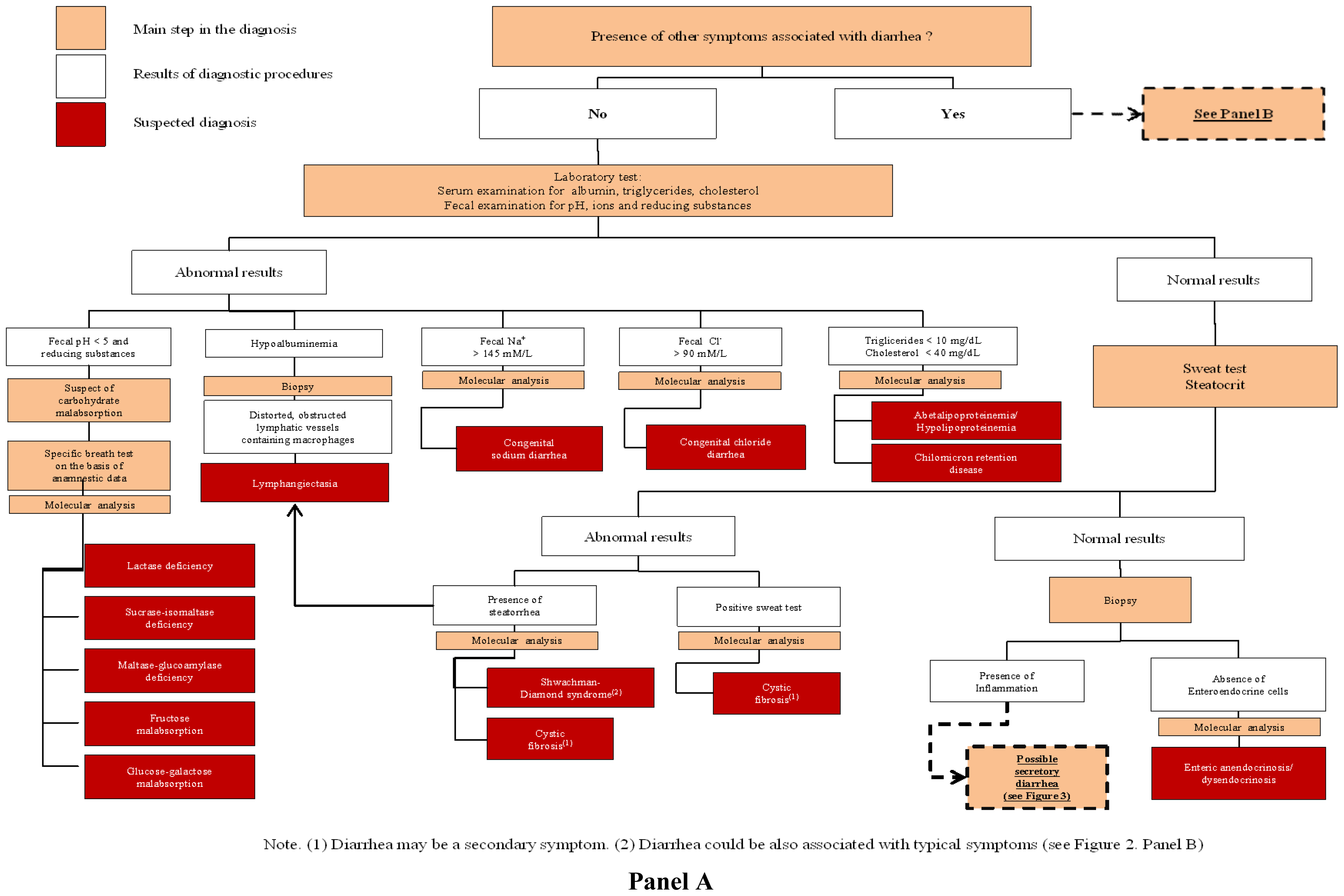
3.1. Congenital Osmotic Diarrheal Disorders
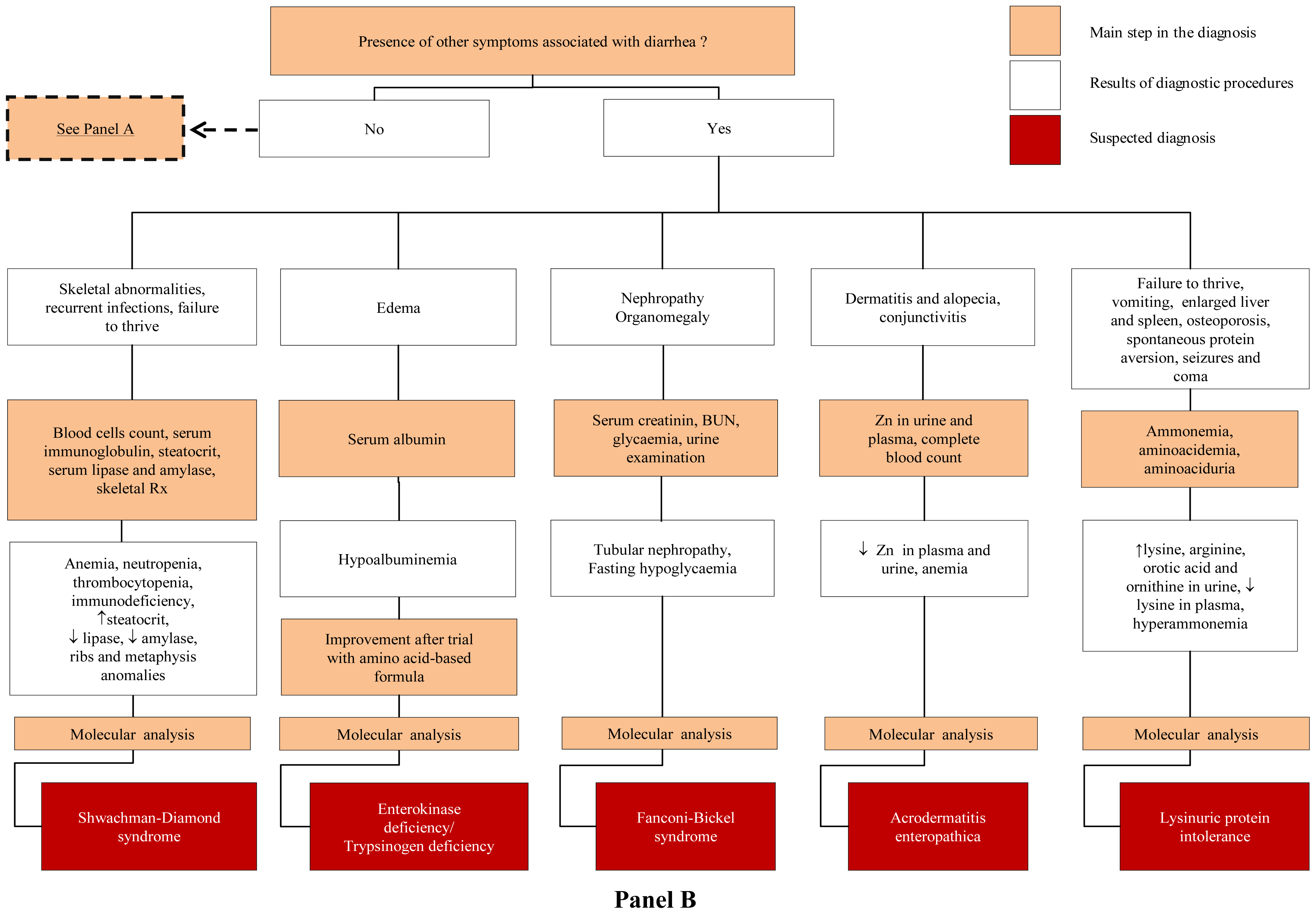
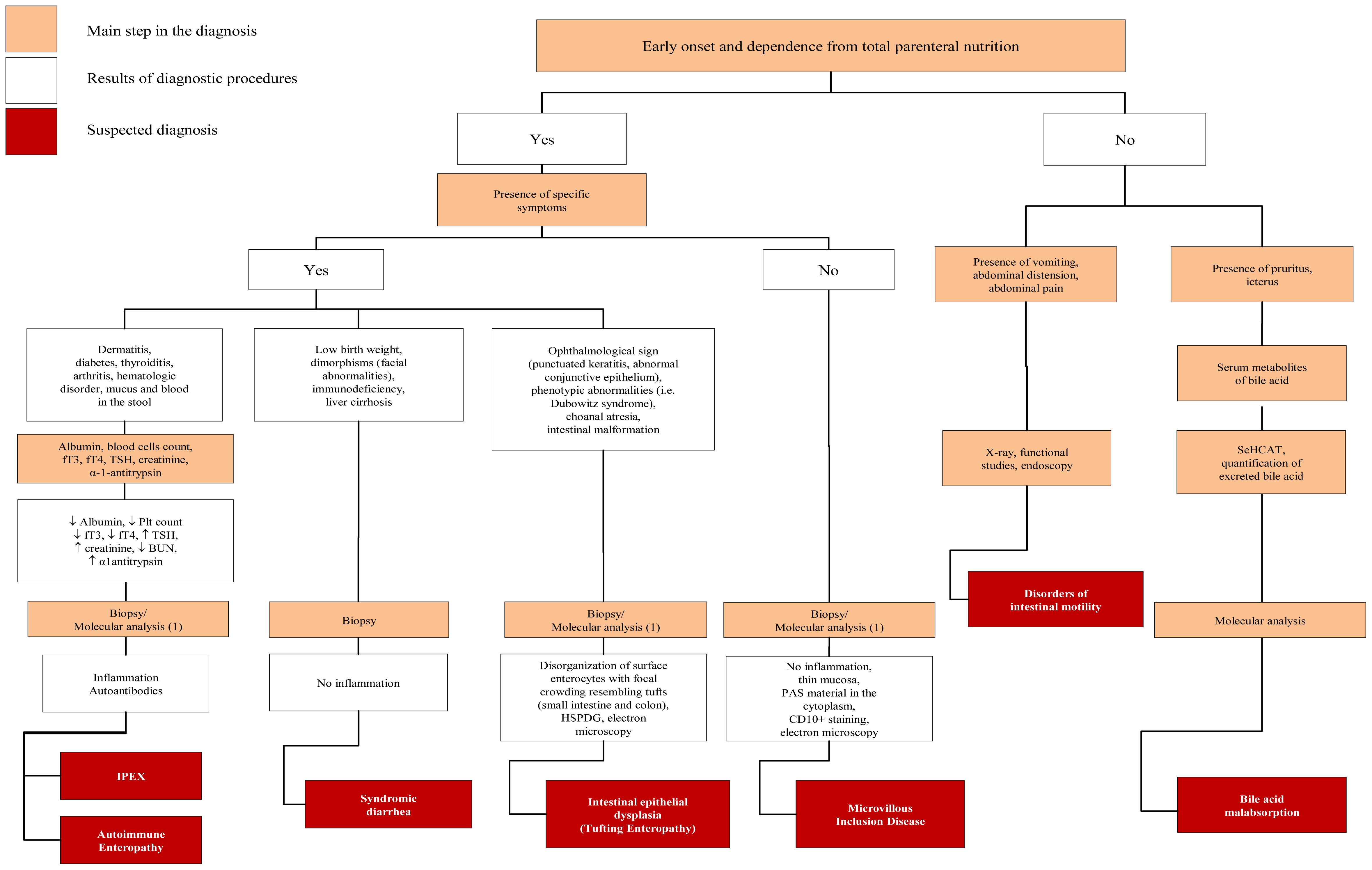
3.2. Congenital Secretory Diarrheal Disorders
4. Genetic Basis of CDDs
4.1. Defects of Digestion, Absorption and Transport of Nutrients and Electrolytes
4.2. Defect of Enterocyte Differentiation and Polarization
4.3. Defects of Enteroendocrine Cells Differentiation
4.4. Defects of Modulation of Intestinal Immune Response
5. Molecular Diagnosis
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations
| ADE | acrodermatitis enteropathica |
| AIRE | autoimmune regulator |
| ALP | abetalipoprotenemia |
| APL | absence of pancreatic lipase |
| APS1 | autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1 |
| CCD | congenital chloride diarrhea |
| CDD | congenital diarrheal disorders |
| CF | cystic fibrosis |
| CFTR | cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator |
| CMD | congenital malabsorptive diarrhea |
| CRD | chilomicron retention disease |
| CSD | congenital sodium diarrhea |
| CTE | congenital tufting enteropathy |
| EpCAM | epithelial cellular adhesion molecule |
| EKD | enterokinase deficiency |
| FBS | Fanconi-Bickel syndrome |
| FM | fructose malabsorption |
| GGM | glucose-galactose malabsorption |
| GLUT | glucose transporter |
| HLP | hypobetalipoproteinemia |
| HP | hereditary pancreatitis |
| IPEX | immune dysfunction, polyendocrinopathy, X-linked |
| LD | lactase deficiency |
| LPI | lysinuric protein intolerance |
| MTTP | microsomal triglyceride transfer protein |
| MVID | microvillous inclusion disease |
| MGD | maltase-glucoamylase deficiency |
| MGAM | maltase-glucoamylase (gene and protein) |
| NHE | sodium-proton exchanger |
| PBAM | primary bile acid malabsorption |
| PCD | proprotein convertase 1/3 deficiency |
| SDS | Shwachman-Diamond syndrome |
| SID | sucrase-isomaltase deficiency |
| SLC | solute carrier |
| SNP | single nucleotide polymorphism |
| SPINT | serine protease inhibitor |
| THE | Tricho-Hepato-Enteric syndrome |
- List of Gene Designations: AIRE; CFTR; EpCAM; FOXP3; Interleukin-2 receptor (subunit CD25); MGAM; MTTP; MYO5B; NEUROG3; NHE; PCD; SBDS; SLC2A2; SLC5A1; SLC7A7; SLC10A2; SLC26A3; SLC39A4; SPINT2
- Financial DisclosureThis work was not sponsored by any organization.
References
- Guarino, A.; Spagnuolo, M.I.; Russo, S.; Albano, F.; Guandalini, S.; Capano, G.; Cucchiara, S.; Vairano, P.; Liguori, R.; Casola, A.; et al. Etiology and risk factors of severe and protracted diarrhea. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr 1995, 20, 173–178. [Google Scholar]
- Berni Canani, R.; Cirillo, P.; Terrin, G. Chronic and Intractabile Diarrhea. In Essential Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition; Guandalini, S., Ed.; McGraw-Hill: Chicago, IL, USA, 2005; pp. 25–47. [Google Scholar]
- Berni Canani, R.; Terrin, G.; Cardillo, G.; Tomaiuolo, R.; Castaldo, G. Congenital diarrheal disorders: Improved understanding of gene defects is leading to advances in intestinal physiology and clinical management. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr 2010, 50, 360–366. [Google Scholar]
- Ruemmele, F.M. Chronic enteropathy: Molecular basis. Nestle Nutr. Workshop Ser. Pediatr. Program 2007, 59, 73–85. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaiuolo, R.; Spina, M.; Castaldo, G. Molecular diagnosis of Cystic Fibrosis: Comparison of four analytical procedures. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med 2003, 41, 26–32. [Google Scholar]
- Passariello, A.; Terrin, G.; Baldassarre, M.E.; de Curtis, M.; Paludetto, R.; Berni Canani, R. Diarrhea in neonatal intensive care unit. World J. Gastroenterol 2010, 16, 2664–2668. [Google Scholar]
- Sebastio, G.; Sperandeo, M.P.; Andria, G. Lysinuric protein intolerance: Reviewing concepts on a multisystem disease. Am. J. Med. Genet. C 2011, 157, 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Swallow, D.M.; Poulter, M.; Hollox, E.J. Intolerance to lactose and other dietary sugars. Drug Metab. Dispos 2001, 29, 513–516. [Google Scholar]
- Wedenoja, S.; Pekansaari, E.; Höglund, P.; Mäkelä, S.; Holmberg, C.; Kere, J. Update on SLC26A3 mutations in congenital chloride diarrhea. Hum. Mutat 2011, 32, 715–722. [Google Scholar]
- Berni Canani, R.; Terrin, G.; Cirillo, P.; Castaldo, G.; Salvatore, F.; Cardillo, G.; Coruzzo, A.; Troncone, R. Butyrate as an effective treatment of congenital chloride diarrhea. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 630–634. [Google Scholar]
- Berni Canani, R.; Terrin, G. Recent progress in congenital diarrheal disorders. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep 2011, 13, 257–264. [Google Scholar]
- Booth, I.W.; MacNeish, A.S. Mechanisms of diarrhoea. Baillieres Clin. Gastroenterol 1993, 7, 215–242. [Google Scholar]
- Wedenoja, S.; Höglund, P.; Holmberg, C. Review article: The clinical management of congenital chloride diarrhoea. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2010, 31, 477–85. [Google Scholar]
- Robayo-Torres, C.C.; Quezada-Calvillo, R.; Nichols, B.L. Disaccharide digestion: Clinical and molecular aspects. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol 2006, 4, 276–287. [Google Scholar]
- Morinville, V.; Perrault, J. Genetic disorders of the pancreas. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am 2003, 32, 763–787. [Google Scholar]
- Marcil, V.; Peretti, N.; Delvin, E.; Levy, E. Digestive and absorptive processes of lipids. Gastroenterol. Clin. Biol 2004, 28, 1257–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, P.R.; Newnham, E.; Barrett, J.S.; Shepherd, S.J.; Muir, J.G. Review article: Fructose malabsorption and the bigger picture. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther 2007, 25, 349–363. [Google Scholar]
- Holzinger, A.; Maier, E.M.; Buck, C.; Mayerhofer, P.U.; Kappler, M.; Haworth, J.C.; Moroz, S.P.; Hadorn, H.B.; Sadler, J.E.; Roscher, A.A. Mutations in the proenteropeptidase gene are the molecular cause of congenital enteropeptidase deficiency. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2002, 70, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Leturque, A.; Brot-Laroche, E.; Le Gall, M. GLUT2 mutations, translocation, and receptor function in diet sugar managing. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab 2009, 296, E985–E992. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, S.; Kury, S.; Giraud, M.; Dréno, B.; Kharfi, M.; Bézieau, S. An update on mutations of the SLC39A4 gene in acrodermatitis enteropathica. Hum. Mutat 2009, 30, 926–933. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Cortina, G.; Wu, S.V.; Tran, R.; Cho, J.H.; Tsai, M.J.; Bailey, T.J.; Jamrich, M.; Ament, M.E.; Treem, W.R.; et al. Mutant neurogenin-3 in congenital malabsorptive diarrhea. N. Engl. J. Med 2006, 355, 270–280. [Google Scholar]
- Ruemmele, F.M.; Müller, T.; Schiefermeier, N.; Ebner, H.L.; Lechner, S.; Pfaller, K.; Thöni, C.E.; Goulet, O.; Lacaille, F.; Schmitz, J.; et al. Loss-of-function of MYO5B is the main cause of microvillus inclusion disease: 15 novel mutations and a CaCo-2 RNAi cell model. Hum. Mutat 2010, 31, 544–551. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, C.L.; Christie, J.; Ramsdell, F.; Brunkow, M.E.; Ferguson, P.J.; Whitesell, L.; Kelly, T.E.; Saulsbury, F.T.; Chance, P.F.; Ochs, H.D. The immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat. Genet 2001, 27, 20–21. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Ju, S.T. Genetic control of the inflammatory T-cell response in regulatory T-cell deficient scurfy mice. Clin. Immunol 2010, 136, 162–169. [Google Scholar]
- Montalto, M.; D’Onofrio, F.; Santoro, L.; Gallo, A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Gasbarrini, G. Autoimmune enteropathy in children and adults. Scand. J. Gastroenterol 2009, 44, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar]
- Kuokkanen, M.; Kokkonen, J.; Enattah, N.S.; Ylisaukko-Oja, T.; Komu, H.; Varilo, T.; Peltonen, L.; Savilahti, E.; Jarvela, I. Mutations in the translated region of the lactase gene (LCT) underlie congenital lactase deficiency. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2006, 78, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Nichols, B.L.; Avery, S.E.; Karnsakul, W.; Jahoor, F.; Sen, P.; Swallow, D.M.; Luginbuehl, U.; Hahn, D.; Sterchi, E.E. Congenital maltase-glucoamylase deficiency associated with lactase and sucrase deficiencies. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr 2002, 35, 573–579. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, H.F.; Butler, R.N.; Brooks, D.A. Intestinal fructose transport and malabsorption in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol 2011, 300, G202–G206. [Google Scholar]
- Heinz-Erian, P.; Muller, T.; Krabichler, B.; Schranz, M.; Becker, C.; Rüschendorf, F.; Nürnberg, P.; Rossier, B.; Vujic, M.; Booth, I.W.; et al. Mutations in SPINT2 cause a syndromic form of congenital sodium diarrhea. Am. J. Hum. Genet 2009, 84, 188–196. [Google Scholar]
- Muller, T.; Wijmenga, C.; Phillips, A.D.; Janecke, A.; Houwen, R.H.; Fischer, H.; Ellemunter, H.; Frühwirth, M.; Offner, F.; Hofer, S.; et al. Congenital sodium diarrhea is an autosomal recessive disorder of sodium/proton exchange but unrelated to known candidate genes. Gastroenterology 2000, 119, 1506–1513. [Google Scholar]
- Figarella, C.; de Caro, A.; Leupold, D.; Poley, J.R. Congenital pancreatic lipase deficiency. J. Pediatr 1980, 96, 412–416. [Google Scholar]
- Rebours, V.; Levy, P.; Ruszniewski, P. An overview of hereditary pancreatitis. Dig. Liver Dis 2011, 44, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Amato, F.; Bellia, C.; Cardillo, G.; Castaldo, G.; Ciaccio, M.; Elce, A.; Lembo, F.; Tomaiuolo, R. Extensive molecular analysis of patients bearing CFTR-related disorders. J. Mol. Diagn 2012, 14, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Narcisi, T.M.; Shoulders, C.C.; Chester, S.A.; Read, J.; Brett, D.J.; Harrison, G.B.; Grantham, T.T.; Fox, M.F.; Povey, S.; de Bruin, T.W.; et al. Mutations of the microsomal triglyceride-transfer-protein gene in abetalipoproteinemia. Am. J. Hum. Genet 1995, 57, 1293–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Benayoun, L.; Granot, E.; Rizel, L.; Allon-Shalev, S.; Behar, D.M.; Ben-Yosef, T. Abetalipoproteinemia in Israel: Evidence for a founder mutation in the Ashkenazi Jewish population and a contiguous gene deletion in an Arab patient. Mol. Genet. Metab 2007, 90, 453–457. [Google Scholar]
- Schonfeld, G. Familial hypobetalipoproteinemia: A review. J. Lipid Res 2003, 44, 878–883. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Magnolo, A.L.; Sundaram, M.; Zhou, H.; Yao, E.F.; di Leo, E.; Loria, P.; Wang, S.; Bamji-Mirza, M.; Wang, L.; et al. Nonsynonymous mutations within APOB in human familial hypobetalipoproteinemia: Evidence for feedback inhibition of lipogenesis and postendoplasmic reticulum degradation of apolipoprotein B. J. Biol. Chem 2010, 285, 6453–6464. [Google Scholar]
- Boocock, G.R.; Morrison, J.A.; Popovic, M.; Richards, N.; Ellis, L.; Durie, P.R.; Rommens, J.M. Mutations in SBDS are associated with Shwachman-Diamond syndrome. Nat. Genet 2003, 33, 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- Burroughs, L.; Woolfrey, A.; Shimamura, A. Shwachman-Diamond syndrome: A review of the clinical presentation, molecular pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Hematol. Oncol. Clin. North Am 2009, 23, 233–248. [Google Scholar]
- Pecache, N.; Patole, S.; Hagan, R.; Hill, D.; Charles, A.; Papadimitriou, J.M. Neonatal congenital microvillus atrophy. Postgrad. Med. J 2004, 80, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, J.S.; Seo, J.K.; Shim, J.O.; Hwang, S.H.; Park, H.S.; Kang, G.H. Tufting enteropathy with EpCAM mutations in two siblings. Gut Liver 2010, 4, 407–410. [Google Scholar]
- Fabre, A.; Martinez-Vinson, C.; Roquelaure, B.; Missirian, C.; André, N.; Breton, A.; Lachaux, A.; Odul, E.; Colomb, V.; Lemale, J.; et al. Novel mutations in TTC37 associated with Tricho-Hepato-Enteric syndrome. Hum. Mutat 2011, 32, 277–281. [Google Scholar]
- Goulet, O.; Vinson, C.; Roquelaure, B.; Brousse, N.; Bodemer, C.; Cézard, J.P. Syndromic (phenotypic) diarrhea in early infancy. Orphanet. J. Rare. Dis 2008, 28, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- Rubio-Cabezas, O.; Jensen, J.N.; Hodgson, M.I.; Codner, E.; Ellard, S.; Serup, P.; Hattersley, A.T. Permanent neonatal diabetes and enteric anendocrinosis associated with biallelic mutations in NEUROG3. Diabetes 2011, 60, 1349–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Pinney, S.E.; Oliver-Krasinski, J.; Ernst, L.; Hughes, N.; Patel, P.; Stoffers, D.A.; Russo, P.; de León, D.D. Neonatal diabetes and congenital malabsorptive diarrhea attributable to a novel mutation in the human neurogenin-3 gene coding sequence. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab 2011, 96, 1960–1965. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, R.S.; Creemers, J.W.; Farooqi, I.S.; Raffin-Sanson, M.L.; Varro, A.; Dockray, G.J.; Holst, J.J.; Brubaker, P.L.; Corvol, P.; Polonsky, K.S.; et al. Small-intestinal dysfunction accompanies the complex endocrinopathy of human proprotein convertase 1 deficiency. J. Clin. Invest 2003, 112, 1550–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Michels, A.W.; Gottlieb, P.A. Autoimmune polyglandular syndromes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol 2010, 6, 270–277. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco Quirós, A.; Arranz Sanz, E.; Bernardo Ordiz, D.; Garrote Adrados, J.A. From autoimmune enteropathy to the IPEX (immune dysfunction, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked) syndrome. Allergol. Immunopathol 2009, 37, 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Harbuz, R.; Lespinasse, J.; Boulet, S.; Francannet, C.; Creveaux, I.; Benkhelifa, M.; Jouk, P.S.; Lunardi, J.; Ray, P.F. Identification of new FOXP3 mutations and prenatal diagnosis of IPEX syndrome. Prenat. Diagn 2010, 30, 1072–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Heino, M.; Peterson, P.; Kudoh, J.; Shimizu, N.; Antonarakis, S.E.; Scott, H.S.; Krohn, K. APECED mutations in the autoimmune regulator (AIRE) gene. Hum. Mutat 2001, 18, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Faiyaz-Ul-Haque, M.; Bin-Abbas, B.; Al-Abdullatif, A.; Abdullah Abalkhail, H.; Toulimat, M.; Al-Gazlan, S.; Almutawa, A.M.; Al-Sagheir, A.; Peltekova, I.; Al-Dayel, F.; et al. Novel and recurrent mutations in the AIRE gene of autoimmune polyendocrinopathy syndrome type 1 (APS1) patients. Clin. Genet 2009, 76, 431–440. [Google Scholar]
- Caudy, A.A.; Reddy, S.T.; Chatila, T.; Atkinson, J.P.; Verbsky, J.W. CD25 deficiency causes an immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked-like syndrome, and defective IL-10 expression from CD4 lymphocytes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol 2007, 119, 482–487. [Google Scholar]
- Castaldo, G.; Martinelli, P.; Massa, C.; Fuccio, A.; Grosso, M.; Rippa, E.; Paladini, D.; Salvatore, F. Prenatal diagnosis of cystic fibrosis: A case of twin pregnancy diagnosis and a review of 5 years’ experience. Clin. Chim. Acta 2000, 298, 121–133. [Google Scholar]
- Rantanen, E.; Hietala, M.; Kristoffersson, U.; Nippert, I.; Schmidtke, J.; Sequeiros, J.; Kaariainen, H. Regulations and practices of genetic counselling in 38 European countries: The perspective of national representatives. Eur. J. Hum. Genet 2008, 16, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar]
- Castaldo, G.; Lembo, F.; Tomaiuolo, R. Review: Molecular diagnostics: Between chips and customized medicine. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med 2010, 48, 973–982. [Google Scholar]
- Tomaiuolo, R.; Sangiuolo, F.; Bombieri, C.; Bonizzato, A.; Cardillo, G.; Raia, V.; D’Apice, M.R.; Bettin, M.D.; Pignatti, P.F.; Castaldo, G.; et al. Epidemiology and a novel procedure for large scale analysis of CFTR rearrangements in classic and atypical CF patients: A multicentric Italian study. J. Cyst. Fibros 2008, 7, 347–351. [Google Scholar]
- Taruscio, D.; Falbo, V.; Floridia, G.; Salvatore, M.; Pescucci, C.; Cantafora, A.; Marongiu, C.; Baroncini, A.; Calzolari, E.; Cao, A.; et al. Quality assessment in cytogenetic and molecular genetic testing: The experience of the Italian project on standardization and quality assurance. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med 2004, 42, 915–922. [Google Scholar]
- Elce, A.; Boccia, A.; Cardillo, G.; Giordano, S.; Tomaiuolo, R.; Paolella, G.; Castaldo, G. Three novel CFTR polymorphic repeats improve segregation analysis for cystic fibrosis. Clin. Chem 2009, 55, 1372–1379. [Google Scholar]
| Disease | OMIM number | Transmission and incidence | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Genes encoding brush-border enzymes | |||
| Congenital lactase deficiency (LD) | 223000 | AR, 1:60.000 in Finland; lower in other ethnic groups | Osmotic |
| Congenital sucrase-isomaltase deficiency (SID) | 222900 | AR, 1:5.000; higher incidence in Greenland, Alaska and Canada | Osmotic |
| Congenital maltase-glucomaylase deficiency (MGD) | -- | Few cases described | Osmotic |
| Enterokinase deficiency (EKD) | 226200 | AR | Osmotic |
| Genes encoding membrane carriers | |||
| Glucose-galactose malabsorption (GGM) | 606824 | AR, few hundred cases described | Osmotic |
| Fructose malabsorption (FM) | 138230 | - | Osmotic |
| Fanconi-Bickel syndrome (FBS) | 227810 | AR | Osmotic |
| Acrodermatitis enteropathica (ADE) | 201100 | AR, 1:500.000 | Osmotic |
| Congenital chloride diarrhea (CCD, DIAR 1) | 214700 | AR, sporadic; frequent in some ethnies | Osmotic |
| Congenital sodium diarrhea (CSD, DIAR 3) | 270420 | AR | Osmotic |
| Lysinuric protein intolerance (LPI) | 222700 | AR, about 1:60.000 in Finland and in Japan; rare in other ethnic groups | Osmotic |
| Primary bile acid malabsorption (PBAM) | 613291 | AR | Secretory |
| Cystic fibrosis (CF) | 219700 | AR, 1:2.500 | Osmotic |
| Genes encoding pancreatic enzymes and pancreatic ions transporters | |||
| Hereditary pancreatitis (HP) | 167800 | AD | Osmotic |
| Congenital absence of pancreatic lipase (APL) | 246600 | -- | Osmotic |
| Genes encoding proteins of lipoprotein metabolism | |||
| Abetalipoproteinemia (ALP) | 200100 | AR, about 100 cases described; higher frequency among Ashkenazi | Osmotic |
| Hypobetalipoproteinemia (HLP) | 107730 | Autosomal co-dominant | Osmotic |
| Chilomicron retention disease (CRD) | 246700 | AR, about 40 cases described | Osmotic |
| Genes encoding ribosomial proteins | |||
| Shwachman-Diamond syndrome (SDS) | 260400 | AR 1:10–200.000 | Osmotic |
| Disease | OMIM number | Transmission and incidence | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Microvillous inclusion disease (MVID, DIAR 2) | 251850 | AR; rare; higher frequency among Navajo | Secretory |
| Congenital tufting enteropathy (CTE, DIAR 5) | 613217 | AR; 1:50–100.000; higher frequency among Arabians | Secretory |
| Tricho-Hepato-Enteric syndrome (THE) | 222470 | AR, 1:400.000 | Secretory |
| Disease | OMIM number | Transmission and incidence | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Congenital malabsorptive diarrhea (CMD, DIAR 4) | 610370 | AR; few cases described | Osmotic |
| Proprotein convertase 1/3 deficiency (PCD) | 600955 | AR | Osmotic |
| Disease | OMIM number | Transmission and incidence | Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autoimmune polyglandular syndrome type 1 (APS1) | 240300 | AR; AD (1 family) | Secretory |
| Immune dysfunction, polyendocrinopathy, X-linked (IPEX) | 601410 | X linked (autosomal cases described), very rare | Secretory |
| IPEX-like syndrome | -- | not X-linked | Secretory |
© 2012 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Terrin, G.; Tomaiuolo, R.; Passariello, A.; Elce, A.; Amato, F.; Di Costanzo, M.; Castaldo, G.; Canani, R.B. Congenital Diarrheal Disorders: An Updated Diagnostic Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4168-4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044168
Terrin G, Tomaiuolo R, Passariello A, Elce A, Amato F, Di Costanzo M, Castaldo G, Canani RB. Congenital Diarrheal Disorders: An Updated Diagnostic Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2012; 13(4):4168-4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044168
Chicago/Turabian StyleTerrin, Gianluca, Rossella Tomaiuolo, Annalisa Passariello, Ausilia Elce, Felice Amato, Margherita Di Costanzo, Giuseppe Castaldo, and Roberto Berni Canani. 2012. "Congenital Diarrheal Disorders: An Updated Diagnostic Approach" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 13, no. 4: 4168-4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044168
APA StyleTerrin, G., Tomaiuolo, R., Passariello, A., Elce, A., Amato, F., Di Costanzo, M., Castaldo, G., & Canani, R. B. (2012). Congenital Diarrheal Disorders: An Updated Diagnostic Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(4), 4168-4185. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms13044168





