A Comparative Study of the Second-Order Hydrophobic Moments for Globular Proteins: The Consensus Scale of Hydrophobicity and the CHARMM Partial Atomic Charges
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Molecular Shape and Size
3.2. Distance Distribution Functions
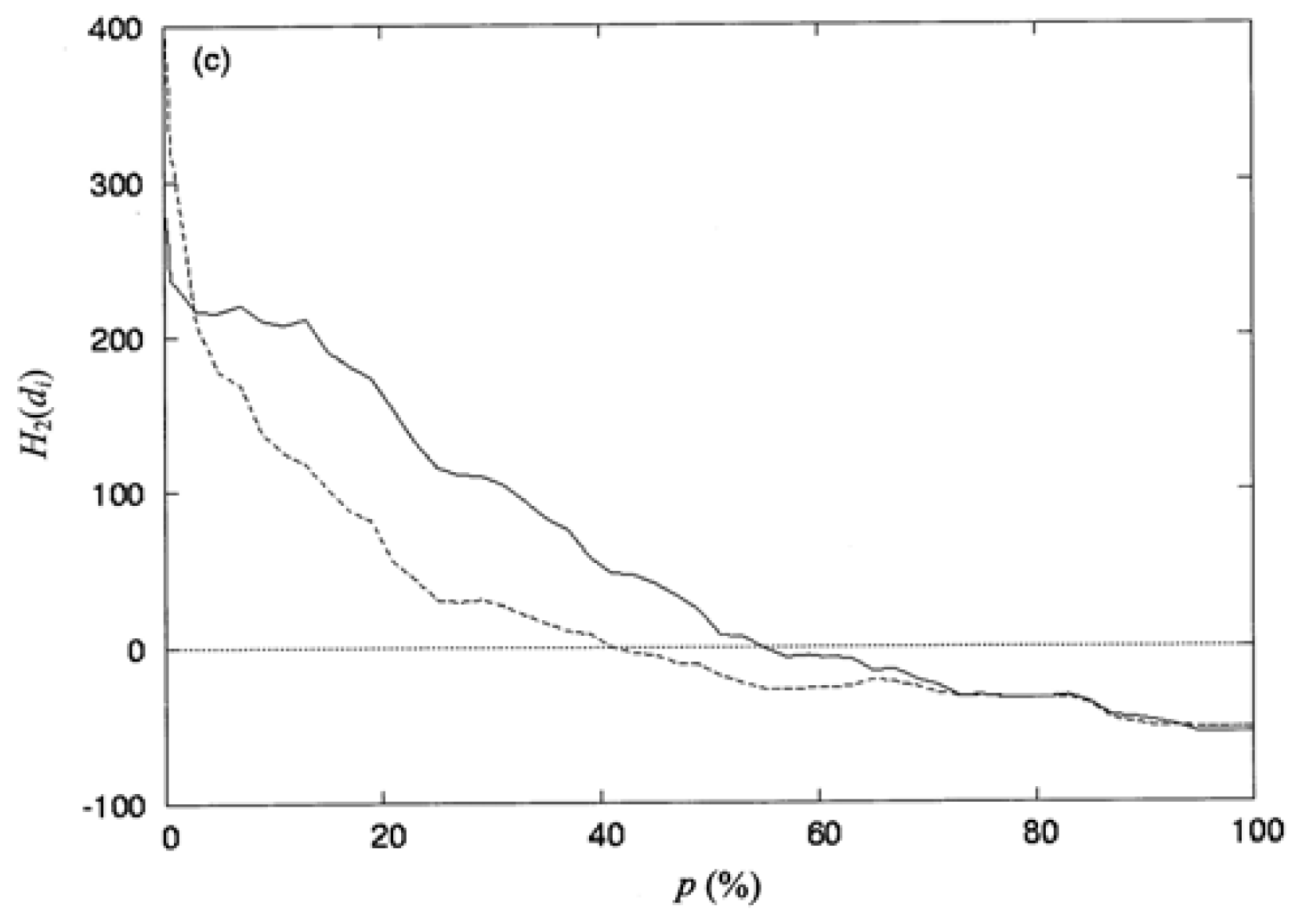
3.3. The Second-Order Hydrophobic Moment
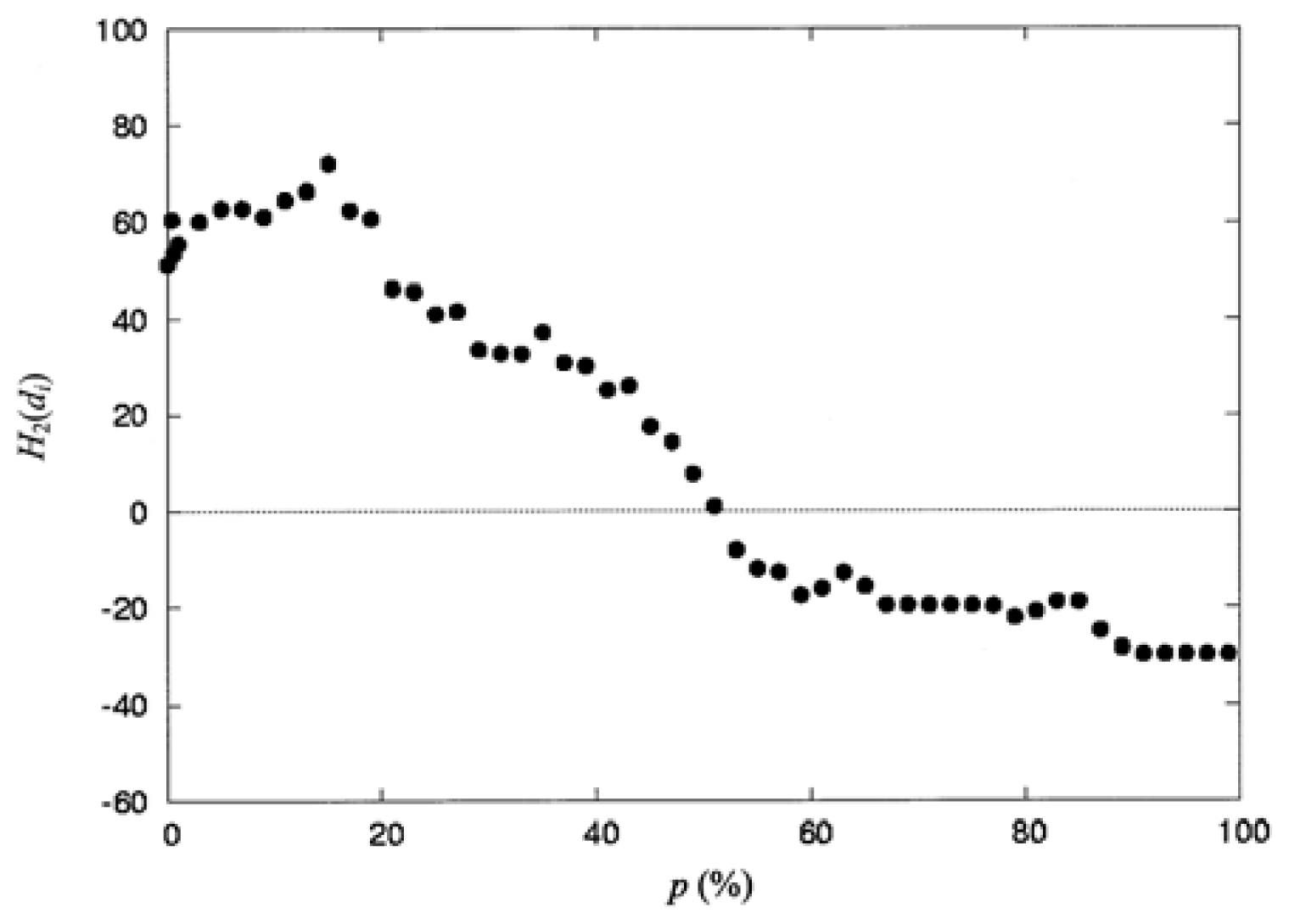
3.4. The Locations of the Spatial Profile of the Proteins at p_ (%) or at d̄_ (Å)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Dill, K.A. Dominant forces in protein folding. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 7133–7155. [Google Scholar]
- Rose, G.D.; Wolfenden, R. Hydrogen bonding, hydrophobicity, packing, and protein folding. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct 1993, 22, 381–415. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, H.S.; Dill, K.A. Origins of structure in globular proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6388–6392. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, B.D. Hydrophobic moments of protein structures: spatially profiling the distribution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 4996–5001. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, D.; Weiss, R.M.; Terwilliger, T.C.; Wilcox, W. Hydrophobic moments and protein structure. Faraday Symp. Chem. Soc 1982, 17, 109–120. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Silverman, B.D.; Royyuru, A.K.; Athma, P. Spatial profiling of protein hydrophobicity: native vs. decoy structures. Proteins 2003, 52, 561–572. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, R.; Royyuru, A.; Athma, P.; Suits, F.; Silverman, B.D. Magnitude and spatial orientation of the hydrophobic moments of multi-domain proteins. Int. J. Bioinform. Res. Appl 2006, 2, 161–176. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, D.; Weiss, R.M.; Terwilliger, T.C. The helical hydrophobic moment: a measure of the amphiphilicity of a helix. Nature 1982, 299, 371–374. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, D.; Weiss, R.M.; Terwilliger, T.C. The hydrophobic moment detects periodicity in protein hydrophobicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 140–144. [Google Scholar]
- Silverman, B.D. Hydrophobic moments of tertiary protein structures. Proteins 2003, 53, 880–888. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg, D.; Schwarz, E.; Komaromy, M.; Wall, R. Analysis of membrane and surface protein sequences with the hydrophobic moment plot. J. Mol. Biol 1984, 179, 125–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, J.; Daman, O.A.; Harris, F.; Phoenix, D.A. Investigation of hydrophobic moment and hydrophobicity properties for transmembrane α-helices. Theor. Biol. Med. Model 2004, 1, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, B.; Richards, F.M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J. Mol. Biol 1971, 55, 379–400. [Google Scholar]
- Gromiha, M.M.; Oobatake, M.; Kono, H.; Uedaira, H.; Sarai, H. Role of structural and sequence information in the prediction of protein stability changes: comparison between buried and partially buried mutations. Protein Eng 1999, 12, 549–555. [Google Scholar]
- Gromiha, M.M. Factors influencing the thermal stability of buried protein mutants. Polymer 2003, 44, 4061–4066. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, G.; Woell, S.; Argos, P. Protein thermal stability, hydrogen bonds, and ion pairs. J. Mol. Biol 1997, 269, 631–643. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, U.; Bahadur, R.P.; Chakrabarti, P. Quantifying the accessible surface area of protein residues in their local environment. Protein Eng 2002, 15, 659–667. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Zhou, H.-X. Prediction of solvent accessibility and sites of deleterious mutations from protein sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 2005, 33, 3193–3199. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Huang, B. Prediction of protein accessible surface areas by support vector regression. Proteins 2004, 57, 558–564. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, M.N.; Rajapakse, J.C. Two-stage support vector regression approach for predicting accessible surface areas of amino acids. Proteins 2006, 63, 542–550. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, F.; Davis, M.J.; Bodén, M.; Teasdale, R.D. predicting the solvent accessibility of transmembrane residues from protein sequence. J. Proteome Res 2006, 5, 1063–1070. [Google Scholar]
- Brooks, B.R.; Bruccoleri, R.E.; Olafson, B.D.; States, D.J.; Swaminathan, S.; Karplus, M. CHARMM: A program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J. Comput. Chem 1983, 4, 187–217. [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki, Y.; Tanford, C. The solubility of amino acids and two glycine peptides in aqueous ethanol and dioxane solutions. J. Biol. Chem 1971, 246, 2211–2217. [Google Scholar]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, K.A.; Nicholls, A.; Friedman, R.; Honig, B. Extracting hydrophobic free energies from experimental data: relationship to protein folding and theoretical models. Biochemistry 1991, 30, 9686–9697. [Google Scholar]
- Griep, S.; Hobohm, U. PDBselect 1992-2009 and PDBfilter-select. Nucleic Acids Res 2010, 38, D318–D319. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The protein data bank. Nucleic Acids Res 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, T.T.; Zhang, L.X. Effect of secondary structure on the conformations and folding behaviors of protein-like chains. Polymer 2004, 45, 7759–7766. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, W.Q.; Zhang, L.X. Conformational properties and dynamics of protein-like chains confined in an infinite cylinder. Eur. Polym. J 2006, 42, 573–579. [Google Scholar]
- Tran, H.T.; Pappu, R.V. Toward an accurate theoretical framework for describing ensembles for proteins under strongly denaturing conditions. Biophys. J 2006, 91, 1868–1886. [Google Scholar]
- Hyeon, C.; Dima, R.I.; Thirumalai, D. Size, shape, and flexibility of RNA structures. J. Chem. Phys 2006, 125, 194905–194914. [Google Scholar]
- Fernandes, M.X.; Bernadó, P.; Pons, M.; de la Torre, J.G. An analytical solution to the problem of the orientation of rigid particles by planar obstacles. Application to membrane systems and to the calculation of dipolar couplings in protein NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2001, 123, 12037–12047. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.K.; Vacatello, M.; Yoon, D.Y. Off-lattice Monte Carlo simulations of polymer melts confined between two plates. J. Chem. Phys 1988, 89, 5206–5215. [Google Scholar]
- Eisenhaber, F.; Argos, P. Improved strategy in analytic surface calculation for molecular systems: Handling of singularities and computational efficiency. J. Comput. Chem 1993, 14, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar]
- InsightII, version 2000; Accelrys, Inc: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001.
- Press, W.H.; Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.A.; Vetterling, W.T. Numerical recipes in FORTRAN; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Flory, P.J. Principles of Polymer Chemistry; Cornel University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1953. [Google Scholar]
- de Gennes, P.G. Scaling Concepts in Polymer Physics; Cornel University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, M.; Edwards, S.F. The Theory of Polymer Dynamics; Clarendon Press: Oxford, UK, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, I.C. Phase transition behavior of the isolated polymer chain. Macromolecules 1979, 12, 980–988. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, H.S.; Dill, K.A. Polymer principles in protein structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem 1991, 20, 447–490. [Google Scholar]
- Uzawa, T.; Kimura, T.; Ishimori, K.; Morishima, I.; Matsui, T.; Ikeda-Saito, M.; Takahashi, S.; Akiyama, S.; Fujisawa, T. Time-resolved small-angle X-ray scattering investigation of the folding dynamics of heme oxygenase: implication of the scaling relationship for the submillisecond intermediates of protein folding. J. Mol. Biol 2006, 35, 997–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-J.; Eichinger, B.E. Computer simulation of end-linked networks: telechelic poly(oxyethylene) cross-linked with plurifunctional isocyanates. Macromolecules 1989, 22, 1441–1448. [Google Scholar]
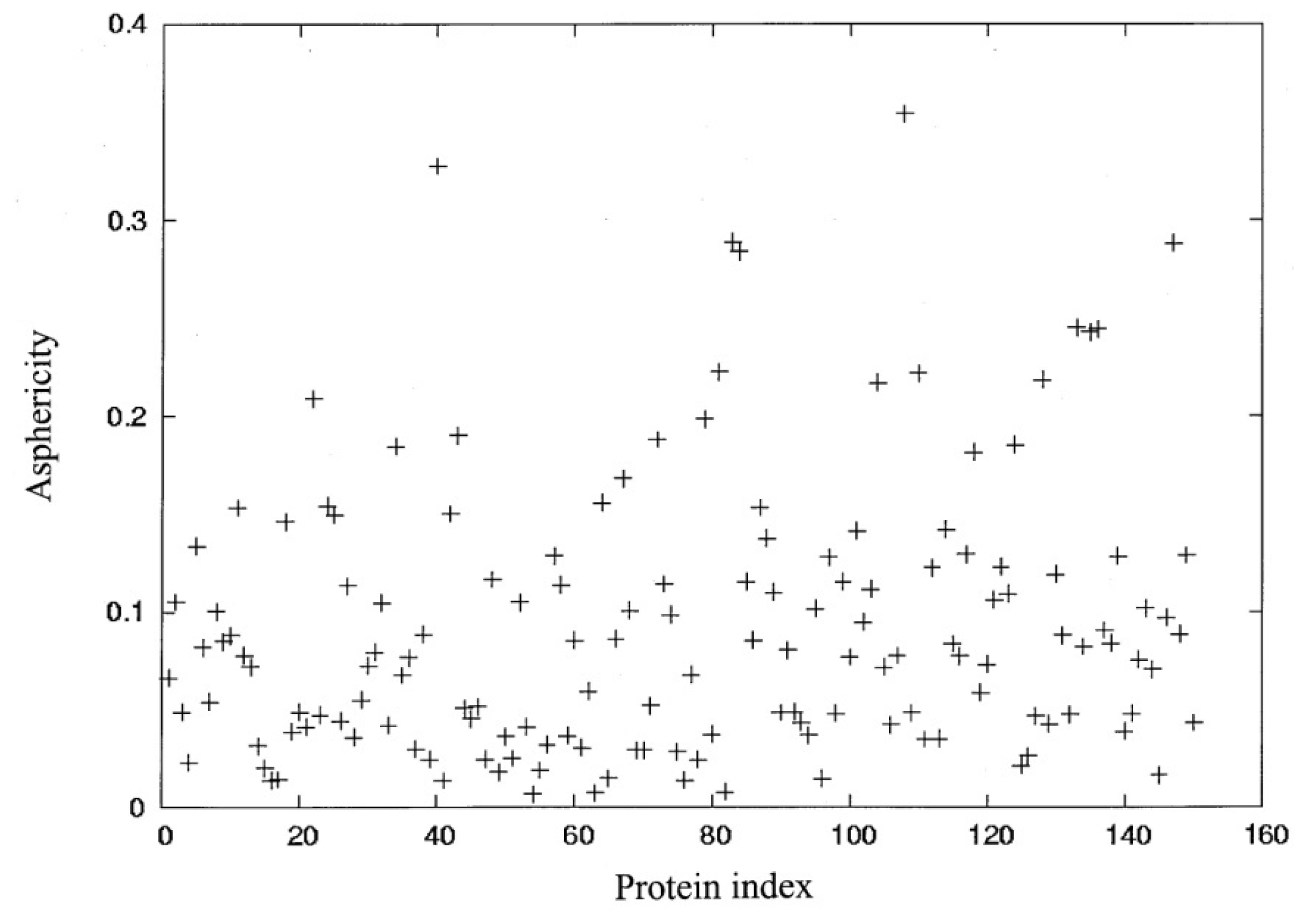
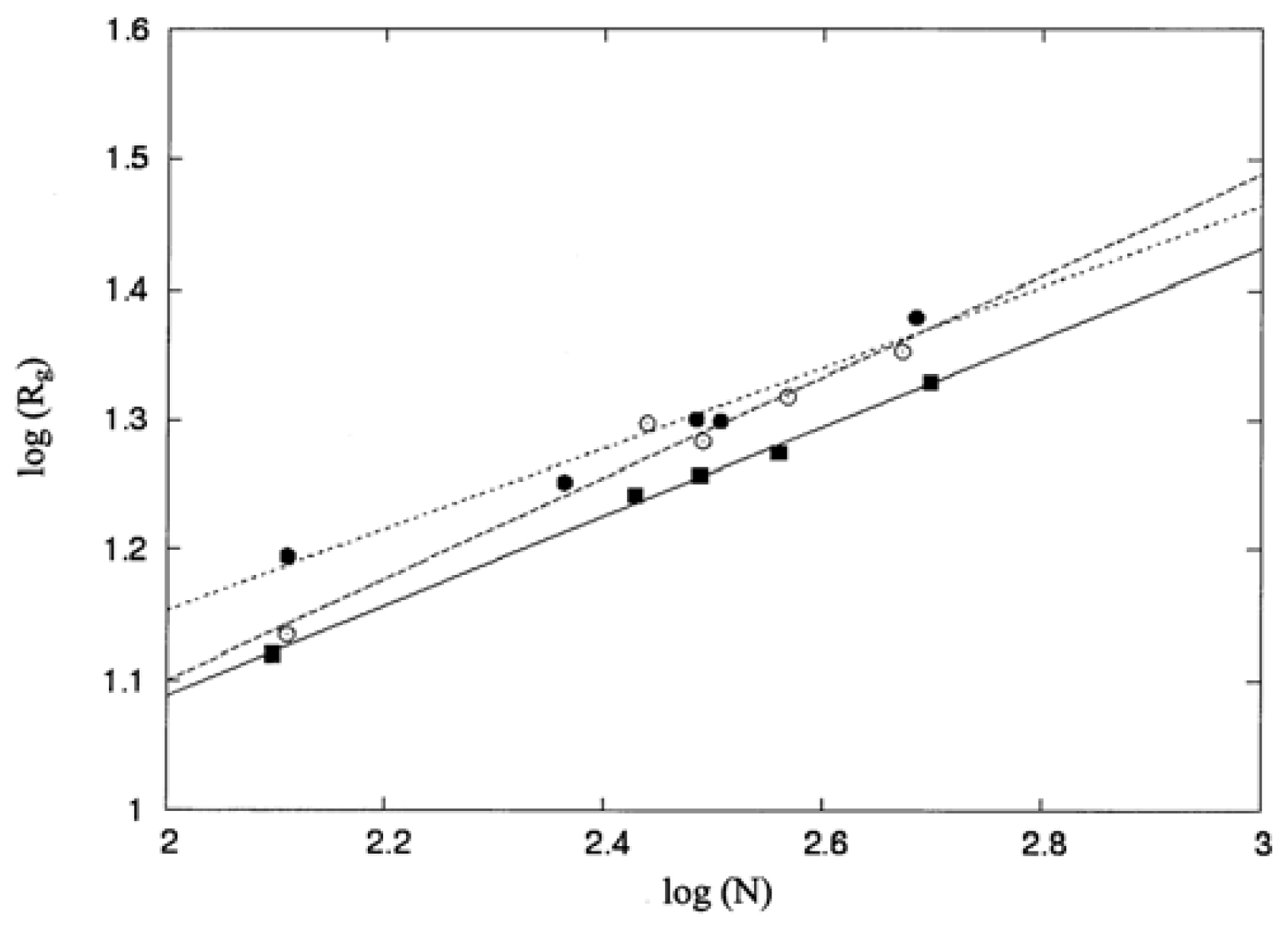
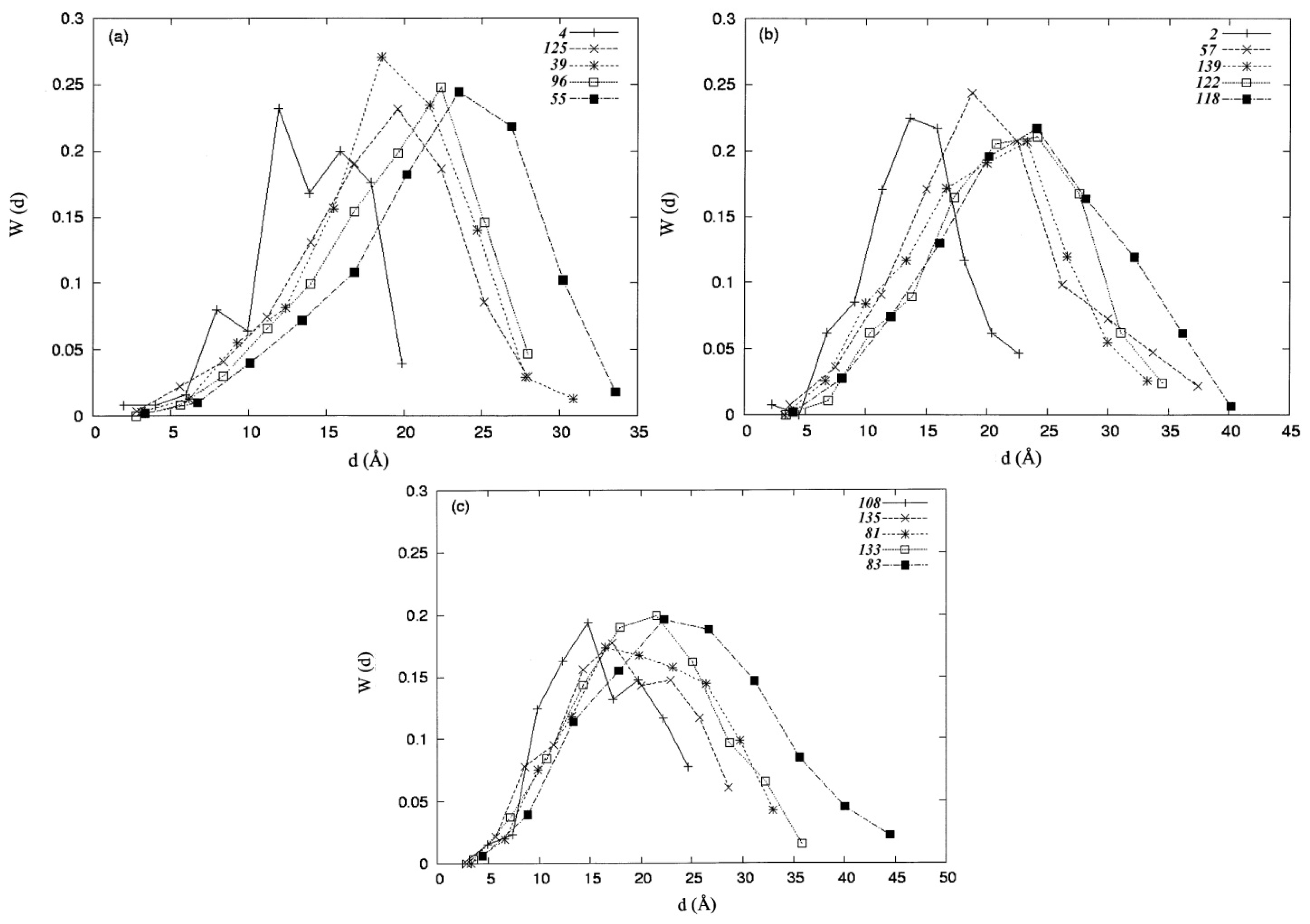

| Protein | Protein index | PDB code | No. residues |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | |||
| Photoactive yellow protein | 4 | 3PYP | 125 |
| Exonuclease III | 125 | 1AKO | 268 |
| Carboxypeptidase A | 39 | 2CTC | 307 |
| Cellulase cela | 96 | 1CEM | 363 |
| Myrosinase | 55 | 1E70 | 499 |
| II | |||
| Lysozyme | 2 | 3LTZ | 129 |
| Dienoyl-coa isomerase | 57 | 1DCIA | 275 |
| Sulfate-Binding protein | 139 | 1SBP | 309 |
| Maltodextrin-binding protein | 122 | 3MBP | 370 |
| Alpha-amylase | 118 | 1JAE | 470 |
| III | |||
| Cytochrome C′ | 108 | 1CPQ | 129 |
| Molybdate transport protein | 135 | 1AMF | 231 |
| L-arabinose-binding protein | 81 | 1ABE | 305 |
| Phosphate-binding protein | 133 | 2ABH | 321 |
| Leucine aminopeptidase | 83 | 1LAM | 484 |
| Residue | ASA a | Consensus scale (hi) b |
|---|---|---|
| Ala | 116.5 | 0.25 |
| Arg | 249.7 | −1.80 |
| Asn | 163.2 | −0.64 |
| Asp | 156.2 | −0.72 |
| Cys | 140.2 | 0.04 |
| Gln | 188.9 | −0.69 |
| Glu | 183.8 | −0.62 |
| Gly | 84.9 | 0.16 |
| His | 204.3 | −0.40 |
| Ile | 183.6 | 0.73 |
| Leu | 193.5 | 0.53 |
| Lys | 211.3 | −1.10 |
| Met | 205.9 | 0.26 |
| Phe | 223.7 | 0.61 |
| Pro | 148.3 | −0.07 |
| Ser | 124.8 | −0.26 |
| Thr | 144.1 | −0.18 |
| Trp | 266.3 | 0.37 |
| Tyr | 236.0 | 0.02 |
| Val | 158.0 | 0.54 |
| PDB code | α1a | α2a | α3a | 02 ×δ b | 103× S c | a d | b d | Rge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | ||||||||
| 3PYP | 41.11 | 61.82 | 71.06 | 2.33 | −4.33 | 16.04 | 18.85 | 13.19 |
| 1AKO | 78.40 | 96.64 | 129.61 | 2.18 | 3.05 | 20.92 | 25.46 | 17.45 |
| 2CTC | 84.32 | 100.38 | 141.79 | 2.48 | 5.30 | 21.49 | 26.63 | 18.07 |
| 1CEM | 93.46 | 116.77 | 143.17 | 1.49 | 0.39 | 22.93 | 26.76 | 18.80 |
| 1E70 | 110.18 | 169.06 | 176.62 | 1.91 | −5.02 | 26.42 | 29.72 | 21.35 |
| II | ||||||||
| 3LTZ | 35.84 | 48.75 | 101.55 | 10.49 | 57.61 | 14.54 | 22.53 | 13.64 |
| 1DCIA | 72.74 | 96.28 | 223.74 | 12.84 | 83.38 | 20.56 | 33.45 | 19.82 |
| 1SBP | 56.12 | 105.62 | 206.44 | 12.79 | 51.45 | 20.17 | 32.13 | 19.21 |
| 3MBP | 74.47 | 115.72 | 242.46 | 12.28 | 65.10 | 21.81 | 34.82 | 20.80 |
| 1JAE | 88.54 | 105.91 | 312.60 | 18.13 | 151.02 | 22.05 | 39.53 | 22.52 |
| III | ||||||||
| 1CPQ | 26.97 | 39.53 | 178.83 | 35.41 | 410.89 | 12.89 | 29.90 | 15.66 |
| 1AMF | 35.21 | 75.05 | 208.33 | 24.30 | 188.55 | 16.60 | 32.27 | 17.85 |
| 1ABE | 53.21 | 89.04 | 256.31 | 22.25 | 183.73 | 18.86 | 35.80 | 19.96 |
| 2ABH | 65.13 | 68.09 | 262.66 | 24.53 | 242.78 | 18.25 | 36.24 | 19.90 |
| 1LAM | 44.08 | 141.19 | 388.73 | 28.90 | 211.84 | 21.46 | 44.09 | 23.94 |
| P (%) | np a | H2(di) b | P (%) | np a | H2(di) b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 13 | 51.14 | 47.0 | 88 | 14.18 |
| 0.40 | 17 | 60.63 | 49.0 | 90 | 7.79 |
| 0.60 | 18 | 53.46 | 51.0 | 92 | 1.01 |
| 1.00 | 21 | 55.51 | 53.0 | 98 | −8.13 |
| 3.00 | 24 | 60.15 | 55.0 | 99 | −11.95 |
| 5.00 | 30 | 62.87 | 57.0 | 102 | −12.64 |
| 7.00 | 30 | 62.87 | 59.0 | 103 | −17.51 |
| 9.00 | 33 | 61.17 | 61.0 | 104 | −16.08 |
| 11.0 | 39 | 64.58 | 63.0 | 106 | −12.87 |
| 13.0 | 42 | 66.37 | 65.0 | 109 | −15.63 |
| 15.0 | 44 | 72.18 | 67.0 | 111 | −19.49 |
| 17.0 | 48 | 62.50 | 69.0 | 111 | −19.49 |
| 19.0 | 50 | 60.74 | 71.0 | 114 | −19.64 |
| 21.0 | 54 | 46.35 | 73.0 | 114 | −19.64 |
| 23.0 | 57 | 45.69 | 75.0 | 114 | −19.64 |
| 25.0 | 63 | 41.04 | 77.0 | 117 | −19.73 |
| 27.0 | 64 | 41.57 | 79.0 | 119 | −22.16 |
| 29.0 | 66 | 33.47 | 81.0 | 120 | −20.88 |
| 31.0 | 68 | 32.77 | 83.0 | 121 | −18.87 |
| 33.0 | 70 | 32.65 | 85.0 | 121 | −18.87 |
| 35.0 | 73 | 37.21 | 87.0 | 123 | −24.80 |
| 37.0 | 76 | 30.78 | 89.0 | 124 | −28.33 |
| 39.0 | 77 | 30.14 | 91.0 | 125 | −29.56 |
| 41.0 | 81 | 25.23 | 93.0 | 125 | −29.56 |
| 43.0 | 82 | 26.02 | 95.0 | 125 | −29.56 |
| 45.0 | 86 | 17.47 | 97.0 | 125 | −29.56 |
| PDB code | Correlation coefficient (R) a | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| |qi| ≥ 0.25 b | |qi|≥ 0.27 c | |qi| ≥ 0.3 d | |
| I | |||
| 3PYP | 0.89 | 0.89 | 0.94 |
| 1AKO | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.87 |
| 2CTC | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.91 |
| 1CEM | 0.85 | 0.86 | 0.92 |
| 1E70 | 0.88 | 0.87 | 0.91 |
| II | |||
| 3LTZ | 0.63 | 0.63 | 0.85 |
| 1DCIA | 0.78 | 0.79 | 0.82 |
| 1SBP | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.86 |
| 3MBP | 0.59 | 0.59 | 0.82 |
| 1JAE | 0.86 | 0.87 | 0.91 |
| III | |||
| 1CPQ | 0.81 | 0.81 | 0.96 |
| 1AMF | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.88 |
| 1ABE | 0.72 | 0.74 | 0.81 |
| 2ABH | 0.62 | 0.62 | 0.77 |
| 1LAM | 0.87 | 0.87 | 0.90 |
| PDB code | p_(%)a | d̄ _ (Å) b | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |qi| ≥ 0.3 c | C scale d | |qi| ≥ 0.3 e | C scale f | |
| I | ||||
| 3PYP | 49 | 53 | 11.45 | 11.79 |
| 1AKO | 59 | 53 | 15.79 | 15.45 |
| 2CTC | 47 | 49 | 16.14 | 16.24 |
| 1CEM | 41 | 49 | 16.80 | 17.10 |
| 1E70 | 33 | 51 | 18.52 | 19.57 |
| II | ||||
| 3LTZ | 39 | 55 | 11.56 | 12.16 |
| 1DCIA | 49 | 57 | 16.66 | 17.33 |
| 1SBP | 61 | 61 | 17.43 | 17.43 |
| 3MBP | 51 | 61 | 18.72 | 19.07 |
| 1JAE | 49 | 53 | 20.56 | 20.65 |
| III | ||||
| 1CPQ | 53 | 81 | 13.92 | 14.70 |
| 1AMF | 49 | 59 | 15.49 | 15.77 |
| 1ABE | 41 | 71 | 17.23 | 18.39 |
| 2ABH | 37 | 61 | 17.00 | 17.95 |
| 1LAM | 43 | 55 | 20.67 | 21.20 |
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsai, C.-F.; Lee, K.-J. A Comparative Study of the Second-Order Hydrophobic Moments for Globular Proteins: The Consensus Scale of Hydrophobicity and the CHARMM Partial Atomic Charges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 8449-8465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128449
Tsai C-F, Lee K-J. A Comparative Study of the Second-Order Hydrophobic Moments for Globular Proteins: The Consensus Scale of Hydrophobicity and the CHARMM Partial Atomic Charges. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2011; 12(12):8449-8465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128449
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsai, Cheng-Fang, and Kuei-Jen Lee. 2011. "A Comparative Study of the Second-Order Hydrophobic Moments for Globular Proteins: The Consensus Scale of Hydrophobicity and the CHARMM Partial Atomic Charges" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 12, no. 12: 8449-8465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128449
APA StyleTsai, C.-F., & Lee, K.-J. (2011). A Comparative Study of the Second-Order Hydrophobic Moments for Globular Proteins: The Consensus Scale of Hydrophobicity and the CHARMM Partial Atomic Charges. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 12(12), 8449-8465. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12128449




