Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies of Quantum and Electronic Confinement Effects in Nanostructured Materials
Abstract
:Introduction
Quantum Confinement Effect
Concept Definition

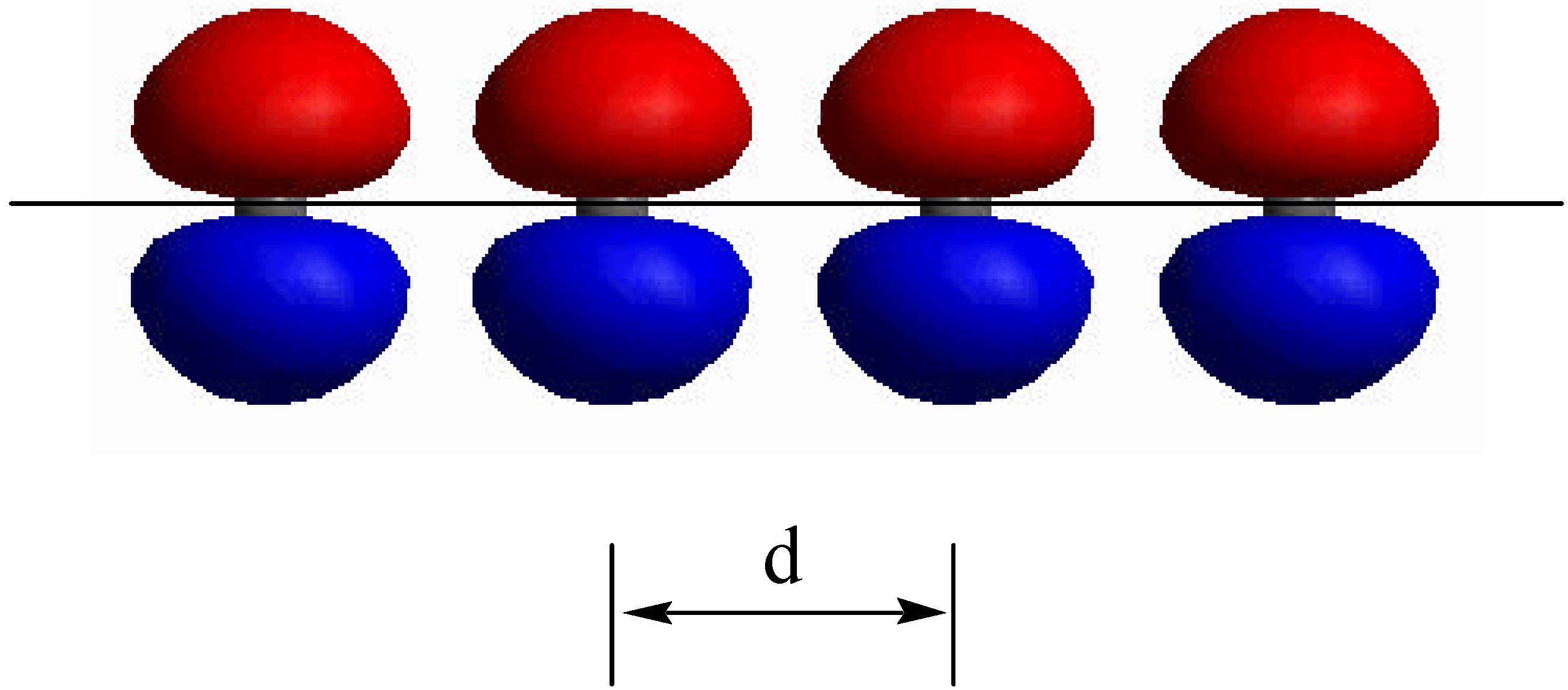
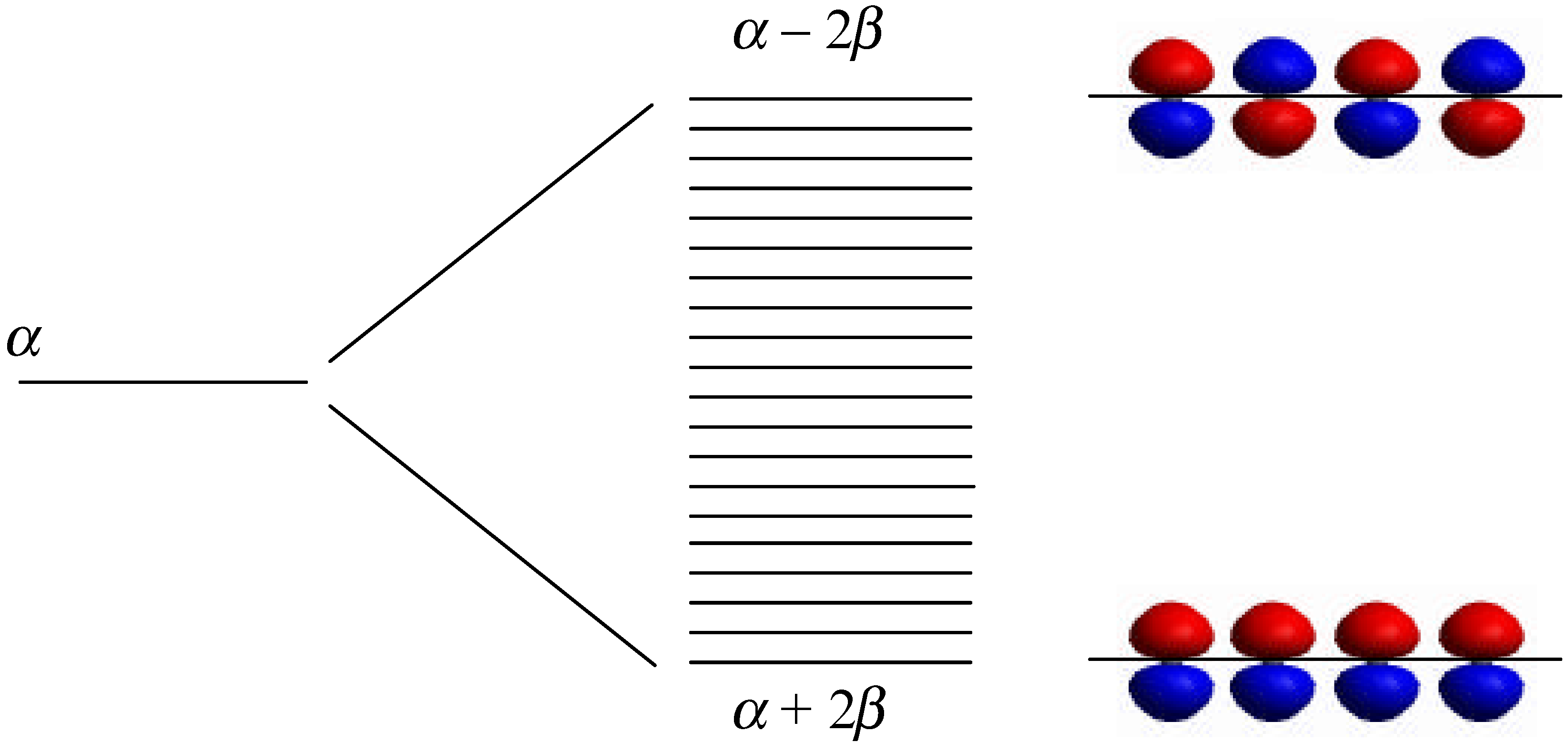
Model Design
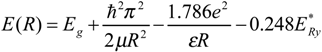
 is the effective Rydberg energy, e4/2ε2ℏ2(me*-1 + mh*-1). The first term in the above equation is the band gap of the bulk materials, the second represents the particle-in-a-box quantum localization energy and has a simple 1 / R2 dependence, the third term the Coulomb energy with a 1 / R dependence, and the last term is the result of the spatial correlation effect. This last size-independent term is usually small but can become significant for semiconductors with small dielectric constant. Therefore, the cluster radius can be easily determined according to the above formula based on the absorption spectra.
is the effective Rydberg energy, e4/2ε2ℏ2(me*-1 + mh*-1). The first term in the above equation is the band gap of the bulk materials, the second represents the particle-in-a-box quantum localization energy and has a simple 1 / R2 dependence, the third term the Coulomb energy with a 1 / R dependence, and the last term is the result of the spatial correlation effect. This last size-independent term is usually small but can become significant for semiconductors with small dielectric constant. Therefore, the cluster radius can be easily determined according to the above formula based on the absorption spectra.Case Study

Electronic Confinement Effect
Concept Definition
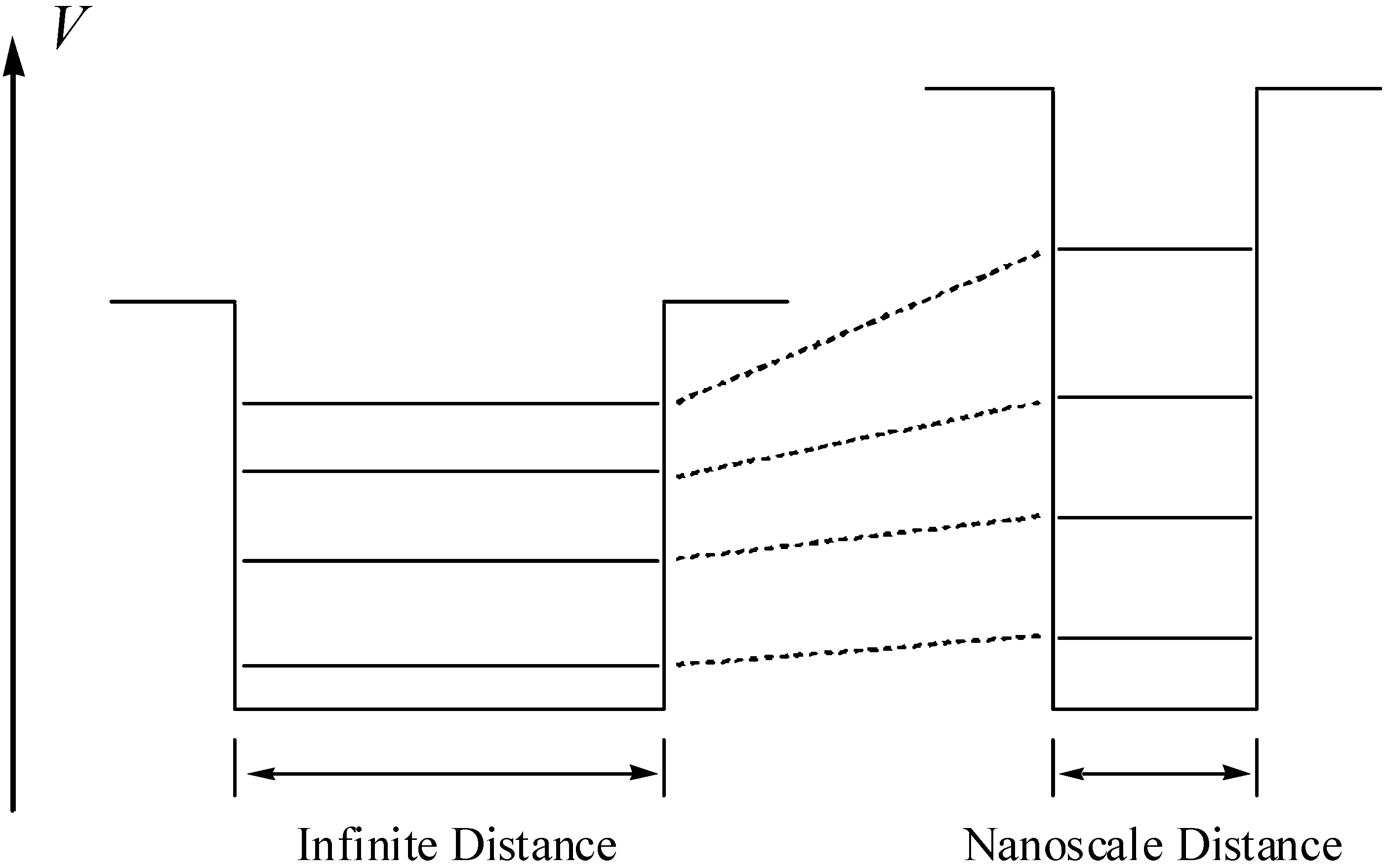
Model Design

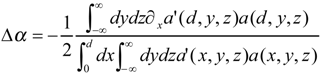


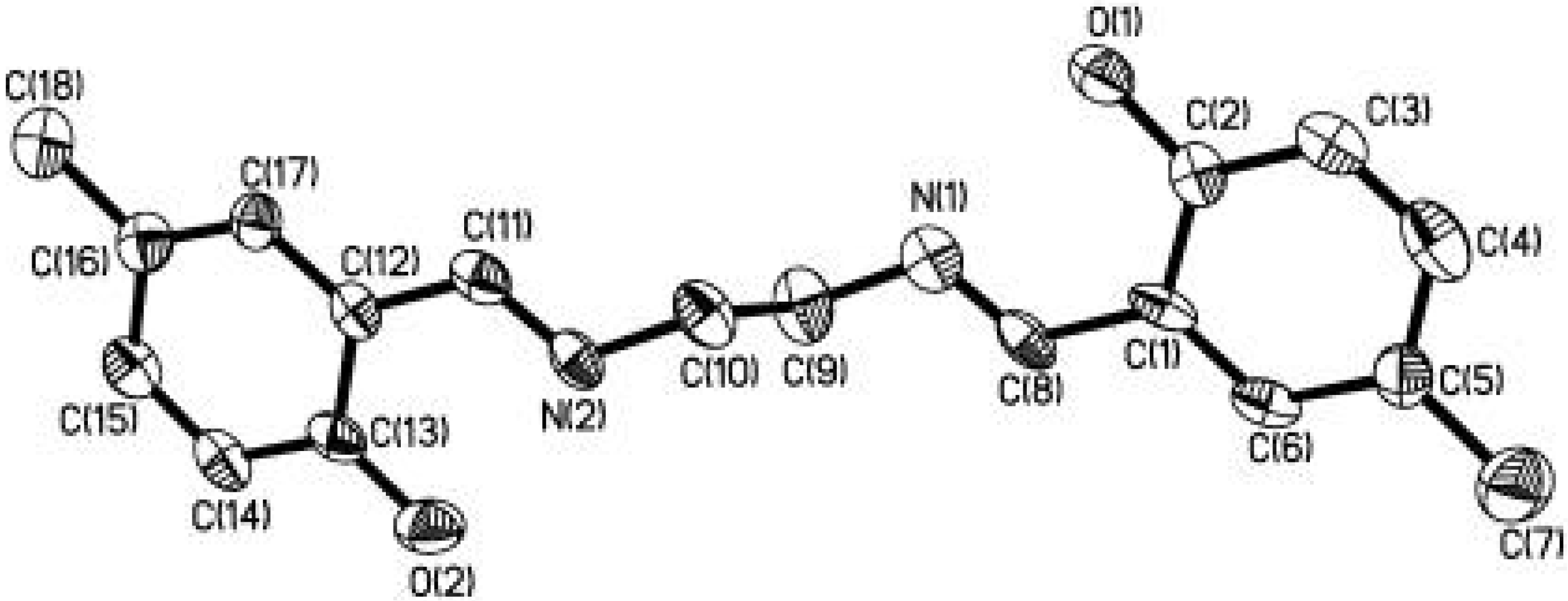
Case Study
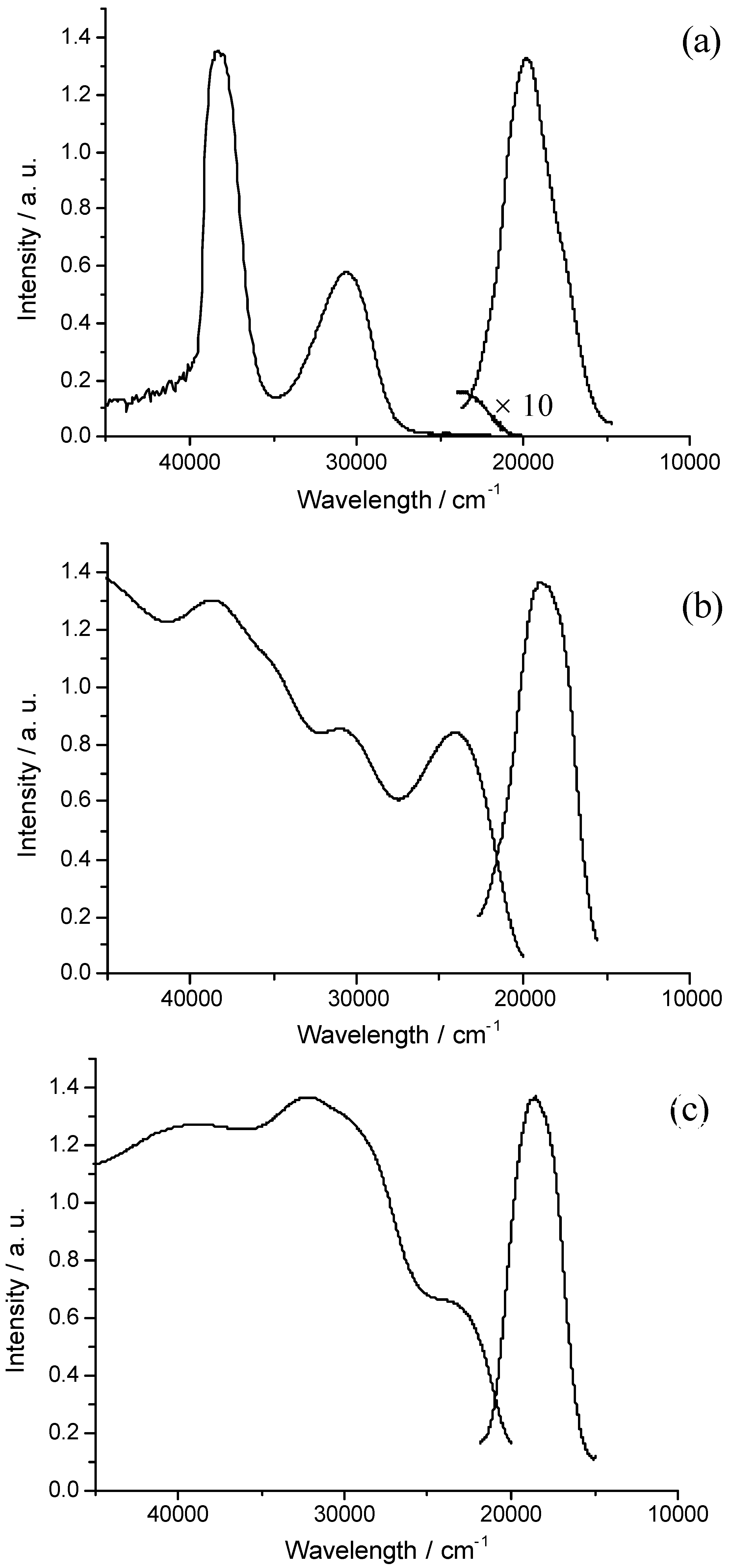
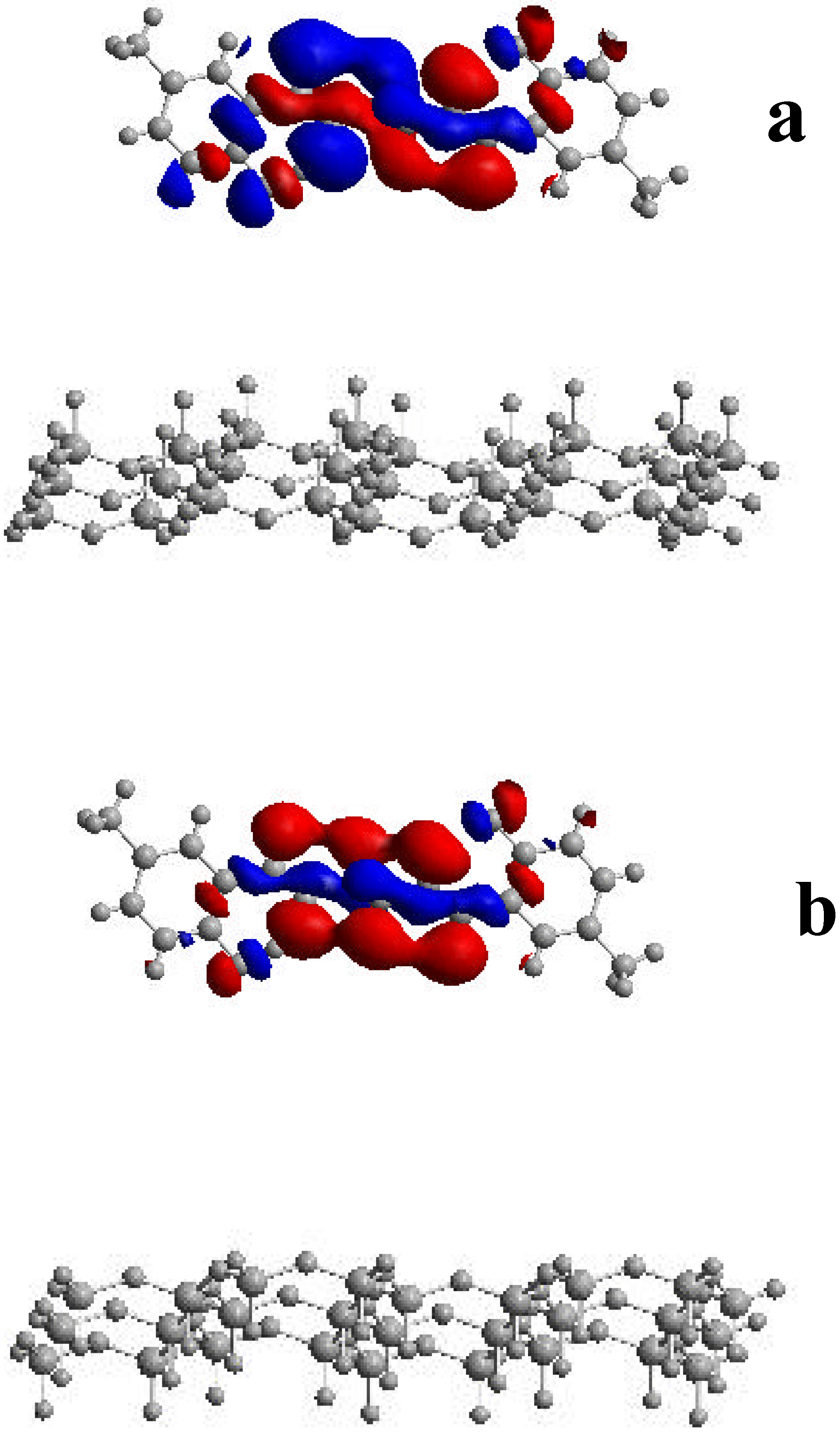
Concluding Remarks

Acknowledgements
References
- Frontiers in Materials Science (Special Report). Science 1997, 277, 1213.
- Nanoscale Materials (Special Issue). Acc. Chem. Res. 1999, 32, 387.
- Organic-Inorganic Nanocomposite Materials (Special Issue). Chem. Mater. 2001, 13, 3059.
- Kresge, C. T.; Leonowicz, M. E.; Roth, W. J.; Vartuli, J. C.; Beck, J. S. Nature 1992, 359, 710.
- Liu, J.; Shiu, Y.; Nie, Z.; Chang, J. H.; Wang, L.-Q.; Fryxell, G. E.; Samuels, W. D.; Exarhos, G. J. J. Phys. Chem. A 2000, 104, 8328.
- Ozin, G. A. Adv. Mater. 1994, 6, 71.Ozin, G. A. Chem. Commun. 2000, 419.
- Stein, A.; Melde, B. J.; Schroden, R. C. Adv. Mater. 2000, 12, 1403.
- Wu, C.-G.; Bein, T. Science 1994, 264, 1757.
- Sanchez, C.; Ribot, F. New J. Chem. 1994, 18, 1007.
- Knox, R. S. Theory of Excitons; New York: Academic Press, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Brus, L. E. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 5566.Brus, L. E. J. Chem. Phys. 1984, 80, 4403.
- Wang, Y.; Herron, N. Phys. Rev. B 1990, 42, 7253.Wang, Y.; Herron, N. J. Phys. Chem. 1991, 95, 525.
- Steigerwald, M. L.; Brus, L. E. Acc. Chem. Res. 1990, 23, 183.
- Weller, H. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 1993, 32, 41.
- Burdett, J. K. Prog. Solid State Chem. 1984, 15, 173.
- Bol, A. A.; Meijerink, A. J. Lumin. 2000, 87-89, 315.
- Gong, X.; Chen, W. J.; Wu, P. F.; Chan, W. K. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1998, 73, 2875.
- Bhargava, R. N.; Gallagher, D.; Hong, X.; Nurmikko, A. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1994, 72, 416.
- Wang, Z.-X.; Zhang, L. Z.; Xiong, Y.; Tang, G.-Q.; Zhang, G.-L.; Chen, W.-J. J. Chem. Res. 2002, 7, 348.
- Corma, A. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 2373.
- Ganschow, M.; Wark, M.; Wöhrle, D.; Schulz-Ekloff, G. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 161.
- Bockstette, M.; Wöhrle, D.; Braun, I.; Schulz-Ekloff, G. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 1998, 23, 83.
- Blatter, F.; Frei, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 7501.
- Blatter, F.; Frei, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 1812.
- Sun, H.; Blatter, F.; Frei, H. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1996, 118, 6873.
- Zicovich-Wilson, C. M.; Corma, A.; Viruela, P. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 10863.
- Corma, A.; García, H.; Sastre, G.; Viruela, P. M. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 4575.
- Cohen de Lara, E.; Kahn, R. Guideline for Mastering the Properties of Molecular Sieves; NATO ASI Series; 1990; Volume 221, p. 169. [Google Scholar]
- Rabo, J. A.; Gajda, G. J. Guideline for Mastering the Properties of Molecular Sieves; NATO ASI Series; 1990; Volume 221, p. 273. [Google Scholar]
- Derouane, E. Guideline for Mastering the Properties of Molecular Sieves; NATO ASI Series; 1990; Volume 221, p. 225. [Google Scholar]
- Van Santen, R. A. Guideline for Mastering the Properties of Molecular Sieves; NATO ASI Series; 1990; Volume 221, p. 201. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L. Z.; Cheng, P.; Liao, D.-Z. J. Chem. Phys. 2002, 117, 5959.
- Zhang, L. Z.; Cheng, P. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2003, 19, 7.
- Douhal, A.; Lahmani, F.; Zewail, A. H. Chem. Phys. 1996, 207, 477.
- Cohen, M. D.; Flavian, S. J. Chem. Soc. B 1967, 321.
- Zhang, L. Z.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, P.; Tang, G.-Q.; Liao, D.-Z. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2002, 358, 278.
- Fu, H.-B.; Yao, J.-N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1434.
- Zhang, L. Z.; Xiong, Y.; Cheng, P.; Tang, G.-Q.; Wang, L.-J.; Liao, D.-Z. J. Mater. Chem. 2001, 11, 2903.
- Langley, P. J.; Hulliger, J. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1999, 28, 279.
© 2003 by MDPI ( http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes.
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.Z.; Sun, W.; Cheng, P. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies of Quantum and Electronic Confinement Effects in Nanostructured Materials. Molecules 2003, 8, 207-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/80100207
Zhang LZ, Sun W, Cheng P. Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies of Quantum and Electronic Confinement Effects in Nanostructured Materials. Molecules. 2003; 8(1):207-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/80100207
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Lei Z., Wei Sun, and Peng Cheng. 2003. "Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies of Quantum and Electronic Confinement Effects in Nanostructured Materials" Molecules 8, no. 1: 207-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/80100207
APA StyleZhang, L. Z., Sun, W., & Cheng, P. (2003). Spectroscopic and Theoretical Studies of Quantum and Electronic Confinement Effects in Nanostructured Materials. Molecules, 8(1), 207-222. https://doi.org/10.3390/80100207



