Molecular Polarizability of Sc and C (Fullerene and Graphite) Clusters
Abstract
:Introduction
Electrostatic properties
Interacting induced dipoles polarization model for molecular polarizabilities
- A damping function has been used in the calculation of the symmetrical field gradient tensor in order to prevent the polarizability from going to infinity [47].
- The interaction between bonded atoms and atoms with a distance lying in an interval defined by [rinf, rsup] has been neglected. The starting values for this interval are [0,1030] and rinf is incremented if resonance conditions are detected.
- To build up the many-body polarizability matrix the atomic polarizability tensors given by have been used instead of the scalar polarizability .
Calculation results and discussion
| Scn | <α> (Å3)a | <α> ref.b |
|---|---|---|
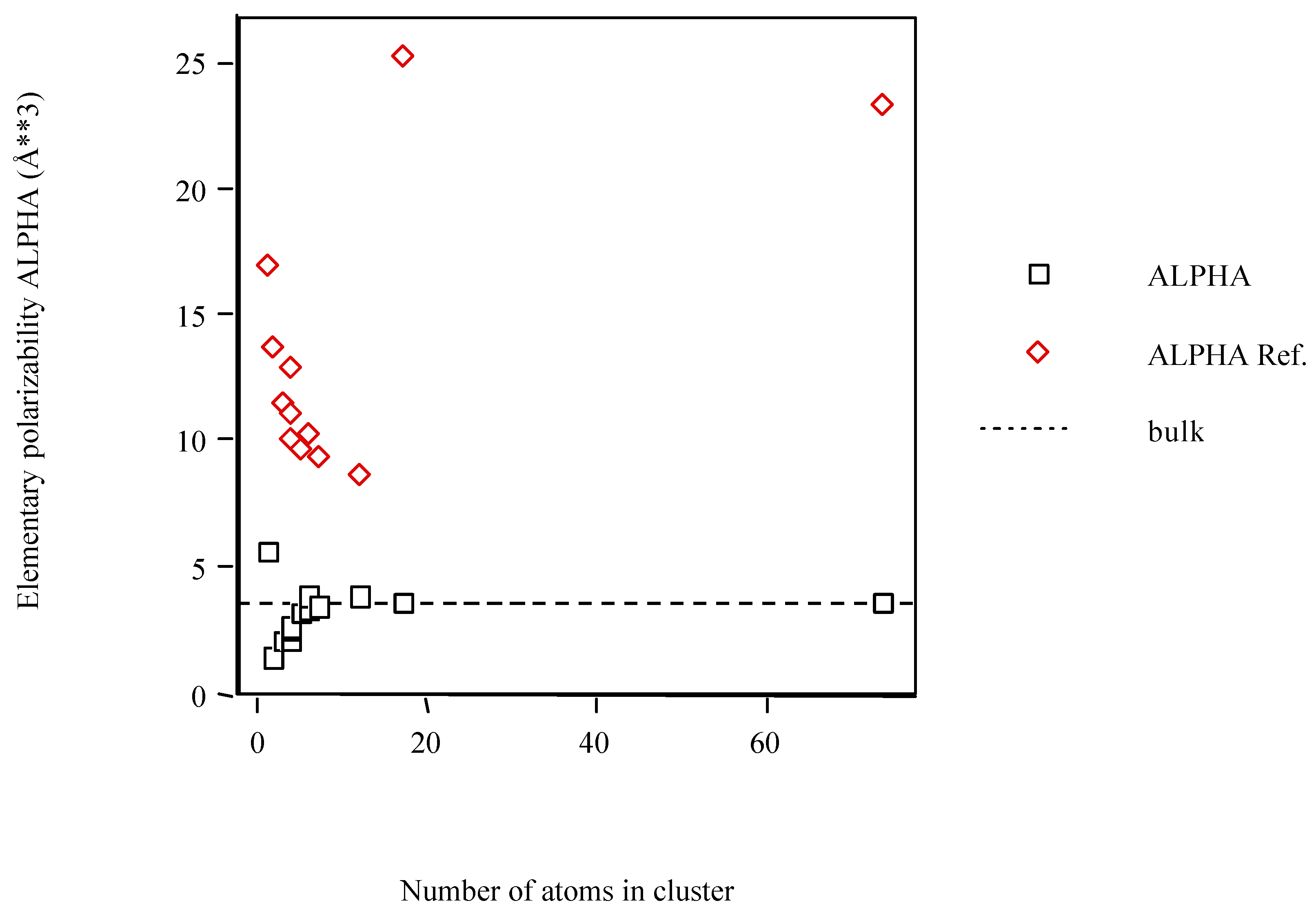
| Sc | 5.631 | 16.893 |
| Sc2 | 1.418 | 13.744 |
| Sc3 | 2.103 | 11.557 |
| Sc4 D4h | 2.111 | 12.873 |
| Sc4 D2h | 2.461 | 11.163 |
| Sc4 Td | 2.657 | 10.041 |
| Sc5 | 3.116 | 9.690 |
| Sc6 Oh | 3.367 | 10.330 |
| Sc6 D3d | 3.904 | 10.330 |
| Sc7 | 3.429 | 9.321 |
| Sc12 | 3.891 | 8.724 |
| Sc17 h.c.p. | 3.590 | 25.278 |
| Sc74 h.c.p. | 3.630 | 23.471 |
| Cn fullerene | <α> (Å3)a | <α> ref.b |
|---|---|---|
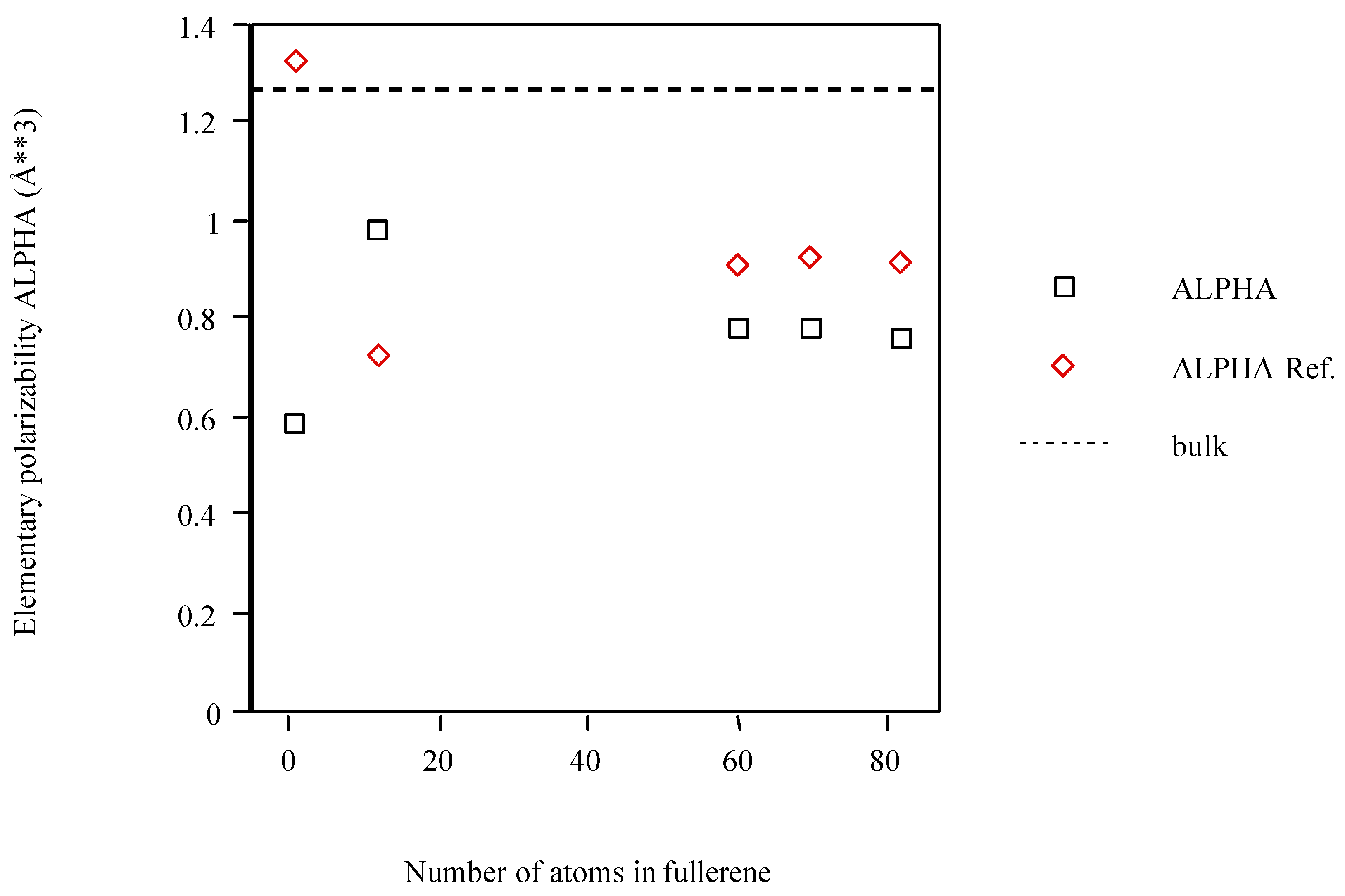
| C | 0.588 | 1.322 |
| C12 | 0.978 | 0.722 |
| C60 | 0.782 | 0.904 |
| C70 | 0.781 | 0.920 |
| C82 | 0.763 | 0.911 |
| Cn graphite | <α> (Å3)a | <α> ref.b |
|---|---|---|
| C | 0.588 | 1.322 |
| C6 | 0.746 | 1.024 |
| C10 | 0.775 | 1.067 |
| C13 | 0.789 | 1.074 |
| C16 | 0.795 | 1.091 |
| C19 | 0.805 | 1.109 |
| C22 | 0.798 | 1.116 |
| C24 | 0.796 | 1.117 |
| C42 | 0.813 | 1.185 |
| C54 | 0.839 | 1.212 |
| C84 | 0.851 | 1.273 |
| C96 | 0.875 | 1.293 |

Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Benichou, E.; Antoine, R.; Rayane, D.; Vezin, B.; Dalby, F. W.; Dugourd, Ph.; Broyer, M.; Ristori, C.; Chandezon, F.; Huber, B. A.; Rocco, J. C.; Blundell, S. A.; Guet, C. Measurement of static electric dipole polarizabilities of lithium clusters: Consistency with measured dynamic polarizabilities. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 59, R1–R4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maroulis, G.; Xenides, D. Enhanced linear and nonlinear polarizabilities for the Li4 cluster. How satisfactory is the agreement between theory and experiment for the static dipole polarizability? J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 4590–4593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentealba, P. Static dipole polarizabilities of small neutral carbon clusters Cn (n=8). Phys. Rev. A 1998, 58, 4232–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentealba, P.; Reyes, O. Density functional study of LinHm clusters. Electric dipole polarizabilities. J. Phys. Chem. A 1999, 103, 1376–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, K.; Pederson, M.; Wang, C.-Z.; Ho, K.-M. Calculated polarizabilities of intermediate-size Si clusters. Phys. Rev. A 1999, 59, 3685–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Yang, J.; Chan, C. T. Calculated polarizabilities of small Si clusters. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 61, 025201-1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, K.; Yang, J.; Yuan, L.; Zhu, Q. Hybrid density-functional study of Si13 clusters. Phys. Rev. A 2000, 62, 045201-1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohm, U.; Goebel, D.; Karamanis, P.; Maroulis, G. Electric dipole polarizability of As4, a challenging problem for both experiment and theory. J. Phys. Chem. A 1998, 102, 1237–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F. Molecular polarizability of Scn, Cn, and endohedral Scn@Cm clusters. Microelectronic Eng. 2000, 51-52, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F. Theoretical characterization of iron and manganese porphyrins for catalyzed saturated alkane hydroxylations. J. Mol. Catal. 1997, A-119, 393–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F.; Sánchez-Marín, J.; Nebot-Gil, I. Interacting induced dipoles polarization model for molecular polarizabilities. Application to benzothiazole (A)-benzobisthiazole (B) oligomers: A-B13-A. J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem) 1998, 426, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F.; Sánchez-Marín, J.; Nebot-Gil, I. Torsional effects on the molecular polarizabilities of the benzothiazole (A)-benzobisthiazole (B) oligomer A-B13-A. J. Mol. Graphics 1996, 14, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F.; Sánchez-Marín, J.; Nebot-Gil, I. Interacting induced dipoles polarization model for molecular polarizabilities. Reference molecules, amino acids and model peptides. J. Mol. Struct. (Theochem) 1999, 463, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F.; Ortí, E.; Sánchez-Marín, J. Vectorized TOPO program for the theoretical simulation of molecular shape. J. Chim. Phys. Phys.-Chim. Biol. 1991, 88, 2435–2441. [Google Scholar]
- Mulliken, R. S. Chem. Phys. 1934, 2, 782.
- Huheey, J. E. The electronegativity of groups. J. Phys. Chem. 1965, 69, 3284–3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanderson, R. T. An interpretation of bond lengths and classification of bonds. Science 1951, 114, 670–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bratsch, S. G. Electronegativity equalization with Pauling units. J. Chem. Educ. 1984, 61, 588–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, A. I. Physical properties and chemical constitution. XXIII. Miscellaneous compounds. Investigation of the so-called coördinate or dative link in esters of oxy acids and in nitro paraffins by molecular refractivity determinations. Atomic, structural, and group parachors and refractivities. J. Chem. Soc. 1948, 1833–1855. [Google Scholar]
- Gresh, N.; Claverie, P.; Pullman, A. Intermolecular interactions: Reproduction of the results of ab initio supermolecule computations by an additive procedure. Int. J. Quantum Chem., Symp. 1979, 13, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applequist, J.; Carl, J. R.; Fung, K.-K. An atom dipole interaction model for molecular polarizability. Application to polyatomic molecules and determination of atom polarizabilities. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1972, 94, 2952–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Applequist, J. Atom charge transfer in molecular polarizabilities. Application of the Olson-Sundberg model to aliphatic and aromatic hydrocarbons. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 6016–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, J. P. Quantum Chemistry; Academic Press: New York, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Mulliken, R. S. The theory of molecular orbitals. J. Chim. Phys. Phys.-Chim. Biol. 1949, 46, 497–542. [Google Scholar]
- Mulliken, R. S. Magic formula, structure of bond energies, and isovalent hybridization. J. Phys. Chem. 1952, 56, 295–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliken, R. S.; Rieke, C. A.; Orloff, D.; Orloff, H. Formulas and numerical tables for overlap integrals. J. Chem. Phys. 1949, 17, 1248–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitwieser Jr., A. Molecular Orbital Theory for Organic Chemists; John Wiley and Sons: New York, 1961. [Google Scholar]
- Mulliken, R. S. Overlap integrals and chemical binding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1950, 72, 4493–4503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streitwieser Jr., A.; Nair, P. M. Molecular orbital treatment of hyperconjugation. Tetrahedron 1959, 5, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parr, R. G.; Crawford Jr., B. L. Molecular orbital calculations of vibrational force constants. I. Ethylene J. Chem. Phys. 1948, 16, 526–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewar, M. J. S. A molecular orbital theory of organic chemistry. II. The structure of mesomeric systems. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 3345–3350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetta, M.; Winstein, S. Neighboring carbon and hydrogen. XVI. 1,3-interactions and homoallylic resonance. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 18–21. [Google Scholar]
- Kreevoy, M. M. A theoretical study of 1,4-dithiadiene by the L.C.A.O.-M.O. method. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 5543–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joachim, C.; Treboux, G.; Tang, H. A model conformation flip-flop molecular switch. In Molecular Electronics: Science and Technology; AIP Conference Proceedings No. 262. AIP: New York, 1992; pp. 107–117. [Google Scholar]
- Torrens, F.; Ruiz-López, M.; Cativiela, C.; García, J. I.; Mayoral, J. A. Conformational aspects of some asymmetric Diels-Alder reactions. A molecular mechanics + polarization study. Tetrahedron 1992, 48, 5209–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrens, F.; Sánchez-Marín, J.; Rivail, J.-L. Interacting induced dipoles polarization in a force field for dipeptide models (glycine derivative). An. Fís. (Madrid) 1994, 90, 197–204. [Google Scholar]
- Torrens, F. Polarization force fields for peptides implemented in ECEPP2 and MM2. Mol. Simul. 2000, 24, 391–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silberstein, L. Philos. Mag. 1917, 33, 92.
- Silberstein, L. Philos. Mag. 1917, 33, 215.
- Silberstein, L. Philos. Mag. 1917, 33, 521.
- Born, M. Optik, (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 1933). 308.
- Stuart, H. A. Die Struktur des freien Moleküls; Springer-Verlag: Berlin, 1952; p. 363. [Google Scholar]
- Kauzmann, W. Quantum Chemistry; Academic Press: New York, 1957; p. 568. [Google Scholar]
- Mahan, G. D. Davydov splittings in anthracene. J. Chem. Phys. 1964, 41, 2930–2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, W.; Chase, M. Generalized susceptibility theory. I. Theories of hypochromism. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1967, 39, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, M. R. Dipole Davydov splittings in crystalline anthracene, tetracene, naphthalene, and phenanthrene. J. Chem. Phys. 1969, 50, 5117–5128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voisin, C.; Cartier, A.; Rivail, J.-L. Computation of accurate electronic molecular polarizabilities. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 7966–7971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allinger, N. L. Conformational analysis. 130. MM2. A hydrocarbon force field utilizing V1 and V2 torsional terms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1977; 99, 8127–8134. [Google Scholar]
- Némethy, G.; Pottle, M. S.; Scheraga, H. A. Energy parameters in polypeptides. 9. Updating of geometrical parameters, nonbonded interactions, and hydrogen bond interactions for the naturally occurring amino acids. J. Phys. Chem. 1983, 87, 1883–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiehler, J.; Hinze, J. Calculation of static polarizabilities and hyperpolarizabilities for the atoms He through Kr with a numerical RHF method. J. Phys. B 1995, 28, 4055–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, R.; Schlecht, S.; Woenckhaus, J.; Becker, J. A. Polarizabilities of isolated semiconductor clusters. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1996, 76, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chelikowsky, J. R. The electronic and structural properties of semiconductor clusters and nanostructures. Res. Rep. UMSI 97/132; University of Minnesota Supercomputing Institute, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Jarrold, M. F. Nanosurface chemistry on size-selected silicon clusters. Science 1991, 252, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Heer, W. A. The physics of simple metal clusters: Experimental aspects and simple models. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1993, 65, 611–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brack, M. The physics of simple metal clusters: Self-consistent jellium model and semiclassical approaches. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1993, 65, 677–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoine, R.; Dugourd, Ph.; Rayane, D.; Benichou, E.; Broyer, M.; Chandezon, F.; Guet, C. Direct measurement of the electric polarizability of isolated C60 molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1999, 110, 9771–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, P.; Luo, Y.; Jonsson, D.; Ågren, H. Ab initio calculations of the polarizability and the hyperpolarizability of C60. J. Chem. Phys. 1997, 106, 8788–8791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sample Availability: Not available.
© 2001 by MDPI (http://www.mdpi.org). Reproduction is permitted for noncommercial purposes
Share and Cite
Torrens, F. Molecular Polarizability of Sc and C (Fullerene and Graphite) Clusters. Molecules 2001, 6, 496-509. https://doi.org/10.3390/60600496
Torrens F. Molecular Polarizability of Sc and C (Fullerene and Graphite) Clusters. Molecules. 2001; 6(6):496-509. https://doi.org/10.3390/60600496
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorrens, Francisco. 2001. "Molecular Polarizability of Sc and C (Fullerene and Graphite) Clusters" Molecules 6, no. 6: 496-509. https://doi.org/10.3390/60600496
APA StyleTorrens, F. (2001). Molecular Polarizability of Sc and C (Fullerene and Graphite) Clusters. Molecules, 6(6), 496-509. https://doi.org/10.3390/60600496




