Synthesis and Fluorescence Mechanism of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Utilizing Biopolymer and Urea
Abstract
1. Introduction
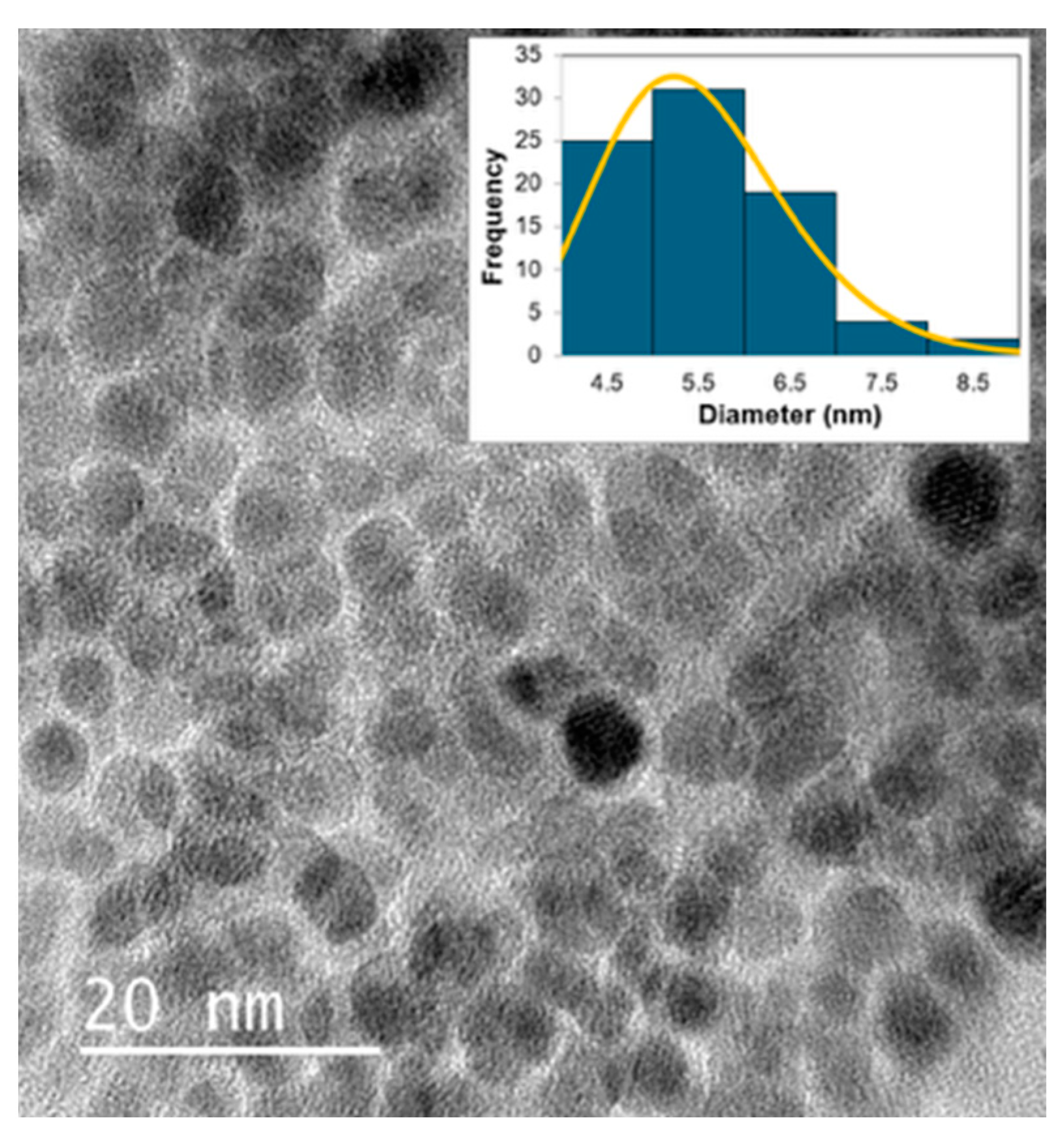
2. Results and Discussion
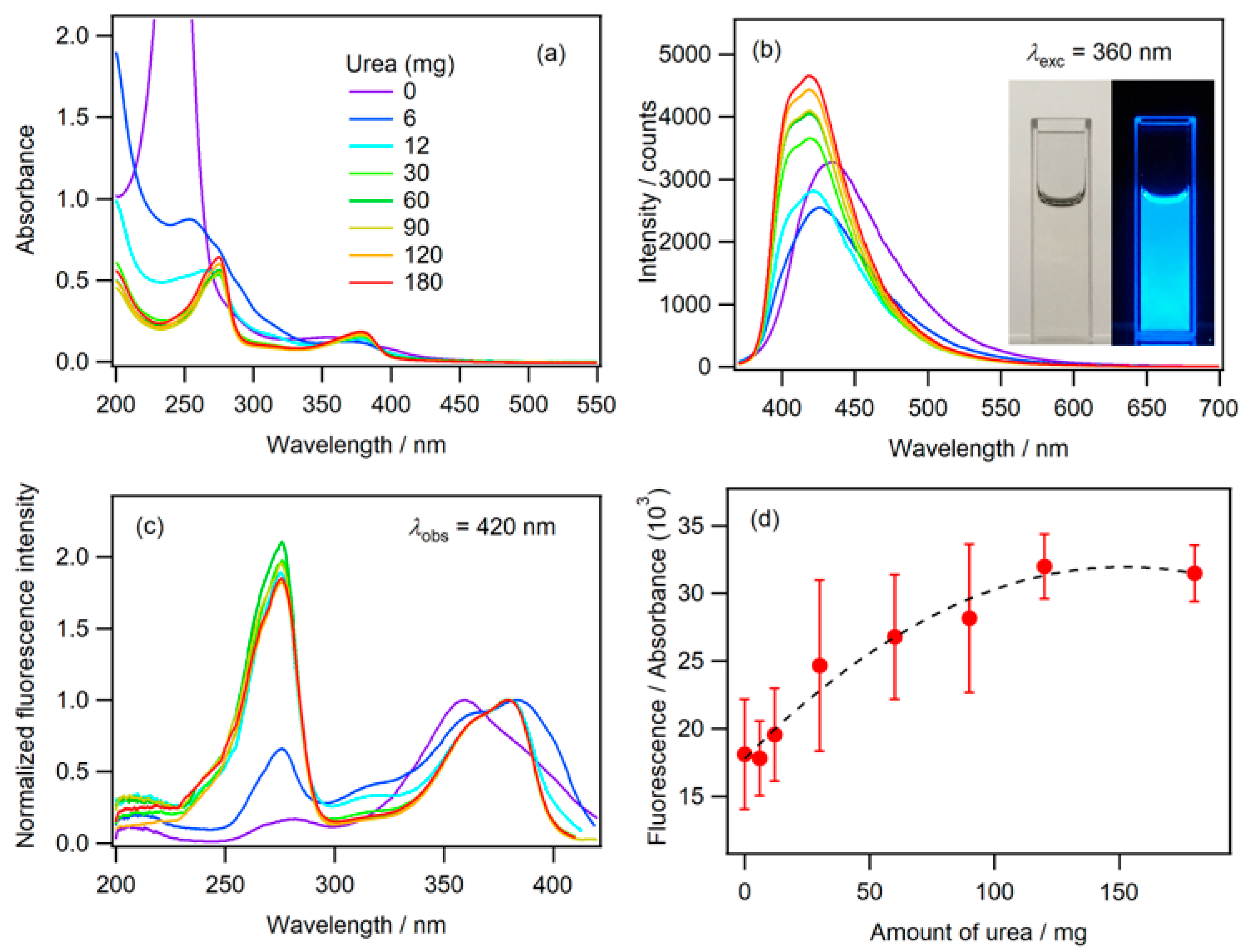
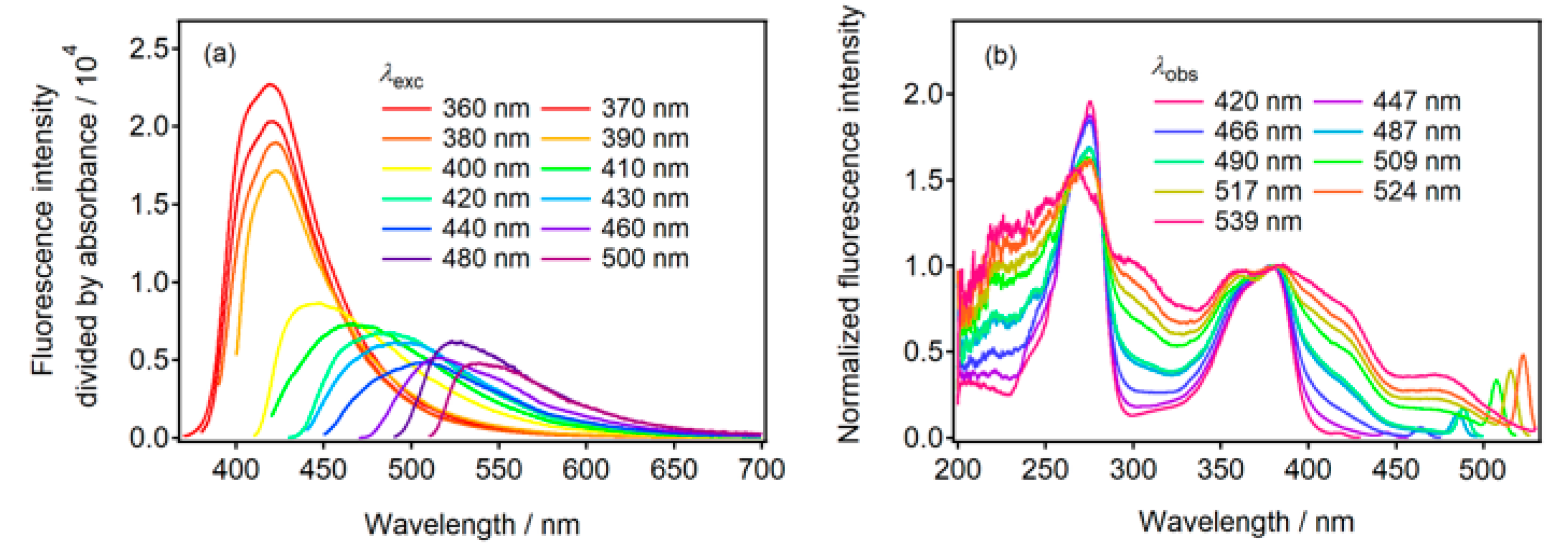
2.1. Fluorescence in Aqueous Phosphoric Acid Solution
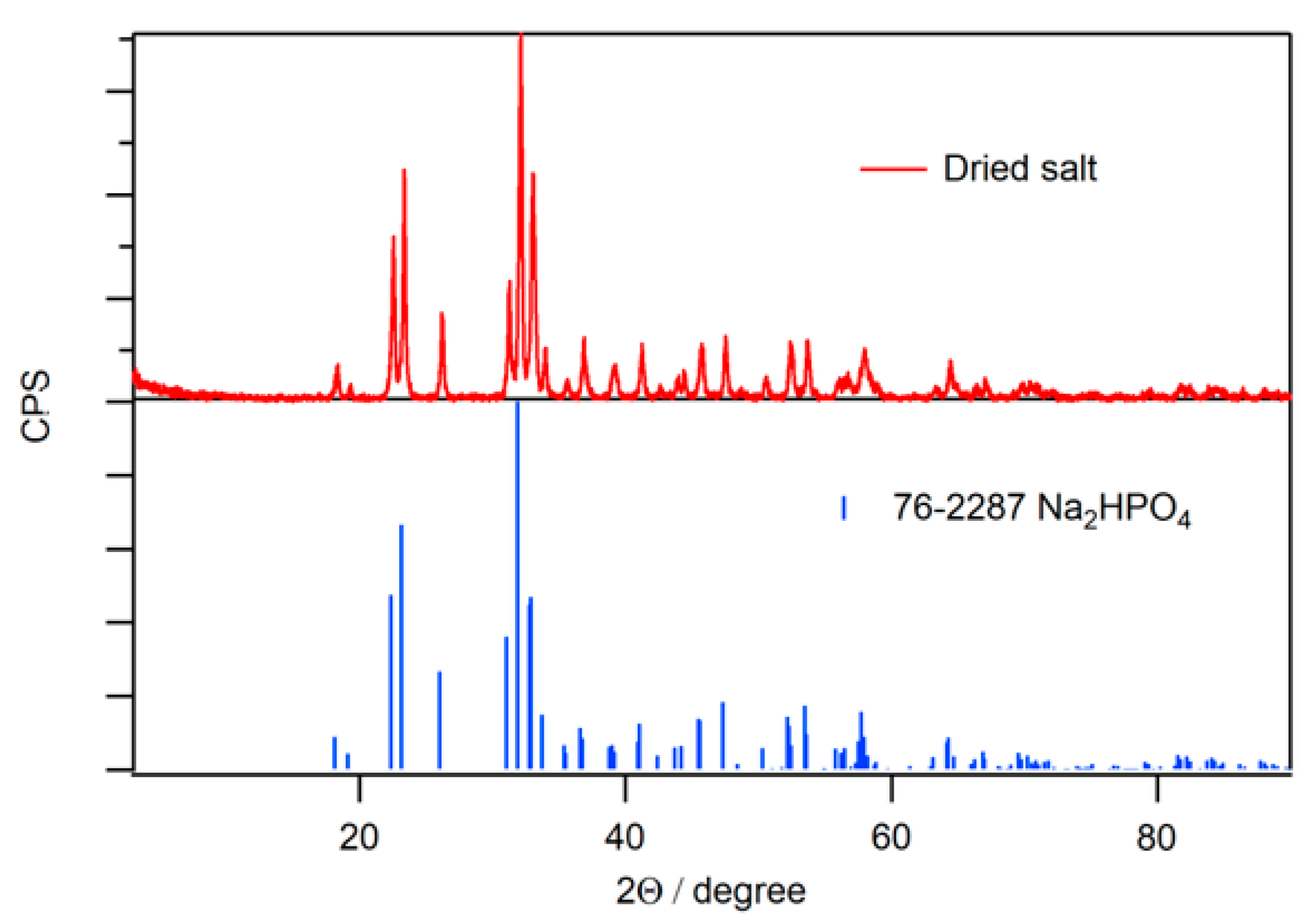
2.2. Fluorescence of Phosphate Salt Containing N-CDs
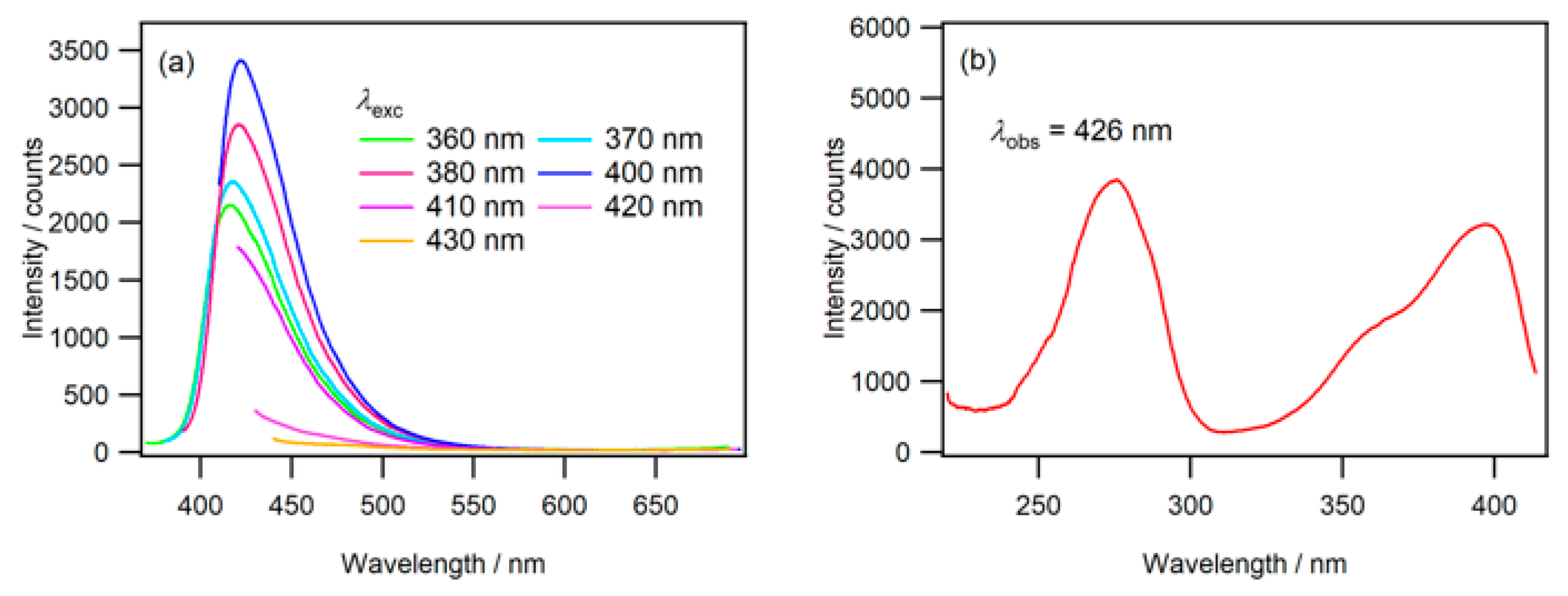
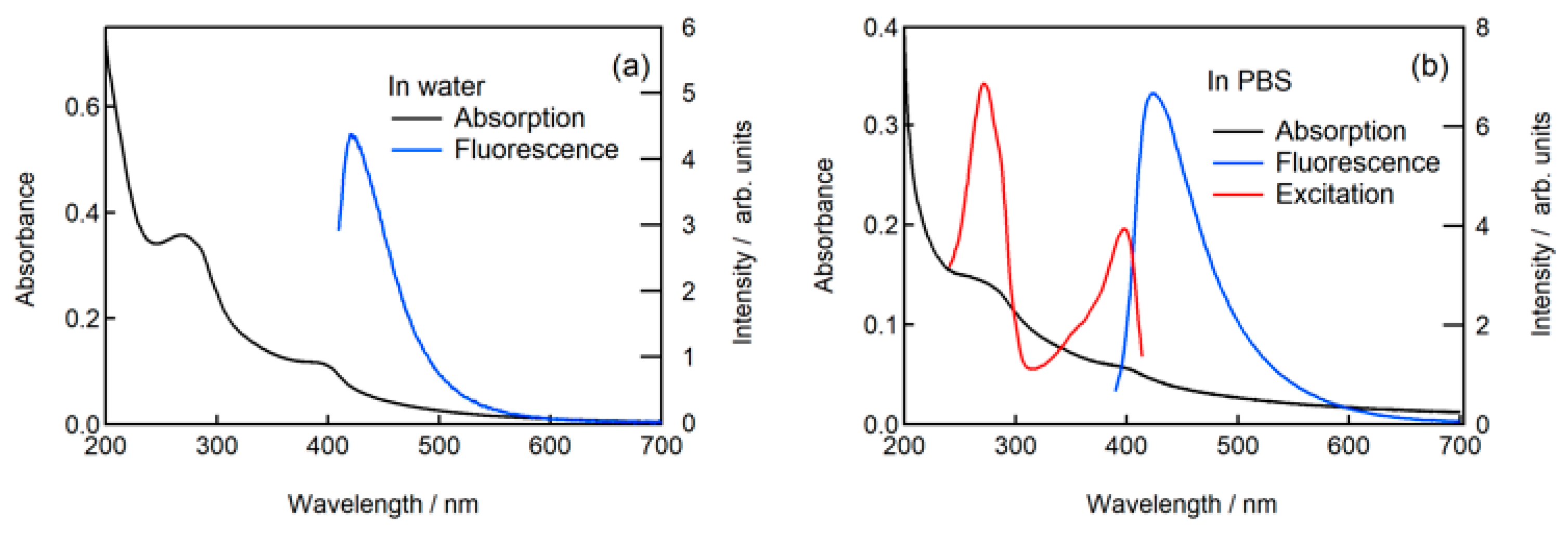
2.3. Fluorescence of N-CDs in Neutral Aqueous Solution
2.4. Fluorescence of N-CDs in Phosphate Buffered Saline
2.5. Formation Mechanism of N-CDs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
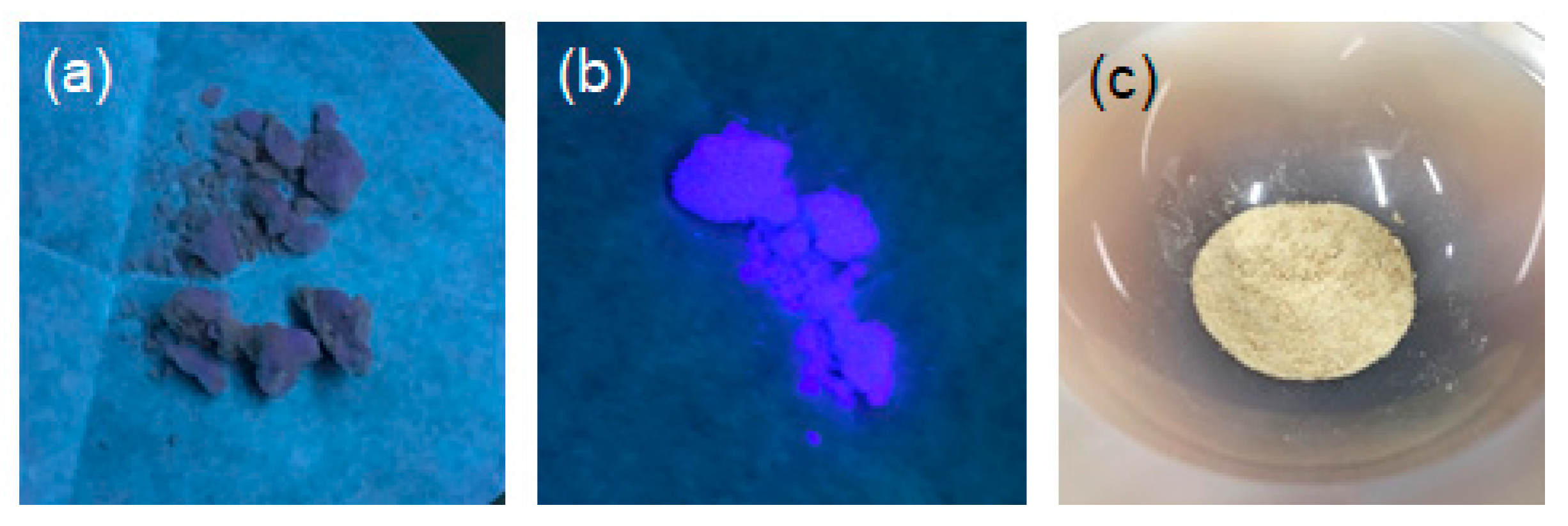
3.2. Synthesis Procedure
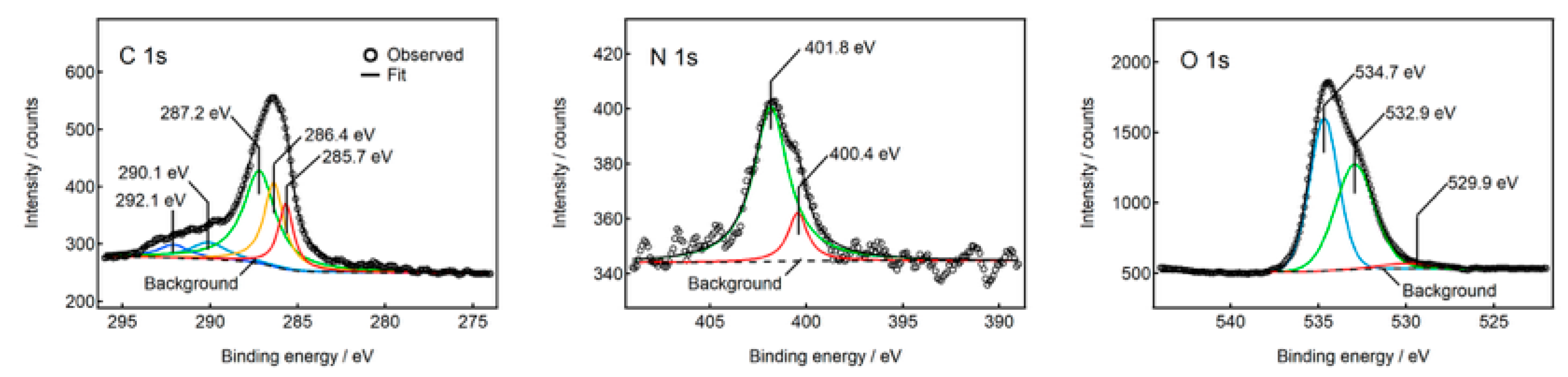
3.3. Characterization Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.; Niu, X.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Zhao, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, X. Switch-on Fluorescence Sensing of Glutathione in Food Samples Based on a Graphitic Carbon Nitride Quantum Dot (g-CNQD)–Hg2+ Chemosensor. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1747–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercelli, B.; Donnini, R.; Ghezzi, F.; Sansonetti, A.; Giovanella, U.; La Ferla, B. Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots obtained hydrothermally from citric acid and urea: The role of the specific nitrogen centers in their electrochemical and optical responses. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 387, 138557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.W.; Bao, Y.W.; Wu, F.G. Fluorescent carbon quantum dots with intrinsic nucleolus-targeting capability for nucleolus imaging and enhanced cytosolic and nuclear drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10664–10677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodadadei, F.; Safarian, S.; Ghanbari, N. Methotrexate-loaded nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots nanocarriers as an efficient anticancer drug delivery system. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 79, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ji, X.; Pan, C.; Sun, Q.; Song, W.; Fang, L.; Chen, Q.; Banks, C.E. A carbon quantum dot decorated RuO2 network: Outstanding supercapacitances under ultrafast charge and discharge. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 3665–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Ray, R.; Gu, Y.; Ploehn, H.J.; Gearheart, L.; Raker, K.; Scrivens, W.A. Electrophoretic analysis and purification of fluorescent single-walled carbon nanotube fragments. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12736–12737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, S.N.; Baker, G.A. Luminescent carbon nanodots: Emergent nanolights. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 6726–6744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cadranel, A.; Margraf, J.T.; Strauss, V.; Clark, T.; Guldi, D.M. Carbon Nanodots for Charge-Transfer Processes. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaik, S.A.; Sengupta, S.; Varma, R.S.; Gawande, M.B.; Goswami, A. Syntheses of N-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots (NCQDs) from Bioderived Precursors: A Timely Update. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2020, 9, 3–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhao, B.; Wen, X.; Zhang, G.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S. Controllable synthesis of green and blue fluorescent carbon nanodots for pH and Cu2+ sensing in living cells. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 77, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundelev, E.V.; Tepliakov, N.V.; Leonov, M.Y.; Maslov, V.G.; Baranov, A.V.; Fedorov, A.V.; Rukhlenko, I.D.; Rogach, A.L. Amino functionalization of carbon dots leads to red emission enhancement. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2019, 10, 5111–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, X.; Qu, D.; Yang, D.; Nie, B.; Zhao, Y.; Fan, H.; Sun, Z. Synthesis of carbon dots with multiple color emission by controlled graphitization and surface functionalization. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Z.; Ma, J.; Shan, X.; Feng, H.; Shao, L.; Chen, J. Highly luminescent N-doped carbon quantum dots as an effective multifunctional fluorescence sensing platform. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 2254–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Y.; Pang, H.; Yang, H.B.; Guo, C.; Shao, J.; Chi, Y.; Li, C.M.; Yu, T. Carbon-based dots co-doped with nitrogen and sulfur for high quantum yield and excitation-independent emission. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7800–7804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, S.; Patra, P.; Pathan, S.H.; Roy, S.; Mitra, S.; Layek, A.; Bhar, R.; Pramanik, P.; Goswami, A. Luminescent S-doped carbon dots: An emergent architecture for multimodal applications. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 2375–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.Y.; Jia, P.Y.; Chen, D.S.; Wang, L.N. Hydrothermal synthesis of N-doped carbon quantum dots and their application in ion-detection and cell-imaging. Spectrochim. Acta A. Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 248, 119282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astafiev, A.A.; Shakhov, A.M.; Tskhovrebov, A.G.; Shatov, A.; Gulin, A.; Shepel, D.; Nadtochenko, V.A. Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nanodots Produced by Femtosecond Laser Synthesis for Effective Fluorophores. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 6810–6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Tang, J.; Li, Y.; Bai, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, W. Preparation and Fluorescent Wavelength Control of Multi-Color Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Nano-Dots. Nanomaterials 2021, 11, 3190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dsouza, S.D.; Buerkle, M.; Brunet, P.; Maddi, C.; Padmanaban, D.B.; Morelli, A.; Payam, A.F.; Maguire, P.; Mariotti, D.; Svrcek, V. The importance of surface states in N-doped carbon quantum dots. Carbon 2021, 183, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Gadly, T.; Gupta, A.; Ballal, A.; Ghosh, S.K.; Kumbhakar, M. Origin of Excitation Dependent Fluorescence in Carbon Nanodots. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 3695–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Trinchi, A.; Atkin, P.; Cole, I. Tunable photoluminescence across the entire visible spectrum from carbon dots excited by white light. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 2970–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Kang, L.; Yang, Z.; Liu, W.; Chen, L. Carbon dots: From intense absorption in visible range to excitation-independent and excitation-dependent photoluminescence. Fuller. Nanotub. Carbon Nanostruc. 2015, 23, 922–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, S.; Prasad, E.; Chadha, A. H-Bonding controls the emission properties of functionalized carbon nano-dots. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 7288–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, H.; Abe, M.; Sato, K.; Uwai, K.; Tokuraku, K.; Iimori, T. Microwave-assisted synthesis and formation mechanism of fluorescent carbon dots from starch. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2022, 3, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakowicz, J.R. Principles of Fluorescence Spectroscopy, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Yu, S.-B.; Wei, J.-S.; Xiong, H.-M. Full-Color Light-Emitting Carbon Dots with a Surface-State-Controlled Luminescence Mechanism. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 484–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigodanza, F.; Burian, M.; Arcudi, F.; Đorđević, L.; Amenitsch, H.; Prato, M. Snapshots into carbon dots formation through a combined spectroscopic approach. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, I.J.; Vázquez Sulleiro, M.; Dolečková, A.; Pizúrová, N.; Medalová, J.; Roy, R.; Nečas, D.; Zajíčková, L. Exploring the Emission Pathways in Nitrogen-Doped Graphene Quantum Dots for Bioimaging. J. Phys. Chem. C. 2021, 125, 21044–21054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, H.B.; Mikhail, M.M.; El-Shahat, M.; Emam, H.E. Clustering of carbon quantum dots from polysaccharides (Cellulose, Alginate, Chitosan) versus heterocyclic compounds: Synthesis, characterization and medical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 9, 100738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safavi, A.; Ahmadi, R.; Mohammadpour, Z.; Zhou, J. Fluorescent pH nanosensor based on carbon nanodots for monitoring minor intracellular pH changes. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 104657–104664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, J.; He, D.; He, X.; Wang, K.; Xu, F.; Liu, J.; Tang, J.; Yang, X.; Huang, J. Label-free carbon-dots-based ratiometric fluorescence pH nanoprobes for intracellular pH sensing. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 7837–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehtesabi, H.; Hallaji, Z.; Najafi Nobar, S.; Bagheri, Z. Carbon dots with pH-responsive fluorescence: A review on synthesis and cell biological applications. Microchim. Acta 2020, 187, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iimori, T.; Imamoto, Y.; Uchida, N.; Kikuchi, Y.; Honda, K.; Iwahashi, T.; Ouchi, Y. Magnetic moment distribution in nanosized antiferromagnetic NiO. J. Appl. Phys. 2020, 127, 023902–023911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Li, D.; Tian, L.; Xiang, W.; Wang, T.; Hu, W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, S.; Chen, J.; Dai, Z. Synthesis of graphene quantum dots from natural polymer starch for cell imaging. Green Chem. 2018, 20, 4438–4442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, S.F.; Yazid, S.N.A.M.; Pang, S.C.; Ng, S.M. Facile synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanodots from starch nanoparticles. Mater. Lett. 2012, 85, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Li, H.; Liu, Y.; Huang, H.; Kang, Z.; Lee, S.T. Water soluble carbon nanoparticles: Hydrothermal synthesis and excellent photoluminescence properties. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 87, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Yang, B.; Li, Z.; Deng, F.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Fluorescent nanoparticles from starch: Facile preparation, tunable luminescence and bioimaging. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 121, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Shu, J.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J. Preparation of carbon quantum dots based on starch and their spectral properties. Luminescence 2015, 30, 388–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.X.; Liu, X.H.; Yang, Y.Z.; Liu, X.G.; Xu, B.S. Rapid and green synthesis of fluorescent carbon dots from starch for white light-emitting diodes. New Carbon Mater. 2018, 33, 276–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolidis, E.; Stergiou, A.; Kioupis, D.; Sadeghpour, A.; Paximada, P.; Kakali, G.; Mandala, I. Production of nanoparticles from resistant starch via a simple three-step physical treatment. Food Hydrocoll. 2023, 137, 108412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.C.R.; Carvalho, F.A.; Franco, M.K.d.O.; Suarez, W.T.; Vilanculo, C.B.; dos Santos, M.H.; Gambarra-Neto, F.F. Novel Hg (II) selective fluorescent green sensor based on carbon dots synthesized from starch and functionalized with methimazole. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 213, 112043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Hao, L.; Shang, L.; Chai, D.-f.; Gao, Y.; Li, J.; Zhao, M.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, G. Maize starch derived boron doped carbon spheres via facile solvothermal route as the photoluminescence sensor for determination of pH and Cr(VI). Nanotechnology 2022, 33, 275707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.Q.; Yang, L.Y.; Fan, X.Y.; Jin, J.C.; Mei, J.; Peng, W.; Jiang, F.L.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y. Low temperature synthesis of highly stable phosphate functionalized two color carbon nanodots and their application in cell imaging. Carbon 2014, 66, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamori, M.; Funazukuri, T. Glucose production by hydrolysis of starch under hydrothermal conditions. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2004, 79, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titirici, M.M.; Antonietti, M. Chemistry and materials options of sustainable carbon materials made by hydrothermal carbonization. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 103–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayat, A.; Saievar-Iranizad, E. Synthesis of green-photoluminescent single layer graphene quantum dots: Determination of HOMO and LUMO energy states. J. Lumin. 2017, 192, 180–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, Y. Colloidal carbon spheres and their core/shell structures with noble-metal nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2004, 116, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, B.; Karak, N. A green and facile approach for the synthesis of water soluble fluorescent carbon dots from banana juice. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 8286–8290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, K.G.; Huš, M.; Baragau, I.-A.; Bowen, J.; Heil, T.; Nicolaev, A.; Abramiuc, L.E.; Sapelkin, A.; Sajjad, M.T.; Kellici, S. Engineering Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Quantum Dots: Tailoring Optical and Chemical Properties through Selection of Nitrogen Precursors. Small 2024, 20, 2310587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogi, T.; Aishima, K.; Permatasari, F.A.; Iskandar, F.; Tanabe, E.; Okuyama, K. Kinetics of nitrogen-doped carbon dot formation via hydrothermal synthesis. New J. Chem. 2016, 40, 5555–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Dried | 0.42 ns (0.778) | 2.0 ns (0.222) | 1.3 ns |
| Moist | 2.7 ns | - | 2.7 ns |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yorozuya, H.; Ashrafi, N.E.; Sato, K.; Islam, A.; Fukae, R.; Tagashira, Y.; Iimori, T. Synthesis and Fluorescence Mechanism of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Utilizing Biopolymer and Urea. Molecules 2025, 30, 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092068
Yorozuya H, Ashrafi NE, Sato K, Islam A, Fukae R, Tagashira Y, Iimori T. Synthesis and Fluorescence Mechanism of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Utilizing Biopolymer and Urea. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092068
Chicago/Turabian StyleYorozuya, Hikaru, Noor E Ashrafi, Kazuya Sato, Ahatashamul Islam, Rikuto Fukae, Yusuke Tagashira, and Toshifumi Iimori. 2025. "Synthesis and Fluorescence Mechanism of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Utilizing Biopolymer and Urea" Molecules 30, no. 9: 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092068
APA StyleYorozuya, H., Ashrafi, N. E., Sato, K., Islam, A., Fukae, R., Tagashira, Y., & Iimori, T. (2025). Synthesis and Fluorescence Mechanism of Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots Utilizing Biopolymer and Urea. Molecules, 30(9), 2068. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30092068






