The α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activities of Phaeochromycins D and E Isolated from Marine Streptomyces sp. FJ0218
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
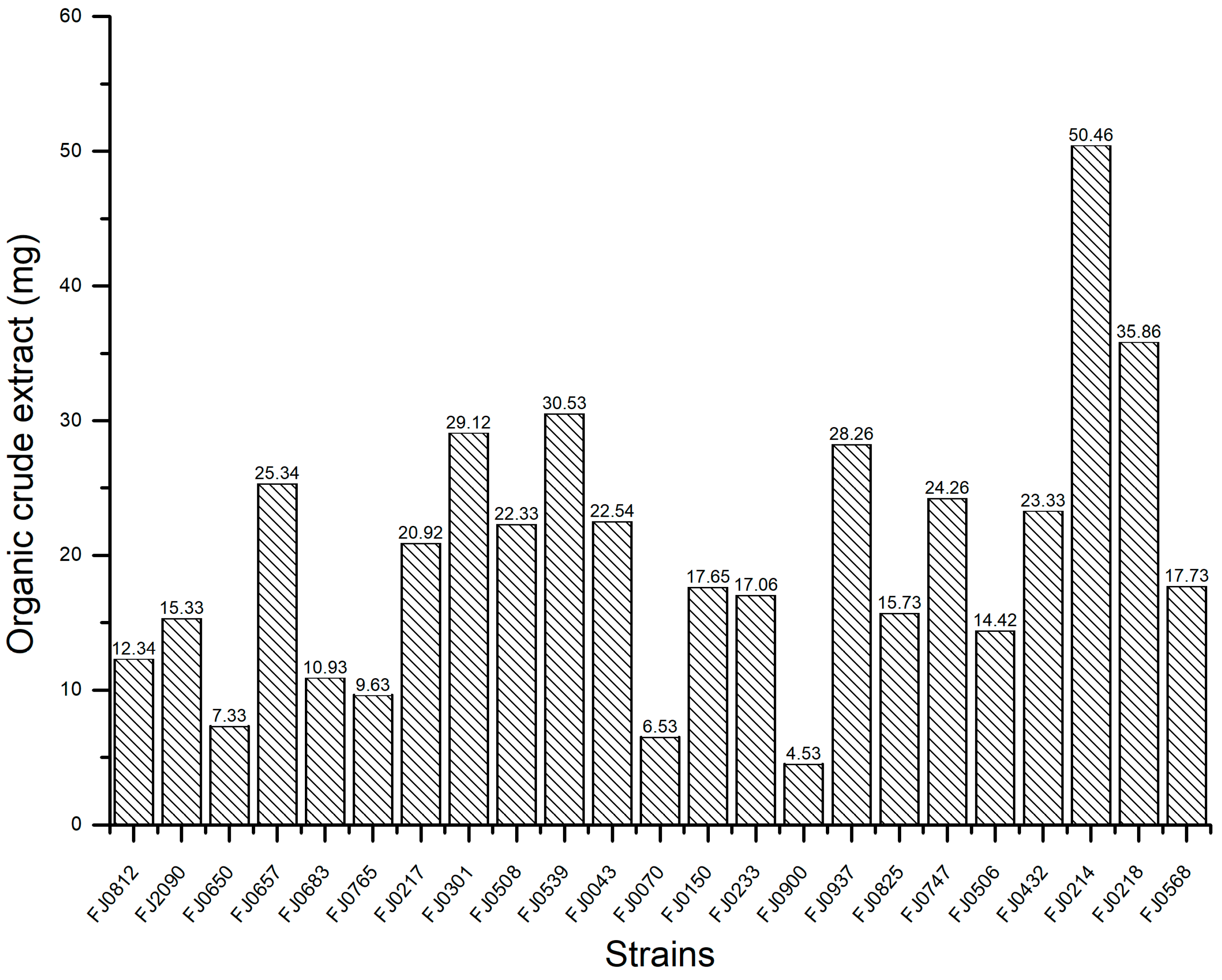
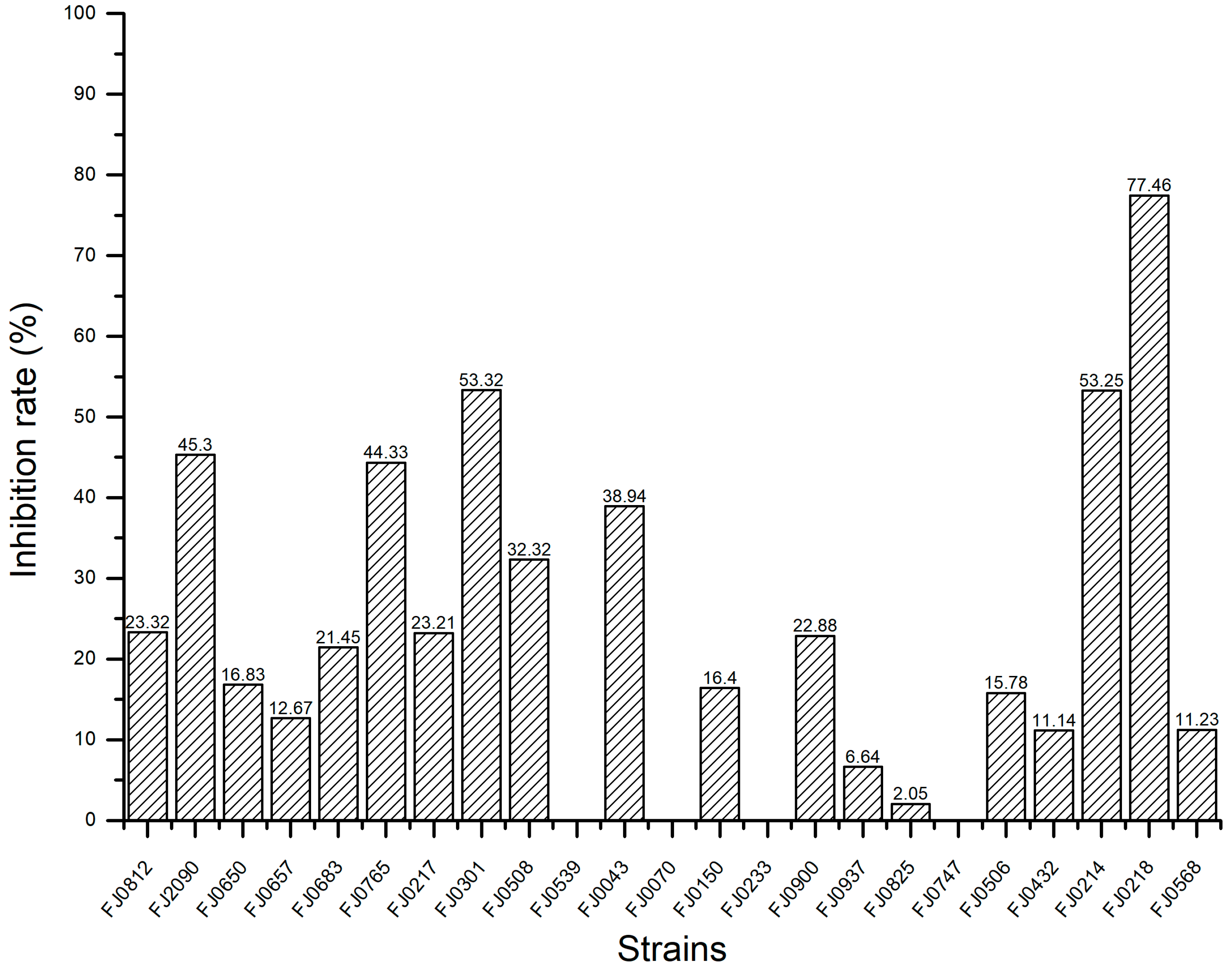
2.1. The α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity of Organic Crude Extracts from Marine Streptomyces
2.2. The Liquid Fermentation, Preparation of Extracts, and Purification Processes
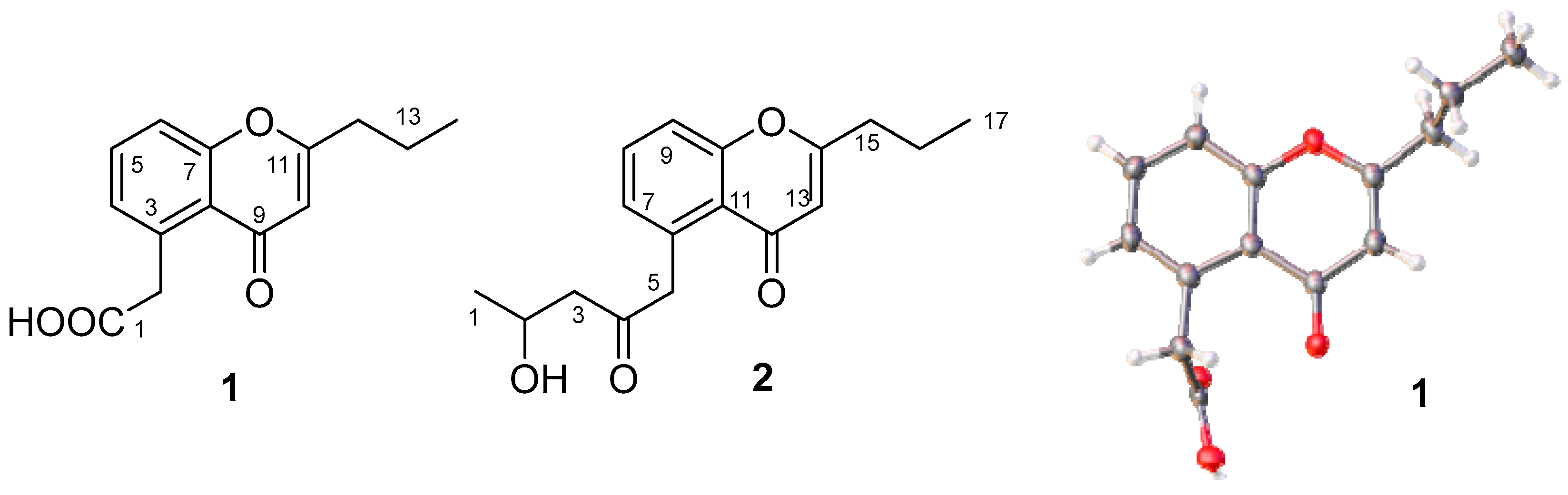
2.3. Structural Identification
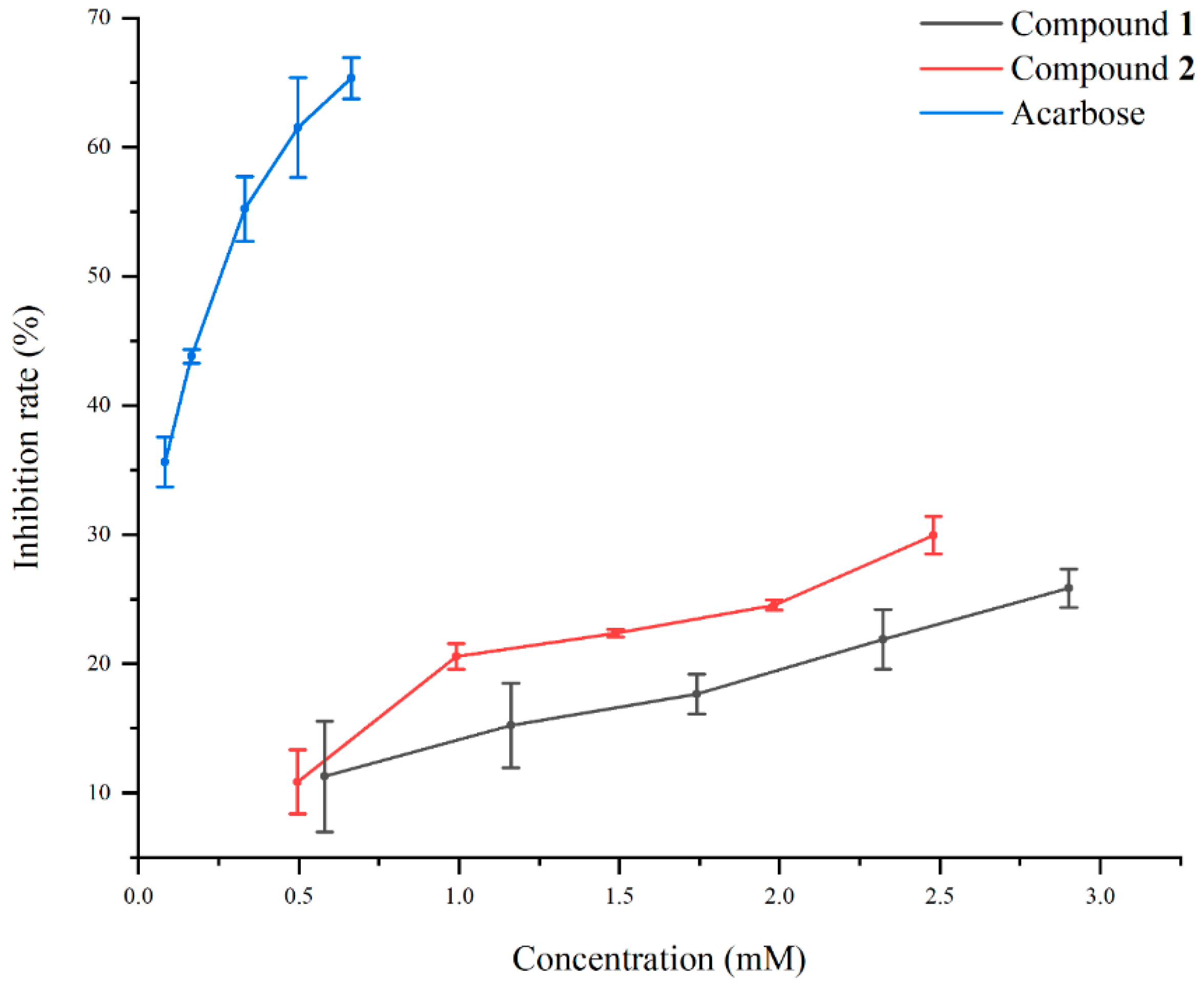
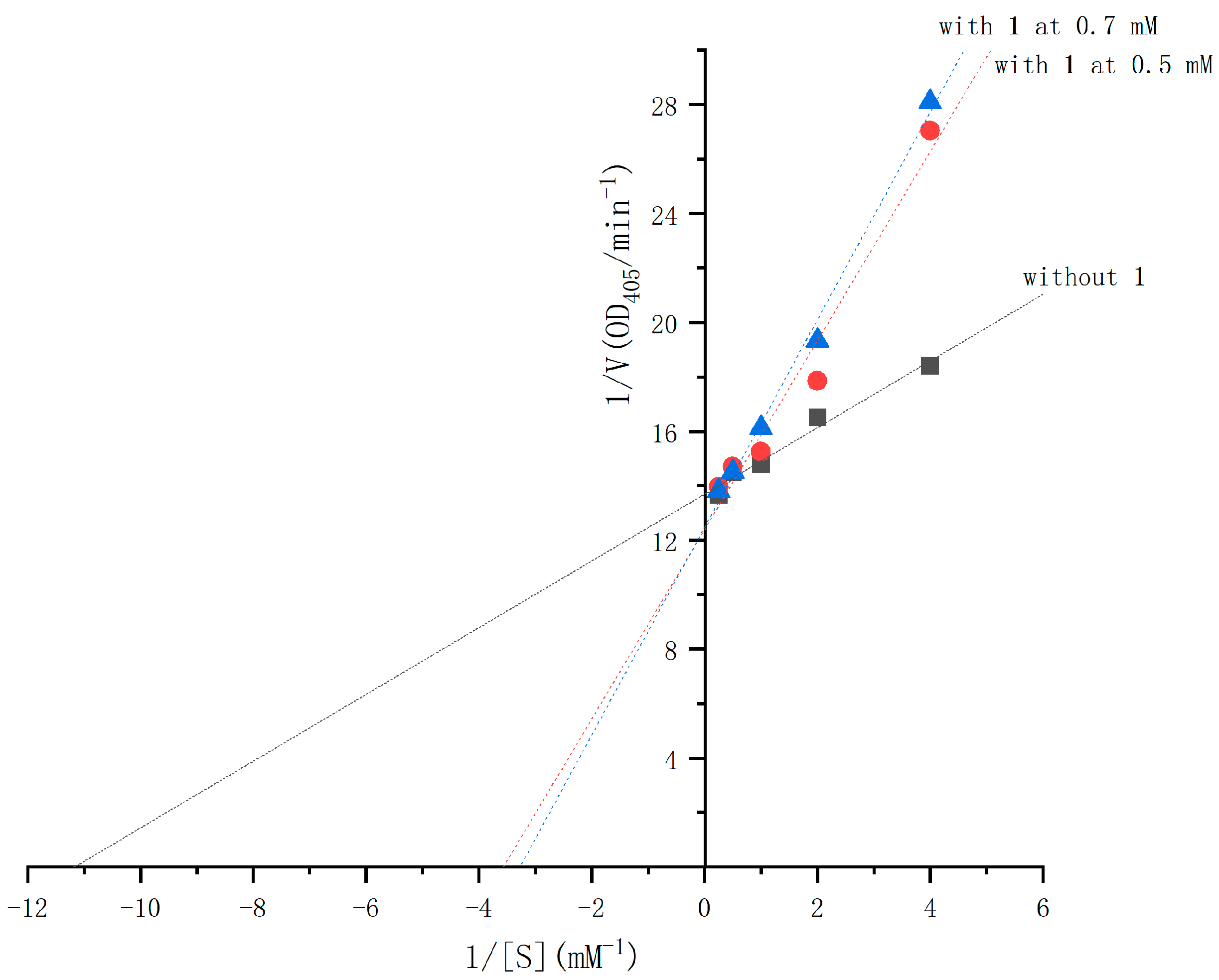
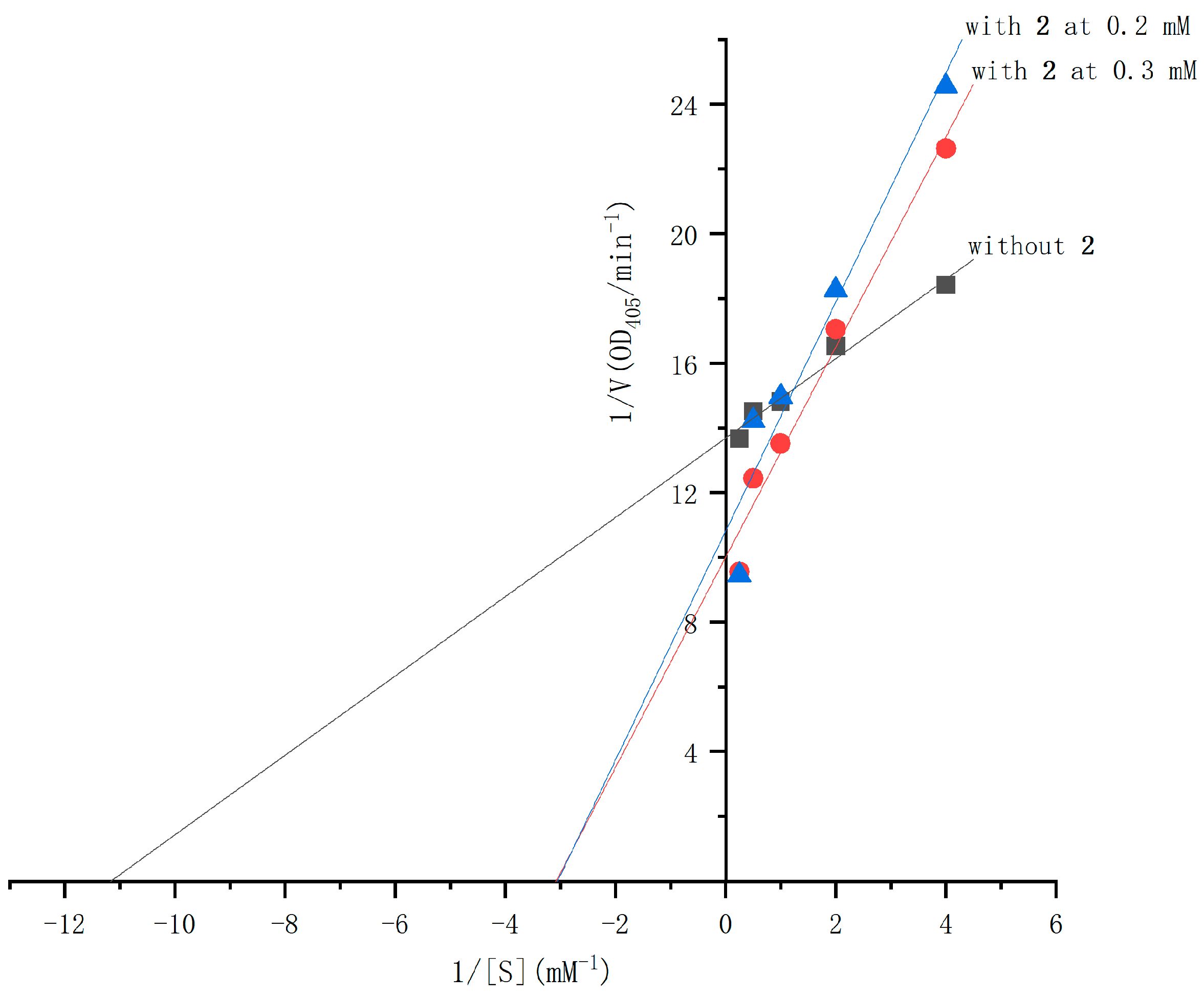
2.4. The α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activities of Compounds 1 and 2
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Strains Materials
3.2. The Liquid Fermentation and Preparation of Extracts of Marine Streptomyces
3.3. Purification and Component Separation
3.4. Structural Characterization
3.5. α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Activity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, R.; Karuranga, S.; Malanda, B.; Saeedi, P.; Basit, A.; Besançon, S.; Bommer, C.; Esteghamati, A.; Ogurtsova, K.; Zhang, P.; et al. Global and regional estimates and projections of diabetes-related health expenditure: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9th edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2020, 162, 108072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, R.J.; Sherif, I.T.; Noy, G.A.; Alberti, K.G. Improved metabolic profiles in insulin-treated diabetic patients given an alpha-glucosidehydrolase inhibitor. Br. Med. J. 1979, 1, 220–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowarah, J.; Singh, V.P. Anti-diabetic drugs recent approaches and advancements. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2020, 28, 115263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNicolantonio, J.J.; Bhutani, J.; O’Keefe, J.H. Acarbose: Safe and effective for lowering postprandial hyperglycaemia and improving cardiovascular outcomes. Open Heart 2015, 2, e000327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, P.; Banerjee, P.; Mandhare, A. Marine natural products as source of new drugs: A patent review (2015–2018). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2019, 29, 283–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramani, R.; Aalbersberg, W. Marine actinomycetes: An ongoing source of novel bioactive metabolites. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 167, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.-m.; Yang, Z.-j.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Z.-k.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.-y. Natural products for treating colorectal cancer: A mechanistic review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddharth, S.; Vittal, R.R. Evaluation of Antimicrobial, Enzyme Inhibitory, Antioxidant and Cytotoxic Activities of Partially Purified Volatile Metabolites of Marine Streptomyces sp.S2A. Microorganisms 2018, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, M.; Qiu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.; Zhang, H.; Wei, B.; Yu, Y.; Ying, Y.; et al. α-Glucosidase Inhibitors from Two Mangrove-Derived Actinomycetes. Molecules 2023, 28, 3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graziani, E.I.; Ritacco, F.V.; Bernan, V.S.; Telliez, J.-B. Phaeochromycins A-E, Anti-inflammatory Polyketides Isolated from the Soil Actinomycete Streptomyces phaeochromogenes LL-P018. J. Nat. Prod. 2005, 68, 1262–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Lu, C.-H.; Zhao, B.-B.; Zheng, Z.-H.; Shen, Y.-M. Phaeochromycins F–H, three new polyketide metabolites from Streptomyces sp. DSS-18. Beilstein. J. Org. Chem. 2008, 4, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, D.; Lv, Q.; Fu, P.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, W. Phaeochromycins I-K, Three Methylene-Bridged Dimeric Polyketides from Streptomyces sp. 166. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 1542–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Ju, J.; Li, Q.; Fu, S. Six Sets of Aromatic Polyketides Differing in Size and Shape Derive from a Single Biosynthetic Gene Cluster. J. Nat. Prod. 2023, 86, 1512–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zeng, W.; Chen, L.; Yu, B.; Guo, Y.; Chen, G.; Liang, Z. Integrated multi-spectroscopic and molecular docking techniques to probe the interaction mechanism between maltase and 1-deoxynojirimycin, an α-glucosidase inhibitor. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 114, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; He, W.; Wang, Z.; Liu, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Tanabe, G.; Muraoka, O.; et al. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 3′-benzylated analogs of 3′-epi-neoponkoranol as potent α-glucosidase inhibitors. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 110, 224–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, S.-L.; Yue, L.-M.; Lim, G.T.; Yang, J.-M.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.-D. Inhibitory effect of raspberry ketone on α-glucosidase: Docking simulation integrating inhibition kinetics. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, L.M.; Lee, J.; Zheng, L.; Park, Y.D.; Ye, Z.M.; Yang, J.M. Computational prediction integrating the inhibition kinetics of gallotannin on α-glucosidase. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 103, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peytam, F.; Takalloobanafshi, G.; Saadattalab, T.; Norouzbahari, M.; Emamgholipour, Z.; Moghimi, S.; Firoozpour, L.; Bijanzadeh, H.R.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Mojtabavi, S.; et al. Design, synthesis, molecular docking, and in vitro α-glucosidase inhibitory activities of novel 3-amino-2,4-diarylbenzo[4,5]imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidines against yeast and rat α-glucosidase. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Peng, Y.; Li, L.; Xie, Z.; Deng, B.; Chen, S.; Li, W. Synthesis, biological evaluation and molecular docking studies of chromone hydrazone derivatives as α-glucosidase inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017, 27, 2957–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.M.; Lan, T.; Ye, G.J.; Huang, J.J.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, Y.R.; Wang, B. Novel oxazolxanthone derivatives as a new type of α-glucosidase inhibitor: Synthesis, activities, inhibitory modes and synergetic effect. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 26, 3370–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.-L.; He, J.-Y.; Zhang, A.; Wan, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, W.-H. Toward potent α-glucosidase inhibitors based on xanthones: A closer look into the structure–activity correlations. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4050–4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, L.; Pang, C.; Huang, M.; Huang, Z.; Gu, L. Synergetic inhibition of genistein and d-glucose on α-glucosidase. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 2947–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O.V.; Bourhis, L.J.; Gildea, R.J.; Howard, J.A.K.; Puschmann, H. OLEX2: A complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009, 42, 339–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.M.; Winder, J.S.; Kellam, S.J. High-throughput microtiter plate-based chromogenic assays for glycosidase inhibitors. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1993, 38, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, S.; Xia, L.; Zhu, X.; Zhu, J.; Cai, M.; Wang, X. Natural Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors Rapid Fishing from Cyperus Rotundus Using Immobilized Enzyme Affinity Screening Combined with UHPLC-QTOF MS. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2019, 18, 1508–1515. [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen, V.B.; Wang, S.-L. New novel alpha-glucosidase inhibitors produced by microbial conversion. Process Biochem. 2018, 65, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hretolu, D.; Sari, S. Flavonoids as alpha-glucosidase inhibitors: Mechanistic approaches merged with enzyme kinetics and molecular modelling. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 19, 1081–1092. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, L.; Dong, Y.; Fang, Z.; Nisar, T.; Zhao, T.; Wang, Z.C.; Guo, Y. Chemical compositions and α-glucosidase inhibitory effects of anthocyanidins from blueberry, blackcurrant and blue honeysuckle fruits. Food Chem. 2019, 299, 125102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, P.; Shi, M.; Wang, F.; Lin, Y.; Zheng, Y. The α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activities of Phaeochromycins D and E Isolated from Marine Streptomyces sp. FJ0218. Molecules 2025, 30, 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091993
Lin P, Shi M, Wang F, Lin Y, Zheng Y. The α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activities of Phaeochromycins D and E Isolated from Marine Streptomyces sp. FJ0218. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091993
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Pingfa, Mianmian Shi, Feifei Wang, Yong Lin, and Yongbiao Zheng. 2025. "The α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activities of Phaeochromycins D and E Isolated from Marine Streptomyces sp. FJ0218" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091993
APA StyleLin, P., Shi, M., Wang, F., Lin, Y., & Zheng, Y. (2025). The α-Glucosidase Inhibition Activities of Phaeochromycins D and E Isolated from Marine Streptomyces sp. FJ0218. Molecules, 30(9), 1993. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091993





