The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Sorption and Wetting Properties of Apple Pectin-Based Packaging Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Film Characterisation
2.2. The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Swelling Index of Apple Pectin Edible Films
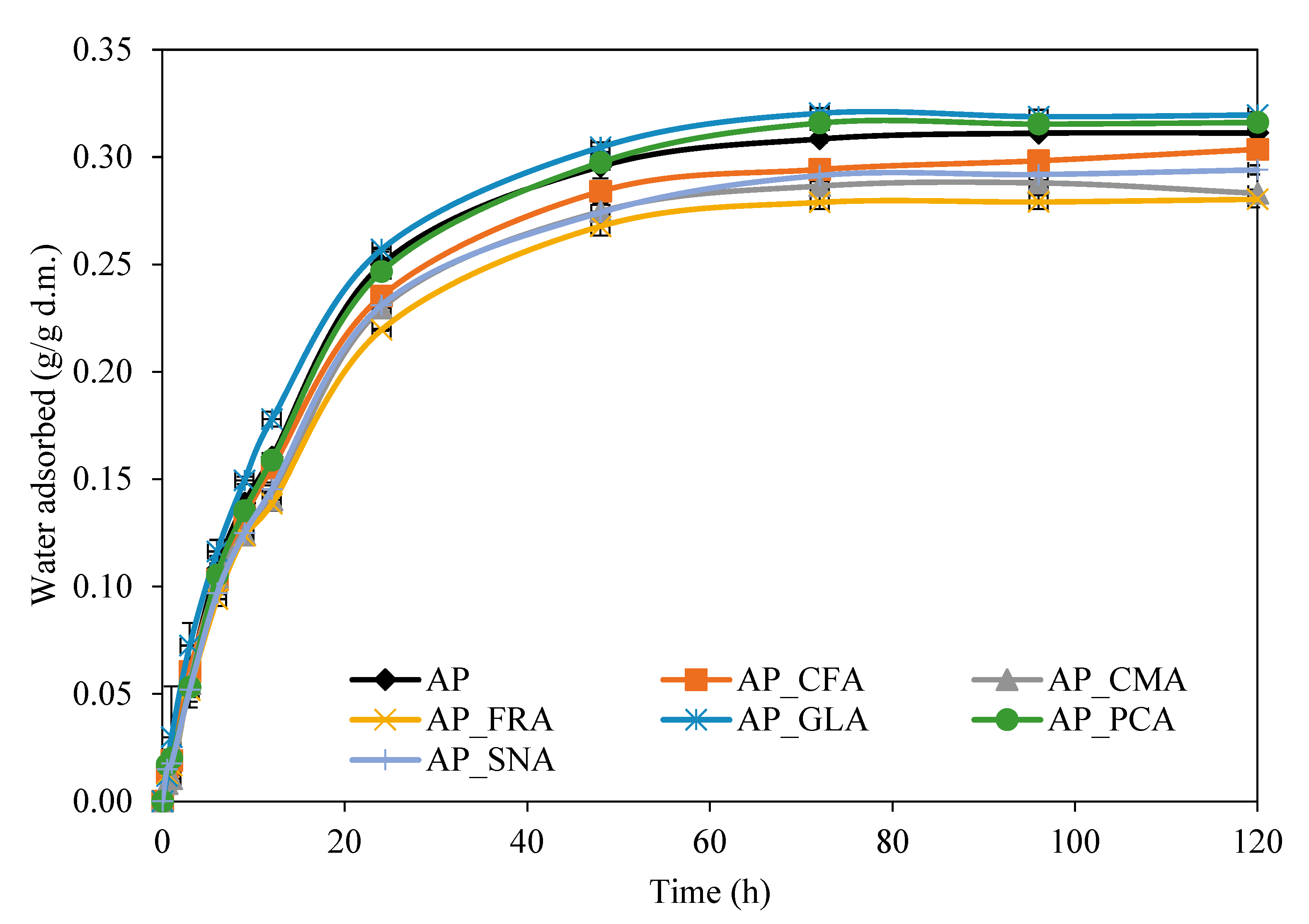
2.3. The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Water Vapour Sorption Kinetics
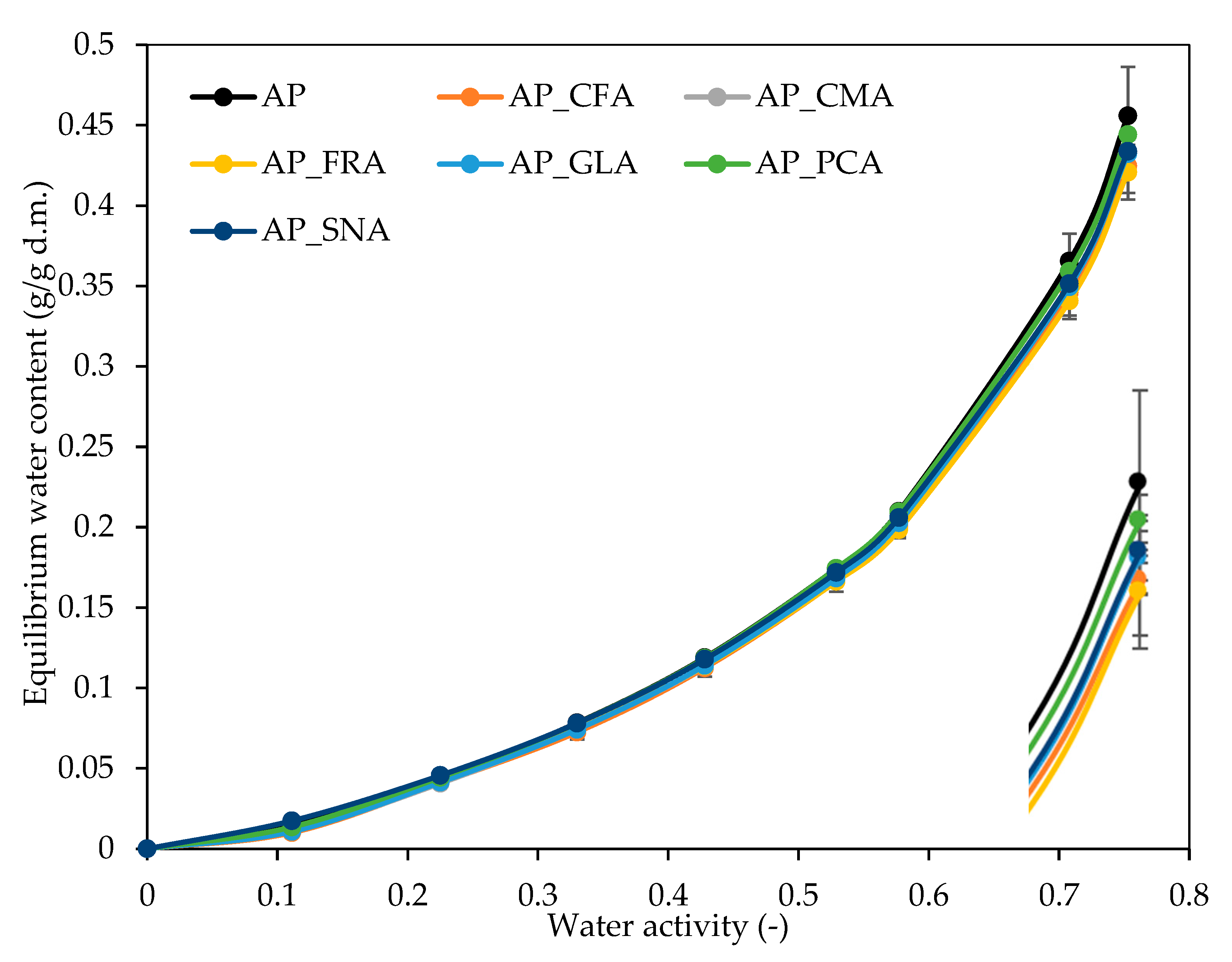
2.4. The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Water Vapour Sorption Isotherms
2.5. The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Water Contact Angle
2.6. The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Microstructure of Pectin Films
2.7. The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Water Vapour Permeability of Pectin Films
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
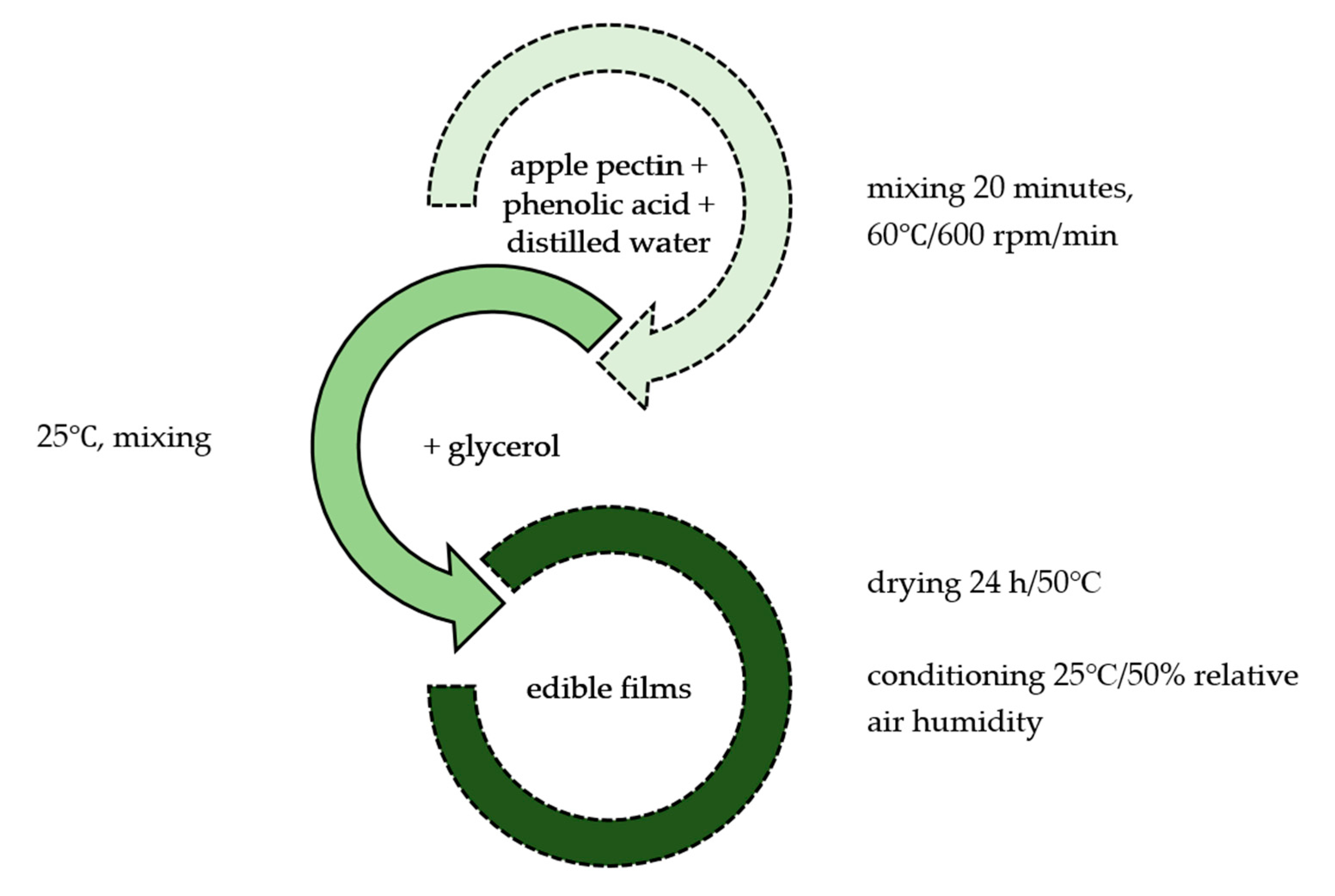
3.2. Film Preparation
3.3. Thickness
3.4. Water Content
3.5. Swelling Index
- is the swelling of the edible films (%);
- is the sample weight before swelling (g);
- is the sample weight after swelling (g).
3.6. Water Solubility
3.7. Water Vapour Sorption Kinetics
3.8. Water Vapour Sorption Isotherms
3.9. Water Contact Angle Measurement
3.10. Scanning Electron Microscopy
3.11. Water Vapour Permeability
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perera, K.Y.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Biopolymer-Based Sustainable Food Packaging Materials: Challenges, Solutions, and Applications. Foods 2023, 12, 2422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikus, M.; Galus, S. Biopolymer active materials for food. Food Sci. Technol. Qual. 2023, 30, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamboni, J.E.; Bonfiglio, G.V.; Slavutsky, A.M.; Bertuzzi, M.A. Evaluation of edible films as single-serve pouches for a sustainable packaging system. Food Chem. Adv. 2023, 3, 100547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nahar, L.; Habibi, E.; Gavril, G.-L.; Abdelfattah, G.M.M.; Wrona, M.; Nerín, C.; Guo, M.; Sarker, S.D. Towards sustainable food packaging using natural compounds: A review of current research update. Food Bioprod. Process. 2025, 150, 260–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Priyadarshi, R.; Łipusiewicz, Ł.; Biswas, D.; Chandel, V.; Rhim, J.-W. Recent progress in pectin extraction, characterization, and pectin-based films for active food packaging applications: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, S.C.; de Oliveira, T.V.; de Fátima Ferreira Soares, N.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A. Sustainable and biodegradable polymer packaging: Perspectives, challenges, and opportunities. Food Chem. 2025, 470, 142652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, F.; Zhang, X.; Tang, W.; Huang, M.; Huang, Q.; Tu, Z. Interaction mechanisms of edible film ingredients and their effect on food quality. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, V.F.R.; Pintado, M.E.; Morais, R.M.S.C.; Morais, A.M.M.B. Recent Highlights in Sustainable Bio-Based Edible Films and Coatings for Fruit and Vegetable Applications. Foods 2024, 13, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikus, M.; Galus, S. Food Coating—Materials, Methods and Application in the Food Industry. Food Sci. Technol. Qual. 2020, 27, 5–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, L.S.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Jaiswal, S. Lipid incorporated biopolymer based edible films and coatings in food packaging: A review. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2024, 8, 100720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plesoianu, A.M.; Nour, V. Pectin-Based Edible Coating Combined with Chemical Dips Containing Antimicrobials and Antibrowning Agents to Maintain Quality of Fresh-Cut Pears. Horticulturae 2022, 8, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohasmizah, H.; Azizah, M. Pectin-based edible coatings and nanoemulsion for the preservation of fruits and vegetables: A review. Appl. Food Res. 2022, 2, 100221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Syarifuddin, A.; Muflih, M.H.; Izzah, N.; Fadillah, U.; Ainani, A.F.; Dirpan, A. Pectin-based edible films and coatings: From extraction to application on food packaging towards circular economy- A review. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2025, 9, 100680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, I.P.; Banta, R.A.; Tyuftin, A.A.; Holmes, J.; Pathania, S.; Kerry, J. Pectin as a biopolymer source for packaging films using a circular economy approach: Origins, extraction, structure and films properties. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 40, 101224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, N.S.; Lee, W.Y. Pectin-Based Active and Smart Film Packaging: A Comprehensive Review of Recent Advancements in Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Smart Colorimetric Systems for Enhanced Food Preservation. Molecules 2025, 13, 1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocira, A.; Kozłowicz, K.; Panasiewicz, K.; Staniak, M.; Szpunar-Krok, E.; Hortyńska, P. Polysaccharides as Edible Films and Coatings: Characteristics and Influence on Fruit and Vegetable Quality—A Review. Agronomy 2021, 11, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidi, L.; Wang, Y.; Wich, P.R.; Selomulya, C. Polysaccharide-based edible films—strategies to minimize water vapor permeability. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2025, 61, 101258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, H.G.R.; Zhao, G. Physicochemical properties of the edible films from the blends of high methoxyl apple pectin and chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 131, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, H.G.R.; Abdellatif, H.R.S.; Ye, F.; Zhao, G. Tuning the physicochemical properties of apple pectin films by incorporating chitosan/pectin fiber. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 159, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurek, M.; Benaida-Debbache, N.; Elez Garofulić, I.; Galić, K.; Avallone, S.; Voilley, A.; Waché, Y. Antioxidants and Bioactive Compounds in Food: Critical Review of Issues and Prospects. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, Y.S. Phenolic Compounds in Active Packaging and Edible Films/Coatings: Natural Bioactive Molecules and Novel Packaging Ingredients. Molecules 2022, 27, 7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, M.M.; Gonçalves, M.P.; Rocha, C.M.R. Effect of ferulic acid on the performance of soy protein isolate-based edible coatings applied to fresh-cut apples. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 80, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Zhou, Z.; Li, K.; Li, K.; Liu, L.; Zhang, W.; Xu, J.; Tu, X.; Du, L.; Zhang, H. Novel edible coating based on shellac and tannic acid for prolonging postarvest shelf life and improving overall quality of mango. Food Chem. 2021, 354, 129510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Cai, W.; Rizwan Khan, M.; Ahmad, N.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, L.; Zhang, W. Application of Tannic Acid and Fe3+ Crosslinking-Enhanced Pectin Films for Passion Fruit Preservation. Foods 2023, 12, 3336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerramathi, B.B.; Kola, M.; Muniraj, B.A.; Aluru, R.; Thirumanyam, M.; Zyryanov, G.V. Structural studies and bioactivity of sodium alginate edible films fabricated through ferulic acid crosslinking mechanism. J. Food Eng. 2021, 301, 110566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Y. Nanocomplexes film composed of gallic acid loaded ovalbumin/chitosan nanoparticles and pectin with excellent antibacterial activity: Preparation, characterization and application in coating preservation of salmon fillets. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 259, 128934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pająk, P.; Przetaczek-Rożnowska, I.; Juszczak, L. Development and physicochemical, thermal and mechanical properties of edible films based on pumpkin, lentil and quinoa starches. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 138, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Lei, Y.; Zhu, R.; Zhao, M.; Lu, J.; Xiao, D.; Jiao, C.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, G.; Li, S. Preparation and characterization of bioactive edible packaging films based on pomelo peel flours incorporating tea polyphenol. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 90, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girgin, B.; Abahuni Uçar, M.; Moroydör Derun, E.; Tugrul, N. Development of Edible Packaging Films from Walnut, Mango, and Orange Peels: Effect of Plasticizers and Essential Oils. ACS Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 5, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biratu, G.; Woldemariam, H.W.; Gonfa, G. Development of active edible films from coffee pulp pectin, propolis, and honey with improved mechanical, functional, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. Carbohydr. Polym. Technol. Appl. 2024, 8, 100557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco, N.; Naal-Ek, M.G.; Ayora-Talavera, T.; Shirai, K.; Román-Guerrero, A.; Fabela-Morón, M.F.; Cuevas-Bernardino, C. Effect of bio-chemical chitosan and gallic acid into rheology and physicochemical properties of ternary edible films. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 125, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athanasopoulou, E.; Bigi, F.; Maurizzi, E.; Karallou, E.I.E.; Pappas, C.S.; Quartieri, A.; Tsironi, T. Synthesis and characterization of polysaccharide-and protein-based edible films and application as packaging materials for fresh fish fillets. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmawati, I.; Pratama, A.W.; Pratama, S.A.; Khozin, M.N.; Firmanda, A.; Irawan, F.H.; Asranudin; Ansori, A.N.M.; Sucipto, T.H. Gallic acid: A promising bioactive agent for food preservation and sustainable packaging development. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2024, 10, 100776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.-Y.; Wang, B.-J.; Weng, Y.-M. Antioxidant andantimicrobial edible zein/chitosan composite films fabricated byincorporation of phenolic compounds and dicarboxylic acids. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 63, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordoñez, R.; Atarés, L.; Chiralt, A. Biodegradable active materials containing phenolic acids for food packaging applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 3910–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veras, J.M.L.; Plácido, G.R.; Romani, V.P.; Alves, J.S.; de Sousa, T.L.; Célia, J.A.; de Oliveira, D.E.C.; Monteiro, L.B. Hygroscopicity of pectin-propolis films: Sorption isotherms and thermodynamic properties. Ciência Rural 2025, 55, e20230667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisitsyn, A.; Semenova, A.; Nasonova, V.; Polishchuck, E.; Revutskaya, N.; Kozyrev, I.; Kotenkova, E. Approaches in Animal Proteins and Natural Polysaccharides Application for Food Packaging: Edible Film Production and Quality Estimation. Polymers 2021, 13, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazreen, A.Z.; Jai, J.; Ali, S.A.; Manshor, N.M. Moisture Adsorption Isotherm Model for Edible Food Film Packaging—A Review. Sci. Res. J. 2020, 17, 221–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, S.H. Water sorption and water permeability properties of edible film made from potato peel waste. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 37, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giridhar, G.; Manepalli, R.K.N.R.; Apparao, G. Chapter 8—Contact Angle Measurement Techniques for Nanomaterials. In Thermal and Rheological Measurement Techniques for Nanomaterials Characterization; Thomas, S., Thomas, R., Zachariah, A.K., Mishra, R.K., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 173–195. [Google Scholar]
- Butt, H.-J.; Liu, J.; Koynov, K.; Straub, B.; Hinduja, C.; Roismann, I.; Berger, R.; Li, X.; Vollmer, D.; Steffen, W.; et al. Contact angle hysteresis. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2022, 59, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavassoli-Kafran, E.; Gamage, M.V.; Dumee, L.F.; Kong, L.; Zhao, S. Edible films and coatings for shelf life extension of mango: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 62, 2432–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żelaziński, T. Properties of biocomposites from rapeseed meal, fruit pomace and microcrystalline cellulose made by press pressing: Mechanical and physicochemical characteristics. Materials 2021, 14, 890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santhosh, R.; Ahmed, J.; Thakur, R.; Sarkar, P. Starch-based edible packaging: Rheological, thermal, mechanical, microstructural, and barrier properties—A review. Sustain. Food Technol. 2024, 2, 307–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Santhosh, R.; Thakur, R.; Mulla, M.; Sarkar, P. Thermo-mechanical, rheological, microstructural, and barrier properties of gum-based edible packaging: A review. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 38, 101117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, H.; Liu, Y.; Yun, D.; Zong, S.; Jin, C.; Liu, J. Chitosan Films Functionalized with Different Hydroxycinnamic Acids: Preparation, Characterization and Application for Pork Preservation. Foods 2021, 10, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczmarek-Szczepańska, B.; Zasada, L.; Grabska-Zielińska, S. The Physicochemical, Antioxidant, and Color Properties of Thin Films Based on Chitosan Modified by Different Phenolic Acids. Coatings 2022, 12, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hager, A.-S.; Vallons, K.J.R.; Arendt, E.K. Influence of Gallic Acid and Tannic Acid on the Mechanical and Barrier Properties of Wheat Gluten Films. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 6157–6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Wang, Z.; Kadouh, H.; Zhou, K. The antimicrobial, mechanical, physical and structural properties of chitosan–gallic acid films. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, N.; Fu, Y.; He, J. Preparation and physical properties of soy protein isolate and gelatin composite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2007, 21, 1153–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhim, J.-W.; Lee, J.H.; Ng, P.K.W. Mechanical and barrier properties of biodegradable soy protein isolate-based films coated with polylactic acid. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2007, 40, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
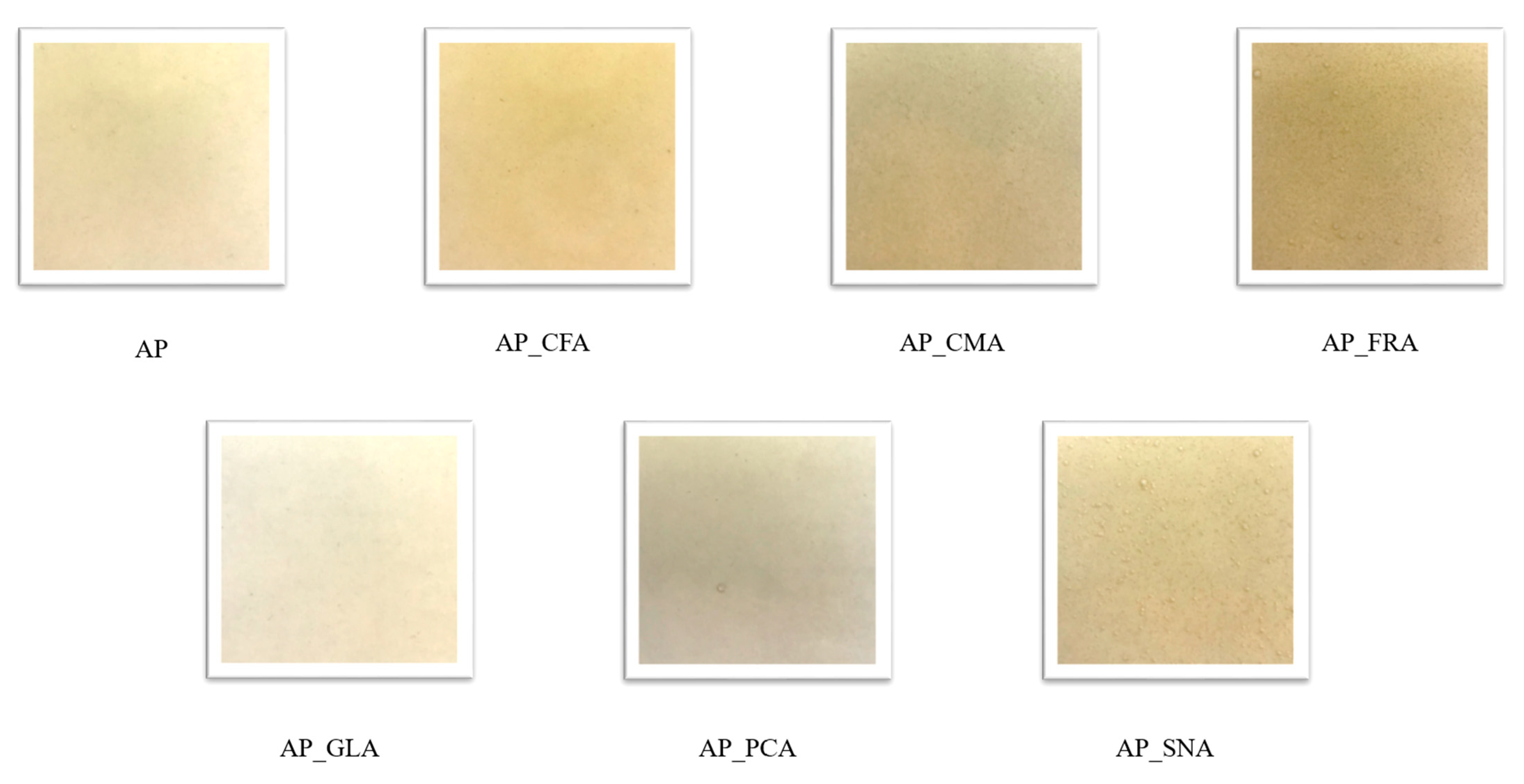

| Film Type | Thickness (µm) | Water Content (%) | Swelling Index (%) | Solubility in Water (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP | 76.76 ± 5.39 a | 14.31 ± 0.01 d | 100 ab | 77.39 ± 8.00 a |
| AP_CFA | 109.79 ± 7.81 b | 10.70 ± 0.01 ab | 88.33 ± 1.06 ab | 70.75 ± 0.29 a |
| AP_CMA | 129.49 ± 7.37 c | 11.36 ± 0.01 abc | 100 ab | 70.22 ± 0.39 a |
| AP_FRA | 121.88 ± 7.67 c | 13.44 ± 0.01 cd | 88.18 ± 0.71 a | 79.11 ± 7.92 a |
| AP_GLA | 85.31 ± 4.05 a | 10.93 ± 0.00 abc | 100 ab | 69.73 ± 2.91 a |
| AP_PCA | 78.26 ± 5.10 a | 12.87 ± 0.01 bcd | 86.63 ± 0.24 a | 66.26 ± 1.20 a |
| AP_SNA | 112.16 ± 6.07 b | 8.91 ± 0.01 a | 100 ab | 69.11 ± 3.29 a |
| Film Type | Water Vapour Diffusion Coefficient (×10−14 m2/s) |
|---|---|
| AP | 0.87 ± 0.04 a |
| AP_CFA | 1.72 ± 0.03 c |
| AP_CMA | 2.80 ± 0.18 e |
| AP_FRA | 2.23 ± 0.13 d |
| AP_GLA | 1.23 ± 0.13 b |
| AP_PCA | 0.88 ± 0.03 a |
| AP_SNA | 1.82 ± 0.08 c |
| Film Type | θ (◦) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Time (s) | ||||
| 0 | 60 | |||
| AP | 58.44 ± 5.62 b |  | 25.71 ± 1.98 a |  |
| AP_CFA | 58.40 ± 4.47 b |  | 60.92 ± 4.93 c |  |
| AP_CMA | 52.29 ± 2.38 ab |  | 26.88 ± 2.12 a |  |
| AP_FRA | 47.00 ± 4.47 a |  | 25.03 ± 9.23 a |  |
| AP_GLA | 47.61 ± 4.02 a |  | 24.81 ± 3.82 a |  |
| AP_PCA | 56.51 ± 5.91 b |  | 56.42 ± 4.27 bc |  |
| AP_SNA | 55.36 ± 2.89 b |  | 43.11 ± 3.95 b |  |
| Film Type | WVP (×10−10 g/m·s·Pa) |
|---|---|
| AP | 7.16 ± 0.42 a |
| AP_CFA | 9.76 ± 0.06 b |
| AP_CMA | 10.68 ± 0.12 c |
| AP_FRA | 10.46 ± 0.16 c |
| AP_GLA | 7.45 ± 0.17 a |
| AP_PCA | 7.46 ± 0.22 a |
| AP_SNA | 10.48 ± 0.22 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikus, M.; Galus, S. The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Sorption and Wetting Properties of Apple Pectin-Based Packaging Films. Molecules 2025, 30, 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091960
Mikus M, Galus S. The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Sorption and Wetting Properties of Apple Pectin-Based Packaging Films. Molecules. 2025; 30(9):1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091960
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikus, Magdalena, and Sabina Galus. 2025. "The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Sorption and Wetting Properties of Apple Pectin-Based Packaging Films" Molecules 30, no. 9: 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091960
APA StyleMikus, M., & Galus, S. (2025). The Effect of Phenolic Acids on the Sorption and Wetting Properties of Apple Pectin-Based Packaging Films. Molecules, 30(9), 1960. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30091960








