Recent Advance on Metal Carbides Reinforced Laser Cladding Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. WC-Reinforced Composite Coatings
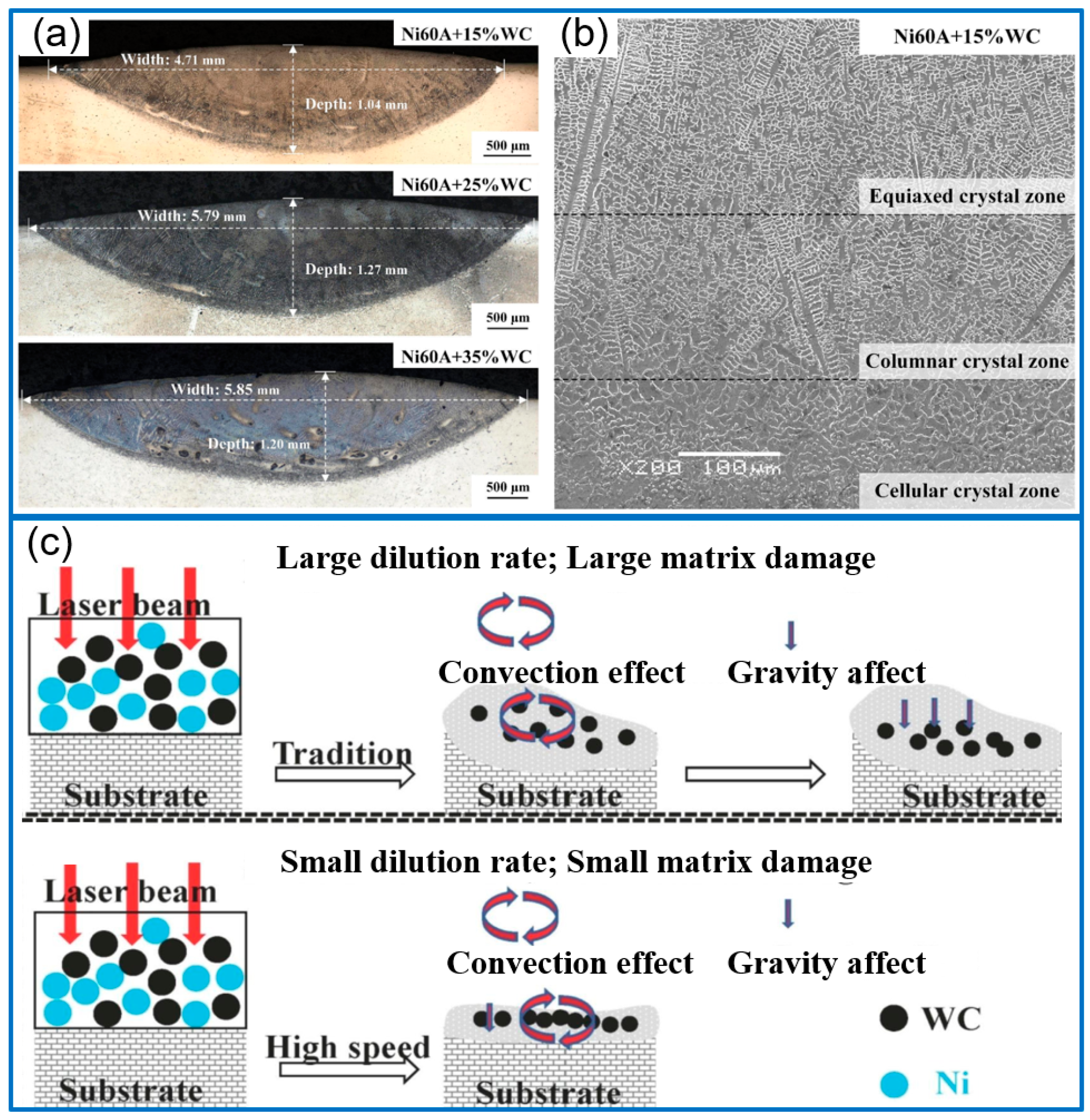
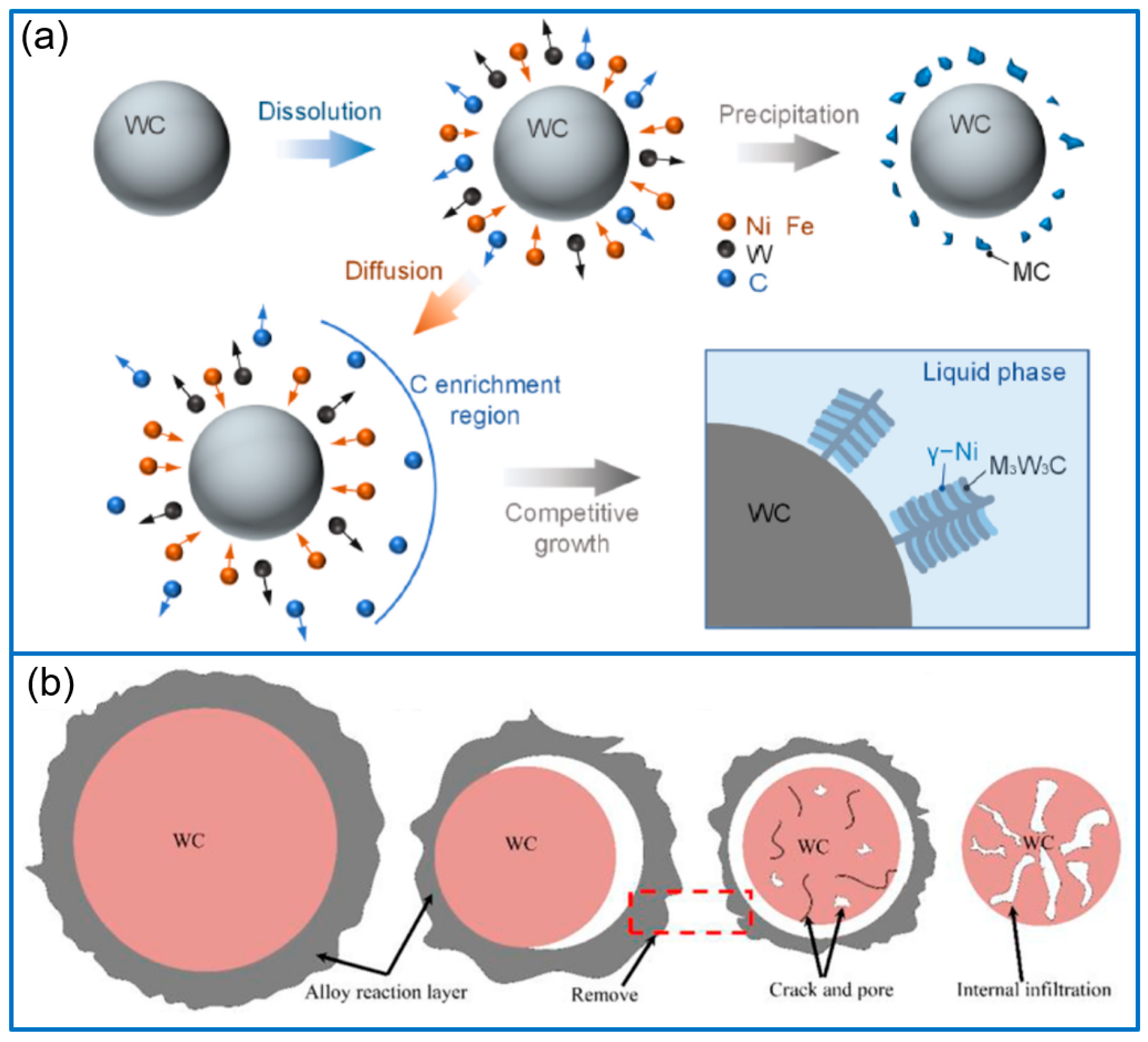
2.1. WC/Ni Composite Coatings
2.2. WC/Co, WC/Fe Composite Coatings
2.3. WC/Other Metal Composite Coatings
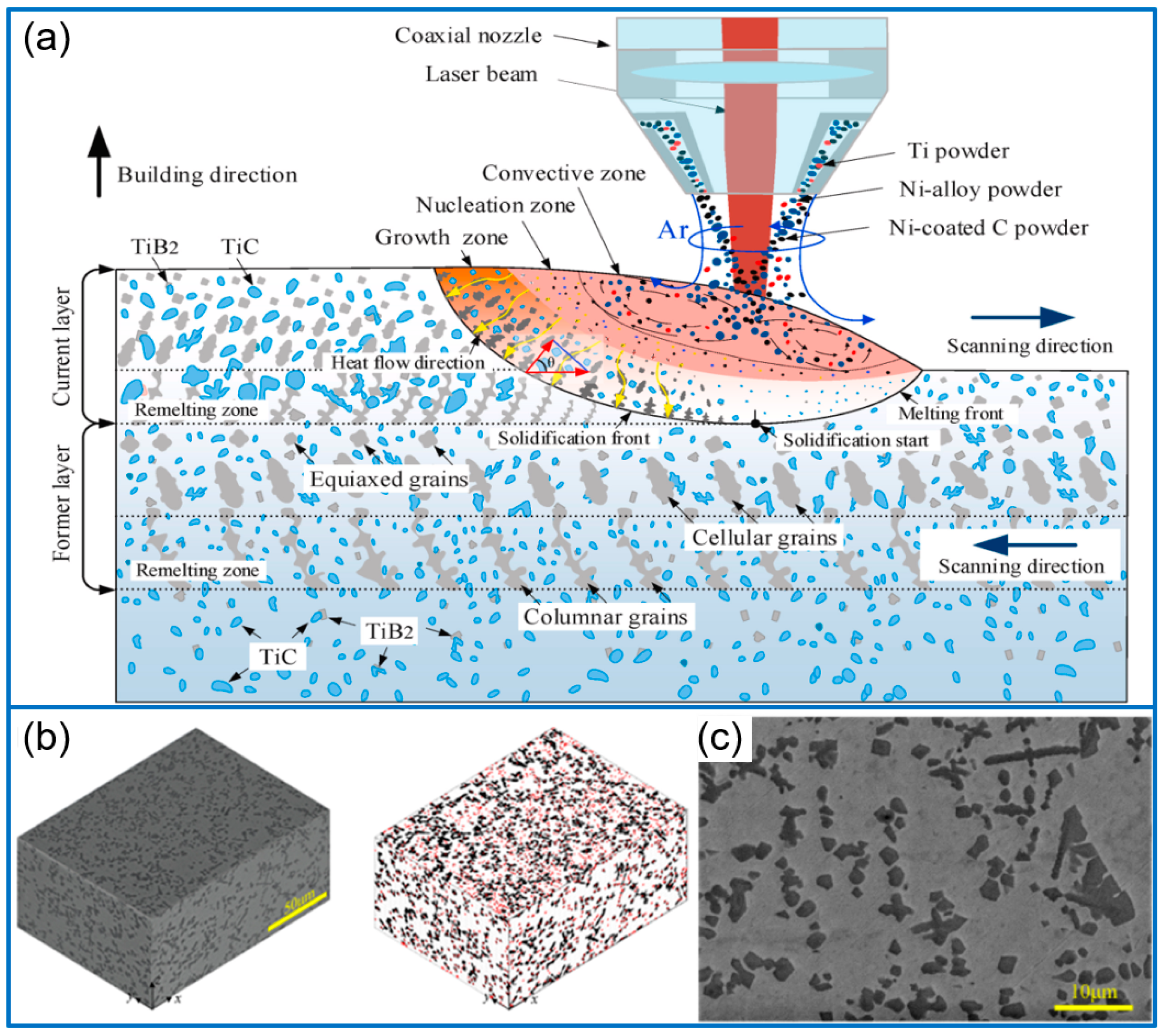
3. TiC-Reinforced Composite Coatings
3.1. TiC/Ni Composite Coatings
3.2. TiC/Fe Composite Coatings
3.3. TiC/High Entropy Alloys Composite Coatings
3.4. TiC/Ti Alloys Composite Coatings
4. NbC-Reinforced Composite Coatings
4.1. NbC/Ni Composite Coatings
4.2. NbC/Fe Composite Coatings
4.3. NbC/HEAs Composite Coatings
5. Tin+1AlCn (MAX Phase) Reinforced Composite Coatings
5.1. Direct Addition of MAX Phases
5.2. In Situ Synthesis of MAX Phases
6. Cr3C2, TaC-Reinforced Composite Coatings
6.1. Cr3C2-Reinforced Coatings
6.2. TaC-Reinforced Coatings
7. Conclusions and Prospects
7.1. Conclusions
- (1)
- As a typical metal carbide reinforcing agent, WC-reinforced coatings have been extensively reported, including WC/Ni, WC/Co, WC/Fe, and WC/other metal composite coatings. The research topics mostly focus on the effect of WC content and particle size, the optimization of process parameters, coating structure design, a combination of WC and other ceramic phases or oxides, the in situ synthesis of WC, the selection of metal matrix, and so on. The main function of WC in composite coatings is to enhance the hardness, mechanical properties, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
- (2)
- Various TiC-reinforced composite coatings are introduced, including TiC/Ni, TiC/Fe, TiC/HEAs, and TiC/Ti alloy composite coatings. The research topics mostly involve the in situ synthesis of TiC by selecting different raw materials, such as Ti powers, nickel-coated graphite, B4C, Cr3C2, or WC. Different from the direct addition of TiC particles in a metal matrix, in situ-generated TiC would refine the grain size by adjusting the nucleation rate. Furthermore, the function of solid solution strengthening and second phase strengthening further enhances the coating hardness and wear resistance.
- (3)
- NbC-reinforced Ni-based, Fe-based, and HEAs coatings have been developed in recent years. Compared with WC- and TiC-based composite coating, the amount of literature about NbC-reinforced composite coatings is much less. In terms of processing method, NbC-reinforced composite coatings are usually prepared by in situ synthesis method, and the powders of Nb, C, Nb, Cr3C2, B4C, or other carbides are adopted as raw materials. The high melting point and high hardness of NbC enable the NbC-reinforced composite coatings with a high hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
- (4)
- Bimetallic carbides Ti2AlC and Ti3AlC2 belong to MAX phases with a typical 2D nano-layered structure. By using MAX as fillers, the researchers have discussed the effect of MAX dosage, the difference between Ti3AlC2 and Ti2AlC, the surface wrapping, and the introduction of other nonmetal elements. While for the works about in situ generation of MAX, the researchers pay more attention to the selection of raw materials and the optimization of component ratio. The in situ-generated MAX products are different from the direct addition of MAX, and thermal annealing treatment is required to induce the formation of MAX phases. The issues about MAX reinforced coatings are related to the universality of raw materials, the uncertainty of MAX substance, and the formation of multi-component products.
- (5)
- In respect to Cr3C2-reinforced composite coatings, researchers have discussed the effect of process parameters and Cr3C2 content, the synergistic effect with Ag particles, and the selection of metal matrices, such as Ni, Fe, and different alloys. Most Cr3C2-based coatings are prepared by direct addition of Cr3C2. TaC-reinforced coatings are mostly prepared by in situ synthesis by using the mixed powders of Ta, C, and metal powders or other metal carbides. The introduction of TaC phases significantly improves the hardness, wear resistance, and erosion resistance of coatings.
7.2. Prospects
- (1)
- The selection of metal carbides in practical application and optimization design. Metal carbides have diversity, and the suitable selection of one or several carbides is really important. Moreover, the molding method including direct addition or in situ synthesis determines the industrialization process of composite coatings. Therefore, researchers must be familiar with the advantages/disadvantages and functionality of each metal carbide, and choose the appropriate metal carbide for the practical requirement.
- (2)
- Defects such as pores and cracks may occur during the actual processing of laser cladding carbide reinforced coatings. The defects generated in composite coatings are generally related to the type, dosage of the filler, and processing parameters. Therefore, the researchers should select appropriate addition amounts and processing parameters, based on the physical feature, and particle size of various carbide fillers.
- (3)
- The design and preparation of multi-functional ceramic coating materials, that is, how to add one or several metal carbides to prepare coatings with multiple excellent properties. This requires researchers to be familiar with the compatibility between metal substrates and carbides, and to select appropriate reinforcing agents based on the type of substrate. For example, a strong tough coating can be obtained by combining MAX-phase ceramics with metals. If the conditions permit, theory calculation results are required to guide the selection of metal carbides.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, D.; Ju, J. Research and Progress of Laser Cladding: Process, Materials and Applications. Coatings 2022, 12, 1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, Y.; Yang, L.; Sun, R.; Zhang, T.; Yang, X. Research and progress of laser cladding on engineering alloys: A review. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 66, 341–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Long, W.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H. A review on ceramic coatings prepared by laser cladding technology. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 176, 110993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.K. Effect of rare earth oxide additive in coating deposited by laser cladding: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 52, 1558–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Xue, P.; Lan, Q.; Meng, G.; Ren, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, P.; Liu, Z. Recent research and development status of laser cladding: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 138, 106915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, J.; Xu, J.; Cheng, X.; Jing, C.; Chen, Z.; Ru, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiao, J. Preparing WC-Ni coatings with laser cladding technology: A review. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 37, 106939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, K.; Fu, H. Improvement of the High Temperature Wear Resistance of Laser Cladding Nickel-Based Coating: A Review. Metals 2023, 13, 840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, X.; Zhao, A.; Cheng, X.; Zhang, Q. Preparation of nickel-based composite coatings by laser cladding technology: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2024, 134, 3107–3137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, K.; Li, J.; Geng, S.; Jing, L.; Skuratov, V. Reinforcements/matrix micro-interface evolution and properties of in-situ Ni60A/WC coatings prepared by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 484, 130834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Li, Y.; Lu, B.; Tan, N.; Cai, L.; Yong, Q. Effect of WC content on microstructure and properties of high-speed laser cladding Ni-based coating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 155, 108449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gu, X.; Lou, C.; Kang, L.; Hou, Q.; Ma, C. Influence of WC ceramic particles on structures and properties of laser cladding Ni50-WC coatings. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, G.; Tang, S.; Wu, J.; Wang, J. Effect of WC on microstructure, molten pool and properties of Ni based coatings by multi-layer laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 174, 110612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; He, X.; Gao, L.; Su, G.; Xu, C.; Xu, N. Study on crack behavior of laser cladding ceramic-metal composite coating with high content of WC. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17460–17470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, N.; Hu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Lu, B.; Hu, D.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Effect of WC particle size on the microstructure and tribological properties of high-speed laser cladding Ni/WC composite coatings. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.X.; Jin, H.; Li, J.D.; Zhang, J.W.; Ban, C.Y. Microstructure and properties of Ni-WC gradient composite coating prepared by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 7905–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Y.; Li, S.; Tian, C.; Chen, B.; Dong, B.; Shu, Z.; Guo, J.; He, X.; Yu, G. Effect of powder feeding rate on mass fraction of WC particles, microstructure evolution and micro-hardness of WC-Ni composite coating by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1013, 178432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Huang, K.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, C.; Li, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, K.; Tan, H.; Yi, X. Wear mechanisms and micro-evaluation of WC + TiC particle-reinforced Ni-based composite coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2023, 197, 112699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Yang, J.; Han, B.; Song, L.; Li, P.; Dong, W.; Xue, X. Comparative investigation on microstructures and properties of WC/Cr3C2 reinforced laser cladding Ni-based composite coatings subjected to ultrasonic impact treatment. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lian, G.; Lin, T.; Lu, H.; Wang, Y. Effects of the proportions of carbon on the microstructure and properties of NbC-reinforced Ni-WC composite coatings by laser cladding in-situ synthesis. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Lian, G.; Feng, M.; Zhang, W.; Chen, R. Microstructure evolution and properties of (Nb,M)C (M=Ti,V and Zr) reinforced Ni-WC coatings by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, R.; Feng, A.; Feng, H. Effect of rare earth La2O3 particles on structure and properties of laser cladding WC-Ni60 composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 479, 130569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Zhang, J.; Chen, Y.; Hou, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Li, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, Y. On enhancing wear resistance of titanium alloys by laser cladded WC-Co composite coatings. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2022, 107, 105902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, N.; Yue, H.; Guo, C.; Dai, W.; Zhang, J.; Li, Q.; Zhao, G.; Hao, G. A comparative investigation on the effects of reinforcement phase addition methods on laser melting deposited WC/Co coatings. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 129, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, P.; Zhu, L.; Xue, P.; Yang, Z.; Wang, S.; Ning, J.; Meng, G.; Lan, Q.; Qin, S. Microstructure and properties of IN718/WC-12Co composite coating by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 9218–9228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Cao, Y.; Hua, K.; Tong, Y.; Li, N.; Sun, L.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Wang, H. Fretting wear resistance at ambient and elevated temperatures of 316 stainless steel improved by laser cladding with Co-based alloy/WC/CaF2 composite coating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 163, 109428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.; Sun, W.L.; Yang, K.X.; Xing, X.F.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhou, H.N.; Lu, J. Wear mechanisms and micro-evaluation on WC particles investigation of WC-Fe composite coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 420, 127341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Shen, G. Phase evolution and wear resistance of in-situ synthesized (Cr, W)23C6-WC composite ceramics reinforced Fe-based composite coatings produced by laser cladding. Vacuum 2021, 190, 110242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, C.; Lian, G.; Huang, X. Effects of WC addition on the morphology, microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe50/TiC/WC laser claddings on AISI 1045 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 427, 127781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Hao, H.; Gao, Q.; Cao, Y.; Han, R.; Qi, H. Strengthening mechanism and high-temperature properties of H13 + WC/Y2O3 laser-cladding coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Lin, D.; Tang, Z.; Song, X.; He, P.; Zhang, S.; Bian, H.; Fu, W.; Song, Y. Eutectic high-entropy alloys and their applications in materials processing engineering: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 189, 211–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xie, D.; Liu, Y.; Lv, F.; Zhou, K.; Jiao, C.; Gao, X.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Zu, H.; et al. Effect of WC on the microstructure and mechanical properties of laser-clad AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high-entropy alloy composite coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 976, 173219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Wang, L.; Gao, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, T.; Zhan, X. Microstructure and element distribution characteristics of Y2O3 modulated WC reinforced coating on Invar alloys by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 153, 108205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Li, G.; Wu, B.; Xu, S.; Wang, L.; Guo, Y. Effect of TiC content on microstructure and properties of TiC/Ni60 coatings on Ti6Al4V alloy deposited by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 168, 109854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Wang, C.; Liu, T.; Song, Q.; Xue, B.; Cui, H. Microstructure and performance optimization of laser cladding nano-TiC modified nickel-based alloy coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 479, 130583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, T.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y.; Guan, C. Process optimization, microstructure and microhardness of coaxial laser cladding TiC reinforced Ni-based composite coatings. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 152, 108129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, T.; Wang, Z. Microstructure and properties of in situ TiC/Ni functionally gradient coatings by powder-fed laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 36789–36801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Guan, C.; Ma, Z.; Cui, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, T.; Gu, R. Modeling and simulation of grinding surface morphology for laser cladding in situ TiC reinforced Ni-based composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 498, 131831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, M.; Miao, X.; Jin, X.; Cui, C. TiC in-situ strengthening mechanism and crack initiation mechanism of SiC/TC4 composite coatings by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt A, 52558–52571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, X.; Li, Y.; Cui, W.; Du, J.; Zhao, Y.; Li, F. Improving the wear and corrosion properties of laser cladded Ni-based composite coatings via regulating in-situ TiB2-TiC. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 9442–9454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Li, Y.; Li, F.; Qi, X.; Sun, X.; Pan, Z.; Niu, J. Wear and corrosion properties of in-situ TiC–TiB2 modified Ni-based composite coatings with different B/C ratios prepared by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt B, 2424–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Lian, G.; Lu, H.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. Defects, organization, and properties of TiB2–TiC Bi-ceramic phase by laser cladding in situ synthesis. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt A, 41097–41116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, R.; Shoja Razavi, R.; Bakhshi, S.R.; Erfanmanesh, M.; Ahmadi Bani, A. Optimization and characterization of laser cladding of NiCr and NiCr–TiC composite coatings on AISI 420 stainless steel. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 4097–4110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, T.; Chen, L.; Gu, P.; Ren, X.; Chen, X. Microstructure and corrosion resistance of TiC/Inconel 625 composite coatings by extreme high speed laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 150, 107919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Ouyang, M.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, C. Design and development of TiC-reinforced 410 martensitic stainless steel coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 12505–12513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, X.; Dejun, K. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser cladded TiC reinforced WC-10Co4Cr coatings at 500 °C. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 40, 109548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.L.; Zhang, C.H.; Sun, X.Y. Design, fabrication, microstructure and properties of in-situ synthesized TiC reinforced stainless steel matrix composite coating by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2023, 204, 113177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Tao, S.; Li, G.; Chen, H. Study on microstructure and properties of laser-clad Fe-based (Ti, V)C composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 464, 129552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.Y.; Zhang, J.W. The influence of laser power on the microstructure and friction performance of laser-prepared TiC-NbC composite coatings on stainless steel surfaces. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, T.; Guan, C.; Zhao, Y. Microstructure and properties of metal parts remanufactured by laser cladding TiC and TiB2 reinforced Fe-based coatings. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 14127–14140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.D.; Liu, X.B.; Yang, C.M.; Zhang, F.Z.; Li, X.G.; Zheng, J.; Liu, J. Strengthening mechanisms of laser cladding TiC/FeCoCrNiCu high-entropy composite coatings: Microstructure evolution and wear behaviors. Tribol. Int. 2024, 199, 109979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Fu, H.; Guo, X.; Lin, J. Microstructure and wear resistance of in-situ TiC reinforced AlCoCrFeNi-based coatings by laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 585, 152703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Niu, Z.; Gao, Z.; Li, J.; Bai, G.; Ke, L.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, C. Microstructure and wear behavior of in-situ synthesized TiC-reinforced CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy prepared by laser cladding. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 670, 160720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Fu, H.; Ma, T.; Wang, K.; Yang, X.; Lin, J. Microstructure and wear resistance of AlCoCrFeNi-WC/TiC composite coating by laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2022, 194, 112479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Niu, W.; Lei, Y.W.; Zheng, Y. Microstructure and wear performance of ex/in-situ TiC reinforced CoCrFeNiW0.4Si0.2 high-entropy alloy coatings by laser cladding. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1002, 175458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, D.D.; Tao, W.W.; Ni, H.M.; Wang, A.Z.; Du, B.; Zhang, S.H.; Lian, X.L.; Wang, D.; Feng, Y.J. TiC distribution and properties of TiC-CrMnFeCoNi coating fabricated by laser cladding with ultrasound. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 468, 129744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Xiao, H.; Ren, L.; Huang, F.; Chen, Y.; Cao, S.; Wu, H.; Zhu, L. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser-cladded TiCx/TiAl composite coatings on TC4 alloy. Tribol. Int. 2024, 192, 109236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, W.; Liu, D.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, X. Effects of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of TiC/TiB composite bioinert ceramic coatings in-situ synthesized by laser cladding on Ti6Al4V. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 755–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Ma, Q. Influence of CeO2 addition on forming quality and microstructure of TiCx-reinforced CrTi4-based laser cladding composite coating. Mater. Charact. 2021, 171, 110732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yang, F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; Wang, H. Microstructure and element distribution of laser cladding TiCx-reinforced CrTi4-based composite coating with CeO2/Ce2O3. Mater. Lett. 2021, 283, 128772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaddam, S.; Nartu, M.S.K.K.Y.; Chesetti, A.; Mantri, S.A.; Mishra, R.S.; Dahotre, N.B.; Banerjee, R. Hierarchical phase evolution during direct laser deposition of an in-situ Ni-NbC composite. Scripta Mater. 2023, 226, 115225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, T.; Sun, J.; Sun, Z.; Wang, Y. Effect of in-situ NbC content on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Ni625 composite coating by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt C, 48074–48083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, G.; Yue, K.; Chen, C.; Huang, L.; Zheng, M. Influences of powder ratios on the mechanical properties of in-situ synthetic NbC coatings. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106318. [Google Scholar]
- Lian, G.; Chen, J.; Lu, H.; Chen, C.; Huang, X. The microstructure and properties of reinforced Ni-20WC coatings by the laser-cladding in-situ synthesis of xNbC. Ceram. Int. 2025, 51, 13135–13151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, W.; Song, B.; Sun, Z.; Yu, T.; Wang, J.; Sun, Q. Effect of various morphology of in situ generated NbC particles on the wear resistance of Fe-based cladding. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 10265–10272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhi, S.; Gao, Q.; Tian, X.; Geng, T.; Guan, X.; Qin, C. Formation behavior of in-situ NbC in Fe-based laser cladding coatings. Mater. Charact. 2016, 119, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yu, T.; Xu, P.; Zhang, B. In-situ NbC reinforced Fe-based coating by laser cladding: Simulation and experiment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 412, 127027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.F.; Zhang, S.; Wu, H.; Wang, R.; Zhang, C.H.; Wu, C.L.; Chen, J.; Chen, H.T. Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of laser cladding iron-based coatings with two types of NbC reinforcement. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 479, 130558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Zhu, L.; Cai, Y.; Yan, Y.; Ge, F.; Shan, M.; Tian, Y.; Han, J.; Jiang, Z. Tribology comparison of laser-cladded CrMnFeCoNi coatings reinforced by three types of ceramic (TiC/NbC/B4C). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 450, 129013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, M.S.; Wang, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, C.H.; Wu, C.L.; Chen, H.T.; Chen, J. Microstructure evolution, corrosion and corrosive wear properties of NbC-reinforced FeNiCoCr-based high entropy alloys coatings fabricated by laser cladding. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2025, 171, 109352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Duan, X.; Jia, D.; Zhou, Y.; van der Zwaag, S. On the formation mechanisms and properties of MAX phases: A review. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 3851–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, S.; Chao, Z.; Dejun, K. Salt spray corrosion behavior and electrochemical performance of laser cladded Ni60–Ti3AlC2 composite coatings in 3.5% NaCl solution. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 36, 106550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Kong, D. Microstructure, tribocorrosion and electrochemical properties of Ti2AlC reinforced Ni60WC coatings by high–speed laser cladding. Mater. Charact. 2025, 221, 114723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Kong, D. Friction–wear performances and oxidation behaviors of Ti3AlC2 reinforced Co–based alloy coatings by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 408, 126816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Chang, X.; Kong, D. Ti2AlC and Ti3AlC2 reinforced CoNi coatings by laser cladding: Nanostructures, tribological properties and density functional theory calculations. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 131, 736–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, S.; Li, Y.; Cai, Y.; Tan, N.; Li, Q.; Zhang, G.; Li, G. Investigation on microstructure and tribological properties of Ti2AlC-Ni reinforced Fe-based prepared by high-speed laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 489, 131143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Ma, G.; Wang, H.; Wang, W.; Mou, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhao, H.; Li, Y.; Tan, N. High-speed laser cladded Ni-based cermet coating with high ceramic phase content derived from core-shell structured powder. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 489, 131110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, S.W.; Pang, M.; Ji, F.Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, G. Microstructure and tribological properties of Ti2AlC-B particle-enhanced self-lubricating coatings on Ti6Al4V by ultrasonic impact treatment and laser cladding. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 34, 105165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.; Cuskelly, D.; Brandt, M.; Kisi, E. Microstructural analysis of in-situ reacted Ti2AlC MAX phase composite coating by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 385, 125360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, P.; Cuskelly, D.; Brandt, M.; Kisi, E. Effects of furnace annealing on in situ reacted Ti2AlC MAX phase composite coatings deposited by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Cao, Y.; Ding, H.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Hua, K.; Wang, H. Fabrication of composite coatings containing in-situ reacted Ti2AlC/Ti2AlN MAX phases by laser cladding and investigation of fretting wear mechanism. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt B, 39138–39149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Xiao, H.; Ren, L.; Feng, J.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, N.; Zhou, X. A new strategy to fabricate Ti2AlC MAX coatings by the two-step laser method. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 448, 128944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, M.; Xiao, H.; Ren, L.; Mo, T.; Lin, B. Microstructure and properties of Ti–Al–C composite coatings prepared by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50 Pt B, 12498–12509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xiao, H.; Chen, N.; Chu, M.; Lin, B.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, G.; Mo, T. Effect of Nb content on the tribological properties of laser-cladded Ti-Al-C MAX phase composite coatings. Tribol. Int. 2025, 204, 110426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Ren, S.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X. Effect of process parameters on microstructure and tribological properties of Ni60A/Cr3C2 laser cladding on 60Si2Mn steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 473, 130005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Liang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhou, J. Effects of NiCr intermediate layer on microstructure and tribological property of laser cladding Cr3C2 reinforced Ni60A-Ag composite coating on copper alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 142, 106963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Lu, Y.; Kong, D. Laser cladded Ni625–xCr3C2 coatings: Microstructure, tribocorrosion and electrochemical properties. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 478, 130487. [Google Scholar]
- Mao, K.; Du, Y.; Cao, H.; Peng, Y.; He, G.; Liang, Q.; Tu, J. Effects of Cr3C2 addition on microstructure and corrosion properties of Cr3C2/15–5PH composite coatings on 12Cr13 by laser cladding. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 41, 110375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, S.; Chen, G. Effect of Process Parameters on the Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Fe3Al/Cr3C2 Composites. Coatings 2024, 14, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Li, W.; Yang, J.; Zhu, S.; Cui, S.; Li, X.; Shao, L.; Zhai, H. Effect of Cr3C2 content on microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of Ni3Al-based coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 466, 129597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, S.E.; Shamanian, M.; Amini Najafabadi, R.; Keshavarzkermani, A.; Esmaeilizadeh, R.; Ali, U.; Marzbanrad, E.; Toyserkani, E. Microstructure and oxidation behavior of NiCr-chromium carbides coating prepared by powder-fed laser cladding on titanium aluminide substrate. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 1668–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghili, S.E.; Shamanian, M. Investigation of powder fed laser cladding of NiCr-chromium carbides single-tracks on titanium aluminide substrate. Opt. Laser Technol. 2019, 119, 105652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesh, L.; Samajdar, I.; Tak, M.; Doherty, R.D.; Gundakaram, R.C.; Prasad, K.S.; Joshi, S.V. Microstructure and phase evolution in laser clad chromium carbide-NiCrMoNb. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 2391–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yan, H.; Zhang, P.; Guo, J.; Yu, Z.; Ringsberg, J.W. Improving surface resistance to wear and corrosion of nickel-aluminum bronze by laser-clad TaC/Co-based alloy composite coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, T.; Tang, H. Microstructure and high-temperature wear behavior of laser clad TaC-reinforced Ni-Al-Cr coating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 592, 153263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, M. Effect of TiC addition on the microstructure and properties of Ni3Ta–TaC reinforced Ni-based wear-resistant coating. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 23194–23202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, M.; Liu, J. Microstructure and properties of in-situ synthesized Ni3Ta-TaC reinforced Ni-based coatings by laser cladding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 405, 126599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, T.; Lv, H.; Hu, D.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; She, J. Microstructure and properties of Ta-reinforced cobalt based composite coatings processed by direct laser deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 447, 128874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
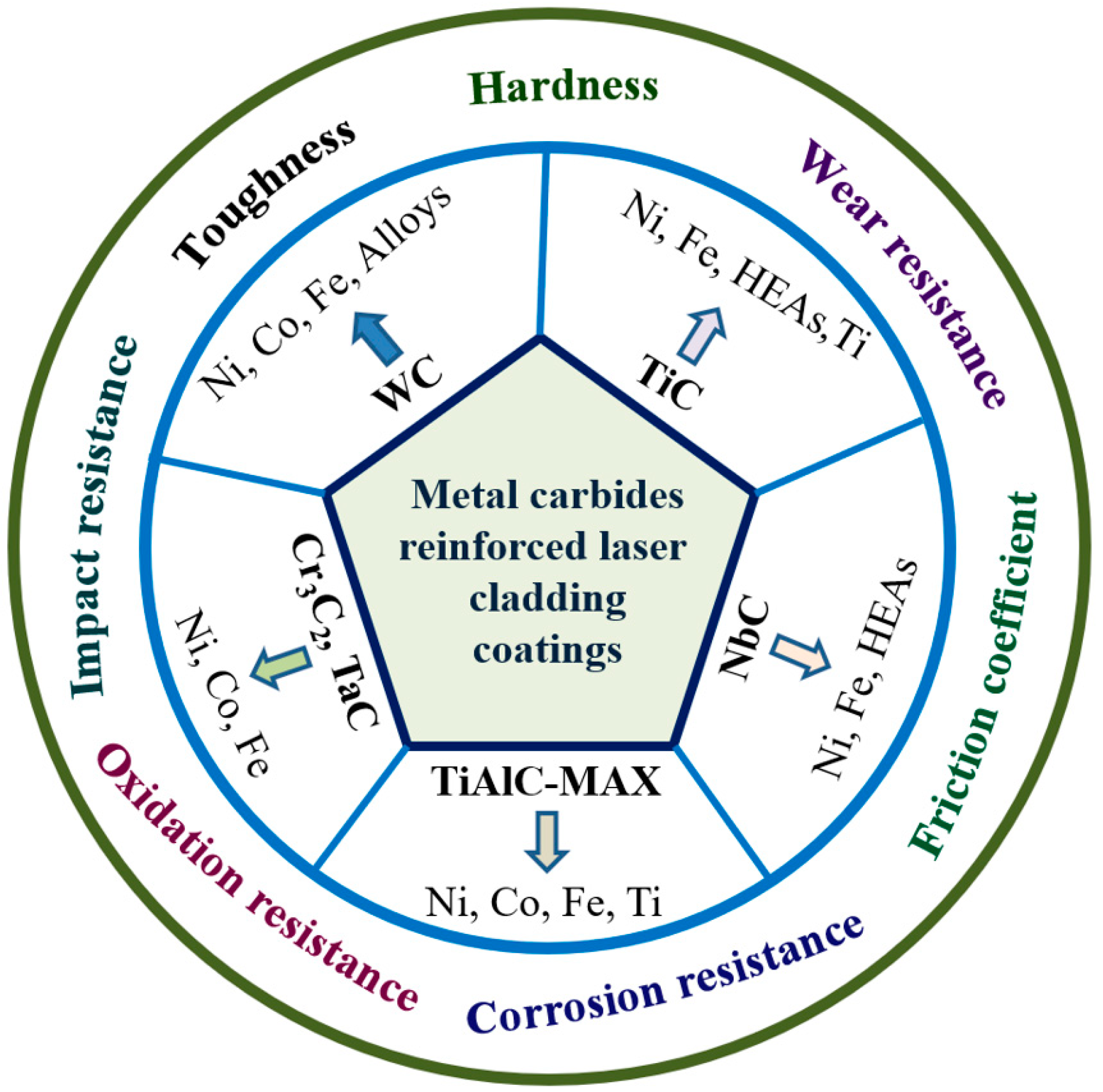
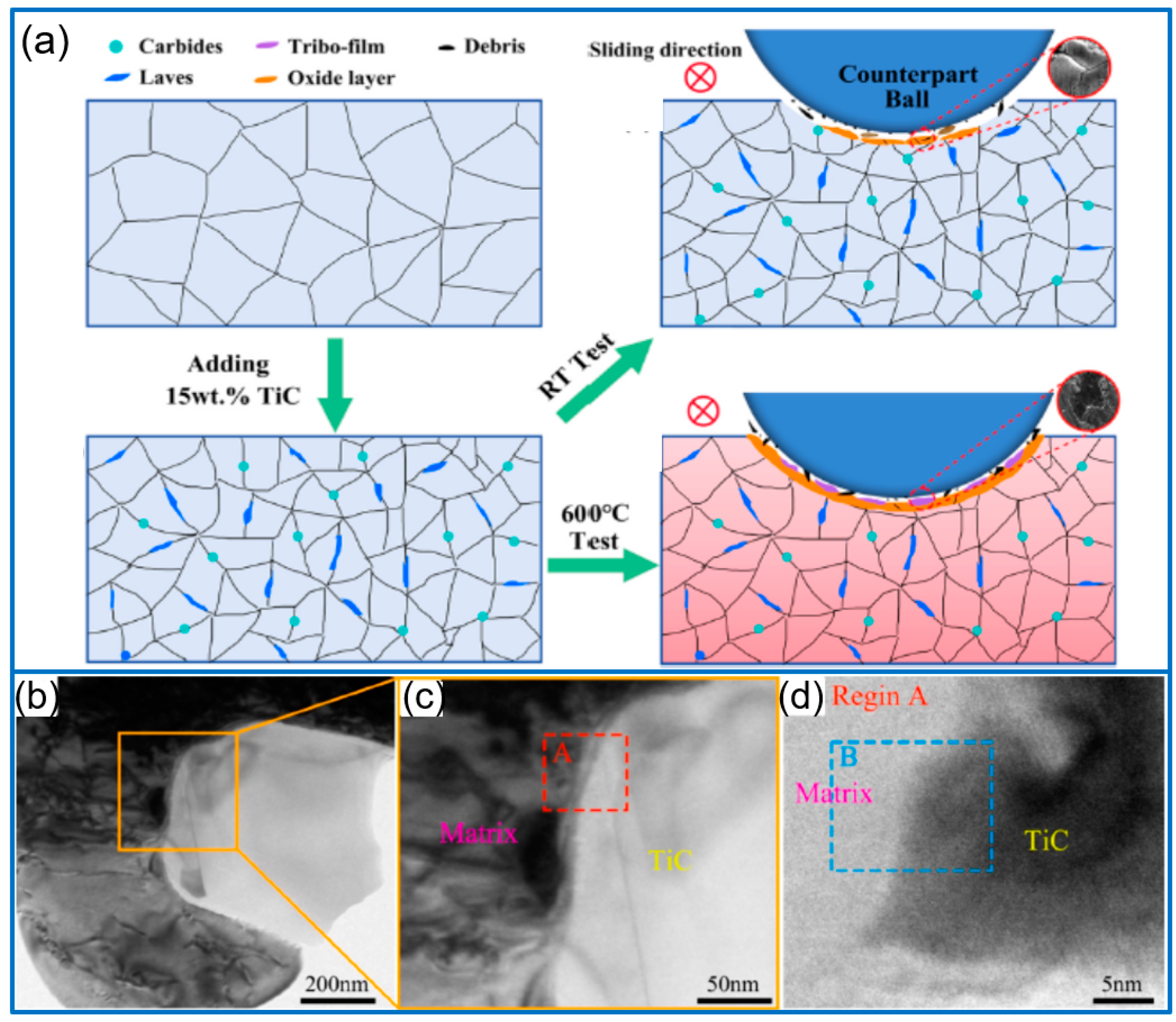
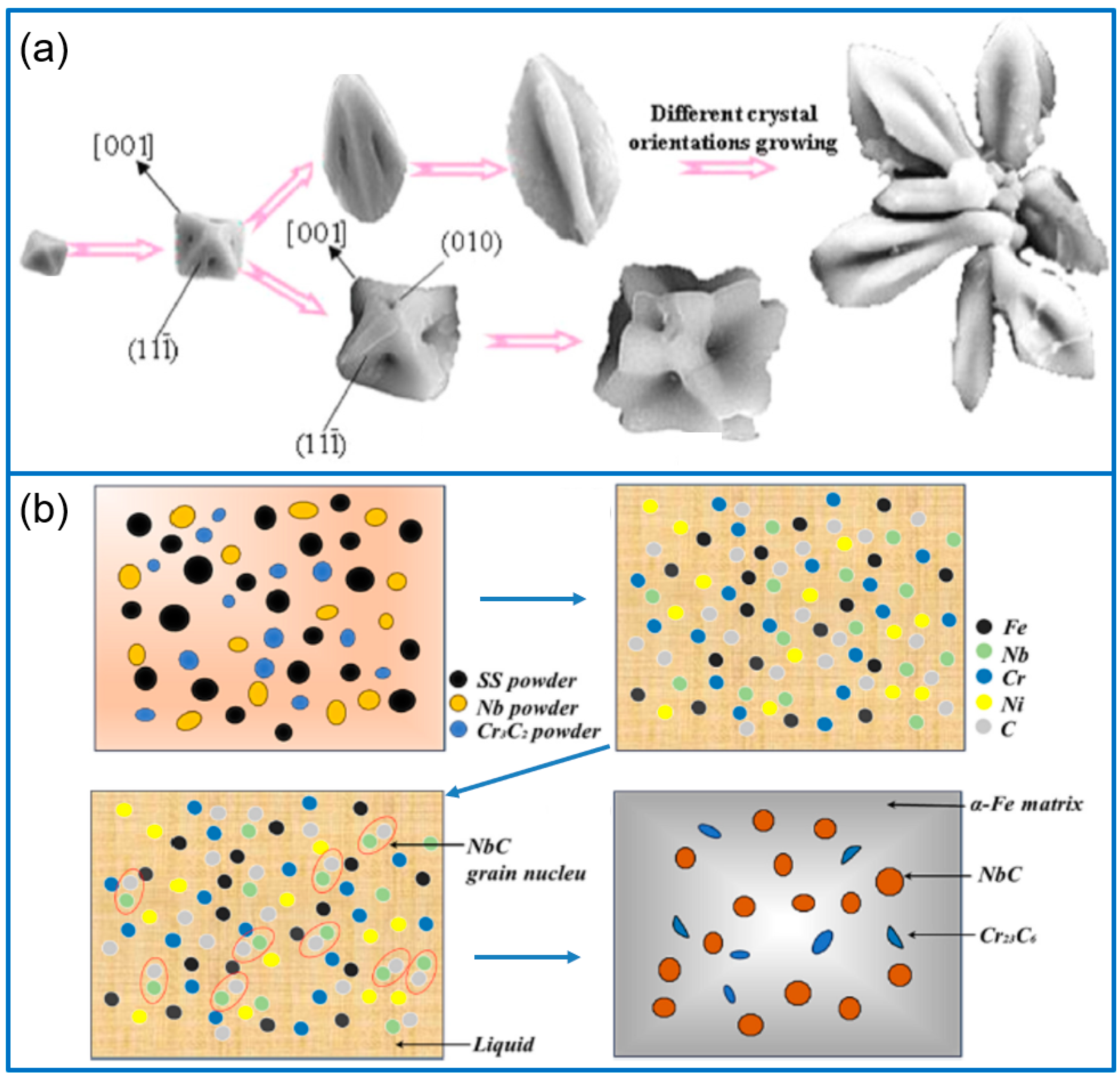

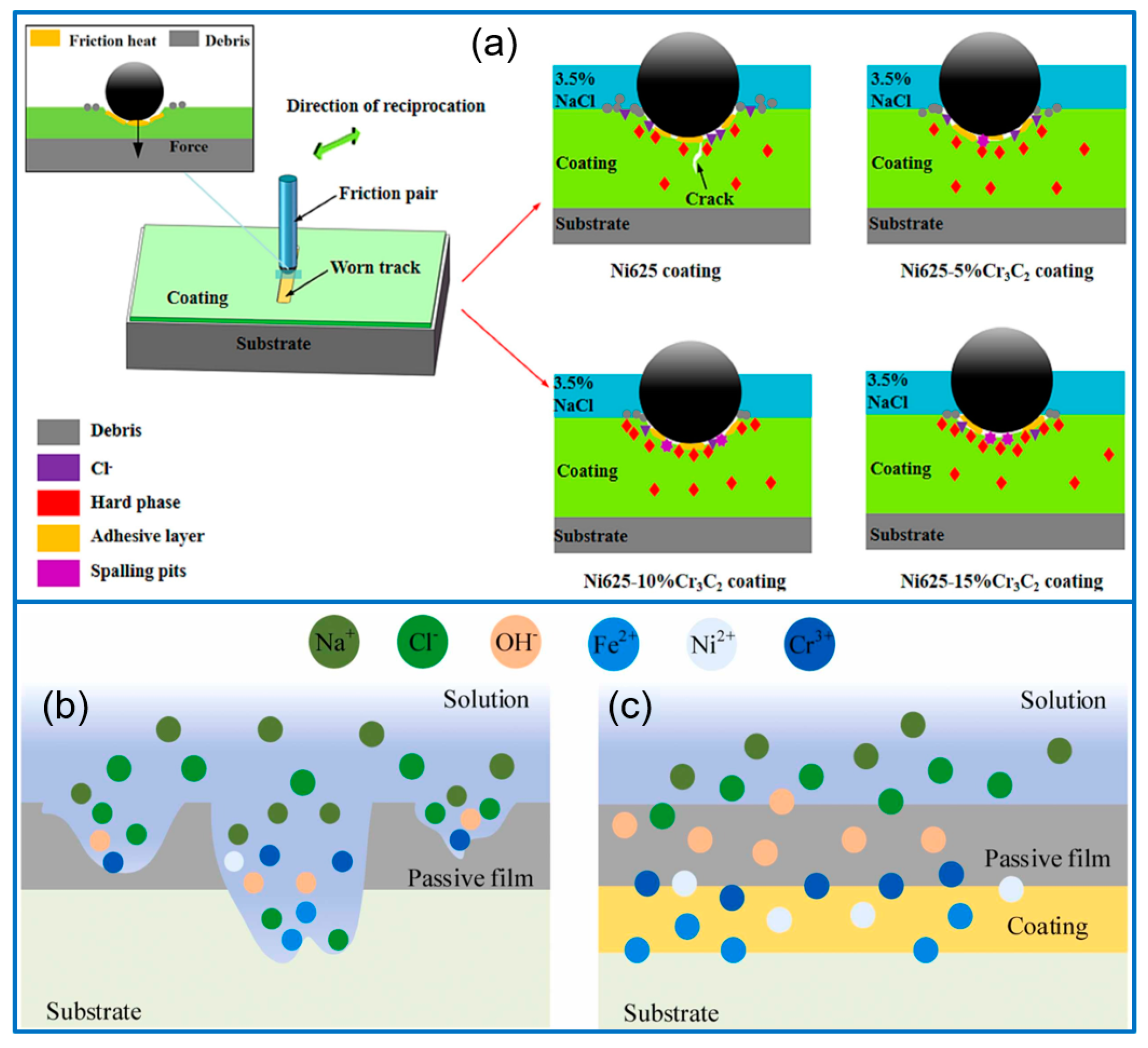
| Carbides | Metal Matrix | Performance Enhancement | Caution |
|---|---|---|---|
| WC | Reinforced Ni, Co, Fe, various alloys | Enhancing the hardness, mechanical performance, wear/corrosion resistance | WC content is <20 wt% |
| TiC | Reinforced Ni, Fe, Ti, HEAs | Enhancing the hardness, wear/corrosion resistance; in situ-generated TiC is better | When TiC content is >15%, pores and microcracks |
| NbC | Reinforced Ni, Fe, HEAs | Enhancing the hardness, wear/corrosion resistance | Compared with direct addition, in situ NbC is better |
| Tin+1AlCn | Reinforced Ni, Co, Fe, Ti | 2D nano-layered structure, enhancing the hardness, wear/corrosion resistance | Require thermal annealing to produce MAX phases |
| Cr3C2 | Reinforced Ni, Fe, TiAl | Enhancing the hardness, wear/corrosion/oxidation resistance | Cr7C3 was stable phase, much stabler than Cr3C2 |
| TaC | Reinforced Ni, Co | Enhancing the hardness, wear/corrosion resistance | In situ formation of TaC avoids the cracks |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, D.; Wang, G.; Dong, W.; Hong, X.; Guo, C. Recent Advance on Metal Carbides Reinforced Laser Cladding Coatings. Molecules 2025, 30, 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081820
Jiang D, Wang G, Dong W, Hong X, Guo C. Recent Advance on Metal Carbides Reinforced Laser Cladding Coatings. Molecules. 2025; 30(8):1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081820
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Dazhi, Guangjin Wang, Wei Dong, Xiaodong Hong, and Chenguang Guo. 2025. "Recent Advance on Metal Carbides Reinforced Laser Cladding Coatings" Molecules 30, no. 8: 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081820
APA StyleJiang, D., Wang, G., Dong, W., Hong, X., & Guo, C. (2025). Recent Advance on Metal Carbides Reinforced Laser Cladding Coatings. Molecules, 30(8), 1820. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30081820






