Ordered Mesopore Channels of SBA-15 for Contaminant Adsorption: Characterization, Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
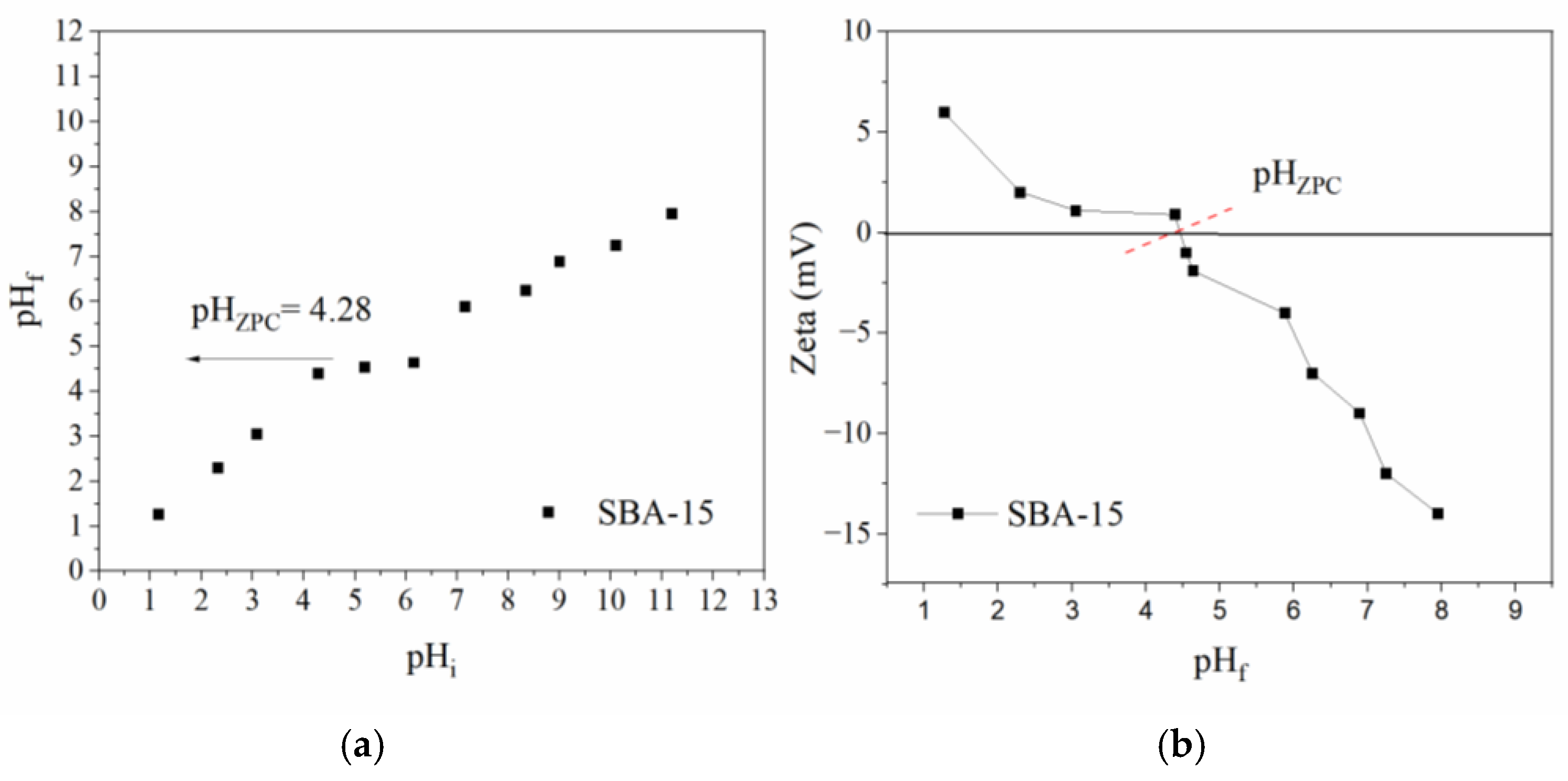
2.1. Characterization of the Nanostructured Mesoporous Material SBA-15
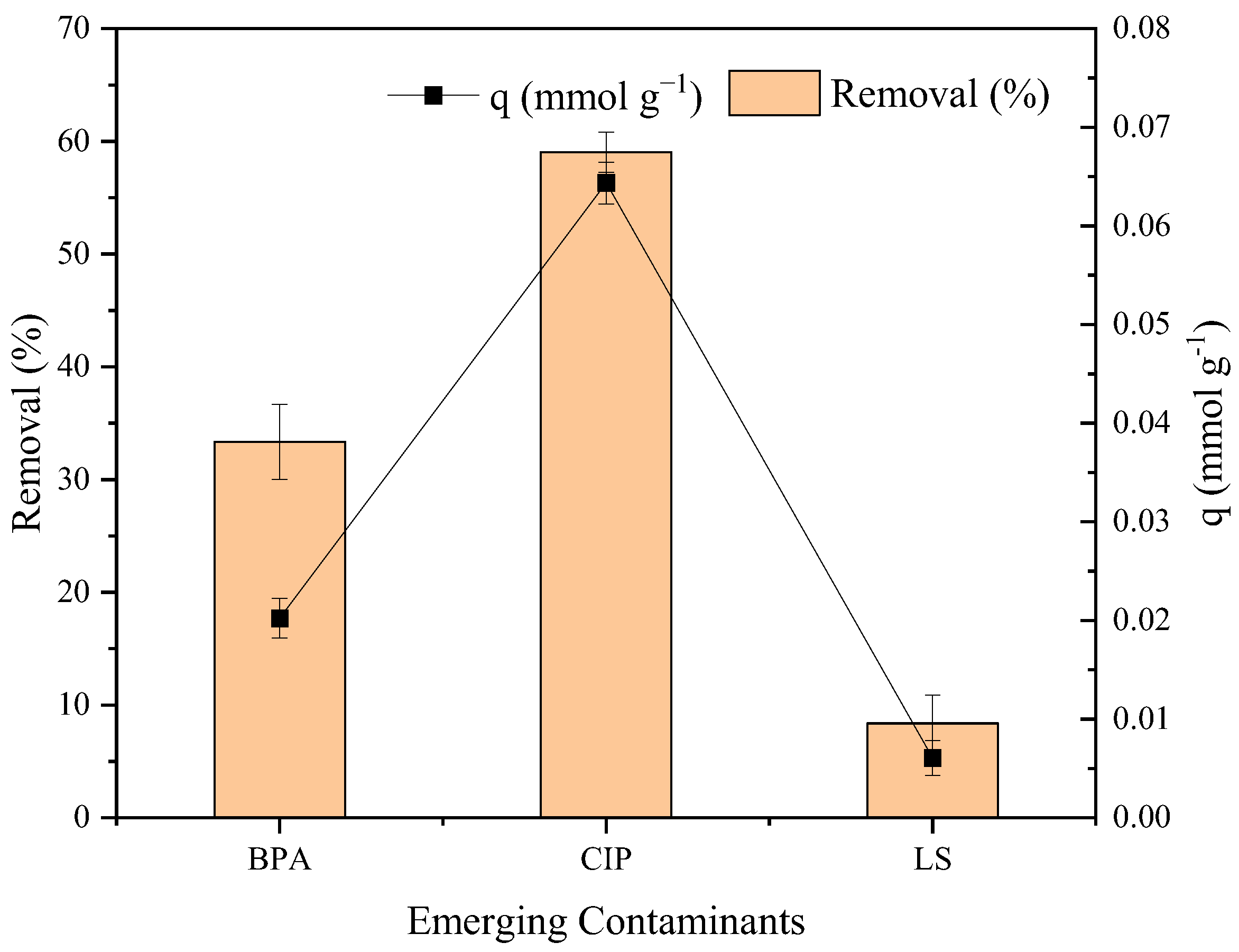
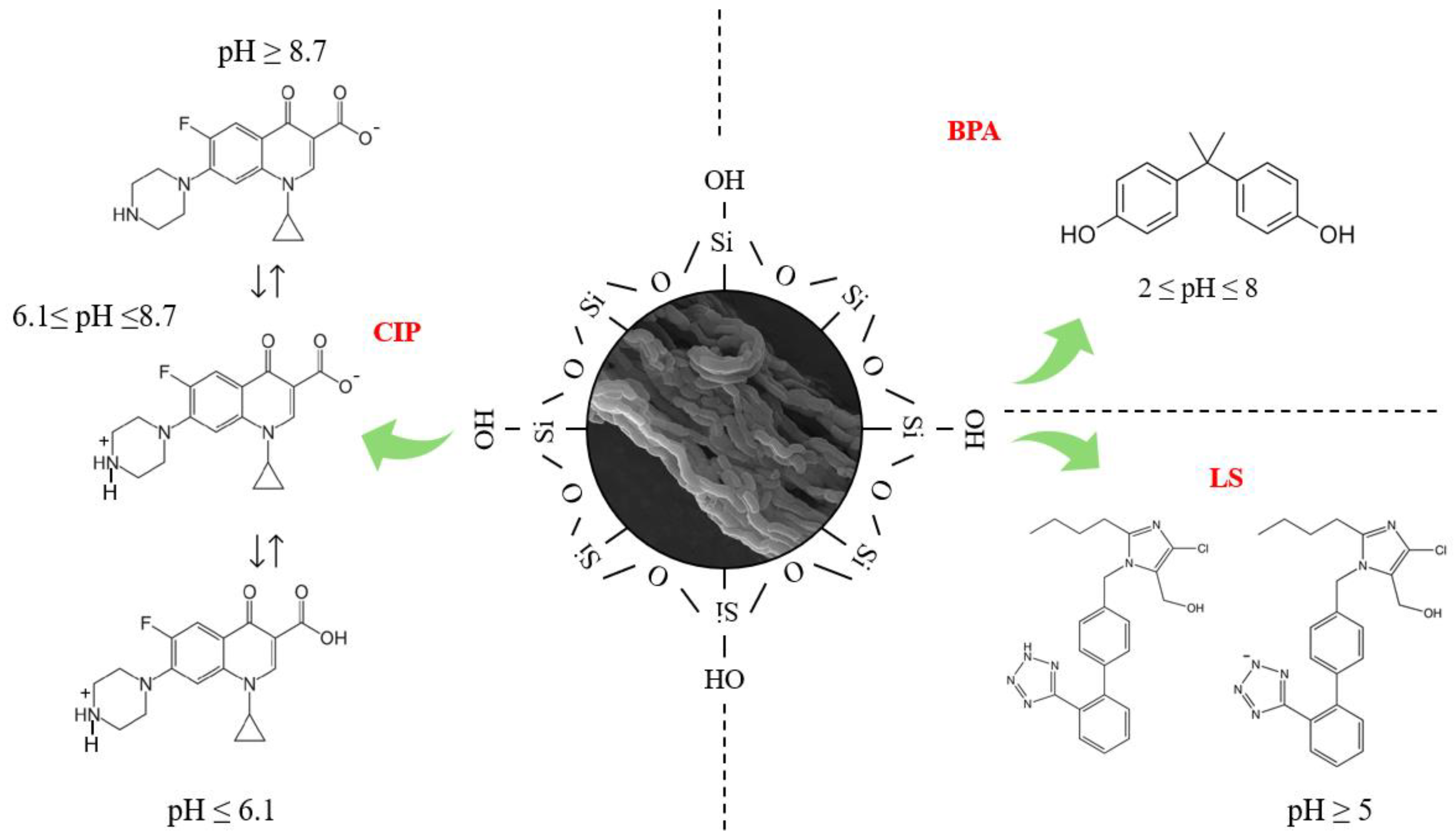
2.2. Affinity and Adsorption Mechanism
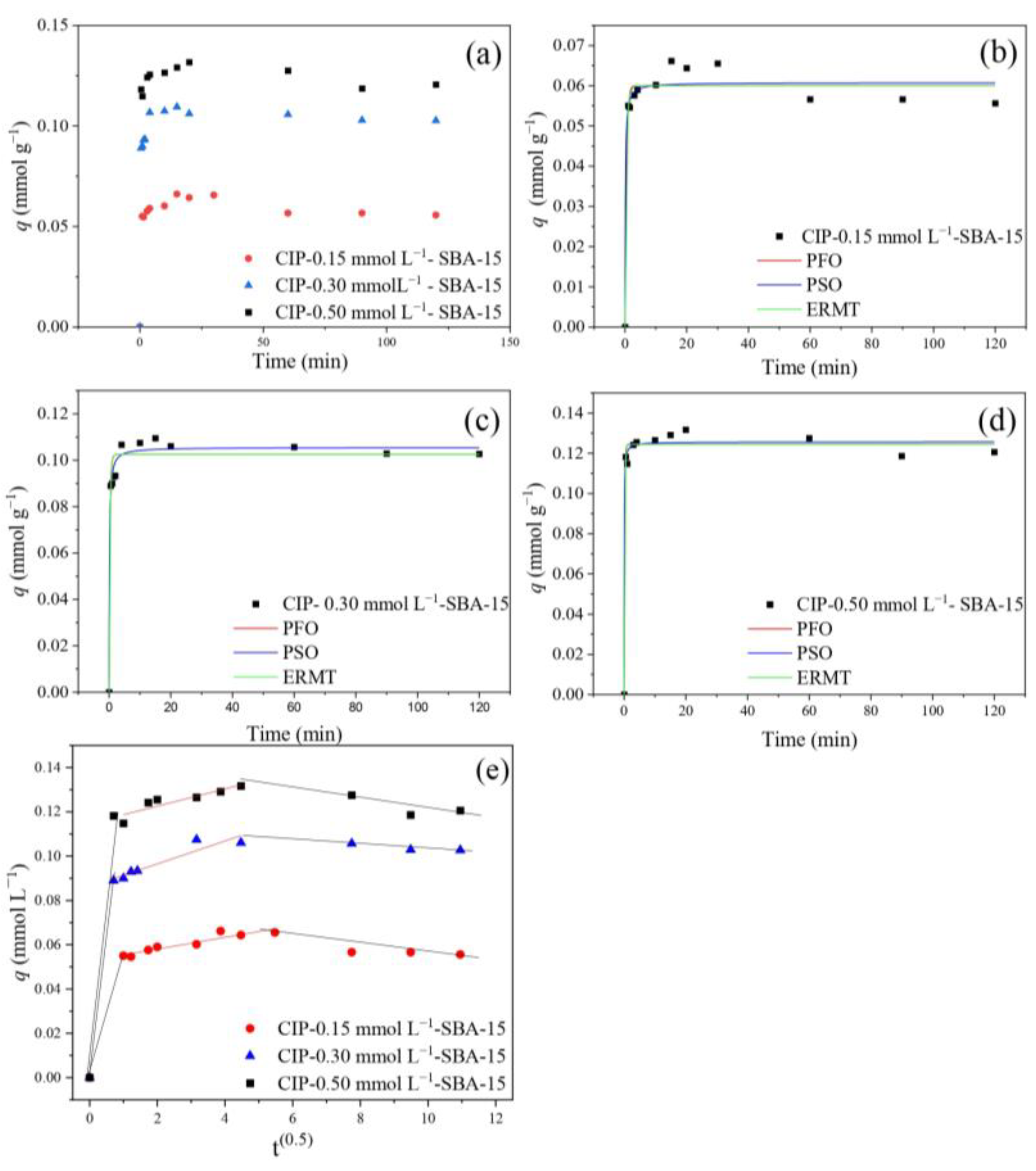
2.3. Kinetic Study to Adsorption of CIP
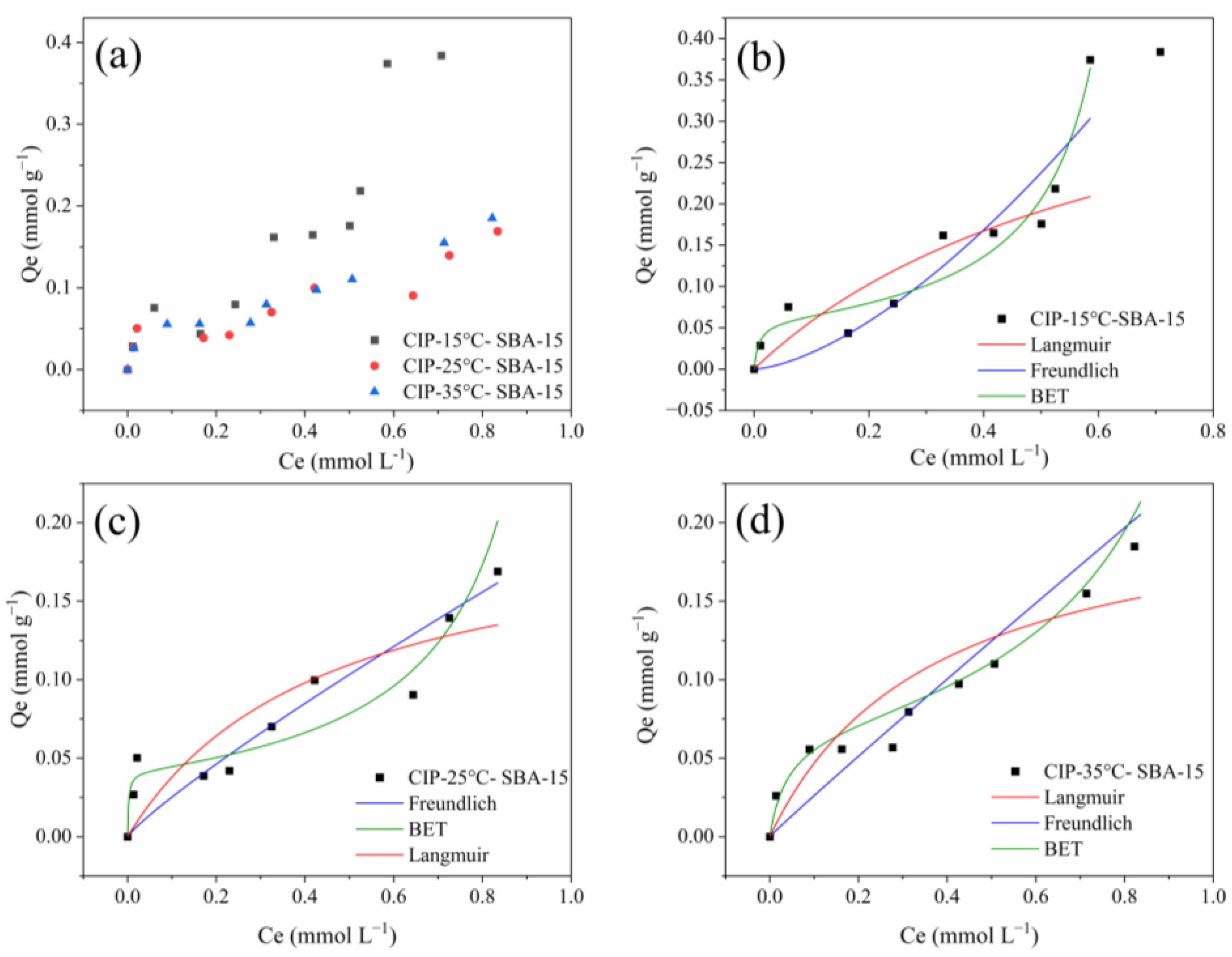
2.4. Equilibrium Isotherm
| Material | qL (mmol g−1) 1 | Dosage (g L−1) | Equilibrium Time (min) | Initial Concentration (C0) (mmol g−1) 1 | Temperature (°C) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBA-15 | 0.207 | 1.5 | 20 | 0.01–1.50 | 25 | This work |
| MCM-41 | 0.210 | 1.5 | 60 | 0.03–0.90 | 25 | Lu et al. [41] |
| Functional silica aerogel | 0.176 | 1.5 | 90 | 0.015–0.38 | 25 | Sert Çok et al. [46] |
| Bulk pomegranate peel | 0.016 | 10 | 240 | 0.03–0.36 | 25 | Hamadeen et al. [47] |
| Activated Carbon (Mangosteen Peel) | 0.090 | 0.75 | 60 | 0.15–1.20 | 25 | Tran et al. [38] |
| Chitosan/biochar hydrogel beads | 0.242 | 5 | 600 | 0.015–0.50 | 30 | Afzal et al. [48] |
| Chitosan/Kaolin/Fe3O4 | 0.144 | 0.75 | 60 | 0.03–0.60 | 25 | Ma et al. [49] |
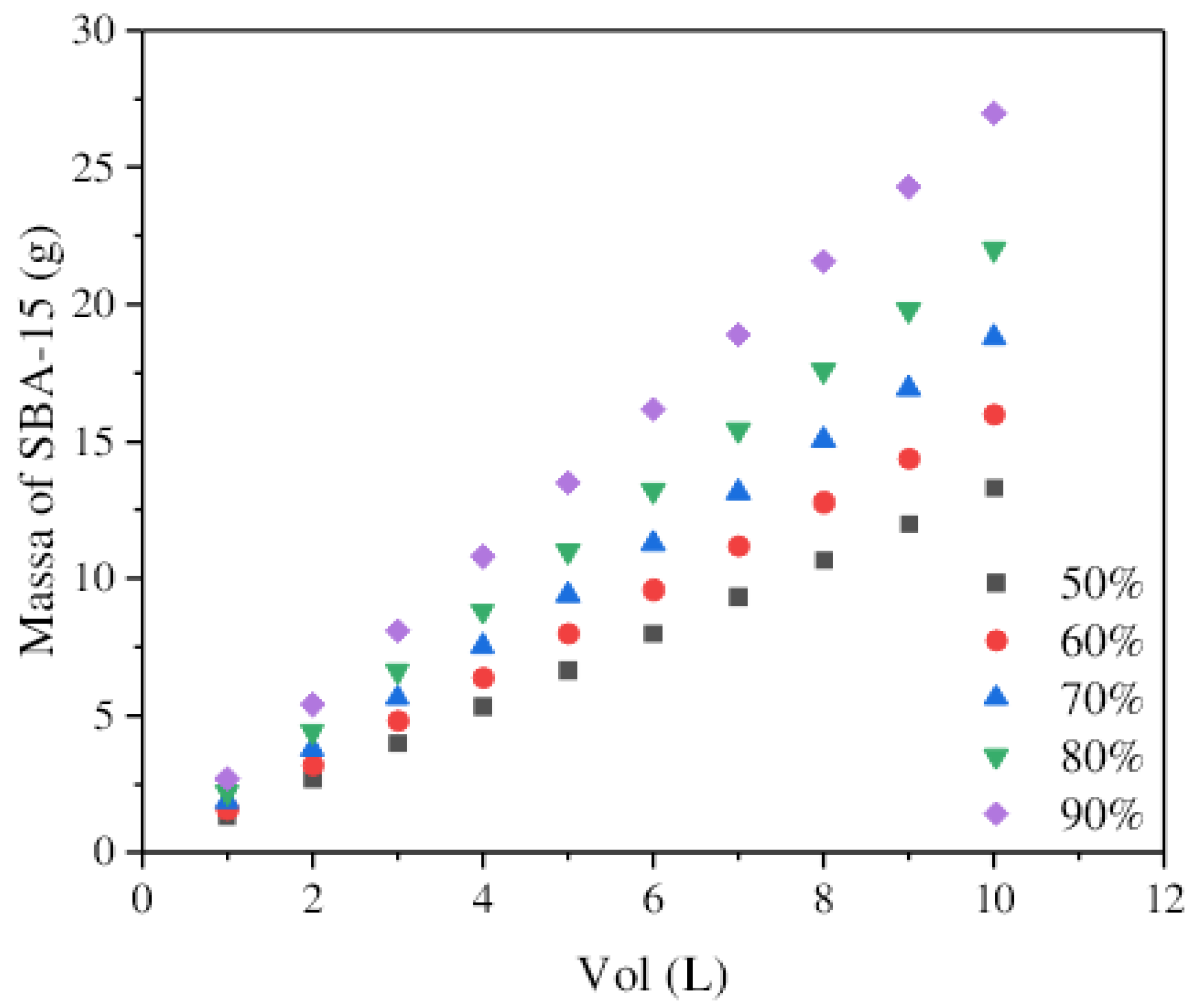
2.5. Simplified Batch Design for CIP-SBA-15
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Nanostructure
3.3. Adsorbate Characterization
3.4. Affinity Test
3.5. Determination of pHZPC and Zeta Potential
3.6. Kinetics, Equilibrium Isotherms, and Thermodynamic Studies
3.7. The Simplified Batch Design
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Solliec, M.; Roy-Lachapelle, A.; Gasser, M.-O.; Coté, C.; Généreux, M.; Sauvé, S. Fractionation and Analysis of Veterinary Antibiotics and Their Related Degradation Products in Agricultural Soils and Drainage Waters Following Swine Manure Amendment. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 543, 524–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheran, M.; Naghdi, M.; Brar, S.K.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Emerging Contaminants: Here Today, There Tomorrow! Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2018, 10, 122–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veetil, D.P.; Mercier, G.; Blais, J.F.; Chartier, M.; Tran, L.H.; Taillard, V. Remediation of Contaminated Dredged Sediments Using Physical Separation Techniques. Soil Sediment Contam. 2014, 23, 932–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Mofijur, M.; Nuzhat, S.; Chowdhury, A.T.; Rafa, N.; Uddin, M.A.; Inayat, A.; Mahlia, T.M.I.; Ong, H.C.; Chia, W.Y.; et al. Recent Developments in Physical, Biological, Chemical, and Hybrid Treatment Techniques for Removing Emerging Contaminants from Wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 416, 125912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Qureshi, M.; Vishwakarma, D.K.; Al-Ansari, N.; Kuriqi, A.; Elbeltagi, A.; Saraswat, A. A Review on Emerging Water Contaminants and the Application of Sustainable Removal Technologies. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, M.K.; Sung, T.I.; Cho, E.S.; Namkung, K.C.; Bae, D.J.; Park, I.H. Magnetic Separation for Contaminants in Wastewater Using Magnetic Micro Bead. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2012, 48, 3768–3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, J.; Banisharif, F.; Khataee, A. Amine-Functionalized Zr-MOF/CNTs Nanocomposite as an Efficient and Reusable Photocatalyst for Removing Organic Contaminants. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolong, N.; Ismail, A.F.; Salim, M.R.; Matsuura, T. A Review of the Effects of Emerging Contaminants in Wastewater and Options for Their Removal. Desalination 2009, 239, 229–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esfandiar, N.; Suri, R.; McKenzie, E.R. Competitive Sorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb and Zn from Stormwater Runoff by Five Low-Cost Sorbents; Effects of Co-Contaminants, Humic Acid, Salinity and PH. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 423, 126938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akinnawo, S.O. Eutrophication: Causes, Consequences, Physical, Chemical and Biological Techniques for Mitigation Strategies. Environ. Chall. 2023, 12, 100733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, G.; Tafese, T.; Abda, E.M.; Kamaraj, M.; Assefa, F. Factors Influencing the Bacterial Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon Contaminants in the Soil: Mechanisms and Impacts. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 9823362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Botella, E.; Valencia, S.; Rey, F. Zeolites in Adsorption Processes: State of the Art and Future Prospects. Chem. Rev. 2022, 122, 17647–17695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alomar, T.; Qiblawey, H.; Almomani, F.; Al-Raoush, R.I.; Han, D.S.; Ahmad, N.M. Recent Advances on Humic Acid Removal from Wastewater Using Adsorption Process. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 53, 103679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Li, C.; Liu, X.; Guo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Lu, G. Synthesis of Length Controllable Mesoporous SBA-15 Rods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 115, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.E.d.; Rigoti, E.; Mello, M.I.S.d.; Pergher, S.B.C. Tuning Textural Properties by Changing the Morphology of SBA-15 Mesoporous Materials. Materials 2024, 17, 2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zholobenko, V.L.; Khodakov, A.Y.; Impéror-Clerc, M.; Durand, D.; Grillo, I. Initial Stages of SBA-15 Synthesis: An Overview. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2008, 142, 67–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laskowski, Ł.; Laskowska, M.; Walcarius, A.; Doskocz, M.; Vila, N.; Karczmarska, A.; Pawlik, P.; Goraus, J.; Balin, K.; Dulski, M. Synthesis and Characterization of SBA-15 Silica Containing Cyclam inside Pores for Capturing Iron Chloride: Analysis of Interactions between Ferrous Chloride and Cyclam in a System with Strongly Dispersed Functional Groups on the SiO2 Surface. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2024, 378, 113243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of Gases, with Special Reference to the Evaluation of Surface Area and Pore Size Distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojeda-López, R.; Pérez-Hermosillo, I.J.; Marcos Esparza-Schulz, J.; Cervantes-Uribe, A.; Domínguez-Ortiz, A. SBA-15 Materials: Calcination Temperature Influence on Textural Properties and Total Silanol Ratio. Adsorption 2015, 21, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genç, N.; Dogan, E.C. Adsorption Kinetics of the Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin on Bentonite, Activated Carbon, Zeolite, and Pumice. Desalin. Water Treat. 2015, 53, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avcı, A.; İnci, İ.; Baylan, N. A Comparative Adsorption Study with Various Adsorbents for the Removal of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2019, 230, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizi, M.; El Bachra, F.E. Evaluation of the Ciprofloxacin Adsorption Capacity of Common Industrial Minerals and Application to Tap Water Treatment. Powder Technol. 2020, 362, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Ferrer, D.; Melo-Banda, J.A.; Silva-Rodrigo, R.; Páramo-García, U.; Verde-Gómez, J.Y.; Del-Angel-Vicente, P. Synthesis of Micro/Nanostructured Carbon from Refined Sugar and Its Electrochemical Performance. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2018, 13, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rekos, K.; Kampouraki, Z.C.; Sarafidis, C.; Samanidou, V.; Deliyanni, E. Graphene Oxide Based Magnetic Nanocomposites with Polymers as Effective Bisphenol-A Nanoadsorbents. Materials 2019, 12, 1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Andrade, J.R.; Oliveira, M.F.; Canevesi, R.L.S.; Landers, R.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Comparative Adsorption of Diclofenac Sodium and Losartan Potassium in Organophilic Clay-Packed Fixed-Bed: X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Characterization, Experimental Tests and Theoretical Study on DFT-Based Chemical Descriptors. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 312, 113427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca Jalil, M.E.; Baschini, M.; Sapag, K. Influence of PH and Antibiotic Solubility on the Removal of Ciprofloxacin from Aqueous Media Using Montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 114, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Han, X.; Xing, B. Adsorption of Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin on Carbon Nanotubes: PH Dependence and Thermodynamics. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 150–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, X.; Feng, J.; Lv, G.; Song, K.; Mei, L.; Liao, L.; Wang, X.; Xu, B. Adsorption Mechanism of Ciprofloxacin from Water by Synthesized Birnessite. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2015, 2015, 148423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bui, T.X.; Choi, H. Adsorptive Removal of Selected Pharmaceuticals by Mesoporous Silica SBA-15. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 602–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokunešoski, M.; Gulicovski, J.; Matović, B.; Logar, M.; Milonjić, S.K.; Babić, B. Synthesis and Surface Characterization of Ordered Mesoporous Silica SBA-15. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2010, 124, 1248–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Marques, V.B.; dos Santos, A.G.; de Lima Leite, R.H.; dos Santos, F.K.G. Functionalization of SBA-15 with EDTA and Its Application in Removing Ca2+ and Mg2+ Ions from Hard Water. Rev. Verde Agroecol. E Desenvolv. Sustentável 2020, 15, 300–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzeddine, Z.; Batonneau-Gener, I.; Pouilloux, Y.; Hamad, H.; Saad, Z. The Applicability of as Synthesized Mesoporous Carbon CMK-3 as a Heavy Metals Adsorbent: Application to Real Water Samples. Energy Sources Part A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2021, 43, 1675–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva de Assis, D.A.; dos Santos, E.G.; Eiras, D. Efficient and Reusable Mesoporous Silica Structures for Ciprofloxacin Removal from Water Media. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 60, 105144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Hu, F.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Dai, H.; Liu, Z. Preparation of a Graphitic Ordered Mesoporous Carbon and Its Application in Sorption of Ciprofloxacin: Kinetics, Isotherm, Adsorption Mechanisms Studies. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2016, 228, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.H.; Abdul Aziz, H.; Palaniandy, P.; Naushad, M.; Zouli, N. Ciprofloxacin Adsorption onto CNT Loaded Pumice: Adsorption Modelling, Kinetics, Equilibriums and Reusability Studies. J. Mol. Liq. 2024, 399, 124388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, H.; Wang, S.; Lin, J.Y.; Wang, Z.; Ren, J. Modification of a Magnetic Carbon Composite for Ciprofloxacin Adsorption. J. Environ. Sci. 2016, 49, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Li, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, C. Magnetic Nickel Cobalt Sulfide/Sodium Dodecyl Benzene Sulfonate with Excellent Ciprofloxacin Adsorption Capacity and Wide PH Adaptability. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 127208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, Q.T.; Do, T.H.; Ha, X.L.; Nguyen, H.P.; Nguyen, A.T.; Ngo, T.C.Q.; Chau, H.D. Study of the Ciprofloxacin Adsorption of Activated Carbon Prepared from Mangosteen Peel. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Zhao, S.; Jing, R.; Shao, Y.; Liu, X.; Lv, F.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Liu, A. Competitive Adsorption of Antibiotic Tetracycline and Ciprofloxacin on Montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 180, 105175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonelli, R.; Malpass, G.R.P.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin onto Thermally Modified Bentonite Clay: Experimental Design, Characterization, and Adsorbent Regeneration. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Xu, S.; Qiu, W.; Sun, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Ma, J. Adsorption and Desorption Behaviors of Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin on Functionalized Spherical MCM-41 for Water Treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Módenes, A.N.; Bazarin, G.; Borba, C.E.; Locatelli, P.P.P.; Borsato, F.P.; Pagno, V.; Pedrini, R.; Trigueros, D.E.G.; Espinoza-Quiñones, F.R.; Scheufele, F.B. Tetracycline Adsorption by Tilapia Fish Bone-Based Biochar: Mass Transfer Assessment and Fixed-Bed Data Prediction by Hybrid Statistical-Phenomenological Modeling. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Carvalho, C.; Costa Rodrigues, D.L.; Lima, É.C.; Santanna Umpierres, C.; Caicedo Chaguezac, D.F.; Machado Machado, F. Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies on the Adsorption of Ciprofloxacin by Activated Carbon Produced from Jerivá (Syagrus romanzoffiana). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 4690–4702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, C.; Jiang, W.; Chang, C. The Langmuir Monolayer Adsorption Model of Organic Matter into Effective Pores in Activated Carbon. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2013, 389, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Almeida, A.S.V.; Mastelaro, V.R.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Prediger, P.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of 17α-Ethinylestradiol onto a Novel Nanocomposite Based on Graphene Oxide, Magnetic Chitosan and Organoclay (GO/MCS/OC): Kinetics, Equilibrium, Thermodynamics and Selectivity Studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 47, 102729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sert Çok, S.; Koç, F.; Len, A.; Almásy, L.; Dudás, Z. Silica Aerogels Modified with Vinyl, Epoxide, Methacrylate Moieties for the Removal of Ciprofloxacin by Adsorption from Water. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 354, 129112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadeen, H.M.; Elkhatib, E.A. New Nanostructured Activated Biochar for Effective Removal of Antibiotic Ciprofloxacin from Wastewater: Adsorption Dynamics and Mechanisms. Environ. Res. 2022, 210, 112929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afzal, M.Z.; Sun, X.F.; Liu, J.; Song, C.; Wang, S.G.; Javed, A. Enhancement of Ciprofloxacin Sorption on Chitosan/Biochar Hydrogel Beads. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 639, 560–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Dai, J.; Dai, X.; Yan, Y. Preparation and Characterization of Chitosan/Kaolin/Fe3O4 Magnetic Microspheres and Their Application for the Removal of Ciprofloxacin. Adsorpt. Sci. Technol. 2014, 32, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huš, M.; Dasireddy, V.D.B.C.; Strah Štefančič, N.; Likozar, B. Mechanism, Kinetics and Thermodynamics of Carbon Dioxide Hydrogenation to Methanol on Cu/ZnAl2O4 Spinel-Type Heterogeneous Catalysts. Appl. Catal. B 2017, 207, 267–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhagiya Singam, E.R.; Zhang, Y.; Magnin, G.; Miranda-Carvajal, I.; Coates, L.; Thakkar, R.; Poblete, H.; Comer, J. Thermodynamics of Adsorption on Graphenic Surfaces from Aqueous Solution. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2019, 15, 1302–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, D.; Xu, Z.; Shi, J.; Shen, L.; He, Z. Adsorption Characteristics of Ciprofloxacin on the Schorl: Kinetics, Thermodynamics, Effect of Metal Ion and Mechanisms. J. Water Reuse Desalin. 2018, 8, 350–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzosike, A.O.; Ofudje, E.A.; Adeogun, A.I.; Akinyele, J.O.; Idowu, M.A. Comparative Analysis of Bisphenol-A Removal Efficiency from Water: Equilibrium, Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Optimization Evaluations. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2022, 19, 4645–4658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sá Costa, H.P.; Duarte, E.D.V.; da Silva, M.G.C.; Vieira, M.G.A. Adsorption of Diclofenac and Losartan Using Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Functionalized with Iron Nanoparticles via the Green Route: Equilibrium, Thermodynamics, and Machine Learning Studies. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fredrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock Copolymer Syntheses of Mesoporous Silica with Periodic 50 to 300 Angstrom Pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarneau, A.; Cambon, H.; Di Renzo, F.; Ryoo, R.; Choi, M.; Fajula, F. Microporosity and Connections between Pores in SBA-15 Mesostructured Silicas as a Function of the Temperature of Synthesis. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie Der Sogenannten Adsorption Gelöster Stoffe. Zeitschr Für Chem. Und Ind. Der Kolloide 1907, 2, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. A Comparison of Chemisorption Kinetic Models Applied to Pollutant Removal on Various Sorbents. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 1998, 76, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, W.J., Jr.; Morris, J.C. Kinetics of Adsorption on Carbon from Solution. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. 1963, 89, 31–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puranik, P.R.; Modak, J.M.; Paknikar, K.M. A Comparative Study of the Mass Transfer Kinetics of Metal Biosorption by Microbial Biomass; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1999; Volume 52. [Google Scholar]
- Langmuir, I. The Adsorption of Gases on Plane Surfaces of Glass, Mica and Platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haring, M.M. Colloid and Capillary Chemistry (Freundlich, Herbert). J. Chem. Educ. 1926, 3, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebadi, A.; Soltan Mohammadzadeh, J.S.; Khudiev, A. What Is the Correct Form of BET Isotherm for Modeling Liquid Phase Adsorption? Adsorption 2009, 15, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milonjić, S.K. A Consideration of the Correct Calculation of Thermodynamic Parameters of Adsorption. J. Serbian Chem. Soc. 2007, 72, 1363–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
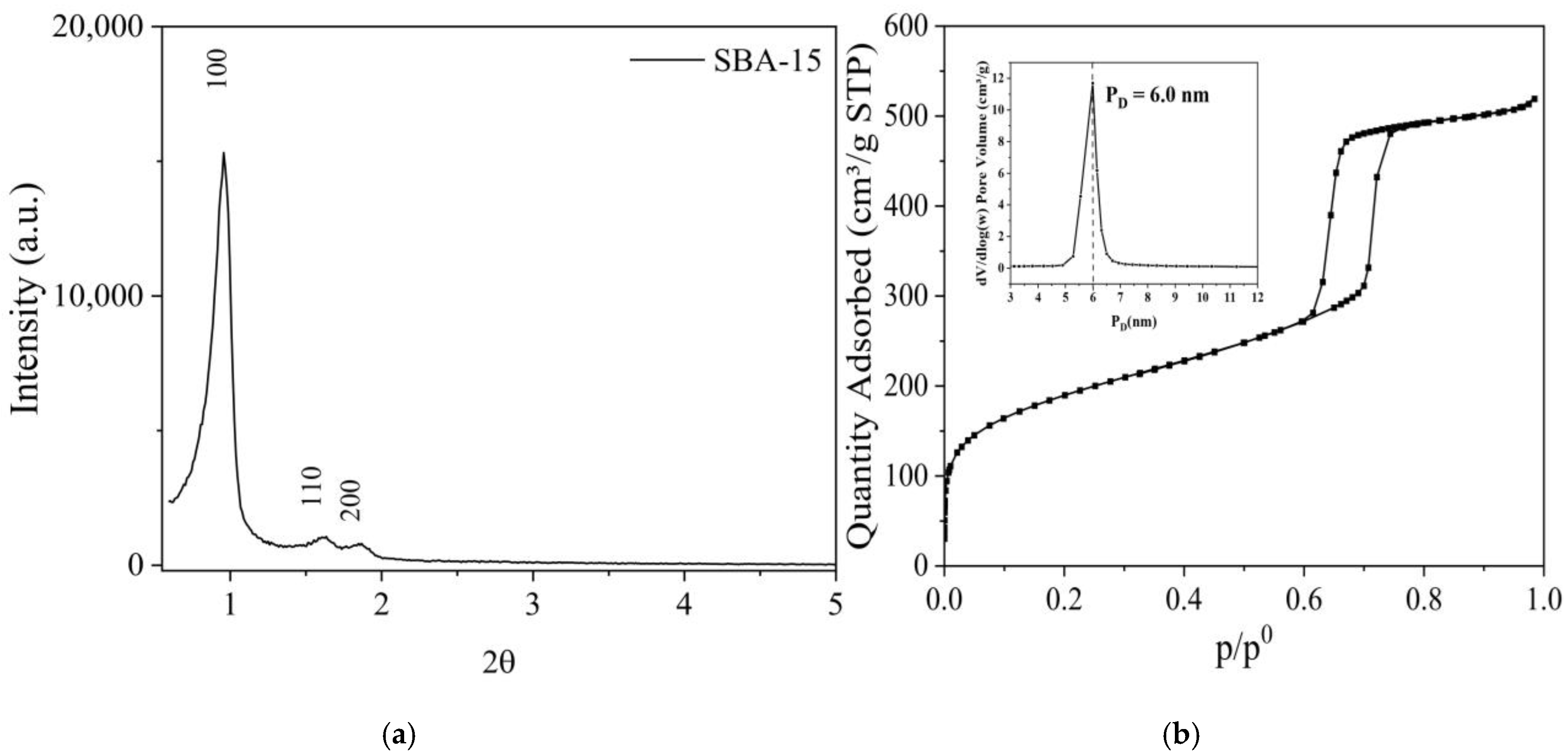
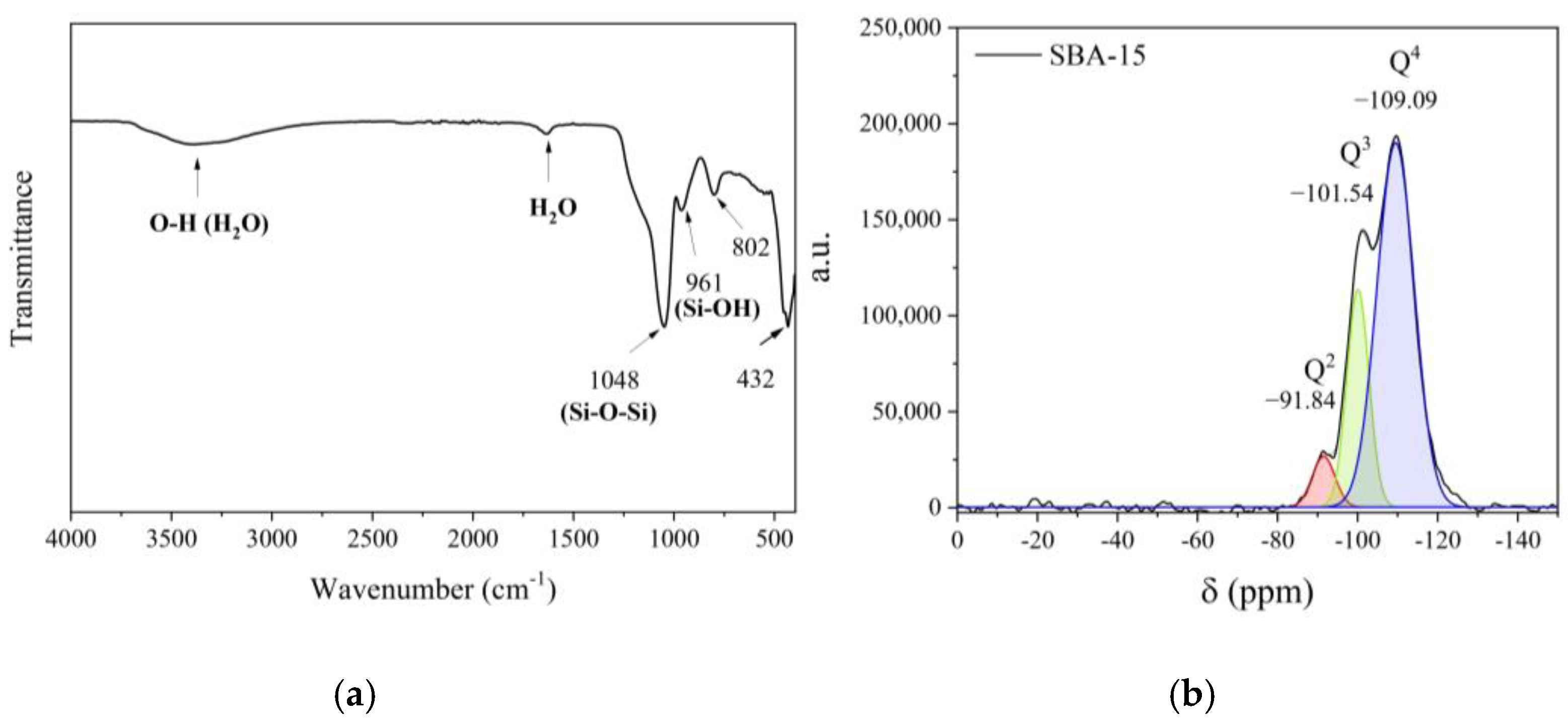
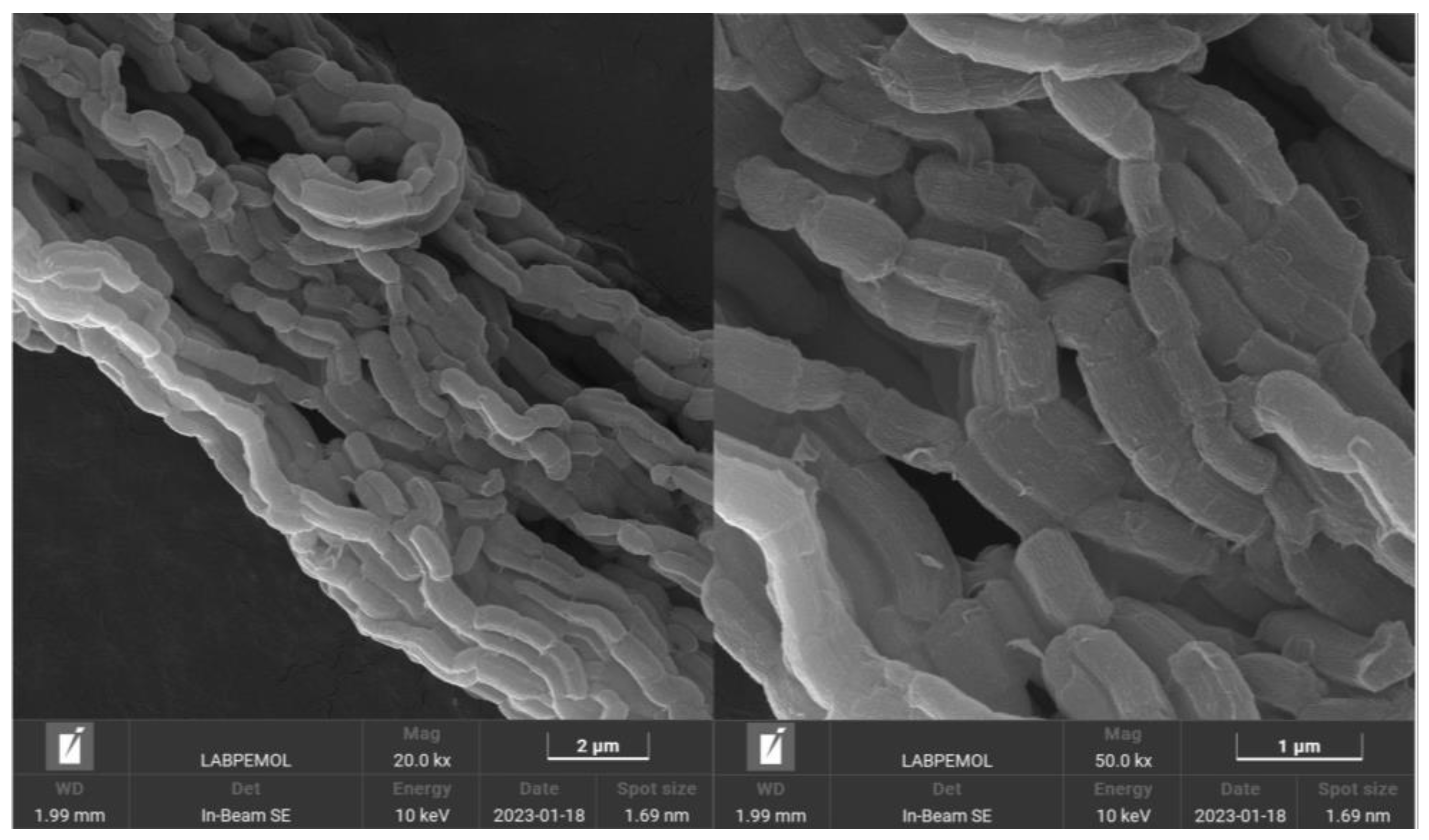
| Material | SBET (m2/g) | Vmeso (cm3/g) | Vmicro (cm3/g) | Sext (m2/g) | DBJH (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBA-15 | 688.7 | 0.731 | 0.073 | 504.8 | 6.0 |
| Material | Signal | δ (ppm) | Area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| SBA-15 | Q2 | −91.84 | 5.73 |
| Q3 | −101.54 | 30.48 | |
| Q4 | −109.09 | 63.79 |
| Models | Parameters | (C0) (mmol L−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.10 | 0.30 | 0.50 | ||
| qe | 0.066 | 0.109 | 0.132 | |
| PFO | qPFO | 0.060 | 0.102 | 0.122 |
| k1 | 2.196 | 3.568 | 5.660 | |
| R2Adj | 0.952 | 0.957 | 0.982 | |
| AICc | −124.559 | −113.199 | −105.539 | |
| MRD (%) | 3.54 | 0.60 | 0.83 | |
| PSO | qPSO | 0.061 | 0.106 | 0.126 |
| k2 | 8.346 | 7.872 | 23.403 | |
| R2Adj | 0.955 | 0.982 | 0.986 | |
| AICc | −87.749 | −76.599 | −79.779 | |
| MRD (%) | 3.46 | 1.35 | 1.06 | |
| IPD | Ki | 0.00264 | 0.00517 | 0.00389 |
| c | 0.0537 | 0.0862 | 0.115 | |
| R2Adj | 0.8678 | 0.859 | 0.764 | |
| AICc | −83.843 | −60.403 | −49.434 | |
| MRD (%) | 4.31 | 8.01 | 18.99 | |
| EMTR | KTM | 1.441 | 1.774 | 2.188 |
| R2 | 0.978 | 0.980 | 0.992 | |
| AICc | −128.222 | −116.880 | −123.290 | |
| MRD (%) | 5.4 | 5.1 | 3.1 | |
| Models | Parameters | Temperature (°C) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | 25 | 35 | ||
| qmax | 0.374 | 0.207 | 0.208 | |
| Langmuir | qL | 0.450 | 0.207 | 0.220 |
| KL | 1.477 | 2.249 | 2.705 | |
| R2Adj | 0.674 | 0.697 | 0.809 | |
| AICc | −44.858 | −55.204 | −58.524 | |
| MRD (%) | 35.32 | 38.17 | 27.41 | |
| Freundlich | KF | 0.693 | 0.189 | 0.244 |
| 1/n | 1.544 | 0.876 | 0.971 | |
| R2Adj | 0.788 | 0.645 | 0.919 | |
| AICc | −36.547 | −35.644 | −50.798 | |
| MRD (%) | 28.44 | 29.44 | 25.51 | |
| BET | qb | 0.059 | 0.041 | 0.068 |
| Kb | 121.581 | 449.752 | 25.871 | |
| Ku | 1.434 | 0.954 | 0.818 | |
| R2Adj | 0.933 | 0.905 | 0.944 | |
| AICc | −62.457 | −63.816 | −71.705 | |
| MRD (%) | 19.66 | 19.56 | 11.53 | |
| T (°C) | ΔH° (kJ mol−1) | ΔS° (J mol−1 K−1) | ΔG° (kJ mol−1) | Ea (kJ mol−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 15 | −55.380 | −89.208 | −29.675 | −52.902 |
| 25 | −28.783 | −52.819 | ||
| 35 | −27.819 | −52.298 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, F.E.d.; Spaolonzi, M.P.; Vieira, M.G.A.; Pergher, S.B.C. Ordered Mesopore Channels of SBA-15 for Contaminant Adsorption: Characterization, Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. Molecules 2025, 30, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051040
Silva FEd, Spaolonzi MP, Vieira MGA, Pergher SBC. Ordered Mesopore Channels of SBA-15 for Contaminant Adsorption: Characterization, Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. Molecules. 2025; 30(5):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051040
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Francisco Emanuel da, Marcela Pires Spaolonzi, Melissa G. A. Vieira, and Sibele B. C. Pergher. 2025. "Ordered Mesopore Channels of SBA-15 for Contaminant Adsorption: Characterization, Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies" Molecules 30, no. 5: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051040
APA StyleSilva, F. E. d., Spaolonzi, M. P., Vieira, M. G. A., & Pergher, S. B. C. (2025). Ordered Mesopore Channels of SBA-15 for Contaminant Adsorption: Characterization, Kinetic, Equilibrium, and Thermodynamic Studies. Molecules, 30(5), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30051040









