Theoretical Investigation of Competitive Adsorption of Light and Heavy Rare Earth Ions on the (001) Surface of Kaolinite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Experimental Results
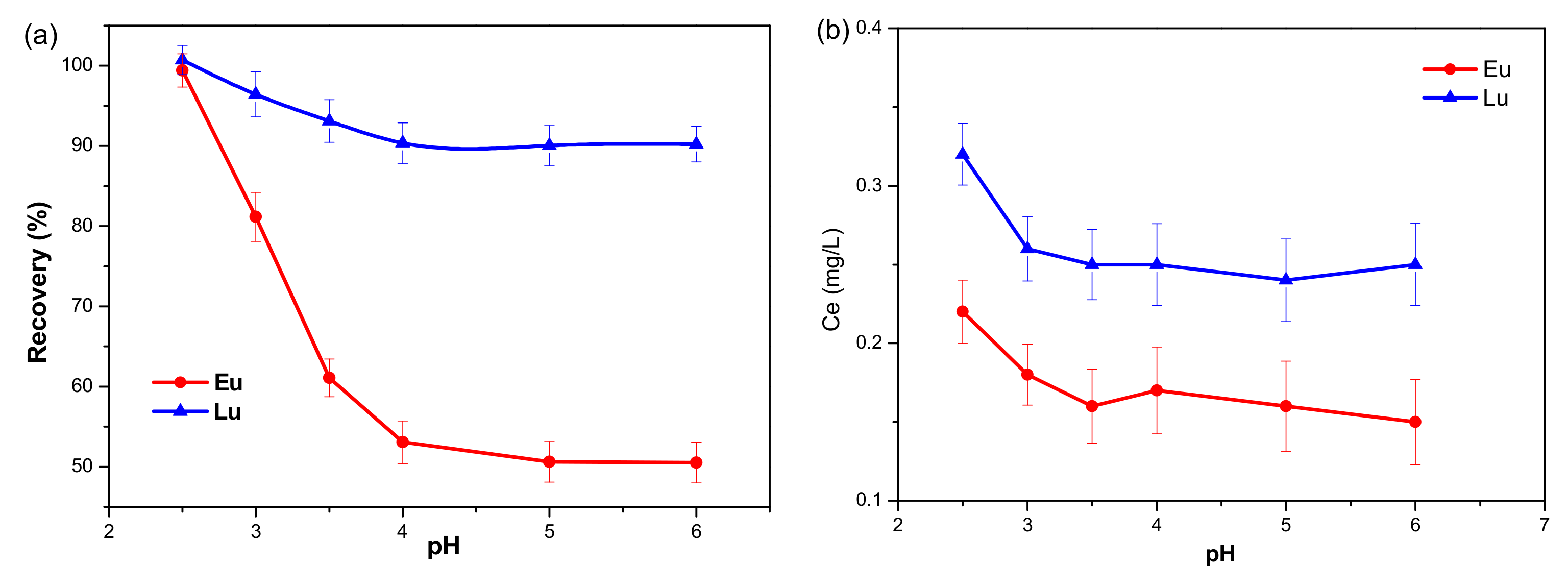
2.1.1. Desorption Characteristics of Eu3+ and Lu3+ from Kaolinite
2.1.2. Adsorption Kinetics
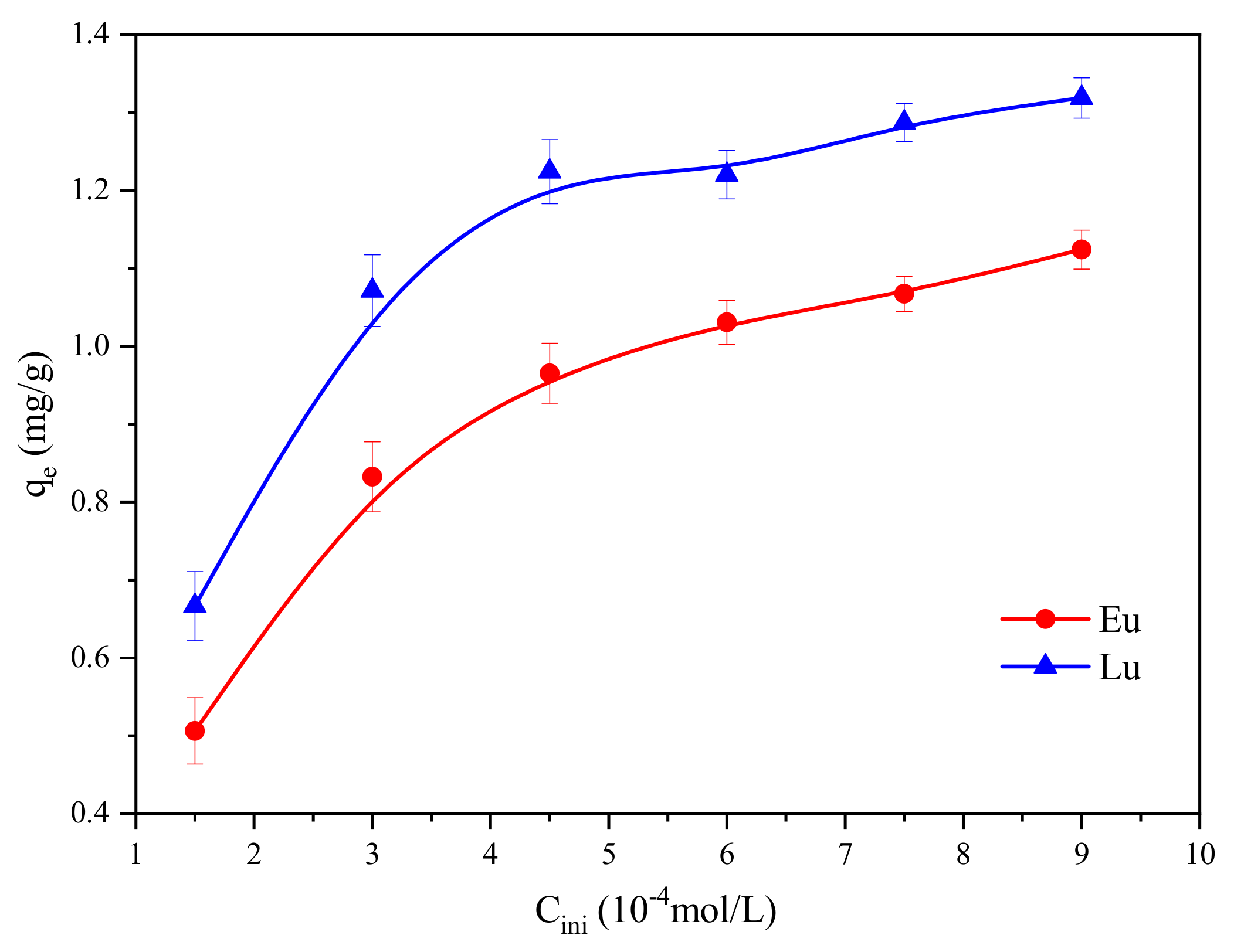
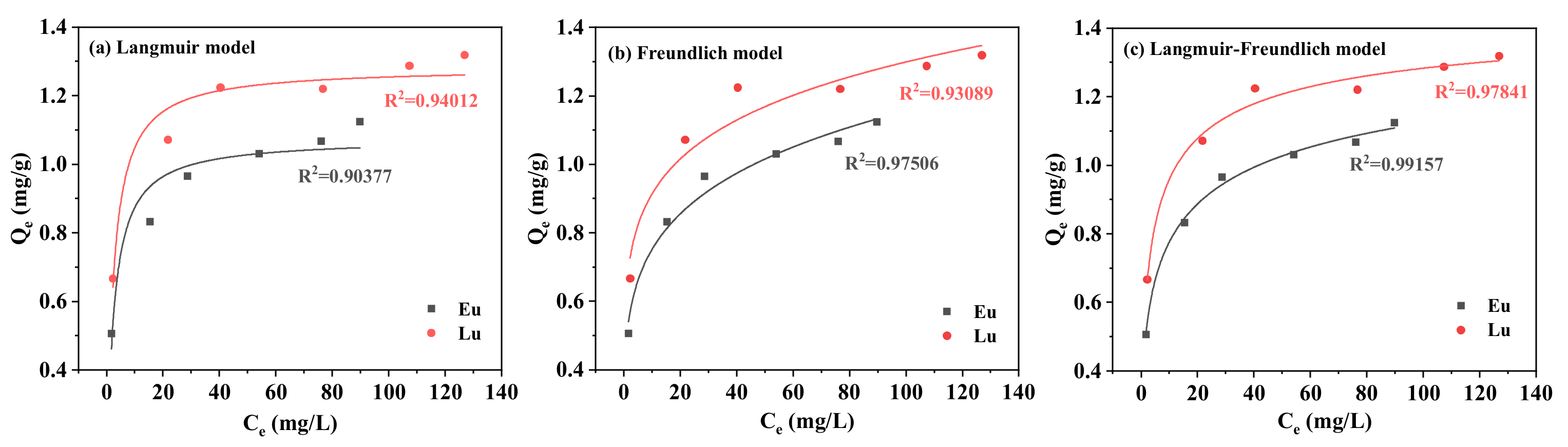
2.1.3. Adsorption Isotherms
2.2. MD Calculation
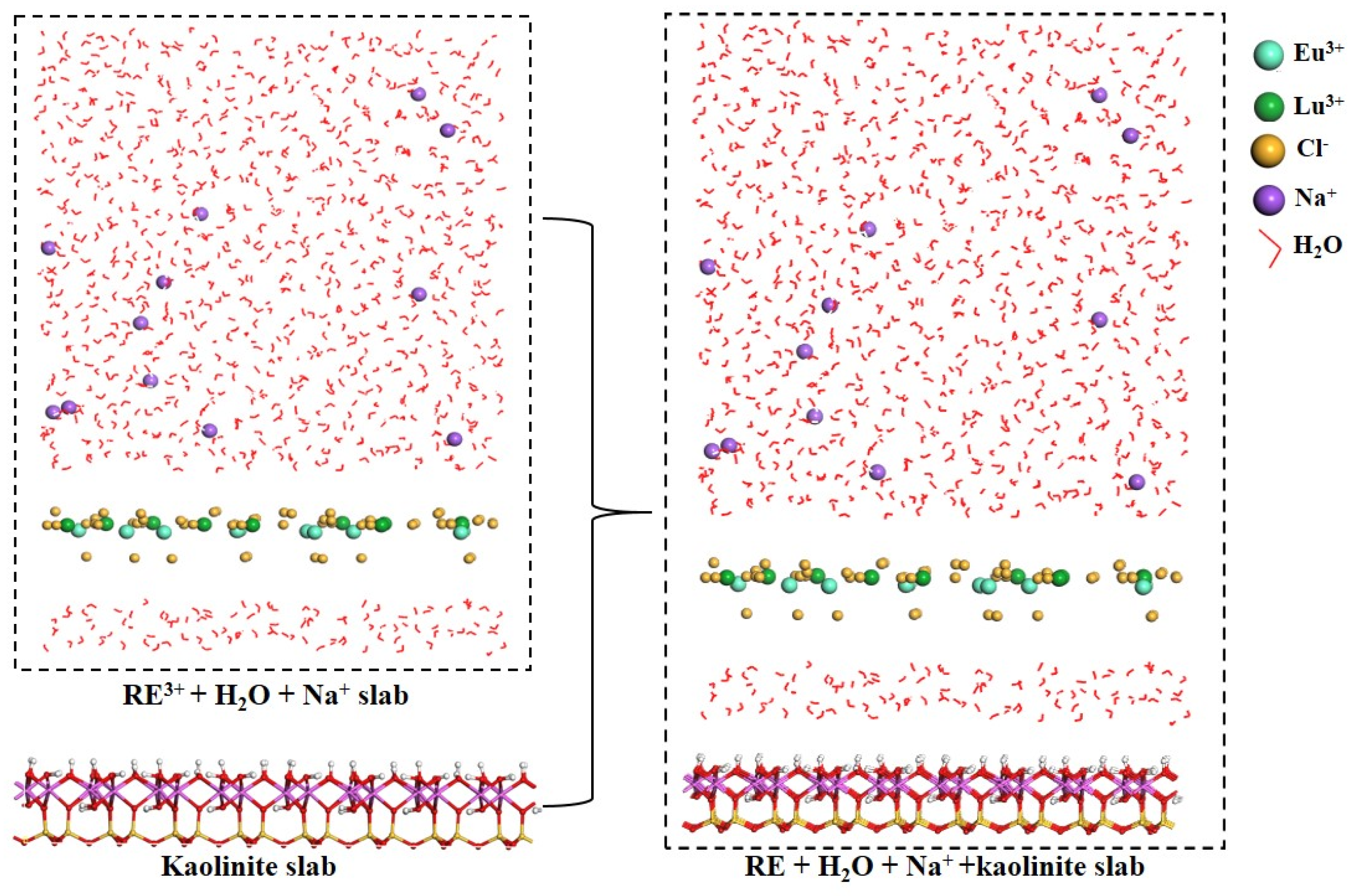
2.2.1. Adsorption Behavior of Eu3+ and Lu3+
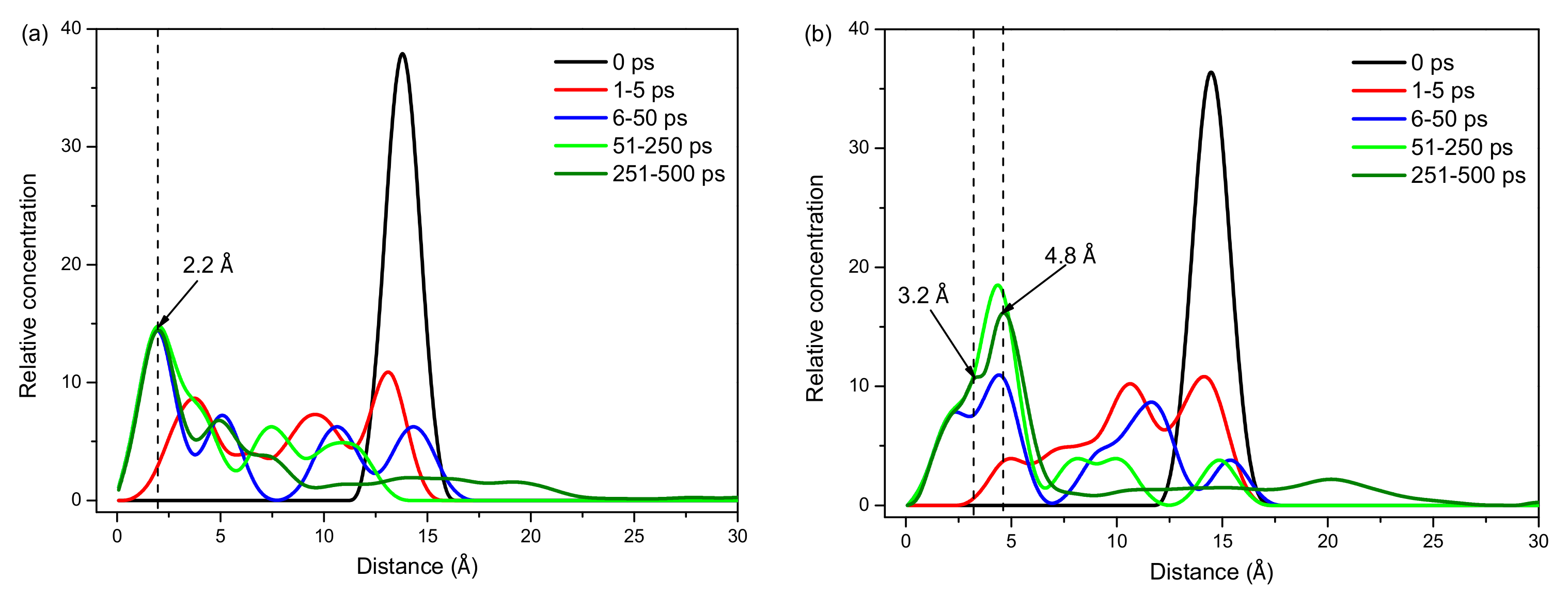
2.2.2. Concentration Distribution of Eu3+ and Lu3+ on the Surface
2.2.3. Diffusion Abilities of Eu3+ and Lu3+
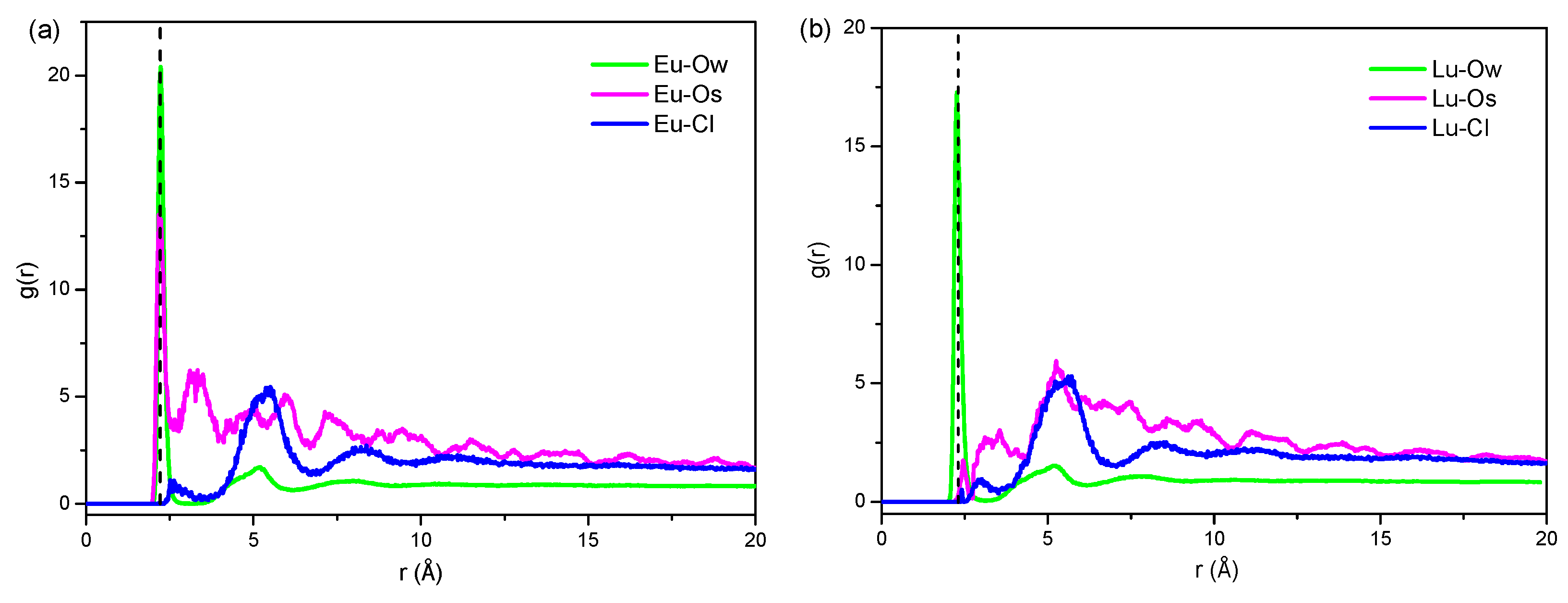
2.2.4. Radial Distribution Function of Eu3+ and Lu3+
3. Experiments and Models
3.1. Experiment Details
3.1.1. Experimental Materials
3.1.2. Desorption of RE Ions from Kaolinite
3.1.3. Effect of Contact Time on Adsorption
3.1.4. Adsorption Isotherm Experiments
3.2. Details of MD Calculations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RE | Rare earth |
| MD | Molecular dynamics |
| DFT | Density functional theory |
| MSD | Mean square displacement |
References
- Marx, J.; Schreiber, A.; Zapp, P.; Walachowicz, F. Comparative Life Cycle Assessment of NdFeB Permanent Magnet Production from Different Rare Earth Deposits. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 5858–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, Z.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Liang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, G. Dy-Modified Mn/TiO2 Catalyst Used for the Selective Catalytic Reduction of NO in Ammonia at Low Temperatures. Molecules 2024, 29, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Song, W.; He, C.; Wang, Z. The Overview of Distribution, Type and Genesis of the Exogenetic Rare Earth Elements (REE) Deposits. Bull. Mineral. Petrol. Geochem. 2015, 34, 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Dong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chai, Y. The Synergistic Extraction of Heavy Rare Earth Elements using EHEHP-type and BTMPP-type Functional Ionic Liquids. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 49500–49507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, J.; Xu, Z.; Chi, R. Process optimization of Rare Earth and Aluminum Leaching from Weathered Crust Elution-deposited Rare Earth Ore with Compound Ammonium Salts. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Chen, Y.; Feng, Z.Y.; Huang, X.W.; Huang, L.; Long, Z.; Cui, D. Leaching Characteristics of Ion-adsorption Type Rare Earths Ore with Magnesium Sulfate. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 2015, 25, 3784–3790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, C.; Wang, D.; Li, F.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, X.; Li, Y. Leaching Ion Adsorption Rare Earth by Aluminum Sulfate for Increasing Efficiency and Lowering the Environmental Impact. J. Rare Earths 2019, 37, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremleva, A.; Krueger, S.; Roesch, N. Density functional model studies of uranyl adsorption on (001) surfaces of kaolinite. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9515–9524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tombacz, E.; Szekeres, M. Surface Charge Heterogeneity of Kaolinite in Aqueous Suspension in Comparison with Montmorillonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2006, 34, 105–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbey, J.; Thomas, F.; Razafitianamaharavo, A.; Caillet, C.; Villieras, F. A Comparative Study of Some Kaolinites Surface Properties. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 172, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Qiu, T.S.; Yan, H.S.; Long, Q.B.; Wu, H.; Li, X.B.; Zhu, D.M. Investigation of Protonation and Deprotonation Processes of Kaolinite and Its Effect on the Adsorption Stability of Rare Earth Elements. Colloids Surf. A 2022, 642, 128596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granados, C.; Vilchis, G.; Jiménez, R.; Quiroz, G. Adsorption Behaviour of La(III) and Eu(III) Ions from Aqueous Solutions by Hydroxyapatite: Kinetic, Isotherm, and Thermodynamic Studies. J. Chem. 2013, 2013, 751696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, G.; Papangelakis, V. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements Adsorbed on Clay Minerals: I. Desorption Mechanism. Hydrometallurgy 2012, 117, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldoveanu, G.; Papangelakis, V. Recovery of Rare Earth Elements Adsorbed on Clay Minerals: II. Leaching with Ammonium Sulfate. Hydrometallurgy 2013, 131, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.F.; Huang, L.; Long, Z.; Feng, Z.Y.; Wang, L. Adsorption Ability of Rare Earth Elements on Clay Minerals and Its Practical Performance. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liang, X.; Ma, L.; Huang, J.; He, H.P.; Zhu, J. Adsorption of REEs on Kaolinite and Halloysite: A Link to the REE Distribution on Clays in the Weathering Crust of Granite. Chem. Geol. 2019, 525, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, B.; Rath, S. Density functional Theory and Molecular Dynamics Insights into the Site-dependent Adsorption of Hydrogen Fluoride on Kaolinite. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 299, 112265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Rao, M.; Wang, F.; Tao, Y.; Lu, L. Density Functional Simulation of Adsorption Behavior within the Dicalcium Silicate-Accelerated Carbonation System. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 16825–16832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hue, K.; Lew, J.; Muo, M.; Matar, O.; Luckham, P.; Muller, E. Molecular Dynamics Simulation of Polyacrylamide Adsorption on Calcite. Molecules 2023, 28, 6367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Wu, H.; Yan, H.S.; Li, X.B.; Zhou, X.W.; Qiu, T.S. Theoretical Investigation of Hydrated [Lu(OH)2]+ Adsorption on Kaolinite(0 0 1) Surface with DFT Calculations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 565, 150473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Yan, H.S.; Qiu, X.H.; Wu, H.; Zhou, X.W.; Wu, H.; Li, X.B.; Qiu, T.S. Adsorption of La on Kaolinite (0 0 1) Surface in Aqueous System: A Combined Simulation with an Experimental Verification. J. Mol. Liq. 2022, 347, 117956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, G.; Min, F.; Qin, L. Atomic-level Insights into the Adsorption of Rare Earth Y(OH)3-nn+ (n = 1–3) Ions on Kaolinite Surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 469, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lai, Y.; Peng, C.L. Adsorption of Rare Earth Yttrium and Ammonium Ions on Kaolinite Surfaces: A DFT study. Theor. Chem. Acc. 2018, 137, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.; Banerjee, T. Study on the Extraction of Acetamiprid and Imidacloprid from an Aqueous Environment Using Menthol-Based Hydrophobic Eutectic Solvents: Quantum Chemical and Molecular Dynamics Insights. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 9, 4227–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, W.C.; Cui, K.Q.; Cheng, C.H.; Ren, Y.Y.; Wu, K. Molecular Simulation of the Water Diffusion Behavior and Electronic Properties of Boron-Nitride-Composited Mineral Oil. Molecules 2024, 29, 4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, S.; Li, F.J.; Yan, H.S.; Qiu, T.S.; Long, Q.B.; Zhou, X.W.; Li, Y.; Xia, Y. Step-Leaching and Pre-Enrichment of Light and Heavy REEs from Kaolinite and Montmorillonite. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 11815–11823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhu, C.; Sun, Y.; Duan, H.; Ye, W.; Wu, D. Adsorption of La(III) onto GMZ Bentonite: Effect of Contact Time, Bentonite Content pH Value and Ionic Strength. J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem. 2012, 292, 1339–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Zhu, C.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, B.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Q.; Ye, W. Preparation, Characterization and Adsorptive Study of Rare Earth Ions using Magnetic GMZ Bentonite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 62–63, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.H.; Yang, L.F.; Zhang, L.; Li, C.C.; Wang, D.S.; Zhou, X.M.; Zhou, X.Z.; Li, Y.X. Classification and High Efficient Leaching of Ion Adsorption Rare Earth Based on Its pH Dependence. Chin. J. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 34, 112–122. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie Der Sogenannten Adsorption Geloster Stoffe. K. Sven. Vetenskapsakad. Handl. 1989, 24, 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.; Mckay, G. Pseudo-second Order Model for Sorption Processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.D.; Li, P.; Liu, W.; Chang, Q.; Han, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.; Li, Q.; Zheng, S. Adsorption Mechanism of Yttrium Ions onto Ion-adsorption Type Rare Earths Ore. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 299, 121641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshameri, A.; He, H.; Xin, C.; Zhu, J.; Wei, X.; Zhu, R.; Wang, H. Understanding the Role of Natural Clay Minerals as Effective Adsorbents and Alternative Source of Rare Earth Elements: Adsorption Operative Parameters. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 185, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption Isotherm Models: Classification, Physical Meaning, Application and Solving Method. Chemosphere 2020, 258, 127279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J. Comparison of Linearization Methods for Modeling the Langmuir Adsorption Isotherm. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 296, 111850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H. Concerning Adsorption in Solutions. J. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–490. [Google Scholar]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Padmesh, T.; Palanivelu, K.; Velan, M. Biosorption of Nickel(II) Ions onto Sargassum Wightii: Application of Two-Parameter and Three-Parameter Isotherm Models. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 133, 304–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppu, G.P.; Clement, T.P. A Modified Langmuir-Freundlich Isotherm Model for Simulating pH-Dependent Adsorption Effects. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2012, 129–130, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizian, S.; Eris, S.; Wilson, L.D. Re-Evaluation of the Century-Old Langmuir Isotherm for Modeling Adsorption Phenomena in Solution. Chem. Phys. 2018, 513, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.N.; Lima, E.C.; Juang, R.-S.; Bollinger, J.-C.; Chao, H.-P. Thermodynamic Parameters of Liquid–Phase Adsorption Process Calculated from Different Equilibrium Constants Related to Adsorption Isotherms: A Comparison Study. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 9, 106674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajahmundry, G.K.; Garlapati, C.; Kumar, P.S.; Alwi, R.S.; Vo, D.-V.N. Statistical Analysis of Adsorption Isotherm Models and Its Appropriate Selection. Chemosphere 2021, 276, 130176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourg, I.C.; Lee, S.S.; Fenter, P.; Tournassat, C. Stern Layer Structure and Energetics at Mica-Water Interfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2017, 121, 9402–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Chen, M.; Zhou, H.J.; Zhu, R.L.; Zhu, J.X.; He, H.P. Competitive Adsorption of Alkali Ions on Aqueous Mica Surface: A Force Field Comparison Molecular Dynamics Study. Appl. Clay Sci. 2022, 219, 106436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, I.F.; Bunker, B.A.; Cygan, R.T. Molecular Dynamics Modeling of Ion Adsorption to the Basal Surfaces of Kaolinite. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 6753–6762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’angelo, P.; Zitolo, A.; Migliorati, V.; Chigllemi, G.; Duvail, M.; Vitorge, P.; Abadie, S.; Spezia, R. Revised Ionic Radii of Lanthanoid(III) Ions in Aqueous Solution. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 4572–4579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.P.; Hu, Y.H.; Wang, D.Z.; Xu, J. Mechanism of interaction between cationic surfactant and kaolinite. J. Cent. South Univ. Nat. Sci. 2024, 35, 228–233. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, L.; Dong, J. Adsorption of Mg2+ and K+ on the Kaolinite (0 0 1) Surface in Aqueous System: A Combined DFT and AIMD Study with an Experimental Verification. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 538, 148158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kong, X.; Zhang, B.; Wang, J. Adsorption of Zn(II) on the Kaolinite(001) Surfaces in Aqueous Environment: A Combined DFT and Molecular Dynamics Study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.; Wang, J. Copper(II) Adsorption on the Kaolinite(001) Surface: Insights From First-Principles Calculations and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RappéA, K.; Casewit, C.; Colwell, K.; Goddard, W.; Skiff, W. UFF, a Full Periodic Table Force Field for Molecular Mechanics and Molecular Dynamics Simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10024–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, H.; Postma, J.; Gunsteren, W.; Hermans, J. Interaction Models for Water in Relation to Protein Hydration, Intermolecular Forces; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]




| RE | Pseudo-First-Order | Pseudo-Second-Order | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe (mg/g) | k1 (min−1) | R2 | qe (mg/g) | k2 (g/mg/min) | R2 | |
| EuLu | 0.28 0.172 | 0.024 0.022 | 0.978 0.954 | 1.078 1.281 | 0.299 0.685 | 0.998 0.999 |
| Adsorption Isotherm Model | Unit | RE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Eu | Lu | ||
| Qmax-exp | mg/g | 1.12 | 1.32 |
| 1. Langmuir model | |||
| QL | mg/g | 1.07 ± 0.04 | 1.28 ± 0.03 |
| KL | L/mg | 0.43 ± 0.12 | 0.45 ± 0.09 |
| adj-R2 | - | 0.90377 | 0.94012 |
| red-χ2 | - | 0.00493 | 0.00354 |
| 2. Freundlich model | |||
| KF | 0.49 ± 0.03 | 0.64 ± 0.06 | |
| nF | − | 0.19 ± 0.02 | 0.15 ± 0.02 |
| adj-R2 | − | 0.97506 | 0.93089 |
| red-χ2 | − | 0.00128 | 0.00408 |
| 3. Langmuir-Freundlich model | |||
| QLF | mg/g | 1.56 ± 0.24 | 1.49 ± 0.14 |
| KLF | L/mg | 0.09 ± 0.08 | 0.30 ± 0.12 |
| nLF | - | 0.41 ± 0.08 | 0.54 ± 0.13 |
| adj-R2 | - | 0.99157 | 0.97841 |
| red-χ2 | - | 4.32 × 10−4 | 0.00128 |
| Ion | Eu3+ | Lu3+ |
|---|---|---|
| D (m2/s) | 7.6 × 10−10 | 6.8 × 10−10 |
| Start Radius (Å) | First Sharp Peak (Å) | Cutoff Radius (Å) | CN | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eu-Ow | 2.01 | 2.23 | 3 | 7.1 |
| Eu-Os | 1.95 | 2.17 | 3 | 1.01 |
| Eu-Cl | 2.49 | 2.93 | 3 | 0.01 |
| Lu-Ow | 1.97 | 2.31 | 3 | 7.9 |
| Lu-Os | 2.41 | 2.47 | 3 | 0.1 |
| Lu-Cl | 2.41 | 2.93 | 3 | 0.01 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, S.; Hua, Y.; Fan, Z.; Long, Q.; Zhang, K.; Lian, X.; Tu, T.; Li, L.; Qiu, T. Theoretical Investigation of Competitive Adsorption of Light and Heavy Rare Earth Ions on the (001) Surface of Kaolinite. Molecules 2025, 30, 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040838
Qiu S, Hua Y, Fan Z, Long Q, Zhang K, Lian X, Tu T, Li L, Qiu T. Theoretical Investigation of Competitive Adsorption of Light and Heavy Rare Earth Ions on the (001) Surface of Kaolinite. Molecules. 2025; 30(4):838. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040838
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Sen, Yijin Hua, Zehao Fan, Qibang Long, Kuifang Zhang, Xuwei Lian, Tao Tu, Li Li, and Tingsheng Qiu. 2025. "Theoretical Investigation of Competitive Adsorption of Light and Heavy Rare Earth Ions on the (001) Surface of Kaolinite" Molecules 30, no. 4: 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040838
APA StyleQiu, S., Hua, Y., Fan, Z., Long, Q., Zhang, K., Lian, X., Tu, T., Li, L., & Qiu, T. (2025). Theoretical Investigation of Competitive Adsorption of Light and Heavy Rare Earth Ions on the (001) Surface of Kaolinite. Molecules, 30(4), 838. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30040838






