Electrochemical Study and Determination of Homovanillic Acid, the Final Metabolite of Dopamine, Using an Unmodified Disposable Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
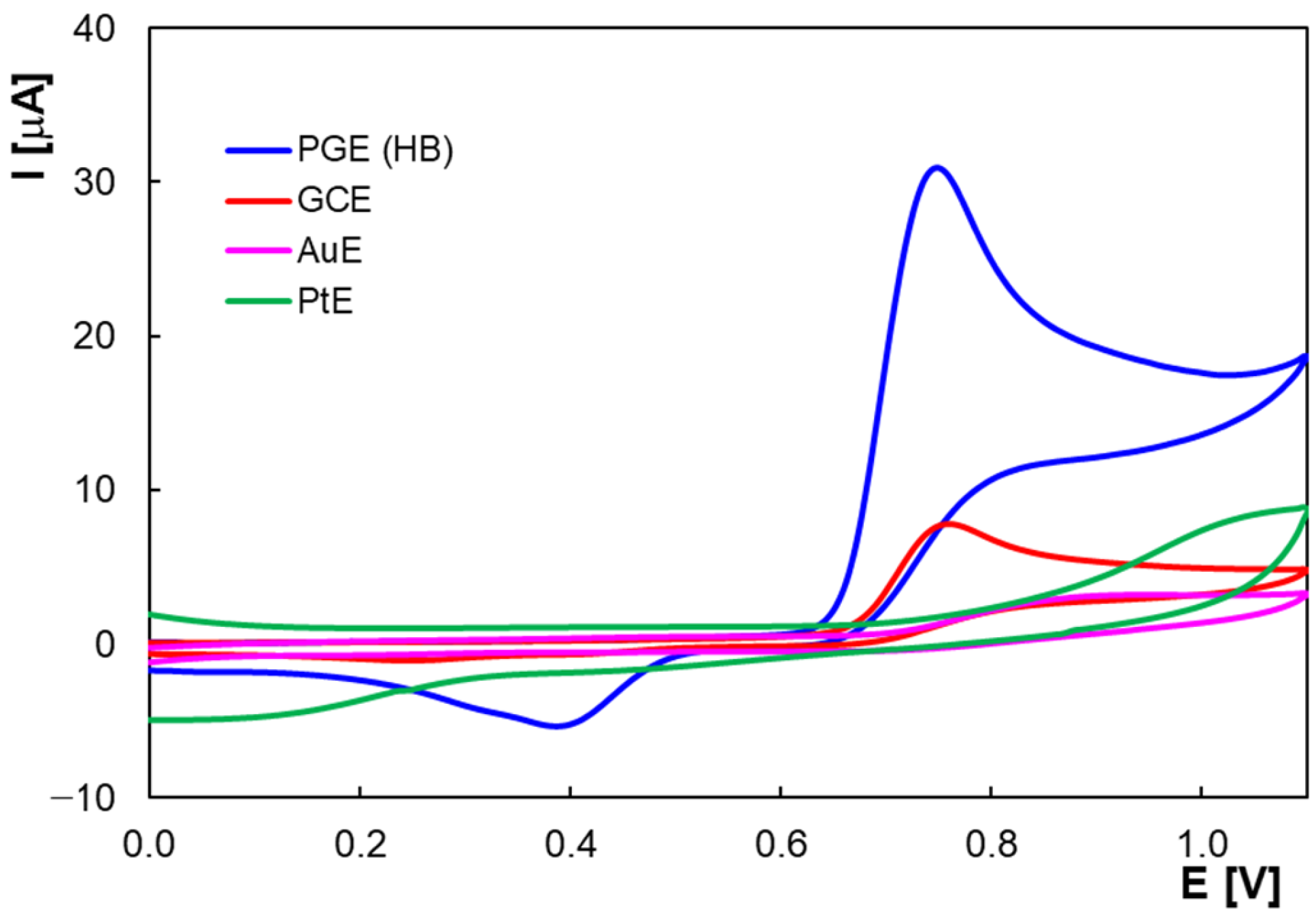
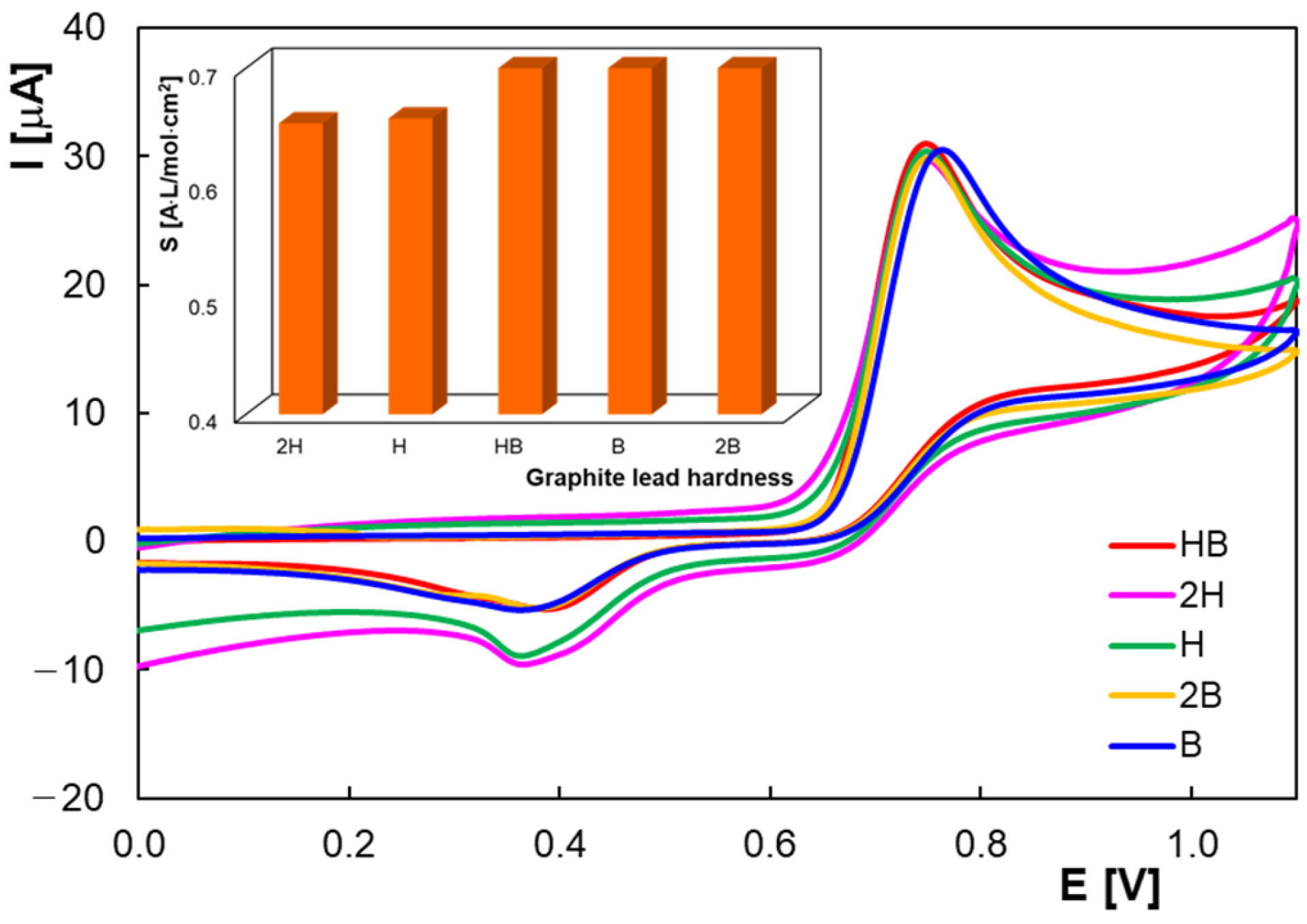
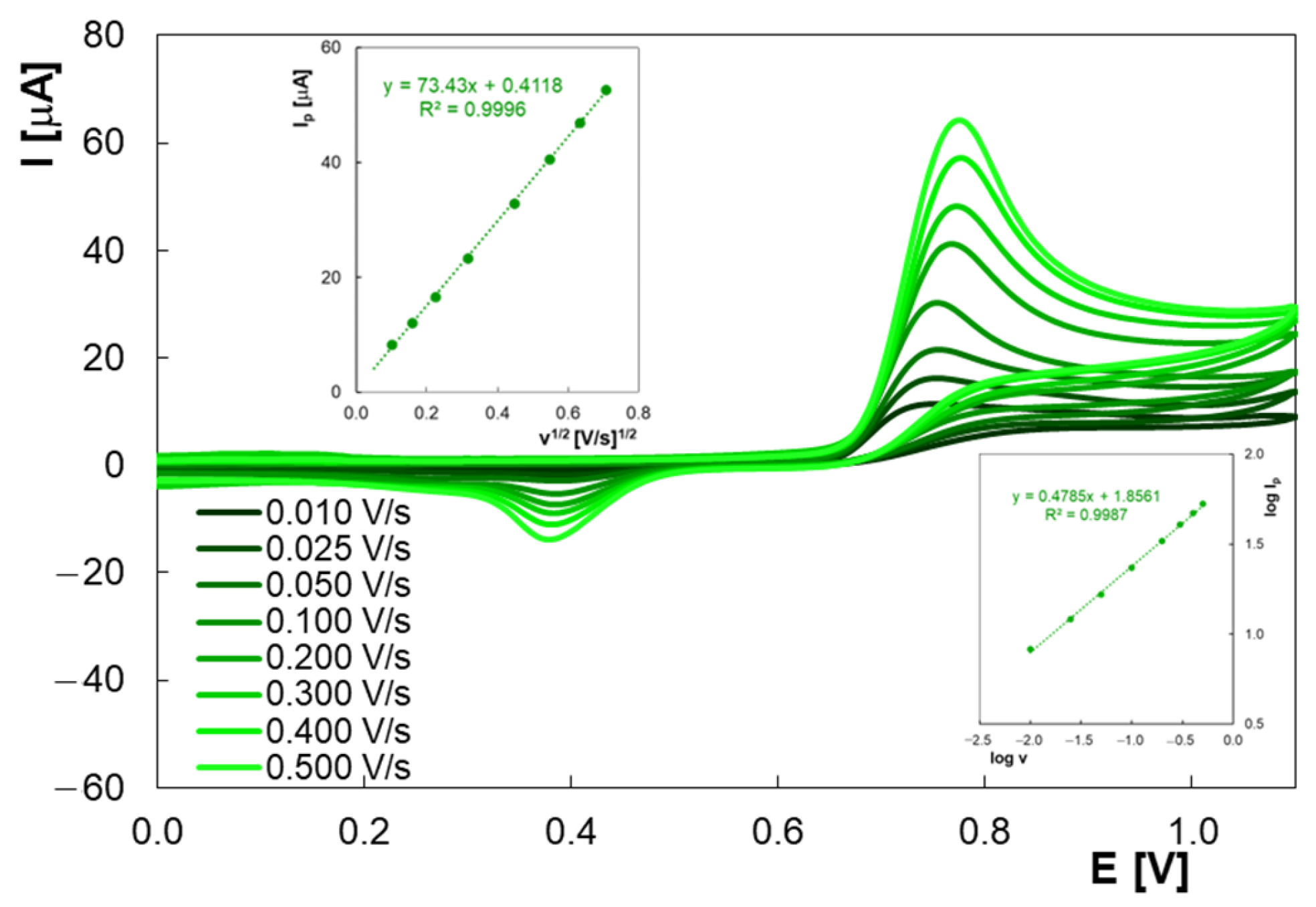
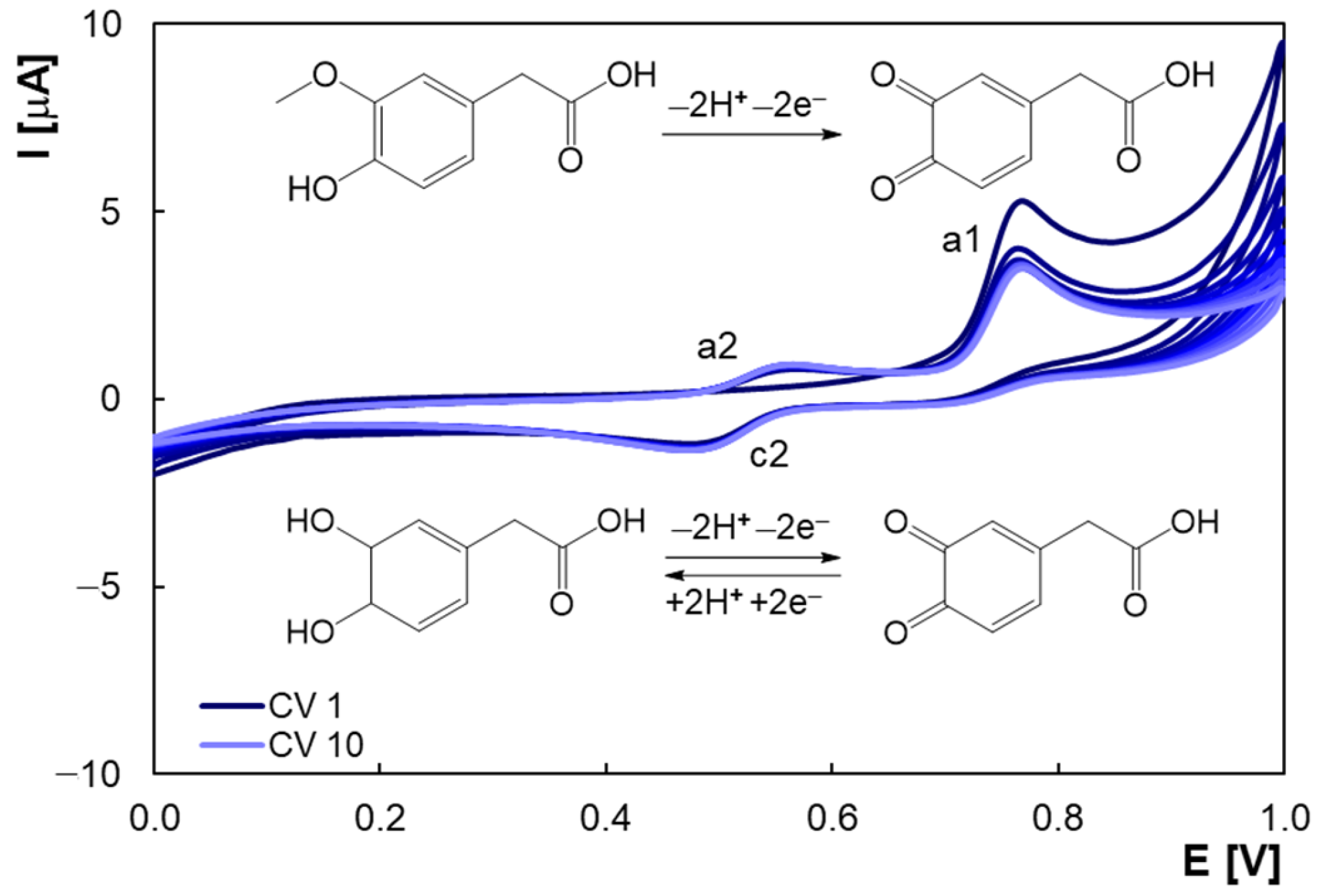
2.1. Voltammetric Behavior of Homovanilic Acid at the Pencil Graphite Electrode
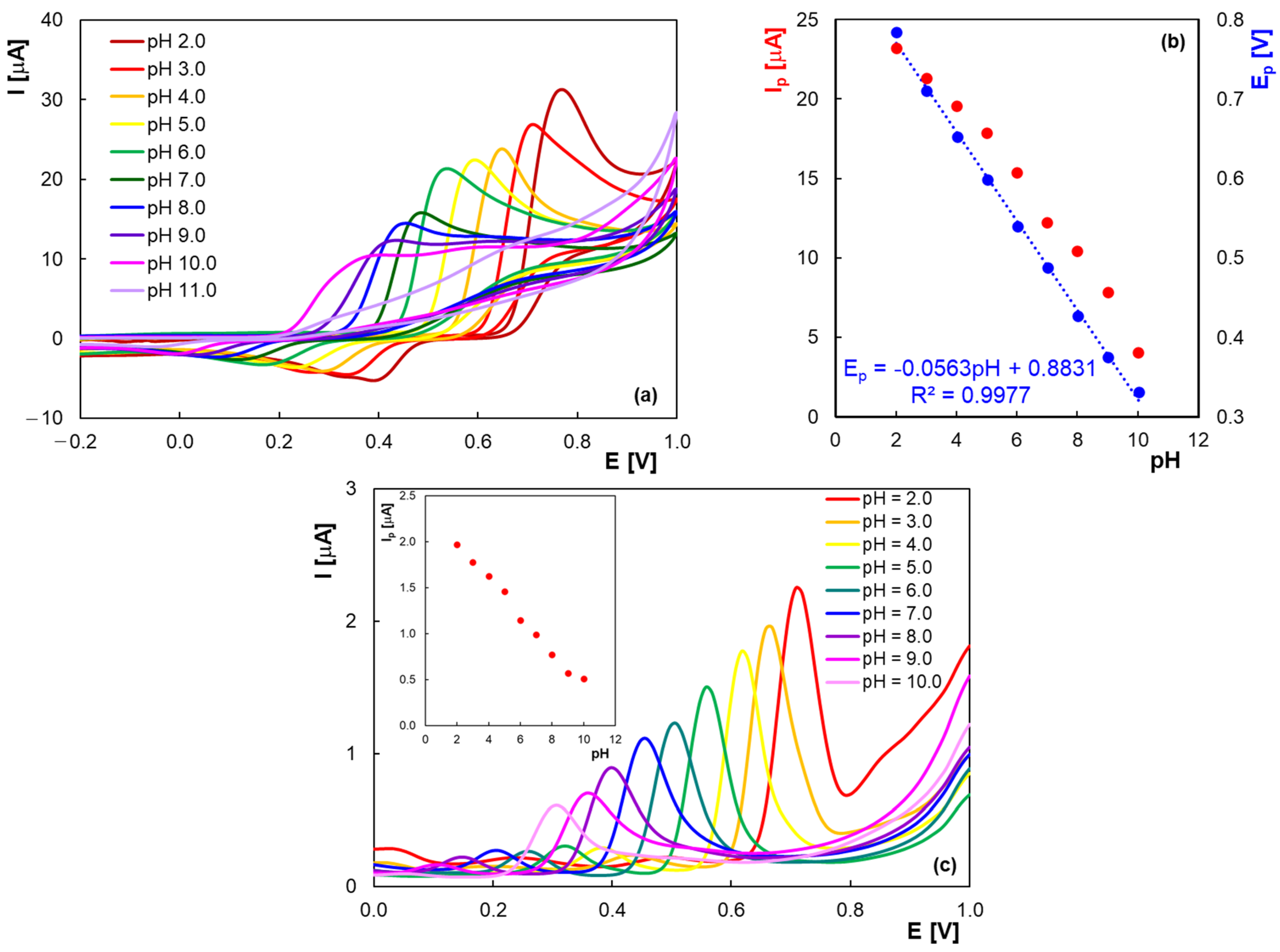
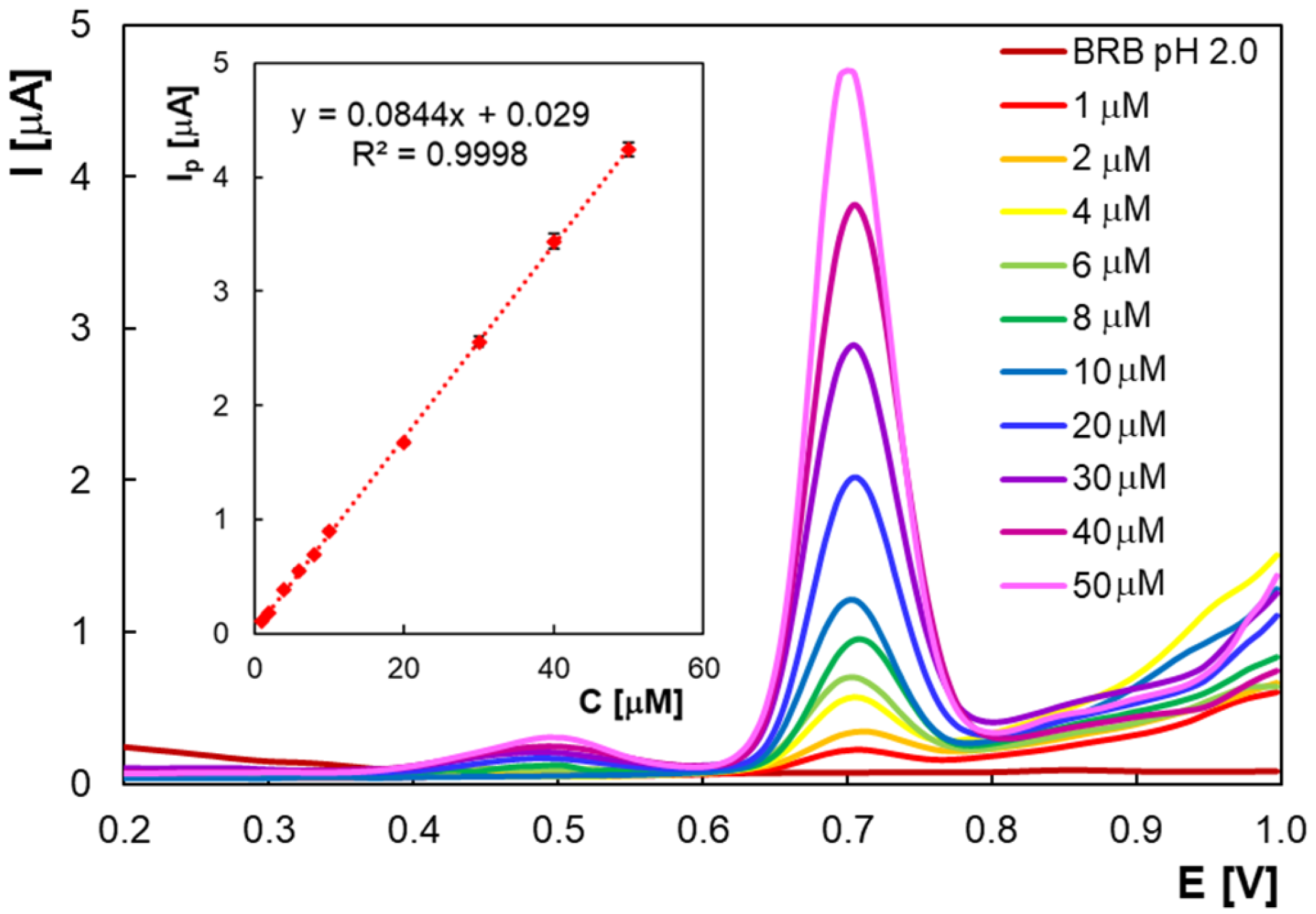
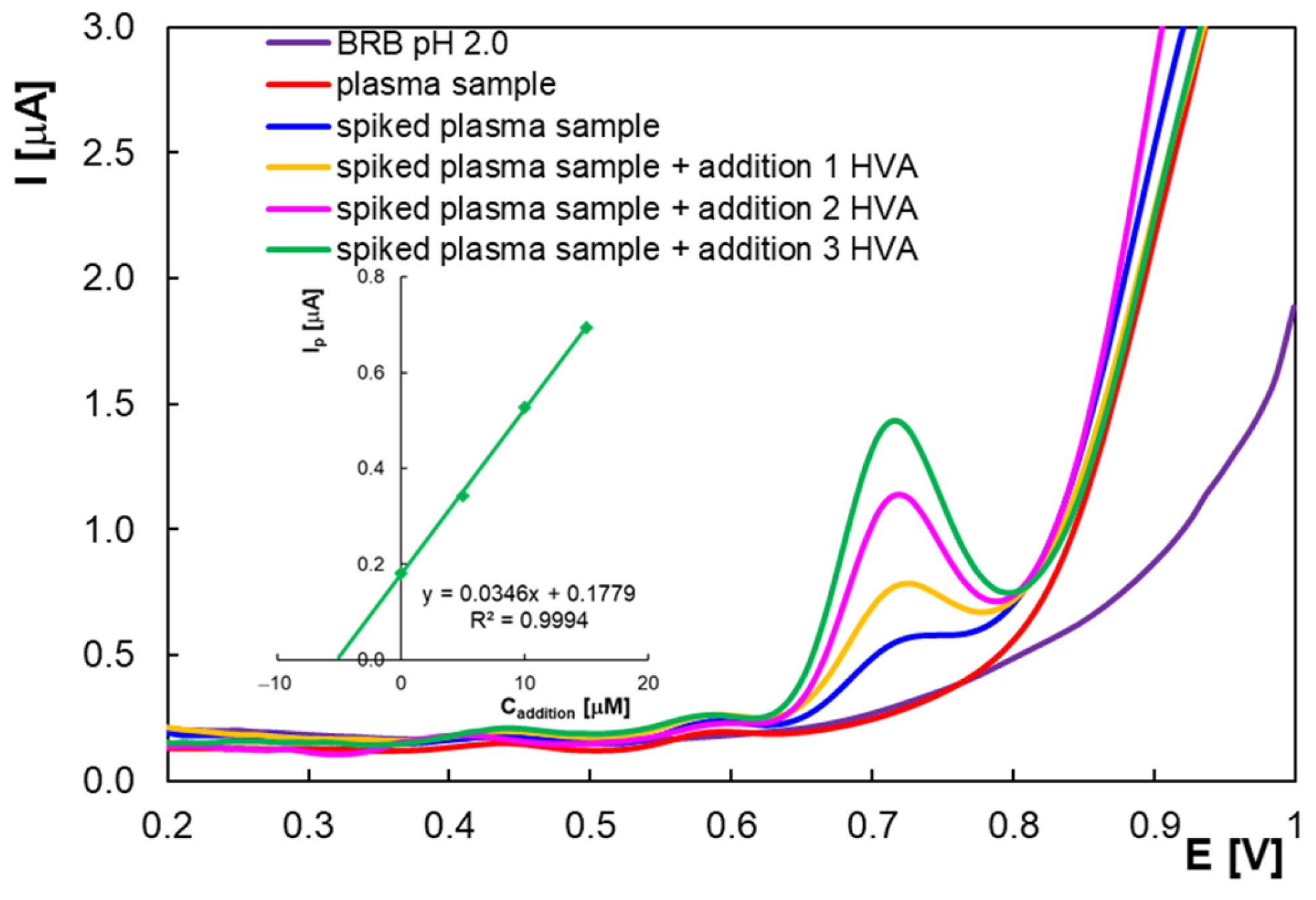
2.2. Quantitative Determination of Homovanillic Acid by Differential Pulse Voltammetry
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Samples
3.2. Instrumentation
3.3. Electrochemical Measurements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Costa, K.M.; Schoenbaum, G. Dopamine. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, R817–R824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olguín, H.J.; Guzmán, D.C.; García, E.H.; Mejía, G.B. The role of dopamine and its dysfunction as a consequence of oxidative stress. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 9730467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Khamlichi, R.; Bouchta, D.; Atia, M.B.; Attar, A.; Choukairi, M.; Tazi, S.; Ihssane, R.; Faiza, C.; Khalid, D.; Khalid, R.T. A novel L-leucine modified sol-gel-carbon electrode for simultaneous electrochemical detection of homovanillic acid, dopamine and uric acid in neuroblastoma diagnosis. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 71, 870–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yatham, L.N.; Liddle, P.F.; Gonzalez, M.; Saraf, G.; Vafai, N.; Lam, R.W.; Sossi, V. A positron emission tomography study of dopamine transporter density in patients with bipolar disorder with current mania and those with recently remitted mania. JAMA Psychiatry 2022, 79, 1217–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, O.D.; Kambeitz, J.; Kim, E.; Stahl, D.; Slifstein, M.; Abi-Dargham, A.; Kapur, S. The nature of dopamine dysfunction in schizophrenia and what this means for treatment: Meta-analysis of imaging studies. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2012, 69, 776–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, R.; Kurihara, M.; Kameyama, M.; Komatsu, H.; Higashino, M.; Hatano, K.; Ihara, R.; Higashihara, M.; Nishina, Y.; Matsubara, T.; et al. Correlations between cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid and dopamine transporter SPECT in degenerative parkinsonian syndromes. J. Neural Transm. 2023, 130, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciobanu, A.M.; Geza, L.; David, I.G.; Popa, D.E.; Buleandra, M.; Ciucu, A.A.; Dehelean, L. Actualities in immunological markers and electrochemical sensors for determination of dopamine and its metabolites in psychotic disorders. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 22, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, F.X.; Stevens, T.J.; Langlais, P.J.; Bird, E.D. Dopamine and homovanilic acid concentrations in striatal and limbic regions of human brain. Ann. Neurol. 1982, 12, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Valencia, I.; Serrano, M.; Ormazabal, A.; Pérez-Dueñas, B.; García-Cazorla, A.; Campistol, J.; Artuch, R. Biochemical diagnosis of dopaminergic disturbances in paediatric patients: Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid homovanillic acid and other biogenic amines. Clin. Biochem. 2008, 41, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishi, A.; Kuroiwa, M.; Miller, D.B.; O’Callaghan, J.P.; Bateup, H.S.; Shuto, T.; Sotogaku, N.; Fukuda, T.; Heintz, N.; Greengard, P.; et al. Distinct roles of PDE4 and PDE10A in the regulation of cAMP/PKA signaling in the striatum. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 10460–10471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sher, L.; Oquendo, M.; Li, S.; Huang, Y.; Grunebaum, M.F.; Burke, A.K.; Malone, K.M.; Mann, J.J. Lower CSF homovanillic acid levels in depressed patients with a history of alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2003, 28, 1712–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katta, S.S.; Nagati, V.; Paturi, A.S.V.; Murakonda, S.P.; Murakonda, A.B.; Pandey, M.K.; Gupta, S.C.; Pasupulati, A.K.; Challagundla, K.B. Neuroblastoma: Emerging trends in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and therapeutic targets. J. Control. Release 2023, 357, 444–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tippett, P.A.; West, R.S.; McEwan, A.J.; Middleton, J.E.; Ackery, D.M. A comparison of dopamine and homovanillic acid excretion, as prognostic indicators in malignant phaeochromocytoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 1987, 166, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaluzna-Czaplinska, J.; Socha, E.; Rynkowski, J. Determination of homovanillic acid and vanillylmandelic acid in urine of autistic children by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Med. Sci. Mon. 2010, 16, CR445–CR450. [Google Scholar]
- Castro-Fornieles, J.; Deulofeu, R.; Martinez-Mallen, E.; Baeza, I.; Fernandez, L.; Lazaro, L.; Toro, J.; Vila, M.; Bernardo, M. Plasma homovanillic acid in adolescents with bulimia nervosa. Psychiatry Res. 2009, 170, 241–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.P.; Javaid, J.I.; Davis, J.M.; Janicak, P.G. Pretreatment plasma homovanillic acid in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder: The influence of demographic variables and the inpatient drug-free period. Biol. Psychiatry 1998, 44, 488–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debellis, M.D.; Lefter, L.; Trickett, P.K.; Putnam, F.W. Urinary catecholamine excretion in sexually abused girls. J. Am. Acad. Child Psychiatr. 1994, 33, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippens, I.H.; Wubben, J.A.; Finsen, B.; ‘t Hart, B.A. Oral treatment with the NADPH oxidase antagonist apocynin mitigates clinical and pathological features of parkinsonism in the MPTP marmoset model. J. Neuroimmune. Pharmacol. 2013, 8, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Yan, H.; Xie, Q.; Huang, S.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, M.; Yao, S. Simultaneous analysis of dopamine and homovanillic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography with wall-jet/thin-layer electrochemical detection. Analyst 2013, 138, 7246–7253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadilkova, K.; Dugaw, K.; Benjamin, D.; Jack, R.M. Analysis of vanillylmandelic acid and homovanillic acid by UPLC-MS/MS in serum for diagnostic testing for neuroblastoma. Clin. Chim. Acta 2013, 424, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenbrand, R.; Garg, U. Quantitation of homovanillic acid (HVA) and vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) in urine using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC/MS). Methods Mol. Biol. 2010, 603, 261–269. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, A.; Heinanen, M.; Jimenez, L.M.; Barbas, C. Direct measurement of homovanillic, vanillylmandelic and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acids in urine by capillary electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2000, 871, 341–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.Z.; Ho, Y.P.; Yeung, J.H.K.; Or, P.M.Y.; To, K.K.W.; Lau, M.W.M.; Arumanayagam, M. Development of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay with monoclonal antibody for quantification of homovanillic in human urine samples. Clin. Chem. 1998, 44, 1674–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravindran, D.S.; Mukundan, S.; Kumar, K.G. A simple and efficient turn-off fluorescence sensor for the nanomolar detection of homovanillic acid using protein mediated blue emitting nickel nanoclusters. Chem. Select 2021, 6, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilbault, G.G.; Brignac, P.J.; Zimmer, M. Homovanillic acid as a fluorometric substrate for oxidative enzymes. Analytical applications of the peroxidase, glucose oxidase, and xanthine oxidase systems. Anal. Chem. 1968, 40, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diñeiro, Y.; Menéndez, M.I.; Blanco-López, M.C.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Tuñón-Blanco, P. Computational approach to the rational design of molecularly imprinted polymers for voltammetric sensing of homovanillic acid. Anal. Chem. 2005, 77, 6741–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revin, S.B.; John, S.A. Simultaneous determination of two important dopamine metabolites at physiological pH by voltammetry. Anal. Meth. 2012, 4, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatefi-Mehrjardi, A.; Ghaemi, N.; Karimi, M.A.; Ghasemi, M.; Islami-Ramchahi, S. Poly-(Alizarin Red S)-modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous electrochemical determination of levodopa, homovanillic acid and ascorbic acid. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 2491–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathera, J.A.; Khudaisha, E.A.; Munama, A.; Qurashib, A.; Kannan, P. Electrochemically reduced fullerene–graphene oxide interface for swift detection of Parkinsons disease biomarkers. Sens. Actuat. B 2016, 237, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluchová, S.; Barek, J.; Tomé, L.I.N.; Brett, C.M.A.; Schwarzová-Pecková, K. Vanillylmandelic and homovanillic acid: Electroanalysis at non-modified and polymer-modified carbon-based electrodes. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 821, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, Y.; Shi, P.; Lei, Y.; Weng, S.; Li, S.; Huang, L.; Lin, X.; Yao, H. Polyvinyl butyral/graphene oxide nanocomposite modified electrode for the integrate determination of terminal metabolites of catecholamines in human urine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2019, 848, 113267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Chen, H.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, T.; Li, K. A simple ultrasensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of homovanillic acid and vanillylmandelic acid in human urine based on MWCNTs-Pt nanoparticles as peroxidase mimics. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 866, 114165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němečková-Makrlíková, A.; Navrátil, T.; Barek, J.; Štenclová, P.; Kromka, A.; Vyskočil, V. Determination of tumour biomarkers homovanillic and vanillylmandelic acid using flow injection analysis with amperometric detection at a boron doped diamond electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1087, 44–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hrdlička, V.; Barek, J.; Navrátil, T. Differential pulse voltammetric determination of homovanillic acid as a tumor biomarker in human urine after hollow fiber-based liquid-phase microextraction. Talanta 2021, 221, 121594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrlíková, A.; Ktena, E.; Economou, A.; Fischer, J.; Navrátil, T.; Barek, J.; Vyskočil, V. Voltammetric determination of tumor biomarkers for neuroblastoma (homovanillic acid, vanillylmandelic acid, and 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid) at screen-printed carbon electrodes. Electroanalysis 2017, 29, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkanova, T.V.; Broncová, G.; Fitl, P.; Král, V.; Barek, J. Voltammetric detection of catecholamine metabolites using Tröger’s base modified electrode. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 734–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Němečková-Makrlíková, A.; Matysik, F.M.; Navrátil, T.; Barek, J.; Vyskočil, V. Determination of three tumor biomarkers (homovanillic acid, vanillylmandelic acid, and 5-hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid) using flow injection analysis with amperometric detection. Electroanalysis 2019, 31, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-nami, S.Y.; Azher, O.A.; Aljuhani, E.; Shah, R.; Al-Qahtani, S.D.; Khalifa, M.E.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Voltammetric behavior of acidic catecholamine metabolites in presence of cationic surfactants. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2021, 168, 106507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulla, I.A.L.; Lowry, J.P.; Serrac, P.A.; O’Neill, R.D. Development of a voltammetric technique for monitoring brain dopamine metabolism: Compensation for interference caused by DOPAC electrogenerated during homovanillic acid detection. Analyst 2009, 134, 893–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejmkova, H.; Adamkova, H.; Barek, J.; Zima, J. Voltammetric and amperometric determination of selected catecholamine metabolites using glassy carbon paste electrode. Monatsh. Chem. 2017, 148, 511–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ola, K.A.; Alfi, A.A.; Hameed, A.; Munshi, A.M.; Al-Ahmed, Z.A.; Keshk, A.A.; Khalifa, M.E.; El-Metwaly, N.M. Zinc ferrite nanostructure/multi-walled carbon nanotubes (ZFO/MWCNTs) nanocomposite as sensor for homovanillic acid detection in urine samples for cancer therapy monitoring. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkanova, T.V.; Sinica, A. Electrochemically deposited cobalt bis(dicarbollide) derivative and the detection of neuroblastoma markers on the electrode surface. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 921, 116674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antherjanam, S.; Saraswathyamma, B.; Senthil Kumar, S.M. Simultaneous electrochemical determination of the tumour biomarkers homovanillic acid and vanillylmandelic acid using a modified pencil graphite electrode. Microchem. J. 2023, 190, 108659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shishkanova, T.V.; Králík, F.; Synytsya, A. Voltammetric detection of vanillylmandelic acid and homovanillic acid using urea-derivative-modified graphite electrode. Sensors 2023, 23, 3727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Buleandra, M.; Popa, D.E.; Cheregi, M.C.; David, V.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; Tartareanu, O.G. Recent developments in voltammetric analysis of pharmaceuticals using disposable pencil graphite electrodes. Processes 2022, 10, 472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Blanco-Lopez, M.C.; Lobo-Castanon, M.J.; Ordieres, A.J.M.; Tunon-Blanco, P. Electrochemical behavior of catecholamines and related compounds at in situ surfactant modified carbon paste electrodes. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, R.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Al-Alamein, A.M.A.; Galal, M.M.; El Mously, D.A. Point-of-care sensor using modified nickel-doped zinc oxide nanoparticle carbon paste electrode for homovanillic acid cancer biomarker detection in urine. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2024, 171, 117509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libansky, M.; Zima, J.; Barek, J.; Dejmkova, H. Voltammetric determination of homovanillic acid and vanillylmandelic acid on a disposable electrochemical measuring cell system with integrated carbon composite film electrodes. Monatsh. Chem. 2016, 147, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, K.; Li, Q.; Li, D.; Jiao, Y.; Wang, L.; Li, L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Gao, R.; Li, F.; et al. A highly selective implantable electrochemical fiber sensor for real-time monitoring of blood homovanillic acid. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 7485–7495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, I.G.; Florea, M.-A.; Cracea, O.G.; Popa, D.E.; Buleandră, M.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; David, V.; Badea, I.A.; Ciucu, A.A. Voltammetric determination of vitamin B1 and vitamin B6 on a disposable electrode. Chem. Pap. 2015, 69, 901–910. [Google Scholar]


| Electrode | Technique | Supporting Electrolyte | Linear Range [μM] | Detection Limit [μM] | Sample | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIP/GCE | DPV | 0.1 M citrate/HCl (40% acetonitrile) (pH 1.1) | 0.05–10 | 0.007 | – | [26] |
| Poly-AMT/GCE | Amp | 0.2 M PB (pH 7.2) | 0.01–100 | 0.000094 | plasma | [27] |
| Poly-ARS/GCE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 3.0) | 0.09–160 | 0.017 | plasma | [28] |
| ERC60–GO–Ph/GCE | SWV | PB (pH 7.0) | 0.1–7.2 | 0.03 | urine | [29] |
| Nafion/GCE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 3.0) | 2–10 10–100 | 0.8 | urine | [30] |
| GCE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 3.0) | 2–10 10–100 | 0.9 | urine | [30] |
| PNR/GCE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 3.0) | 4–100 | 1.2 | urine | [30] |
| PVB/GO/GCE | DPV | PB (pH 6.0) | 0.549–120 | 0.18 | urine | [31] |
| MWCNT-PtNP/GCE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 7.0) | 0.2–80 | 0.08 | urine | [32] |
| BDDE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 3.0) | 2–100 | 0.6 | urine | [30] |
| BDDE | FIA-AD | 0.04 M BRB (pH 3.0) | 1–10 10–100 | 0.44 | - | [33] |
| BDDE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 6.0) | 1.2–100 | 0.4 | urine | [34] |
| SPCE | DPV | 0.04 M BRB (pH 3.0) | 0.2–100 | 0.24 | urine | [35] |
| Poly-CTB/G-SPE | DPV | PB (pH 7.0) | 40–100 | 2.2 | artificial urine | [36] |
| SPCE | FIA-AD | 0.04 M BRB (pH 2.0) | 0.05–100 | 0.065 | - | [37] |
| SPCE | DPV | BRB (pH 9.5) | 0.25–2.5 | 0.4 | urine | [38] |
| PEA/CPE | CV | PB (pH 7.4) | 10–100 | 3 | brain extracellular fluid | [39] |
| GCPE | DPV | BRB (pH 2.0) | 1–100 | 1.26 * | - | [40] |
| ZFO-MWCNT/CPE | DPV | BRB (pH 2.0) | 0.415–3.225 | 0.148 | urine | [41] |
| Ni-ZnO NPs/CPE | DPV | 3.96–0.383 | 1.01 | urine | [48] | |
| Poly-CB-oPD/GE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 7.2) | 9.99–1220 | - | - | [42] |
| Poly-ASA/PGE | DPV | PB (pH 8.0) | 3–61.4 | 1.82 | urine | [43] |
| Urea-derivative/GE | DPV | 0.1 M PB (pH 6.0) | 9.96–624 | - | - | [44] |
| L-leu-Sol-Gel/CE | DPV | PB (pH 4.0) | 0.4–100 | 0.1 | urine | [3] |
| CCFE | DPV | BRB (pH 2.0) | 0.8–100 | 0.3 | - | [49] |
| MIP-CNT fiber | DPV | PB (pH 7.4) | 0.01–2 | 0.00458 | rat caudal vein | [50] |
| PGE | DPV | BRB (pH 2.0) | 1–50 | 0.384 | human plasma | this work |
| Cadded [M] | Intra-Day | Inter-Day | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crecovered ± SD [M] | r.e.% | RSD% | Crecovered ± SD [M] | r.e.% | RSD% | |
| 1.00 × 10−6 | 1.00 × 10−6 ± 2.54 × 10−8 | 0.49 | 2.53 | 1.01 × 10−6 ± 3.33 × 10−8 | 3.31 | 3.25 |
| 1.00 × 10−5 | 1.03 × 10−5 ± 1.78 × 10−7 | 2.80 | 1.73 | 1.03 × 10−5 ± 1.86 × 10−7 | 2.92 | 1.80 |
| 5.00 × 10−5 | 4.99 × 10−5 ± 7.56 × 10−6 | −0.21 | 1.52 | 4.95 × 10−5 ± 1.44 × 10−6 | −0.14 | 2.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Buleandră, M.; Voica, L.G.; Popa, D.E.; Badea, I.A.; Iorgulescu, E.E.; Cheregi, M.C. Electrochemical Study and Determination of Homovanillic Acid, the Final Metabolite of Dopamine, Using an Unmodified Disposable Electrode. Molecules 2025, 30, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020369
Buleandră M, Voica LG, Popa DE, Badea IA, Iorgulescu EE, Cheregi MC. Electrochemical Study and Determination of Homovanillic Acid, the Final Metabolite of Dopamine, Using an Unmodified Disposable Electrode. Molecules. 2025; 30(2):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020369
Chicago/Turabian StyleBuleandră, Mihaela, Lavinia Georgiana Voica, Dana Elena Popa, Irinel Adriana Badea, Emilia Elena Iorgulescu, and Mihaela Carmen Cheregi. 2025. "Electrochemical Study and Determination of Homovanillic Acid, the Final Metabolite of Dopamine, Using an Unmodified Disposable Electrode" Molecules 30, no. 2: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020369
APA StyleBuleandră, M., Voica, L. G., Popa, D. E., Badea, I. A., Iorgulescu, E. E., & Cheregi, M. C. (2025). Electrochemical Study and Determination of Homovanillic Acid, the Final Metabolite of Dopamine, Using an Unmodified Disposable Electrode. Molecules, 30(2), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020369








