Pegylated NIR Fluorophore-Conjugated OBHSA Prodrug for ERα-Targeted Theranostics with Enhanced Imaging and Long-Term Retention
Abstract
1. Introduction
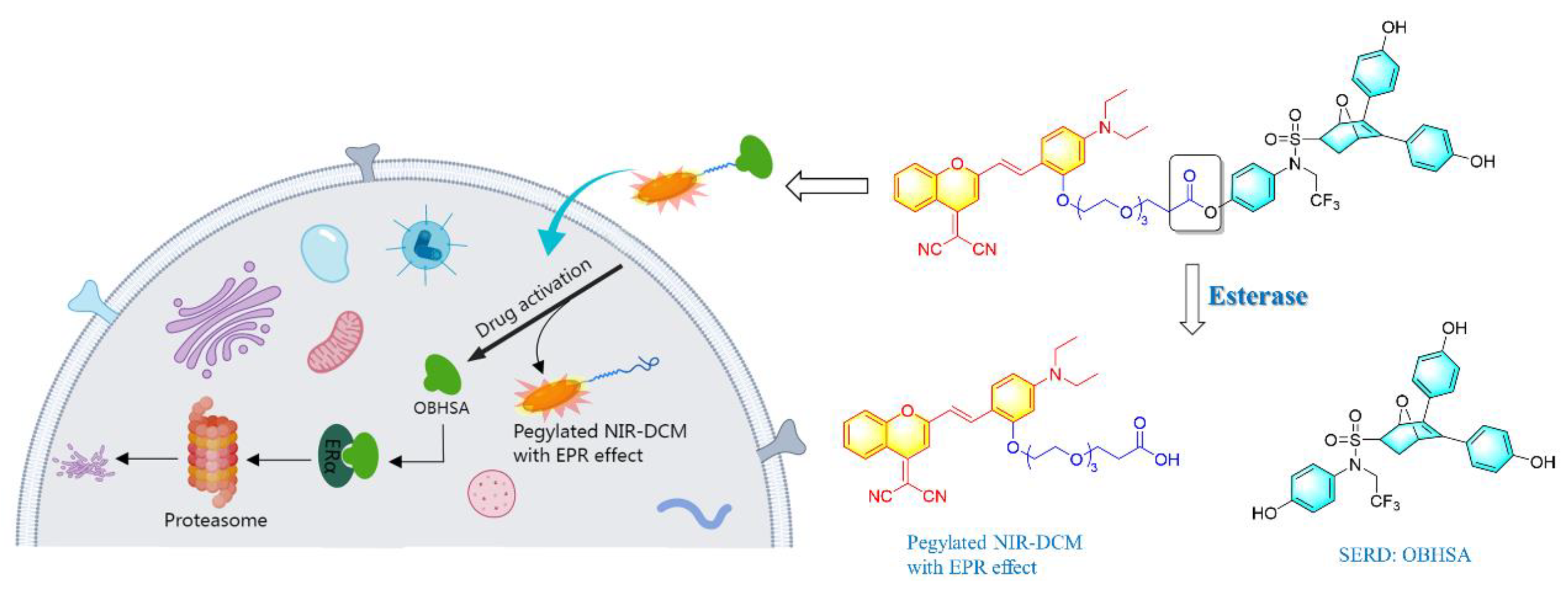
2. Results and Discussion
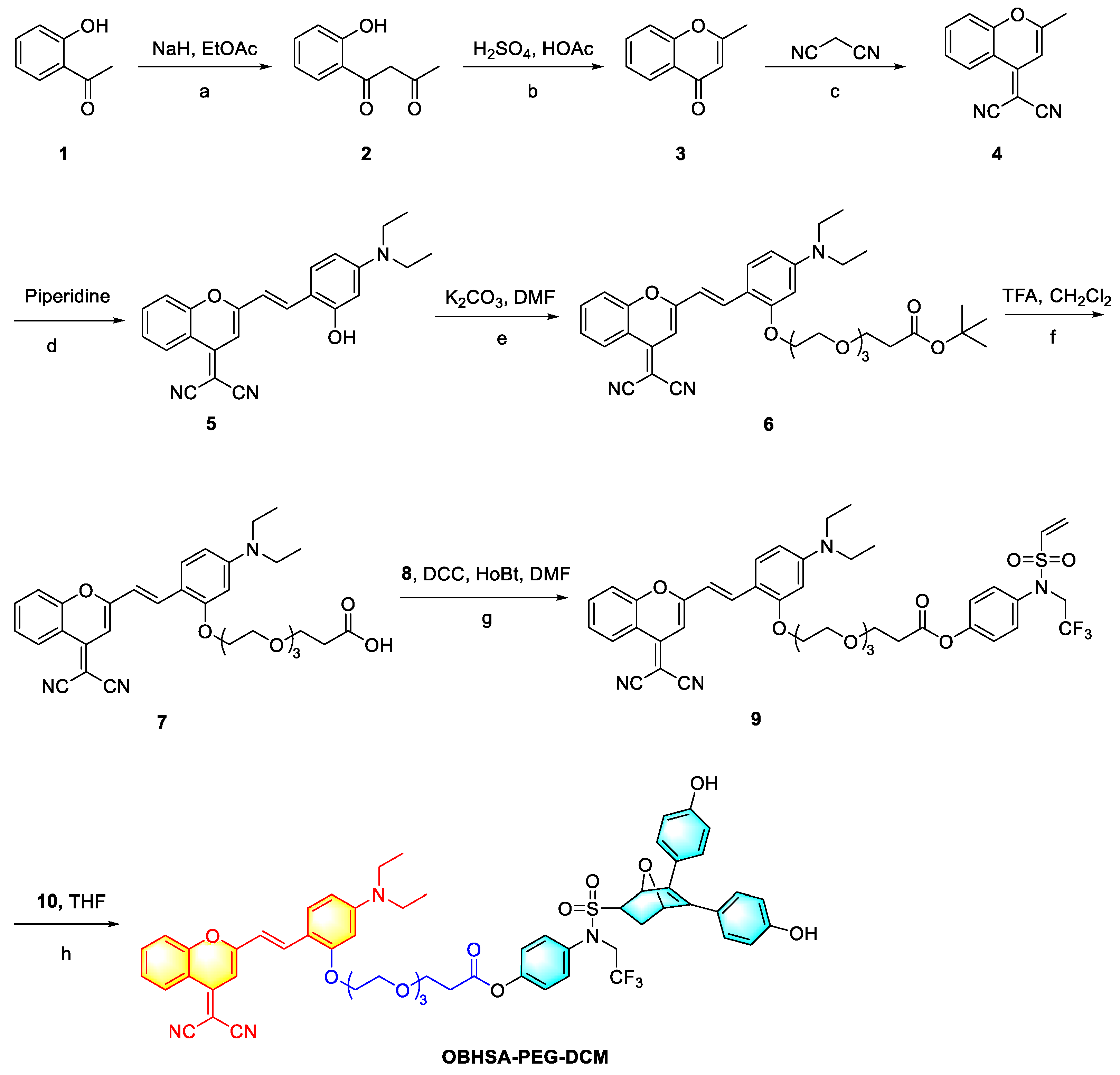
2.1. Synthetic Methodology
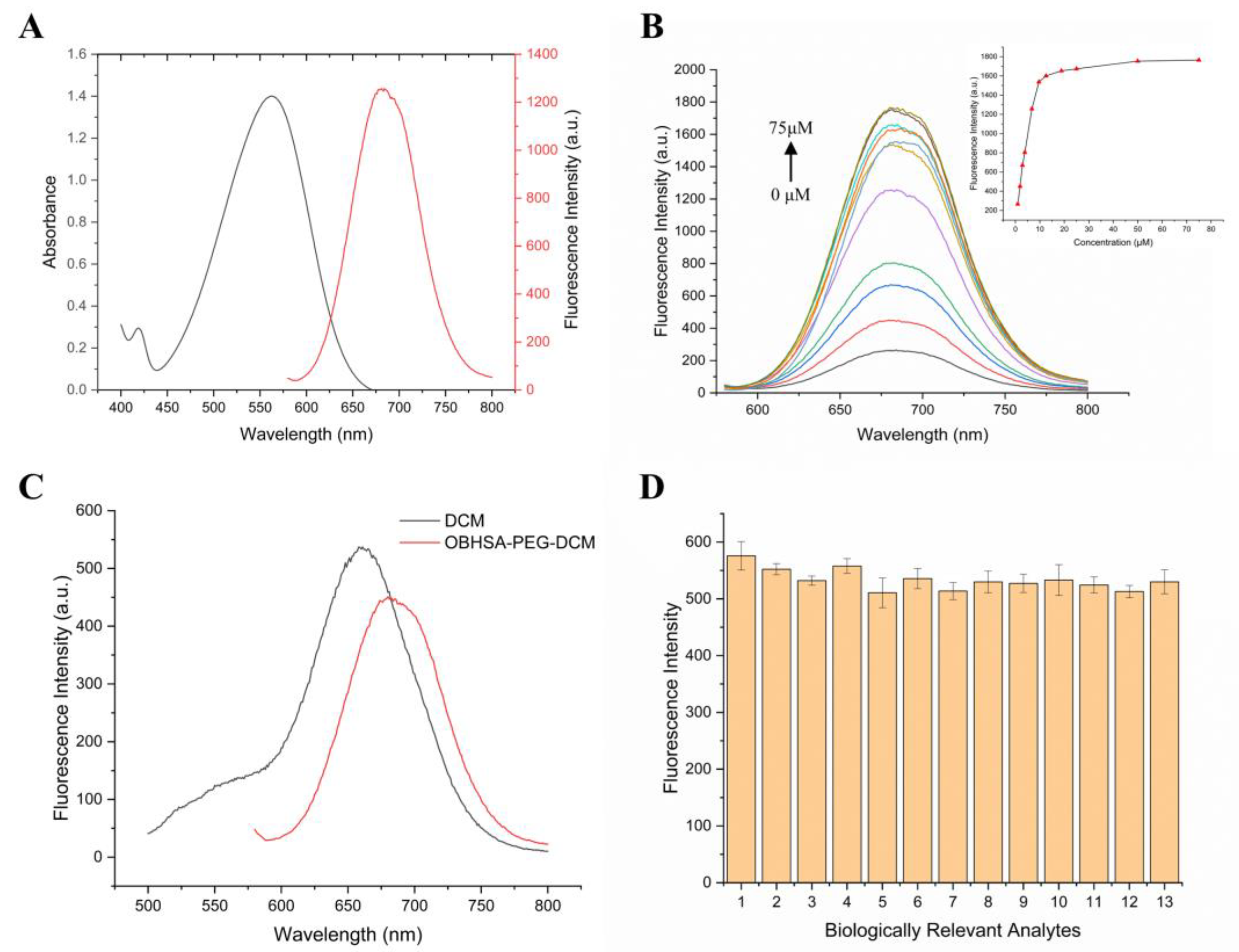
2.2. Photophysical Properties
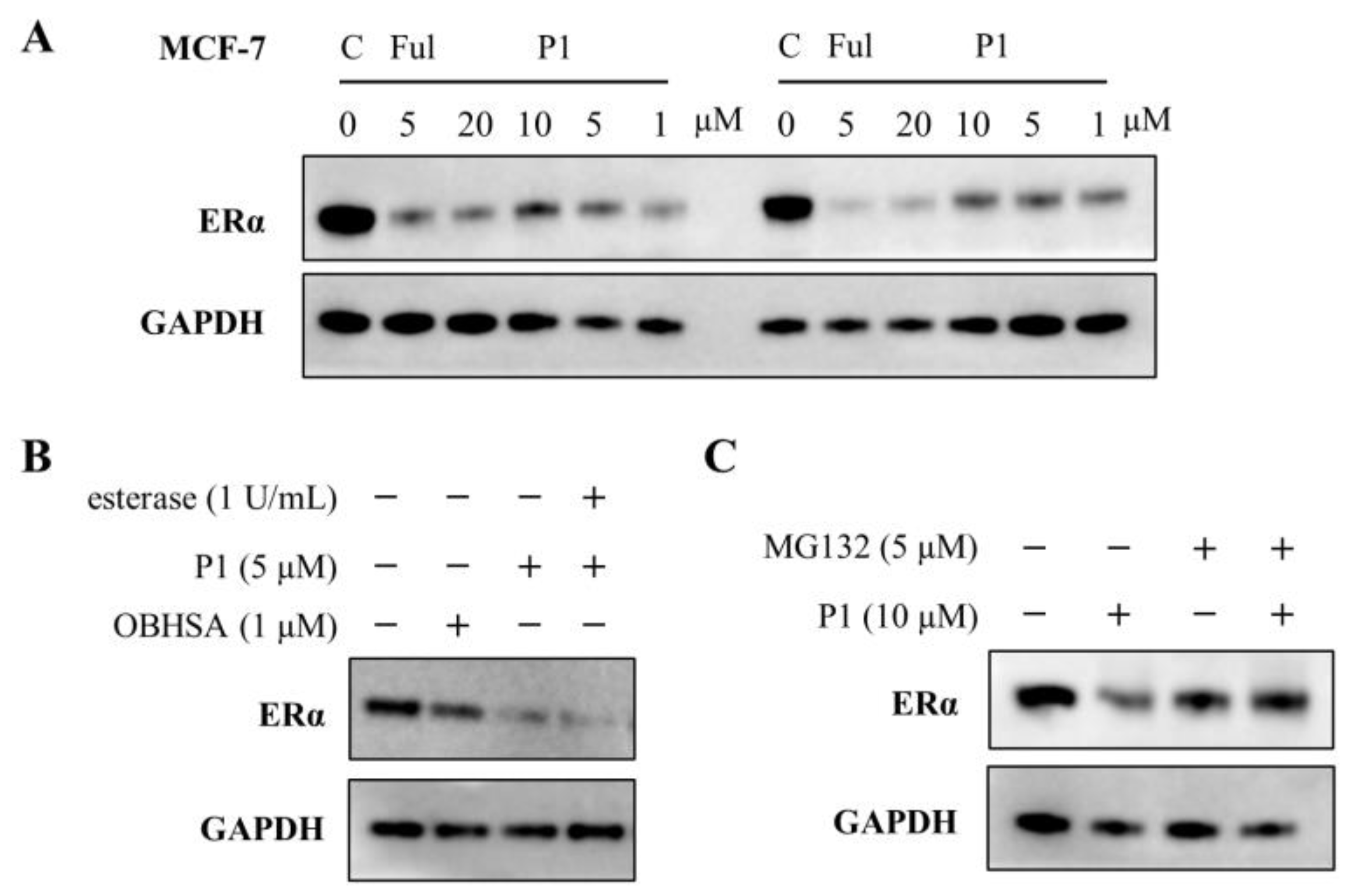
2.3. Hydrolyzed Product and Mechanism Investigation
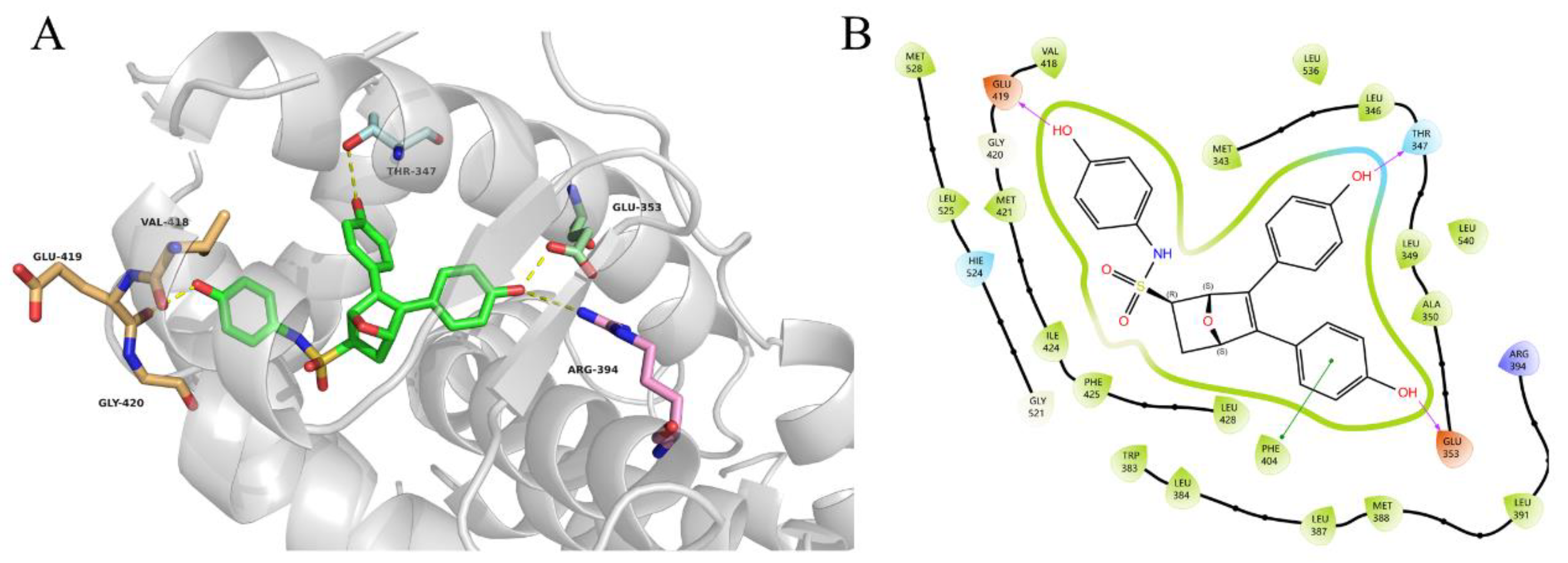
2.4. Evaluation of Inhibitory and Degradation Activities
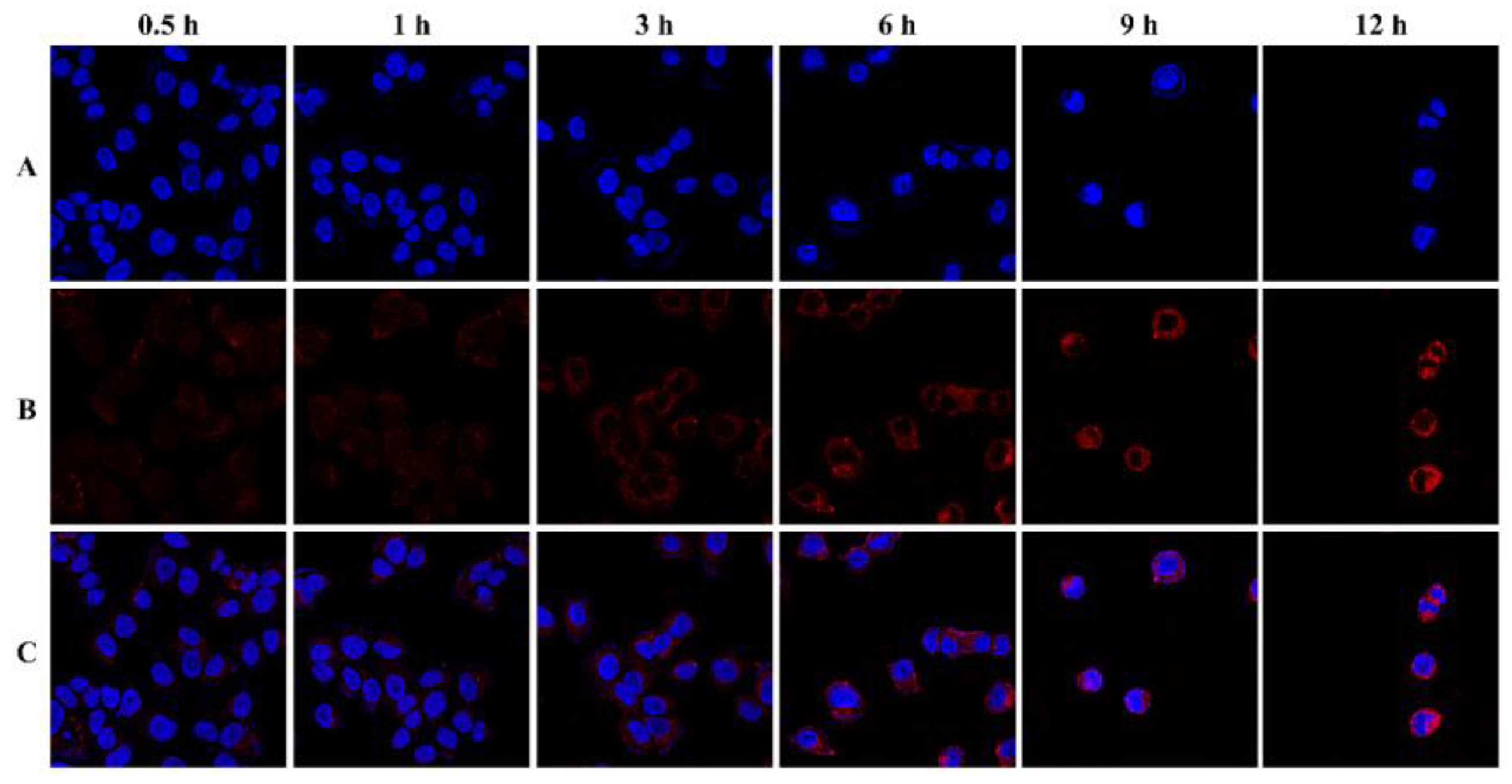
2.5. Cellular and Animal Imaging Investigations
2.6. H&E Staining
3. Conclusions
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Synthesis of OBHSA-PEG-DCM
4.2. HPLC Analysis
4.3. Photophysical Properties
4.4. Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy
4.5. In Vitro Cell Culture and Antiproliferative Assay
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. In Vivo Fluorescence Imaging
4.8. H&E Staining
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. Estrogen receptor transcription and transactivation Estrogen receptor alpha and estrogen receptor beta: Regulation by selective estrogen receptor modulators and importance in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2000, 2, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Power, K.A.; Thompson, L.U. Ligand-induced regulation of ERα and ERβ is indicative of human breast cancer cell proliferation. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 81, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.X.; Zong, D.J.; Sun, J.R.; Chen, D.X.; Ma, M.K.; Jia, L.Q. Rewiring of the Endocrine Network in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 830894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, J.; Wu, Y.; Ma, F.; Kaklamani, V.; Xu, B. Advances in medical treatment of breast cancer in 2022. Cancer Innov. 2023, 2, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, A. Future use of selective estrogen receptor modulators and aromatase inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2001, 7, 4402S–4410S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Awouters, M.; Vanderschueren, D.; Antonio, L. Aromatase inhibitors and selective estrogen receptor modulators: Unconventional therapies for functional hypogonadism? Andrology 2020, 8, 1590–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaillard, S.L.; Andreano, K.J.; Gay, L.M.; Steiner, M.; Jorgensen, M.S.; Davidson, B.A.; Havrilesky, L.J.; Secord, A.A.; Valea, F.A.; Colon-Otero, G.; et al. Constitutively active ESR1 mutations in gynecologic malignancies and clinical response to estrogen-receptor directed therapies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 154, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, N.; Hazra, S.; Thareja, S. Selective Estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) for the treatment of breast cancer: An overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 256, 115422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.S.; Barlaam, B. Selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs) and covalent antagonists (SERCAs): A patent review (2015-present). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2022, 32, 131–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.B.; Min, J.; Deng, X.P.; Feng, T.; Hu, H.B.; Guo, X.Y.; Cheng, Y.; Xie, B.H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, C.C.; et al. Discovery of novel covalent selective estrogen receptor degraders against endocrine-resistant breast cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 4963–4982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kargbo, R.B. Estrogen Receptor Degrading PROTACS for the Treatment of Breast Cancer. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2020, 11, 2361–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Z.; Luo, J.; Tang, C.; Zhang, S.; Ning, W.; Dong, C.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Zhou, H.B. Dual functional small molecule fluorescent probes for image-guided estrogen receptor-specific targeting coupled potent antiproliferative potency for breast cancer therapy. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 3531–3539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waaijer, S.J.H.; Kok, I.C.; Eisses, B.; Schröder, C.P.; Jalving, M.; Brouwers, A.H.; Lub-de Hooge, M.N.; de Vries, E.G.E. Molecular Imaging in Cancer Drug Development. J. Nucl. Med. 2018, 59, 726–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, C.X.; Shi, L.M.; Guo, Z.Q.; Zhu, W.H. Molecularly near-infrared fluorescent theranostics for in vivo tracking tumor-specific chemotherapy. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2019, 30, 1849–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.C.; Zhou, Y.R.; Li, S.; Qu, D.H.; Zhu, W.H.; Tian, H. Real-time near-infrared bioimaging of a receptor-targeted cytotoxic dendritic theranostic agent. Biomaterials 2017, 120, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.D.; Xiao, Y.L.; Lin, J.C.; Li, S.S.; Zhou, H.; Nong, J.X.; Xu, G.Z.; Wang, H.B.; Xu, F.C.; Wu, J.Z.; et al. Near-Infrared II Dye-Protein Complex for Biomedical Imaging and Imaging-Guided Photothermal Therapy. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2018, 7, 1800589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Lee, J.H.; Jeon, H.M.; Han, J.H.; Park, N.; He, Y.; Lee, H.; Hong, K.S.; Kang, C.; Kim, J.S. Folate-Based Near-Infrared Fluorescent Theranostic Gemcitabine Delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11657–11662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Sun, X.; Guo, Z.; Tang, J.; Shen, Y.; James, T.D.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W. In vivo and in situ tracking cancer chemotherapy by highly photostable NIR fluorescent theranostic prodrug. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 3579–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Yuan, Y.; Chen, J.Q.; Zhang, B.H.; Li, D.; Zhou, D.; Jing, P.T.; Xu, G.Y.; Wang, Y.L.; Holá, K.; et al. In vivo theranostics with near-infrared-emitting carbon dots-highly efficient photothermal therapy based on passive targeting after intravenous administration. Light-Sci. Appl. 2018, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.Y.; Qian, J.Q.; Meng, C.; Liu, Y.; Ding, Q.; Wu, H.M.; Li, P.; Ran, F.S.; Liu, G.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; et al. TME-targeting theranostic agent uses NIR tracking for tumor diagnosis and surgical resection and acts as chemotherapeutic showing enhanced efficiency and minimal toxicity. Theranostics 2022, 12, 2535–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasarao, M.; Low, P.S. Ligand-Targeted Drug Delivery. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12133–12164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruoslahti, E. Tumor penetrating peptides for improved drug delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2017, 110–111, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.E.; Tummers, W.S.; Teraphongphom, N.; van den Berg, N.S.; Hasan, A.; Ertsey, R.D.; Nagpal, S.; Recht, L.D.; Plowey, E.D.; Vogel, H.; et al. First-in-human intraoperative near-infrared fluorescence imaging of glioblastoma using cetuximab-IRDye800. J. Neuro-Oncol. 2018, 139, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, H.C.; Conroy, E.; Todor, M.; Wu, D.; Gallagher, W.M.; O’Shea, D.F. An EPR Strategy for Bio-responsive Fluorescence Guided Surgery with Simulation of the Benefit for Imaging. Theranostics 2020, 10, 3064–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.J.; Zhan, P.; De Clercq, E.; Lou, H.X.; Liu, X.Y. Current drug research on PEGylation with small molecular agents. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2013, 38, 421–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.S.; DeLuca, P.P.; Lee, K.C. Emerging PEGylated drugs. Expert Opin. Emerg. 2009, 14, 363–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlQahtani, A.D.; O’Connor, D.; Domling, A.; Goda, S.K. Strategies for the production of long-acting therapeutics and efficient drug delivery for cancer treatment. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 113, 108750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorusso, G.; Rügg, C. The tumor microenvironment and its contribution to tumor evolution toward metastasis. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 130, 1091–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessel, K.M.; Kaplan, R.N. Targeting tumor microenvironment and metastasis in children with solid tumors. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 2022, 34, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.B.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.L.; Li, B.L.; Wen, H.Q.; Zhang, X.C.; Zhang, T.Y.; Zhao, N.; Tang, B.Z. Esterase-Activated Theranostic Prodrug for Dual Organelles-Targeted Imaging and Synergetic Chemo-Photodynamic Cancer Therapy. CCS Chem. 2022, 4, 1028–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.N.; Pang, L.; Cong, H.L.; Shen, Y.Q.; Yu, B. Application and design of esterase-responsive nanoparticles for cancer therapy. Drug Deliv. 2019, 26, 416–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Hu, Z.Y.; Xiao, Y.; Huang, J.; Dong, C.N.; Huang, S.T.; Zhou, H.B. Exploring the PROTAC degron candidates: OBHSA with different side chains as novel selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 172, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Z.; Zhu, W.; Tian, H. Dicyanomethylene-4H-pyran chromophores for OLED emitters, logic gates and optical chemosensors. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 6073–6084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.X.; Tang, C.; Li, C.H.; Ning, W.T.; Hu, Z.Y.; Xin, L.L.; Zhou, H.B.; Huang, J. Novel hybrid conjugates with dual estrogen receptor α degradation and histone deacetylase inhibitory activities for breast cancer therapy. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2021, 40, 116185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Zhang, C.; Nwachukwu, J.C.; Srinivasan, S.; Cavett, V.; Zheng, Y.; Carlson, K.E.; Dong, C.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; Nettles, K.W.; et al. Bicyclic core estrogens as full antagonists: Synthesis, biological evaluation and structure–activity relationships of estrogen receptor ligands based on bridged oxabicyclic core arylsulfonamides. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2012, 10, 8692–8700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekhar, K.; Achar, C.J.; Govindaraju, T. A red-NIR emissive probe for the selective detection of albumin in urine samples and live cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2017, 15, 1584–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, N.; Carlson, K.E.; Nwachukwu, J.C.; Srinivasan, S.; Sharma, A.; Nettles, K.W.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. Exploring the Structural Compliancy versus Specificity of the Estrogen Receptor Using Isomeric Three-Dimensional Ligands. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017, 12, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nin, W.T.; Hu, Z.Y.; Tang, C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, S.L.; Dong, C.; Huang, J.; Zhou, H.B. Novel Hybrid Conjugates with Dual Suppression of Estrogenic and Inflammatory Activities Display Significantly Improved Potency against Breast Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 8155–8173. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, X.P.; Deng, X.F.; Ning, W.T.; Xin, L.L.; Li, Q.Z.; Hu, Z.Y.; Xie, B.H.; Liang, K.W.; Min, C.; Dong, C.E.; et al. Identification of Novel Dual-Target Estrogen Receptor α Degraders with Tubulin Inhibitory Activity for the Treatment of Endocrine-Resistant Breast Cancer. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 11094–11117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srinivasan, S.; Nwachukwu, J.C.; Bruno, N.E.; Dharmarajan, V.; Goswami, D.; Kastrati, I.; Novick, S.; Nowak, J.; Cavett, V.; Zhou, H.B.; et al. Full antagonism of the estrogen receptor without a prototypical ligand side chain. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, R.; Zhou, J.W.; Xin, L.L.; Zhou, H.B.; Huang, J. OBHSA, a novel selective estrogen receptor degrader, overcomes tamoxifen resistance through cell cycle arrest and unfolded protein response-mediated apoptosis in breast cancer. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2024, 244, 106599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.F.; Zhu, M.H.; Srinivasan, S.; Nwachukwu, J.C.; Cavett, V.; Min, J.; Carlson, K.E.; Wang, P.C.; Dong, C.N.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A.; et al. Development of Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator (SERM)-Like Activity Through an Indirect Mechanism of Estrogen Receptor Antagonism: Defining the Binding Mode of 7-Oxabicyclo 2.2.1 hept-5-ene Scaffold Core Ligands. Chemmedchem 2012, 7, 1094–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

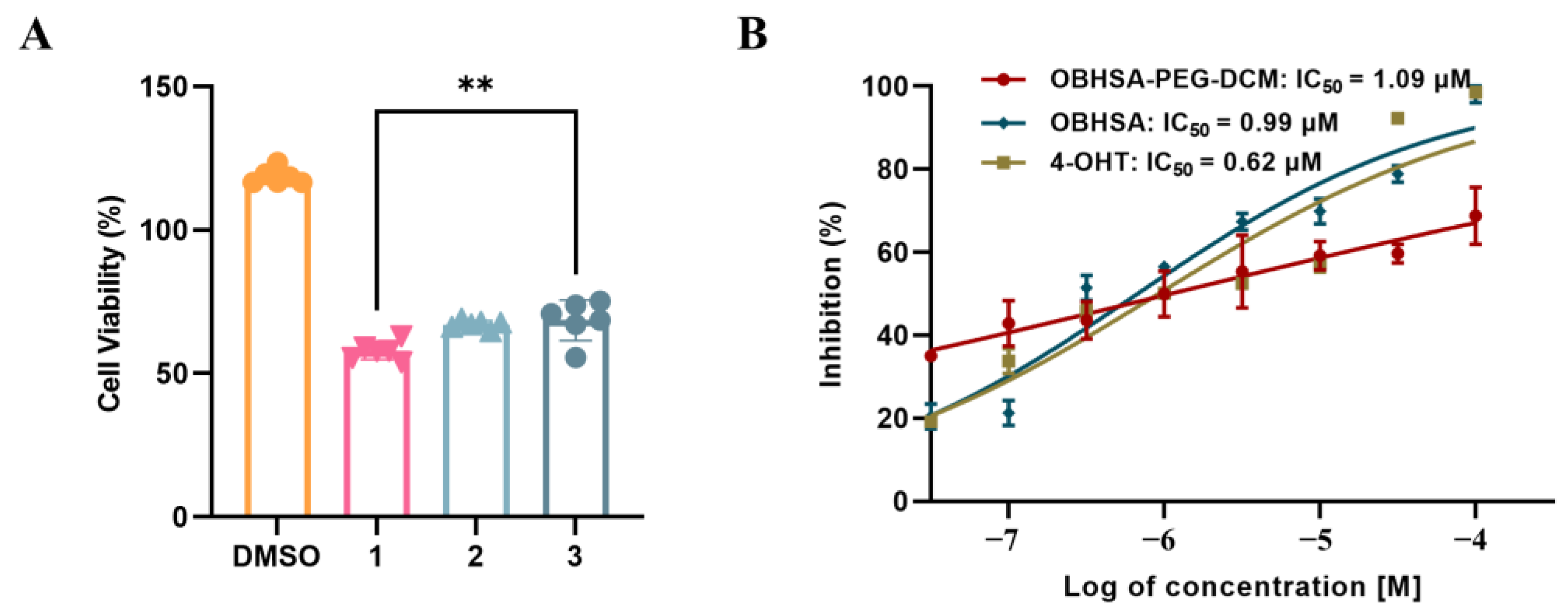


| Compounds | MCF-7 (IC50, µM) | MDA-MB-231 (IC50, µM) | DU145 (IC50, µM) |
|---|---|---|---|
| OBHSA | 0.99 ± 0.07 | >100 | >100 |
| OBHSA-PEG-DCM | 1.09 ± 0.08 | 6.60 ± 2.84 | >100 |
| DCM-PEG | >100 | >100 | >100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, X.; Deng, X.; Xin, L.; Dong, C.; Hu, G.; Zhou, H.-B. Pegylated NIR Fluorophore-Conjugated OBHSA Prodrug for ERα-Targeted Theranostics with Enhanced Imaging and Long-Term Retention. Molecules 2025, 30, 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020305
Wang X, Deng X, Xin L, Dong C, Hu G, Zhou H-B. Pegylated NIR Fluorophore-Conjugated OBHSA Prodrug for ERα-Targeted Theranostics with Enhanced Imaging and Long-Term Retention. Molecules. 2025; 30(2):305. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020305
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Xiaohua, Xiaofei Deng, Lilan Xin, Chune Dong, Guoyuan Hu, and Hai-Bing Zhou. 2025. "Pegylated NIR Fluorophore-Conjugated OBHSA Prodrug for ERα-Targeted Theranostics with Enhanced Imaging and Long-Term Retention" Molecules 30, no. 2: 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020305
APA StyleWang, X., Deng, X., Xin, L., Dong, C., Hu, G., & Zhou, H.-B. (2025). Pegylated NIR Fluorophore-Conjugated OBHSA Prodrug for ERα-Targeted Theranostics with Enhanced Imaging and Long-Term Retention. Molecules, 30(2), 305. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020305






