Drug Screening of Flavonoids as Potential VEGF Inhibitors Through Computational Docking and Cell Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
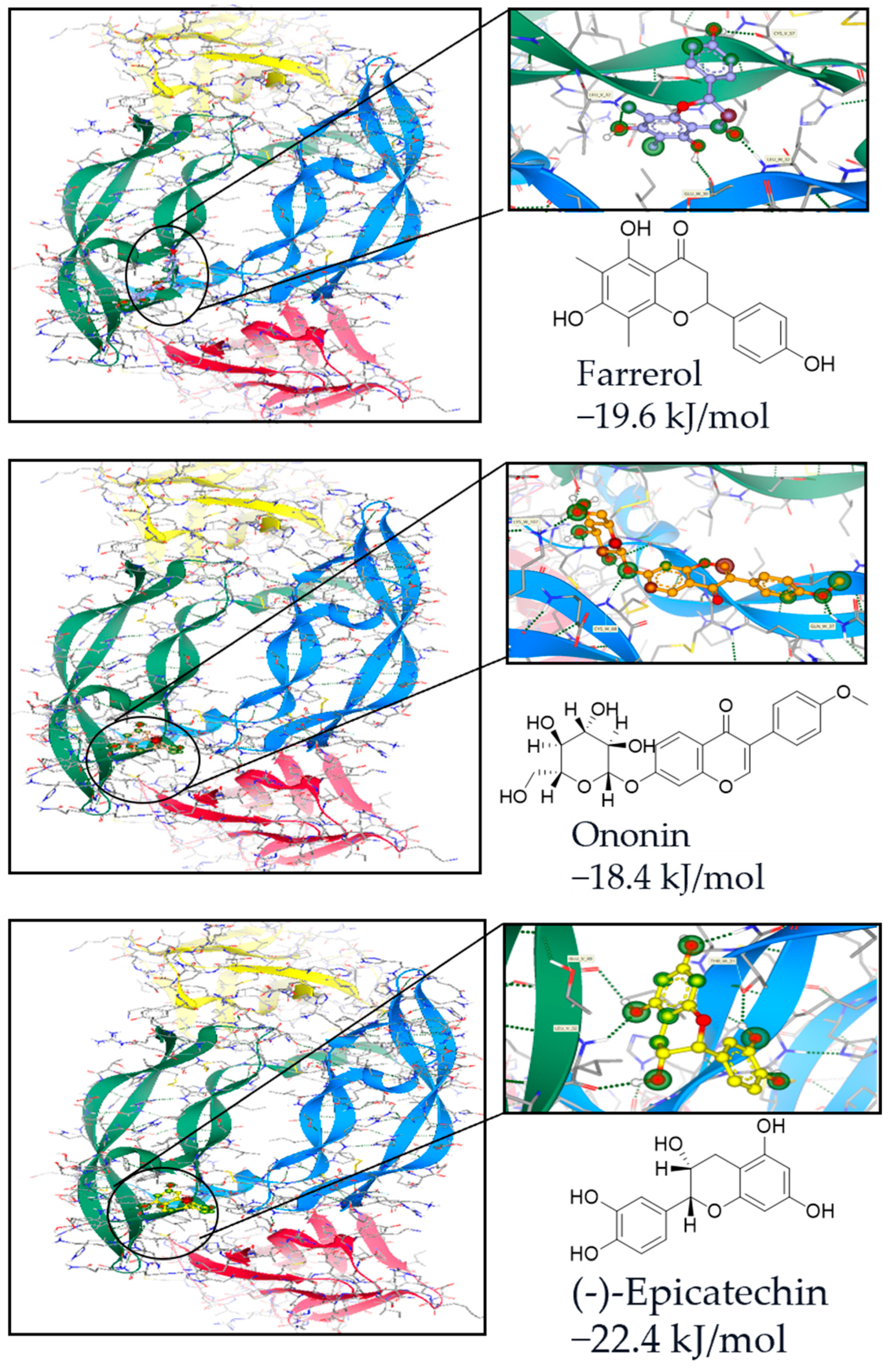
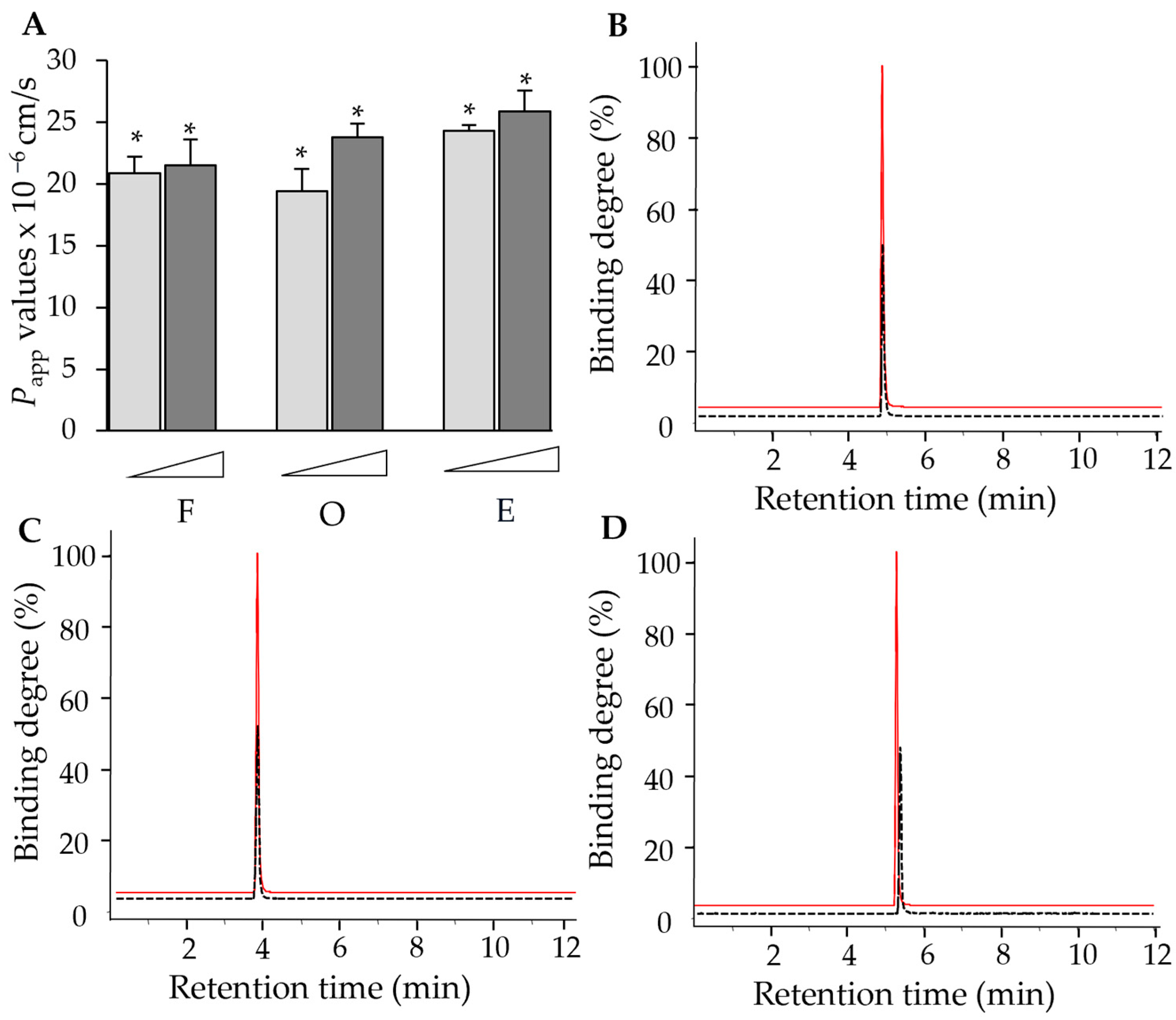
2.1. Computational Analysis-Aided Drug Screening of Flavonoids Against VEGF Protein
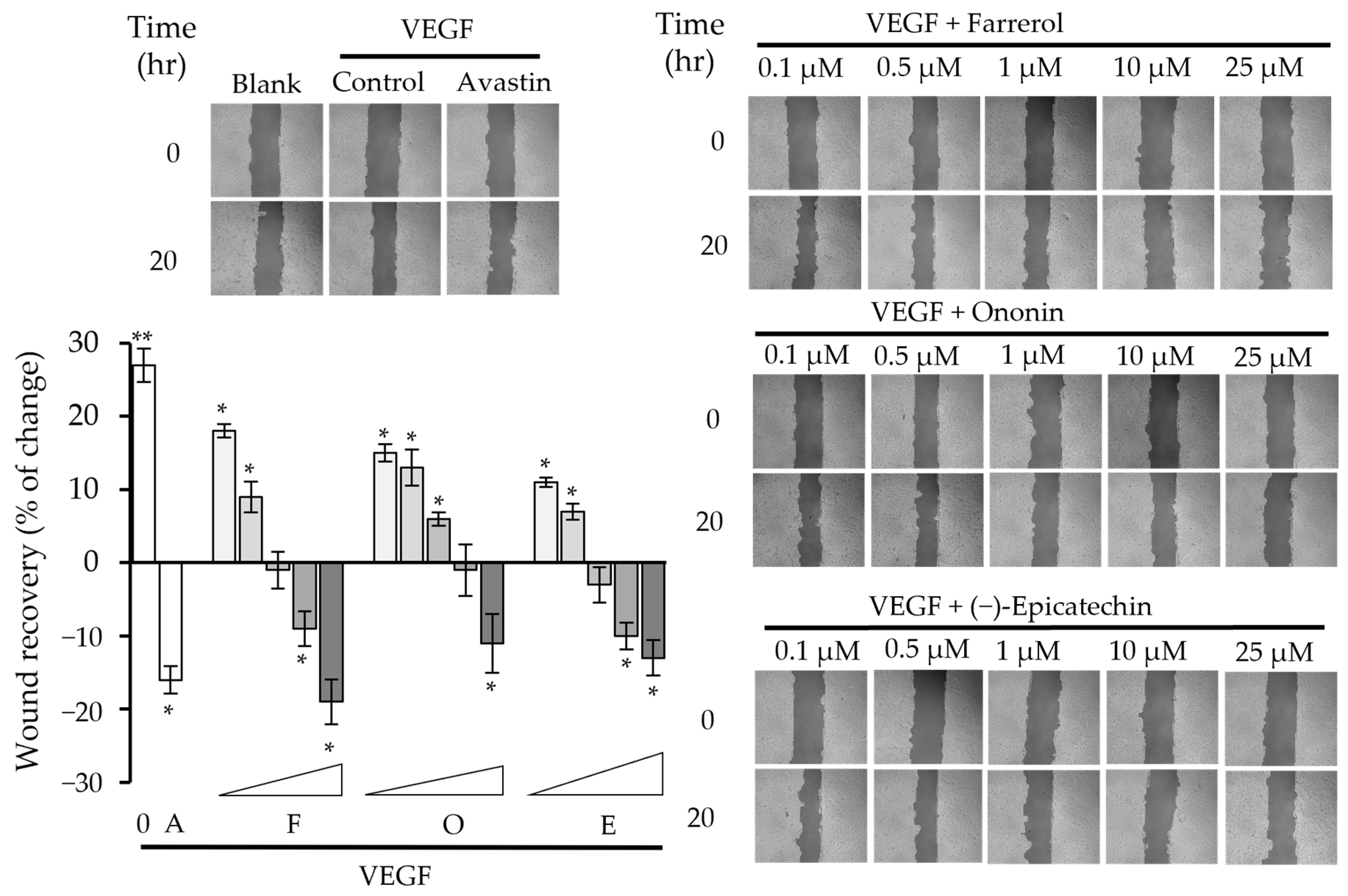
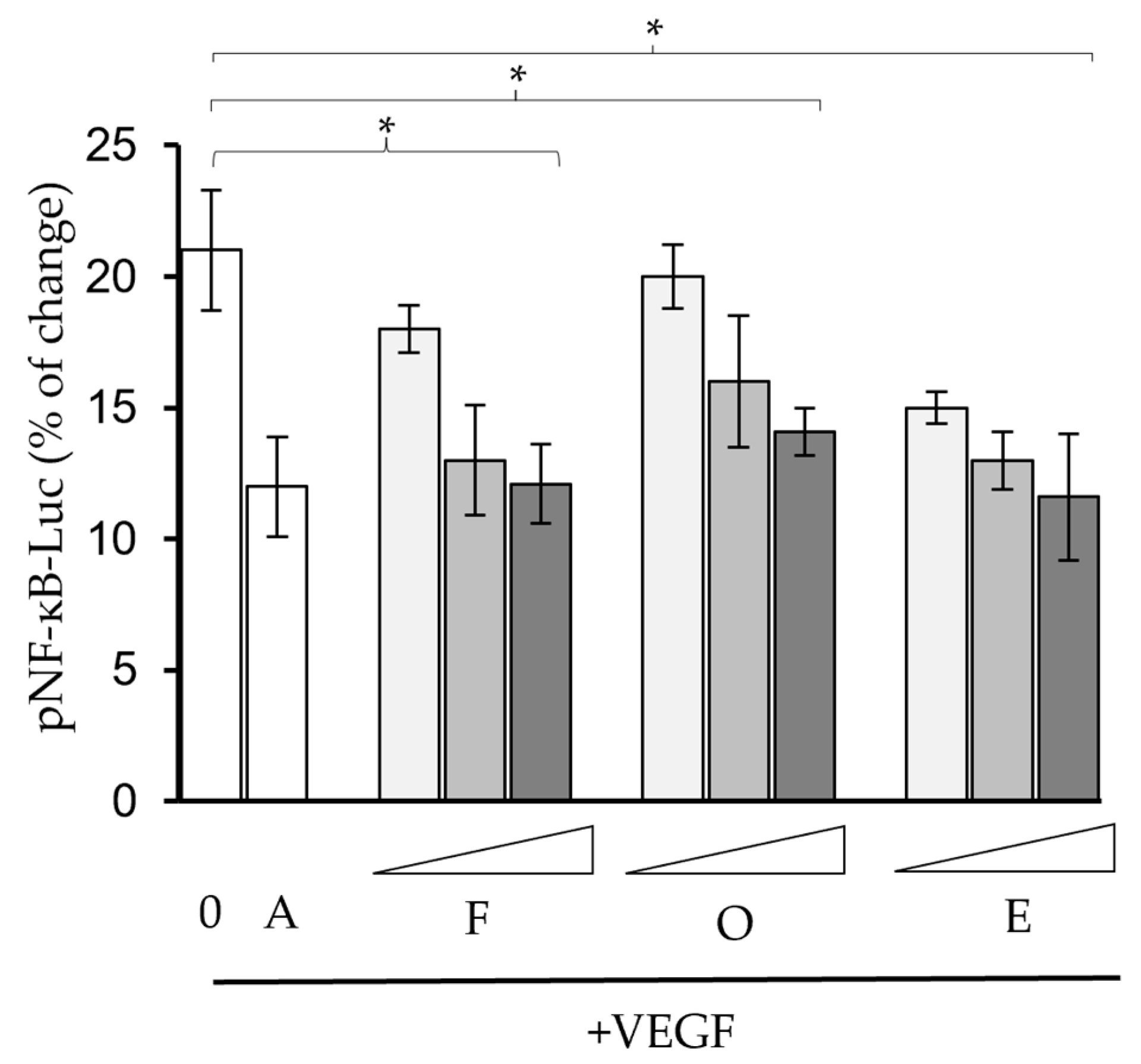
2.2. Phytochemicals Suppressed VEGF-Regulated Biological Activities
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Cultures
4.3. Cell Viability
4.4. Wound Closure Assay
4.5. Computational Docking Study
4.6. Stability Test Through HPLC Analysis
4.7. Transepithelial Permeability of Chemical Transport
4.8. Ultrafiltration-Based Affinity Assay
4.9. Luciferase Activity of NF-κB in RAW 264.3
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mandal, K.; Kent, S.B.H. Total chemical synthesis of biologically active vascular endothelial growth factor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8029–8033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, P.; Dwivedi, S.K.D.; Bhattacharya, R.; Mukherjee, P.; Rao, G. VEGF signaling: Role in angiogenesis and beyond. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2024, 1879, 189079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apte, R.S.; Chen, D.S.; Ferrara, N.F. VEGF in signaling and disease: Beyond discovery and development. Cell 2019, 176, 1248–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.A.; Jeong, M.S.; Ha, K.-T.; Jang, S.B. Structure and function of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor system. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanellies, J.; Fraser, S.; Katerelos, M.; Power, D.A. Vascular endothelial growth factor is a survival factor for renal tubular epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 2000, 278, 905–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noel, A.; Jost, M.; Lambert, V.; Lecomte, J.; Rakic, J.-M. Anti-angiogenic therapy of exudative age-related macular degeneration: Current progress and emerging concepts. TRENDS Mol. Med. 2007, 13, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Yang, B.; Tang, B.; Gong, G.; Kam, H.; Gao, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, R.; Lee, S.M.-Y. Differential angiogenic activities of naringin and naringenin in zebrafish in vivo and human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 49, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Mao, W.; Li, Y.; Qi, C.; He, Y. Myricetin inhibits breast tumor growth and angiogenesis by regulating VEGF/VEGFR2 and p38MAPK signaling pathways. Anatonical Rec. 2019, 302, 2186–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Li, X.; Lin, X. A review on applications of computational methods in drug screening and design. Molecules 2020, 25, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, R.J.; Rixe, O. Axitinib—A selective inhibitor of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor. Targ. Oncol. 2009, 4, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beneta, L.Z.; Hoseya, C.M.; Ursub, O.; Opreaba, T.I. BDDCS, the rule of 5 and drugability. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2016, 101, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Camilleri, P.; Brown, M.B.; Hutt, A.J.; Kirton, S.B. Revisiting the general solubility equation: In silico prediction of aqueous solubility incorporating the effect of topographical polar surface area. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 420–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T. ADME evaluation in drug discovery. 8. The prediction of human intestinal absorption by a support vector machine. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 2408–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X.; Han, F.; Chen, Z.; Wang, Y. The blood–brain barrier: Structure, regulation, and drug delivery. Nature 2023, 8, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, A.; Lepailleur, S.; Mignani, S.M.; Dallemagne, P.; Rochai, C. hERG toxicity assessment: Useful guidelines for drug design. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 195, 112290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juvale, I.I.A.; Hamid, A.A.A.; Halim, K.B.A.; Has, A.T.C. P-glycoprotein: New insights into structure, physiological function, regulation and alterations in disease. Heliyon 2022, 8, e09777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blessy, M.; Ruchi, D.P.; Prajesh, N.P.; Agrawal, Y.K. Development of forced degradation and stability indicating studies of drugs—A review. J. Pharm. Anal. 2014, 4, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Leach, D.N.; Wohlmuth, H.; De Voss, J.J.; Blanchfield, J.T. Caco-2 cell permeability of flavonoids and saponins from Gynostemma pentaphyllum: The immortal herb. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 21561–21569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabravolski, S.A.; Khotina, V.A.; Omelchenko, A.V.; Kalmykov, V.A.; Orekhov, A.N. The role of the VEGF family in atherosclerosis development and its potential as treatment targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, J.; Fang, Y.; Han, D.; Tan, X.; Jiang, H.; Gong, X.; Wang, X.; Hong, W.; Wei, W. Activation of nuclear factor-κB in the angiogenesis of glioma: Insights into the associated molecular mechanisms and targeted therapies. Cell Prolif. 2021, 54, e12929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melincovici, C.S.; Boşca, A.B.; Şuşman, S.; Mărginean, M.; Mihu, C.; Istrate, M.; Moldovan, I.M.; Roman, A.L.; Mihu, C.M. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)—Key factor in normal and pathological angiogenesis. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2018, 59, 455–467. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, G.H.; Rossant, J.; Gertsentein, M.; Breitman, M.L. Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 1995, 376, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Zhang, D.; Chen, J.; Ouyang, L.; Wu, F.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L. Recent progress on vascular endothelial growth factor receptor inhibitors with dual targeting capabilities for tumor therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghalehbandi, S.; Yuzugulen, J.; Pranjol, Z.I.; Pourgholami, M.H. The role of VEGF in cancer-induced angiogenesis and research progress of drugs targeting. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2023, 949, 175586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/ (accessed on 1 August 2024).
- Ferrara, N.; Hillan, K.J.; Gerber, H.-P.; Novotny, W. Discovery and development of bevacizumab, an anti-VEGF antibody for treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2014, 3, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escalante, C.P.; Zalpour, A. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibitor-induced hypertension: Basics for primary care providers. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2011, 2011, 816897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, W.-H.; Duan, R.; Xia, Y.-T.; Xiong, Q.-P.; Wang, H.-Y.; Chan, G.K.-L.; Liu, S.-Y.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Qin, Q.-W.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Binding of resveratrol to vascular endothelial growth factor suppresses angiogenesis by inhibiting the receptor signaling. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1127–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.-H.; Chan, G.K.-L.; Wang, H.-Y.; Kong, X.-P.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Synergy of ginkgetin and resveratrol in suppressing VEGF-induced angiogenesis: A therapy in treating colorectal cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khater, M.; Greco, F.; Osborn, H.M.I. Antiangiogenic activity of flavonoids: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Molecules 2020, 25, 4712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subbaraj, G.K.; Kumar, Y.S.; Kulanthaivel, L. Antiangiogenic role of natural flavonoids and their molecular mechanism: An update. Egypt. J. Intern. Med. 2021, 33, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Zhang, Y.H. Flavonoids with anti-angiogenesis function in cancer. Molecules 2024, 29, 1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, M.; Sinha, S.; Sudarshan, K.; Aidhen, I.S.; Doble, M. Inhibition of the enzymes in the leukotriene and prostaglandin pathways in inflammation by 3-aryl isocoumarins. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 124, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudarshan, K.; Aidhen, I.S. Convenient Synthesis of 3-Glycosylated Isocoumarins. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2017, 2017, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.S.; Gao, X.; Hu, W.; Wang, X.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Scutellarin potentiates the skin regenerative function of self-growth colony, an optimized platelet-rich plasma extract, in cultured keratinocytes through VEGF receptor and MAPK signaling. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 4836–4845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.X.; Xia, T.C.-X.; Mak, M.S.-H.; Kwan, K.K.-L.; Zheng, B.Z.-Y.; Xiao, J.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Luteolin stimulates the NGF-induced neurite outgrowth in cultured PC12 cells through binding with NGF and potentiating its receptor signaling. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 11515–11525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; McCallum, S.A.; Xiao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Linhardt, R.J. Binding affinities of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) for heparin-derived oligosaccharides. Biosci. Rep. 2012, 32, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, K.Y.-Z.; Choi, R.C.-Y.; Guo, A.J.-Y.; Bi, C.W.-C.; Zhu, K.Y.; Du, C.Y.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Lau, D.T.-W.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Tsim, K.W.-K. The membrane permeability of astragali radix-derived formononetin and calycosin is increased by angelicae sinensis radix in caco-2 cells: A synergistic action of an ancient herbal decoction Danggui Buxue Tang. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 70, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Analytes | Precision | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-Day (n = 6) a | Inter-Day (n = 6) b | |||
| Mean Peak Area c | RSD (%) | Mean Peak Area c | RSD (%) | |
| Farrerol (acidic) | 31,803.7 | 4.09 | 38,145.2 | 5.89 |
| Farrerol (neutral) | 31,542.0 | 4.79 | 36,478.1 | 4.43 |
| Farrerol (basic) | 33,332.4 | 2.81 | 35,412.4 | 6.54 |
| Ononin (acidic) | 254,398.2 | 1.93 | 275,981.3 | 4.12 |
| Ononin (neutral) | 313,200.4 | 1.61 | 265,877.4 | 3.65 |
| Ononin (basic) | 273,422.8 | 3.12 | 274,514.7 | 4.78 |
| Epicatechin (acidic) | 2751.5 | 3.98 | 2510.4 | 11.91 |
| Epicatechin (neutral) | 2826.6 | 1.38 | 2601.7 | 7.56 |
| Epicatechin (basic) | 2726.0 | 4.85 | 2519.4 | 13.58 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, S.; Tang, R.W.-L.; Ye, Y.; Xia, C.; Wu, J.; Duan, R.; Leung, K.-W.; Dong, T.T.-X.; Tsim, K.W.-K. Drug Screening of Flavonoids as Potential VEGF Inhibitors Through Computational Docking and Cell Models. Molecules 2025, 30, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020257
Lin S, Tang RW-L, Ye Y, Xia C, Wu J, Duan R, Leung K-W, Dong TT-X, Tsim KW-K. Drug Screening of Flavonoids as Potential VEGF Inhibitors Through Computational Docking and Cell Models. Molecules. 2025; 30(2):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020257
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Shengying, Roy Wai-Lun Tang, Yutong Ye, Chenxi Xia, Jiahui Wu, Ran Duan, Ka-Wing Leung, Tina Ting-Xia Dong, and Karl Wah-Keung Tsim. 2025. "Drug Screening of Flavonoids as Potential VEGF Inhibitors Through Computational Docking and Cell Models" Molecules 30, no. 2: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020257
APA StyleLin, S., Tang, R. W.-L., Ye, Y., Xia, C., Wu, J., Duan, R., Leung, K.-W., Dong, T. T.-X., & Tsim, K. W.-K. (2025). Drug Screening of Flavonoids as Potential VEGF Inhibitors Through Computational Docking and Cell Models. Molecules, 30(2), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30020257







