Targeting Bacterial Adenylate Kinase mRNA with a Chimeric Antisense Oligonucleotide for Rational Antibacterial Drug Development
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
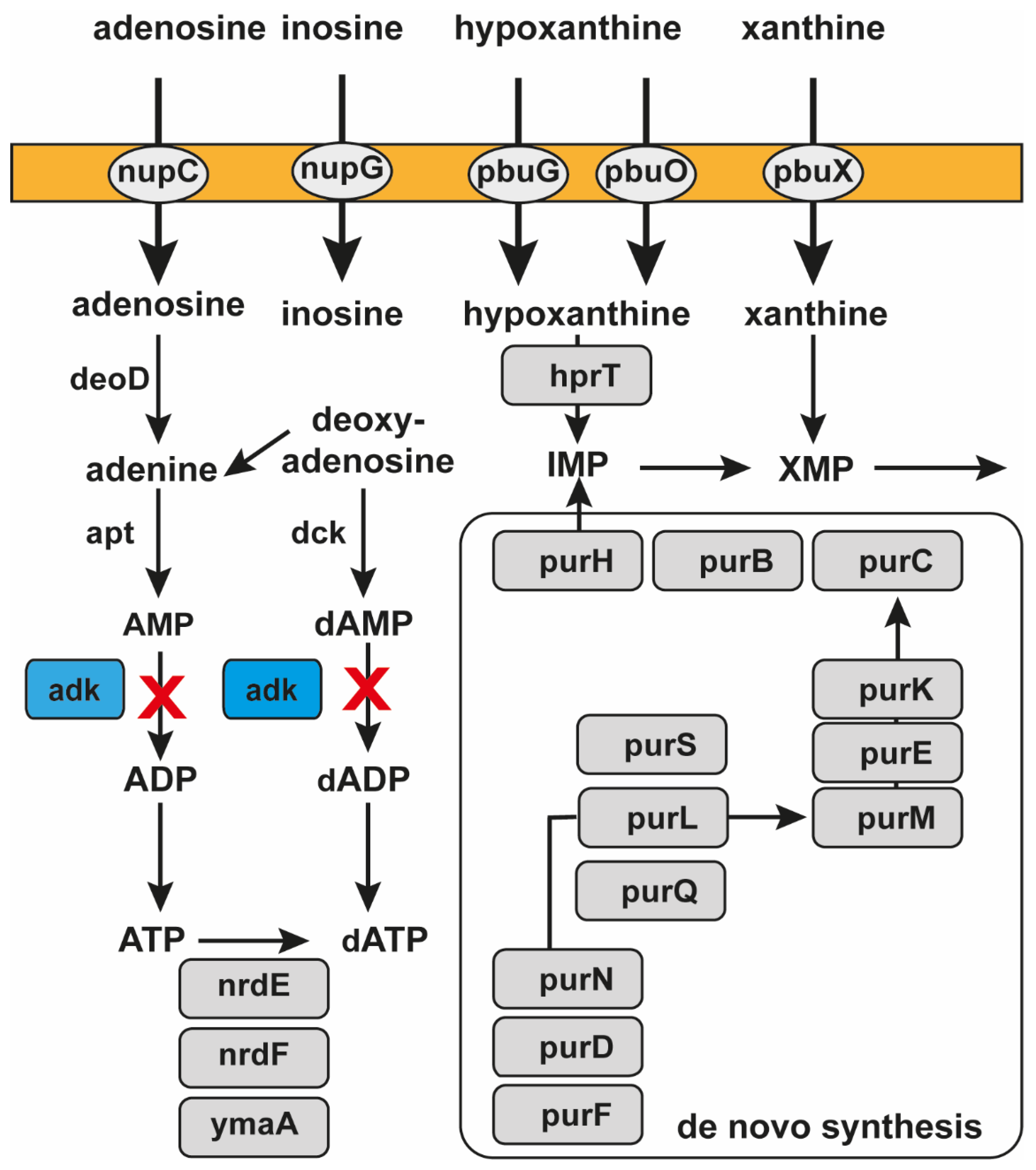
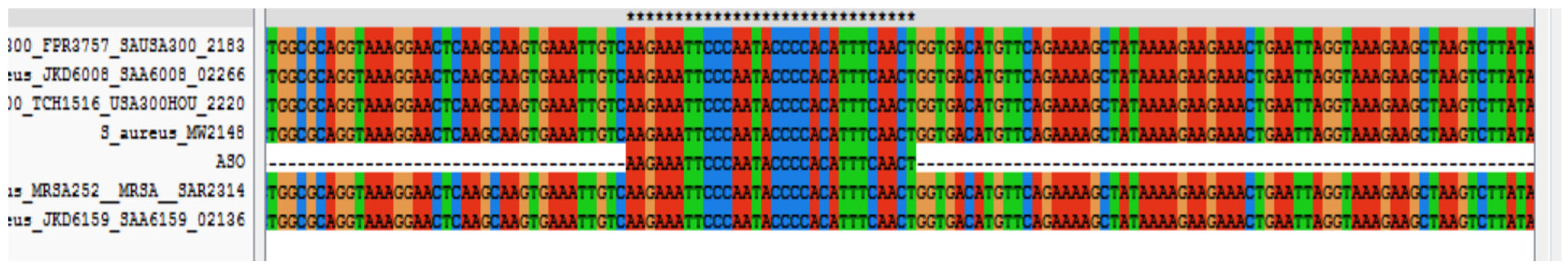
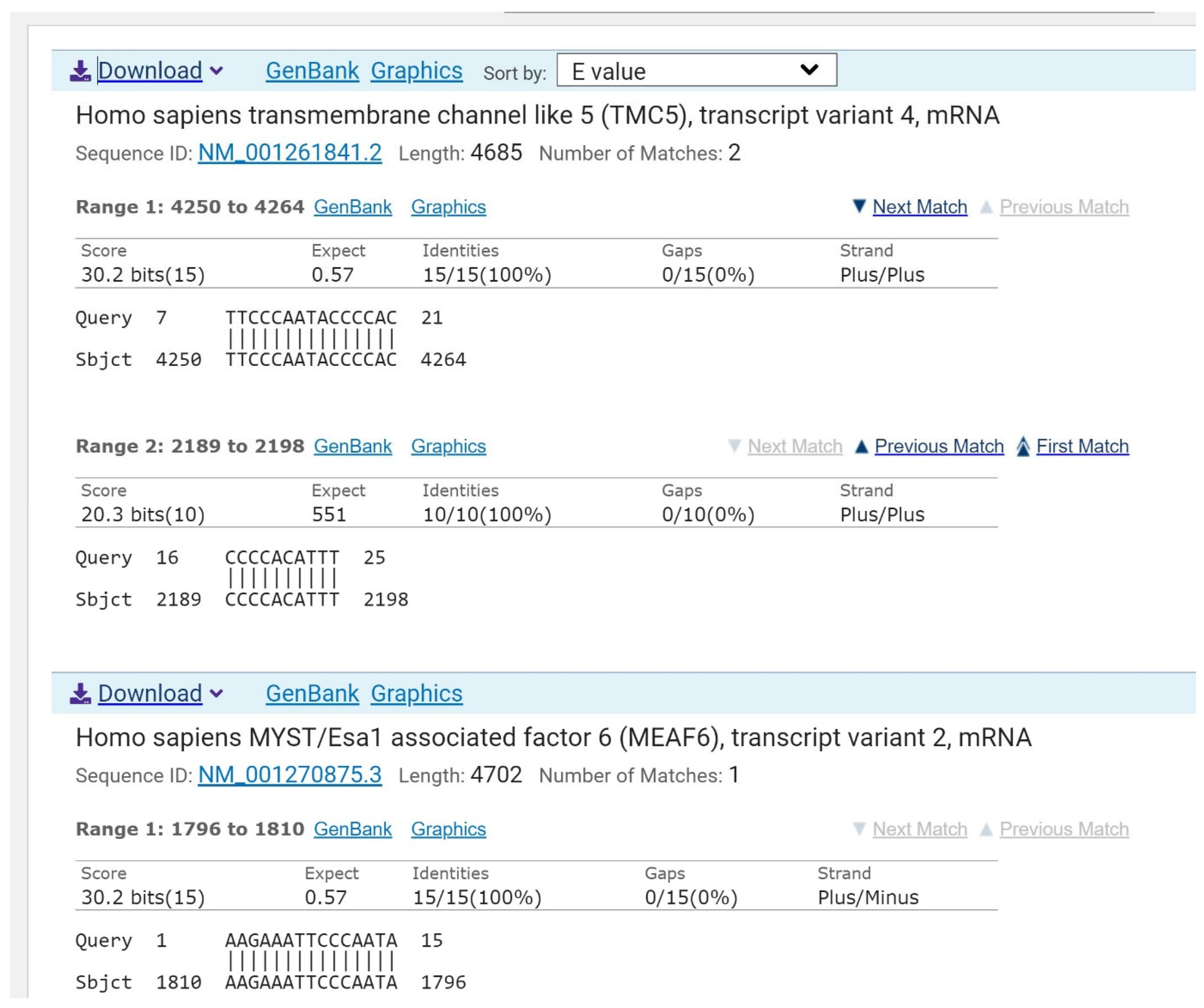
2.1. Assessing mRNA of Adenylate Kinase as a Target for Antibacterial Drug Development
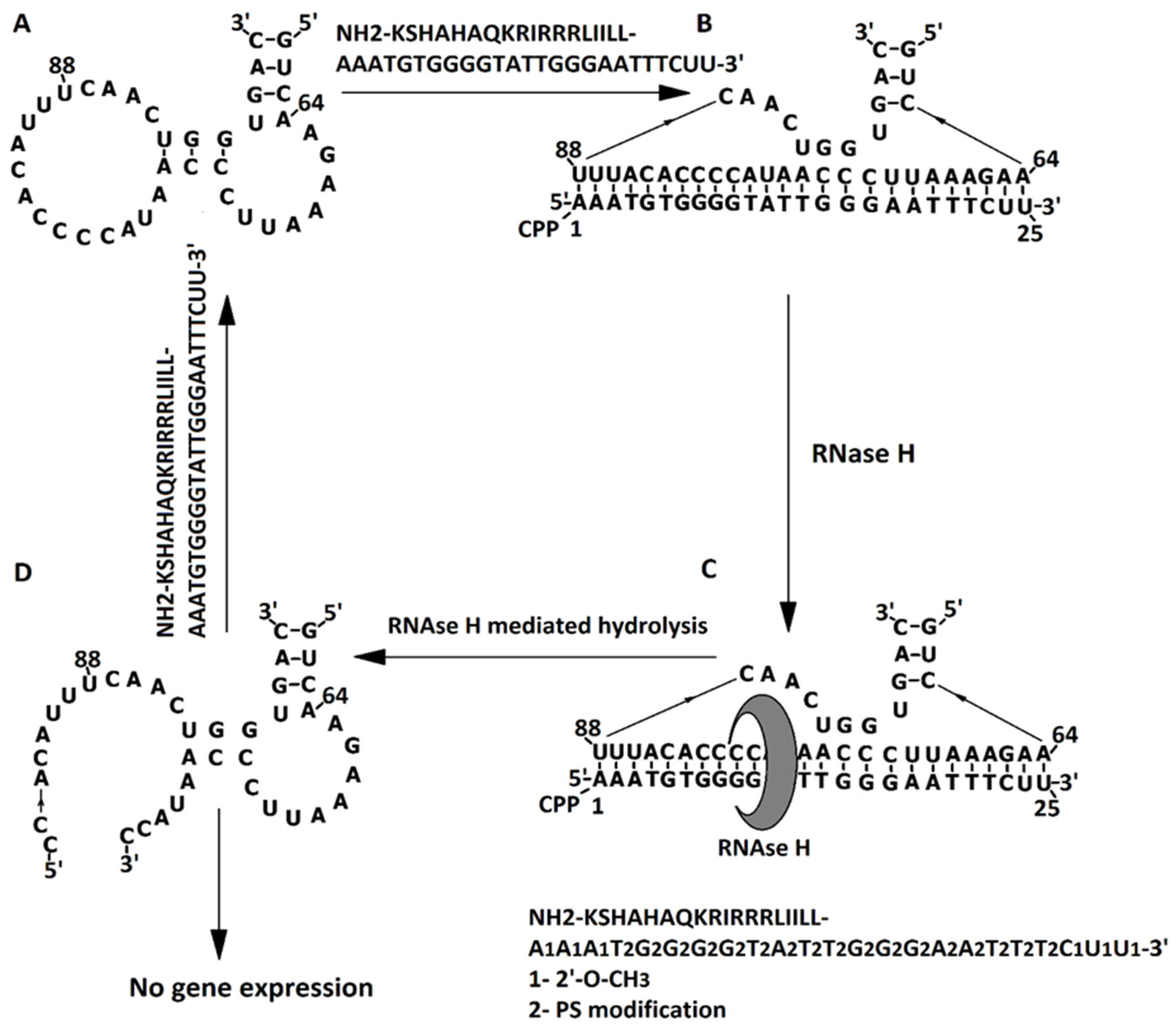
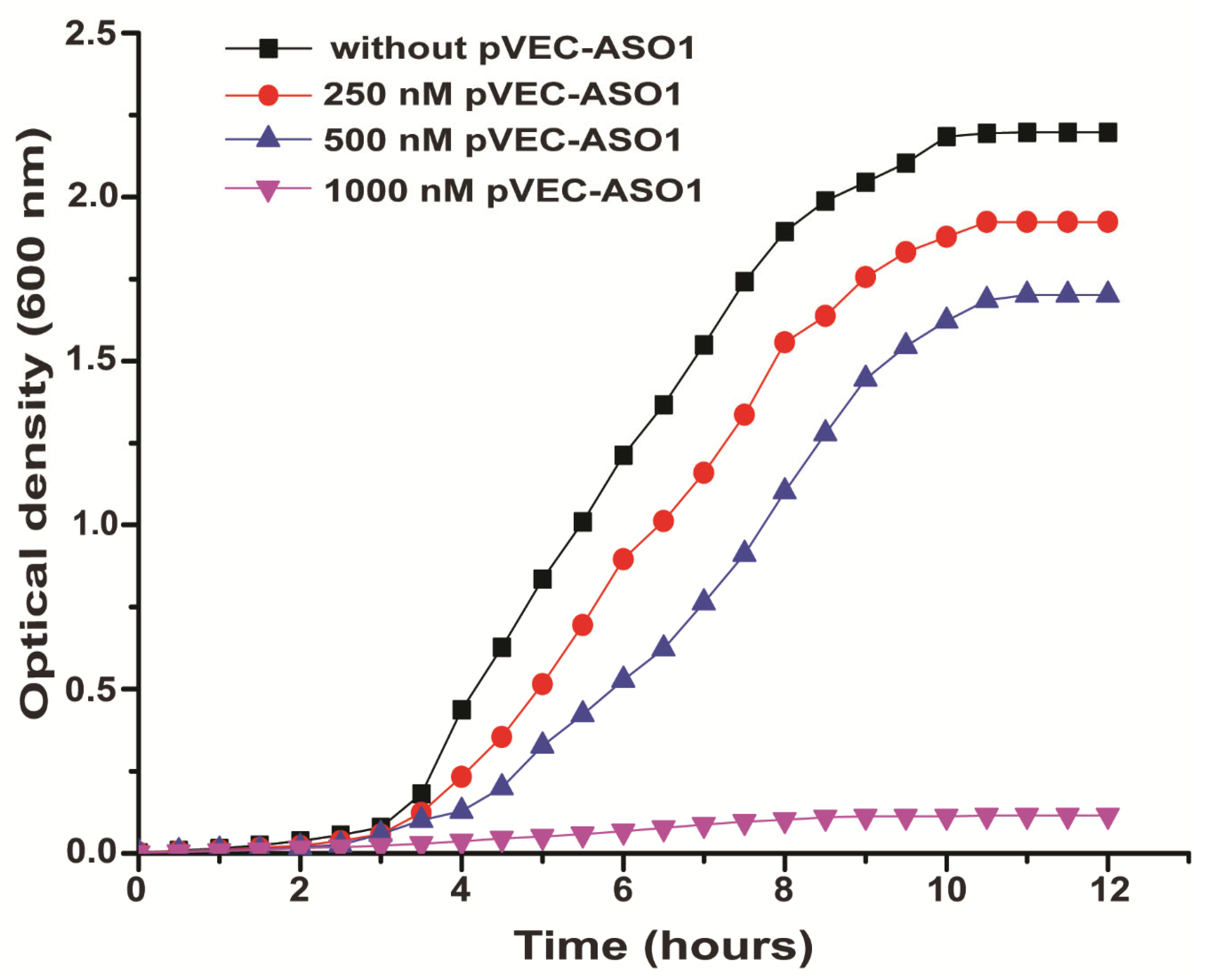
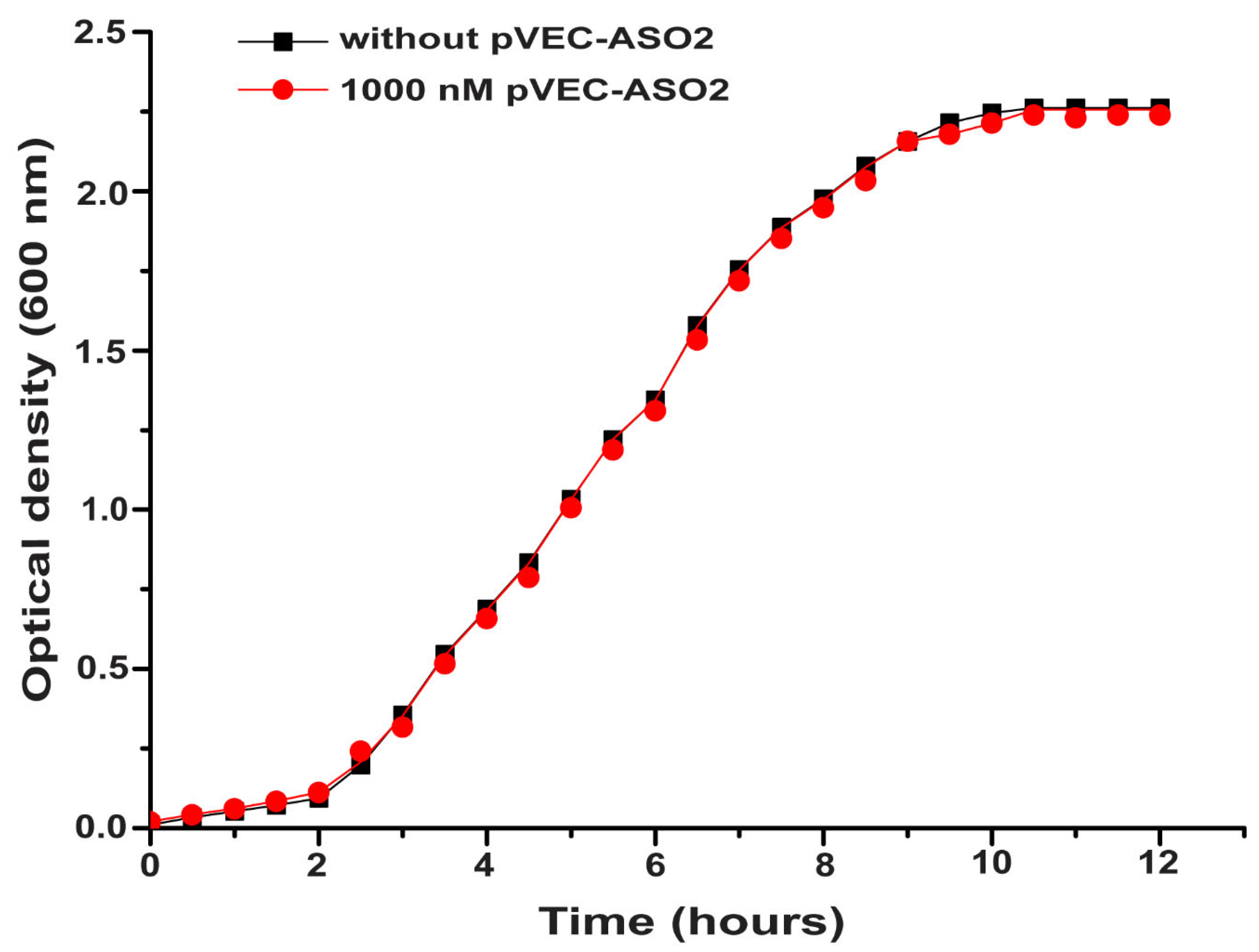
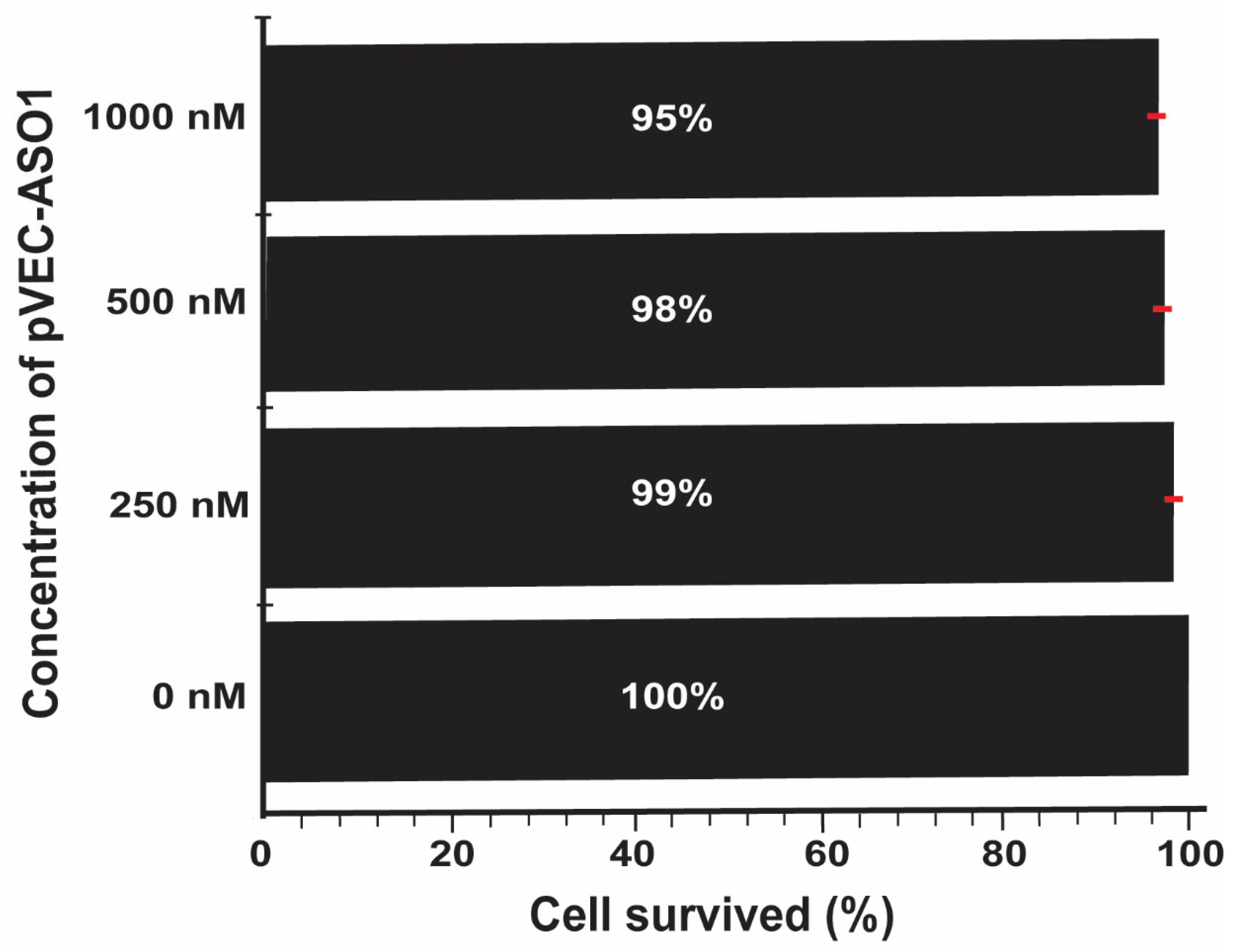
2.2. Bacterial Growth Inhibition by Targeting ADK mRNA with pVEC-ASO1
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Bioinformatics Databases and Software Used
4.3. In Vitro Experiments with Bacteria and Human Cell Cultures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ventola, C.L. The antibiotic resistance crisis: Part 1: Causes and threats. Pharmacol. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Blair, J.M.; Webber, M.A.; Baylay, A.J.; Ogbolu, D.O.; Piddock, L.J. Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.D.; Temkin, E.; Carmeli, Y. The negative impact of antibiotic resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, C.E.; Yarotsky, E.; Mason, E.O.; Kaplan, S.L.; Hulten, K.G. Molecular Characterization of Staphylococcus aureus Isolates From Children With Periorbital or Orbital Cellulitis. J. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. Soc. 2018, 7, 205–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcelin, J.R.; Challener, D.W.; Tan, E.M.; Lahr, B.D.; Baddour, L.M. Incidence and Effects of Seasonality on Nonpurulent Lower Extremity Cellulitis After the Emergence of Community-Acquired Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2017, 92, 1227–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, C.; Garland, E.; Hulten, K.G.; Mason, E.; Kaplan, S.L. Pediatric Periorbital and Orbital Cellulitis Caused by Staphylococcus aureus from 2002 to 2015. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, 670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Acar, M.C.; Lin, S.; González-Gutiérrez, J.F. Staphylococcal infectious folliculitis. (Part II). Rev. Cent. Dermatol. Pascua 2018, 26, 92–95. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, S.D.; Malachowa, N.; DeLeo, F.R. Pathogenesis of Staphylococcus aureus abscesses. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 1518–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, L.; Ma, C.; Qiao, H.; Drabik, C.; Hurley, C.; Jones, D.; Judkiewicz, S.; Faden, H. Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole Therapy Reduces Failure and Recurrence in Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Skin Abscesses after Surgical Drainage. J. Pediatr. 2016, 169, 128–134.E1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, M.; Takedomi, H.; Ando, Y.; Omura, K. Neck carbuncle associated with methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia. BMJ Case Rep. 2018, 2018, bcr-2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasai, N.; Nakaminami, H.; Iwasaki, M.; Iwao, M.; Misegawa, K.; Hasui, M.; Sato, M.; Yamamoto, S.; Yoshida, T.; Asano, T.; et al. Clonal change of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolated from patients with impetigo in Kagawa, Japan. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggal, S.D.; Bharara, T.; Jena, P.P.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, A.; Gur, R.; Chaudhary, S. Staphylococcal bullous impetigo in a neonate. World J. Clin. Cases 2016, 4, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrd, A.L.; Deming, C.; Cassidy, S.K.B.; Harrison, O.J.; Ng, W.I.; Conlan, S.; Program, N.C.S.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A.; Kong, H.H. Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis strain diversity underlying pediatric atopic dermatitis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaal4651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, J.; Bassiouni, A.; Drilling, A.; Psaltis, A.J.; Vreugde, S.; Wormald, P.J. The persistence of intracellular Staphylococcus aureus in the sinuses: A longitudinal study. Rhinology 2017, 55, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simoni, G.; Maccauro, G.; Fenga, D.; De Santis, V.; Orani, R.A.; Centofanti, F.; Rosa, M.A. Arthrodesis of the ankle joint in septic osteoarthritis: Six years long term outcomes in authors’ personal experience. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zapotoczna, M.; McCarthy, H.; Rudkin, J.K.; O’Gara, J.P.; O’Neill, E. An Essential Role for Coagulase in Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Development Reveals New Therapeutic Possibilities for Device-Related Infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1883–1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallejo, J.G.; Cain, A.N.; Mason, E.O.; Kaplan, S.L.; Hulten, K.G. Staphylococcus aureus Central Nervous System Infections in Children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2017, 36, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, V.H.; Babu, A.R.; Srinivas, D.; Siddaiah, N.; Somanna, S. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus central nervous system infections—Analysis and outcome. Br. J. Neurosurg. 2015, 29, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchenir, L.; Renaud, C.; Khan, S.; Bitnun, A.; Boisvert, A.A.; McDonald, J.; Bowes, J.; Brophy, J.; Barton, M.; Ting, J.; et al. The Epidemiology, Management, and Outcomes of Bacterial Meningitis in Infants. Pediatrics 2017, 140, e20170476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Self, W.H.; Wunderink, R.G.; Williams, D.J.; Zhu, Y.; Anderson, E.J.; Balk, R.A.; Fakhran, S.S.; Chappell, J.D.; Casimir, G.; Courtney, D.M.; et al. Staphylococcus aureus Community-acquired Pneumonia: Prevalence, Clinical Characteristics, and Outcomes. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 63, 300–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Wu, Y.; Riehle, A.; Ma, J.; Kamler, M.; Gulbins, E.; Grassme, H. Staphylococcus aureus Survives in Cystic Fibrosis Macrophages, Forming a Reservoir for Chronic Pneumonia. Infect. Immun. 2017, 85, e00883-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.-N.; Jan, I.-S.; Chang, H.-C.; Liu, J.-L.; Hsu, C.-L.; Tsao, W.-C.; Wu, H.; Wang, J.-Y. Community-Acquired and Health Care-Associated Staphylococcus Aureus Pneumonia. In B58. Clinical Studies in Lung Infections and Pneumonia: Treatment and Outcomes; American Thoracic Society: New York, NY, USA, 2019; p. A3701. [Google Scholar]
- Coombs, G.W.; Daley, D.A.; Thin Lee, Y.; Pearson, J.C.; Robinson, J.O.; Nimmo, G.R.; Collignon, P.; Howden, B.P.; Bell, J.M.; Turnidge, J.D.; et al. Australian Group on Antimicrobial Resistance Australian Staphylococcus aureus Sepsis Outcome Programme annual report, 2014. Commun. Dis. Intell. 2016, 40, E244–E254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sams, M.; Olsen, M.A.; Joshi, R.; Ranganathan, P. Staphylococcus aureus sepsis in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Li, Q.Y.; Zhang, G.L.; Tian, X.Y.; Chen, D.P.; Luo, Z.X. Current status of antibiotic therapy for Staphylococcus aureus sepsis in children. Chin. J. Contemp. Pediatr. 2019, 21, 387–392. [Google Scholar]
- Bergin, S.P.; Holland, T.L.; Fowler, V.G., Jr.; Tong, S.Y.C. Bacteremia, Sepsis, and Infective Endocarditis Associated with Staphylococcus aureus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2017, 409, 263–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.M.; Sorabella, R.A.; Vasan, S.; Grbic, M.; Lambert, D.; Prasad, R.; Wang, C.; Kurlansky, P.; Borger, M.A.; Gordon, R.; et al. Influence of Staphylococcus aureus on Outcomes after Valvular Surgery for Infective Endocarditis. J. Cardiothorac. Surg. 2017, 12, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauridsen, T.K.; Park, L.; Tong, S.Y.; Selton-Suty, C.; Peterson, G.; Cecchi, E.; Afonso, L.; Habib, G.; Pare, C.; Tamin, S.; et al. Echocardiographic Findings Predict In-Hospital and 1-Year Mortality in Left-Sided Native Valve Staphylococcus aureus Endocarditis: Analysis From the International Collaboration on Endocarditis-Prospective Echo Cohort Study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2015, 8, e003397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, K.; Bal, A.M.; Gould, I.M.; David, M.Z.; Dryden, M.; Giannitsioti, E.; Hijazi, K.; Meisner, J.A.; Esposito, S.; Scaglione, F.; et al. An update on Staphylococcus aureus infective endocarditis from the International Society of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (ISAC). Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, A.D.; Showler, A.; Burry, L.; Steinberg, M.; Ricciuto, D.R.; Fernandes, T.; Chiu, A.; Raybardhan, S.; Science, M.; Fernando, E.; et al. Impact of Infectious Disease Consultation on Quality of Care, Mortality, and Length of Stay in Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia: Results From a Large Multicenter Cohort Study. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 60, 1451–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, M.; Schmitz, R.P.; Hagel, S.; Pletz, M.W.; Gagelmann, N.; Scherag, A.; Schlattmann, P.; Brunkhorst, F.M. Infectious disease consultation for Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia—A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Infect. 2016, 72, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMullan, B.J.; Bowen, A.; Blyth, C.C.; Van Hal, S.; Korman, T.M.; Buttery, J.; Voss, L.; Roberts, S.; Cooper, C.; Tong, S.Y.; et al. Epidemiology and Mortality of Staphylococcus aureus Bacteremia in Australian and New Zealand Children. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, 979–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.; Elaldi, N.; Balkan, I.I.; Arslan, F.; Batirel, A.A.; Bakici, M.Z.; Gozel, M.G.; Alkan, S.; Celik, A.D.; Yetkin, M.A.; et al. Mortality predictors of Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia: A prospective multicenter study. Ann. Clin. Microbiol. Antimicrob. 2016, 15, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herkel, T.; Uvizl, R.; Doubravska, L.; Adamus, M.; Gabrhelik, T.; Htoutou Sedlakova, M.; Kolar, M.; Hanulik, V.; Pudova, V.; Langova, K.; et al. Epidemiology of hospital-acquired pneumonia: Results of a Central European multicenter, prospective, observational study compared with data from the European region. Biomed. Pap. Med. Fac. Univ. Palacky Olomouc Czech Repub. 2016, 160, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustave, C.A.; Tristan, A.; Martins-Simoes, P.; Stegger, M.; Benito, Y.; Andersen, P.S.; Bes, M.; Le Hir, T.; Diep, B.A.; Uhlemann, A.C.; et al. Demographic fluctuation of community-acquired antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus aureus lineages: Potential role of flimsy antibiotic exposure. ISME J. 2018, 12, 1879–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penchovsky, R.; Stoilova, C.C. Riboswitch-based antibacterial drug discovery using high-throughput screening methods. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 65–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traykovska, M.; Penchovsky, R. Targeting SAM-I Riboswitch Using Antisense Oligonucleotide Technology for Inhibiting the Growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.; Penchovsky, R. Genome-wide bioinformatics analysis of FMN, SAM-I, glmS, TPP, lysine, purine, cobalamin, and SAH riboswitches for their applications as allosteric antibacterial drug targets in human pathogenic bacteria. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2019, 23, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlova, N.; Traykovska, M.; Penchovsky, R. Targeting FMN, TPP, SAM-I, and glmS Riboswitches with Chimeric Antisense Oligonucleotides for Completely Rational Antibacterial Drug Development. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.; De Hoyos, C.L.; Migawa, M.T.; Vickers, T.A.; Sun, H.; Low, A.; Bell, T.A., 3rd; Rahdar, M.; Mukhopadhyay, S.; Hart, C.E.; et al. Chemical modification of PS-ASO therapeutics reduces cellular protein-binding and improves the therapeutic index. Nat. Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penchovsky, R.; Pavlova, N.; Kaloudas, D. RSwitch: A Novel Bioinformatics Database on Riboswitches as Antibacterial Drug Targets. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. 2021, 18, 804–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guidotti, G.; Brambilla, L.; Rossi, D. Cell-Penetrating Peptides: From Basic Research to Clinics. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2017, 38, 406–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traykovska, M.; Otcheva, L.A.; Penchovsky, R. Targeting TPP Riboswitches Using Chimeric Antisense Oligonucleotide Technology for Antibacterial Drug Development. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2022, 5, 4896–4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, M.; Birch, D.; Nielsen, H.M. Applications and Challenges for Use of Cell-Penetrating Peptides as Delivery Vectors for Peptide and Protein Cargos. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boisguerin, P.; Deshayes, S.; Gait, M.J.; O’Donovan, L.; Godfrey, C.; Betts, C.A.; Wood, M.J.; Lebleu, B. Delivery of therapeutic oligonucleotides with cell penetrating peptides. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2015, 87, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielinska, A.; Shivdasani, R.A.; Zhang, L.Q.; Nabel, G.J. Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides. Science 1990, 250, 997–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, J.W.; Ott, J.; Eckstein, F. The Rapid Generation of Oligonucleotide-Directed Mutations at High-Frequency Using Phosphorothioate-Modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985, 13, 8765–8785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozbas-Turan, S.; Akbuga, J.; Sezer, A.D. Topical application of antisense oligonucleotide-loaded chitosan nanoparticles to rats. Oligonucleotides 2010, 20, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, L.; Liu, C.; Jiang, K.; Chen, X.; Feng, L.; Pan, W.; Wei, G.; Lu, W. A novel penetratin-modified complex for noninvasive intraocular delivery of antisense oligonucleotides. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Putten, M.; Young, C.; van den Berg, S.; Pronk, A.; Hulsker, M.; Karnaoukh, T.G.; Vermue, R.; van Dijk, K.W.; de Kimpe, S.; Aartsma-Rus, A. Preclinical Studies on Intestinal Administration of Antisense Oligonucleotides as a Model for Oral Delivery for Treatment of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2014, 3, e211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyermann, J.; Lochmann, D.; Zimmer, A. Comparison of antisense oligonucleotide drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2004, 100, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traykovska, M.; Penchovsky, R. Engineering Antisense Oligonucleotides as Antibacterial Agents That Target FMN Riboswitches and Inhibit the Growth of Staphylococcus aureus, Listeria monocytogenes, and Escherichia coli. ACS Synth. Biol. 2022, 11, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Traykovska, M.; Popova, K.B.; Penchovsky, R. Targeting glmS Ribozyme with Chimeric Antisense Oligonucleotides for Antibacterial Drug Development. ACS Synth. Biol. 2021, 10, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Name | Sequence | Target |
|---|---|---|
| pVEC-ASO1 | 5′-A1A1A1T2G2T2G2G2G2G2T2A2T2T2G2G2G2A2A2T2T2T2C1U1U1 | ADK |
| pVEC-ASO2 | 5′-U1A1C2G2C2T2C2G2G2A1C1 | non |
| pVEC | NH2-KSHAHAQKRIRRRLIILL-COOH | non |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Otcheva, L.A.; Traykovska, M.; Penchovsky, R. Targeting Bacterial Adenylate Kinase mRNA with a Chimeric Antisense Oligonucleotide for Rational Antibacterial Drug Development. Molecules 2025, 30, 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163425
Otcheva LA, Traykovska M, Penchovsky R. Targeting Bacterial Adenylate Kinase mRNA with a Chimeric Antisense Oligonucleotide for Rational Antibacterial Drug Development. Molecules. 2025; 30(16):3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163425
Chicago/Turabian StyleOtcheva, Lozena A., Martina Traykovska, and Robert Penchovsky. 2025. "Targeting Bacterial Adenylate Kinase mRNA with a Chimeric Antisense Oligonucleotide for Rational Antibacterial Drug Development" Molecules 30, no. 16: 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163425
APA StyleOtcheva, L. A., Traykovska, M., & Penchovsky, R. (2025). Targeting Bacterial Adenylate Kinase mRNA with a Chimeric Antisense Oligonucleotide for Rational Antibacterial Drug Development. Molecules, 30(16), 3425. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30163425









