Targeting RARγ Decreases Immunosuppressive Macrophage Polarization and Reduces Tumor Growth
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
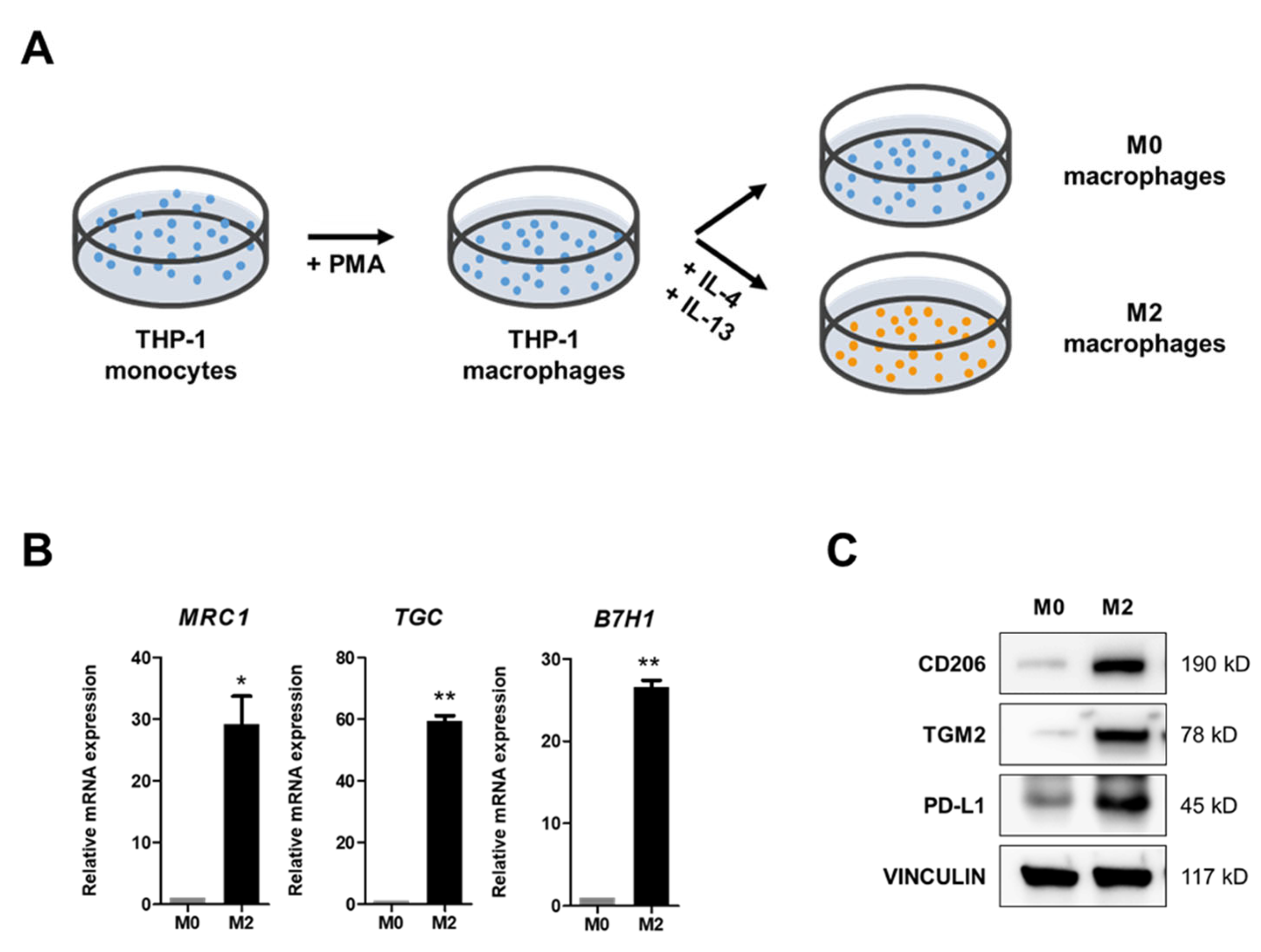
2.1. IL-4 and IL-13 Treatments Induce M2 Polarization of M0 Macrophages
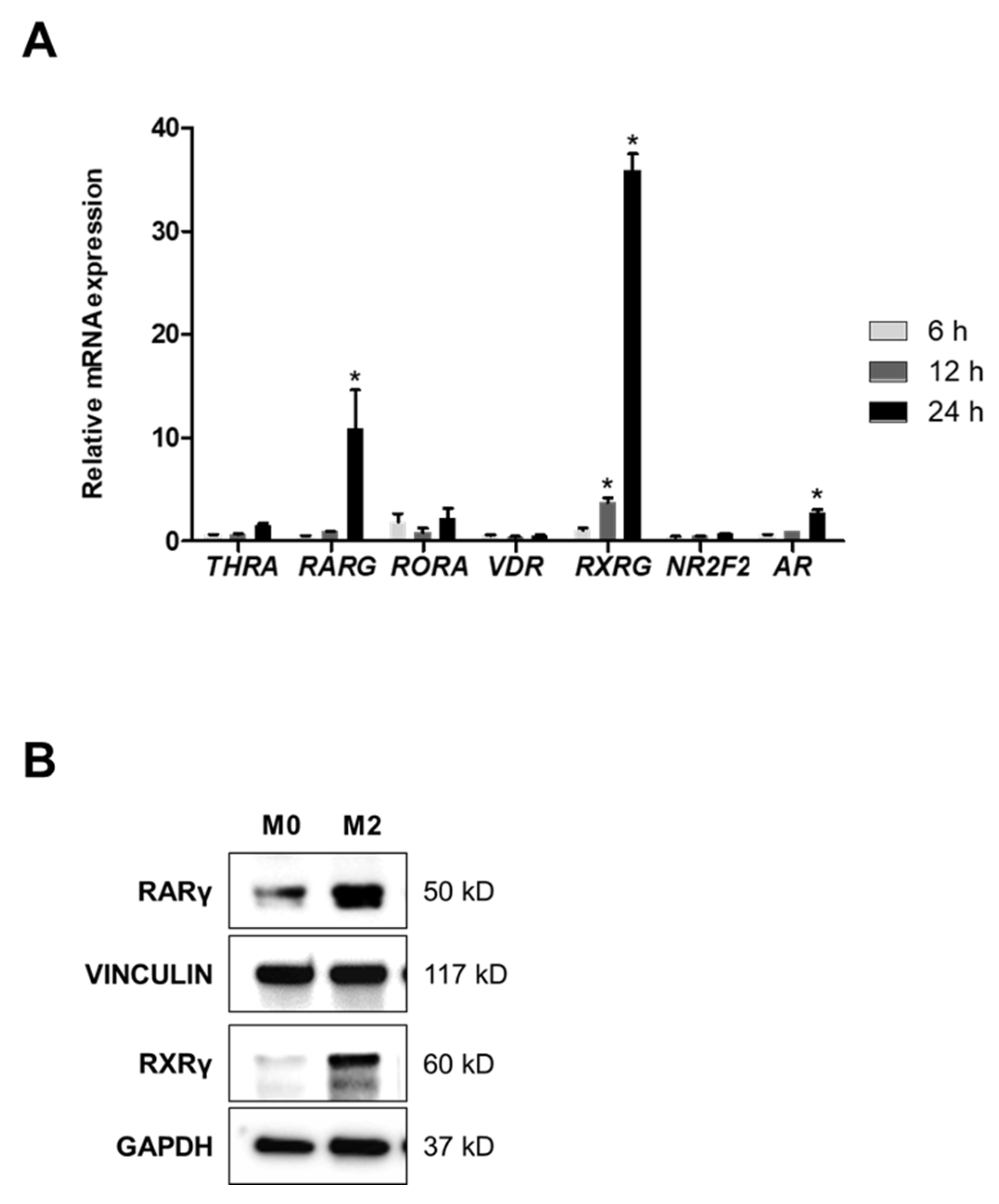
2.2. A Heterodimer of RARγ and RXRγ Mediates M2 Polarization
2.3. Inhibition of RARγ Suppresses M2 Polarization
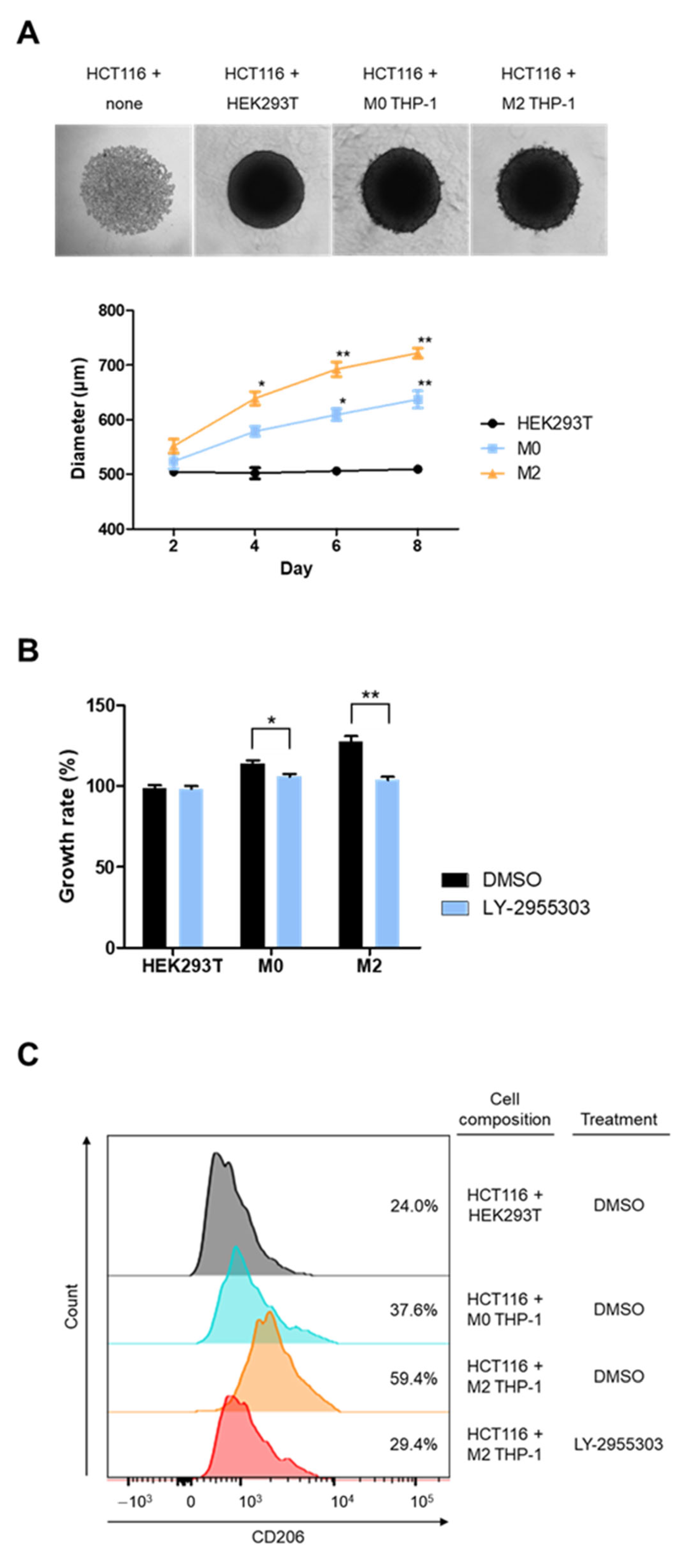
2.4. RARγ Inhibitor Impedes Macrophage-Associated Tumor Growth in Spheroid Culture
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. Spheroidal Co-Culture of THP-1 and HCT116 Cells
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Real-Time Quantitative PCR (qPCR) Analysis
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. siRNA Transfection
4.7. Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorting (FACS)
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Anderson, N.M.; Simon, M.C. The tumor microenvironment. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, R921–R925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.H.; Kim, D.H.; Chun, K.S. Tumor microenvironment regulation by reactive oxygen species-mediated inflammasome activation. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2025, 48, 115–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Visser, K.E.; Joyce, J.A. The evolving tumor microenvironment: From cancer initiation to metastatic outgrowth. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 374–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, B.; Zhang, B.; Li, B.; Wu, H.; Jiang, M. Cold and hot tumors: From molecular mechanisms to targeted therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Shao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wang, F.X.C.; Mu, J.; Li, J.; Yao, H.; Chen, K. Role of tumor microenvironment in cancer progression and therapeutic strategy. Cancer Med. 2023, 12, 11149–11165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Liu, J.; Qian, H.; Zhuang, Q. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: From basic science to anticancer therapy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1322–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajewski, T.F.; Schreiber, H.; Fu, Y.-X. Innate and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nat. Immunol. 2013, 14, 1014–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassetta, L.; Pollard, J.W. Targeting macrophages: Therapeutic approaches in cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 887–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, T. Tumor-Associated Macrophages in Tumor Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 583084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Kang, T.; Chen, S. The role of tumor-associated macrophages in tumor immune evasion. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 150, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, U.; Sarkar, T.; Mukherjee, S.; Chakraborty, S.; Dutta, A.; Dutta, S.; Nayak, D.; Kaushik, S.; Das, T.; Sa, G. Tumor-associated macrophages: An effective player of the tumor microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1295257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Saeed, A.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Xu, H.; Xiao, G.G.; Rao, L.; Duo, Y. Macrophages in immunoregulation and therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Allavena, P.; Marchesi, F.; Garlanda, C. Macrophages as tools and targets in cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 799–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Taylor, P.R. Monocyte and macrophage heterogeneity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo, B.; Zhu Chen, L.; Paniagua-Sancho, M.; Marchal, J.A.; Peran, M.; Giovannetti, E. Deciphering the performance of macrophages in tumour microenvironment: A call for precision immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2024, 17, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.; Luo, J.; Guo, W.; Sun, L.; Lin, L. Targeting M2-like tumor-associated macrophages is a potential therapeutic approach to overcome antitumor drug resistance. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, M.; Zhao, Y. The Regulatory Network of Transcription Factors in Macrophage Polarization. ImmunoTargets Ther. 2025, 14, 555–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, M.; Ji, C.; Liu, X.; Gu, B.; Dong, T. Macrophage polarization in the tumor microenvironment: Emerging roles and therapeutic potentials. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 177, 116930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bied, M.; Ho, W.W.; Ginhoux, F.; Bleriot, C. Roles of macrophages in tumor development: A spatiotemporal perspective. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 983–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Sioud, M. Tumor-Associated Macrophage Subsets: Shaping Polarization and Targeting. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 7493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Chen, X.; Guo, C.; Wang, W. Tumour-associated macrophages heterogeneity drives resistance to clinical therapy. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2022, 24, e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, Y.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Ge, S.; Zhong, F.; Xia, G.; Sun, C. Tumor-Associated Macrophages: A Potential Target for Cancer Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 693517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Song, Y.; Du, W.; Gong, L.; Chang, H.; Zou, Z. Tumor-associated macrophages: An accomplice in solid tumor progression. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Z.; Ding, S. The Crosstalk Between Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) and Tumor Cells and the Corresponding Targeted Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 590941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Li, F.; Jin, S.; Ho, P.C.; Liu, P.S.; Xie, X. Functional polarization of tumor-associated macrophages dictated by metabolic reprogramming. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altucci, L.; Leibowitz, M.D.; Ogilvie, K.M.; de Lera, A.R.; Gronemeyer, H. RAR and RXR modulation in cancer and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2007, 6, 793–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino-Lagos, K.; Guo, Y.; Noelle, R.J. Retinoic acid: A key player in immunity. BioFactors 2010, 36, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Geng, X.; Hou, J.; Wu, G. New insights into M1/M2 macrophages: Key modulators in cancer progression. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.; Rochette-Egly, C. The molecular physiology of nuclear retinoic acid receptors. From health to disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1812, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Zhou, S.; Gustafsson, J.A. Nuclear Receptors: Recent Drug Discovery for Cancer Therapies. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1207–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szanto, A.; Narkar, V.; Shen, Q.; Uray, I.P.; Davies, P.J.; Nagy, L. Retinoid X receptors: X-ploring their (patho)physiological functions. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11 (Suppl. S2), S126–S143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Xu, J.; Lan, H. Tumor-associated macrophages in tumor metastasis: Biological roles and clinical therapeutic applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, F.; Wang, R.; Yi, Z.; Luo, P.; Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Z.; Xia, Z.; Zhang, H.; Cheng, Q. Tissue macrophages: Origin, heterogenity, biological functions, diseases and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talukdar, P.D.; Chatterji, U. Transcriptional co-activators: Emerging roles in signaling pathways and potential therapeutic targets for diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Shi, Y.; Yin, B. Macrophage barrier in the tumor microenvironment and potential clinical applications. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kzhyshkowska, J.; Shen, J.; Larionova, I. Targeting of TAMs: Can we be more clever than cancer cells? Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 1376–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Liu, J.; Dang, P.; Hu, S.; Yuan, W.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, C. Roles of tumor-associated macrophages in anti-PD-1/PD-L1 immunotherapy for solid cancers. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Tan, H.; Dai, J.; Lin, J.; Zhao, K.; Hu, H.; Zhong, C. Targeting macrophages in cancer immunotherapy: Frontiers and challenges. J. Adv. Res. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.; Luo, Y. Targeting macrophages in cancer immunotherapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2021, 6, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Wang, R.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, X.; Song, J. Macrophage Polarisation in the Tumour Microenvironment: Recent Research Advances and Therapeutic Potential of Different Macrophage Reprogramming. Cancer Control 2025, 32, 10732748251316604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavudi, K.; Nuguri, S.M.; Olverson, Z.; Dhanabalan, A.K.; Patnaik, S.; Kokkanti, R.R. Targeting the retinoic acid signaling pathway as a modern precision therapy against cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2023, 11, 1254612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezold, V.; Rosenstock, P.; Scheffler, J.; Geyer, H.; Horstkorte, R.; Bork, K. Glycation of macrophages induces expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and reduces phagocytic efficiency. Aging 2019, 11, 5258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, F.O.; Gordon, S. The M1 and M2 paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment. F1000Prime Rep. 2014, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Primer Sequences (5′ → 3′) | |
|---|---|---|
| THRA | F | GAAAGCGAAAAAGAAAGAACGG |
| R | AGGAATAGGTGGGATGGAGG | |
| RARA | F | ACGAGAGTGTAGAAGTGGG |
| R | TTGTAGATGCGGGGTAGAG | |
| RARB | F | ACCATCGCAGACCAAATTAC |
| R | TCATCCATTTCCAAAGGCAG | |
| RARG | F | GGTCTACAAGCCATGCTTC |
| R | ACCCTTCTTCCTTCACCTC | |
| PPARA | F | CGCAAACTTGGACCTGAAC |
| R | AGCAAATGATAGCAGCCAC | |
| PPARD | F | GGGAAGAGGAGGAGAAAGAG |
| R | CATGAACACCGTAGTGGAAG | |
| PPARG | F | TTCAAACACATCACCCCCC |
| R | GCTCTTTAGAAACTCCCTTGTC | |
| NR1D1 | F | TCCCCTTCTTCCTCATCTTC |
| R | GTCCCCACACACTTTACAC | |
| NR1D2 | F | ATGGAGGTGAATGCAGGAG |
| R | TGGAGAAGATGGAACAGAAGAG | |
| RORA | F | ACATACAGCCTTCCCCAGAC |
| R | AATTGCCACATCACCTCCC | |
| RORB | F | ACAATGCTTCTTATTCCTGCC |
| R | GACATCCTCCCAAACTTCAC | |
| NR1F3 | F | AAAGCAGGAGCAATGGAAG |
| R | GGGAGTGGGAGAAGTCAAAG | |
| NR1H2 | F | CTTCCACTACAACGTGCTC |
| R | ACTGTGACTGTGACTCCTG | |
| NR1H3 | F | TGCCTGACATTCCTCCTGAC |
| R | GCCCCTTTTTCCGCTTTTG | |
| NR1H4 | F | AACATTCCCATTTACCTACCAC |
| R | TGCTACCTCAGTTTCTCCC | |
| VDR | F | ATCACCAAGGACAACCGAC |
| R | TCCCTCCACCATCATTCAC | |
| NR1I2 | F | GCCAAAGTCATCTCCTACTTC |
| R | ATCAGCACATACTCCTCCTC | |
| HNF4A | F | AAGCCATCATCTTCTTTGACC |
| R | ATCTGCTCGATCATCTGCC | |
| HNF4G | F | CAACATCCCCTCCATTAACAC |
| R | TAGCCCATTCCACCAAGAC | |
| RXRA | F | CTTCCTTCACCAAGCACATC |
| R | ACTCCACCTCATTCTCGTTC | |
| RXRB | F | GCTTCTTCAAACGCACCATC |
| R | ATCCCCATCCTTGTCCTTTC | |
| RXRG | F | GCAAGAAGAAAGACAGAGGAG |
| R | TGCCCGAAGCAAAATGAC | |
| NR2C1 | F | GATAATTCTCCAGACCAAGGAC |
| R | GCTTCATTCCAAACGCAATAC | |
| NR2C2 | F | TGGCAGATGGGATAGACAC |
| R | TGAGAGGAAAAGCAGACGG | |
| NR2E1 | F | AGGAATGGGGAAAAAGAGGG |
| R | ATGGACAGACAGATGGAGAG | |
| NR2E3 | F | CCTCCTCTCCATACTCCTCTTC |
| R | AGTTCACTCCACGCCTCTTC | |
| NR2F1 | F | CCGCAGGAACTTAACTTACAC |
| R | GCATTCTTCCTCGCTGAAC | |
| NR2F2 | F | TCCAAGAGCAAGTGGAGAAG |
| R | AAGGGAGGCGAAGCAAAAG | |
| ESR1 | F | ATCTGCCAAGGAGACTCGCTAC |
| R | TCCCACCTTTCATCATTCCCAC | |
| ESR2 | F | ATGCTCACTTCTGCGCTGTC |
| R | CACACTTCACCATTCCCACTTC | |
| ESRRA | F | AAGACAGCAGCCCCAGTGAATG |
| R | AGACAGCGACAGCGATGAGAAG | |
| ESRRB | F | AAGCACATCCCAGGCTTCTC |
| R | CACAAACTCCTCCTTCTCCAC | |
| ESRRG | F | TTCAGCCAGCCAAAAAGCC |
| R | TCGCCCATCCAATGATAACC | |
| NR3C1 | F | TTACCACAACTCACCCCTAC |
| R | TGCCTTTGCCCATTTCAC | |
| AR | F | TGCCCATTGACTATTACTTTCC |
| R | TCCCTGCTTCATAACATTTCC | |
| NR4A1 | F | TTCAAAACCCAAGCAGCC |
| R | TACATCCCCAGCATCTTCC | |
| NR4A2 | F | TGACACCCAGCATATCCAG |
| R | CAATCCATTCCCCAAAGCC | |
| NR5A1 | F | ACAGCAGAAGAAGGCACAG |
| R | GAAAGGCAGGGTAGAGGTAG | |
| NR5A2 | F | ACCAGAACTGCCAAATTGAC |
| R | CCCAAACTTATTCCTTCCTCC | |
| NR6A1 | F | TATTTGCCCTGCTTTGCC |
| R | ATCACCTCCATCCCTTCATC | |
| NR0B1 | F | TGCAGAAGATCCTCACCAC |
| R | CAGCATTTGGAAAGAAAGCAC | |
| NR0B2 | F | GCCCAGCATACTCAAGAAG |
| R | TCCAGACAGCATTGAAGCC | |
| 36B4 | F | CAGCAAGTGGGAAGGTGTAATCC |
| R | CCCATTCTATCATCAACGGGTACAA | |
| Antibody | Source | Catalog # | Dilution | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TGM2 | Cell Signaling Technology (Danvers, MA, USA) | #3557 | 1:2000 | WB |
| CD206 | Cell Signaling Technology | #91992 | 1:2000 | WB |
| CD206 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology (Dallas, TX, USA) | #sc-376232 | 1:100 | FACS |
| PD-L1 | Abcam (Waltham, MA, USA) | #ab210931 | 1:2000 | WB |
| RAR-γ | Cell Signaling Technology | #8965 | 1:2000 | WB |
| RXR-γ | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | #sc-365252 | 1:2000 | WB |
| Vinculin | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | #sc-73614 | 1:2000 | WB |
| GAPDH | Santa Cruz Biotechnology | #sc-47724 | 1:2000 | WB |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, J.; Oh, J.; Min, S.-H.; Yu, J.H.; Bae, J.-S.; Jeon, H.-J. Targeting RARγ Decreases Immunosuppressive Macrophage Polarization and Reduces Tumor Growth. Molecules 2025, 30, 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153099
Park J, Oh J, Min S-H, Yu JH, Bae J-S, Jeon H-J. Targeting RARγ Decreases Immunosuppressive Macrophage Polarization and Reduces Tumor Growth. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153099
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Jihyeon, Jisun Oh, Sang-Hyun Min, Ji Hoon Yu, Jong-Sup Bae, and Hui-Jeon Jeon. 2025. "Targeting RARγ Decreases Immunosuppressive Macrophage Polarization and Reduces Tumor Growth" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153099
APA StylePark, J., Oh, J., Min, S.-H., Yu, J. H., Bae, J.-S., & Jeon, H.-J. (2025). Targeting RARγ Decreases Immunosuppressive Macrophage Polarization and Reduces Tumor Growth. Molecules, 30(15), 3099. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153099







