The Urate-Lowering Effects and Renal Protective Activity of Iridoid Glycosides from Paederia foetida in Rats with Hyperuricemia-Induced Kidney Injury: A Pharmacological and Molecular Docking Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
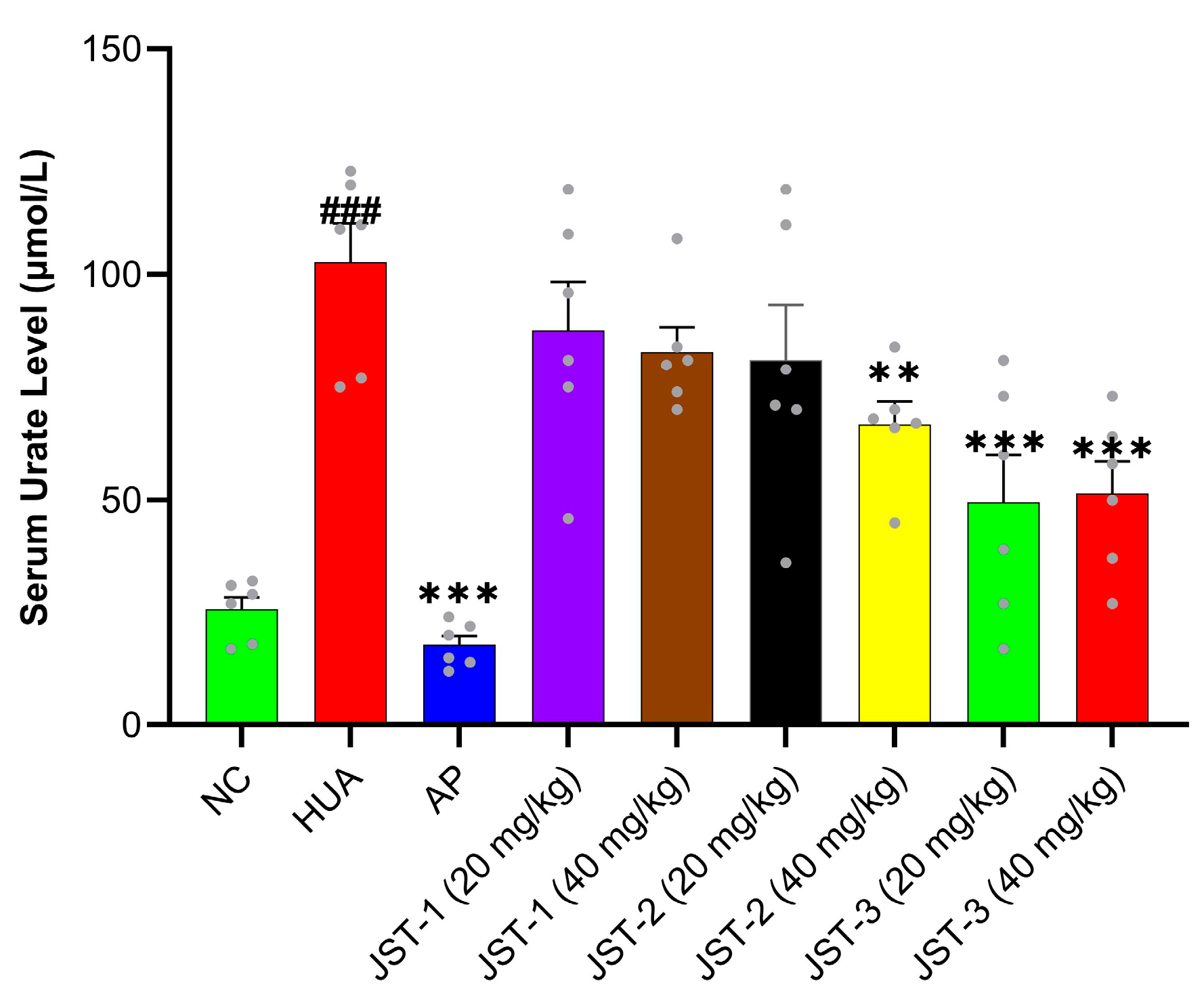
2.1. The Effects of Three Iridoid Glycosides on Acute Hyperuricemia
2.2. The Effects of Three Iridoid Glycosides on Body Weight, Kidney Weight, and Organ Coefficients in HUA Rats
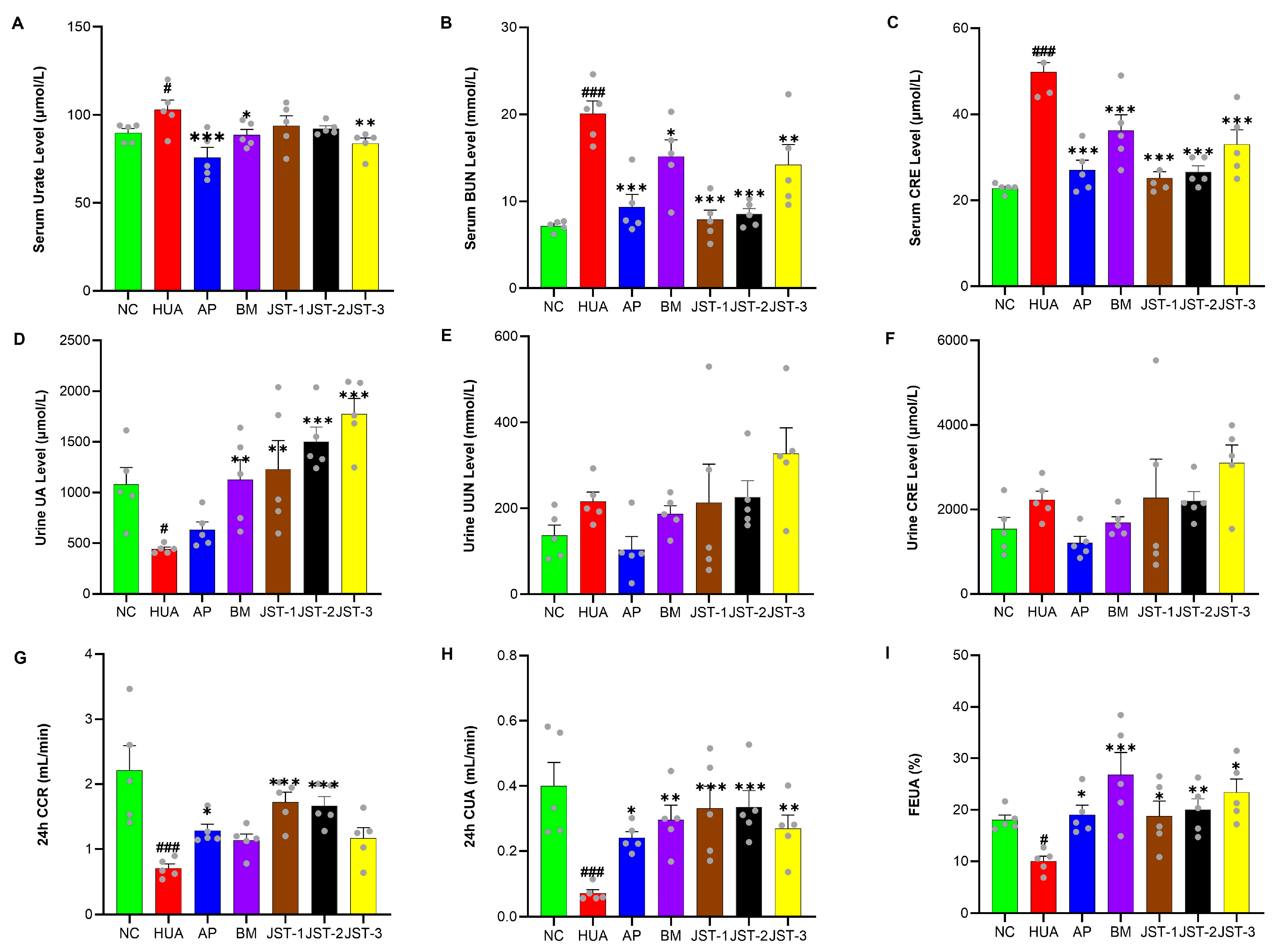
2.3. The Effects of Three Iridoid Glycosides on Renal Function Indicators in HUA Rats After Single-Dose Administration
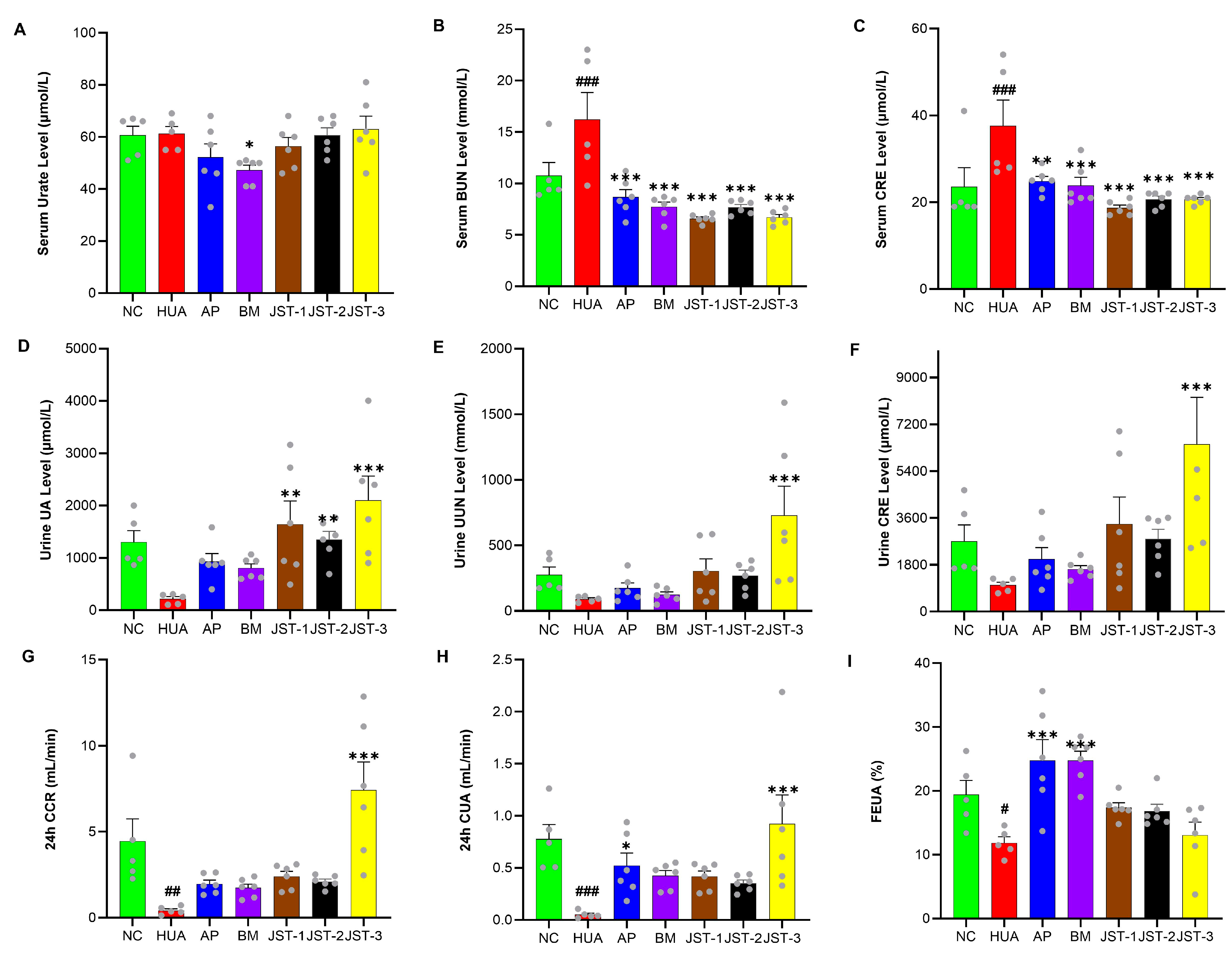
2.4. The Effects of Three Iridoid Glycosides on Renal Function Indicators in HUA Rats After One Week of Administration
2.5. Pathological Observation of Kidney Tissues
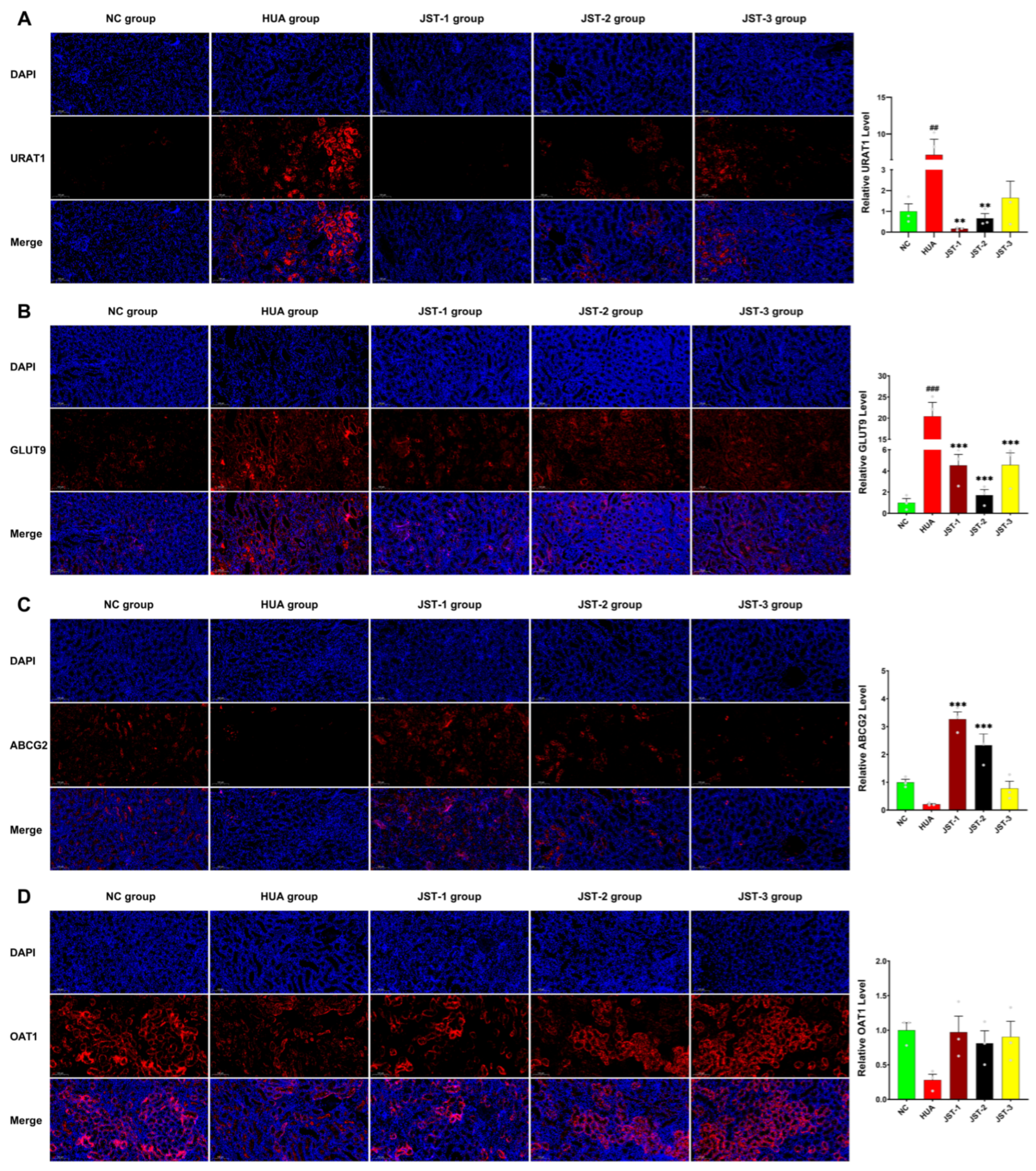
2.6. The Effects of Three Iridoid Glycosides on Urate Transporter Protein Expression in the Kidneys
2.7. Results of Molecular Docking
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Chemicals
4.2. Extraction and Purification
4.3. Experimental Animals
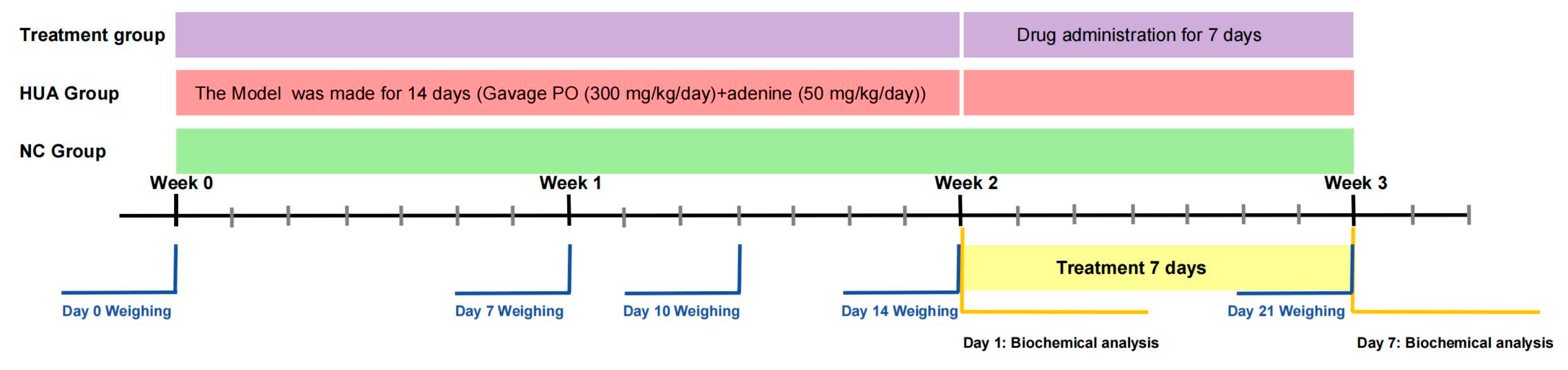
4.4. Animal Protocol
4.4.1. Acute Hyperuricemia
4.4.2. Hyperuricemia-Induced Kidney Injury
4.5. Biochemical Analysis
4.6. Organ Coefficient Determination
4.7. Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) Staining Analysis
4.8. Immunofluorescence (IF) Analysis
4.9. Molecular Docking
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HUA | Hyperuricemia |
| SD rat | Sprague-Dawley Rat |
| UA | Uric Acid |
| BUN | Blood Urea Nitrogen |
| UUN | Urine Urea Nitrogen |
| CRE | Creatinine |
| CCR | Creatinine Clearance Rate |
| CUA | Uric Acid Clearance Rate |
| FEUA | Fraction Excretion of Uric Acid |
| AP | Allopurinol |
| BM | Benzbromarone |
| PO | Potassium Oxonate |
| JST-1 | Paederosidic Acid |
| JST-2 | Paederosidic Acid Methyl Ester |
| JST-3 | Paederoside |
| CB | Column Volume |
| URAT1 | URAT1, Uric Acid Transporter 1 |
| GLUT9 | Glucose Transporter 9 |
| ABCG2 | ATP-Binding Cassette Transporter G2 |
| OAT1 | Organic Anion Transporter 1 |
| OAT3 | Organic Anion Transporter 3 |
| ADME | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excretion |
References
- Alvarez-Lario, B.; Macarron-Vicente, J. Uric acid and evolution. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 2010–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandal, A.K.; Mount, D.B. The molecular physiology of uric acid homeostasis. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2015, 77, 323–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weaver, D.J., Jr. Uric acid and progression of chronic kidney disease. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2019, 34, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zeng, C. Update on the epidemiology, genetics, and therapeutic options of hyperuricemia. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 3167–3181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen-Xu, M.; Yokose, C.; Rai, S.K.; Pillinger, M.H.; Choi, H.K. Contemporary Prevalence of Gout and Hyperuricemia in the United States and Decadal Trends: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007–2016. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019, 71, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Wang, H.; Xia, W.; Chang, X.; Wang, M.; An, L. Prevalence and correlates of hyperuricemia in the middle-aged and older adults in China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gherghina, M.-E.; Peride, I.; Tiglis, M.; Neagu, T.P.; Niculae, A.; Checherita, I.A. Uric Acid and Oxidative Stress-Relationship with Cardiovascular, Metabolic, and Renal Impairment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumagai, T.; Ota, T.; Tamura, Y.; Chang, W.X.; Shibata, S.; Uchida, S. Time to target uric acid to retard CKD progression. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2017, 21, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; Gosling, A.L.; Gaffo, A.; Abhishek, A. Gout. Lancet 2021, 397, 1843–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, J.S.; Simmonds, H.A. Uric acid, gout and the kidney. J. Clin. Pathol. 1981, 34, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fau, T.J.; Terplan, K.L. The kidney in gout. Medicine 1996, 39, 405–467. [Google Scholar]
- He, J.; Liu, G.; Kong, F.; Tan, Q.; Wang, Z.; Yang, M.; He, Y.; Jia, X.; Yan, C.; Wang, C.; et al. Structural basis for the transport and substrate selection of human urate transporter 1. Cell Rep. 2024, 43, 114628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auberson, M.; Stadelmann, S.; Stoudmann, C.; Seuwen, K.; Koesters, R.; Thorens, B.; Bonny, O. SLC2A9 (GLUT9) mediates urate reabsorption in the mouse kidney. Pflug. Arch. 2018, 470, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukal, S.; Guin, D.; Rawat, C.; Bora, S.; Mishra, M.K.; Sharma, P.; Paul, P.R.; Kanojia, N.; Grewal, G.K.; Kukreti, S.; et al. Multidrug efflux transporter ABCG2: Expression and regulation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2021, 78, 6887–6939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L. OAT1 structures reveal insights into drug transport in the kidney. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2023, 30, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.; Sui, X.; Ahmed, S.; Wang, Z.; Long, C. Ethnobotany and diversity of medicinal plants used by the Buyi in eastern Yunnan, China. Plant Divers. 2020, 42, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, P.R.C.; Reddy, C.S.; Raza, S.; Dutt, C. Folklore medicinal plants of North Andaman Islands, India. Fitoterapia 2008, 79, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wu, L.; Wu, R.; Sun, M.; Fu, K.; Kuang, T.; Wang, Z. Comparison of medicinal preparations of Ayurveda in India and five traditional medicines in China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 284, 114775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Shin, H.T.; Kwon, Y.H.; Yi, M.H.; Yoon, J.W.; Kim, G.S.; Park, G.H.; Sung, J.W. The Vascular Plant Species in the Korean Demilitarized zone (DMZ). J. Asia Pac. Biodivers. 2013, 6, 31–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Quang, D.N.; Hashimoto, T.; Tanaka, M.; Dung, N.X.; Asakawa, Y. Iridoid glucosides from roots of Vietnamese Paederia scandens. Phytochemistry 2002, 60, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, P.P.; Marbaniang, K.; Sen, S.; Dey, B.K.; Talukdar, N.C. A review on phytochemistry of Paederia foetida Linn. Phytomed. Plus 2023, 3, 100411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au, D.T.; Wu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Chen, H.; Lu, G.; Zhao, Z. Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants used by Hakka in Guangdong, China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 117, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NguyêñXuãn, D.; Loi, D.T. Selection of traditional medicines for study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1991, 32, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bordoloi, M.; Bordoloi, P.K.; Dutta, P.P.; Singh, V.; Nath, S.; Narzary, B.; Bhuyan, P.D.; Rao, P.G.; Barua, I.C. Studies on some edible herbs: Antioxidant activity, phenolic content, mineral content and antifungal properties. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 23, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chau, C.F.; Wu, S.H. The development of regulations of Chinese herbal medicines for both medicinal and food uses. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-L.; Xing, F.-W. Ethnobotanical study on medicinal plants around Mt.Yinggeling, Hainan Island, China. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 124, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surendran, S.; Prasannan, P.; Jeyaram, Y.; Palanivel, V.; Pandian, A.; Ramasubbu, R. Knowledge on ethnogynaecology of Indian Tribes—A comprehensive review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 303, 115880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, W.; Pang, M.; Dong, L.; Huang, X.; Wang, S.; Zhou, L. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of iridoid glycosides from Paederia scandens (LOUR.) Merrill (Rubiaceae) on uric acid nephropathy rats. Life Sci. 2012, 91, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, S.-X.; Zhu, W.-J.; Pang, M.-Q.; Jeffry, J.; Zhou, L.-L. Protective effect of iridoid glycosides from Paederia scandens (LOUR.) Merrill (Rubiaceae) on uric acid nephropathy rats induced by yeast and potassium oxonate. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 64, 57–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgohain, M.P.; Chowdhury, L.; Ahmed, S.; Bolshette, N.; Devasani, K.; Das, T.J.; Mohapatra, A.; Lahkar, M. Renoprotective and antioxidative effects of methanolic Paederia foetida leaf extract on experimental diabetic nephropathy in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Sheng, S.; Wu, L.; Wang, H.; Xue, H.; Wang, R. Flavonoid-rich extract of Paederia scandens (Lour.) Merrill improves hyperuricemia by regulating uric acid metabolism and gut microbiota. Food Chem. 2025, 471, 142857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Le, X.; Zhang, B.; Shen, L.; Wu, T.; Zhou, H. Application of Iridiod Glycosides from Paederia scandens L. on Uric Acid Nephropathy. Chin. J. Pharm. 2020, 51, 908–915. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.-S.; Hu, X.-F.; Wu, X.-J.; Yang, M.; Sun, W. Paederosidic acid protect bone mass in lipopolysaccharide-treated rats by reducing oxidative stress and inflammatory. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Shi, L.; Song, M.; Meng, Y. Antitumor activity of paederosidic acid in human non-small cell lung cancer cells via inducing mitochondria-mediated apoptosis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 269, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govind, J.; Kapadiaa, S.C.S.; Tokudab, H.; Ueda, S.; Nishinob, H. Inhibitory effect of iridoids on Epstein-Barr virus activation by a short-term in vitro assay for anti-tumor promoters. Cancer Lett. 1996, 102, 223–226. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Kong, B.; Gu, J.-W.; Kuang, Y.-Q.; Cheng, L.; Yang, W.-T.; Cheng, J.-M.; Ma, Y.; Yang, X.-K. Anticonvulsant and sedative effects of paederosidic acid isolated from Paederia scandens (Lour.) Merrill. in mice and rats. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2013, 111, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Gu, Y.; Meng, G.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Sun, S.; et al. Genetic Risk, Adherence to a Healthy Lifestyle, and Hyperuricemia: The TCLSIH Cohort Study. Am. J. Med. 2023, 136, 476–483.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas-Santos, A.B.; Neogi, T. Management of Gout and Hyperuricemia in CKD. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2017, 70, 422–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanai, H.; Adachi, H.; Hakoshima, M.; Katsuyama, H. Molecular Biological and Clinical Understanding of the Pathophysiology and Treatments of Hyperuricemia and Its Association with Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular Diseases and Chronic Kidney Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Bakris, G.L.; Borghi, C.; Chonchol, M.B.; Feldman, D.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Merriman, T.R.; Moe, O.W.; Mount, D.B.; Lozada, L.G.S.; et al. Hyperuricemia, Acute and Chronic Kidney Disease, Hypertension, and Cardiovascular Disease: Report of a Scientific Workshop Organized by the National Kidney Foundation. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 851–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vareldzis, R.; Perez, A.; Reisin, E. Hyperuricemia: An Intriguing Connection to Metabolic Syndrome, Diabetes, Kidney Disease, and Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2024, 26, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, R.J.; Nakagawa, T.; Sanchez-Lozada, L.G.; Shafiu, M.; Sundaram, S.; Le, M.; Ishimoto, T.; Sautin, Y.Y.; Lanaspa, M.A. Sugar, uric acid, and the etiology of diabetes and obesity. Diabetes 2013, 62, 3307–3315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Han, S.; Yang, Q.; Fan, S. Beneficial herb-drug interaction of Gnaphalium affine extract on benzbromarone: A pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study in rats. Phytomedicine 2022, 102, 154203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, J.W.; Wagh, P.; Wagh, V.D.; Sachan, P.; Joshi, N.S.; Goyal, S.; Tripathi, A.K. Paederia foetida Linn (Rubiaceae): Chemical Diversity, Phytopharmacological Potential, Quantitative Analysis and Clinical Approaches. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.-M.; Xu, Y.-F.; Chen, Z.; Huang, L.-F.; Chen, S.-L. UPLC/Q-TOF-MS analysis of iridoid glycosides and metabolites in rat plasma after oral administration of Paederia scandens extracts. Chin. J. Nat. Med. 2015, 13, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Jiang, Y.; Han, T.; Zheng, C.; Qin, L. A phytochemical, pharmacological and clinical profile of Paederia foetida and P. scandens. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2014, 9, 879–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarma, M.K.; Saha, D.; Das, B.K.; Das, T.; Azizov, S.; Kumar, D. A delve into the pharmacological targets and biological mechanisms of Paederia foetida Linn.: A rather invaluable traditional medicinal plant. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023, 396, 2217–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Saidhareddy, P.; Jiang, X. Construction of sulfur-containing moieties in the total synthesis of natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2020, 37, 246–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavric, B.; Fau Nera, E.A. Use of the uricase-inhibited rat as an animal model in toxicology. Clin. Toxicol. 1978, 13, 47–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clifford, A.J.; Riumallo, J.A.; Young, V.R.; Scrimshaw, N.S. Effect of Oral Purines on Serum and Urinary Uric Acid of Normal, Hyperuricemic and Gouty Humans. J. Nutr. 1976, 106, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.J.; Lozada, L.G.S.; Lanaspa, M.A.; Piani, F.; Borghi, C. Uric Acid and Chronic Kidney Disease: Still More to Do. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Liu, X.-Z.; Yang, Q.; Han, S.-Y.; Fan, S.-Y. Enhanced Efficacy and Reduced Hepatotoxicity by Combination of Gnaphalium affine Extract and Benzbromarone in the Treatment of Rats with Hyperuricemic Nephropathy. Pharm. Front. 2021, 3, e129–e137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, S.; Yi, L.; Gao, M.; Cai, J.; Yang, C.; Ma, Y.; Mo, Y.; Wang, Q. Levistolide a Attenuates Acute Kidney Injury in Mice by Inhibiting the TLR-4/NF-kappaB Pathway. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2024, 18, 5583–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyman, J.L. Blood urea nitrogen and creatinine. Emerg. Med. Clin. N. Am. 1986, 4, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, J.; Friedman, E. Renal function status. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2013, 200, 827–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, E. Reduced glomerular function and prevalence of gout: NHANES 2009-10. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, T.R.; Choi, H.S.; Kim, C.S.; Bae, E.H.; Ma, S.K.; Sung, S.-A.; Kim, Y.-S.; Oh, K.H.; Ahn, C.; Kim, S.W. Hyperuricemia has increased the risk of progression of chronic kidney disease: Propensity score matching analysis from the KNOW-CKD study. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forcet, C.; Stein, E.; Pays, L.; Corset, V.; Llambi, F.; Tessier-Lavigne, M.; Mehlen, P. Netrin-1-mediated axon outgrowth requires deleted in colorectal cancer-dependent MAPK activation. Nature 2002, 417, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, D.; Zhao, X.; Wang, F.; Wang, G. A brief review of urate transporter 1 (URAT1) inhibitors for the treatment of hyperuricemia and gout: Current therapeutic options and potential applications. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2021, 907, 174291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y. Contents Determination and Pharmacokinetic Study of Effective Components in Paederia scandens. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Shan, M.; Yu, S.; Yan, H.; Guo, S.; Xiao, W.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Ding, A.; Wu, Q.; Li, S.F.Y. A Review on the Phytochemistry, Pharmacology, Pharmacokinetics and Toxicology of Geniposide, a Natural Product. Molecules 2017, 10, 1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.; Lai, H.; Peng, W.; Zhou, X.; Zhu, L.; Tu, H.; Yuan, K.; Yang, Z. Monotropein: A comprehensive review of biosynthesis, physicochemical properties, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacology. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 2, 1109940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Xia, C.; Lian, W.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J.; He, J.; et al. Phytochemistry, synthesis, analytical methods, pharmacological activity, and pharmacokinetics of loganin: A comprehensive review. Phytother. Res. 2022, 36, 2272–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Xu, X.; Li, W.; Fu, X.; Han, W.; Li, G. Investigating the Vital Role of the Identified Abietic Acid from Helianthus annuus L. Calathide Extract against Hyperuricemia via Human Embryonic Kidney 293T Cell Model. Molecules 2023, 28, 5141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Z.; Jiang, J.; Tao, H.; Luo, S.; Meng, X.; Yu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, C. Traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology of Pterocephalus hookeri (Clarke, C.B.) Höeck: A review. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 28761–28774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhouibi, R.; Affes, H.; Ben Salem, M.; Moalla, D.; Marekchi, R.; Charfi, S.; Hammami, S.; Sahnoun, Z.; Jamoussi, K.; Zeghal, K.M.; et al. Creation of an adequate animal model of hyperuricemia (acute and chronic hyperuricemia); study of its reversibility and its maintenance. Life Sci. 2021, 268, 118998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Cheng, D.; Yuan, Y.; Zhong, L.; Zhao, K.; An, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, Y. Establishment and evaluation of hyperuricemic nephropathy model induced by different doses of potassium oxanate combined with adenine in rats. West China Med. J. 2021, 36, 643–650. [Google Scholar]




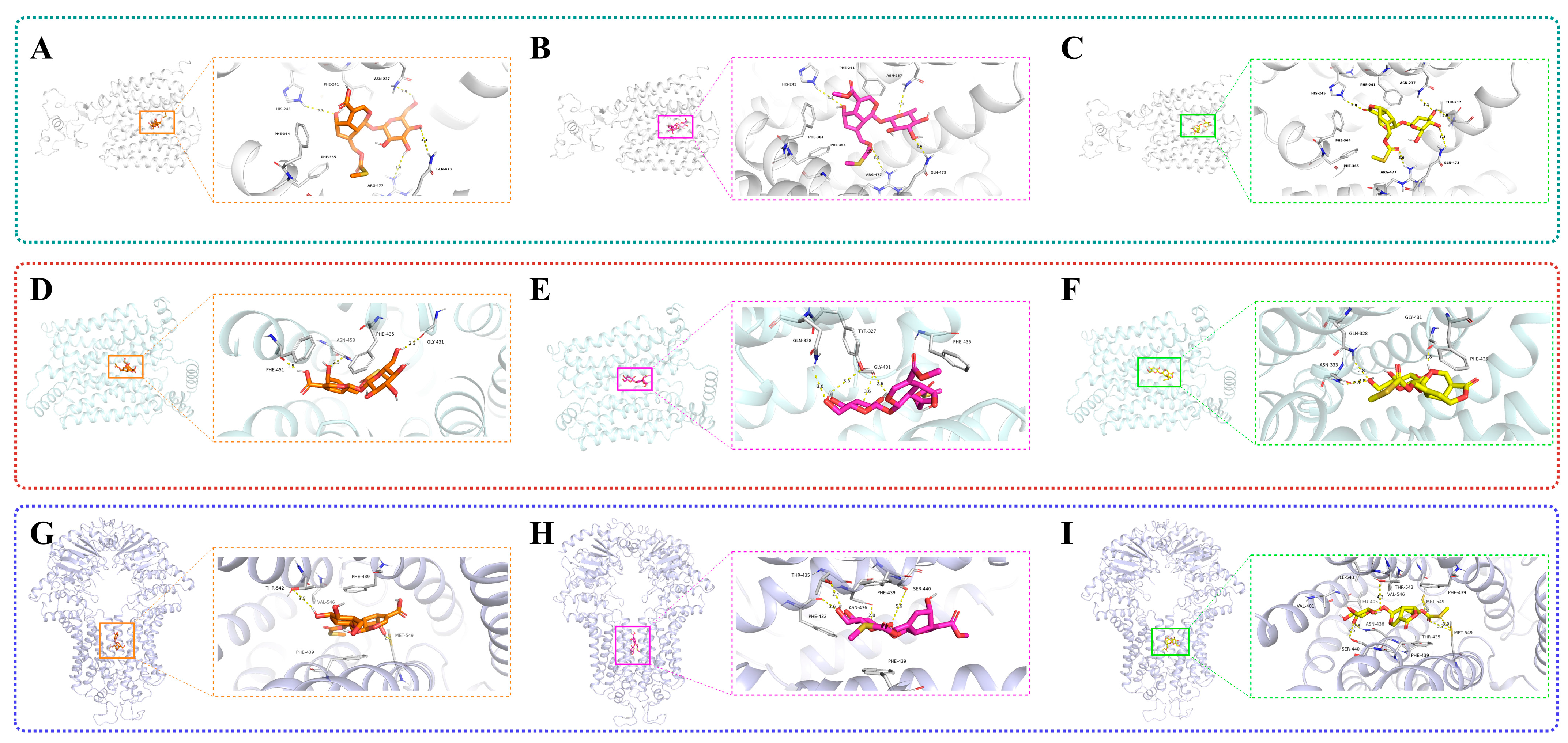


| Target | Ligand Compound | Ligand Compound | Binding Score (kcal mol−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Target (PDB ID) | Target Structure | Ligand Compound | 3D Structure | ||
| URAT1 (9JE0) | 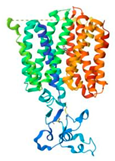 | Paederosidic acid (JST-1) | 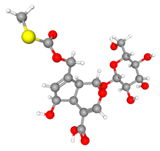 | JST-1 | −7.5 |
| JST-2 | −7.4 | ||||
| JST-3 | −8.0 | ||||
| GLUT9 (8Y66) | 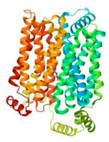 | Paederosidic acid methyl ester (JST-2) | 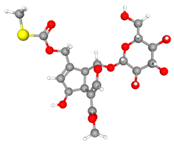 | JST-1 | −7.7 |
| JST-2 | −7.3 | ||||
| JST-3 | −7.6 | ||||
| ABCG2 (6VXJ) | 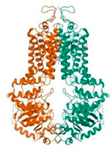 | Paederoside (JST-3) | 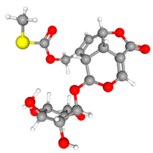 | JST-1 | −7.0 |
| JST-2 | −7.2 | ||||
| JST-3 | −7.8 | ||||
| Antibody | Company | Catalog Number | Dilution Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCRP/ABCG2 Polyclonal antibody | Proteintech | 27286-1-AP | 1:400 |
| URAT1 Polyclonal antibody | 14937-1-AP | 1:300 | |
| SLC2A9 Polyclonal antibody | 26486-1-AP | 1:200 | |
| OAT1 Polyclonal antibody | 26574-1-AP | 1:400 | |
| SLC22A8 Antibody | Abmart (Shanghai, China) | TD7196F | 1:400 |
| Goat Anti-Rabbit IgG H&L (HRP) | Abcam (Cambridge, UK) | Ab6721 | 1:1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, H.; Yue, X.; Shen, L.; Wu, L.; Li, X.; Wu, T. The Urate-Lowering Effects and Renal Protective Activity of Iridoid Glycosides from Paederia foetida in Rats with Hyperuricemia-Induced Kidney Injury: A Pharmacological and Molecular Docking Study. Molecules 2025, 30, 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153098
Zhou H, Yue X, Shen L, Wu L, Li X, Wu T. The Urate-Lowering Effects and Renal Protective Activity of Iridoid Glycosides from Paederia foetida in Rats with Hyperuricemia-Induced Kidney Injury: A Pharmacological and Molecular Docking Study. Molecules. 2025; 30(15):3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153098
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Haifeng, Xinyi Yue, Longhai Shen, Lifeng Wu, Xiaobo Li, and Tong Wu. 2025. "The Urate-Lowering Effects and Renal Protective Activity of Iridoid Glycosides from Paederia foetida in Rats with Hyperuricemia-Induced Kidney Injury: A Pharmacological and Molecular Docking Study" Molecules 30, no. 15: 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153098
APA StyleZhou, H., Yue, X., Shen, L., Wu, L., Li, X., & Wu, T. (2025). The Urate-Lowering Effects and Renal Protective Activity of Iridoid Glycosides from Paederia foetida in Rats with Hyperuricemia-Induced Kidney Injury: A Pharmacological and Molecular Docking Study. Molecules, 30(15), 3098. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules30153098






