A Highly Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the Organic Cation Transporters’ Mediated Metformin Uptake and Its Inhibition in Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
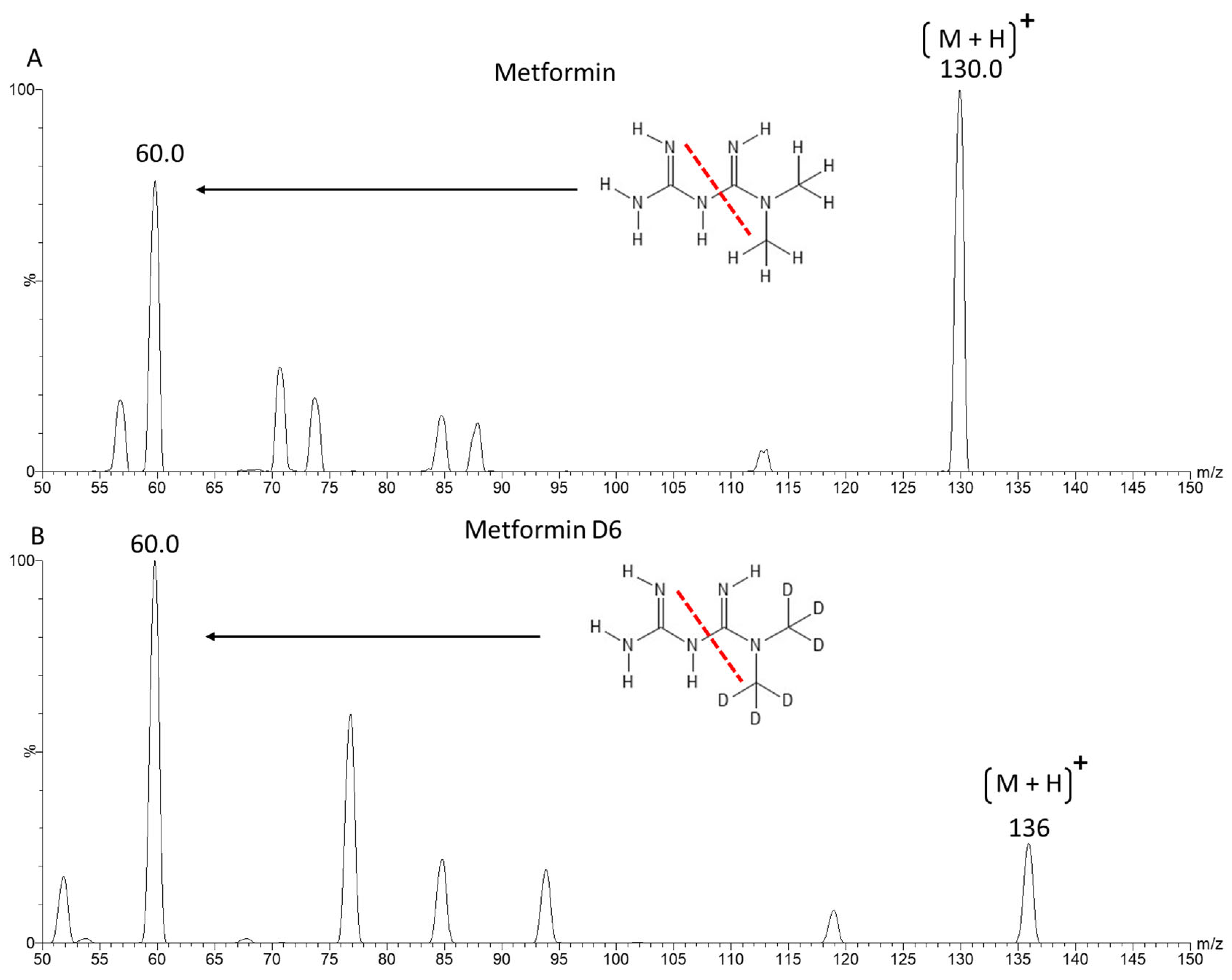
2.1. Mass Spectrometry
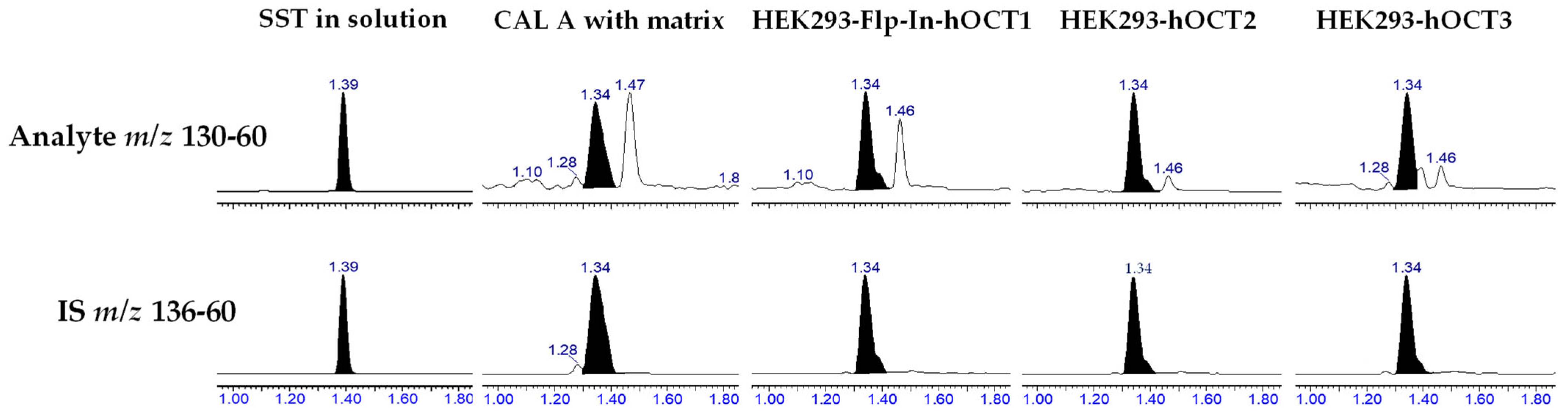
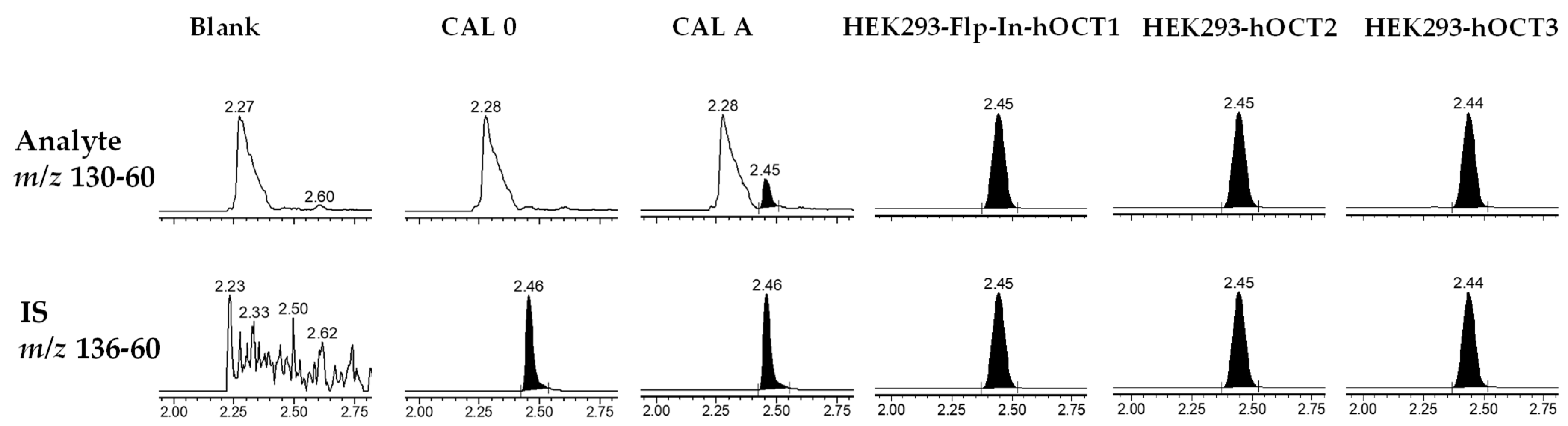
2.2. Method Development
2.3. Validation
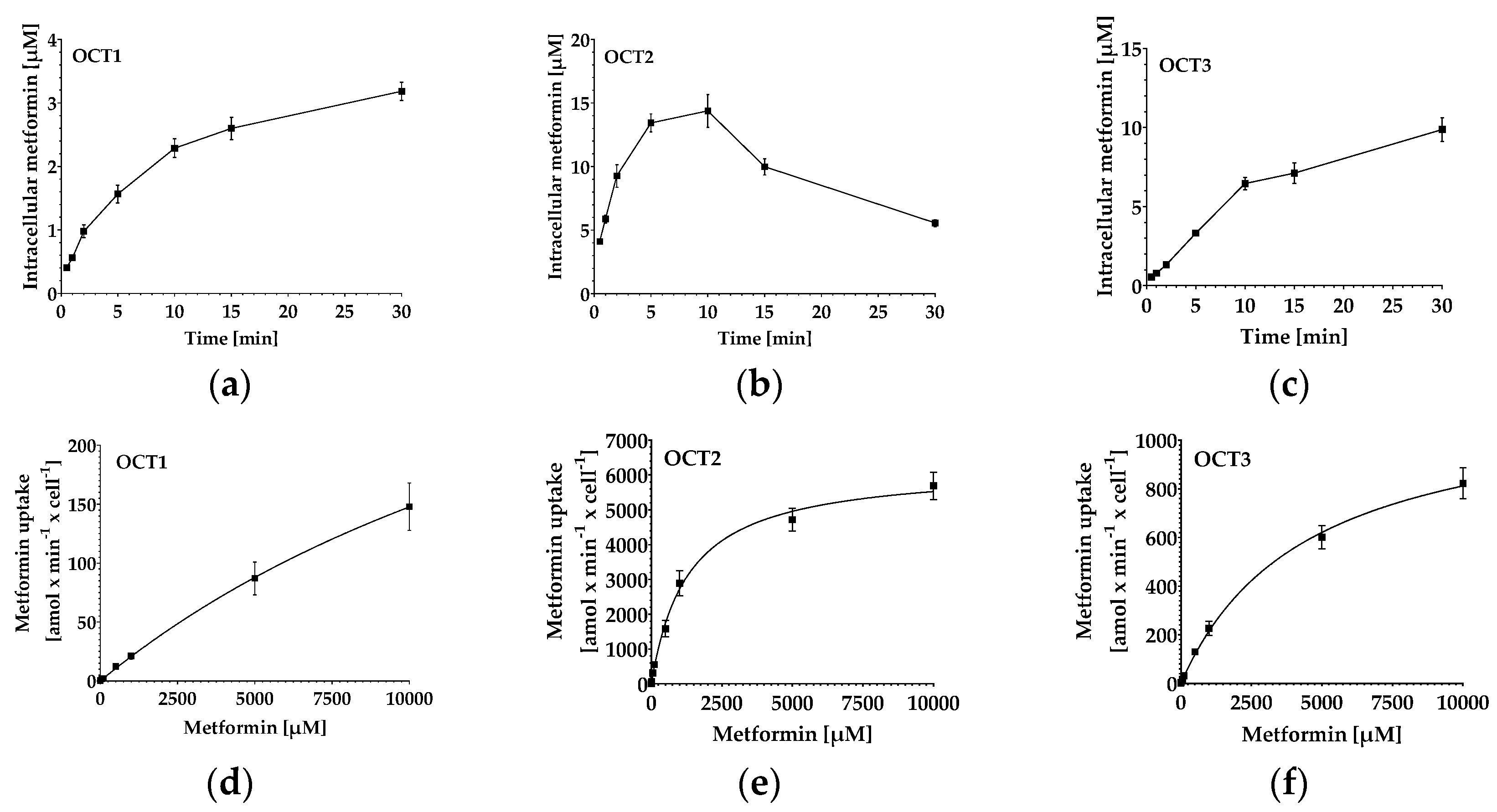
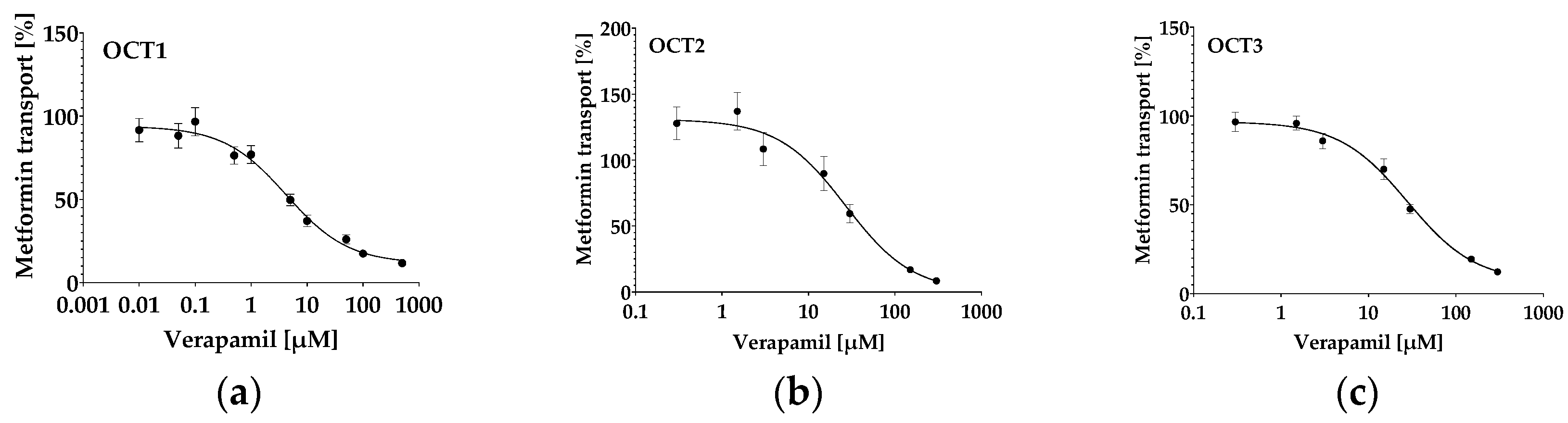
2.4. Quantification of Metformin in HEK293-hOCT1-3 Cells: Uptake Kinetics and Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Standard Solutions
4.3. Instrumental Analysis Parameters
4.4. Sample Preparation
4.5. Validation
4.6. Cell Lines Used and Their Culture
4.7. Establishment of OCT-Inhibition Assays in HEK293 Cell Lines Overexpressing OCT1, OCT2, or OCT3
4.8. Calculations and Statistical Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koepsell, H. Organic cation transporters in health and disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2020, 72, 253–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samodelov, S.L.; Kullak-Ublick, G.A.; Gai, Z.; Visentin, M. Organic Cation Transporters in Human Physiology, Pharmacology, and Toxicology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, N.; Turk, D.; Selzer, D.; Ishiguro, N.; Ebner, T.; Wiebe, S.; Müller, F.; Stopfer, P.; Nock, V.; Lehr, T. A comprehensive whole-body physiologically based pharmacokinetic drug-drug-gene interaction model of metformin and cimetidine in healthy adults and renally impaired individuals. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2020, 59, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burt, H.J.; Neuhoff, S.; Almond, L.; Gaohua, L.; Harwood, M.D.; Jamei, M.; Rostami-Hodjegan, A.; Tucker, G.T.; Rowland-Yeo, K. Metformin and cimetidine: Physiologically based pharmacokinetic modelling to investigate transporter mediated drug-drug interactions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 88, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use, European Medicines Agency, Guideline on the Investigation of Drug Interactions. 2017, Revision 1. Available online: www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-investigation-drug-interactions-revision-1_en.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwiQzpSDscmIAxWQhv0HHQNaFjMQFnoECBUQAQ&usg=AOvVaw36XYOpw7GL94n7wBUvzoqT (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration. Drug Development and Drug Interactions: Table of Substrates, Inhibitors and Inducers. 2023. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/drug-interactions-labeling/drug-development-and-drug-interactions-table-substrates-inhibitors-and-inducers (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- Nies, A.T.; Hofmann, U.; Resch, C.; Schaeffeler, E.; Rius, M.; Schwab, M. Proton pump inhibitors inhibit metformin uptake by organic cation transporters (OCTs). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Misaka, S.; Knop, J.; Singer, K.; Hoier, E.; Keiser, M.; Müller, F.; Glaeser, H.; König, J.; Fromm, M.F. The Nonmetabolized β-Blocker Nadolol Is a Substrate of OCT1, OCT2, MATE1, MATE2-K, and P-Glycoprotein, but Not of OATP1B1 and OATP1B3. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 512–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, N.; Masuda, S.; Tanihara, Y.; Ueo, H.; Okuda, M.; Katsura, T.; Inui, K. Metformin is a superior substrate for renal organic cation transporter OCT2 rather than hepatic OCT1. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 20, 379–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, G.G.; Punt, J.; Arora, M.; Day, R.O.; Doogue, M.P.; Duong, J.K.; Furlong, T.J.; Greenfield, J.R.; Greenup, L.C.; Kirkpatrick, C.M.; et al. Clinical pharmacokinetics of metformin. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2011, 50, 81–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayoub, B.M.; Mowaka, S. LC-MS/MS Determination of Empagliflozin and Metformin. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2017, 55, 742–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wattamwar, T.; Mungantiwar, A.; Halde, S.; Pandita, N. Development of simultaneous determination of empagliflozin and metformin in human plasma using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and application to pharmacokinetics. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 26, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Shrivastav, P.S.; Shah, J.V.; George, A. Simultaneous quantitation of metformin and dapagliflozin in human plasma by LC-MS/MS: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bay, C.; Uhl, P.; Burhenne, J.; Haefeli, W.E.; Sauter, M. Quantification of arginine rich cyclic cell-penetrating peptide-lipid-conjugates using trifluoroacetic acid-based UPLC-MS/MS analysis. ChemRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vath, M.; Gallagher, L.; Shou, W.; Weller, H.; Elkin, L.; Zhang, J. Development of an LC-MS/MS method for high throughput quantification of metformin uptake in transporter inhibition assays. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2014, 967, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Jeong, H.-C.; Kim, T.E.; Kwang-Hee Shin, K.H. Bioanalytical Method Using Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry (UHPL-CHRMS) for the Detection of Metformin in Human Plasma. Molecules 2020, 25, 4625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonopoulos, N.; Machairas, G.; Migias, G.; Vonaparti, A.; Brakoulia, V.; Pistos, C.; Gennimata, D.; Panderi, I. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring of Metformin and Rosuvastatin in Human Plasma. Molecules 2018, 23, 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, K.; Adamson, J.H.; Owira, P. The development and validation of a LC-MS/MS method for the quantitation of metformin, rifampicin and isoniazid in rat plasma using HILIC chromatography. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1095, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherf-Clavel, O.; Kinzig, M.; Stoffel, M.S.; Fuhr, U.; Sörgel, F. A HILIC-MS/MS assay for the quantification of metformin and sitagliptin in human plasma and urine: A tool for studying drug transporter perturbation. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 175, 112754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.W.; Bedwell, D.W.; Zamek-Gliszczynski, M.J. Ablation of Both Organic Cation Transporter (Oct)1 and Oct2 Alters Metformin Pharmacokinetics but Has No Effect on Tissue Drug Exposure and Pharmacodynamics. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2012, 40, 1170–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Chang, Q.; Yang, N.; Gu, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, L.; Aa, J.; Wang, G.; Sun, J. Quantitative determination of metformin, saxagliptin and 5-hydroxy saxagliptin simultaneously by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography—Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry and its application to a bioequivalence study with a single-pill combination in human. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2018, 1081–1082, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, S.; Ahmed, I.; Ahmad, I.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Thangam, S. Development and Validation of a Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Metformin and Sitagliptin in Human Plasma by LC-MS-MS and Its Application in a Bioequivalence Study. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2015, 53, 1549–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, D.; Elshahed, M.S.; Nasr, T.; Aboutaleb, N.; Zakaria, O. Novel LC–MS/MS method for analysis of metformin and canagliflozin in human plasma: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. BMC Chem. 2019, 13, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.; Vora, A.; Wairkar, S.; Yc, M. Design of experiment-based LC-MS/MS method development for simultaneous estimation of nateglinide and metformin hydrochloride in rat plasma. J. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 56, e4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ALquadeib, B.T.; Aloudah, N.M.; Almurshedi, A.S.; Alfagih, I.M.; Alsdosari, B.N.; Almeleky, A.S.; Almubeyedh, N.M. Development and Validation of a Simple and Sensitive LC-MS/MS Method for Quantification of Metformin in Dried Blood Spot Its Application as an Indicator for Medication Adherence. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 3225–3233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gai, S.; Huan, A.; Feng, T.; Gou, N.; Wang, X.; Lu, C.; Tang, H.; Xu, D.; Zhang, G.; Wang, L. LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of rivaroxaban and metformin in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic interaction study. Bioanalysis 2019, 11, 2269–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattamwar, T.; Mungantiwar, A.; Gujar, S.; Pandita, N. Development of LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of Canagliflozin and Metformin in human plasma and its pharmacokinetic application in Indian population under fast and fed conditions. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2020, 1154, 122281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sengupta, P.; Bhaumik, U.; Gosh, A.; Sarkar, A.; Chatterjee, B.; Bose, A.; Pal, T.K. LS-MS-MS Development and validation for simultaneous quantitation of metformin, glimepiride and pioglitazone in human plasma and its application to a bioequivalent study. Chromatographia 2009, 69, 1243–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgawish, M.S.; Nasser, S.; Salama, I.; Abbas, A.M.; Mostafa, S.M. Liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the simultaneous determination of metformin and pioglitazone in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic and drug-drug interaction studies. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2019, 1124, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Chen, M.; Gao, Y.; Hu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhang, W.; Huang, W. In vivo pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic effects of metformin mediated by the gut microbiota in rats. Life Sci. 2019, 226, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, B.A.; Mahrouse, M.A.; Fawzy, M.G.; Fawzy, M.G. A validated LC-MS/MS method for simultaneous determination of linagliptin and metformin in spiked human plasma coupled with solid phase extraction: Application to a pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 163, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, B.C.L.; Fachi, M.M.; de Campos, M.L.; Dgaut Degaut, F.L.; Peccinini, R.G.; Pontarolo, R. A new HPLC-MS/MS method for the simultaneous quantification of SGLT2 inhibitors and metformin in plasma and its application to a pharmacokinetic study in healthy volunteers. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2019, 33, e4663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowaka, S.; Elkady, E.F.; Almazar, M.M.; Ayoub, B.M. Enhanced LC-MS/MS determination of alogliptin and metformin in plasma: Application to a pharmacokinetic study. Microchem. J. 2017, 130, 360–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Patel, D.; Akter, K.A.; Bagchi, S.; Sifat, A.E.; Nozohouri, R.; Ahn, Y.; Karamyan, V.T.; Bickel, U.; et al. Evaluation of Systemic and Brain Pharmacokinetic Parameters for Repurposing Metformin Using Intravenous Bolus Administration. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2024; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Zhang, Y.; Akter, K.A.; Nozohouri, S.; Archie, S.R.; Patel, D.; Villalba, H.; Abbruscato, T. Permeability of Metformin across an In Vitro Blood-Brain Barrier Model during Normoxia and Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation Conditions: Role of Organic Cation Transporters (Octs). Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhari, K.; Wang, J.; Xu, Y.; Winters, A.; Wang, L.; Dong, X.; Cheng, E.Y.; Liu, R.; Yang, S.H. Determination of metformin bio-distribution by LC-MS/MS in mice treated with a clinically relevant paradigm. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0234571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Bratty, M.; Alhazmi, H.A.; Akhtar, S.; Lalitha, K.G.; Asmari, M. Development and Validation of LC–MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Metformin and Four Gliptins in Human Plasma. Chromatographia 2017, 80, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandel, N.S.; Avizonis, D.; Reczek, C.R.; Weinberg, S.E.; Menz, S.; Neuhaus, R.; Christian, S.; Haegebarth, A.; Algire, C.; Pollak, M. Are Metformin Doses Used in Murine Cancer Models Clinically Relevant? Cell Metab. 2016, 23, 569–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gergov, M.; Nenonen, T.; Ojanperä, I.; Ketola, R.A. Compensation of Matrix Effects in a Standard Addition Method for Metformin in Postmortem Blood Using Liquid Chromatography–Electrospray–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Anal. Toxicol. 2015, 39, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Pent, Y.; Wan, P.; Yin, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, J. Simultaneous determination and pharmacokinetic study of metformin and pioglitazone in dog plasma by LC-MS-MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2014, 52, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Gu, Q.; Qiu, F.; Zhong, D. Rapid determination of metformin in human plasma by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 802, 377–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Shah, J.V.; Sanyal, M.; Shrivastav, P.S. LC-MS/MS analysis of metformin, saxagliptin and 5-hydroxy saxagliptin in human plasma and its pharmacokinetic study with a fixed-dose formulation in healthy Indian subjects. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e6809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.A.; Shrivastav, P.S.; Sharma, V.; Yadav, M.S. Challenges in simultaneous extraction and chromatographic separation of metformin and three SGLT-2 inhibitors in human plasma using LC-MS/MS. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 175, 112790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.; Allakonda, L.; Satheeshkumar, N. A validated UHPLC-QTOF-MS method for quantification of metformin and teneligliptin in rat plasma: Application to pharmacokinetic interaction study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 143, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solbach, T.F.; Grube, M.; Fromm, M.F.; Zolk, O. Organic cation transporter 3: Expression in failing and nonfailing human heart and functional characterization. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2011, 58, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuehne, A.; Floerl, S.; Hagos, Y. Investigations with Drugs and Pesticides Revealed New Species- and Substrate-Dependent Inhibition by Elacridar and Imazalil in Human and Mouse Organic Cation Transporter OCT2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Sheardown, S.A.; Brown, C.; Owen, R.P.; Zhang, S.; Castro, R.A.; Ianculescu, A.G.; Yue, L.; Lo, J.C.; Burchard, E.G.; et al. Effect of genetic variation in the organic cation transporter 1 (OCT1) on metformin action. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1422–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elsby, R.; Chidlaw, S.; Outteridge, S.; Pickering, S.; Radcliffe, A.; Sullivan, R.; Jones, H.; Butler, P. Mechanistic in vitro studies confirm that inhibition of the renal apical efflux transporter multidrug and toxin extrusion (MATE) 1, and not altered absorption, underlies the increased metformin exposure observed in clinical interactions with cimetidine, trimethoprim or pyrimethamine. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2017, 5, e00357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, M.J.; Tuerkova, A.; Römer, S.; Wenzel, C.; Seitz, T.; Gaedcke, J.; Oswald, S.; Brockmöller, J.; Zdrazil, B.; Tzvetkov, M.V. Differences in Metformin and Thiamine Uptake between Human and Mouse Organic Cation Transporter 1: Structural Determinants and Potential Consequences for Intrahepatic Concentrations. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2020, 48, 1380–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koepsell, H. Update on drug-drug interaction at organic cation transporters: Mechanisms, clinical impact, and proposal for advanced in vitro testing. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2021, 17, 635–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Guidance for Industry, Bioanalytical Method Validation. 2018. Available online: www.fda.gov/downloads/Drugs/GuidanceComplianceRegulatoryInformation/Guidances/ucm070107.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use, European Medicines Agency, Guideline on Validation of Bioanalytical Methods, 2009, EMEA/CHMP/EWP/192217/2009. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/enGB/documentlibrary/Scientificguideline/2011/08/WC500109686.pdf (accessed on 17 April 2024).
- Matuszewski, B.K.; Constanzer, M.L.; Chavez-Eng, C.M. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.-K.; Reichold, M.; Edemir, B.; Ciarimboli, G.; Warth, R.; Koepsell, H.; Thévenod, F. Organic cation transporters OCT1, 2, and 3 mediate high-affinity transport of the mutagenic vital dye ethidium in the kidney proximal tubule. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2009, 296, F1504–F1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saadatmand, A.R.; Tadjerpisheh, S.; Brockmöller, J.; Tzvetkov, M.V. The prototypic pharmacogenetic drug debrisoquine is a substrate of the genetically polymorphic organic cation transporter OCT1. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, T.; Stalmann, R.; Dalila, N.; Chen, J.; Pojar, S.; Dos Santos Pereira, J.N.; Krätzner, R.; Brockmöller, J.; Tzvetkov, M.V. Global genetic analyses reveal strong inter-ethnic variability in the loss of activity of the organic cation transporter OCT1. Genome Med. 2015, 7, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| LLOQ 0.05 ng/mL | QC A 0.15 ng/mL | QC B 18.7 ng/mL | QC C 37.5 ng/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intra-day | ||||
| 1 Mean [ng/mL] | 0.0536 | 0.141 | 16.7 | 32.0 |
| Accuracy (%) | 107 | 93.9 | 89.0 | 85.4 |
| Precision (% CV) | 9.97 | 3.49 | 3.09 | 3.85 |
| 2 Mean [ng/mL] | 0.0471 | 0.132 | 16.8 | 34.0 |
| Accuracy (%) | 94.2 | 88.3 | 89.4 | 90.7 |
| Precision (% CV) | 9.60 | 3.04 | 3.24 | 4.11 |
| 3 Mean [ng/mL]) | 0.0498 | 0.142 | 16.8 | 33.3 |
| Accuracy (%) | 99.7 | 95.0 | 89.6 | 88.9 |
| Precision (% CV) | 8.28 | 6.47 | 5.36 | 2.94 |
| Inter-day | ||||
| Mean [ng/mL] | 0.0512 | 0.139 | 16.8 | 33.3 |
| Accuracy (%) | 102 | 92.7 | 89.4 | 88.9 |
| Precision (% CV) | 11.2 | 5.40 | 3.87 | 3.22 |
| QC A 0.15 ng/mL | QC B 18.7 ng/mL | QC C 37.5 ng/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Autosampler (24 h at 10–15 °C) | |||
| Accuracy (%) | 100 | 102 | 103 |
| Bench-top (4 h) Accuracy (%) | 101 | 90.4 | 87.5 |
| Freeze and thaw | |||
| Accuracy (%) | 92.7 | 99.7 | 96.7 |
| Four weeks at −20 °C | |||
| Accuracy (%) | 97.3 | 95.8 | 86.4 |
| QC A 0.15 ng/mL | QC B 18.7 ng/mL | QC C 37.5 ng/mL | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix effect (%) | 114 | 95.7 | 96.9 |
| IS-normalised matrix effect (%) | 115 | 94.5 | 98.7 |
| Recovery (%) | 94.2 | 100 | 96.6 |
| Kinetic Parameter | OCT1 | OCT2 | OCT3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Km [mM] | 24.4 ± 10.1 | 6.3 ± 0.9 | 4.6 ± 1.1 |
| Vmax [amol/min/cell] | 515 ± 233 | 1513 ± 706 | 1197 ± 318 |
| IC50 of metformin transport inhibition by verapamil [µM] | 4.6 ± 1.4 | 23.3 ± 6.3 | 28.4 ± 3.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bajraktari-Sylejmani, G.; Bay, C.; Gebauer, L.; Burhenne, J.; Weiss, J.; Sauter, M. A Highly Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the Organic Cation Transporters’ Mediated Metformin Uptake and Its Inhibition in Cells. Molecules 2024, 29, 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215162
Bajraktari-Sylejmani G, Bay C, Gebauer L, Burhenne J, Weiss J, Sauter M. A Highly Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the Organic Cation Transporters’ Mediated Metformin Uptake and Its Inhibition in Cells. Molecules. 2024; 29(21):5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215162
Chicago/Turabian StyleBajraktari-Sylejmani, Gzona, Cindy Bay, Lukas Gebauer, Jürgen Burhenne, Johanna Weiss, and Max Sauter. 2024. "A Highly Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the Organic Cation Transporters’ Mediated Metformin Uptake and Its Inhibition in Cells" Molecules 29, no. 21: 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215162
APA StyleBajraktari-Sylejmani, G., Bay, C., Gebauer, L., Burhenne, J., Weiss, J., & Sauter, M. (2024). A Highly Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Quantification of the Organic Cation Transporters’ Mediated Metformin Uptake and Its Inhibition in Cells. Molecules, 29(21), 5162. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29215162








