Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Aptasensor with Supramolecular Architecture for Prostate-Specific Antigen
Abstract
1. Introduction
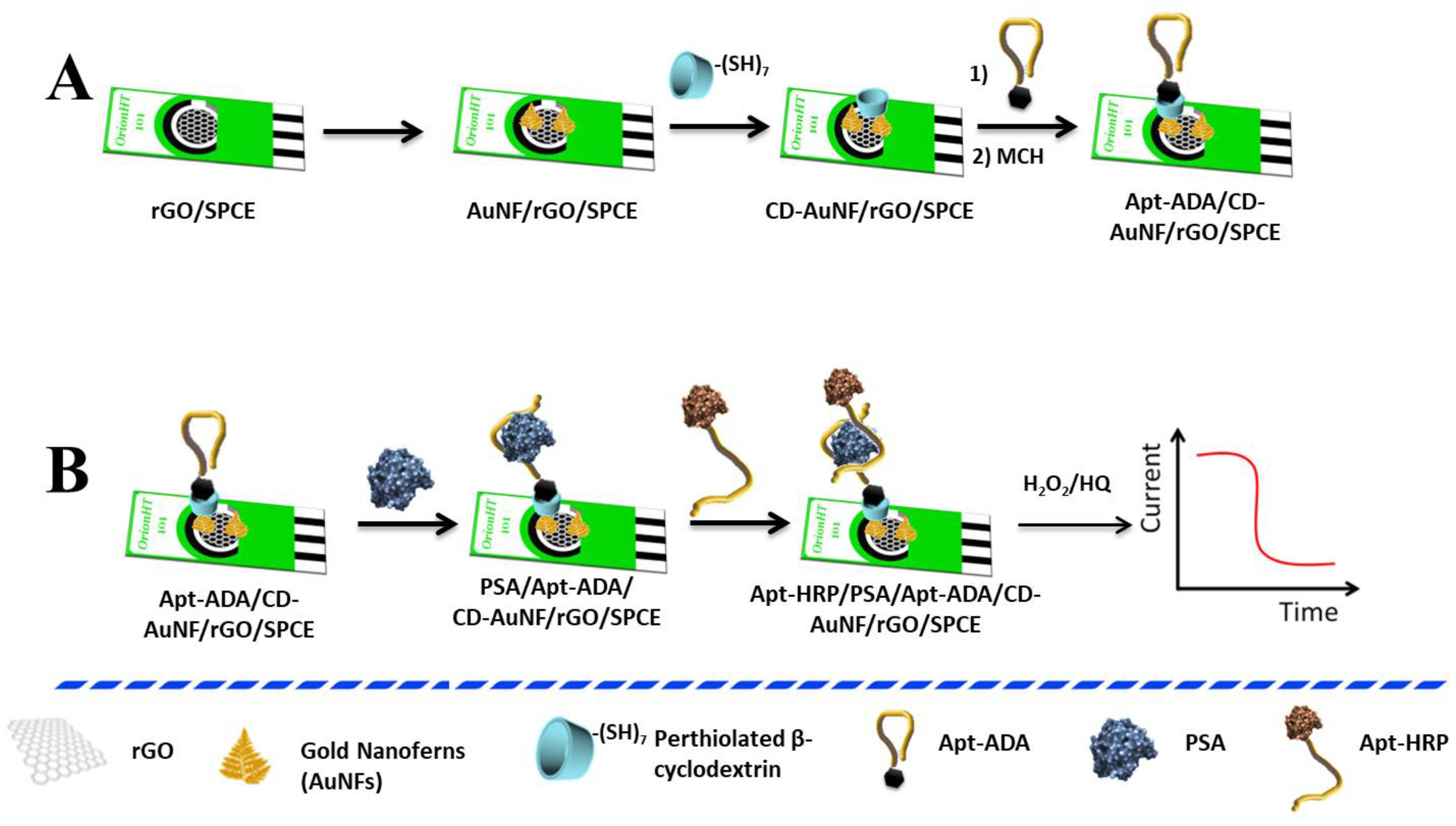
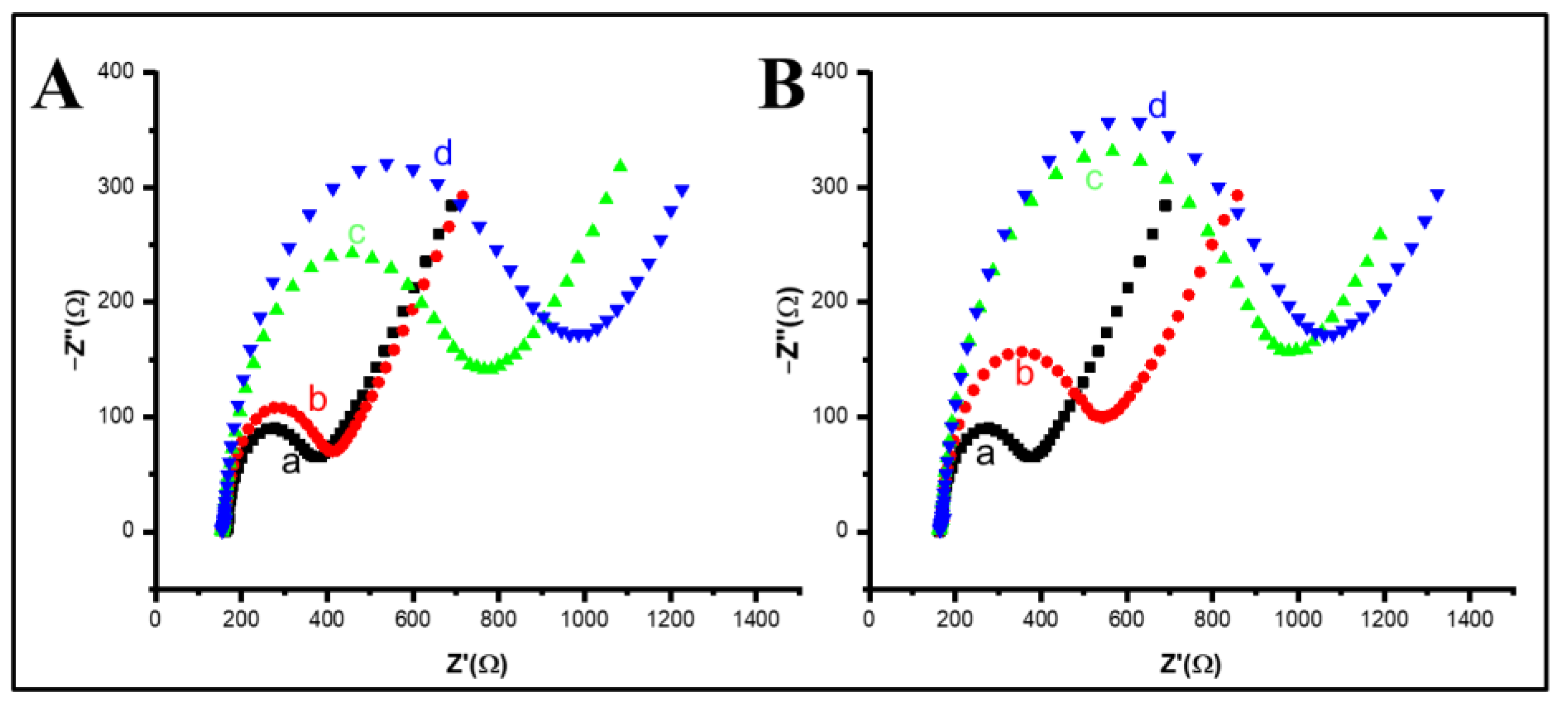
2. Results and Discussion
3. Conclusions
4. Reagents and Apparatus
- Preparation of the anti-PSA aptamer-adamantane conjugate (Apt-ADA).
- Preparation of the anti-PSA aptamer–horseradish peroxidase conjugate (Apt–HRP).
- Preparation of aptamer-functionalized electrodes (MCH/Apt–ADA/CD-AuNFs/rGO/SPCE).
- Amperometric determination.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lichtenberg, J.Y.; Ling, Y.; Kim, S. Non-Specific Adsorption Reduction Methods in Biosensing. Sensors 2019, 19, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villalonga, A.; Mayol, B.; Villalonga, R.; Vilela, D. Electrochemical aptasensors for clinical diagnosis. A review of the last five years. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 369, 132318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzotto, D.; Burgess, I.J.; Doneux, T.; Sagara, T.; Yu, H.Z. Beyond Simple Cartoons: Challenges in Characterizing Electrochemical Biosensor Interfaces. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frutiger, A.; Tanno, A.; Hwu, S.; Tiefenauer, R.F.; Vörös, J.; Nakatsuka, N. Nonspecific Binding—Fundamental Concepts and Consequences for Biosensing Applications. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 8095–8160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, I.H.; Kim, D.H.; Park, S. Electrochemical biosensors: Perspective on functional nanomaterials for on-site analysis. Biomater. Res. 2020, 24, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, F.; Guo, Y. Recent Trends in Nanomaterial-Based Biosensors for Point-of-Care Testing. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollella, P.; Fusco, G.; Tortolini, C.; Sanzò, G.; Favero, G.; Gorton, L.; Antiochia, R. Beyond graphene: Electrochemical sensors and biosensors for biomarkers detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 89, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Graphene electrochemistry: An overview of potential applications. Analyst 2010, 135, 2768–2778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reghunath, R.; devi, K.; Singh, K.K. Recent advances in graphene based electrochemical glucose sensor. Nano-Structures & Nano-Objects 2021, 26, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, Q.; Chen, W. Graphene-based Electrochemical Glucose Sensors: Fabrication and Sensing Properties. Electroanalysis 2018, 30, 2504–2524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunbosun Lawal, A. Recent developments in electrochemical sensors based on graphene for bioanalytical applications. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2023, 41, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimcheva, N. Nanostructures of noble metals as functional materials in biosensors. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2020, 19, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Chatterjee, S. Nanomaterials based electrochemical sensors for biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 5425–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Morrin, A.; Killard, A.J.; Smyth, M.R. Application of nanoparticles in electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Electroanalysis 2006, 18, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, I.; Alatawi, H.; Alsefri, S.; Moore, E. Electrochemical Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide/Gold Nanoparticles in a Single Step for Carbaryl Detection in Water. Sensors 2022, 22, 5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Liu, G. Electrochemical Deposition of Gold Nanoparticles on Reduced Graphene Oxide by Fast Scan Cyclic Voltammetry for the Sensitive Determination of As(III). Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Sun, S.; Huang, M. Electrodeposition of Gold Nanoparticles on Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide for High Performance Supercapacitor Electrode Materials. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2016, 11, 3643–3650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneş, F.; Shin, H.J.; Biswas, C.; Han, G.H.; Kim, E.S.; Chae, S.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Lee, Y.H. Layer-by-layer doping of few-layer graphene film. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 4595–4600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Kuang, Y.; Ardoña, H.A.M. Evolution of Supramolecular Systems Towards Next-Generation Biosensors. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, R.; Díez, P.; Eguílaz, M.; Martínez, P.; Pingarrón, J.M. Supramolecular immobilization of xanthine oxidase on electropolymerized matrix of functionalized hybrid gold nanoparticles/single-walled carbon nanotubes for the preparation of electrochemical biosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4312–4319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, R.; Cao, R.; Fragoso, A. Supramolecular chemistry of cyclodextrins in enzyme technology. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 3088–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortiz, M.; Fragoso, A.; O’Sullivan, C.K. Detection of antigliadin autoantibodies in celiac patient samples using a cyclodextrin-based supramolecular biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 2931–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Guo, Z.; Su, F.; Gao, L.; Pang, X.; Cao, W.; Du, B.; Wei, Q. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunoassay for CEA through host–guest interaction of β-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene and Cu@Ag core–shell nanoparticles with adamantine-modified antibody. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 63, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Liu, Z.; Guo, Y.; Guo, S. Cyclodextrin functionalized graphene-gold nanoparticle hybrids with strong supramolecular capability for electrochemical thrombin aptasensor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 68, 429–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yue, X.; Li, Y.; Wu, F.; Meng, M.; Yin, Y.; Xi, R. A novel electrochemical aptasensor for exosomes determination and release based on specific host-guest interactions between cucurbit [7]uril and ferrocene. Talanta 2021, 232, 122451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, A.; Parrado, C.; Díaz, R.; Sánchez, A.; Mayol, B.; Martínez-Ruíz, P.; Vilela, D.; Villalonga, R. Supramolecular Enzymatic Labeling for Aptamer Switch-Based Electrochemical Biosensor. Biosensors 2022, 12, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campanhã Vicentini, F.; Ravanini, A.E.; Figueiredo-Filho, L.C.S.; Iniesta, J.; Banks, C.E.; Fatibello-Filho, O. Imparting improvements in electrochemical sensors: Evaluation of different carbon blacks that give rise to significant improvement in the performance of electroanalytical sensing platforms. Electrochem. Acta 2015, 157, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelliere, R.; Cosio, T.; Campione, E.; Corvino, M.; D’Amico, M.P.; Micheli, L.; Signori, E.; Contini, G. Lable.free electrochemical immunosensor as a reliable point-of-care device for the detection of interleukin-6 in serum samples from patients with psoriasis. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1251360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, R.S. Theory and Aplication of Cyclic Voltammetry for Measurement of Electrode Reaction Kinetics. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 11–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perone, S.P. Evaluation of Stationary Electrode Polarography and Cyclic Voltammetry for the Study of Rapid Electrode Processes. Anal. Chem. 1966, 38, 1158–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Liu, Z.; Lu, G. Study of the electrochemical behavior of Ni(II) impurity in MgCl2–KCl–NaCl melt. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2024, 54, 2329–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancelliere, R.; Di Tinno, A.; Cataldo, A.; Bellucci, S.; Kumbhat, S.; Micheli, L. Nafion-based label-free immunosensor as a reliable warning system: The case of AFB1 detection in cattle feed. Microchem. J. 2023, 191, 108868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loock, H.P.; Wentzell, P.D. Detection limits of chemical sensors: Applications and misapplications. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 173, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, M.; Nirala, N.R.; Srivastava, S.K.; Prakash, R. A comparative Study of Aptasensor Vs Immunosensor for Label-Free PSA Cancer Detection on GQDs-AuNRs Modified Screen-Printed Electrodes. Sci. Reports 2018, 8, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raouafi, A.; Sánchez, A.; Raouafi, N.; Villalonga, R. Electrochemical aptamer-based bioplatform for ultrasensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 297, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnaimi, A.; Al-Hamry, A.; Makableh, Y.; Adiraju, A.; Kanoun, O. Gold Nanoparticles-MWCNT Based Aptasensor for Early Diagnosis of Prostate Cancer. Biosensors 2022, 12, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdani, Z.; Yadegari, H.; Heli, H. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical nanobiosensor for prostate specific antigen determination. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 566, 116–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, B.; Mao, K.; Liu, N.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Z. Graphene nanocomposites modified electrochemical aptamer sensor for rapid and highly sensitive detection of prostate specific antigen. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 121, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehzari, H.; Amiri, M.; Safari, M. Enzyme-free sandwich-type electrochemical immunosensor for highly sensitive prostate specific antigen based on conjugation of quantum dots and antibody on surface of modified glassy carbon electrode with core–shell magnetic metal-organic frameworks. Talanta 2020, 210, 120641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, X.; Zhao, T.; Gui, X.; Jin, B. A NiFe PBA/AuNPs nanocomposite sensitive immunosensor for electrochemical detection of PSA. Anal. Methods 2024, 16, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Miao, P.; Hu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Geng, X.; Chen, Y.; Feng, L. Signal-on electrochemical aptasensors with different target-induced conformations for prostate specific antigen detection. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1152, 338282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Bai, Z.; Wang, D.; Bai, Y.; Li, X.; Ni, Z. Electrochemical aptasensor based on 3D graphene aerogel for prostate specific antigen detection. Microchem. J. 2023, 195, 109436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özyurt, C.; Uludağ, İ.; Kemal Sezgintürk, M. An ultrasensitive and disposable electrochemical aptasensor for prostate-specific antigen (PSA) detection in real serum samples. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2023, 415, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, W.; Lee, S.; Cho, Y. Dual-responsive immunosensor that combines colorimetric recognition and electrochemical response for ultrasensitive detection of cancer biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 920–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argoubi, W.; Sánchez, A.; Parrado, C.; Raouafi, N.; Villalonga, R. Label-free electrochemical aptasensing platform based on mesoporous silica thin film for the detection of prostate specific antigen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Liu, H.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Yan, M.; Song, X.; Yu, J. Multiplexed aptasensor for simultaneous detection of carcinoembryonic antigen and mucin-1 based on metal ion electrochemical labels and Ru(NH3)63+ electronic wires. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 99, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalonga, A.; Vegas, B.; Paniagua, G.; Eguílaz, M.; Mayol, B.; Parrado, C.; Rivas, G.; Díez, P.; Villalonga, R. Amperometric aptasensor for carcinoembryonic antigen based on a reduced graphene oxide/gold nanoparticles modified electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 877, 114511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Optimized Parameter | Range | Optimal Value |
|---|---|---|
| [Apt–ADA] | 5–40 µM | 30 µM |
| Incubation time of Apt–ADA | 15–90 min | 60 min |
| Incubation time of PSA | 15–90 min | 60 min |
| [Apt–HRP] | 0–15 µM | 5 µM |
| Incubation time of Apt–HRP | 15–60 min | 30 min |
| ΔE (mV) | Ipa/Ipc | K0 10−3 (cm/s) | Rct (Ω) | A (cm2) | K0′ 10−3 (cm/s) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bare SPCE | 201 | 0.96 | 0.74 | 498 | 0.122 | 0.88 |
| rGO/SPCE | 176 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 471 | 0.138 | 0.82 |
| AuNF/rGO/SPCE | 121 | 0.93 | 2.41 | 25.6 | 0.177 | 11.74 |
| CD-AuNF/rGO/SPCE | 216 | 0.95 | 0.62 | 373 | 0.118 | 1.21 |
| Apt-ADA/CD-AuNF/rGO/SPCE | 297 | 0.83 | 0.30 | 681 | 0.078 | 1.00 |
| MCH/Apt-ADA/CD-AuNF/rGO/SPCE | 297 | 0.95 | 0.30 | 798 | 0.095 | 0.70 |
| PSA/MCH/Apt-ADA/CD-AuNF/rGO/SPCE | 302 | 0.94 | 0.29 | 932 | 0.093 | 0.61 |
| Apt-HRP/PSA/MCH/Apt-ADA/CD-AuNF/rGO/SPCE | 398 | 0.89 | 0.15 | 1100 | 0.076 | 0.64 |
| Detection System | Method | Linearity Range (ng/mL) | LOD (ng/mL) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apt-PSA/GQDs-AuNRs/SPCE | DPV | 0.14–11.6 | 0.14 | [34] |
| Anti-PSA/GQDs-AuNRs/SPCE | 0.42 | |||
| Apt-PSA/MB/cDNA/GO-COOH/SPCE | DPV | 0.001–100 | 6.4 × 10−5 | [35] |
| Apt-PSA/MWCNTs-AuNP/SPCE | DPV | 1–100 | 0.001 | [36] |
| MIP-Ppy/AuE | DPV | 0.01–4 | 0.002 | [37] |
| Apt-PSA/AuNPs/THI/rGO/GCE | DPV | 0.05–200 | 0.01 | [38] |
| Ab1/CHIT-MOF/GCE and Ab2-QDs | DPV | 0.001–100 | 4.5 × 10−4 | [39] |
| BSA/Ab-PSA/NiFe PBA/AuNPs/GCE | DPV | 0.0005–1 | 0.00023 | [40] |
| MB/Apt-PSA (sterm-loop)/AuE | SWV | 0.01–500 | 1.24 × 10−3 | [41] |
| Apt-PSA/GA/AuNPs/Nafion/SPCE | EIS | 0.05–50 | 0.0306 | [42] |
| ITO/CTES/Apt-PSA | EIS | 0.000001–0.0015 | 8.76 × 10−6 | [43] |
| Ab1-Biot/Strep/Ppy/ITO and HRP/Ab2-PpyNPs | Potentiometric | 0.001–40 | 7 × 10−4 | [44] |
| Apt-ADA/CD/AuNFs/rGO/SPCE and HRP-Apt | Amperometric | 0.5–50 | 0.11 | This Work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Villalonga, A.; Díaz, R.; Ojeda, I.; Sánchez, A.; Mayol, B.; Martínez-Ruiz, P.; Villalonga, R.; Vilela, D. Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Aptasensor with Supramolecular Architecture for Prostate-Specific Antigen. Molecules 2024, 29, 4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194714
Villalonga A, Díaz R, Ojeda I, Sánchez A, Mayol B, Martínez-Ruiz P, Villalonga R, Vilela D. Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Aptasensor with Supramolecular Architecture for Prostate-Specific Antigen. Molecules. 2024; 29(19):4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194714
Chicago/Turabian StyleVillalonga, Anabel, Raúl Díaz, Irene Ojeda, Alfredo Sánchez, Beatriz Mayol, Paloma Martínez-Ruiz, Reynaldo Villalonga, and Diana Vilela. 2024. "Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Aptasensor with Supramolecular Architecture for Prostate-Specific Antigen" Molecules 29, no. 19: 4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194714
APA StyleVillalonga, A., Díaz, R., Ojeda, I., Sánchez, A., Mayol, B., Martínez-Ruiz, P., Villalonga, R., & Vilela, D. (2024). Sandwich-Type Electrochemical Aptasensor with Supramolecular Architecture for Prostate-Specific Antigen. Molecules, 29(19), 4714. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules29194714










